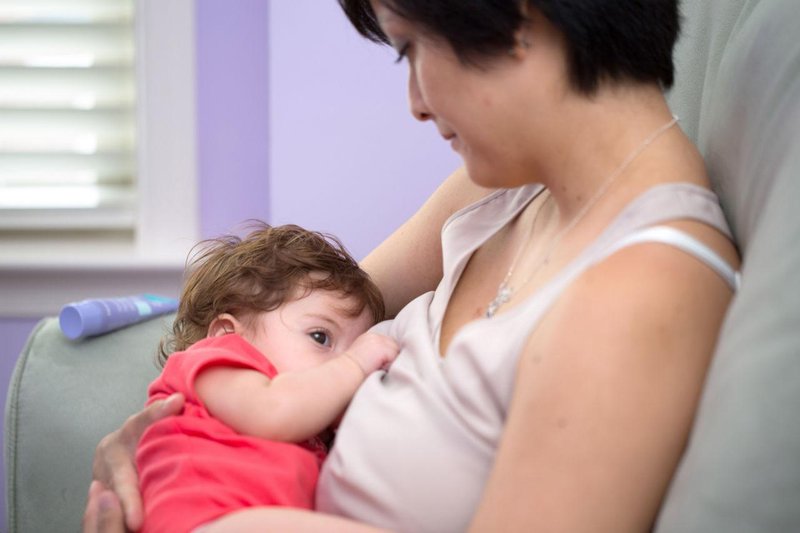
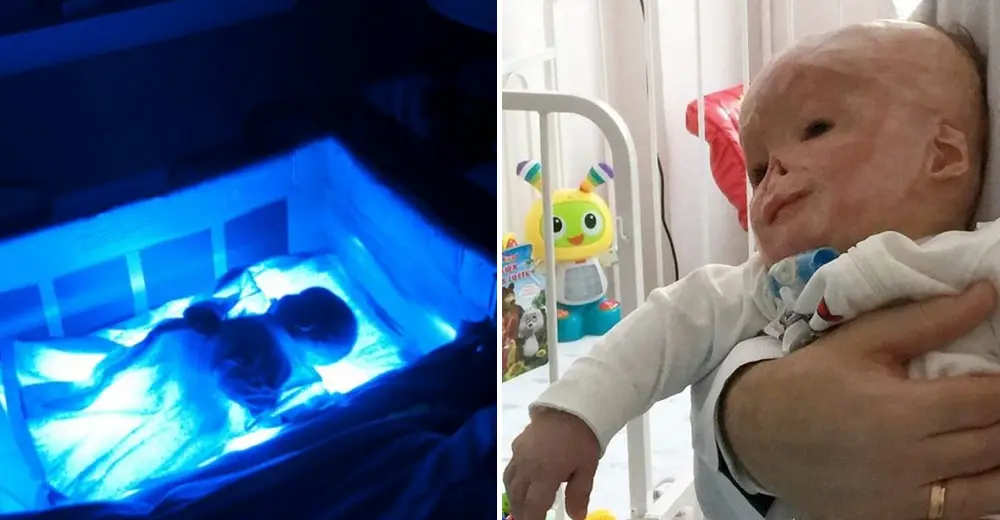
Newborn baby sick after feeding
Reflux | Breastfeeding Challenges | Start for Life
Breastfeeding challenges
There may be times when breastfeeding is challenging. Never ignore any issues you may have – talk to your health visitor, midwife, GP or breastfeeding specialist as soon as possible, they will be able to help you sort it out quickly.
Here are some common breastfeeding issues, and tips on what to do.
- Colic
- Constipation
- Mastitis
- Milk supply
- Reflux
- Sore nipples
- Thrush
- Tongue-tie
Baby reflux
If your baby brings up milk, or is sick during or after feeding, this is known as reflux. Reflux, also called posseting or spitting up, is quite common and your baby should grow out of it, usually by the time they are 12 months old.
What causes baby reflux?
The muscle at the bottom of the food pipe acts as a kind of door into the stomach – so when food or milk travels down, the muscle opens allowing the food into the stomach.
However, while this muscle is still developing in the first year, it can open when it shouldn't (usually when your baby's tummy is full) allowing some food and stomach acid to travel back up again. Acid in the stomach is normal and a necessary part of the digestion process – it helps break down food.
In most babies, reflux is nothing to worry about as long as they are healthy and gaining weight as expected.
Baby reflux symptoms
- Constant or sudden crying when feeding.
- Bringing up milk during or after feeds (regularly).
- Frequent ear infections.
- Lots of hiccups or coughing.
- Refusing, gagging, or choking during feeds.
- Poor weight gain.
- Waking up at night a lot.
GORD
When reflux becomes painful and it happens frequently, this is known as 'gastro-oesophageal reflux disease' (GORD). GORD is more serious than mild, everyday reflux. The strong stomach acid can irritate and make the food pipe sore and inflamed, which is painful for your baby and may result in them needing medication.
The main signs and symptoms of GORD in your baby are:
- spitting up frequently
- abdominal pain
- feeding difficulties
- seeming unsettled and grizzly after a feed
These symptoms can lead to your baby not gaining weight, or even losing weight.
Silent reflux
Silent reflux can be confusing as there are no obvious signs or clues (such as spitting up). It's when the food travels back up the food pipe – but it's swallowed rather than spat out so is harder to identify. But your baby may display similar symptoms to those of regular reflux.
Breastfeeding Friend from Start for Life
The Breastfeeding Friend, a digital tool from Start for Life, has lots of useful information and expert advice to share with you – and because it's a digital tool, you can access it 24 / 7.
Breastfeeding tips for babies with reflux
- Feeding little and often (smaller feeds stop their tummy getting too full).
- Burping them requently during feeds – have a look at our guide to burping your baby for techniques.

- Try a different feeding position – check out our our guide to breastfeeding positions.
- Keep your baby upright, for at least an hour after feeding, this should help keep the milk down.
If you are mixed feeding (combining breastmilk and formula feeds), have a look at our advice on bottle feeding and reflux.
When to see the GP
If your baby has difficulty feeding or refuses to feed, regularly brings milk back up and seems uncomfortable after a feed, talk to your pharmacist, GP, or health visitor. They'll be able to give you practical advice on how to ease the symptoms and manage it – they may also need to rule out other causes (such as cow's milk allergy).
It might be helpful to keep a record of when your baby feeds, with details of how often and how much your baby brings the food back up, and how often your baby cries or seems distressed. This will help your health visitor or GP decide if your baby needs treatment.
Reflux in babies - NHS
Reflux is when a baby brings up milk, or is sick, during or shortly after feeding. It's very common and usually gets better on its own.
It's very common and usually gets better on its own.
Check if your baby has reflux
Reflux usually starts before a baby is 8 weeks old and gets better by the time they're 1.
Symptoms of reflux in babies include:
- bringing up milk or being sick during or shortly after feeding
- coughing or hiccupping when feeding
- being unsettled during feeding
- swallowing or gulping after burping or feeding
- crying and not settling
- not gaining weight as they're not keeping enough food down
Sometimes babies may have signs of reflux but will not bring up milk or be sick. This is known as silent reflux.
Things you can try to ease reflux in babies
Your baby does not usually need to see a doctor if they have reflux, as long as they're happy, healthy and gaining weight.
Do
-
ask a health visitor for advice and support
-
get advice about your baby's breastfeeding position or how to bottle feed your baby
-
hold your baby upright during feeding and for as long as possible after feeding
-
burp your baby regularly during feeds
-
give formula-fed babies smaller feeds more often
-
make sure your baby sleeps flat on their back (they should not sleep on their side or front)
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if your baby:
- is not improving after trying things to ease reflux
- gets reflux for the first time after they're 6 months old
- is older than 1 and still has reflux
- is not gaining weight or is losing weight
Urgent advice: Ask for an urgent GP appointment or call 111 if your baby:
- has vomit that's green or yellow, or has blood in it
- is projectile vomiting (being sick with more force than usual)
- has blood in their poo
- has a swollen or tender tummy
- has a very high temperature or they feel hot or shivery
- keeps being sick and cannot keep fluid down
- has diarrhoea that lasts for over a week or has signs of dehydration
- will not stop crying and is very distressed
- is refusing to feed
Also call your GP or 111 if you have any other concerns about your baby.
Treatment for reflux in babies
A GP or specialist may sometimes recommend treatments for reflux.
If your baby is formula-fed, you may be given:
- a powder that's mixed with formula to thicken it
- a pre-thickened formula milk
If the thickening powder does not help or your baby is breastfed, a GP or specialist might recommend medicines that stop your baby's stomach producing as much acid.
Very rarely, surgery might be needed to strengthen the muscles to stop food or milk travelling back up. This is usually only after trying other things or if their reflux is severe.
Causes of reflux
Reflux usually happens because your baby's food pipe (oesophagus) has not fully developed, so milk can come back up easily.
Your baby's oesophagus will develop as they get older and the reflux should stop.
Page last reviewed: 13 December 2021
Next review due: 13 December 2024
Colds while breastfeeding.
Colds in the cold season do not bypass breastfeeding women. However, you should not despair in this situation. You can create the most reliable protective barrier using the following recommendations:
- Do not stop breastfeeding your baby during this period. Your child is protected from infection much before symptoms begin to appear. With milk, he receives antibodies to the causative agent of the disease. Acute respiratory diseases are not a contraindication to breastfeeding. Therefore, feed the child to health, but in a mask. The mask must be changed every 2 hours. Your breast milk is your baby's immune defense against all possible complications.
- Wash your hands thoroughly. The virus can be transmitted in two ways: by airborne droplets and through touch.
 Hands should be washed regularly before contact with the child, which will protect him from infection.
Hands should be washed regularly before contact with the child, which will protect him from infection. - Be sure to get treated. How exactly to treat a breastfeeding woman from an infection? It all depends on the type of pathogen and the condition of the mother. But there are a few key rules. A high temperature can and should be reduced if a woman does not tolerate it well. Paracetamol during breastfeeding is sometimes simply an irreplaceable thing. This drug will help get rid of headaches and bring down the temperature. At the same time, it will not bring any harm to either the mother or the baby. This is the safest remedy available today.
- For the treatment of viral infections (colds, flu, etc.), in addition to antipyretic and symptomatic agents, special antiviral agents based on interferon preparations can be used. But a doctor must prescribe such funds for you. Although some of them, such as geneferon, viferon, can be used independently. Other antiviral drugs are best discussed with your doctor.
- A course of antibiotics is needed to treat a bacterial infection (otitis, tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, mastitis, etc.). Their choice, dosage and rules of admission only on the recommendation of a specialist.
- To relieve nasal congestion during lactation, use drugs to relieve swelling from the mucous membrane, which will help restore normal breathing (saline solutions and vasoconstrictor drugs).
- For a breastfeeding woman, topical antiseptics are ideal for a sore throat. For rinsing, you can use purchased solutions (for example, Chlorhexidine), or prepared at home (with sea salt).
- To combat the cough of a nursing mother, you can resort to natural-based remedies, such as licorice, thyme. During lactation, it is not forbidden to take drugs based on ambroxol. Inhalation with this substance will be the most effective. It is convenient to carry out this procedure using a nebulizer (a device for inhalation).
It is very important to treat a cold and not forget about your well-being! With properly selected therapy, relief comes on day 3, but some symptoms can persist up to 7-10 days. In doubtful situations, you should consult a doctor for advice. So you can avoid complications in the form of tonsillitis, sinusitis and pneumonia.
In doubtful situations, you should consult a doctor for advice. So you can avoid complications in the form of tonsillitis, sinusitis and pneumonia.
obstetric observation department
Stasevich S. M.
Feeding when sick | Medela
If you or your baby are unwell, you may wonder if it is safe to breastfeed. The great news is that breastfeeding when you're sick is most often good for both of you. Read more about this in our article.
Share this information
Did you know that a breastfed baby is usually much less prone to illness? Although it is impossible to avoid them completely, the protective properties of breast milk help babies get sick less often and recover faster than formula-fed babies.
Breast milk contains antibacterial and antiviral agents. 2 The longer you breastfeed your baby, the lower the risk of colds and flu, ear and respiratory infections, nausea and diarrhoea. 1 Scientists are already exploring the use of breast milk to treat everything from conjunctivitis to cancer. 3.4
1 Scientists are already exploring the use of breast milk to treat everything from conjunctivitis to cancer. 3.4
Should a sick baby be breastfed?
Yes. Breastfeeding promotes recovery and also helps to calm the baby. Breast milk contains antibodies, white blood cells, stem cells, and protective enzymes that help fight infections and help your baby recover faster. 1,5,6 In addition, the composition of breast milk (the balance of vitamins and nutrients) is constantly adjusted to the baby's body to help him recover as soon as possible. Thus, you will spend less time on sick leave and visit the doctor less often. 7
“Breastfeeding gives the baby everything she needs when she is sick. This is his medicine, food, drink and comfort. For a baby, this is the best thing in the world,” says Sarah Beeson, a health visitor from the UK.
Surprisingly, when a child becomes ill, the composition of breast milk changes. When you come into contact with pathogens of bacterial and viral infections, your body begins to produce antibodies to fight them, which are then passed through milk to your baby. 8 When your baby is sick, the levels of immune-boosting cells (white blood cells) in your milk also skyrocket. 5
When you come into contact with pathogens of bacterial and viral infections, your body begins to produce antibodies to fight them, which are then passed through milk to your baby. 8 When your baby is sick, the levels of immune-boosting cells (white blood cells) in your milk also skyrocket. 5
In addition, breast milk is very easy to digest, making it ideal for babies with indigestion.
“At 12 months my daughter contracted norovirus and could only breastfeed,” recalls Maya, a mother of two in Spain. produce more milk. It was amazing. After 48 hours, I was able to meet the daily requirement for milk. It saved my baby from a drip."
It should be taken into account that sometimes during an illness it is necessary to change the habitual breastfeeding regimen. For example, with a cold, a baby may want to eat more often, but little by little, both to calm down and because of nasal congestion, which makes it difficult to apply to the chest for a long time. If your baby has a stuffy nose, an upright breastfeeding position may be more comfortable, so don't be afraid to try different breastfeeding positions.
If your baby has a stuffy nose, an upright breastfeeding position may be more comfortable, so don't be afraid to try different breastfeeding positions.
What should I do if my baby is seriously unwell and cannot breastfeed?
Occasionally, if a baby is not feeling well, they may not have the appetite or energy to feed. If your baby is not eating well, seek advice from your healthcare provider, nurse practitioner, or lactation consultant to help prevent dehydration.
You may be asked to express milk to feed your baby with a bottle, a Soft Cup*, or other suitable method that requires minimal effort from the baby. Pumping on a regular breastfeeding schedule will also help keep your milk supply stable.
You can express milk with one of our convenient breast pumps, such as the modern electronic Swing Flex** or the Harmony** manual breast pump. Rest assured, freshly expressed breast milk is just as good as breast milk, so your baby will get all the protection and support it needs.
If you have concerns about your baby's health or how much milk they are drinking, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Can I continue to breastfeed if I become ill myself?
You may not want to do this if you feel unwell, but in most cases it is best to continue breastfeeding. If you have a cold, runny nose, diarrhoea, vomiting, or mastitis, continue breastfeeding as normal with your doctor's approval. The baby is unlikely to become infected through breast milk. What's more, the antibodies in your milk will help reduce your baby's risk of contracting the same 13 virus.
“Breastfeeding when sick is not only safe most of the time, but also beneficial. Your baby is the least at risk of catching your upset stomach or cold, as he is already in close contact with you and receives a daily dose of protective antibodies from milk, ”says Sarah Beeson.
If there is a risk of contracting a viral infection by airborne droplets, it is advisable to temporarily switch to expressing breast milk and bottle feeding.
In order not to lose the amount of milk produced when the body is still weakened by the disease, it is best to use the Swing Maxi Flex ** double breast pump, which helps to stimulate lactation, increase the amount of milk (by 18% on average) and increase its fat content (+1% ) 14 .
However, breastfeeding and pumping when sick can be very tiring. You need to take care of yourself so that you can take care of the baby. Try to drink more fluids, eat when you can, and get plenty of rest. Crawl under the covers for a few days and ask family or friends to help care for your baby if possible, so you can put all your energy into recovery.
“Don't worry about your milk supply, it will last. Most importantly, do not stop breastfeeding abruptly so that mastitis does not develop, ”adds Sarah.
Proper hygiene is very important to reduce the risk of spreading the disease. Wash your hands with soap and water before and after breastfeeding and pumping, preparing and eating food, using the toilet and changing diapers. Use a tissue when coughing and sneezing, or cover your mouth with the crook of your elbow (not your palm) if you don't have a tissue handy. Be sure to wash or sanitize your hands after coughing, sneezing, and blowing your nose.
Use a tissue when coughing and sneezing, or cover your mouth with the crook of your elbow (not your palm) if you don't have a tissue handy. Be sure to wash or sanitize your hands after coughing, sneezing, and blowing your nose.
Can I take medication while breastfeeding?
In agreement with the attending physician and compliance with the dosage, it is permissible to take certain medications. 9.10
.
“When talking to a doctor or pharmacist for any reason, always state that you are breastfeeding,” she continues.
What about long-term treatment?
If you are on long-term treatment for diabetes, asthma, depression, or other chronic conditions, the benefits of breastfeeding may outweigh the risks. “Breastfeeding is often possible for almost any disease, with the exception of some very rare conditions,” Sarah says, “you will be very familiar with the drugs you are taking, and during pregnancy you can discuss them with your doctor or other specialist. There is guidance on the safe use of various medicines that all healthcare professionals use.” In any case, you should consult with your doctor.
There is guidance on the safe use of various medicines that all healthcare professionals use.” In any case, you should consult with your doctor.
“I was on high doses of epilepsy medication, but I was still able to breastfeed,” recalls Nicola, a mother from the UK. “I saw a neurologist to ensure my son was safe and to minimize the risk of a seizure. Seizures can happen due to lack of sleep, and I fed day and night, but I took good care of myself, and my husband supported me. It was a positive experience."
What if I have to go to the hospital?
If you need to be hospitalized or urgently hospitalized, there are different ways to continue feeding your baby healthy breast milk so that you can return to normal breastfeeding after you are discharged.
“Express and freeze breast milk so that the caregiver can feed the baby. Practice at home ahead of time and be sure to let your doctors know that you are a breastfeeding mother, both before entering the hospital and while in it, ”recommends Sarah.
“If the baby is very small, you may be allowed to take him with you. Find out if the hospital has a supervising doctor or lactation consultant to contact. This specialist will support you, especially if you are in a general ward. If hospitalization is urgent, warn the doctors that you have a baby so that they take this into account.
Surgery under local or general anesthesia does not necessarily mean that breastfeeding will have to be stopped, or milk will need to be pumped and discarded. By the time you recover from surgery and can hold your baby, the amount of anesthetic in your breast milk will be minimal, so breastfeeding will be safe in most cases. 10 However, in any case, it is best to consult your doctor or attending physician beforehand.
To ensure that the situation of treatment or departure does not affect the baby's diet, it is advisable to create a breast milk bank. This should be done daily by expressing one extra serving and freezing it in the handy, durable Medela Breast Milk Storage Bags. Even stored for several months and then thawed, your carefully prepared milk will still be incomparably healthier than formula.
Even stored for several months and then thawed, your carefully prepared milk will still be incomparably healthier than formula.
For hygienic and easy pumping, use a breast pump with 2-Phase Expression technology for a fast, full flow of milk. For example, the ultra-comfortable Swing Flex** breastpump that adapts to the shape of your breasts and allows you to pump milk in a comfortable position, even lying back on the pillows 15 .
Don't forget to sterilize your breast pump with the Quick Clean microwave bags. Medela milk storage bags do not need to be handled as they are aseptically packaged and ready to use immediately.
Are there times when breastfeeding is not allowed?
In some cases, for the safety of the baby, breastfeeding should be stopped for a while, and instead, milk should be expressed and drained to maintain milk production until the end of treatment. This includes radiotherapy and chemotherapy for cancer, herpes sores on the chest, and infections such as tuberculosis, measles, or blood poisoning that can be transmitted through breast milk. 11.12 Consult with a qualified professional about your condition to decide if you can continue breastfeeding in such cases.
11.12 Consult with a qualified professional about your condition to decide if you can continue breastfeeding in such cases.
For quality lactation support during this period, you can use the dual electronic breast pump with innovative Flex technology or rent a Symphony Clinical Breast Pump** if available. A list of cities where you can rent a breast pump can be found on the "Rent a Medela Clinical Breast Pump" page.
Literature
1 Victora CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet . 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
2 Lönnerdal B. Bioactive proteins in breast milk. J Pediatric Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7. - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
3 Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet]. Topical treatment with breastmilk: randomized trials. [ cited 2018 Apr 4]. Available from https://www.breastfeeding.asn.au - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet]. "Topical treatment with breast milk: a randomized trial". [cited 4 April 2018] See article at https://www.breastfeeding.asn.au
4 Ho JCS et al. HAMLET–A protein-lipid complex with broad tumoricidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;482(3):454-458. - Ho J.S.S. et al., "HAMLET - a protein-lipid complex with extensive antitumor activity". Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2017;482(3):454-458.
5 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology . 2013;2(4): e 3. - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
Clin Transl Immunology . 2013;2(4): e 3. - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
6 Hassiotou F, Hartmann PE. At the dawn of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells . Adv Nutr . 2014;5(6):770-778. - Hassiot F, Hartmann PI, "On the threshold of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells." Adv. 2014;5(6):770-778.
7 Ladomenou F et al. Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child . 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study. " Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(12):1004-1008.
" Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(12):1004-1008.
8 Hanson LA. Breastfeeding provides passive and likely long-lasting active immunity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol . 1998;81(6):523-533. — Hanson, L.A., "Breastfeeding provides passive and likely long-term active protection against disease." Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998;81(6):523-533.
9 Hale TW, Rowe HE. Medications and Mothers' Milk 2017. 17th ed. New York, USA: Springer Publishing Company; 2017. 1095 p . — Hale T.W., Rowe H.I., Medications and Breast Milk 2017. 17th edition. New York, USA: Publishing House Springer Publishing Company ; 2017. p. 1095.
10 Reece-Stremtan S et al. ABM Clinical Protocol# 15: Analgesia and anesthesia for the breastfeeding mother, Revised 2017. Breastfeed Med . 2017;12(9):500-506. - Rees-Stromtan S. et al., AVM Clinical Protocol #15: Analgesia and Anesthesia for Nursing Mothers, 2017 edition. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2017;12(9):500-506.
Breastfeed Med . 2017;12(9):500-506. - Rees-Stromtan S. et al., AVM Clinical Protocol #15: Analgesia and Anesthesia for Nursing Mothers, 2017 edition. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2017;12(9):500-506.
11 Lamounier JA et al. Recommendations for breastfeeding during maternal infections. J Pediatr 2004;80(5 Suppl ):181-188. - Lamunier J.A. et al., Guidelines for Breastfeeding during Maternal Infectious Diseases. J Pediatrician (Journal of Pediatrics) (Rio J). 2004;80(5 Suppl):181-188.
12 Hema M et al., Management of newborn infant born to mother suffering from tuberculosis: Current recommendations & gaps in knowledge. Indian J Med Res . 2014;140(1):32-39. - Hema M. et al., "Working with the Infant Born to a Mother with Tuberculosis: Current Recommendations and Gaps".