Is it ok to feed baby breast milk and formula
How to combine breast and bottle feeding
It can take several weeks for you and your baby to feel happy and confident with breastfeeding.
Once you've both got the hang of it, it's usually possible to offer your baby bottles of expressed milk or formula alongside breastfeeding.
This is sometimes called mixed or combination feeding.
Why combine breast and bottle?
You may want to combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding if you:
- are breastfeeding and want to use a bottle to offer your baby some expressed breast milk
- want to breastfeed for some of your baby's feeds, but give bottles of formula for 1 or more feeds
- are bottle feeding your baby and want to start breastfeeding
- need to leave your baby and want to make sure they have some milk while you're away
Introducing formula feeds can affect the amount of breast milk you produce. There is also a small amount of evidence to show babies may not breastfeed as well because they learn to use a different kind of sucking action at the bottle than at the breast.
These things can make breastfeeding more difficult, especially in the first few weeks when you and your baby are still getting comfortable with breastfeeding.
Your breastmilk supply will usually not be affected if you start bottle feeding your baby when they are a bit older, you are both comfortable with breastbeeding, and you breastfeed every day.
Introducing formula feeds
If you're combining breastfeeding with formula feeds both you and your baby can carry on enjoying the benefits of breastfeeding.
If you choose to introduce infant formula:
- it's best to do it gradually to give your body time to reduce the amount of milk it makes – this helps lower your chance of getting uncomfortable, swollen breasts, or mastitis
- if you're going back to work, start a few weeks beforehand to give both of you time to readjust
- if your baby is 6 months old or more and can drink milk from a cup, you may not need to introduce a bottle at all
For more information, see drinks and cups for babies.
Giving your baby their first bottle
It may take a while for a breastfed baby to get the hang of bottle feeding, because they need to use a different sucking action.
- it usually helps to give the first few bottles when your baby is happy and relaxed – not when they're very hungry
- it may help if someone else gives the first bottle feeds, so that your baby is not near you and smelling your breast milk
- you might want to try using a different position for bottle and breastfeeding
See more advice on how to bottle feed.
Restarting breastfeeding
If you want to start breastfeeding more and give your baby fewer bottles, it's a good idea to ask your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter for support.
These tips may help too:
- Hold and cuddle your baby as much as possible, ideally skin to skin. This will encourage your body to make milk and your baby to feed.

- Express your breast milk regularly. Expressing releases the hormone prolactin, which stimulates your breasts to make milk. About 8 times a day, including once at night is ideal. It may be easier to express by hand to begin with – your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can show you how.
- Try bottlefeeding while holding your baby skin to skin and close to your breasts.
- If your baby is latching on, feed little and often. Do not worry if your baby does not feed for long to begin with. See tips on how to get your baby properly positioned and attached.
- Choose times when your baby is relaxed, alert and not too hungry, and do not force your baby to stay at the breast.
- Decrease the number of bottles gradually, as your milk supply increases.
- Consider using a lactation aid (supplementer). A tiny tube is taped next to your nipple and passes into your baby's mouth so your baby can get milk via the tube as well as from your breast.
 This helps to support your baby as they get used to attaching to the breast. Your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can give you more information.
This helps to support your baby as they get used to attaching to the breast. Your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can give you more information.
See more tips on boosting your milk supply.
Help and support with mixed feeding
If you have any questions or concerns about combining breast and bottle feeding:
- talk to your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter
- call the National Breastfeeding Helpline on 0300 100 0212 (9.30am to 9.30pm, every day)
- find breastfeeding support near you
Video: why combine breast and bottle feeding?
In this video, 3 mothers discuss ways to combine breast and bottle feeding.
Media last reviewed: 22 March 2020
Media review due: 22 March 2023
Page last reviewed: 8 October 2019
Next review due: 8 October 2022
Breastfeeding vs.
 Formula Feeding (for Parents)
Formula Feeding (for Parents)Choosing whether to breastfeed or formula feed their baby is one of the biggest decisions expectant and new parents will make.
Healt experts believe breast milk is the best nutritional choice for infants. But breastfeeding may not be possible for all women. For many, the decision to breastfeed or formula feed is based on their comfort level, lifestyle, and specific medical situations.
For moms who can't breastfeed or who decide not to, infant formula is a healthy alternative. Formula provides babies with the nutrients they need to grow and thrive.
Some mothers worry that if they don't breastfeed, they won't bond with their baby. But the truth is, loving mothers will always create a special bond with their children. And feeding — no matter how — is a great time to strengthen that bond.
The decision to breastfeed or formula feed your baby is a personal one. Weighing the pros and cons of each method can help you decide what is best for you and your baby.
All About Breastfeeding
Nursing can be a wonderful experience for both mother and baby. It provides ideal nourishment and a special bonding experience that many mothers cherish.
A number of health organizations — including the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the American Medical Association (AMA), and the World Health Organization (WHO) — recommend breastfeeding as the best choice for babies. Breastfeeding helps defend against infections, prevent allergies, and protect against a number of chronic conditions.
The AAP recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for the first 6 months. Beyond that, breastfeeding is encouraged until at least 12 months, and longer if both the mother and baby are willing.
Here are some of the many benefits of breastfeeding:
Fighting infections and other conditions. Breastfed babies have fewer infections and hospitalizations than formula-fed infants. During breastfeeding, antibodies and other germ-fighting factors pass from a mother to her baby and strengthen the immune system. This helps lower a baby's chances of getting many infections, including:
This helps lower a baby's chances of getting many infections, including:
- ear infections
- diarrhea
- respiratory infections
- meningitis
Breastfeeding also may protect babies against:
- allergies
- asthma
- diabetes
- obesity
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Breastfeeding is particularly beneficial for premature babies.
Nutrition and ease of digestion. Often called the "perfect food" for a human baby's digestive system, breast milk's components — lactose, protein (whey and casein), and fat — are easily digested by a newborn.
As a group, breastfed infants have less difficulty with digestion than do formula-fed infants. Breast milk tends to be more easily digested so that breastfed babies have fewer bouts of diarrhea or constipation.
Breast milk also naturally contains many of the vitamins and minerals that a newborn requires. One exception is vitamin D — the AAP recommends that all breastfed babies begin receiving vitamin D supplements during the first 2 months and continuing until a baby consumes enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates formula companies to ensure they provide all the necessary nutrients (including vitamin D) in their formulas. Still, commercial formulas can't completely match breast milk's exact composition. Why? Because milk is a living substance made by each mother for her individual infant, a process that can't be duplicated in a factory.
Free. Breast milk doesn't cost a cent, while the cost of formula quickly adds up. And unless you're pumping breast milk and giving it to your baby, there's no need for bottles, nipples, and other supplies that can be costly. Since breastfed babies are less likely to be sick, that may mean they make fewer trips to the doctor's office, so fewer co-pays and less money are paid for prescriptions and over-the-counter medicines.
Different tastes. Nursing mothers usually need 300 to 500 extra calories per day, which should come from a wide variety of well-balanced foods. This introduces breastfed babies to different tastes through their mothers' breast milk, which has different flavors depending on what their mothers have eaten. By tasting the foods of their "culture," breastfed infants more easily accept solid foods.
This introduces breastfed babies to different tastes through their mothers' breast milk, which has different flavors depending on what their mothers have eaten. By tasting the foods of their "culture," breastfed infants more easily accept solid foods.
Convenience. With no last-minute runs to the store for more formula, breast milk is always fresh and available whether you're home or out and about. And when women breastfeed, there's no need to wash bottles and nipples or warm up bottles in the middle of the night.
Smarter babies. Some studies suggest that children who were exclusively breastfed have slightly higher IQs than children who were formula fed.
"Skin-to-skin" contact. Many nursing mothers really enjoy the experience of bonding so closely with their babies. And the skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection between mother and infant.
Beneficial for mom, too. The ability to totally nourish a baby can help a new mother feel confident in her ability to care for her baby. Breastfeeding also burns calories and helps shrink the uterus, so nursing moms may be able to return to their pre-pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Also, studies show that breastfeeding helps lower the risk of breast cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, and also may help decrease the risk of uterine and ovarian cancer.
Breastfeeding also burns calories and helps shrink the uterus, so nursing moms may be able to return to their pre-pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Also, studies show that breastfeeding helps lower the risk of breast cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, and also may help decrease the risk of uterine and ovarian cancer.
p
Breastfeeding Challenges
Breastfeeding can be easy from the get-go for some mothers, but take a while to get used to for others. Moms and babies need plenty of patience to get used to the routine of breastfeeding.
Common concerns of new moms, especially during the first few weeks and months, may include:
Personal comfort. Initially, many moms feel uncomfortable with breastfeeding. But with proper education, support, and practice, most moms overcome this.
Latch-on pain is normal for the first week to 10 days, and should last less than a minute with each feeding. But if breastfeeding hurts throughout feedings, or if their nipples and/or breasts are sore, it's a good idea for breastfeeding mothers to get help from a lactation consultant or their doctor. Many times, it's just a matter of using the proper technique, but sometimes pain can mean that something else is going on, like an infection.
Many times, it's just a matter of using the proper technique, but sometimes pain can mean that something else is going on, like an infection.
Time and frequency of feedings. Breastfeeding requires a big time commitment from mothers, especially in the beginning, when babies feed often. A breastfeeding schedule or the need to pump breast milk during the day can make it harder for some moms to work, run errands, or travel.
And breastfed babies do need to eat more often than babies who take formula, because breast milk digests faster than formula. This means mom may find herself in demand every 2 or 3 hours (maybe more, maybe less) in the first few weeks.
Diet. Women who are breastfeeding need to be aware of what they eat and drink, since these can be passed to the baby through the breast milk. Just like during pregnancy, breastfeeding women should not eat fish that are high in mercury and should limit consumption of lower mercury fish.
If a mom drinks alcohol, a small amount can pass to the baby through breast milk. She should wait at least 2 hours after a single alcoholic drink to breastfeed to avoid passing any alcohol to the baby. Caffeine intake should be kept to no more than 300 milligrams (about one to three cups of regular coffee) or less per day because it can cause problems like restlessness and irritability in some babies.
She should wait at least 2 hours after a single alcoholic drink to breastfeed to avoid passing any alcohol to the baby. Caffeine intake should be kept to no more than 300 milligrams (about one to three cups of regular coffee) or less per day because it can cause problems like restlessness and irritability in some babies.
Maternal medical conditions, medicines, and breast surgery. Medical conditions such as HIV or AIDS or those that involve chemotherapy or treatment with certain medicines can make breastfeeding unsafe. A woman should check with her doctor or a lactation consultant if she's unsure if she should breastfeed with a specific condition. Women should always check with the doctor about the safety of taking medicines while breastfeeding, including over-the-counter and herbal medicines.
Mothers who've had breast surgery, such as a reduction, may have difficulty with their milk supply if their milk ducts have been severed. In this situation, a woman should to talk to her doctor about her concerns and work with a lactation specialist.
p
All About Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formulas are a nutritious alternative to breast milk, and even contain some vitamins and nutrients that breastfed babies need to get from supplements.
Manufactured under sterile conditions, commercial formulas attempt to duplicate mother's milk using a complex combination of proteins, sugars, fats, and vitamins that aren't possible to create at home. So if you don't breastfeed your baby, it's important to use only commercially prepared formula and not try to make your own.
Besides medical concerns that may prevent breastfeeding, for some women, breastfeeding may be too difficult or stressful. Here are other reasons women may choose to formula feed:
Convenience. Either parent (or another caregiver) can feed the baby a bottle at any time (although this is also true for women who pump their breast milk). This allows mom to share the feeding duties and helps her partner to feel more involved in the crucial feeding process and the bonding that often comes with it.
Flexibility. Once the bottles are made, a formula-feeding mother can leave her baby with a partner or caregiver and know that her little one's feedings are taken care of. There's no need to pump or to schedule work or other obligations and activities around the baby's feeding schedule. And formula-feeding moms don't need to find a private place to nurse in public.
Time and frequency of feedings. Because formula is less digestible than breast milk, formula-fed babies usually need to eat less often than breastfed babies.
Diet. Women who opt to formula feed don't have to worry about the things they eat or drink that could affect their babies.
page 7
Formula Feeding Challenges
As with breastfeeding, there are some challenges to consider when deciding whether to formula feed.
Lack of antibodies. None of the antibodies found in breast milk are in manufactured formula. So formula can't provide a baby with the added protection against infection and illness that breast milk does.
Can't match the complexity of breast milk. Manufactured formulas have yet to duplicate the complexity of breast milk, which changes as the baby's needs change.
Planning and organization. Unlike breast milk — which is always available, unlimited, and served at the right temperature — formula feeding your baby requires planning and organization to make sure that you have what you need when you need it. Parents must buy formula and make sure it's always on hand to avoid late-night runs to the store.
And it's important to always have the necessary supplies (like bottles and nipples) clean, easily accessible, and ready to go — otherwise, you will have a very hungry, very fussy baby to answer to. With 8-10 feedings in a 24-hour period, parents can quickly get overwhelmed if they're not prepared and organized.
Expense. Formula can be costly. Powdered formula is the least expensive, followed by concentrated, with ready-to-feed being the most expensive. And specialty formulas (such as soy and hypoallergenic) cost more — sometimes far more — than the basic formulas. During the first year of life, the cost of basic formula can run about $1,500.
And specialty formulas (such as soy and hypoallergenic) cost more — sometimes far more — than the basic formulas. During the first year of life, the cost of basic formula can run about $1,500.
Possibility of producing gas and constipation. Formula-fed babies may have more gas and firmer bowel movements than breastfed babies.
Making a Choice
Deciding how you will feed your baby can be a hard decision. You'll really only know the right choice for your family when your baby comes.
Many women decide on one method before the birth and then change their minds after their baby is born. And many women decide to breastfeed and supplement with formula because they find that is the best choice for their family and their lifestyle.
While you're weighing the pros and cons, talk to your doctor or lactation consultant. These health care providers can give you more information about your options and help you make the best decision for your family.
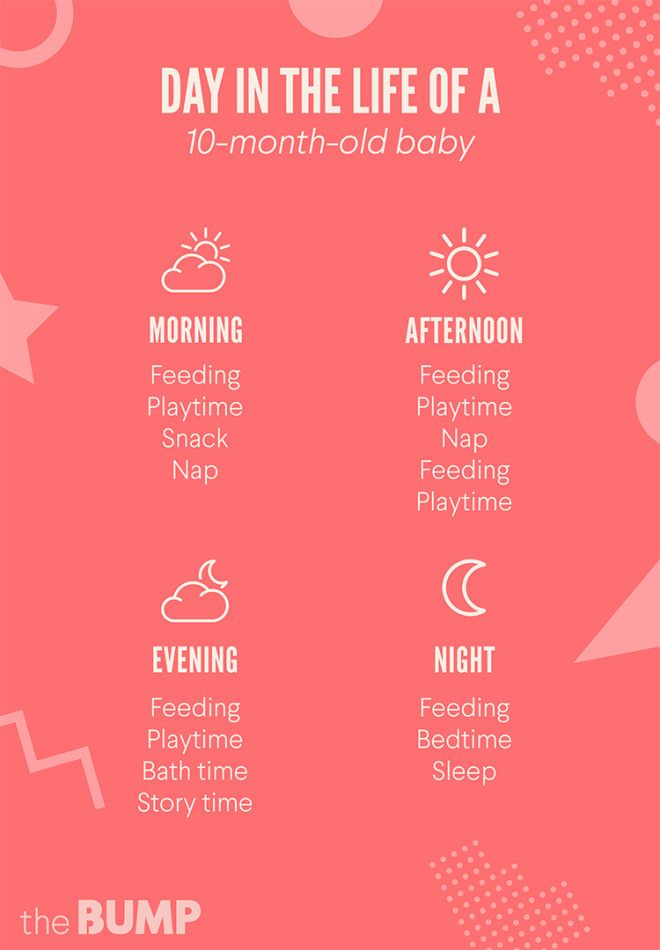
Mixed feeding of newborns: how to organize breastfeeding
No young mother is immune from the situation when a baby will need to be transferred from exclusive breastfeeding to a mixed one. When is it necessary and how to properly organize a new regime?
When is it necessary and how to properly organize a new regime?
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months Read more
Follow-up dry milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 2 NutriValio for feeding children from 6 to 12 months More
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
In our pediatric practice, the term "mixed feeding" refers to the combination of breast milk feeding (at least 250-200 ml) with its artificial substitutes (supplementary feeding, which is introduced if necessary up to 4 months).
First of all, it should be said that the decision to transfer the baby to mixed feeding (both breastfeeding and artificial mixture) must be made together with the pediatrician. If you decide to supplement the baby with a formula on your own, without good reason, you will only violate lactation.
If you decide to supplement the baby with a formula on your own, without good reason, you will only violate lactation.
As a rule, a woman is forced to introduce supplementary feeding with a mixture for one of two reasons - the baby does not have enough breast milk or the mother needs to go to work or school. And if everything is clear with the second situation without comment, then it is better to talk about the first in more detail.
Hypogalactia is a decrease in lactation. How to understand that the child does not have enough milk?
-
The infant rarely urinates (reduced daily urine volume is also called "dry diaper syndrome"). The liquid usually becomes concentrated, with a pungent odor.
-
Stool - rare or atypical (too liquid or thick, discolored).
-
The child is not gaining weight well. In the first 6 months, the baby should recover by 150-200 g per week, after six months - by 100-150 g.
 Of course, these are average figures, but you can focus on them.
Of course, these are average figures, but you can focus on them.
If you notice these symptoms, then you need to take action. First of all, a woman is recommended to try all the ways to improve lactation (no matter how wonderful the mixture is, breast milk for a child is the most valuable food). If milk is still not enough, you need to introduce artificial nutrition.
There are two types of mixed feeding:
Remember that milk should remain the main food for the baby - offer the baby the breast as often as possible (this is a necessary condition for lactation to increase, because mixed feeding is often a temporary measure, and under favorable conditions, the mother can return to natural feeding).
You can feed your baby with a mixture not only from a bottle (the fact is that it is easier for a child to suck from a nipple and often babies refuse to breastfeed, realizing this). You can feed the baby from a special silicone spoon - in this case, put the mixture on the cheek, and not on the tongue. You can use a "syringe" (for example, a medicine dispenser) or a pipette. There are SNS systems - a bottle with a thin tube that is fixed on the mother's nipple. When a baby suckles, he receives both breast milk and formula. This is the ideal solution for hypogalactia as it helps to maintain close skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby, which has a beneficial effect on restoring lactation. If you are switching to mixed feeding due to the fact that you need to leave home, it is better for your assistant to accustom the child to the bottle - so the child will not smell you and reach for the breast.
You can use a "syringe" (for example, a medicine dispenser) or a pipette. There are SNS systems - a bottle with a thin tube that is fixed on the mother's nipple. When a baby suckles, he receives both breast milk and formula. This is the ideal solution for hypogalactia as it helps to maintain close skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby, which has a beneficial effect on restoring lactation. If you are switching to mixed feeding due to the fact that you need to leave home, it is better for your assistant to accustom the child to the bottle - so the child will not smell you and reach for the breast.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
For supplementary feeding, choose a high-quality, balanced mixture. Valio Baby baby food is made from the highest quality natural cow's milk and is as close as possible to the composition of breast milk. It will help the baby gain weight and strengthen the body.
3.04 24
FoodShare:
Oksana Ivargizova
Medical Institute. Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
Breast milk and formula: what do they have in common?
1 Cribb VL et al. Contribution of inappropriate complementary foods to the salt intake of 8-month-old infants. Eur J Clin Nutr . 2012;66(1):104. - Cribb V.L. et al., "Effects of inappropriate complementary foods on salt intake in 8-month-old infants". Yur J Klin Nutr. 2012;66(1):104.
Contribution of inappropriate complementary foods to the salt intake of 8-month-old infants. Eur J Clin Nutr . 2012;66(1):104. - Cribb V.L. et al., "Effects of inappropriate complementary foods on salt intake in 8-month-old infants". Yur J Klin Nutr. 2012;66(1):104.
2 Lönnerdal B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am 9 Clin Nutr . 2003;77(6):1537 S -1543 S - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
3 Savino F et al. Breast milk hormones and their protective effect on obesity. Int J Pediatric Endocrinol. 2009;2009:327505. - Savino F. et al., "What role do breast milk hormones play in protecting against obesity." Int J Pediatrician Endocrinol. 2009;2009:327505.
2009;2009:327505.
4 Hassiotou F, Hartmann PE. At the Dawn of a New Discovery: The Potential of Breast Milk Stem Cells. Adv Nutr . 2014;5(6):770-778. - Hassiot F, Hartmann PI, "On the threshold of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells." Adv. 2014;5(6):770-778.
5 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clinic Transl Immunology . - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
6 Pannaraj PS et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(7):647-654. - Pannaraj P.S. et al., "Bacterial communities in breast milk and their association with the emergence and development of the neonatal gut microbiome". JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
7 Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama.Glycobiology. 2012;22(9):1147-1162. - Bode L., "Oligosaccharides in breast milk: a sweet mother for every baby." Glycobiology (Glycobiology). 2012;22(9):1147-1162.
8 Deoni SC et al. Breastfeeding and early white matter development: A cross-sectional study. neuroimage. 2013;82:77-86. - Deoni S.S. et al., Breastfeeding and early white matter development: a cross-sectional study. Neuroimaging. 2013;82:77-86.
9 Birch E et al. Breast-feeding and optimal visual development. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993;30(1):33-38. - Birch, I. et al., "Breastfeeding and Optimum Vision Development." J Pediatrician Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993;30(1):33-38.
10 Sánchez CL et al. The possible role of human milk nucleotides as sleep inducers. Nutr Neurosci . 2009;12(1):2-8. - Sanchez S.L. et al., "Nucleotides in breast milk may help the baby fall asleep." Nutr Neurosai. 2009;12(1):2-8.
Nutr Neurosci . 2009;12(1):2-8. - Sanchez S.L. et al., "Nucleotides in breast milk may help the baby fall asleep." Nutr Neurosai. 2009;12(1):2-8.
11 Moukarzel S, Bode L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and the Preterm Infant: A Journey in Sickness and in Health. Clin Perinatol. 2017;44(1):193-207. - Mukarzel S., Bode L., "Breast milk oligosaccharides and the full-term baby: a path to illness and health." Klin Perinatol (Clinical perinatology). 2017;44(1):193-207.
12 Beck KL et al. Comparative Proteomics of Human and Macaque Milk Reveals Species-Specific Nutrition during Postnatal Development. J Proteome Res . 2015;14(5):2143-2157. - Beck K.L. et al., "Comparative proteomics of human and macaque milk demonstrates species-specific nutrition during postnatal development." G Proteom Res. 2015;14(5):2143-2157.
13 Michaelsen KF, Greer FR. Protein needs early in life and long-term health. Am J Clin Nutr . 2014;99(3):718 S -722 S . - Mikaelsen KF, Greer FR, Protein requirements early in life and long-term health. Am J Clean Nutr. 2014;99(3):718S-722S.
Protein needs early in life and long-term health. Am J Clin Nutr . 2014;99(3):718 S -722 S . - Mikaelsen KF, Greer FR, Protein requirements early in life and long-term health. Am J Clean Nutr. 2014;99(3):718S-722S.
14 Howie PW et al. Positive effect of breastfeeding against infection. BMJ .1990;300(6716):11-16. — Howie PW, "Breastfeeding as a defense against infectious diseases." BMJ. 1990;300(6716):11-16.
15 Duijts L et al. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in infancy. Pediatrics , 2010;126(1): e 18-25. - Duitz L. et al., "Prolonged exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in the first year of life." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2010;126(1):e18-25.
16 Ladomenou F et al. Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child . 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child.2010;95(12):1004-1008.
Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child . 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child.2010;95(12):1004-1008.
17 Vennemann MM et al. Does breastfeeding reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome?. Pediatrics . 2009;123(3): e 406- e 410. - Wennemann M.M. et al., "Does Breastfeeding Reduce the Risk of Sudden Infant Death?" Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2009;123(3):e406-e410.
18 Straub N et al. Economic impact of breast-feeding-associated improvements of childhood cognitive development, based on data from the ALSPAC. Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6. - Straub N.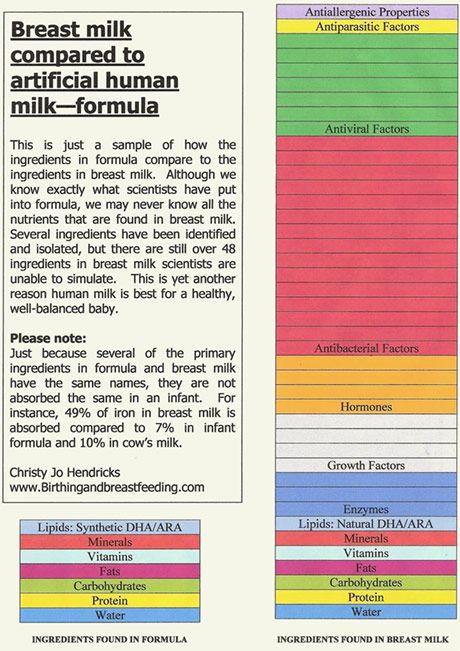 et al., "Economic Impact of Breastfeeding-Associated Cognitive Child Development (ALSPAC)". Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6.
et al., "Economic Impact of Breastfeeding-Associated Cognitive Child Development (ALSPAC)". Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6.
19 Heikkilä K et al. Breast feeding and child behavior in the Millennium Cohort Study. Arch Dis Child . 2011;96(7):635-642 - Heikkila K. et al., Breastfeeding and Child Behavior in a Millennial Cohort Study. Arch Dis Child. 2011;96(7):635-642.
20 Singhal A et al. Infant nutrition and stereoacuity at age 4–6 y. Am J Clin Nutr , 2007;85(1):152-159. - Singhal A. et al., Nutrition in infancy and stereoscopic visual acuity at 4-6 years of age. Am F Clean Nutr. 2007;85(1):152-159.
21 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
22 Horta B et al. Long - term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):30-37. - Horta B.L. et al., "Long-term effects of breastfeeding and their impact on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis." Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):30-37.
23 Lund-Blix NA. Infant feeding in relation to islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible children: the MIDIA Study. Diabetes Care . 2015;38(2):257-263. - Lund-Blix N.A. et al., "Breastfeeding in the context of isolated autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed children: a study MIDIA ". Diabitis Care. 2015;38(2):257-263.
- Lund-Blix N.A. et al., "Breastfeeding in the context of isolated autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed children: a study MIDIA ". Diabitis Care. 2015;38(2):257-263.
24 Amitay EL, Keinan-Boker L. Breastfeeding and Childhood Leukemia Incidence: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review0. JAMA Pediatr 2015;169(6): e 151025. - Amitai I.L., Keinan-Boker L., "Breastfeeding and incidence of childhood leukemia: a meta-analysis and systematic review." JAMA Pediatrics 2015;169(6):e151025.
25 Bener A et al. Does continued breastfeeding reduce the risk for childhood leukemia and lymphomas? Minerva Pediatr. 2008;60(2):155-161. - Bener A. et al., "Does long-term breastfeeding reduce the risk of leukemia and lymphoma in a child?". Minerva Pediatrician. 2008;60(2):155-161.
26 Dewey KG. Energy and protein requirements during lactation. Annu Rev Nutr . 1997;17:19-36. - Dewey K. J., "Energy and Protein Requirements During Lactation". Anna Rev Nutr. 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36.
Annu Rev Nutr . 1997;17:19-36. - Dewey K. J., "Energy and Protein Requirements During Lactation". Anna Rev Nutr. 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36.
27 Victoria CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
28 Jordan SJ et al. Breastfeeding and Endometrial Cancer Risk: An Analysis From the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium. Obstet Gynecol . 2017;129(6):1059-1067. — Jordan S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of endometrial cancer: an analysis of epidemiological data from the Endometrial Cancer Consortium". Obstet Ginekol (Obstetrics and Gynecology). 2017;129(6):1059-1067.
29 Li DP et al.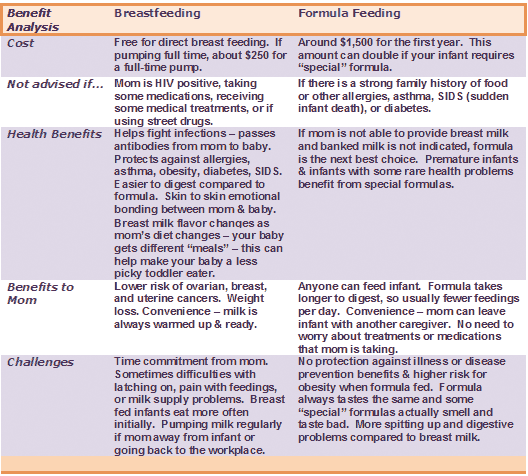 Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev . 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas W Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev . 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas W Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
30 Peters SAE et al. Breastfeeding and the Risk of Maternal Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women. J Am Heart Assoc . 2017;6(6). - Peters S.A. et al., "Breastfeeding and Maternal Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women". J Am Hart Assoc. 2017;6(6):e006081.
31 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet ; 2011 Jan 20 - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer, 20 January 2011 [cited 4 April 2018]
32 Doan T et al.