One month baby feeding chart
Newborn and Baby Feeding Chart in the 1st Year
Whether you’re a first-time parent or a seasoned caregiver, figuring out why your baby is crying can feel like a guessing game. Fortunately, paying attention to your baby’s daily feeding schedule can help reduce some of the guesswork.
By following a feeding schedule, you might be able to avoid some of the fussiness associated with hunger, and you’ll be able to more easily tell whether he’s more likely to be wet or tired instead.
Whether your little one’s a newborn, a 6-month old, or even a 1-year-old, read on to find out how to come up with a feeding schedule and adjust it to your baby’s needs as he grows and develops.
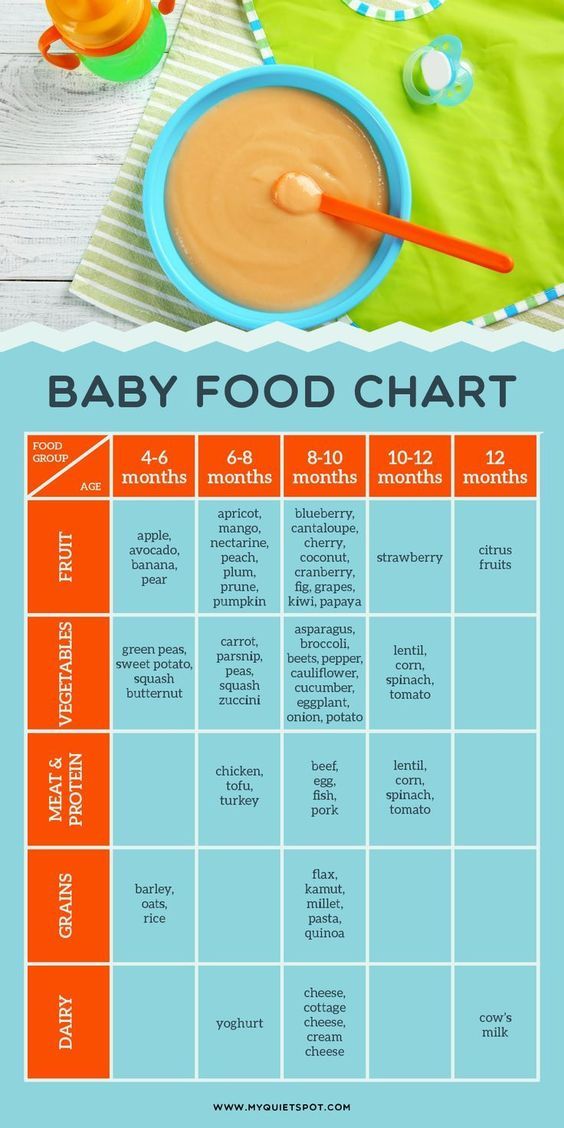
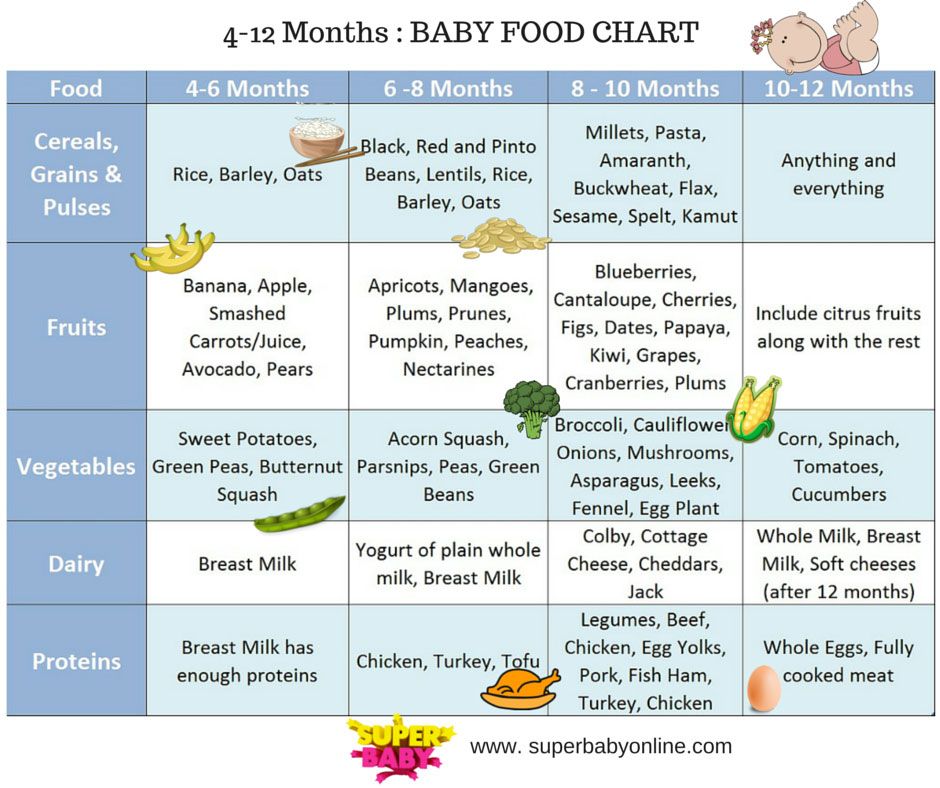
Baby Feeding Chart at a Glance
As you watch for those delightful baby milestones — from first smiles and giggles to sitting and crawling — it can be hard to keep track of everything related to your baby’s feeding schedule. Fortunately, you don’t have to. We've assembled all the necessary details in the chart below, including feeding frequency and portion information.
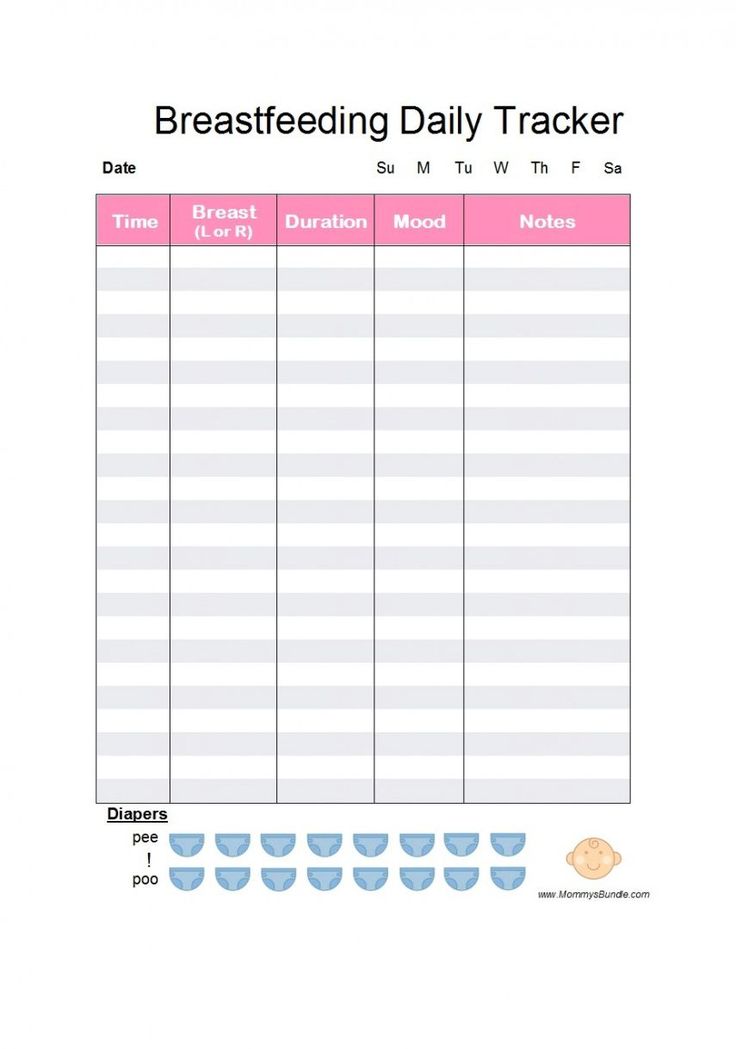
Feeding Schedule for Breastfed Newborns
From the moment your baby is born, she begins to grow at a surprisingly quick pace. To fuel her development and keep her well fed, be prepared to nurse about every two to three hours.
By the time she’s a week old, your little one may begin to nap for longer periods, giving you more time between feedings. If she’s sleeping, you can maintain your baby’s feeding schedule by waking her up gently when it’s time to feed.
Tips to keep in in mind if you’re breastfeeding:
The length of time between feedings is measured from when your baby begins nursing, not when she stops.
Ensure your little one latches on properly. This can be difficult when you’re starting out, especially for first-time moms, but over time your baby may begin to latch comfortably.
 Speaking to a lactation consultant could be helpful.
Speaking to a lactation consultant could be helpful.As your baby grows she may nurse at a faster rate.
Alternate between breasts during each feeding.
Look for signs that your baby is full. She may turn away from the breast, nurse at a slower rate, or lose interest. Once she seems full, end the feeding
Your baby’s healthcare provider may recommend adding vitamin D oral supplements to your baby’s diet. Follow the provider's instructions to ensure your baby gets the proper dosage.
Nursing your baby on demand or every couple of hours around the clock can seem like a lot—and it is! At the newborn stage, your baby can’t take in much milk in a single sitting, so frequent feeding is needed to make sure she's getting enough. Later on, as your baby's daily routine (including her sleep and awake time) becomes more predictable, you'll have an easier time following a regular feeding schedule.
Feeding Schedule for Formula-Fed Newborns
Formula-fed newborns will need about two to three ounces (60 – 90 milliliters) of formula per feeding to start with. Newborns, fed from bottles are able to take in more during a feeding than a breastfed infants. This allows you to space out feedings by about three to four hours.
Newborns, fed from bottles are able to take in more during a feeding than a breastfed infants. This allows you to space out feedings by about three to four hours.
As your baby reaches her 1-month milestone, she will need at least four ounces per feeding to get the nourishment she requires. Your newborn’s feeding schedule will gradually become more predictable over time, and you’ll need to adjust the amount of formula as she grows.
3-Month-Old Feeding Schedule
Now that you and your baby have begun to develop a routine, it can be difficult to make slight alternations. However, as your baby grows and her feeding needs change, you’ll need to adjust your baby’s feeding schedule accordingly.
For Your Breastfed Baby
At 3 months, your baby is becoming more active, will begin to breastfeed less often, and may sleep for longer periods of time at night.
You may have to nurse just six to eight times per day at this stage (or about every three to four hours).
If your baby’s healthcare provider sees that he’s gaining weight and growing at a regular pace, then he’s probably getting the right amount of nutrition.
The number of wet and soiled diapers is also a great indicator as to whether or not he is eating well. Your baby should have about four to six wet diapers a day.
See your baby’s healthcare provider if you’re concerned that your little one may not be getting enough to eat.
For Your Formula-Fed Baby
As your little one continues to grow, you’ll notice that he wants to eat more during each feeding and begins to sleep for longer intervals at night.
Slight adjustments to your 3-month old’s feeding schedule may include:
Increasing the amount of formula to about 5 ounces per feeding
Giving your baby formula about six to eight times per day
Switching the newborn nipple size or style on your baby’s bottles to make it easier for him to drink from the bottle.
6-Month-Old Feeding Schedule
At this stage, your baby’s healthcare provider may recommend you expand your baby’s diet to include solid foods. With these menu additions on the horizon, having a 6-month-old feeding schedule will come in handy!
With these menu additions on the horizon, having a 6-month-old feeding schedule will come in handy!
When a baby ready to try solid foods, a single grain baby cereal mixed with breast milk or formula has traditionally been the first solid food to be introduced, followed by pureed vegetables and fruits. However, there's no medical evidence that indicates introducing foods in any special order offers any benefits.
Keep in mind that solids are only a supplement at this stage, and that breast milk or formula is still your baby’s most important source of nutrition. Continue to include about 32 ounces of breast milk or formula in your 6-month-old’s feeding schedule of three to five feedings per day to ensure your baby gets the necessary vitamins and minerals.
You may be able to start weaning your baby off of night feedings; however, every baby is unique. Speak to your baby’s healthcare provider to see if it’s time to cut down on nighttime feedings and to learn what you can do to encourage the process.
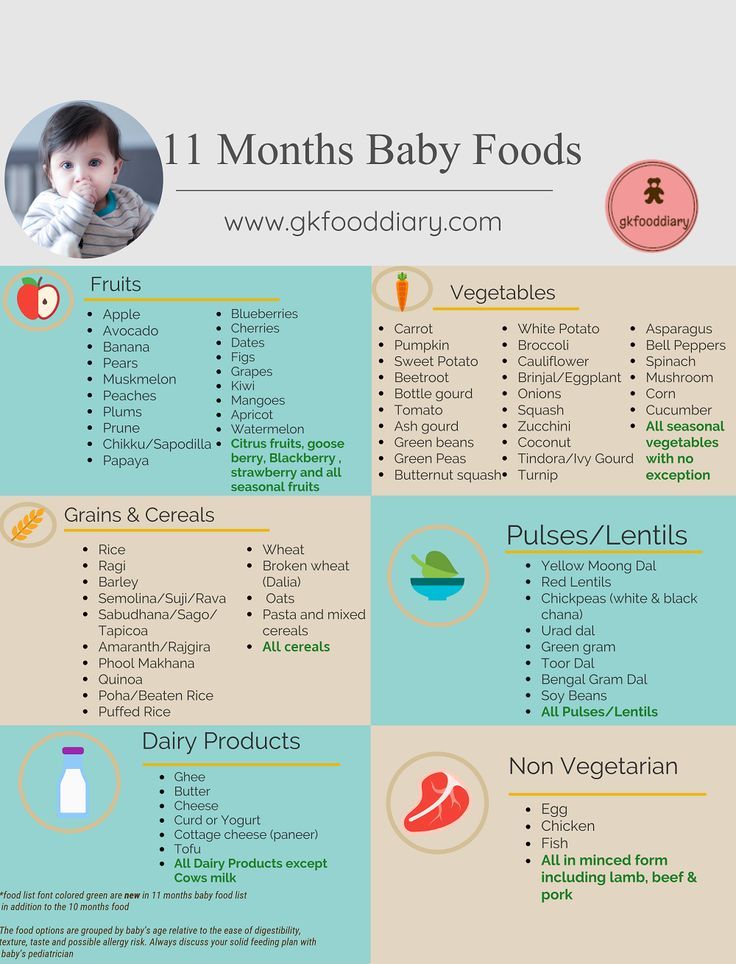
7 to 9-Month-Old Feeding Schedule
Months seven through nine can be a good time to add a greater variety and quantity of solid foods to your baby’s diet. He may need fewer daytime feedings, now — about four to five.
Purees of meats, veggies, and fruits are recommended at this stage. Introduce your baby to these new flavors as single ingredient purees then gradually add combinations to his meals.
Your baby may slowly begin to wean off breast milk or formula as his growing body demands solid foods for nutrition.
There is no correct time to wean off breast milk or formula. Speak to your baby’s healthcare provider to learn more about the cues and signs that can let you know when your baby is ready for more solid foods.
10 to 12-Month-Old Feeding Schedule
Exploring new textures may now be a big part of your little one’s meals. As he grows, he may begin to self-feed with finger foods such as cut-up bananas, dry cereal, and pasta and even demand certain flavors that he enjoys more.
As you continue to replace breast milk or formula with solids, your baby’s healthcare provider can help determine how to balance out your baby’s meals.
Blends of different foods can be introduced during mealtime and added to your baby’s feeding schedule. Your baby may eat about three to four times per day. Be sure to avoid offering foods that pose choking hazards such as grapes, peanuts, and popcorn.
Finger feeding can be fun for your little one. Always be sure that his food is cut up into pieces that are small enough for him to be able to pick up and chew without being at risk of choking. After some practice, he’ll be on his way toward wholesome, independent eating habits.
1-Year-Old Feeding Schedule
Now that you’re celebrating your baby’s first birthday, it’s also time to celebrate his feeding accomplishments. Your baby’s feeding schedule can now include almost all the healthy and nutritious foods you eat, with a few minor exceptions such as raw honey and choking hazards like nuts.
Your baby may be eating less frequently now, as he is able to take in more food in one sitting. Give your 1-year-old approximately three meals and about two or three snacks a day.
This is the time to add cow’s milk to your baby’s diet. However, too much milk is not always good, and should be kept to about 16 to 24 ounces per day if your baby is able to tolerate lactose. Check with your baby's healthcare provider if you have any questions about how and when to introduce cow's milk.
You can continue to nurse your baby if you wish. There is no correct time to wean him off of breast milk; rather, it is recommended that to continue breastfeeding for as long as it is right for you and your little one. Consult with your baby’s healthcare provider if you have questions about the weaning process.
As your baby grows and develops, his feeding needs will change. Having a baby feeding schedule at the ready can help you track your baby’s mealtimes and anticipate when he’ll start to be hungry.
This is just one of the ways you can help keep your little one happy and developing well. Having a feeding schedule in place also gives you some extra freedom to spend more time enjoying his many milestones.
Of course, if at any time you have questions or concerns, reach out to your baby’s healthcare provider for personalized guidance and advice.
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day. Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.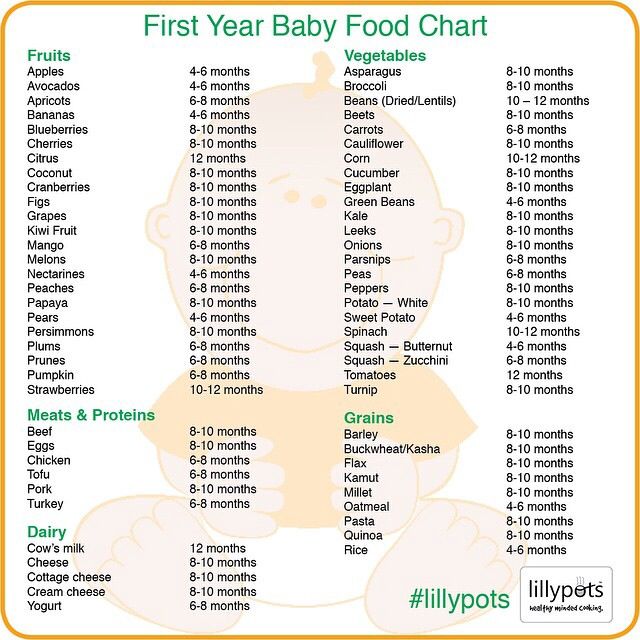
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough. If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings. They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique. No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Last Updated
- 5/16/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician.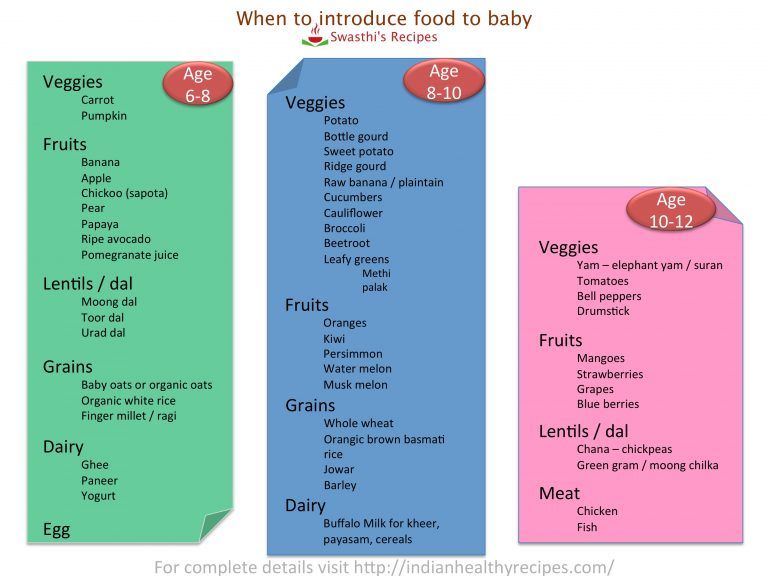 There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Scheme of the first feeding of a child (table) with artificial and breastfeeding, what can be given to a baby
The need for the introduction of complementary foods in modern mothers has long been beyond doubt. Pediatricians, pediatric nutritionists and other graduates unanimously say that at some point both mother's milk and formula are not enough to satisfy the growing needs of the child's body for useful trace elements and vitamins. That's when it's time to introduce complementary foods. The fact that your baby is ready to get new experiences and try tastes so far unknown to him is indicated by the presence of the following signs:
• doubling the initial weight of the child,
• ability to sit with support,
• child does not push food out of his mouth,
• curiosity and desire to try something from the common table.
Signs of malnutrition in a child, constant feeling of hunger and anxiety associated with it, weight loss can also be important signals for the start of complementary foods. In these cases, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialist and share your observations with him.
In these cases, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialist and share your observations with him.
Contents: Hide
- When to start the introduction of complementary foods
- with which products to start the completenance of complementary foods
- We avoid errors
- Table of complementary foods for months with artificial feeding
- Table of complementary foods when breastfeeding
- start introducing complementary foods
The timing of the introduction of complementary foods is still debated. But if we bring scientific reasoning to a common denominator, then the conclusion suggests itself that complementary foods can be introduced from about six months, and for children with certain medical indications - from 3-5 months. Many experts believe that half a year is the ideal time for complementary foods, when the first colic is over, and the digestive system has matured enough to try new foods. The exact answer to the question of when to introduce complementary foods in a particular child can only be given by a pediatrician.
 In some situations, it may be necessary to introduce new dishes into the baby's diet as early as 4 months, and someone will be ready for this only after six months.
In some situations, it may be necessary to introduce new dishes into the baby's diet as early as 4 months, and someone will be ready for this only after six months. What foods should I start introducing complementary foods with
Fruits, vegetables or cereals? Which of these foods are best for starting complementary foods? Experts have long answered this question as follows: if the baby is underweight, suffers from frequent loose stools, it is advisable to start with cereals (of course, gluten-free and dairy-free), and if everything is fine with weight, then vegetables will be the first in line. Also, vegetable complementary foods are recommended for breastfed children with constipation problems, rickets, or those born prematurely, whose weight is normal or exceeds the standards.
Why not fruit? Everything is simple. Fruits have a bright and sweet taste, and after trying an apple or banana first, the baby is likely to refuse zucchini or broccoli, which do not have the same rich taste.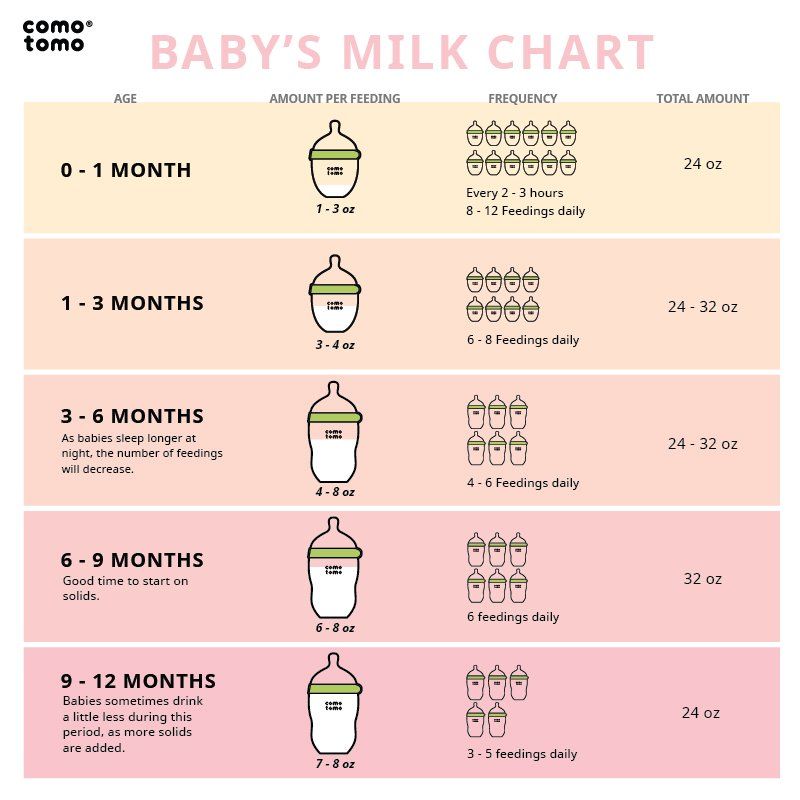 Therefore, the introduction of fruit purees and juices into the diet is postponed until vegetable purees become a familiar dish on the menu. As for cereals, buckwheat, rice and corn are first introduced, as they are characterized by the absence of gluten, saturate and are well digested.
Therefore, the introduction of fruit purees and juices into the diet is postponed until vegetable purees become a familiar dish on the menu. As for cereals, buckwheat, rice and corn are first introduced, as they are characterized by the absence of gluten, saturate and are well digested. Read also: How to properly teach a child to different tastes
Avoiding mistakes
In order for the introduction of complementary foods not to become a test for either the baby or the mother, you need to follow some recommendations. Most importantly, be patient and don't get too upset if things don't go according to plan. Each child is individual, as are their taste preferences and needs.
• Start complementary foods if the baby is perfectly healthy. Contraindications for the introduction of new products will be teething, colds, stress associated with separation or moving, recent or planned vaccinations.
• New foods are introduced gradually, starting with half a teaspoon.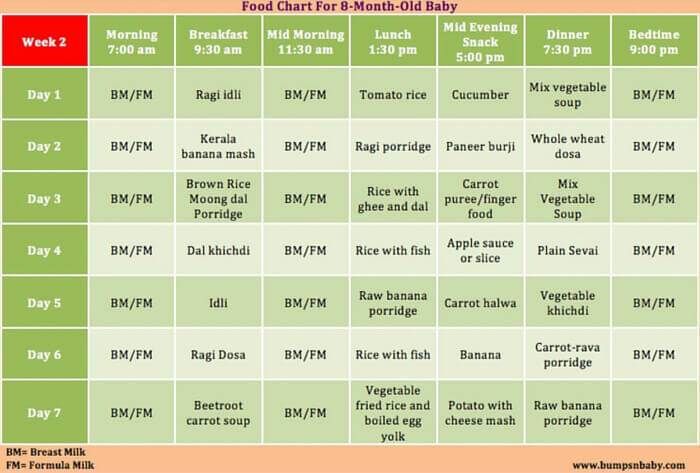 In the absence of allergies or digestive problems, the amount of the product is approximately doubled the next day. Sometimes the introduction of a new product stretches up to a week. Do not rush, give the child the opportunity to "taste" this dish. If the baby flatly refuses the offer, postpone the acquaintance for at least a week.
In the absence of allergies or digestive problems, the amount of the product is approximately doubled the next day. Sometimes the introduction of a new product stretches up to a week. Do not rush, give the child the opportunity to "taste" this dish. If the baby flatly refuses the offer, postpone the acquaintance for at least a week.
• Do not force your child to eat. After all, your goal is to introduce your child to new tastes and help develop good eating habits.
• The best time for the first feeding is after the morning feed until 12 noon, when the baby is already hungry and ready to eat something else. In case something goes wrong, you will know about it during the day, not at night.
• In the event of an adverse reaction to the product, such as an allergy, seek medical advice immediately. Then, in agreement with the doctor, offer this dish after a certain period of time.
• Gradually increase the amount recommended by your pediatrician. If you don't fit within a week, don't worry. Listen to your child and act accordingly.
Listen to your child and act accordingly.
• Always start feeding with complementary foods. Only then offer breast milk or formula.
• Stick to a 5-meal schedule. Feed your baby at the same time every day.
• Food offered to the baby must be thermally processed - boiled or steamed. The dish should be at a comfortable temperature - about 37 ° C.
• Purees and cereals should be of a liquid consistency so that a child who does not yet know how to chew can comfortably eat them. Thicker dishes with lumps and pieces are introduced into the diet by about a year, when there are already several teeth.
• Do not use salt, sugar or spices when preparing complementary foods. Also, do not add them in order to force the child to eat something. Let the baby get used to natural tastes.
• Complementary foods are prepared at one time and should never be refrigerated until the next meal. Everything should be only the first freshness.
• If you prefer ready-made baby food, carefully study the top manufacturers, pay special attention to the shelf life when buying.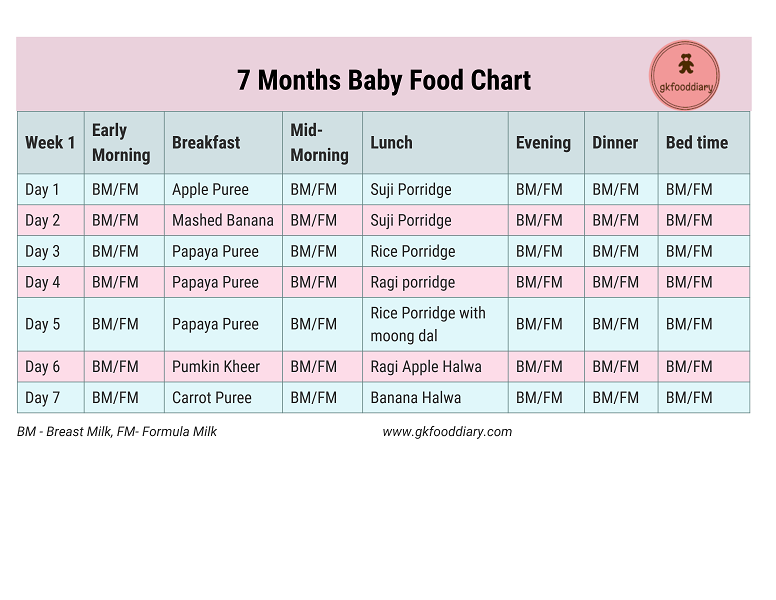
When introducing complementary foods, be guided by the data in the tables, which indicate which products, in what quantity and in what months experts recommend giving. 6 months
7 months
8 months
9 months
10 months
11 months
12 months
vegetables
150 g
170 g
180 g
180 g
180 g
200 g
200 g
Porridge
50–100 g
150 g
068
180 g
180 g
180 g
200 g
200 g
fruit
60 g
70 g
80 g
100 g
100 g
100 g
meat
50 g
60 g
60 g 9000
70 g
70 g
70 g
Cottage cheese
9000
068
10-30 g
30 g
40 g
50 g
50 g
Zhelki
1/4
1/4
1/2
1/2
1/2
Fish
9000
30 g
50 g
60 g
Vegetable
1 ml
3-5 ml
5 ml
5 ml
5 ml
9 Sl.
1 ml
3-5 ml
5 ml
5 ml
9006 8 months
9 months
10 months
11 months
12 months
Silent porridge
10–150 g
150–180 g
150–180 g
180–200 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g 9000 g
068
200 g
200 g
200 g
Vegetables
10–120 g
80–120 g
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000073
150 g
170 g
180 g
200 g
200 g
Military0007
-
-
-
-
-
-
160–200 ml
Fruits
5–60 g
50-60 g
60 g 9000 g 9000 g 900–100 g 900-100 G0007
100–120 g
100–120 g
100–120 g
meat
-
10-30 g
30–70 g
60–70 g
60–70 g
9000 9000
9007 9007 9007 9007 900EA0119 Cottage cheese -
-
5–10 g
40 g
40 g
50 g
yolk
-
-
½
½
½
½ --1
fish
-
-
-
10–40 g
10–40 g
50–60 g
9 vegetable oil
-
-
1 ml
3-5 ml
5 ml
5 ml
5 ml
Cream oil
-
-
1-3 g
3-4 g
5 g
5 g
5 g
, as you can see, the schemes for the introduction of pectoral and artificial feeding are not too much.
 In any case, starting to introduce new foods into the baby's diet, you will have to give the baby milk or formula for a long time, which are still the basis of his nutrition.
In any case, starting to introduce new foods into the baby's diet, you will have to give the baby milk or formula for a long time, which are still the basis of his nutrition. How to introduce solid foods by month
3 months
If your doctor advises your breastfeeding or formula-fed baby to introduce complementary foods at 3 months, start with what the specialist has recommended to you. If these are vegetables, start with the classic - zucchini puree. This vegetable contains many beneficial nutrients and fiber. Start with half a teaspoon, carefully observing the reaction of the child's body. Be sure to supplement your baby with breast milk or formula afterwards. In case the child does not like the zucchini, try giving broccoli or cauliflower. Well, if the doctor advised porridge, feel free to choose buckwheat or corn.
4-5 months
After your baby has tasted zucchini, broccoli and cauliflower, it's time to add other vegetables: carrots, potatoes, green peas.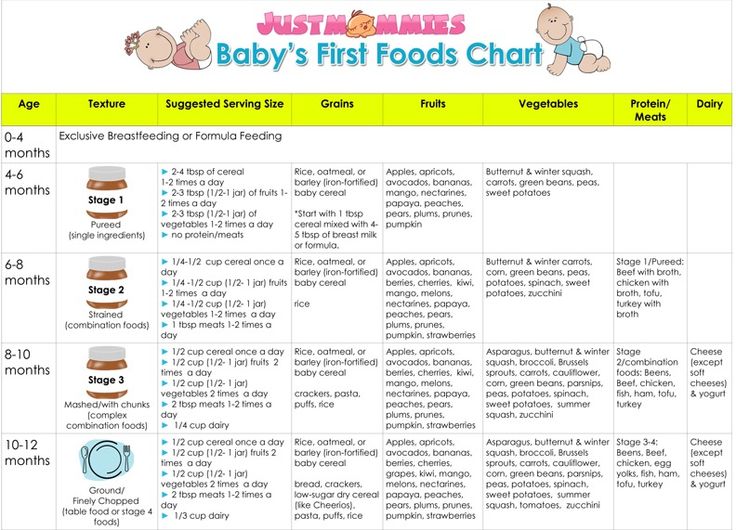 Do not overdo it with carrots, give it no more than 2 times a week. It is even better if this root crop is combined with other vegetables. It's porridge time! Gluten-free, water-cooked buckwheat, rice or corn. If the baby refuses to eat such cereals, add some breast milk or the usual mixture to them.
Do not overdo it with carrots, give it no more than 2 times a week. It is even better if this root crop is combined with other vegetables. It's porridge time! Gluten-free, water-cooked buckwheat, rice or corn. If the baby refuses to eat such cereals, add some breast milk or the usual mixture to them.
6 months
Time to pamper your baby with dried fruit compote, and formula-fed children start giving milk porridge. You can use a milk mixture to prepare such cereals, and in some cases, milk diluted with water. But in general, pediatricians do not advise introducing cow's milk into a child's diet before 8 months, as this can cause allergic reactions.
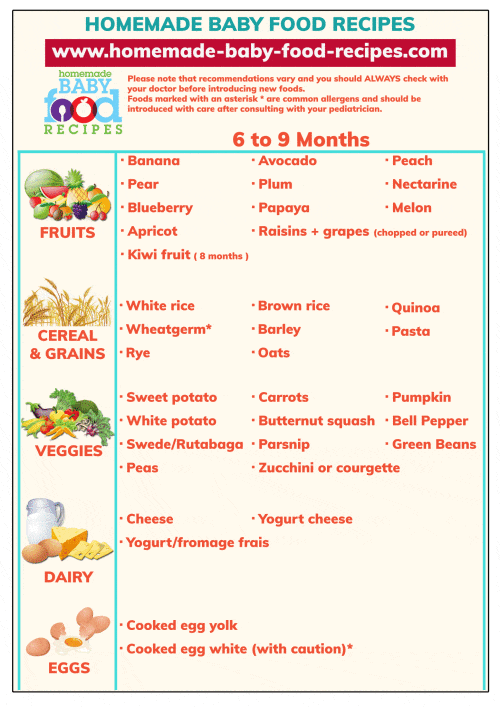
7 months
After the baby gets used to vegetable purees, you can try to give fruit purees and, if desired, juices, which should be diluted with water. There has been a lot of negative talk about juice lately. There is no fiber in them, but there are a lot of acids, which may not be completely safe for the stomach and have a high sugar content. So consult a pediatrician and think carefully about whether to give the baby juices or still prefer mashed potatoes and compotes. An excellent alternative to juices is children's herbal teas. Start introducing your baby to fruits with apples (preferably green varieties), bananas, and pears. The baby's menu is replenished with a new product - meat. Rabbit meat, turkey meat are best suited. Chicken and veal are also considered a good option. Low-fat pulp without streaks is taken. It is boiled or brought to readiness for a couple, then crushed in a blender or meat grinder. Meat with a gradual increase in its quantity is given as part of vegetable purees. Also at 7 months, it's time to give the baby a pumpkin.
So consult a pediatrician and think carefully about whether to give the baby juices or still prefer mashed potatoes and compotes. An excellent alternative to juices is children's herbal teas. Start introducing your baby to fruits with apples (preferably green varieties), bananas, and pears. The baby's menu is replenished with a new product - meat. Rabbit meat, turkey meat are best suited. Chicken and veal are also considered a good option. Low-fat pulp without streaks is taken. It is boiled or brought to readiness for a couple, then crushed in a blender or meat grinder. Meat with a gradual increase in its quantity is given as part of vegetable purees. Also at 7 months, it's time to give the baby a pumpkin.
8 months
An important moment in the introduction of complementary foods during artificial and breastfeeding occurs exactly at 8 months. It's time to give the baby a yolk. Watch the reaction of the body very carefully: if there are any manifestations of allergies. In case of a negative reaction of the body to chicken yolk, exclude it from the menu and try quail. It is best to give this product in the morning feeding from 9 to 11 hours. Along with vegetable and butter, gluten cereals are also introduced: oatmeal, millet, barley, pearl barley. It's time to give your child a taste of light vegetable soups. The components of the dish should be familiar to the child. Do not experiment by introducing dishes into the diet even with one unknown ingredient. Meatballs, boiled or steamed, are added to the meat in the form of mashed potatoes.
In case of a negative reaction of the body to chicken yolk, exclude it from the menu and try quail. It is best to give this product in the morning feeding from 9 to 11 hours. Along with vegetable and butter, gluten cereals are also introduced: oatmeal, millet, barley, pearl barley. It's time to give your child a taste of light vegetable soups. The components of the dish should be familiar to the child. Do not experiment by introducing dishes into the diet even with one unknown ingredient. Meatballs, boiled or steamed, are added to the meat in the form of mashed potatoes.
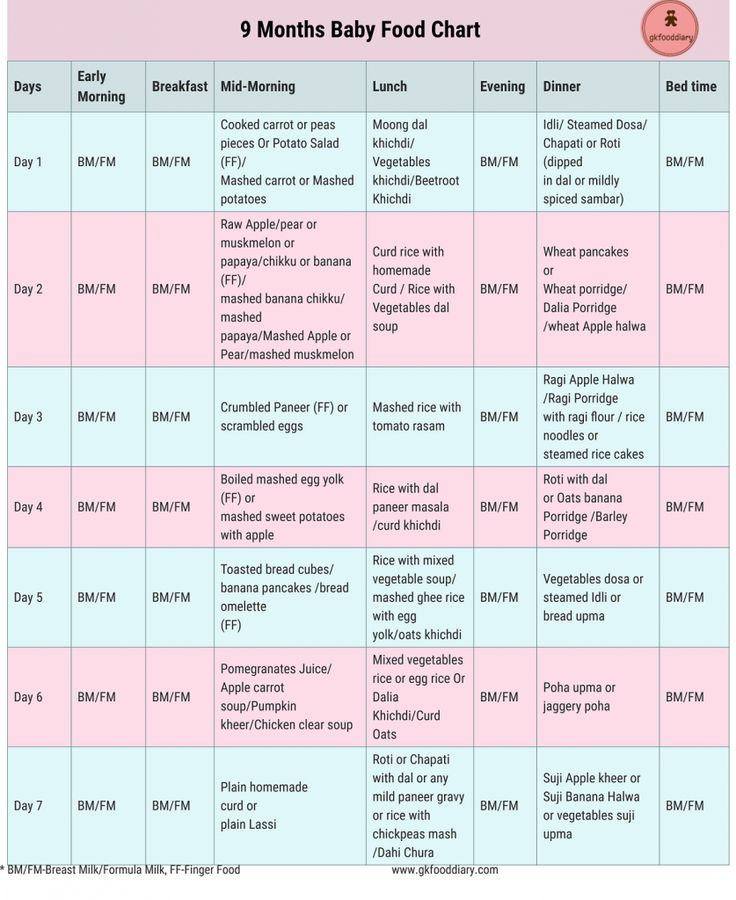
9 months
At this age, the baby should be introduced to the diet of low-fat fish: pollock, hake, perch, cod. For these purposes, fillets are taken and steamed, stewed or boiled. For the first time, fish are given in very small quantities. Start with once a week, gradually increasing to two. Remember that either fish or meat is given on the same day, without mixing these 2 products. If at the age of 8 months there were no prunes on the menu of the child, it's time to fix it. Dried fruit compote is also an excellent option, which at first is best diluted with water. However, you definitely shouldn’t get carried away with dried apricots, it’s better to wait until the baby reaches the age of one.
Dried fruit compote is also an excellent option, which at first is best diluted with water. However, you definitely shouldn’t get carried away with dried apricots, it’s better to wait until the baby reaches the age of one.
Months 10–12
The diet characteristic of this period is characterized by an increase in portions to their maximum values indicated in the scheme. Also, it is at this age that the last feeding is gradually replaced by milk or kefir.Now that you've come across a set of essential tips, you're ready to start weaning. Once again, consult with a specialist, be patient, not forgetting to listen to the baby's body. We are confident that you will succeed. The main thing here, as in any other business, is a positive attitude. It all depends on you and your desire to raise a healthy and happy baby with competent eating behavior. Don't stop if you fail and don't get frustrated if things don't go according to plan. Everything will definitely work out.
#Feeding children up to one year old #Complementary foods
Complementary feeding scheme | Nutriclub
Regardless of whether your child is receiving breast milk or infant formula, at about six months of age, according to WHO* recommendations, the first complementary foods should be introduced. But where to start feeding? And how to do it right? Let's talk in order.
It is at the age of 6 months that the baby's body responds best to new foods. The first complementary foods in combination with breast milk should provide the child with all the useful substances necessary for his growth and development. Also, the timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the development of the chewing skills of the baby. Russian pediatric practice also allows for earlier introduction of complementary foods - from 4-5 months **.
How many months to introduce complementary foods?
To know when it's time to consider introducing food other than milk or formula, watch for signs of complementary feeding.
 It's time to start complementary foods if:
It's time to start complementary foods if: - The baby sits with support, does not roll over on its side
- The child shows food interest: follows the spoon with his eyes when you eat, tries to steal something from your plate
- Ejection reflex faded, child opens mouth when offered food
Consult your paediatrician before introducing complementary foods. And in order to introduce complementary foods correctly, read the complementary feeding scheme below.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods
- All new products are introduced with ½ teaspoon and then gradually adjusted to the age norm.
- New products are best given in the morning or afternoon to be able to track the reaction throughout the day.
- Do not introduce a new product until the previous one has been brought to the age norm.
- Complementary foods are offered before feeding with breast milk or its substitute.
- Until the volume of the product per feeding is brought to the age norm, you should continue to supplement the baby with breast milk or infant formula. Thus, the volume of the complementary food product will gradually increase, and the volume of milk or formula, on the contrary, will decrease until it completely disappears.
Complementary feeding scheme
Age Foods and portion sizes 4-5 months Complementary foods at this early age should be introduced if the child is not gaining weight well or is at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia. Complementary foods are introduced to healthy children from 5 months. There are a number of contraindications for an early start of complementary foods, consult your pediatrician!
What foods can we start with:
- Vegetable purees
- Dairy-free cereals.
6 months What foods should be in the baby's diet if you introduced complementary foods at 5 months:
- Dairy-free cereals - up to 150 g
- Vegetable puree - up to 150 g
What new foods are introduced into the diet:
- Meat puree - up to 30 g
- Vegetable oil - up to 1 tsp.
- Fruit puree - up to 60 g
7 months What foods should be in the baby's diet by the end of the 7th month: - Porridge - 150 g.
- Vegetable puree - 170g
- Meat Puree - 30g
- Fruit puree - 70g
- Vegetable oil - 1 tsp
What new foods are introduced into the diet:
- Butter - up to ½ tsp.
- Boiled egg yolk - up to ¼ pc.
- Fruit juice - 70 ml.
- Baby biscuits - 1-2 pieces
8 months What foods should be in the baby's diet by the end of the 7th month:
- Porridge - 180 g.
- Vegetable puree - 170g
- Meat Puree - 50g
- Fruit puree - up to 80 g.
- Vegetable oil - ½ tsp.
- Butter - ½ tsp.
- Boiled egg yolk - ½ pc.
- Fruit juice up to 70 ml.
- Baby biscuits 1-2 pcs.
What new foods are introduced into the diet:
- Baby kefir or yoghurt - up to 100 ml, as an alternative to breast milk or formula in one of the feedings
9-12 months What foods should be in the diet of a child at this age:
- Porridge for breakfast and/or dinner*
- Vegetable puree - for lunch and/or dinner
- Meat puree - about 50 g.
- Fruit puree - for afternoon tea and/or breakfast
- Vegetable oil - ½ tsp.
- Butter - 1 tsp.
- Boiled egg yolk - ½ pc.
- Fruit juice and/or compote up to 100 ml.
- Baby biscuits - up to 2 pcs.
- Baby kefir or yoghurt up to 200 ml.
What new foods are introduced into the diet:
- Meatballs or fish (as an alternative to mashed meat) - 50 g
- Bread or croutons - 10 g
- Curd - 50-70 g; as an alternative to 100 ml of kefir or yogurt in one of the feedings
After 9-12 months volumes of previously introduced products will continue to increase, but remember that the older the child, the more pronounced the individual characteristics, therefore, the food needs of children at this age may differ.
Focus on your baby's weight gain, appetite, and your own common sense.
If you think your child is malnourished or is not gaining weight well, consult a pediatrician.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020You will also be interested
- Learn more
- Possum baby food

- Feeding newborn baby with syringe

- Should i feed my baby fruits or vegetables first
- Iron rich foods for babies 6 months

- Infantino baby food processor

- Nhs baby food allergy

- South indian food for 1 year old baby

- Roast beef baby food

- Baby deer feeding schedule

- How many times should i feed my newborn baby

- What to feed baby rabbits 3 days old

