Lactose free food for babies
Lactose-Free Diet - Pediatric Nutrition - Golisano Children's Hospital
Golisano Children's Hospital / / Lactose-Free Diet
Lactose is the sugar that is found naturally in milk and milk products, as well as foods with ingredients such as milk or whey. In order for the body to use lactose, it has to break it down using an enzyme called lactase. Lactose intolerance is a condition that occurs when a person does not produce enough lactase to break down the lactose in food.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance include:
- Abdominal cramping
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea
These symptoms may occur shortly after eating foods that contain lactose, but sometimes will not occur until hours later. This is because people vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate.
When milk products are eliminated from the diet because of lactose intolerance, an important source of calcium and other vitamins and minerals is eliminated. Because of this, your child will need to get calcium from other sources, or may need to take a calcium supplement. Be sure to consult with your child's doctor or dietitian before giving any supplements. The amount of calcium a child needs will depend on their size and age.
Avoiding Lactose
There are many different words that are used to describe the different forms that lactose may come in. Read food labels, and stay away from foods with any of the following ingredients:
- Milk
- Skim milk powder
- Skim milk solids
- Lactose
- Whey
- Caseinate
- Curd
The following ingredients are okay to use:
- Lactase
- Lactalbumin
- Lactylate
- Calcium compounds
Reading food/nutrition labels is a very important habit to get into when looking for foods that do not contain lactose. Lactose can come in many "hidden" forms, and even products that do not appear to have milk included, may in fact have a milk product as an ingredient.
Lactose can come in many "hidden" forms, and even products that do not appear to have milk included, may in fact have a milk product as an ingredient.
Lactose-Free Foods
Following are lists of lactose-free foods, and foods to avoid:
| Food Group | Enjoy | Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Beverages | Teas, regular iced tea, regular carbonated beverages, soy milk, cocoa powder, Nestle's Quik | Milk (all types), powdered milk, sweetened/condensed milk, instant hot cocoa, instant iced tea, Ovaltine, chocolate drink mixes, cream, half-n-half and diet soda |
| Breads/Cereals/Crackers | Vienna bread, French bread, Jewish rye bread, Italian bread, graham crackers, soda crackers, Ritz crackers, hot or cold cereals without added milk solids (read the label) | Breads/rolls containing milk, prepared baking mixes (muffins, biscuits, pancakes, etc. ), Zwieback, corn nuts, instant cereal with added milk solids ), Zwieback, corn nuts, instant cereal with added milk solids |
| Potatoes and Starches | Items prepared without milk or milk products: macaroni, noodles, rice, spaghetti, white/sweet potatoes | Products with milk added, such as instant potatoes, frozen French fries, Scalloped/au gratin potatoes, macaroni and cheese mixes |
| Vegetables | Fresh, frozen, and canned vegetables without added milk products | Creamed or breaded vegetables or vegetables with margarine added |
| Fruit | Fresh, canned or frozen fruit not processed with milk/milk products | Any canned or frozen fruit processed with milk or milk products |
| Meat and Meat Substitutes | Plain meat, fish, poultry, eggs, Kosher prepared meat products, soybean meat substitutes, dried peas, beans, lentils, and nuts | Breaded or creamed eggs, fish, meat or poultry, luncheon meats, sausage, hot dogs containing cheese or cheese products |
| Fats and Oils | Bacon, shortening, Miracle Whip, milk-free margarine, diet imitation margarine, salad dressings without milk products, vegetable oils, olives, mayonnaise, Coffee Rich and Rich's Whipped Topping | Sour cream, cream cheese, chip dips, sauces and salad dressings made with milk products and peanut butter with added milk solids |
| Soups/Combination Foods | Bouillon, broth, vegetable soups, clear, soups, consommes, homemade soups made with allowed ingredients | Chowders, ream soups, canned and dehydrated soups containing milk products |
| Seasonings | Pure monosodium glutamate (msg), soy sauce, carob powder, olives, gravy made with water, Baker's cocoa, pure seasonings and spices, sugar, honey, corn syrup, jam, jelly, marmalade, and molasses | Condiments with milk solids or lactose added |
| Desserts | Angel food cake, homemade cookies, cakes or pies made from allowed ingredients, tofu desserts, pure-sugar candies, marshmallows, and gelatin | Desserts prepared with milk/milk products, pudding, sherbet, ice cream, custard, frozen yogurt, toffee, peppermint, butterscotch, chocolate, caramels, reduced-calorie desserts made with sugar substitute, or chewing gum made with lactose. |
Additional Resources
For more information or lactose-free products:
- Resources for Products see www.missrobens.com for their catalog.
- The Food Allergy Network and Anaphylaxis Network for information and membership.
Lactose intolerant babies and toddlers
Read time: 8 minutes
What to know about the difference between a cow’s milk protein allergy and lactose intolerance in babies and toddlers:
What is lactose intolerance and how can it be managed in babies and toddlers?
Learn the difference between lactose intolerance and lactose overload in babies
Understand what a cow’s milk protein allergy is and how to help your baby or toddler eat while avoiding dairy.
Some babies can’t tolerate dairy, whether through the mother’s diet in breast milk, in formula, or once they’ve started solids. But how do you know if it’s lactose intolerance, a dairy allergy, or something else entirely?
Read on to learn how to figure out if your little one may be intolerant to lactose, or if their symptoms may indicate a milk protein allergy.
Lactose itself is the sugar naturally found in dairy products.1 People with lactose intolerance do not have enough of the enzyme lactase, which helps the body break down and digest this milk sugar. Without lactase, bacteria break down the excess lactose, creating more fluid and gas, which is where the symptoms of lactose intolerance come from.2
Symptoms of lactose intolerance include:
Gas
Bloating, cramping, abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Nausea or even vomiting1,2
Symptoms usually show up between 30 minutes and 2 hours after having dairy.6
What causes lactose intolerance?A lack of the digestive enzyme lactase is sometimes genetic.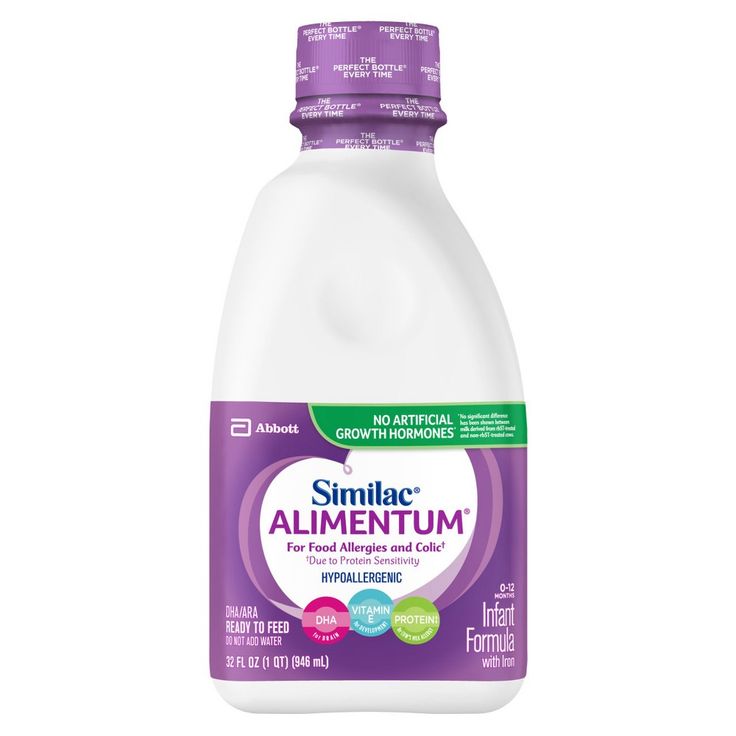 2 Other times lactose intolerance may occur as a result of infections in the intestines or other illnesses such as Crohn’s disease, Celiac disease, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome; or as a temporary symptom of a virus your child may have.3,4
2 Other times lactose intolerance may occur as a result of infections in the intestines or other illnesses such as Crohn’s disease, Celiac disease, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome; or as a temporary symptom of a virus your child may have.3,4
One of the most common causes of lactose intolerance, however, is the slow natural decline of lactase that happens over time.5 This may start to occur after the age of 5 years.
Premature babies born before 34 weeks may also experience temporary lactase deficiency.5 Though this normally improves fairly quickly.4
Babies born at full term usually have plenty of lactose since it is a primary component of breastmilk (just like all mammalian milks).5,7 For this reason, lactose intolerance is generally not common in babies, but may start showing up in toddlers sometime after the age of three years. 1
1
Read more: Is Your Baby Reacting to Something in Your Breastmilk?
Diagnosis of lactose intoleranceIf you suspect your little one has lactose intolerance, call their health care provider. Sometimes just a medical and diet history can help their doctor figure out if your baby is not able to digest lactose well.4 Other times, more tests may be needed.
Tests that may help identify lactose intolerance:
Hydrogen breath test. If your toddler is not able to digest lactose, there will be more hydrogen in their breath than usual.
Stool acidity. Taking a stool sample may help the doctor see if your little one is not digesting lactose. The stool will be more acidic.4
If your baby or toddler is diagnosed with lactose intolerance, the best treatment is avoiding or limiting dairy products and choosing lactose free products when they are available. 2
2
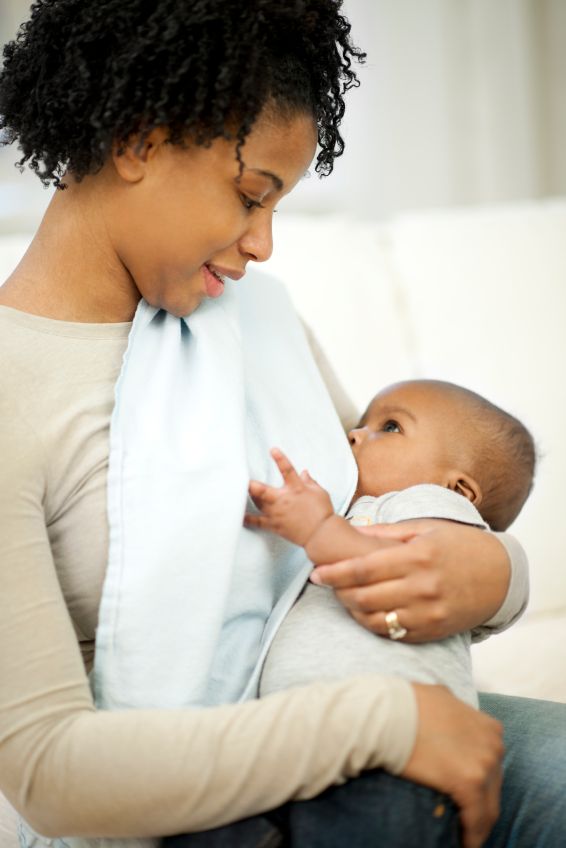
While lactose intolerance is very rare in babies, should you feel your little one has a problem with lactose there is no need to stop breastfeeding. Simply minimize dairy in your diet and continue to breastfeed. However, keep in mind that your baby’s symptoms might actually be ‘lactose overload’ or cow’s milk protein intolerance. Keep reading to learn more about these alternate diagnoses.
For a baby on formula, you may consider a low lactose (‘sensitive’) formula to see if that is helpful. The pediatrician can help guide this decision.
The good news is that most people who are lactose intolerant can in fact continue to drink or eat a certain amount of dairy without it causing symptoms.2 Some people may be able to have one serving of dairy, while others may tolerate a little more or less. Try different amounts to see if your toddler can still have a bit of dairy in their diet.
There are also dairy products that naturally have less lactose in them or are manufactured to be lactose-free which your toddler may be able to tolerate, including yogurt, cow’s milk, as well as hard cheeses such as cheddar or swiss. And of course, always be sure to provide your baby or toddler with foods in a texture they are developmentally ready to eat!
And of course, always be sure to provide your baby or toddler with foods in a texture they are developmentally ready to eat!
Read about: What Type of Milk Should my Toddler Drink?
What is lactose overload?Some women overproduce breastmilk, causing their little ones to take in a high volume of milk before they’re able to get a decent amount of the fat from the feed.8 This may cause something called ‘lactose overload’, or too much lactose for baby’s little tummy to digest at one time.8
Many times, lactose overload is mistaken for lactose intolerance, but with some changes in breastfeeding this issue can be managed and resolved.8,9
Symptoms of lactose overload include frothy or explosive stools that are a bit smelly and more than 10 urine diapers per day.8,9 A baby with lactose overload may have good or even higher-than-average weight gain. 9
9
Interestingly, a baby who is suffering from lactose overload may always seem hungry, even though they are gaining enough weight.9 This is because when baby is not getting enough fat, they are not registering the fullness and satisfaction that fat triggers in the brain.8
Management of lactose overloadThe most important thing is to first figure out if oversupply is the main culprit. The help of a lactation consultant will be important to get to the bottom of lactose overload.
If oversupply is the issue, the lactation consultant may recommend block feeding for a few days.8,9 This will help baby more fully empty a breast and get higher-fat feeds. Once symptoms are relieved, it’s time to go back to regular breastfeeding.9
For some mothers, the issue is not oversupply but rather feeding on a schedule or not feeding often enough. 8,9 All of these may allow the breasts to fill up too much and provide baby with too much lactose and not enough fat.
8,9 All of these may allow the breasts to fill up too much and provide baby with too much lactose and not enough fat.
Be sure to feed your little one on demand, or when baby asks to feed.11 This is normally anywhere between 8 and 12 times per 24 hours depending on baby’s age.10
Read more:
What is Breastmilk Oversupply and How to Manage it
Should I Breastfeeding On Demand or on a Schedule
What is a cow’s milk protein allergy?While lactose intolerance is rare in babies, some little ones believed to have lactose intolerance may actually have an allergy or intolerance to the cow’s milk proteins whey and casein.
A cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA or CMA) or intolerance (CMPI) happens when the body has an overreactive immune response to the protein, triggering an allergic reaction.12 CMA is one of the most common allergies in young children, affecting about 1 to 3% of babies and toddlers. 13,14
13,14
Fortunately, most children will eventually outgrow this as they get older and their digestive and immune systems mature.16
Symptoms of a cow’s milk protein allergyReactions usually happen within 1 to 2 hours after being exposed to cow’s milk protein, whether from breastmilk, formula, or from eating it in a meal.13 Reactions may range from mild to life-threatening.
In babies, symptoms of a milk protein allergy may include:
Colic, crying
Gassiness, bloating, discomfort
Eczema
Blood or mucous in the stool
Frequent stools
Vomiting16
In toddlers, symptoms of a milk protein allergy may include:
Red, itchy hives on the skin
Coughing and wheezing
Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
Vomiting
Anaphylaxis12,13
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur within seconds to up to 2 hours after exposure to an allergen. 15 It can, among other things, cause a sudden drop in blood pressure and impaired breathing. If your child has known allergies, make sure you speak to your physician or allergist to get an emergency plan in place so that you are always prepared.
15 It can, among other things, cause a sudden drop in blood pressure and impaired breathing. If your child has known allergies, make sure you speak to your physician or allergist to get an emergency plan in place so that you are always prepared.
Wondering if your little one has lactose intolerance or a milk protein allergy? Reach out to our team of registered dietitians and lactation consultants for free! They’re here to help on our free to live chat from Monday – Friday 8am - 6pm (ET). Chat Now!
Diagnosis of cow’s milk protein allergyIf you feel your little one has an allergy, speak with their healthcare provider immediately. Their doctor will ask about their diet and when the symptoms tend to show up.
Tests that may help identify a milk protein allergy:
Skin prick test: usually done by an allergist
IgE test: a blood test that can help diagnose an allergy
Diet elimination: Taking out all dairy from the diet for 3 to 4 weeks to see if symptoms improve12
A diet elimination should be done with the help of a dietitian to ensure that your little one continues to get the nutrients they need for growth and development even when eliminating a food group.
Formula fed babies will likely need to switch to a non-dairy formula. Note that soy formula may or may not be a good alternative as some babies with CMA may also have a reaction to soy protein.16
When breastfeeding an infant allergic to cow’s milk protein, all dairy will need to be eliminated from your diet. When eliminating dairy, whether from your own diet or for an allergic toddler, reading labels is critical.
The following list includes some of the ingredients that indicate the presence of milk in the product:
Milk, cheese, cottage cheese, yogurt, sour cream
Lactose, lactulose, lactoferrin, lactic acid starter
Whey
Casein and caseinates
Curds
Milk by-products (like butter, ghee, and buttermilk)
Dry milk solids or powder, condensed or evaporated milk17
You may wonder how you or your child’s nutritional status may be impacted when foregoing dairy products. Fortunately, there are many foods that can supply the important nutrients that dairy provides, such as protein, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D.18
Fortunately, there are many foods that can supply the important nutrients that dairy provides, such as protein, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D.18
All whole fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, meat, poultry, fish, grains, and eggs are dairy free. When it comes to meeting your and your child’s nutritional needs, choose a variety of these non-dairy-containing foods.
Food sources of calcium: Fortified plant-based milk alternatives, fortified orange juice, canned sardines and salmon with bones, fortified dairy alternatives such as a non-dairy yogurt, tofu, soybeans, spinach, kale.19
Read more: Why Calcium Matters for Babies, Tots, and Mama
Food sources of vitamin D: Salmon, fortified plant-based milk alternatives, fortified cereals, egg, canned light tuna, portabella mushrooms – but most importantly: sunlight!20
Read more: Why Vitamin D Matters for Babies, Tots, and Mama
Food sources of protein: Fish, poultry, meat, beans, legumes, peas, nuts, seeds, tofu, eggs, whole grains.
Read more: Protein: Getting Enough and the Best Sources
Second: Look for dairy alternativesThere are many non-dairy substitutes on the market, such as coconut yogurt, plant-based milk alternatives such as almond- and oatmilk; and even vegan dairy-free butter! These allow you to still cook and bake dairy-free with ease, as well as enjoy dairy-like foods in your day.
If you are choosing a plant-based milk alternative, look for ones that are fortified with calcium and vitamin D.
Read more: What Type of Milk Should my Toddler Drink?
Reach out to your child’s healthcare providerIf you suspect that your child has lactose intolerance or a cow’s milk protein allergy, call their healthcare provider immediately. They can make sure you and your little one are getting the support you need and help you make informed decisions for moving forward. They may also recommend further testing or recommend your child be seen by an allergist.
Remember that if your baby does not have an allergy to milk protein, that lactose intolerance in babies is not very common. Check in with a lactation consultant to help determine if what your baby is experiencing may be lactose overload, and what to do if it is.
Let's Chat!We know parenting often means sleepless nights, stressful days, and countless questions and confusion, and we want to support you in your feeding journey and beyond.
Our Happy Baby Experts are a team of lactation consultants and registered dietitians certified in infant and maternal nutrition – and they’re all moms, too, which means they’ve been there and seen that. They’re here to help on our free, live chat platform Monday - Friday 8am - 6pm (ET).Chat Now!
Read more about the experts that help write our content!
For more on this topic, check out the following articles and recipes:Nutrients to look for at 6-12 months
Guidance when raising a child with food allergies
Introducing Major Allergens to your Infant
Does my Child Have a Food Allergy or a Food Intolerance?
Sources
Lactose Free Infant Formula | What does it mean and which is better
In the article we will talk about lactose-free baby food. Pediatricians prescribe it for medical reasons. You will find out in what cases a lactose-free mixture is used, and why it is useful to have it even in a house where there is a healthy baby.
Pediatricians prescribe it for medical reasons. You will find out in what cases a lactose-free mixture is used, and why it is useful to have it even in a house where there is a healthy baby.
Lactose-free formula is a lifesaver for lactase deficiency and rotavirus
Lactose is milk sugar. Or the carbohydrate found in animal milk. It takes part in the absorption of vitamins and calcium, is a breeding ground for the reproduction of beneficial bacteria in the intestines. Lactose is the main source of energy for newborns.
Lactase is an enzyme that is produced in the intestines of an infant and helps digest lactose. Sometimes this enzyme is not produced enough. Then lactose is not completely broken down. This leads to bloating, diarrhea and restlessness of the baby.
Pediatricians diagnose lactase deficiency.
It is important to know that lactase deficiency is congenital - it is a very rare hereditary disease. At risk are babies whose next of kin suffer from lactose intolerance. Parents, knowing this, need to be on the alert.
Parents, knowing this, need to be on the alert.
Much more often lactase deficiency - acquired - due to illness or other causes. Her symptoms go away after treatment and elimination of the cause. And you can again give the child dairy products.
Infants who are artificially and sometimes breastfed are transferred to a lactose-free or low-lactose diet temporarily or until they switch to adult food.
When lactose-free formula is prescribed
Unlike a low-lactose formula, which is recommended for temporary lactase deficiency, a lactose-free diet is used in cases of serious health problems. These are congenital lactase deficiency - galactosemia or rotavirus infection.
Lactose-free formula for rotavirus
Formula-fed babies with rotavirus need to switch to a lactose-free diet. With rotavirus infection, dairy products aggravate the symptoms of the disease, therefore, are prohibited.
If your baby is an artificial baby, stock up on a jar of soy formula for an emergency. After all, with an intestinal infection, the last thing you want to do is waste time looking for food for your child. And if it is not useful, cook porridge on it for the baby when he grows up.
After all, with an intestinal infection, the last thing you want to do is waste time looking for food for your child. And if it is not useful, cook porridge on it for the baby when he grows up.
Nature has taken care of babies who receive mother's milk. It contains immunoglobulins and other substances that facilitate the course of the disease.
Therefore, pediatricians recommend not to interrupt breastfeeding during the period of rotavirus.
Lactose free formula - which is better
Mothers sometimes worry about whether a lactose-free diet can provide a child with all the necessary substances. There is no doubt that lactose-free formula, like any other, is a complete baby food. After all, this issue is under the control of the state. Activities for the production of baby food are subject to mandatory certification.
Lactose-free mixtures are of two types: on vegetable protein, for example, soy or hypoallergenic.
If the child is not allergic to soy, then it is better to use soy.
What does hypoallergenic formula mean? This means that they cannot cause allergies. All components are selected in such a way that they will be sure to be absorbed by the body. Hypoallergenic mixtures or hydrolysates are a product where proteins are partially broken down and are better absorbed. But hydrolysates are prescribed in the most difficult cases. They are bitter, and babies are reluctant to eat them.
Do not rush to transfer the child to a hypoallergenic diet, unless there are serious indications.
The line of Israeli baby food includes low-lactose and soy formulas:
Materna Extra Care Comfort - low lactose;
Materna Soy 0+ and 12+ are soy nutrition with an improved composition, adapted to the age characteristics of newborns and toddlers from one year old.
Give us a call and a free consultation will help you determine what nutrition your child needs.
All Materna baby food is made without palm oil, without sugar and without GMOs.
How to switch a child to lactose-free formula
The transition scheme depends on the cause. If you are transferring a child to a dairy-free diet due to rotavirus, then you need to change the diet at the same time. Just replace your food with soy. The baby may have a period of getting used to a new product. But this is a lesser evil than to continue to feed him with milk.
If the transition to soy nutrition is planned, we recommend introducing it according to our scheme.
Reaction to lactose-free formula
When transferring a child to another diet, watch his reaction. If soy was chosen as the lactose-free mixture, and an undesirable reaction occurred to it, an allergy to soy should be ruled out. To do this, take a blood test and consult a doctor.
Best Lactose Free Formulas: List of Lactose Free Dairy Formulas for Babies and Children
Milk formulas allow not only to feed a baby in the absence of breast milk, but also to make him complementary foods, saturating him with the necessary vitamins. What lactose-free formulas for newborns are included in the rating today, which ones are the best? More on this and more below.
What lactose-free formulas for newborns are included in the rating today, which ones are the best? More on this and more below.
Content
- 1 Nutrilon (Nutricia) Lactose free (from birth) 400 g
- 2 Bellakt BL (from birth to 12 months) 400 g0080
- 4 Nutrilak (InfaPrim) Premium lactose free (from birth) 350 g
- 5 NAN (Nestli) Lactose free (from birth) 400 g
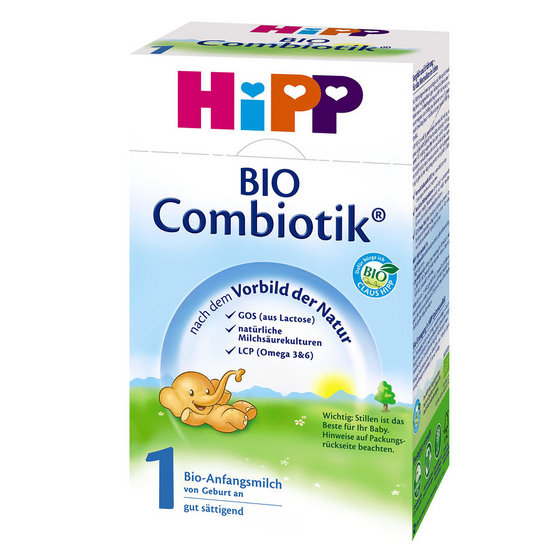
Nutrilon (Nutricia) Lactose free (from birth) 400 g
A list of the best lactose-free formulas for infants, specially formulated for those who are lactose intolerant. Due to the unique composition, it provides the process of rapid relief of lactase deficiency and normalization of the intestinal barrier function. It has nucleotides in its composition and improves the digestion process. Develops the brain and vision. Contains in its composition polysaccharides with maltose and glucose with oils, calcium caseinate, minerals, fish oil, soy lecithin, cysteine, choline and other substances. Does not contain sugar, preservatives and starch. Produced in a jar in the form of a dry mix.
Does not contain sugar, preservatives and starch. Produced in a jar in the form of a dry mix.
Doctors often advise using a colic and constipation mixture for newborns to solve bowel problems.
Bellakt BL (from birth to 12 months) 400 g
From 310 ₽
Good mixture based on skimmed cow's milk with the addition of maltodextrin, vegetable oil, whey protein, docosahexagenic acid, refined fish oil, arachiminite and nucleotide premix. Contains useful vitamins and minerals necessary for the growth and normal development of the child. Keeps well for 100 months. It is produced in a cardboard box and is suitable for lactose-free nutrition for children up to 1 year old. Does not contain dangerous and harmful components that destroy the structure of the baby's brain.
Similac (Abbott) Alimentum (from birth) 400 g
From 1081 ₽
Dry wellness formula, included in the rating of lactose-free formulas for children, does not contain milk protein with palm oil, preservatives and gluten. Produced in a metal four-hundred-gram jar. Formulated with maltodextrin, safflower and soybean oil, hydrolysing casein, sucrose, minerals, emulsifier, xanthan gum, arachidonic acid. Includes vitamins and minerals, easily digestible fats needed by a child who has severe allergies and lipid malabsorption.
Produced in a metal four-hundred-gram jar. Formulated with maltodextrin, safflower and soybean oil, hydrolysing casein, sucrose, minerals, emulsifier, xanthan gum, arachidonic acid. Includes vitamins and minerals, easily digestible fats needed by a child who has severe allergies and lipid malabsorption.
Nutrilak (InfaPrim) Premium lactose-free (from birth) 350 g
From 499 ₽
Lactose-free infant formula for infants who have lactase deficiency, galactosemia and diarrhea. Contains glucose syrup with maltodextrin, sunflower and soybean oil, milk protein and fat, fish oil, choline and other useful trace elements. Produced in a cardboard box and does not include sugar with palm oil, preservative and starch.
NAN (Nestli) Lactose free (from birth) 400 g
. Has a shelf life of 730 days. Suitable for nutrition of children who have lactase deficiency. Contains easily digestible carbohydrates with lactobacilli. It is sold on the market and in online stores in a metal can.