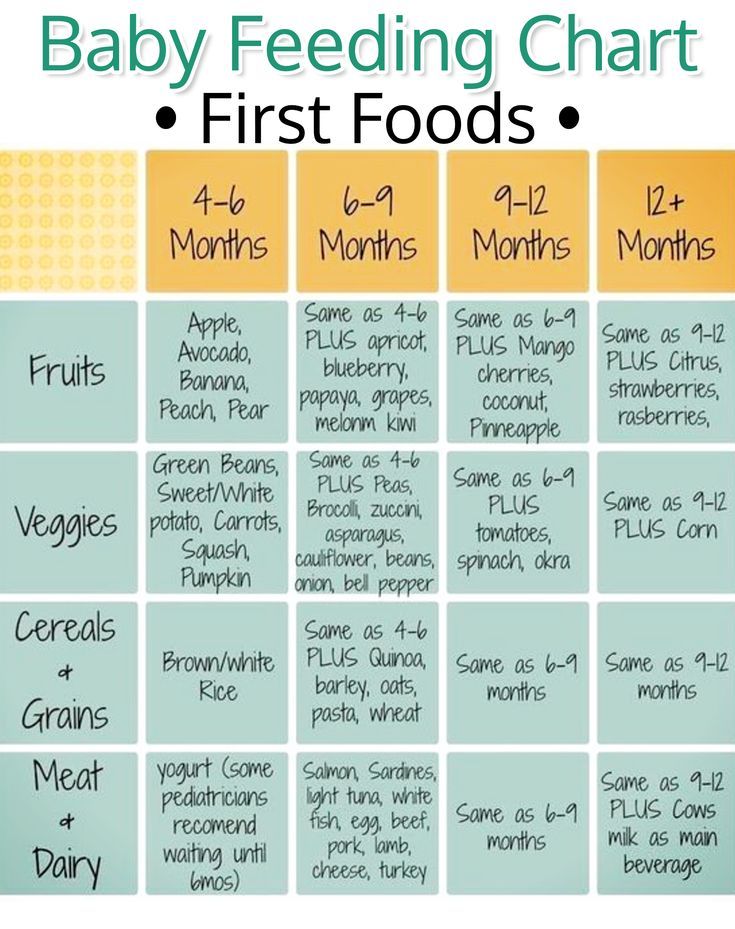
My baby is 5 months old what can i feed him
5 month old feeding schedule: Timings and food types
A general feeding schedule can help parents and caregivers organize their day. However, feeding on demand — when the baby shows signs of being hungry — ensures that the baby gets enough food.
At 5 months old, a baby should get the majority of their nutrition from breastmilk or formula. Most babies do not require solids at this stage. Anyone considering starting a baby on solid food before they are 6 months old should talk to a pediatrician first.
Share on PinterestAll or most of a 5-month-old baby’s diet should comprise of breastmilk or formula.At 5 months, breastmilk or formula is the most important ingredient in a healthful diet.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommend exclusively breastfeeding for about 6 months. However, for those who are unable or choose not to breastfeed, formula milk is available for babies of all ages.
Most 5-month-old babies should not be eating solids. Even when a baby shows signs of readiness for solids, this should only be a small portion of their diet. Always check with a pediatrician before starting a baby less than 6 months old on solids.
Parents and caregivers should not try to restrict a baby’s food intake, regardless of a baby’s growth. Instead, devise a loose schedule and then feed babies when they are hungry.
According to one source, this means getting to know a baby’s hunger cues, which might include licking their lips, rooting, or sucking hands.
A 2013 analysis of more than 10,000 children compared children whose parents or caregivers fed them on demand with those who received food according to a predetermined schedule.
The analysis found that parents and caregivers who followed a feeding schedule had higher confidence and better sleep. However, the study revealed that schedule-fed babies went on to do less well at school than demand-fed babies.
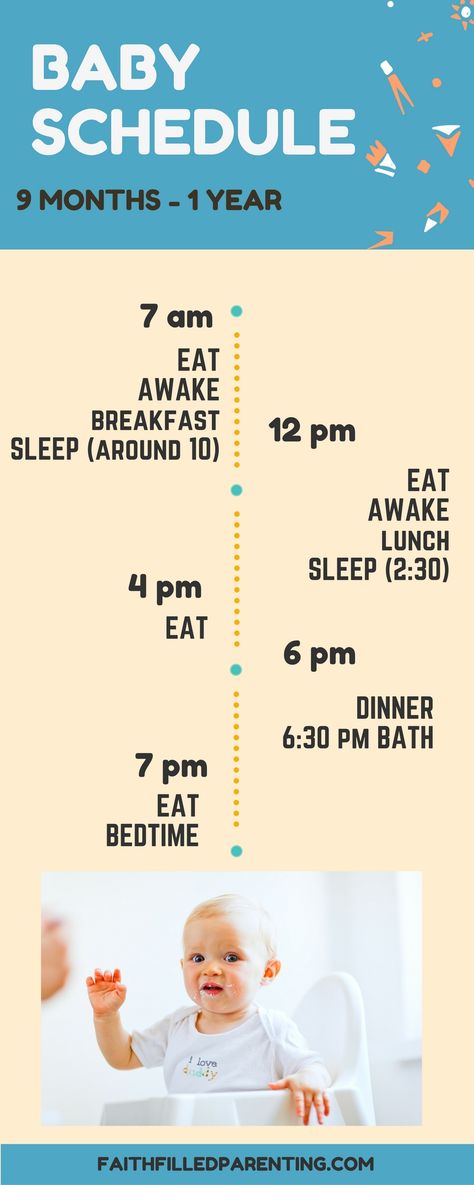
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), most babies need to eat at least every 2–3 hours, which is about five to six times per day.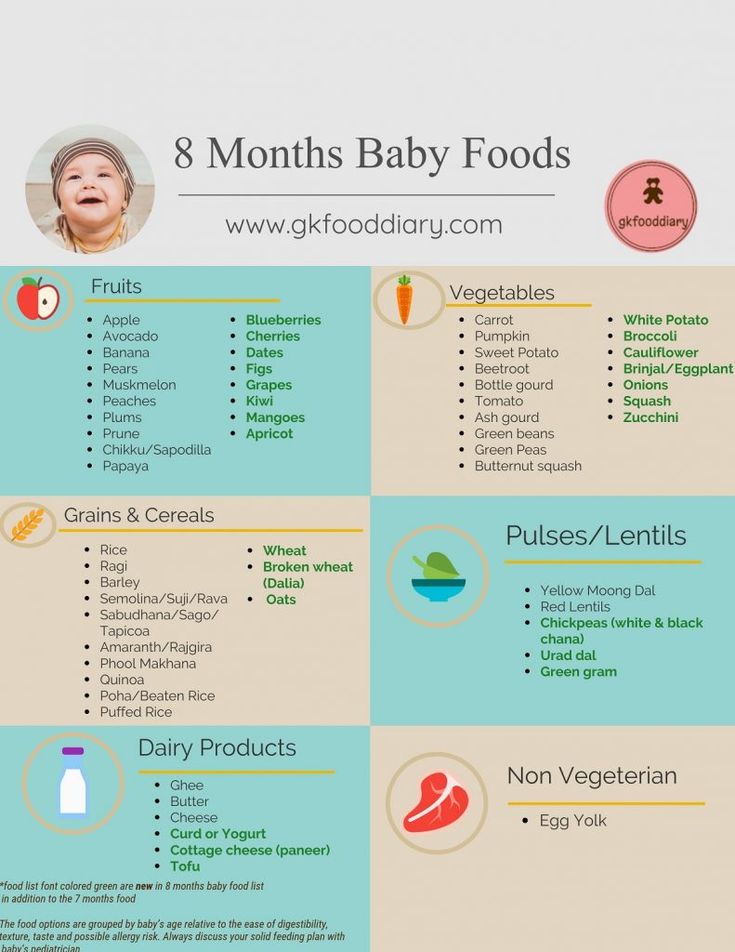 At 5 months, some babies sleep through the night. Others still wake to feed.
At 5 months, some babies sleep through the night. Others still wake to feed.
Parents and caregivers who follow a schedule should try to remain flexible. A baby who is hungry an hour before snacktime needs to eat, just as a baby who is tired early should go to sleep.
Formula or breastmilk
Formula or breastmilk is the most important ingredient in a 5-month-old’s diet. According to Infant Nutrition and Feeding, babies should get five or more nursing sessions per day or 26 to 39 ounces (oz) of iron-fortified formula.
Some babies nurse more during growth spurts or when they do not feel well. Likewise, people who use a combination of formula and breastmilk may nurse slightly less often and give less formula.
Some research suggests that doing a “dream feed,” which involves the parent or caregiver feeding the baby relatively early in the evening before going to bed, helps babies sleep longer at night.
Other liquids
Do not give 5-month-old babies juice, cow’s milk, or water.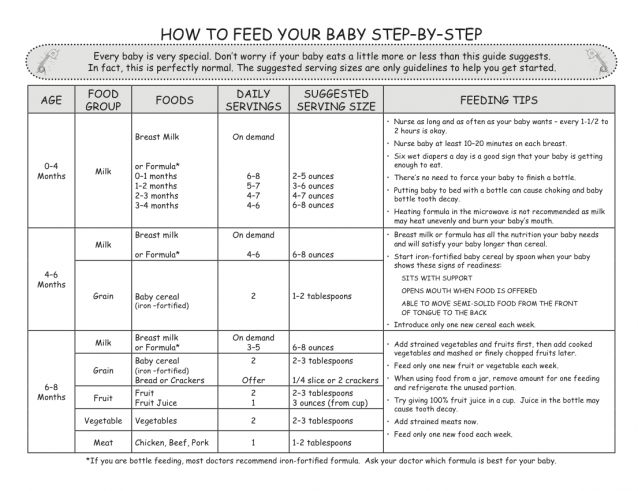 Babies get water from formula or breastmilk. The World Health Organization (WHO) explain that giving babies water to drink increases the risk of diarrhea and may cause them to drink less breastmilk or formula.
Babies get water from formula or breastmilk. The World Health Organization (WHO) explain that giving babies water to drink increases the risk of diarrhea and may cause them to drink less breastmilk or formula.
Solids
Most parents and caregivers should breastfeed or formula-feed the baby for at least 6 months. The CDC indicate that a baby might be ready for solids a little earlier if:
- they have good control over their head
- they can sit on their own without support
- they lean forward or open their mouth when a caregiver offers food
The American Academy of Pediatrics warn against introducing solids before 4 months as this can lead to increased weight gain.
Most babies do not need solids at this age. Some people may use solids as a supplement to formula or breastmilk but never give a baby solids without talking to a pediatrician first.
According to the Sleep Foundation, most 5-month-olds take two to four naps a day. Some naps may be longer than others. For example, a baby might take a short early morning nap, then a longer nap late in the morning and in the mid-afternoon.
For example, a baby might take a short early morning nap, then a longer nap late in the morning and in the mid-afternoon.
Some people feed the baby right before they go to bed, hoping this will help them sleep longer. Others use an eat, play, sleep schedule. Neither is “right.”
Instead, people should choose the approach that works for them. Some babies need to nurse just before sleep. Others are eager to fall asleep after a play session.
Some tips that can help shape a schedule around a baby’s eating and sleeping routines include:
- Be prepared to feed a baby when they awake. Expect babies to be particularly hungry and need more food after long naps and in the morning.
- Each person must consider which schedule works best for them and the people around them. Some people choose to play, then feed, then put the baby to sleep, while others adopt a feed, play, sleep approach.
- Know that a child’s napping needs may change when they are unwell, growing, or stressed.
 Similarly, many babies nurse for comfort during challenging times. Allowing a baby to nurse when they want, even if it is not feeding time, may help soothe them.
Similarly, many babies nurse for comfort during challenging times. Allowing a baby to nurse when they want, even if it is not feeding time, may help soothe them. - Do not put solid foods in a bottle, including before naptime.
All babies and families are different. Most babies eventually develop a rhythm that parents and caregivers can slowly shape into a schedule.
While some people prefer a fairly strict schedule, others take a more relaxed approach. Neither approach is right.
As long as babies get enough food and eat every 2–4 hours, it is fine to experiment with different schedules.
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor. It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here. Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done. Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods. The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal.
 The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods. - Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.
Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
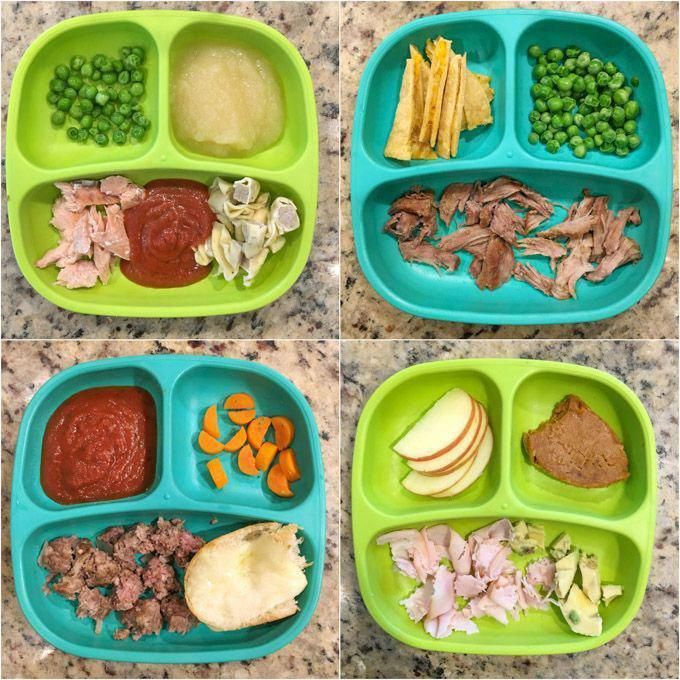
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.
 ) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Sources
BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
AAP. 2021. Starting solid foods. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren. org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Starting-Solid-Foods.aspx [Accessed February 2022]
org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Starting-Solid-Foods.aspx [Accessed February 2022]
AAP. 2021. Sample menu for an 8 to 12 month old. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Sample-One-Day-Menu-for-an-8-to-12-Month-Old.aspx [Accessed February 2022]
CDC. 2020. How much and how often to feed. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/InfantandToddlerNutrition/foods-and-drinks/how-much-and-how-often.html [Accessed February 2022]
Stanford University. Undated. Feeding guide for the first year. Stanford Children's Health and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford. https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=feeding-guide-for-the-first-year-90-P02209 [Accessed February 2022]
USDA. 2020. ChooseMyPlate.gov. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://www.choosemyplate.gov/ [Accessed February 2022]
USDA. 2020. Infant nutrition and feeding. U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://wicworks.fns.usda.gov/resources/infant-nutrition-and-feeding-guide [Accessed February 2022]
U.S. Department of Agriculture. https://wicworks.fns.usda.gov/resources/infant-nutrition-and-feeding-guide [Accessed February 2022]
USDA and DHHS. 2020. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th Edition. U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://DietaryGuidelines.gov [Accessed February 2022]
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
what foods can be given to a child
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
25408 views
Complementary foods are any foods other than breast milk and infant formula. Often they are introduced into the baby's diet after the fourth, fifth or sixth month of life. Is this approach correct and how can I feed a child at 5 months?
Often they are introduced into the baby's diet after the fourth, fifth or sixth month of life. Is this approach correct and how can I feed a child at 5 months?
When do complementary foods start at five months
Current research shows that the optimal age for introducing complementary foods for all children is four to six months. This period is even called the "critical window". It is then that the foundations of the tolerance of different types of food are laid in the body and the need for new nutrients arises. The baby may already lack the nutrients that he receives from mother's milk or formula. The baby needs vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, additional sources of energy and other important nutrients. It's time to introduce him to a variety of taste sensations and form taste habits for life. And of course, learn important chewing skills.
The age of 4-6 months for the introduction of complementary foods is also recommended by the European Nutrition Committee ESPGHAN, the Union of Pediatricians of Russia and other specialists in nutrition and health of children. At the same time, the terms are individual, and you should always consult with a specialist. But for a healthy child, in the absence of additional indications, the best age to start complementary foods is four to five to six months.
At the same time, the terms are individual, and you should always consult with a specialist. But for a healthy child, in the absence of additional indications, the best age to start complementary foods is four to five to six months.
It used to be thought that exclusive breastfeeding should introduce complementary foods earlier. But recently, scientists have found that at this age, breast milk no longer always fills the need for micronutrients, especially iron. Thus, the age of 4 to 6 months for the start of complementary feeding is now recognized as the “gold standard” for both breastfeeding and formula feeding [1] .
What foods to introduce into the baby's diet
The best first complementary foods that will complement the diet of a child at 5 months, experts consider children's vegetable purees or children's dairy-free cereals. In this case, the choice depends on the characteristics of the child. For children with reduced body weight or frequent stools, porridge is more suitable, and for babies with excess weight and constipation, mashed potatoes.
The first vegetable purees should consist of only one type of vegetable. Frutonyan's assortment includes mashed marrows, cauliflower and broccoli. It is these vegetables that experts recommend because of their delicate fiber. The composition of products is not allowed the presence of flavorings, dyes, preservatives, added starch, sugar and salt.
The first porridge for feeding should also be one-component. Start with gluten-free cereals: buckwheat, corn or rice. Pediatricians insist on cereals of industrial production, which are enriched with useful components.
Buckwheat, rice and corn porridge "FrutoNyanya" correspond to all recommendations. They contain a complex of vitamins (C, E, PP, pantothenic acid, B2, B1, B6, A, folic acid, D3, biotin, B12) and minerals (iron, zinc, iodine).
It is far from always possible to supplement the nutrition of a child at 5 months with complementary foods the first time. Sometimes it takes 10-15 attempts for the baby to accept a new product. Parents must be calm and consistent, and then everything will definitely work out. And from six months, you can offer your baby several different cereals or mashed potatoes.
Parents must be calm and consistent, and then everything will definitely work out. And from six months, you can offer your baby several different cereals or mashed potatoes.
It is best if by the year the child’s diet contains 3-4 types of vegetables and the same number of cereals. And you can not delay the introduction of baby meat puree after six months, as these products supplement the diet with essential nutrients.
Complementary feeding rules at five months
Understanding how you can feed a child at 5 months, you can move on to how to do it.
- Use a spoon to feed porridge or puree. Don't give food on your finger.
- A new product is introduced into the diet gradually. For the first time, the portion should be minimal, no more than 1/5 of the recommended rate. Then the amount is gradually increased and brought to the required level within a week.
- Each time after feeding, closely monitor tolerance. To make it easier to control the possible reaction of the body, complementary foods should be introduced in the morning.

- Complementary foods should not be introduced during infectious diseases, and should not be combined with vaccination. After the next vaccination, at least 3-5 days should pass.
- Complementary foods are given to a child who is hungry - that is, before breastfeeding or formula. When breastfeeding, it is important to keep it for the entire duration of the introduction of different types of complementary foods, that is, at least up to a year.
- Complementary foods contain less water than breast milk or infant formula. Therefore, babies are offered water in small portions between feedings. In addition to complementary foods, a child needs 150-200 ml of water per day. It is better to use special bottled, but boiled is also suitable.
Sample menu for a 5 month old baby
- Vegetable puree: 150 g daily + 1–3 g vegetable oil;
- porridge: 150g daily + 1-3g butter.

Once the complementary foods have stabilized, its tentative five-month schedule looks like this:
As they grow older, other foods are added to complementary foods: fruit, meat purees, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurts, baby juices, baby cookies, and so on.
How to feed a baby at 5 months: which porridge and puree to choose
Experts advise not to cook cereals on your own, but to start complementary foods with industrial-made cereals. By choosing a responsible brand, parents can be sure of the quality and safety of the product.
What about puree? In this matter, pediatricians are also on the side of finished products. Purees produced at the factory have a number of advantages:
- high quality raw material;
- compliance with strict hygiene requirements;
- laboratory-tested chemical composition, including vitamin content regardless of the season;
- optimum degree of grinding.
It hardly makes sense to cook mashed potatoes on your own, which is inferior in quality to the factory one. It is better to devote this time to communication and games with the child, so that he grows up not only healthy, but also the happiest.
It is better to devote this time to communication and games with the child, so that he grows up not only healthy, but also the happiest.
List of sources
1. Union of Pediatricians of Russia. The program for optimizing the feeding of children of the first life in the Russian Federation. Guidelines: 2019. // URL: https://www.pediatr-russia.ru/information/dokumenty/other-docs/nacprog1year_2019.pdf#page=46 (Accessed 03.12.2021).
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
Scientific adviser to PROGRESS JSC, Ph.D. PEDIATRIC ADVICE
Doctor, when is the best time to introduce complementary foods? What are the dangers of introducing complementary foods too early or too late?
In fact, there are no universal recommendations regarding the introduction of complementary foods, - says Solomiya Maksimchuk, - because each baby has its own characteristics, so the approach should be individual. Therefore, answering the first question - when it is advisable to introduce complementary foods, I cannot name a specific figure, because in fact complementary foods are introduced at 3 months, and at 4, and at 6, and at 8 - depending on the indications. In my medical practice, there were children who were one year old, and no matter how we tried to introduce complementary foods, everything was in vain - the kids did not show any food interest, especially those who were breastfed. They had a good weight gain, psychomotor development, but they did not show food interest, and this is not very good, because the children did not form and did not prepare the gastrointestinal tract for the perception of other foods. What, then, can be advised to a mother who is faced with this problem? In this case, I am more guided not by my professional experience, but by the experience of the mother, understanding how difficult it is to force a child to eat if he does not want to.
Therefore, answering the first question - when it is advisable to introduce complementary foods, I cannot name a specific figure, because in fact complementary foods are introduced at 3 months, and at 4, and at 6, and at 8 - depending on the indications. In my medical practice, there were children who were one year old, and no matter how we tried to introduce complementary foods, everything was in vain - the kids did not show any food interest, especially those who were breastfed. They had a good weight gain, psychomotor development, but they did not show food interest, and this is not very good, because the children did not form and did not prepare the gastrointestinal tract for the perception of other foods. What, then, can be advised to a mother who is faced with this problem? In this case, I am more guided not by my professional experience, but by the experience of the mother, understanding how difficult it is to force a child to eat if he does not want to.
In which case is it advisable to introduce complementary foods earlier, in which case - adhering to standard norms?
In the case of breastfeeding (if the baby is completely healthy), I start talking about this when the baby is 6 months old. With artificial feeding, we are talking about the introduction of complementary foods when the baby is 4 months old. Some mothers are of the opinion that breast milk contains all the necessary micronutrients, so you should not rush to complementary foods. Of course, this is true - if the mother adheres to the right diet, she eats fully. But in fact, complementary foods help prepare the baby’s herbal system - the child learns different tastes, because it’s no secret that when a baby receives only breast milk, some digestive juices are released, and in the case of complementary foods, completely different ones, therefore, introducing complementary foods, we gradually prepare an enzymatic system.
With artificial feeding, we are talking about the introduction of complementary foods when the baby is 4 months old. Some mothers are of the opinion that breast milk contains all the necessary micronutrients, so you should not rush to complementary foods. Of course, this is true - if the mother adheres to the right diet, she eats fully. But in fact, complementary foods help prepare the baby’s herbal system - the child learns different tastes, because it’s no secret that when a baby receives only breast milk, some digestive juices are released, and in the case of complementary foods, completely different ones, therefore, introducing complementary foods, we gradually prepare an enzymatic system.
Which foods are the first to be introduced into complementary foods, because there are different views on this issue - someone advises fermented milk products, someone vegetable purees or juice?
It all depends on the specific situation. If complementary foods are introduced at 3 months, indications are necessary for this - these are digestive disorders of the baby, the child's tendency to constipation. In this case, I recommend giving fermented milk products to the child at the first stage of the introduction of complementary foods. For children who are bottle-fed and have digestive problems, I recommend fermented milk mixtures (horses are considered the first complementary foods). If we are talking about a completely healthy child, first of all, I advise you to introduce vegetable puree - it is easily digested by the children's gastrointestinal tract. Usually, this is a puree of zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, parsnips, parsley, white carrots, potatoes. Unfortunately, in our area there is not a wide variety of products. Pediatricians should take this into account when advising the mother what to choose at the beginning of complementary foods in winter, because if we advise a zucchini in February, will we find it on the shelves, and if so, will this exotic product benefit the baby?
In this case, I recommend giving fermented milk products to the child at the first stage of the introduction of complementary foods. For children who are bottle-fed and have digestive problems, I recommend fermented milk mixtures (horses are considered the first complementary foods). If we are talking about a completely healthy child, first of all, I advise you to introduce vegetable puree - it is easily digested by the children's gastrointestinal tract. Usually, this is a puree of zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, parsnips, parsley, white carrots, potatoes. Unfortunately, in our area there is not a wide variety of products. Pediatricians should take this into account when advising the mother what to choose at the beginning of complementary foods in winter, because if we advise a zucchini in February, will we find it on the shelves, and if so, will this exotic product benefit the baby?
The first complementary foods start with a small amount - a teaspoon per day. Prepare, for example, zucchini puree. We give the baby half a teaspoon of puree once a day - at lunchtime, and every next day we increase the amount of the product. On average, in 14 days it is possible to increase the amount of complementary foods to 50-70 grams - it all depends on how the child perceives the new food. When a child eats more - up to 100 grams of vegetables, we can diversify the menu - add boiled broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini. When a child eats mostly 2-3 vegetables, we can introduce the next complementary foods (mashed potatoes based on several vegetables are considered one complementary food). The next step is the introduction of fruit puree. Provided that the child responds well to the first complementary foods, after 3 weeks, vegetable complementary foods in the amount of 100 grams can be introduced. And then at 6.5-7 months you can introduce fruits - apples of green or yellow varieties in a baked form.
We give the baby half a teaspoon of puree once a day - at lunchtime, and every next day we increase the amount of the product. On average, in 14 days it is possible to increase the amount of complementary foods to 50-70 grams - it all depends on how the child perceives the new food. When a child eats more - up to 100 grams of vegetables, we can diversify the menu - add boiled broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini. When a child eats mostly 2-3 vegetables, we can introduce the next complementary foods (mashed potatoes based on several vegetables are considered one complementary food). The next step is the introduction of fruit puree. Provided that the child responds well to the first complementary foods, after 3 weeks, vegetable complementary foods in the amount of 100 grams can be introduced. And then at 6.5-7 months you can introduce fruits - apples of green or yellow varieties in a baked form.
At the same time, we add a certain amount of fat - olive or sunflower oil - to the prepared vegetable mixture.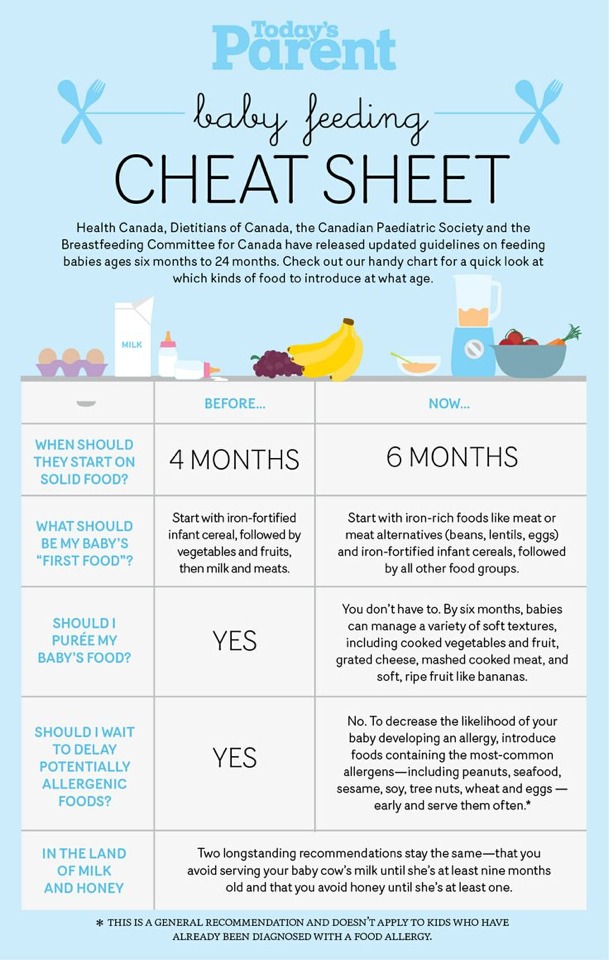 After the introduction of vegetables and fruits, depending on the age, we introduce the yolk or meat. Regarding when it is worth introducing fruit juices - at one time pediatricians focused considerable attention on this. Today, if a child is breastfed, we do not insist on a drinking regimen or suggest adding water or herbal decoctions from chamomile, dill, fennel to drinking. Fruit juices must be administered concurrently when the child consumes a certain amount of fruit. It can be apple juice - by no means multivitamin or citrus.
After the introduction of vegetables and fruits, depending on the age, we introduce the yolk or meat. Regarding when it is worth introducing fruit juices - at one time pediatricians focused considerable attention on this. Today, if a child is breastfed, we do not insist on a drinking regimen or suggest adding water or herbal decoctions from chamomile, dill, fennel to drinking. Fruit juices must be administered concurrently when the child consumes a certain amount of fruit. It can be apple juice - by no means multivitamin or citrus.
What if the baby does not accept a certain product?
If a rash appears on the baby’s skin, the baby is worried about intestinal disorders, anxiety associated with abdominal pain, or if there is a tendency to constipation-diarrhea due to the introduction of a certain product, we leave in the diet products of all previous stages of complementary foods, but one that provoked disorders, cancel. If it is difficult for the mother to understand which particular product caused the disorders, it is necessary to return to the initial level for a certain time - breastfeeding, which at the same time will encourage the mother to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet or a balanced diet. If the baby is on artificial feeding, it is necessary to return to the use of the mixture, without complementary foods. Then, at a slightly more intense pace, you need to take the same steps to introduce complementary foods as before, carefully observing the reaction of the baby.
If the baby is on artificial feeding, it is necessary to return to the use of the mixture, without complementary foods. Then, at a slightly more intense pace, you need to take the same steps to introduce complementary foods as before, carefully observing the reaction of the baby.
At what stages of complementary feeding do we introduce cereals, meat, fish, egg yolk? What foods do we start introducing when teeth are erupting in a baby?
After vegetables and fruits, we introduce the yolk into complementary foods, then meat or cereals, the next is sour-milk complementary foods. However, I want to note that the presence of teeth has nothing to do with the introduction of complementary foods, because in fact, children do not chew for a long time. The purpose of complementary foods and the task of the child is to be able to form a food lump in the oral cavity. Then, when the baby swallows liquid food, he hardly retains it in his mouth. And complementary foods make it possible to retain food, enveloping it with saliva and then swallowing it in small portions. In some babies, teething happens even a year, but they have complete complementary foods.
In some babies, teething happens even a year, but they have complete complementary foods.
Regarding the timing of complementary foods - meat is given to the baby after about 7 months. Rabbit meat, turkey fillet, beef, quail are best suited. I am often asked whether it is possible to give a child chicken meat during the complementary feeding period. If you are sure that the chicken is home grown without the addition of hormones, chicken is also suitable for the baby's diet.
I recommend eating fish after 10 months - in any case, not red varieties (red fish can be given to a child only after two years of life). The best option is white sea fish of low-fat varieties. When introducing cereals into the diet, it must be remembered that they must be adapted by age - it is these cereals that contain the destroyed grain shell, which contains the most harmful carbohydrates, in particular, gluten. Once upon a time, parents ground rice or buckwheat, but because of these products, the baby had problems with digestion, because there was a certain load on his body. At the beginning of complementary foods, it is better to give free-flowing adapted dairy-free cereals - we breed them in water. When the child has taken this complementary food well, we can introduce milk porridge. For children who are breastfed and are underweight after 4 months, there are other recommendations. As a breastfeeding aficionado, my advice is to stimulate a mother's lactation by reviewing her diet. At the same time, it is advisable to introduce dairy-free cereals, since they provide more calories than vegetables. There are also cases when a child is one year old and mothers replace breastfeeding with formula milk from a bottle. In fact, the baby does not need additional nutrients, moreover, there is no need for supplementation or feeding from a bottle - this is a step back.
At the beginning of complementary foods, it is better to give free-flowing adapted dairy-free cereals - we breed them in water. When the child has taken this complementary food well, we can introduce milk porridge. For children who are breastfed and are underweight after 4 months, there are other recommendations. As a breastfeeding aficionado, my advice is to stimulate a mother's lactation by reviewing her diet. At the same time, it is advisable to introduce dairy-free cereals, since they provide more calories than vegetables. There are also cases when a child is one year old and mothers replace breastfeeding with formula milk from a bottle. In fact, the baby does not need additional nutrients, moreover, there is no need for supplementation or feeding from a bottle - this is a step back.
Were there cases of anemia among children under one year of age? How to prevent this problem?
Although not often, there are cases of anemia in the practice of a pediatrician. Iron deficiency anemia in a baby occurs in the majority in the absence of a child’s nutritional interest, when it is not possible to adequately introduce complementary foods. But it is necessary to take into account the fact that if the child has low hemoglobin, then the mother has it even lower, because the baby receives everything that is possible during lactation. Therefore, first of all, we work with mom's diet. At the same time, we are taking more intensive steps in replacement feeding - introducing red meats, in particular beef, if age permits (at 8-9months), offal: boiled beef tongue, beef, turkey, rabbit liver, apples, buckwheat for children under one year of age.
Iron deficiency anemia in a baby occurs in the majority in the absence of a child’s nutritional interest, when it is not possible to adequately introduce complementary foods. But it is necessary to take into account the fact that if the child has low hemoglobin, then the mother has it even lower, because the baby receives everything that is possible during lactation. Therefore, first of all, we work with mom's diet. At the same time, we are taking more intensive steps in replacement feeding - introducing red meats, in particular beef, if age permits (at 8-9months), offal: boiled beef tongue, beef, turkey, rabbit liver, apples, buckwheat for children under one year of age.
Up to what age is it best to breastfeed a baby?
When it comes to the formation of immunity, breastfeeding up to 6 months of a child's life is most appropriate, because the baby needs the protection that he receives from his mother. After 6 months of life, the child's immune system independently forms antibodies.