How often to feed 3 month old breastfed baby
3 Month Old Baby: Development and Milestones
3-Month-Old Baby
What a charmer! At 3-months-old, baby is probably smiling plenty, and they’ve likely started to imitate what they hear and see (so watch what you do, mama!). You should chat with baby throughout the day, describing what you're doing, how you're doing it and where you're going—this is how they’ll eventually learn to talk! Just don't go too crazy though. Baby is a quick learner, but they need you to keep things clear and simple, and to recognize when they need a break.
As your 3-month-old baby continues to grow and develop, there are lots of things you’ll want to keep an eye on and a few key 3-month-old baby milestones to watch for. With a whole three months under your parenting belt, you may feel more confident in your child-rearing skills, but you likely have a lot of questions: How often do you feed a 3-month-old baby? How can you play with a 3-month-old? And let’s not forget: When will my 3-month-old sleep through the night? Ready for the lowdown? Here’s everything you need to know about your budding little person.
In this article.
3-month-old development
3-month-old health
3-month-old feeding
3-month-old sleep
3-month-old schedule
Activities for a 3-month-old
3-month-old baby checklist and tips
3-Month-Old Development
Baby is becoming even more active and social at the three-month mark, right? They’re more in control of their body and more aware of people and interacting with them, which makes for lots of fun at playtime.
3-month-old baby weight and length
Parents want to know: How much should a 3-month-old weigh and measure? The average weight of a 3-month-old baby is 12.9 pounds for girls and 14.1 pounds for boys; average length is 23.5 inches for girls and 24.2 inches for boys.
Whether baby’s close to the average or not, the important thing is that they’re growing at a healthy rate. They’ve likely gained another 1.5 to 2 pounds and grown 1 to 1.5 inches this month. The size of baby’s head may have gone up by a half inch too.
It’s common for a baby to experience a 3-month-old growth spurt. Signs of a growth spurt are having an especially hungry or cranky baby. Baby might wake more at night too. Don’t worry—growth spurts are temporary! Let baby eat, sleep or cuddle more if that’s what they seem to want, and try not to get too frustrated by the sudden change. It can be exhausting for you, but growth spurts usually only last one to three days at a time.
3-month-old’s five senses
At 3-months-old, baby’s senses have developed rapidly.
- They’re working at becoming a great communicator, making eye contact with you, and they can now recognize your face.
- They follow moving objects with their eyes.
- They smile when they hear your voice.
3-month-old baby milestones
Read for all the cuteness to ensue? There are impressive developmental milestones approaching. So what should a 3-month-old be doing? Here’s a peek:
- They’re mimicking some sounds, movements and expressions and starting to babble.

- Let baby play on the floor or under a baby gym, since they love to kick up a storm and swing at things and bat at any dangling toys they see.
- A 3-month-old at tummy time probably raises their head and chest, holding up their upper body with their arms.
- They open and close their hands.
- When you hold baby upright, they’ll push down with their feet onto the floor or your lap.
- They bat at hanging toys above.
- They can grasp and shake a toy.
- You might be wondering, can a baby sit at 3 months of age? Every baby is unique, but many begin sitting up with support anywhere between the three- and five-month marks. The bigger and stronger baby gets, the easier it will be for them to sit up solo.
- Another big question: Can a 3-month-old baby see the TV? At this age, babies are beginning to see more vivid colors and can recognize faces at a distance. Regardless, most experts advise against introducing television or digital screens at such a young age.

You’ll also want to look out for these signs of a developmental or medical problem at the three-month stage; they’re worth a call to the doctor:
- Baby doesn’t respond to loud sounds or smile at the sound of your voice.
- Baby doesn’t follow moving objects with their eyes.
- Baby doesn’t smile socially.
- Baby can’t grasp or hold objects.
- Baby doesn’t bring their hands or objects to their mouth.
- Baby’s eyes still seem crossed most of the time.
- Baby doesn’t babble.
- Baby doesn’t pay attention to new faces.
- Baby doesn’t push down with their feet when they’re held upright and they’re placed on a flat surface.
3-Month-Old Health
There are lots of health questions parents of 3-month-olds have. Below are some of the most common, with links to detailed articles to help you answer them:
3-Month-Old Feeding
In the last couple months, baby’s appetite has certainly increased! And they know how to tell you when they’re hungry. Of course, you’ve probably gotten in such a routine with feeding that you know when they’re about to do that hungry cry.
Of course, you’ve probably gotten in such a routine with feeding that you know when they’re about to do that hungry cry.
How much should a 3-month-old eat?
- Bottle feeding: How much formula for a 3-month-old baby? Typically five ounces about six to eight times a day will suffice.
- Breastfeeding: How often should a 3-month-old nurse? Feedings are typically about every three or four hours at this age but each breastfed baby may be slightly different. What’s important is that baby seems content, your boobs seem to have been emptied (they’re soft) and baby’s gaining weight healthily.
To double-check that baby’s getting enough breast milk, you can also track their diapers. How many wet diapers for a 3-month-old baby? About four or five very wet ones per day indicate that your little one is getting ample milk.
Three-month-old babies may start eating less than they did previously. Breastfed babies do get more efficient, so it’s normal for your baby to feed in about half the time it took them to feed as a newborn. If you see all the signs that baby’s getting enough to eat, it’s perfectly normal. If not, it could be a sign of a problem, so talk to the pediatrician.
If you see all the signs that baby’s getting enough to eat, it’s perfectly normal. If not, it could be a sign of a problem, so talk to the pediatrician.
What can baby eat this month?
Baby is still only able to eat breast milk and/or formula. Many parents ask: “Can I give my 3-month-old water?” Nope! Most doctors recommend parents wait until baby’s ready for solid foods before they get water. Don’t worry, baby’s getting plenty of hydration from breast milk or formula and needs the nourishment it provides.
How often do you feed a 3-month-old baby?
Three-month-olds will likely still need to be fed every three to four hours during the day. When in doubt, look for hunger cues. Before crying for their food, baby may lick their lips, stick out their tongue, repeatedly open their mouth, suck on things or touch their hands to their mouths. These can all be signals that it’s feeding time.
3-month-old feeding schedule
Image: Megan Rubey
3-Month-Old Sleep
Three months in and you’re ready to get this whole sleep thing settled. Want answers to the most common sleep questions among parents of 3-month-olds? Curious minds want to know:
Want answers to the most common sleep questions among parents of 3-month-olds? Curious minds want to know:
How long do 3-month-olds sleep and nap?
Three-month-olds typically sleep about 15 hours a day, and more of those hours are falling at night. In fact, it’s common for 3-month-olds to sleep about 10 hours at night, maybe with at least one five- or six-hour stretch. Baby is probably taking three naps totaling five hours of daytime sleep.
How can I get my 3-month-old to sleep?
It’s harder than you might think to get a tired baby to actually go to sleep! You’ve probably heard the usual advice: Keep the room dark and cool, rock and sing to your baby, and put baby to sleep while they’re sleepy but not yet asleep. Still, there are some nights when none of that seems to work. Try some other parents’ tried-and-true tricks for calming a fussy baby; they just might help you get your little one to snooze—finally.
What should my 3-month-old’s bedtime be?
The ideal bedtime for a 3-month-old baby depends on your family’s schedule, but many experts believe 7:30 p. m.—give or take—is ideal at this age. As baby begins to sleep for longer stretches at night, you’ll want to gradually make bedtime earlier, which (surprisingly!) encourages baby to sleep even longer.
m.—give or take—is ideal at this age. As baby begins to sleep for longer stretches at night, you’ll want to gradually make bedtime earlier, which (surprisingly!) encourages baby to sleep even longer.
Does my 3-month-old baby have sleep regression?
You may notice a bit of 3-month-old sleep regression. Baby might be waking more often at night because of a growth spurt, or it might be a developmental thing. Around 3 or 4 months, babies’ brains are becoming more alert and because of that, they want to be using that brainpower more often. Growth spurts can last a few days but true sleep regression (which typically happens closer to 4 months) can last two to six weeks.
3-month-old sleep schedule
Here’s a peek at a typical 3-month-old sleep schedule:
Image: Megan Rubey
3-Month-Old Schedule
Three-month-old babies are creatures of habit—bedtime, nap and feeding routines keep them happy.
3-month-old schedule example
A 3-month-old’s daily schedule might look something like this:
Image: Megan Rubey
Activities for a 3-Month-Old
Be sure to squeeze in some playtime with your 3-month-old baby each day. So how can you engage and play with a 3-month old? There are tons of ways to entertain your cutie pie at this stage.
So how can you engage and play with a 3-month old? There are tons of ways to entertain your cutie pie at this stage.
- Give baby a mirror and let them admire their reflection.
- Sing, read and talk to your 3-month-old baby; encourage them to make sounds of their own. This sweet back-and-forth is the basis of an early conversation!
- Place a soft and colorful toy on baby’s chest and let them look, touch and play with it. A play gym or mobile can also provide plenty of amusement.
- Continue to put baby on a mat for tummy time. The more baby gets used to being on their tummy, the more they’ll be inclined to start working toward a scoot or crawl.
3-Month-Old Baby Checklist and Tips
- Make sure you have your four-month baby checkup scheduled.
- Look for signs of readiness for eating solid foods. The pediatrician may recommend you start as early as the four-month mark.
- If you’re going back to work after maternity leave, best wishes! You’ve got this!
- How often should I bathe my 3-month-old baby? Don’t worry about giving baby a bath more than once every few days.

- Find some new things to do with your 3-month-old baby.
- Take baby’s 3-month-old baby milestone photo.
A heads up that in the coming weeks, you’ll be entering new and exciting territory. Baby will work on those important 3-month-old baby milestones, and you’ll have even more to look forward to as they approach month four. Baby will master the art of holding their head up and maybe even begin rolling over from their tummy to their back.
Medical content was reviewed by Dina DiMaggio, MD, a board-certified pediatrician at Pediatric Associates of NYC and NYU Langone Health in New York City, and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics. She is also the coauthor of The Pediatrician’s Guide to Feeding Babies and Toddlers.
What's Normal and What's Not
If there’s one universal parenting truth, it’s that you’re going to be talking about baby poop a lot. (Cue questions: How often should a newborn poop? How can you help baby poop? What does green baby poop mean? What exactly should normal baby poop look like?) And while it may not be a typical topic of conversation for the dinner table, it’s something you’ll find yourself thinking about all the time. Baby’s poop—the color, consistency and amount—can provide important clues into the health of your infant, says Wendy Sue Swanson, MD, a pediatrician and chief medical officer at SpoonfulOne.
Baby’s poop—the color, consistency and amount—can provide important clues into the health of your infant, says Wendy Sue Swanson, MD, a pediatrician and chief medical officer at SpoonfulOne.
Another reason why it’s a perpetual theme throughout the diaper years? Because baby’s poop habits change all the time. In fact, when it comes to baby poop, there’s a whole spectrum of what’s considered the norm. There are a lot of factors that can contribute to color, consistency and frequency. What’s normal for a breastfed baby (i.e. mustard-like poop) may not be normal for a formula-fed baby (soft and yellow, green or brown-ish). A little one that’s eating solid foods will also have a baby poop that’s very different from an infant that’s still exclusively breastfeeding or formula-feeding. Suffice to say, baby’s poop will evolve and so will your idea of “normal.”
So what is considered normal baby poop—and when should you be concerned? We’ll help you sort it all out with our comprehensive baby poop guide. Here’s what to expect from that first diaper change, all the way up through potty training.
Here’s what to expect from that first diaper change, all the way up through potty training.
In this article:
Baby’s First Poop
How Often Should a Newborn Poop
Baby Poop Color: Green Baby Poop
Baby Not Pooping: How to Help Baby Poop
Types of Baby Poop When to See the Doctor
Baby’s First Poop
Unlike many of your child’s milestones, you likely won’t take a picture of baby’s first poop—but it’s an important one. Usually sticky and darkish green-black in color, baby’s first poop is called meconium and is made up of everything baby ingested in utero, including amniotic fluid, skin cells and water. But within the first few days of life, your newborn’s poop should progressively get more watery and lighter in color. If it doesn’t, or if baby isn’t consistently pooping in the first few days of life, it could be a sign that they’re not getting proper nutrition and need a follow-up visit with the pediatrician, Swanson says.
How Often Should a Newborn Poop?
In the first four to six weeks of life, regardless of whether your infant is breastfed or formula-fed, you should expect your newborn to poop after nearly every feeding, Swanson says. And depending on whether you’re breastfeeding, formula feeding or combination feeding, the stools will likely look different. Breastfed baby poop is often yellow, seedy and runny, while a formula-fed baby’s poop may be darker and thicker.
And depending on whether you’re breastfeeding, formula feeding or combination feeding, the stools will likely look different. Breastfed baby poop is often yellow, seedy and runny, while a formula-fed baby’s poop may be darker and thicker.
After six weeks, as baby’s digestive tract develops, their poop habits may change. How often should a newborn poop? It depends. While one to three times or more a day is a benchmark, it’s common for breastfed babies to not poop as frequently as formula-fed babies.
How often should a breastfed baby poop?
Is your breastfed baby not pooping? Don’t panic. Because breast milk is digested differently than formula, it’s not unusual for a breastfed baby to pee regularly (creating six to eight wet diapers a day) but not poop for several days. “It’s common for a breastfed baby to go two or three days without pooping, and it’s possible for them to go up to seven days,” Swanson says. If your breastfed baby isn’t pooping, it’s more important to watch their demeanor than their diapers. If they seem content and their belly is soft, they’re likely fine. But if their belly feels rigid or baby seems uncomfortable, it could be a sign they’re constipated, Swanson adds.
If they seem content and their belly is soft, they’re likely fine. But if their belly feels rigid or baby seems uncomfortable, it could be a sign they’re constipated, Swanson adds.
How often should a formula-fed baby poop?
Formula-fed babies tend to have poop that’s a bit darker and firmer than breastfed baby poop. Their poop may be the consistency of hummus and color can range from yellow to greenish-brown or tan. Formula-fed babies will likely poop at least once a day; if they don’t poop for two or more days, it could signal constipation. Equally important is the consistency of baby’s poop. “Log or pellet-like shapes could indicate constipation,” Swanson says. It’s important to address this with your pediatrician, since constipation could mean an allergy or be a sign that it’s time to try another brand of baby formula.
Baby Poop Color: What Does It Mean?
When it comes to assessing potential health issues, a pediatrician often checks baby’s poop color. Before you panic, remember that what goes in must come out—especially for babies who are beginning to eat table food. In other words, if baby has beets for lunch, you’re probably going to see red in a few hours. Still, pediatricians agree it’s smart to keep tabs on the colors you see. If you do spot something unusual, bag up the diaper and bring it along to your appointment—it can help a doctor make an assessment. From green baby poop to red, orange, black and beyond, here’s what each baby poop color could mean:
Before you panic, remember that what goes in must come out—especially for babies who are beginning to eat table food. In other words, if baby has beets for lunch, you’re probably going to see red in a few hours. Still, pediatricians agree it’s smart to keep tabs on the colors you see. If you do spot something unusual, bag up the diaper and bring it along to your appointment—it can help a doctor make an assessment. From green baby poop to red, orange, black and beyond, here’s what each baby poop color could mean:
Image: Lindsey Balbierz
Green baby poop
With formula-fed infants, it’s normal for baby poop to be a greenish-tan color. Sometimes the iron in baby formula can cause dark green baby poop and isn’t a reason for concern. Green baby poop can also signal teething or that baby is getting over a stomach bug. If baby has green poop and is also fussy at feedings or seems gassy and uncomfortable, it could be a sign they have a cow’s milk allergy and are reacting to the formula, Swanson says, which means you should consult your doctor about other options. For a breastfed baby, green baby poop might signal something else. “Bright green baby poop in a breastfed infant, especially if it’s frothy, may mean they’re getting too much foremilk and not enough of the fattier hindmilk,” Swanson says. Try keeping baby on one breast per feeding or hand express a bit of milk before letting them latch and see if this solves the problem.
For a breastfed baby, green baby poop might signal something else. “Bright green baby poop in a breastfed infant, especially if it’s frothy, may mean they’re getting too much foremilk and not enough of the fattier hindmilk,” Swanson says. Try keeping baby on one breast per feeding or hand express a bit of milk before letting them latch and see if this solves the problem.
White baby poop
If baby is still being breastfed or formula-fed, chalky, whitish or gray baby poop definitely warrants a call to the pediatrician, since it can be a sign the liver isn’t functioning the way it should be.
Orange baby poop
Many of baby’s first solid foods can result in orange-colored baby poop (think: carrots and sweet potatoes). A breastfed baby may also have orange-ish tinted stool if Mom has been on medication or been eating artificially colored foods, since the dyes may make their way into breast milk. Orange poop generally doesn’t indicate a problem, but if you’re worried, call your pediatrician, Swanson says.
Red baby poop
Flecks of red are no big deal. If you’re breastfeeding, there might be tiny amounts of blood baby swallowed from cracks in your nipple. Red flecks might also appear if baby is constipated and straining too hard to poop. If you’re just starting baby on table foods, you may have to play diet detective to suss out any food culprits. Stools that look genuinely bloody or are bright red may indicate an infection, allergy, GI injury or other medical concern and should be addressed immediately.
Black baby poop
If a newborn’s poop is still looking black by day three, it may be a sign they’re not getting adequate nutrition or digesting milk the way they should. If you see black poop when baby’s a bit older, it could be caused by iron in their diet, which is no big deal. If baby isn’t taking an iron supplement and the poop looks black, it could be a sign of GI tract bleeding and should be seen by a doctor. “But it’s not red!” you say? Blood actually turns from red to black as it travels through baby’s intestines, according to Madhavi Kapoor, MD, clinical assistant professor in the department of pediatrics at NYU Langone Medical Center.
Yellow baby poop
Mustard yellow is a normal baby poop color for both breastfed and formula-fed infants. If baby’s stool is bright yellow, the color change could be a result of medications or food eaten by Mom.
Gray baby poop
If baby is eating solids, poop may be gray depending on what your child ate, Swanson says. If baby hasn’t yet started table food, then it’s important to assess, as it could indicate a liver or gallbladder problem.
How to Help Baby Poop
Before having a baby, you probably never imagined you’d wish for a dirty diaper. But a poop can provide sweet relief for an uncomfortable baby and a worried parent. There are a few common reasons why baby is not pooping: Dehydration, eating starchy foods like bananas, a time shift due to traveling or occasionally an allergy or intolerance. In older babies, especially those on the cusp of potty training, withholding poop can be psychological—they may be afraid of the potty or upset over an external issue, like a caregiver change or thrown-off schedule.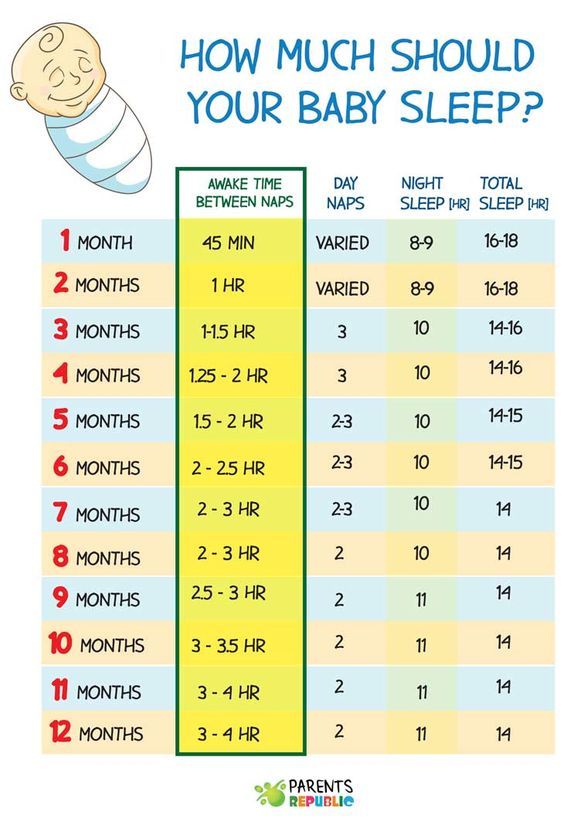
Luckily, many at-home remedies to help baby poop are simple, effective and recommended by pediatricians—but it’s best to use them only occasionally. “I warn parents not to become dependent on a ‘trick’ to make a baby poop,” Swanson says. “If it’s a persistent problem, it’s something I like to see in the office.”
Here are some ideas on how to get a newborn to poop, as well as what to do when an older baby is not pooping .
• Bicycle legs. Peddling an infant’s legs to and from their chest, as if they’re riding a bicycle, can be a gentle way to stimulate your child’s digestive system, Swanson says. Older babies generally don’t need this trick, since crawling, climbing and pulling up to stand help keep things moving.
• Warm bath. The warmth and stimulation of the water can relax muscles and help baby poop.
• Rectal stimulation. For occasional use only, Swanson suggests gentle rectal stimulation by gently inserting a rectal thermometer or using a gas-relieving product, such as Fridababy’s Windi ($13, Fridababy. com). However, Swanson cautions this shouldn’t become your go-to trick. “If used too often, the baby may become reliant on rectal stimulation to poop.”
com). However, Swanson cautions this shouldn’t become your go-to trick. “If used too often, the baby may become reliant on rectal stimulation to poop.”
• Water or juice. Constipation can be a sign of dehydration. If baby has started eating solids, offering a few ounces of water or pear juice may help move things along. Constipation may also be a sign baby needs to nurse more or be offered a bottle more regularly. If you’re at all concerned, talk to your pediatrician.
• Glycerin suppositories. Another occasional-use tool, Swanson says glycerin suppositories can be helpful for constipation. Ask your doctor first, especially if baby is younger than a year.
• The four P’s: Prunes, plums, peaches and pears. These four fruits are a great natural way to help baby poop. If baby has started solids, add a serving or two into your child’s daily diet to keep things moving.
• Veggies. The high-fiber content in vegetables makes them all-stars when it comes to dealing with constipation.
• Whole grains. When planning baby’s meals, try incorporating some whole grains: Brown rice, whole-wheat pasta and multigrain cereals or bread maximize bran intake, which can help soften stool and make it easier for baby to poop.
Is it normal for baby to grunt?
If you hear baby making grunting noises, don’t fret. They’re just learning how to have a bowel movement. Infants let out moans and groans as they go; their abdominal muscles aren’t very strong yet, so pooping requires more effort and energy and engages the diaphragm, resulting in some sound effects. It’s not uncommon to see babies straining or making faces while they’re at it too. This is completely normal, and doesn’t necessarily indicate a problem like constipation.
Types of Baby Poop
While it’s normal to get a teeny bit less obsessive over every single diaper change as baby grows, it’s still important to keep an eye out for potential problems and warning signs. While some odd consistencies may have a simple explanation (hello, raisins!), others may need to be discussed with your doctor. Here are some types of baby poop to watch out for:
Here are some types of baby poop to watch out for:
Diarrhea
In infancy, loose stools can be a sign of an allergy, either to the milk proteins in formula or, if you’re breastfeeding, to something you ate. As baby gets older, watery stools may be a sign of teething (baby is swallowing more saliva, leading to runnier poop), but could also be a sign of a stomach bug. In that case, keeping your child hydrated with plenty of water or milk is essential. If the diarrhea is accompanied by a fever of 100.4 or higher, or baby is younger than 3 months old, it’s a good idea to call your pediatrician, Kapoor says.
Blood in baby stool
While a few flecks can be normal, anything more than that should be brought to your pediatrician’s attention. “Blood in the stool could be caused by constipation, infection, injury or allergy, so going to the doctor is essential,” Kapoor says.
Mucus in baby stool
A common sign of teething or a cold, occasional mucus is no big deal. However, “if you notice it frequently or in large amounts, it could be a sign of a GI tract issue and should be discussed with your pediatrician,” Kapoor says.
However, “if you notice it frequently or in large amounts, it could be a sign of a GI tract issue and should be discussed with your pediatrician,” Kapoor says.
Stringy baby poop
A cousin to mucus, stringy baby poop could be a sign of a cold or teething, or just the result of something baby has been eating. If it shows up frequently in baby’s diaper, it’s a good idea to call your pediatrician.
Foamy baby poop
“In a breastfed infant, foamy stool may be a sign that baby is getting too much foremilk,” Kapoor says. For an easy solve, try completing a feeding on just one breast. In a formula-fed baby, frothy baby poop could indicate an infection or allergy.
Pebble-like stool
This is a classic sign of constipation or withholding stool in older babies. Try some home constipation cures and go to the doctor if baby doesn’t poop within the next 24 hours.
Doctors agree that if you see anything unusual, spot a baby poop problem accompanied by a high fever or if baby is crying inconsolably, you should call the doctor, who can help guide you through possible causes and next steps. And don’t be shy about bagging the diaper for your doctor’s inspection. “We see it all the time, and we aren’t disgusted,” Kapoor says. “It can help us best figure out what the issue may be.”
And don’t be shy about bagging the diaper for your doctor’s inspection. “We see it all the time, and we aren’t disgusted,” Kapoor says. “It can help us best figure out what the issue may be.”
When to See the Doctor
Yes, you can tell a lot about baby’s health by monitoring the color and consistency of their poop. But if you notice any of the following, you should consult your doctor for advice:
- Breastfeed baby hasn’t pooped in over three days
- Formula-fed baby hasn’t pooped in over five days
- Baby poop is thick, hard or or pebbly
- Baby poop is red or black
- Baby poop is white, gray or clay-colored
In the coming days, weeks and months, you’ll likely take up a mission to analyze the contents of your infant’s diaper; checking for normal baby poop is par for the course. The truth is: Everybody poops—and you want to make sure your little one is happy and healthy! To that end, keep our baby poop guide bookmarked as a reference to help you navigate this sometimes sticky, but always interesting stage of parenthood!
About the experts:
Madhavi Kapoor, MD, is a clinical assistant professor in the department of pediatrics at NYU Langone Medical Center. She received her medical degree from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School in Dallas.
She received her medical degree from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School in Dallas.
Wendy Sue Swanson, MD, is a pediatrician and chief medical officer at SpoonfulOne and BeforeBrands. Previously, the executive director of digital health for Seattle Children’s Hospital, she earned her medical degree from University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine in Philadelphia.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
What to Know About Using Gripe Water for Colic and Tummy Troubles
Why Babies Get Hiccups (and How to Get Rid of Them)
How to Identify and Relieve Baby Constipation
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.
5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding necessary for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3. 5 hours or in some other way?
5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.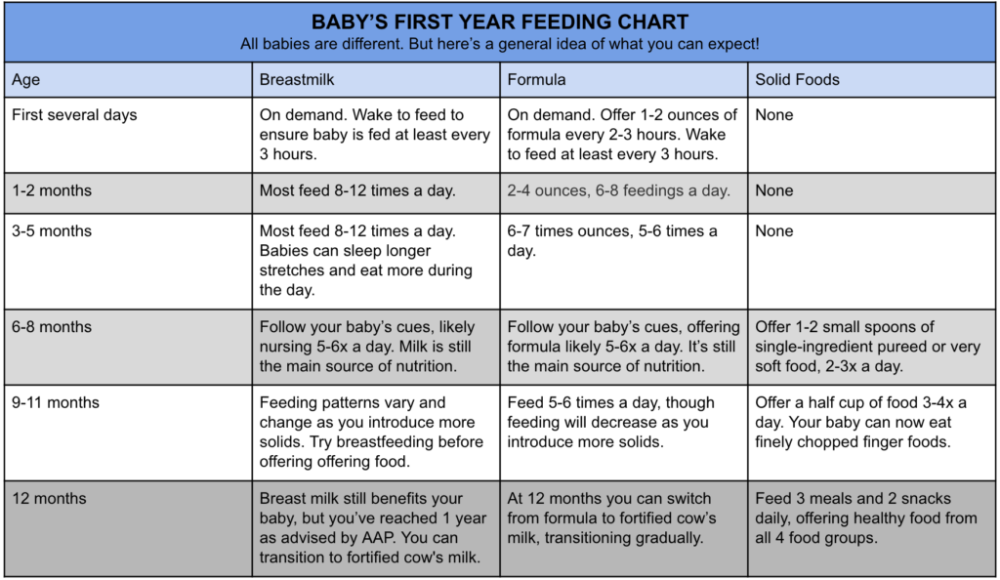
This whole process is biologically justified. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with the breast in his mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
Daytime naps of a one-month-old infant feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2.5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for suckling. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person deliberately harming an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed noticeably less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen. And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
- At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.

- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications. At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.

- At seven months, the frequency of application is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times. The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
- In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking.
 I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ... - Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons. The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
- At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast.
 The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning. - At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a dummy or finger to fall asleep or calm down, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
- At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking.
 The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for pleasure. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for pleasure. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Moms who don't think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when breastfeeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is not true. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
This is not true. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking back at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle.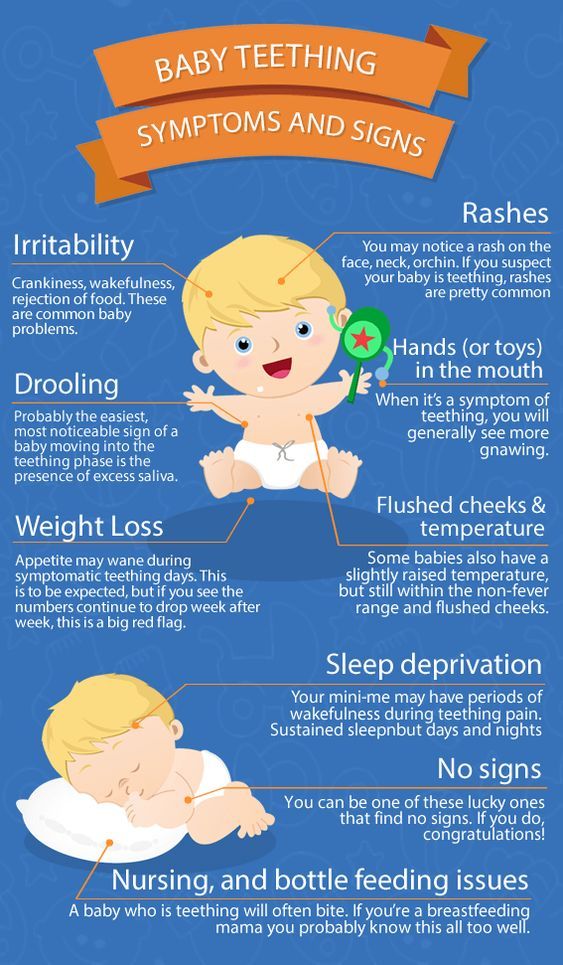 It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes when I advise mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists. These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
Breastfeeding is important not only for the baby, it is also important for the mother. During on-demand feeding, the woman's feelings change, a stronger attachment to the baby is formed, the woman becomes more sensitive to the needs of the baby. Deeper affection and understanding are not only preserved in infancy. They persist for life. For clarity, imagine what happens to a woman’s feelings if she tries to “withstand” a child, endures his crying, anxiety. What happens to a woman if she uses the recommendation from one very popular parenting book: "Go to the child if he cries for more than 15 minutes"? Speaking in abstract terms, humanity is interested in reviving the practice of breastfeeding. The revival of this practice is impossible without mothers realizing the true reasons for the child's need for attachment to the breast.
Deeper affection and understanding are not only preserved in infancy. They persist for life. For clarity, imagine what happens to a woman’s feelings if she tries to “withstand” a child, endures his crying, anxiety. What happens to a woman if she uses the recommendation from one very popular parenting book: "Go to the child if he cries for more than 15 minutes"? Speaking in abstract terms, humanity is interested in reviving the practice of breastfeeding. The revival of this practice is impossible without mothers realizing the true reasons for the child's need for attachment to the breast.
Lilia Kazakova, pediatrician,
leader of lactation and childcare counselors
Breastfeeding after 1 month: what to expect
Do you know when breast milk production stabilizes? And how does the frequency and duration of feedings change as the baby grows? You will find answers to these questions in our recommendations for breastfeeding after the first month.
Share this information
Congratulations: You made it through the first month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production is stabilizing, and there is little or no leakage from the breast. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production is stabilizing, and there is little or no leakage from the breast. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
When does breastfeeding decrease?
The "normal" feeding frequency for babies aged one to six months varies considerably, with some needing four times a day, others asking to be breastfed 13 times a day. 3
“From the age of one month, the amount of milk a baby consumes per feed increases, so that he can go without food for longer,” explains Cathy Garbin, an internationally recognized expert on breastfeeding, “A baby’s stomach grows, so he eat more at one time. In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.”
In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.”
Feeding can last from 12 minutes to one hour -
the habits of babies vary so much! 3 But if the child is gaining weight and falls within this range, there is no cause for concern.
What is most surprising, no matter how often the baby eats, he consumes approximately the same amount of milk per day - both at one month and at six, when it is time to start complementary foods with solid food. 4
“However, sometimes the baby eats more and sometimes less, especially when he is unwell. It’s better to just listen to his needs,” Katie explains.
Is breastmilk sufficient for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk contains everything a baby needs for the first 90,079 six months of life—exclusively breastfed babies don't even need to drink more water! 5 Until about six months of age, a child's digestive system is simply not adapted to the digestion of solid food, and he will be able to drink cow's milk only after a year.
In addition, breastfeeding during this period prepares the child for further development. It strengthens the muscles of the mouth, develops the jaw and helps straighten the teeth 6.7 . All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
In addition, when your baby is sick, your body produces breast milk that is
rich in antibodies that help fight infection. 9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as he grows and becomes more active.
Breastfeeding is also very comfortable once you get used to it. Claudia, a mother of two from the UK, notes: “No need to sterilize a mountain of bottles, prepare formula, carry it all with you, warm it up - in general, breastfeeding turned out to be very convenient, especially when my babies grew up and we began to leave the house more often. ".
".
At what age does a breastfed baby start sleeping through the night?
Waking up at night is normal for babies. Most babies between the ages of one and six months consume a fifth of their daily milk requirement at night, so nighttime feedings should not be neglected if you want your baby to get the required amount of calories. 3
"It really depends on what you mean by 'sleep through the night,'" says Cathy. "And it's better than waking up every two hours anyway! I have met infants who, starting at six weeks old, fell asleep at 19:00 and woke up at 7:00, but most continue to wake up frequently at night after this age. All children are different."
In Wales, a study of over 700 infants found that almost 80% of children aged 6 to 12 months wake up at least once a night, and 25% of them wake up three times or more. And it did not depend on what type of feeding the child is on - breastfeeding or artificial. 10
And if nighttime awakenings are unavoidable anyway, breastfeeding is at least comfortable! Maina, a mother of two from Australia, agrees: “You can even take a nap while feeding in the middle of the night - both the body and the baby do their job on autopilot.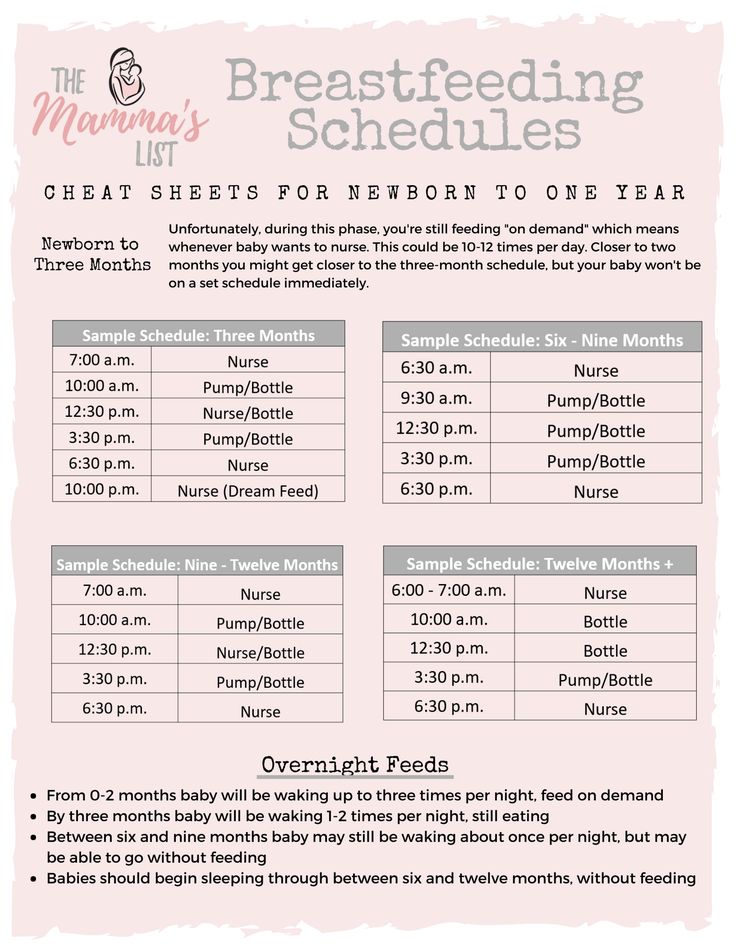 No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
My child wakes up more often. Perhaps he is hungry?
Around four months of age, a baby's sleep patterns change as they develop deep and light sleep phases like an adult. Because of this, he may wake up more often at night. “At four months, sleep is more of a problem than feeding,” Cathy admits. “It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.”
Some people call this " a four-month sleep regression ", but "progress" is more appropriate here. From the outside it may look like a step back, but in fact the child is approaching an important stage of development. He learns quickly, begins to become aware of the world around him, his perception is sharpened and, perhaps, there is anxiety about being separated from his mother. Crying when waking up and being able to eat milk cuddled up to mommy’s chest is a way for a baby to calm down.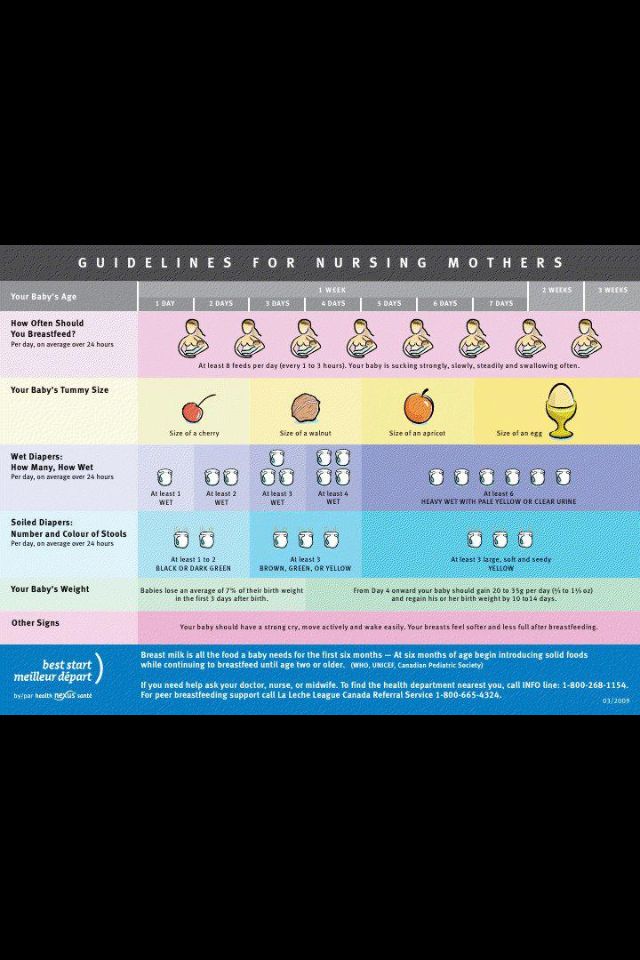 11–13
11–13
Resist the urge to “supplement” your baby with formula or start solid foods early
in an attempt to improve his sleep. Breast milk contains
hormones that make you sleepy and help you both relax
. Research shows that breastfeeding mothers actually sleep longer at night than mothers of formula-fed or mixed-fed babies
. 14
How does teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething usually begins around four months of age. When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
However, breastfeeding can be an excellent sedative.
Studies have shown that babies who are breastfed
during the vaccination period cry less and forget pain more quickly. 15 Breastfeeding during teething can have the same calming effect.
An unpleasant side effect may be the child's attempts to try out his new teeth on the mother's breast. “Sometimes children flirt and bite their mother’s nipples.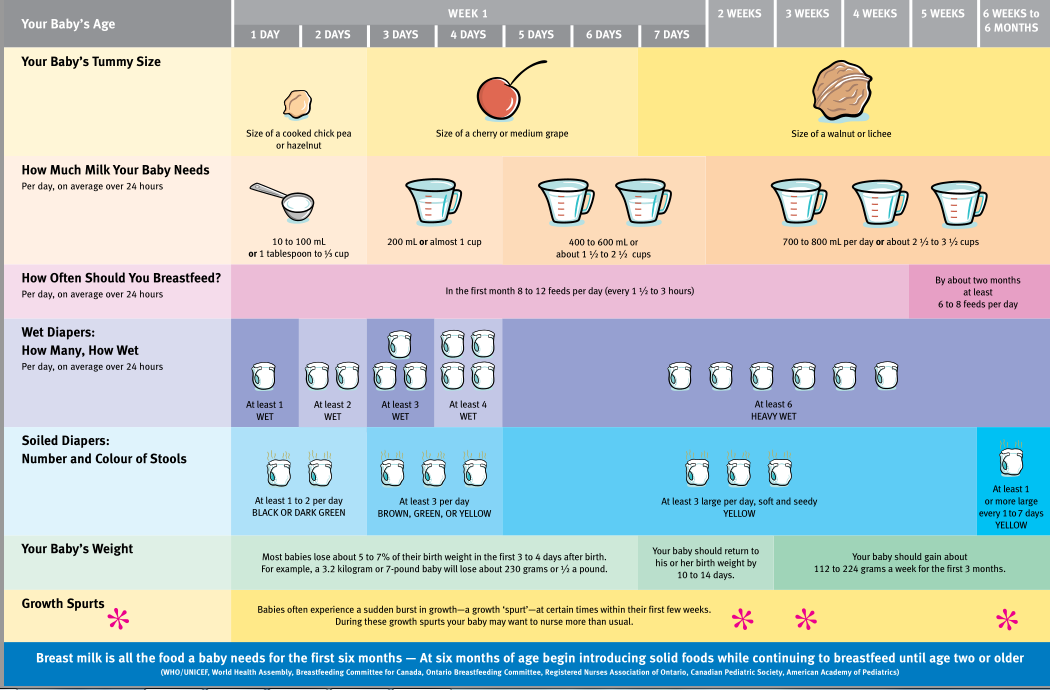 This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
How to continue feeding if you have to be separated from the baby?
It happens that during the first six months, when the baby is still fully breastfed, the mother needs to be away for several hours - or even longer if she has to go to work or go away on business for a couple of days.
But this does not mean that you should stop breastfeeding. You can still feed your baby healthy breast milk - just express it and have someone give it to your baby when you're away. Here's Katie's advice:
“Start expressing milk a couple of days in advance, in small batches, 40-60 ml at a time. So you will have the necessary supply for the time of your absence, but at the same time the amount of milk produced will remain the same.
If you have to return to work, check with your employer about your daily schedule. Many mothers breastfeed their babies in the morning, evening and night, and pump milk at lunchtime to relieve discomfort and create a reserve for the next day.
This usually turns out to be much easier than one might think, and today in many companies the conditions are in place for this, notes Cathy, “Breast pumps make it easy to solve this problem.”
Natalie, a mother from the USA, shares her experience: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes up, and sometimes again before leaving for work, in order to maintain milk production and not lose contact with the child. At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding."
Can breastfeeding continue after the introduction of solid foods?
When your baby begins to show interest in food and can sit up on his own - usually around six months of age - it's time to start solid foods. However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
Start complementary foods with solid foods, but remember that breast milk remains a more important source of calories and nutrients until the baby is eight to nine months old. By this time, he will be eating much more solid food, but he will still need to breastfeed four to five times a day. By 12 months, the frequency of feeding may be two to six times a day. All babies are different, and many of them at this age are still getting half their daily calorie intake from breast milk.”
Don't forget that breast milk can be added to solid foods, such as cereals and purees, so that the baby can taste the familiar taste. If possible, use milk expressed just before feeding (not thawed) and add just before serving to keep bacteria and nutrients alive. 16
You may be pressured by others to stop breastfeeding when your baby is six months old, but the longer you breastfeed or pump, the better for you and your baby.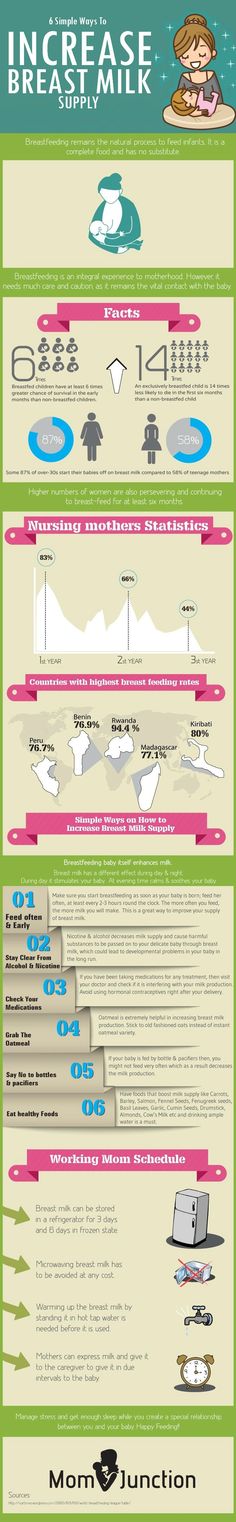
How long can I continue breastfeeding?
“The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding along with solid foods until at least two years of age because it plays an important role in supporting immunity,” says Cathy. feels bad".
At eight months, the baby sometimes breastfeeds four times a day, but by one year old, the frequency of feedings can be reduced to two times a day. You yourself will understand which feeding regimen is more suitable for you and your baby. For example, Jane, a mother of two from the US, breastfed until the age of two: “I breastfed when I was at home - in the evenings and on weekends, when the children wanted to be close to me,” says Jane, “It helped a lot when they were sick . Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort."
“When my son got a little older and bolder, he still often asked me to breastfeed him - as if to calm down and gain strength,” recalls Amy, a mother of two children from Canada, “When he happened to hit or skin his knee , breastfeeding was a wonderful way to comfort him. ”
”
If your baby is over a year old and you are still breastfeeding, people around you will probably tell you that this way he will never wean. But if children are not pressured, they usually refuse to breastfeed themselves between the ages of two and four. 17
“I didn’t intend to breastfeed for so long, but as a result, I still breastfeed my four-year-old daughter and 22-month-old son,” says Suzanne, mother of two from the UK, “I breastfeed my youngest before and after work, and in I express milk on business trips. The eldest daughter likes to breastfeed a little before bed or when she is upset - this is a great way to make contact. When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.”
For more information on what to expect and lots of tips and tricks, see our guide Breastfeeding Problems After the First Month.
Literature
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-21. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol and Neonatal Nurse. 2012;41(1):114-121.
3 Kent JC Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
2006;117(3):e387-95.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans R Soc Trop Med 1990;84(4):602-604. - Elmroth C, Bidinger PD, "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
6 Victora CG et al . Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect.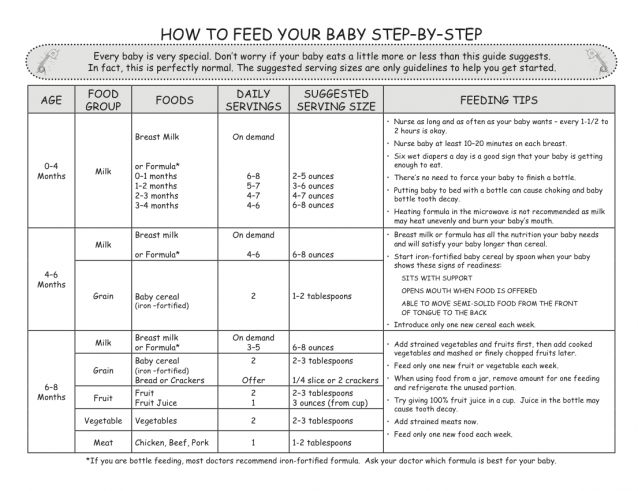 Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490.
Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104( S 467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition influences the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk.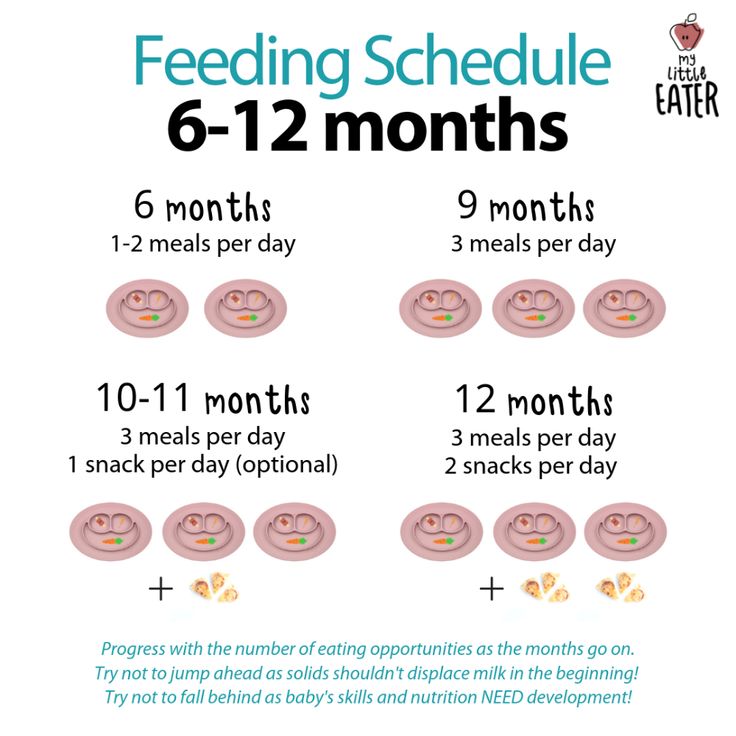 Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb] - All about baby sleep. [Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018].
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - The science of baby sleep. [Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay ; December 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - "The Myth of Baby Sleep Regression - What's Really Happening to Your Baby?" [Internet]. Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
14 Kendall - Tackett K ET Al . The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression.