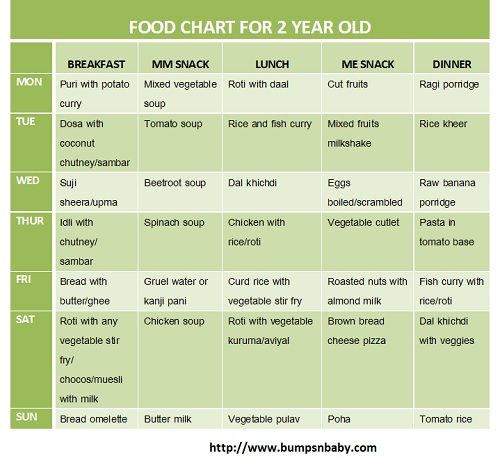
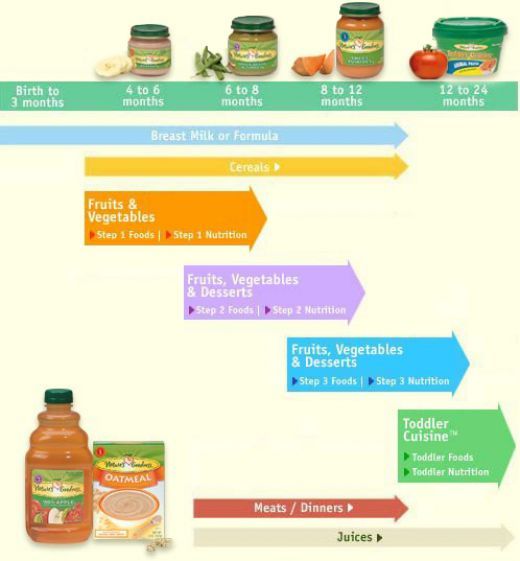
Iron rich food for babies india
Iron-Rich Foods for Toddlers: 10 to Try
Iron is an essential nutrient that the body uses to produce hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that helps your blood carry oxygen to all the other cells in the body.
Iron is essential for:
- supplying the body with oxygen
- muscle metabolism
- maintaining connective tissue
- physical growth
- nerve development
- cell functioning
- producing some hormones
Breast-fed babies usually get enough iron from their mother’s milk, while infants fed with formula should receive iron-fortified formula.
Iron-deficiency anemia
When your toddler switches to eating regular foods, they might not get enough iron. Rest assured, this isn’t common in the United States; only 8 percent of toddlers have iron deficiency.
However, low iron levels can lead to anemia, where the number of red blood cells in your body are too low, potentially causing problems with oxygen getting to key organs.
If your child has low iron levels, you may notice that they:
- are pale
- appear irritable
- don’t want to eat
Longer term, it can lead to:
- slower growth
- delayed motor skill development
- a higher number of infections, as iron supports the immune system
Symptoms may not appear at first, but in time, your child may experience:
- fatigue
- pale skin
- irritability
- fast or irregular heartbeat
- decreased appetite
- slow weight gain
- dizziness
- headaches
- lightheadedness
- difficulty concentrating
Some studies have found that children who drank tea were more likely to have iron-deficiency anemia. One reason for this may be that tannin, found in tea, decreases the body’s ability to absorb iron. Another is that children may be too full to eat after drinking tea.
Related: 10 signs and symptoms of iron deficiency
Iron is essential for a rapidly growing toddler. That’s why a lot of cereals and other toddler foods are fortified with iron.
That’s why a lot of cereals and other toddler foods are fortified with iron.
The recommended daily requirements for iron vary by age.
- age 0–6 months: 0.27 milligrams (mg) per day
- age 6–12 months: 11 mg per day
- ages 1–3 years: 7 mg per day
- ages 4–8 years: 10 mg per day
Infants born preterm or with a low birth weight usually need more iron than those born with a healthy weight.
Heme vs. nonheme iron
Dietary iron has two main forms: heme and nonheme. Plants contain nonheme iron. Meats and seafood contain both heme and nonheme iron.
The body doesn’t absorb nonheme iron as easily as heme iron. This is true for both toddlers and adults. If your child eats a vegetarian or mostly vegetarian diet, aim for twice as much iron as the recommended amount.
The body absorbs iron better when you consume it with a source of vitamin C. To enable the body to absorb more iron, serve iron-rich foods alongside foods rich in vitamin C.
Examples of foods high in vitamin C include:
- orange juice and oranges
- grapefruit
- kiwifruit
- broccoli
- tomatoes
- strawberries
- bell peppers
- papaya
- cantaloupe
- sweet potatoes
Feeding your toddler iron-rich foods alongside foods high in vitamin C can help decrease their risk of developing iron deficiency.
1. Lean meats
Meat and poultry contain large amounts of heme iron, which is easy for the body to digest. Beef, organ meats, and liver in particular have a lot of iron. A 3-ounce serving of beef liver, for example, contains 5 mg of iron.
Dark chicken and turkey meat are also rich sources.
Make your toddler a stew or casserole with soft, well-cooked lean meat. Make sure to remove the fatty part of the meat since there is very little iron in the fatty parts. Spaghetti with meat and tomato sauce is another iron-friendly option.
Related: Top lean proteins you should eat
2.
 Fortified cereals
Fortified cereals Fortified cereals and oatmeal are a good way to ensure your toddler gets enough iron.
A serving of iron-fortified cereals typically has 100 percent of the daily value for iron in just one serving. The exact amount will vary, so be sure to check the label. Dry cereals, like Cheerios, are usually fortified as well.
One cup of plain, uncooked, rolled oats contains around 3.5 mg of iron.
You can top your toddler’s iron-fortified breakfast cereal or oatmeal with some blueberries or strawberries for added vitamin C.
Note that while fortified cereals and juices can provide extra iron, they’re often high in sugar, too.
3. Beans
If you are aiming for a vegetarian diet or your child isn’t a fan of meat, beans are a great compromise. Soybeans, lima beans, kidney beans, lentils, and other beans and pulses contain iron, fiber, and other essential vitamins and minerals.
For example:
- a half cup of white beans has 4 mg of iron
- a half cup of lentils has 3 mg of iron
- a half cup of red kidney beans has 2 mg of iron
Mash some cooked lentils or make a soup or mild chili. Try mashing in some enriched rice with your beans for a complete protein and high-iron meal.
Try mashing in some enriched rice with your beans for a complete protein and high-iron meal.
You can also try serving your toddler some low sugar baked beans with a piece of whole wheat bread for a high iron lunch. A side of mashed sweet potatoes adds vitamin C to the dish.
Chickpeas, known to some as garbanzo beans, are another type of bean high in iron and a great snack for toddlers (and adults!). You can blend the chickpeas to make your own iron-rich hummus.
Be aware that some people have a chickpea allergy. If you’re not sure about giving your child chickpeas, ask your doctor first.
4. Spinach
Dark green leafy vegetables like kale, broccoli, and spinach are among your best vegetable options for iron.
A half cup of boiled, drained spinach contains about 3 mg of iron.
Try serving your toddler finely chopped, steamed spinach or add chopped spinach or other greens to their:
- mac and cheese
- scrambled eggs
- smoothies
Related: Which is better, spinach or kale?
5.
 Raisins and other dried fruit
Raisins and other dried fruitKids love to snack on raisins. The good news is that the dried fruit can give your toddler a boost in iron, while also helping prevent constipation. A quarter cup of raisins has about 1 mg of iron.
Related: Are dried fruits good or bad?
6. Pumpkin seeds
Pumpkin seeds are a good source of protein, fiber, healthy fats, and minerals, including iron. A quarter cup of pumpkin seeds contains 2.5 mg of iron.
Try making a trail mix with raisins, prunes, dried apricots, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds.
Keep in mind that raisins and seeds may be choking hazards for very young children. Mash or cut these foods into small pieces and keep watch on your toddler while they munch on them.
Related: Super healthy seeds you should eat
7. Eggs
Eggs are a good source of essential protein, vitamins, and minerals, including iron. One hard-boiled egg contains 1 mg of iron.
For years, people tried to limit their egg consumption because eggs also contain cholesterol, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Current research suggests, however, that eggs don’t increase the risk of CVD, after all.
Current research suggests, however, that eggs don’t increase the risk of CVD, after all.
Toddlers can eat eggs in many ways, such as:
- soft boiled with toast sticks
- hard boiled, whole or mashed
- scrambled
- as an omelet
- in rice and noodle dishes
You can add chopped spinach and other iron-rich foods to omelets and scrambled eggs. Try different ways to see how your toddler likes them best.
Always make sure the egg is fresh and well cooked. If you can, use fresh, locally sourced organic, free-range eggs.
Related: Top 10 health benefits of eggs
8. Green peas
Green peas contain protein, fiber, iron, and other nutrients. Many toddlers love them, they’re easy to prepare, and they pair well with many dishes.
A half cup of green peas provides 1 mg of iron.
You can boil peas and serve them as a side, mash them with root vegetables for infants, or add them to soups, stews, and savory rice.
Keep a bag of peas in the freezer or get fresh peas in the pod in season. Ask your toddler to help you shell the fresh peas.
Ask your toddler to help you shell the fresh peas.
Peas may pose a choking hazard for young children, so consider mashing them for infants.
Related: Why green peas are healthy and nutritious
9. Tuna
Canned light tuna is a low calorie and low fat addition to your child’s diet that also supplies iron and other important nutrients like protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
Three ounces of light tuna, canned in water, contains 1 mg of iron.
Combine shredded tuna with pureed vegetables to boost your toddler’s iron intake, but hold off if seafood allergies run in your family.
Related: Mercury in tuna. How to eat it safely
10. Tofu
Tofu is a mild and versatile plant-based food that provides complete protein, calcium, iron, and other nutrients. It can provide some of the essential nutrients your toddler needs if they don’t eat meat.
A half cup of tofu contains 3 mg of iron.
Tofu comes in different forms. Firm tofu you can chop and add to salads or stir fries, bake or use to make nuggets. Silken tofu has a softer texture. You can mix it with salad dressings, add it to smoothies, or put fruit with it for a dessert.
Silken tofu has a softer texture. You can mix it with salad dressings, add it to smoothies, or put fruit with it for a dessert.
There have been concerns about whether isoflavones, an ingredient in tofu, could be harmful for hormone balance. Experts currently believe this is “unlikely.”
Related: Using tofu and how to prepare it safely
According to the National Institutes of Health, around 12 percent of infants in their first year, and around 8 percent of toddlers have low iron levels.
It is always best for your child to get their nutrients from food, but if your doctor thinks your child may have iron-deficiency anemia, they may prescribe iron supplements.
Follow the instructions your doctor gives you and keep all supplements out of the reach of children. Consuming too much iron can lead to serious health problems.
Never give your child iron supplements without first consulting a doctor. Most children don’t need supplemental iron.
Babies, Toddler and Kids Iron Rich Foods and Recipes, Tarla Dalal
बच्चों के लिए लोह युक्त आहार - हिन्दी में पढ़ें (Babies, Toddler and Kids Iron Rich Foods recipes in Hindi)
બાળકો લોહ યુક્ત આહાર - ગુજરાતી માં વાંચો (Babies, Toddler and Kids Iron Rich Foods recipes in Gujarati)
iron rich foods for babies and kids. Iron is an essential nutrient at all ages, especially in the growing years, because it is required for making haemoglobin and carrying oxygen from lungs to various parts of the body. Without enough iron, kids tend to become pale and tired because nutrition is not properly distributed to their body parts, they find it difficult to fight infections, and face many other such problems.
Iron is an essential nutrient at all ages, especially in the growing years, because it is required for making haemoglobin and carrying oxygen from lungs to various parts of the body. Without enough iron, kids tend to become pale and tired because nutrition is not properly distributed to their body parts, they find it difficult to fight infections, and face many other such problems.
Iron Rich Foods Include:
Rich sources of iron are Cereals, Millets, and Pulses like roasted Bengal Gram (Chana), cowpea and lentils (Masoor), Green leafy vegetables such as Amaranth, Cow Pea leaves and Shepu. Of the cereal grains and millets, Bajra, Jowar, Bulgur Wheat, Whole Wheat and Ragi are very good sources of iron. Milk although which is a good source of other nutrients, is a poor source of iron.
Paneer and Suva Sandwich
Iron Rich Foods for Babies, Iron Rich Foods for Infants
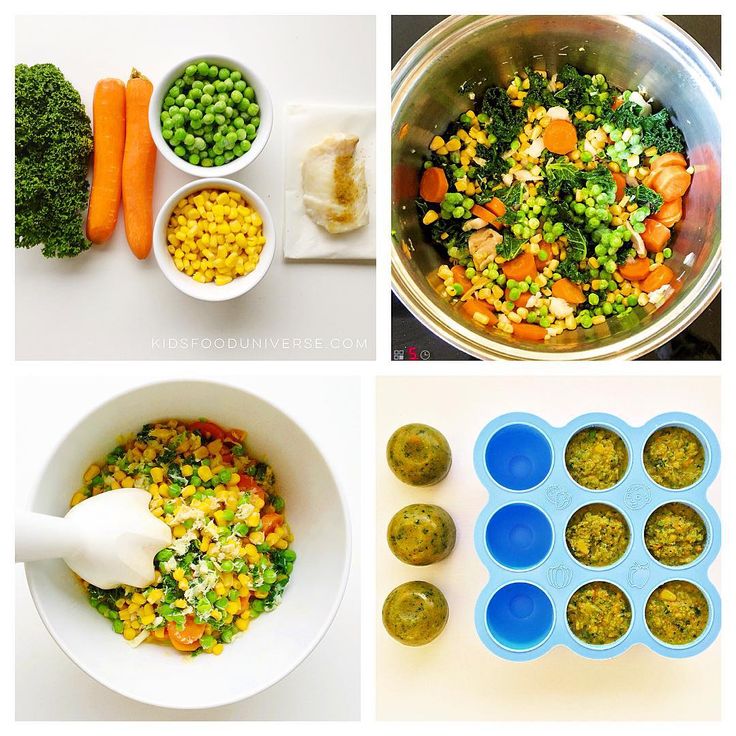
Iron rich recipes for babies aged between 6 months to 12 months should be soft in texture because babies are still undergoing teething. Foods like vegetable mash, porridges, and broths are suitable for infants. Porridges like Bulgur Wheat Porridge and Jowar Ragi and Date Porridge are great to build up iron stores in small babies.
Foods like vegetable mash, porridges, and broths are suitable for infants. Porridges like Bulgur Wheat Porridge and Jowar Ragi and Date Porridge are great to build up iron stores in small babies.
Bulgur Wheat Porridge for Babies
Kids Iron Rich Foods, Snacks
Nothing like a healthy bhel made of Oats after school like Oats-and-Poha-Sukha-Bhel to top up your kids iron levels.
We have created a healthy Chawli Mint Burger with whole wheat bread used to avoid giving kids junk food which leads to body inflammation with sugar and refined foods.
Bulgur Wheat Porridge for Babies
Kids Iron Rich Recipes, Desserts
Date and Almond Balls are ideal and healthy way to kill the sweet cravings of kids along with providing the necessary iron to their body. Halim is the king of iron and great dessert for girls to up their iron content with Halim Ladoo. Or try the Poha Phirni that kids would definitely love to have as a dessert.
Halim Ladoo, Halim Laddu
Kids Iron Rich Foods, Indian Recipes
There is the Punjabi classic Aloo Palak to go with Minty Soya Roti and some Palak Raita, So much of iron if you combine them all in one meal. Enjoy our collection of Iron Rich recipes for kids. We would love to have your feedback.
Aloo Palak
Happy Cooking!
Enjoy our collection of iron rich foods for babies and kids and other kids articles below.
protein rich food for kids
antioxidant kids recipes
healthy foods for kids to gain weight
recipes for kids weight loss
kids calcium rich recipes
Ayurvedic treatment of anemia: preparations and recommendations
Close
Punarnava is an Ayurvedic remedy with a diuretic effect that tones the kidneys and heart. This medicine is useful for keeping the skin healthy, they will also help clear excess Kapha from the stomach and chest. Punarnava acts as an anti-aging agent and can be used in the treatment of urinary disorders. These capsules help reduce excess fluid in the body and edema due to excess Kapha. Punarnava cleanses the blood of toxins, increases the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin content, thereby increasing the oxygen carrying capacity in the body. This remedy is useful in the treatment of edema caused by an imbalance in kapha. This herbal medicine helps to eliminate toxins accumulated through the kidneys and urine. Effective in the treatment of arthritis and gout. Punarnava is helpful in breaking down “fibrin”, a blood clotting protein.
These capsules help reduce excess fluid in the body and edema due to excess Kapha. Punarnava cleanses the blood of toxins, increases the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin content, thereby increasing the oxygen carrying capacity in the body. This remedy is useful in the treatment of edema caused by an imbalance in kapha. This herbal medicine helps to eliminate toxins accumulated through the kidneys and urine. Effective in the treatment of arthritis and gout. Punarnava is helpful in breaking down “fibrin”, a blood clotting protein.
Close
Himalaya Ashvagandha is a natural herbal extract. Ashwagandha is a famous Ayurvedic rejuvenating herb, often referred to as “Indian ginseng”. Increases the body's ability to maintain physical activity and helps relieve stress, fatigue and insomnia.
Does nutrition affect people with anemia?
Yes, bad eating habits can be one of the causes of anemia. Food restricted people and those who take overcooked foods and small amounts of green leafy vegetables may be deficient in folic acid, which is a major cause of anemia.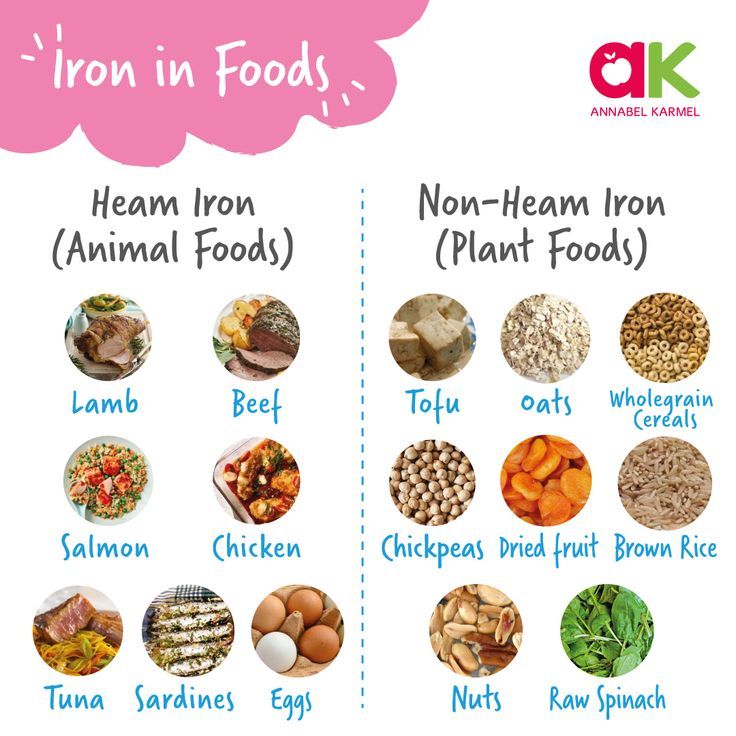
Can anemia be cured?
Yes, anemia is curable. It mostly depends on the type of anemia. Iron and folic acid deficiency is one of the main causes of anemia. These types of anemia are treatable with iron-rich foods. You can also try some herbal products such as Chanderprabha Vati, Punarnava Mandur and Arogyavardhini Vati tablets.
What are the symptoms of iron deficiency?
Symptoms can manifest themselves in different ways, and this mainly depends on the level of hemoglobin. Weakness, fatigue, headache, tingling in the legs, irregular heartbeat, pale skin, and dizziness are some common symptoms of an iron deficiency in your body.
Is the anemia chronic?
Yes, it can lead to some chronic diseases if it persists for more than half a year or even longer. In less than six months, anemia can only be considered in an acute form. In the chronic form, medical treatment is necessary.
Are meat and poultry products good for an anemic person?
Yes, meat and poultry are rich sources of Heme Iron. Eating meat and poultry can increase the absorption of iron in your body. Along with this, green leafy vegetables are also a rich source of iron.
Eating meat and poultry can increase the absorption of iron in your body. Along with this, green leafy vegetables are also a rich source of iron.
If I have anemia during pregnancy, is there a risk of passing it on to my children?
When anemia is severe, a pregnant woman may feel tired, which weakens her immune system and makes her more prone to infections. Anemia increases the risk of having an underweight baby. Cases have been identified where anemia was passed on to children.
Can you offer iron rich foods for vegetarians?
Yes, of course, you can choose rice, cereals, lima beans, peas, broccoli, turnips, nut seeds, dried fruits, spinach and lentils. You can also eat a variety of fruits such as oranges, tomatoes, berries and kiwi because they are high in vitamin C, which aids in the absorption of iron in the body.
Should I eat soy proteins?
No, because unfermented soy is rich in phytic acid, which interferes with the absorption of iron and other nutrients in the body.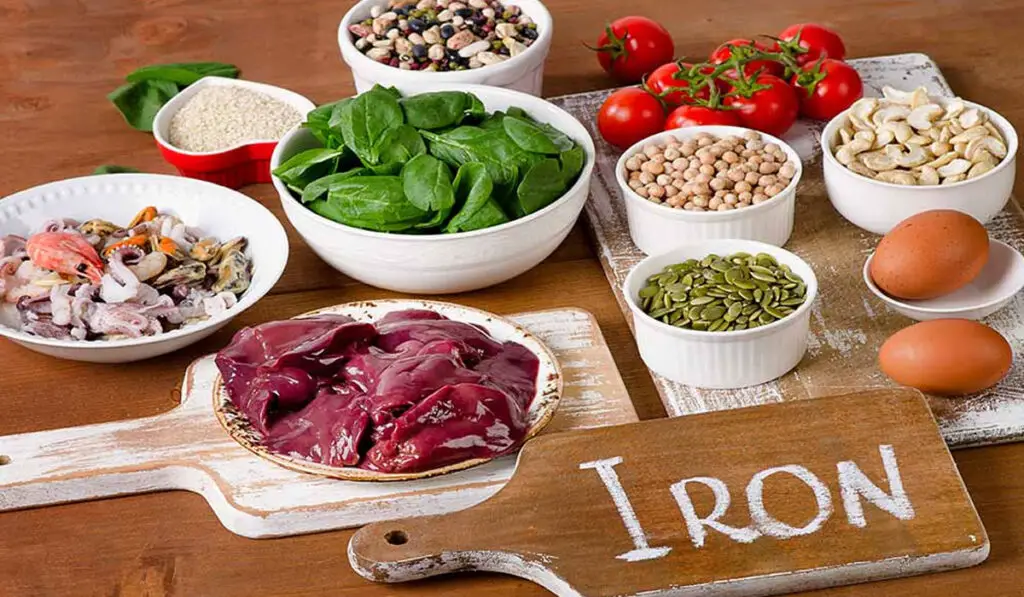
Are herbal remedies effective for anemia?
Yes, all herbal products are very effective for anemia.
I am an alcoholic and also suffer from anemia. How can I get rid of anemia in such a situation?
Alcohol is harmful to an anemic person because it blocks the absorption of iron. Therefore, you should stop using it, but if you cannot do this, then you should drink it an hour or two before meals, when all the iron content will be absorbed by your body.
What is the main cause of anemia?
Not eating enough iron-rich foods, blood loss due to heavy periods, gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcers, and trouble absorbing iron in your body are the main causes of anemia. To get rid of this, it is worth choosing food rich in iron. It is important to understand how to prepare iron-rich foods to ensure digestibility. Pregnancy can also contribute to the development of anemia.
What are the complications of anemia?
Hemoglobin is the main factor that carries oxygen to all parts of your body. An anemic person has a very low hemoglobin content, which will eventually lead to a decrease in oxygen levels in your body tissues or organs. This will lead to a condition such as hypoxia. Due to low oxygen levels, your heart pumps more blood to compensate, and this can lead to heart failure.
An anemic person has a very low hemoglobin content, which will eventually lead to a decrease in oxygen levels in your body tissues or organs. This will lead to a condition such as hypoxia. Due to low oxygen levels, your heart pumps more blood to compensate, and this can lead to heart failure.
Will changing my diet help correct my iron deficiency?
Yes, if you are anemic due to an iron deficiency, by adding some iron-rich foods such as tofu, beans, lentils, cashews and dark green leafy vegetables to your diet, you can overcome your iron deficiency. Vitamin B12 is found in animal products: poultry, meat, eggs and milk.
10 iron-rich foods (list)
Iron is an essential trace element needed by all living organisms. It helps to synthesize collagen and serotonin, supports the immune system and is involved in metabolic processes [1]. But the main function of iron is cellular respiration. This microelement is part of hemoglobin, the protein that makes up red blood cells. It is iron that helps blood cells to bind oxygen and deliver it to the tissues, and then remove the exhaust carbon dioxide from the body. By the way, it also stains the blood red.
It is iron that helps blood cells to bind oxygen and deliver it to the tissues, and then remove the exhaust carbon dioxide from the body. By the way, it also stains the blood red.
Our body is unable to produce iron on its own. He gets it from food, so it is important that the diet is varied. There are two types of iron: heme and non-heme. The former is absorbed more efficiently [2]. It can be found in meat, fish and seafood. The source of the second is plant food. Here is a list of foods with the highest iron content of both types. Including them in the diet will help replenish the micronutrient reserves.
© Ella Olsson/Pexels
Advertising on RBC www.adv.rbc.ru
Daily intake of iron
Women aged 19-50 need iron the most. They need to receive at least 18 mg of the trace element per day. During pregnancy, the need for it increases to 27 mg. Adolescents 14–18 years of age also require an increased iron content: girls - 15 mg, boys - 11 mg. The average daily intake of iron for adult men and older people of both sexes is 8 mg [3]. It increases significantly with intensive sports, regular heavy physical exertion and heavy menstruation.
The average daily intake of iron for adult men and older people of both sexes is 8 mg [3]. It increases significantly with intensive sports, regular heavy physical exertion and heavy menstruation.
Foods high in iron
- Shellfish
- Offal
- Red meat
- Spinach
- Legumes
- Pumpkin seeds
- Quinoa
- Broccoli
- Tofu
- Dark chocolate
Mollusks
Almost all types of mollusks are rich in iron. Thus, one hundred-gram serving of oysters contains about 3 mg of iron, which is 17% of the daily requirement [4]. In addition, this amount also provides 24% of the Daily Value of Vitamin C and 4% of the Daily Value of Vitamin B12. Shellfish are also low in calories, high in protein, and increase levels of "good" cholesterol, which prevents heart disease.
Offal
Liver, kidneys, brain, heart, stomachs and other offal contain large amounts of iron. Although not everyone likes their taste, offal often surpasses meat in terms of nutritional content. For example, to get 36% of the daily value of iron and meet the daily requirement for vitamin A, it is enough to eat only 100 g of beef liver [5]. In addition, offal is a good source of protein, copper, selenium and choline, which is important for the liver.
Although not everyone likes their taste, offal often surpasses meat in terms of nutritional content. For example, to get 36% of the daily value of iron and meet the daily requirement for vitamin A, it is enough to eat only 100 g of beef liver [5]. In addition, offal is a good source of protein, copper, selenium and choline, which is important for the liver.
Red meat
It is the main source of easily digestible heme iron. At the same time, the darker the meat, the more this trace element in it. One 100 gram steamed ground beef patty contains 2.7 mg of iron. This fills the daily requirement by 15% [6]. Meat also serves as a source of protein, zinc, selenium, and B vitamins. But poultry is not so rich in iron: in 100 g of turkey, its content does not exceed 0.7 mg [7].
© Andrijana Bozic /Unsplash
Spinach
Such a rich set of nutrients, as in spinach, is rare. It contains folate, lutein, beta-carotene, calcium, vitamins A and E. In addition, 100 g of the product replenishes 15% of the daily iron requirement. It is non-heme, but at the same time it is quite well absorbed due to the high concentration of vitamin C in spinach. Doctors advise to boil the leaves a little - this will help reduce the amount of oxalic acid, which prevents the absorption of iron [8].
It is non-heme, but at the same time it is quite well absorbed due to the high concentration of vitamin C in spinach. Doctors advise to boil the leaves a little - this will help reduce the amount of oxalic acid, which prevents the absorption of iron [8].
But keep in mind: 100 g of fresh spinach is a big package. It is designed for several people, and it is hardly possible to eat it at a time. In addition, spinach tends to accumulate nitrates, which are often used in its cultivation. Buy the product in trusted farm shops or in special organic packages. Or try growing it yourself - on the windowsill. In winter, instead of fresh spinach, you can take frozen: all its beneficial properties and taste are preserved.
Legumes
This is a must have for vegetarians and vegans. Legumes are one of the best plant sources of iron. Chickpeas, peas, lentils, beans, soybeans - choose what you like. One cup of boiled lentils contains 6.6 mg of iron. This is 37% of the daily norm [9]. And half a cup of boiled beans is enough to fill 10% of the daily requirement for an element [10]. In addition, legumes give a feeling of satiety for a long time and allow you to reduce calorie intake [11].
And half a cup of boiled beans is enough to fill 10% of the daily requirement for an element [10]. In addition, legumes give a feeling of satiety for a long time and allow you to reduce calorie intake [11].
Pumpkin seeds
Pumpkin seeds can be a snack option. 100 g of the product contains 9 mg of iron, or half of the daily recommended amount [12]. But you can't get carried away with them. First, it can cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Secondly, pumpkin seeds are very nutritious. A 100-gram serving provides the body with 559 kcal. To increase your iron levels without harming your health, add a small handful of seeds to your salad, porridge, or soup.
Quinoa
South American groats are often used as a substitute for cereals containing gluten. Add 100 g of boiled seeds to your favorite salad to replenish 8% of the daily iron requirement [13]. Unlike traditional cereals, quinoa is rich in protein containing essential amino acids [14]. Interestingly, our body perceives quinoa as a protein from cow's milk.
© Engin Akyurt /Pexels
Broccoli
A diet rich in broccoli helps improve eyesight, reduces inflammation and slows down aging. Broccoli cleanses the body, removes cholesterol and excess sugar. Use it as a side dish — a glass of cooked broccoli provides 6% of your daily iron requirement [15]. To get the most benefit, steam broccoli for no longer than 5 minutes. This will help preserve vitamin C.
Tofu
Making tofu is like making cheese from milk, which is why many people call it soy cheese. In terms of its nutritional properties, it is almost as good as dairy products - for this, vegans and people with lactose intolerance fell in love with it. 100 g of tofu contains 17 g of protein, which is easily and quickly absorbed by the body. In addition, the same amount of the product helps to cover 15% of the daily requirement of iron [16].
Dark chocolate
Chocolate not only brings pleasure and stimulates the production of the "hormone of happiness", but also helps to normalize iron levels. Choose chocolate that contains at least 70% cocoa [17]. Nutritionists advise eating no more than a quarter of a chocolate bar a day. This will be enough to compensate for 17% of the daily iron requirement, improve the intestinal microflora and improve mood.
Choose chocolate that contains at least 70% cocoa [17]. Nutritionists advise eating no more than a quarter of a chocolate bar a day. This will be enough to compensate for 17% of the daily iron requirement, improve the intestinal microflora and improve mood.
© Dovile Ramoskaite/Unsplash
Iron deficiency is dangerous
Iron deficiency usually has no symptoms at first. But if you do not replenish its reserves on time, you can provoke the development of iron deficiency anemia [18]. Its main symptoms are: weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, drowsiness, loss of appetite, heart palpitations and headaches [19]. There may be a desire to eat something inedible - chalk, clay, paper or ice. With a lack of iron, the cells begin to "suffocate", which is why many vital metabolic processes are disrupted in the body.
Iron deficiency also contributes to reduced immunity and a high risk of infections [20]. In addition, it is one of the causes of hair loss. The trace element is responsible for delivering oxygen to the follicles, thereby strengthening and nourishing the roots. With its deficiency, the hair becomes dry and weak and may begin to fall out [21]. Among other external signs: sores in the corners of the mouth, dry skin, brittle exfoliating nails. According to a study by Japanese scientists, in some cases, iron deficiency causes depression [22].
With its deficiency, the hair becomes dry and weak and may begin to fall out [21]. Among other external signs: sores in the corners of the mouth, dry skin, brittle exfoliating nails. According to a study by Japanese scientists, in some cases, iron deficiency causes depression [22].
© Engin Akyurt/Pexels
If you notice signs of iron deficiency, seek medical attention. He or she will order blood tests, identify the source of the problem, and be able to create a treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Expert's comment
Evgeniya Maevskaya, MD, gastroenterologist and nutritionist GMS Clinic
How often do you need to take a blood test to find out about iron deficiency in time?
The frequency depends on many factors: general health, clinical signs of overt or latent deficiency, being at risk for iron deficiency, or the presence of chronic diseases, including the gastrointestinal tract.
For a potentially healthy person, it is enough to monitor blood counts every six months. However, a general analysis is not enough. At a minimum, it should be supplemented by a study on serum iron and ferritin, otherwise signs of a latent deficiency can be missed. In some cases, a more rare test is needed - for soluble transferrin receptors. This is determined only by the doctor.
However, a general analysis is not enough. At a minimum, it should be supplemented by a study on serum iron and ferritin, otherwise signs of a latent deficiency can be missed. In some cases, a more rare test is needed - for soluble transferrin receptors. This is determined only by the doctor.
Is it possible to make up for iron deficiency only through plant foods? What is your advice for vegetarians and vegans?
Treatment of anemia with dietary iron alone is not possible due to its low content and low bioavailability. Anemia is treated only with iron supplements.
Vegetarians and vegans should eat as varied a diet as possible, including vegetable sources of iron such as sea kale. Shrimps, mussels, and sea fish can serve as a good source of iron if allowed. It is better for vegetarians to undergo an examination and make sure that there is no atrophy in the stomach and problems in the intestines. With atrophy and insufficient acidity of the stomach, the transition of non-heme iron from plant foods to the digestible heme form is significantly difficult, which means that it will not be absorbed.