What to feed baby rabbits 3 days old
Caring for Newborn Baby Rabbits
IF THESE ARE WILD BABIES
It’s that time of year again. Wild babies everywhere. But are they at risk?
Wild rabbits hide their nests in plain view, often in the middle of your yard, bushes, etc. If you find a nest that has been disturbed, do the best you can to restore it and leave the babies in there. If a dog discovers the nest, do your best to restore it (with grass, leaves, whatever mama has used), make sure the kits are in there, and find a way to keep the dog(s) away from the nest. Mama will return for her babies and taking them away will seriously decrease their chance of survival. If you do not see the mama—DON’T WORRY—they only nurse their babies a few minutes a day, then they stay away so as to not draw predators to the nest.
If a kit is injured or an animal brings you an injured baby, if you have no choice but to help a baby, please do not try to care or it yourself—-get it to a rabbit vet or a wildlife rehabilitator
- Local wildlife rehabilitator: https://www.
nwrawildlife.org
- List of rabbit vets: http://rabbit.org/vet-listings/
The best thing you can do for wild babies is to leave them alone (restored to the nest) or, if injured, get them to a rabbit vet or wildlife rehabilitator.
DOMESTIC/PET RABBITS
WHERE TO PUT THE BABIES
Make the babies a soft nest area in a box with clean towels. We like to put one folded towel on the bottom and another bunched on top of that, so the babies can snuggle into it. You can also purchase soft nesting wool from a pet store and put that on top of the towel. You can also take whatever nesting material they were in and put it in the box as well. Cover the box almost entirely with a light towel, making sure that there will be enough air so the babies do not suffocate. Leaving about a one inch gap at the top is usually sufficient. Keep the babies in an out-of-the way, QUIET area, such as an adult’s bedroom. If the room temperature is between 68-72 degrees you will not need to provide extra heat, but if it’s cooler than that you will need to provide extra warmth. Use a heating pad set on low and slip it under one half only of the box. We do it this way so that the babies can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm. DO NOT put babies directly on heating pad, as babies can burn themselves very badly.
Use a heating pad set on low and slip it under one half only of the box. We do it this way so that the babies can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm. DO NOT put babies directly on heating pad, as babies can burn themselves very badly.
If the babies were with their mamma, but she is not caring for them (and you are sure she is ignoring them) you may need to separate her from them so they will not get hurt. Rabbit milk is very caloric and the kittens (baby rabbits) only nurse for a few minutes a day, so if you think that she is not caring for them based only on the fact you don’t see them feed…think again. If you do think they are being neglected, you can check: Are they cold? Are they making crying sounds for more than a few minutes before (or at) feeding time? Are they blue? Is the skin shriveled? Check for dehydration: gently pinch together the skin at the nape of the neck. If it sticks together or stays in a tent, they are dehydrated. A healthy kit has a round belly, is warm, gains weight on a daily basis, and snuggles with its litter mates. If they are dehydrated, cold, losing weight or becoming injured, of course, something must be done
A healthy kit has a round belly, is warm, gains weight on a daily basis, and snuggles with its litter mates. If they are dehydrated, cold, losing weight or becoming injured, of course, something must be done
WHAT TO FEED THE BABIES
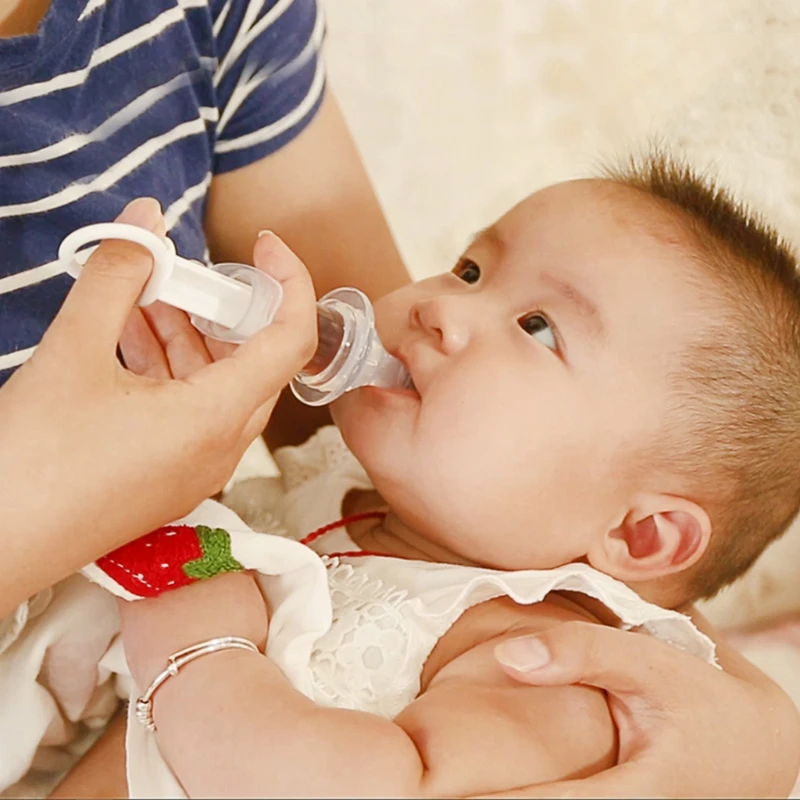
Baby rabbits should be fed Kitten Milk Replacer (KMR) or goat milk, which you can buy at pet stores, or sometimes even a local veterinarian’s office. Because rabbit milk is the most caloric of all mammals, we add in one tablespoon of 100% heavy whipping cream (no sugar) to each can of KMR. Most kits will not nurse from the baby animal bottles you can buy at stores. Instead, use a sterile oral syringe, which can be purchased at most pharmacies. A better alternative are these nipples, which come the a syringe, but you may not be able to find them locally/right away (link).
It is best to feed baby rabbits no more than twice a day, but sometimes it takes more feedings to get an adequate amount into them, especially at first.
How much to feed varies greatly on what breed of rabbit you are feeding, and how big the kit is, but here is a basic guideline for the daily amount to feed a domestic rabbit who will be approximately 5-6 pounds as an adult (average rabbit size). You can increase the amounts as needed for larger breeds.
To help the kits maintain healthy gut bacteria, go to your local health food store (and get a bottle of ACIDOPHILUS. Ask for the capsules that have the “grainy stuff” inside (they are easier to mix than the “powdery stuff”) and add a bit to the formula at each feeding.
ALL amounts below should be divided into two feedings per day.
- Newborn – 1 week
- 4-5 cc formula
- 1-2 weeks
- 10-15 cc formula
- 2-3 weeks
- 15-30 cc formula
- 3-6 weeks, until weaned
- 30 cc formula
HOW DO I DO THIS?
Baby rabbits feed from their mothers while lying on their backs. You may loosely wrap baby in a soft face cloth or hand towel and lay it on your lap or in the crook of your arm. If bunny will NOT eat this way, of course, do the best you can. It is ABSOLUTELY CRUCIAL to let the baby eat at it’s own pace—especially if it is not suckling from the syringe willingly. If you squirt the liquid in too quickly you can aspirate (get liquid in) the lungs and the rabbit will suffocate.
You may loosely wrap baby in a soft face cloth or hand towel and lay it on your lap or in the crook of your arm. If bunny will NOT eat this way, of course, do the best you can. It is ABSOLUTELY CRUCIAL to let the baby eat at it’s own pace—especially if it is not suckling from the syringe willingly. If you squirt the liquid in too quickly you can aspirate (get liquid in) the lungs and the rabbit will suffocate.
Until their eyes open (10 days): After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly. Use a soft cloth or a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the genital area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine. Keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are replicating the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom. The stool will be soft and may be varying shades of green and yellow. If the urine is brown and gritty, the buns are not adequately hydrated and you need to get them to a rabbit vet ASAP—-it is an emergency. Be sure to clean baby’s mouth with a damp cloth or paper towel, so that no milk dries in the hair.
If the urine is brown and gritty, the buns are not adequately hydrated and you need to get them to a rabbit vet ASAP—-it is an emergency. Be sure to clean baby’s mouth with a damp cloth or paper towel, so that no milk dries in the hair.
Baby rabbit eyes open at about 10 days of age. You may start introducing them to hay and pellets at this point, but no veggies or fruits yet. Just leave some timothy or orchard and alfalfa hay and pellets in a corner of the box where the babies can easily get to them. Make sure it the pellets are plain, high fiber and fresh, with no added goodies such as dried banana chips or seeds. Don’t ever leave a deep water dish in which a baby could drown; instead, use something shallow and rinse and fill it frequently.
If you have any questions, please contact us.
Caring For Newborn Baby Rabbits
Save for later!
28 shares
- Share
- Tweet
Whether you have accidentally found a rabbit nest, or you are caring for pet rabbits, newborn baby rabbits require special care and attention.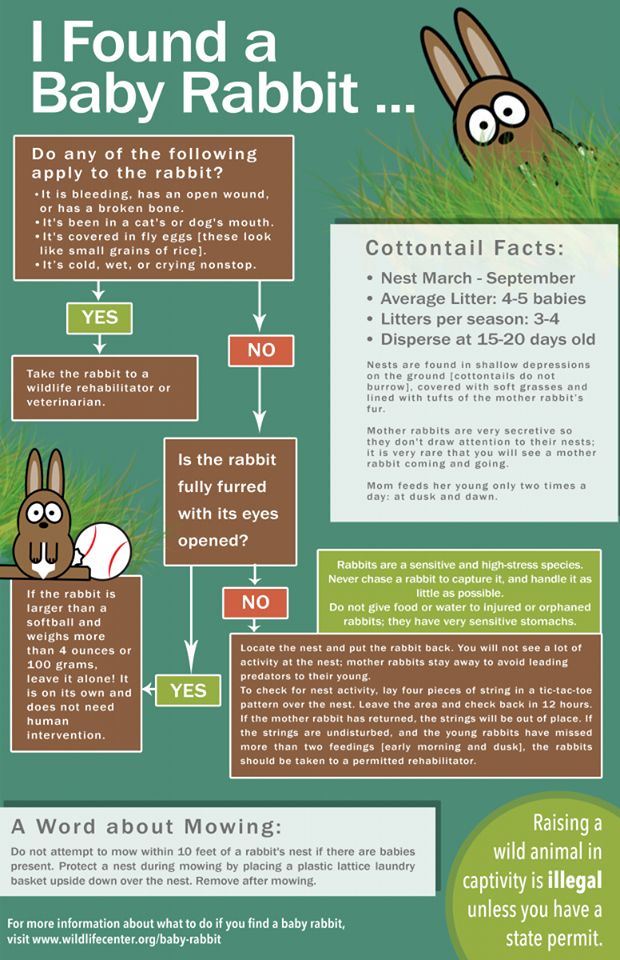
In most cases, their mother knows best, but if you have to help out and care for a baby rabbit, here’s what you need to know.
Caring for Newborn Baby RabbitsIf you find a nest of wild baby rabbits, the best thing to do is leave them where you found them.
If you know that the baby rabbits are orphaned, they should be taken to a wildlife rehabilitation or a veterinarian; you shouldn’t try to care for them on your own.
If you have newborn baby domestic rabbits, here is how to care for them.
Nesting for baby rabbitsProvide a soft, clean nest in a box, and cover the babies with a clean towel. Keep them covered and the box dark until their eyes open.
The box should be kept in a room that is 65-70°, but not warmer.
If the box is in a cold room, you may place an electric heating pad set on low or a warm hot water bottle beneath part of the box or bedding, but always give the baby rabbits room to move away to a cooler spot if they need to.
Related Content: How to Litter Train Rabbits, start them young!
Feeding baby rabbitsFeed baby rabbits KMR Kitten Powder Formula using a small syringe or an eyedropper.
Feed baby rabbits with their bodies upright, with the syringe, pointed downward and a bit sideways, so that excess formula drips out of the side of their mouths, rather than down their throats.
Baby rabbits should be fed twice a day, in the morning and evening.
Amounts to feed domestic baby rabbits:
- Newborn: 2.5 cc per feeding
- One week: 6-7 cc per feeding
- Two weeks: 12 -13 cc per feeding
- Three through six weeks or weaning: up to 15 ccs per feeding
Each individual baby will have their preferences, and smaller rabbits will eat less per feeding. Do not overfeed baby rabbits.
After their eyes are open, you can begin introducing small amounts of rabbit food pellets or hay into their box, to help them transition to adult food.
After each feeding, baby rabbits need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate.
Use a cotton ball or the corner of a clean towel, moistened with warm water.
Gently stroke the anal area until the baby rabbit begins to urinate and defecate, and keep stroking until they stop.
A mother rabbit would normally lick their babies to stimulate them in this way, so it’s important to mimic this behavior until they are old enough to urinate and defecate on their own after every feeding.
How to Tell if a Newborn Baby Rabbit is OrphanedIn the wild, a mother rabbit stays away from her babies, to avoid attracting predators to the nest.
She only visits them once or twice a day, usually at night, and only for a few minutes at a time for feeding.
She may only visit the nest for a total of 5 minutes a day.
So it’s very common for people to think that baby rabbits have been abandoned and aren’t being cared for, when in fact the mother is obeying her instincts to protect the nest.
Before you disturb a nest or remove the babies, it’s important to be SURE that they are abandoned or orphaned.
Baby rabbits are difficult to care for, even by trained rehabbers, and removing them from their nest puts them in greater danger.
Even if you watch a rabbit’s nest closely and don’t see the mother attending the babies, it doesn’t mean they aren’t being cared for.
Here’s how you can tell if newborn baby rabbits are orphans and need help:
Look at the baby bunnies
They should have skin that is healthy and pink or red. Their skin should not be bluish or greyish. The babies should be warm to the touch
Observe the baby rabbits’ stomachs
Their stomachs should be round and healthy, not sunken in
Monitor their sounds and activity.
The babies should have normal, wiggling movement, but be quiet most of the time.
They may start to cry a few minutes before feeding time.
If they are still and sluggish, or cry for extended periods, they may not be being fed
Check for dehydration
Gently pinch their skin together at the nape of their necks. If the skin smooths down flat again, they are well hydrated.
If the skin smooths down flat again, they are well hydrated.
If the skin remains tented, they are dehydrated.
If you think that baby bunnies may be orphaned or abandoned, but aren’t sure, cover the nest up again as you found it.
Then cover the nest with twigs or sticks in a distinctive pattern that you will recognize.
Use a close/tight pattern, because a mother rabbit is discreet and won’t disturb the nest too much when she visits.
If you come back the next day and the twigs haven’t been disturbed, and the babies aren’t healthy, it is probably time to call a professional.
**Want to learn how to walk rabbits? Check out our comprehensive guide about walking rabbits on leash here!**
What to do if You Find Baby RabbitsIf you are keeping domestic rabbits, and your baby bunnies aren’t doing well and need medical care, it’s best to contact a veterinarian who is skilled at caring for rabbits.
When you start keeping rabbits as pets, it’s a good idea to contact your local veterinarians to find one who can treat rabbits, so that you have their contact information when you need it.
Search google for “exotic pet” veterinarians, or check this list from the House Rabbit Society:
https://rabbit.org/vet-listings/
For wild rabbits, you should contact a local wildlife rehabilitation center before disturbing the nest.
Check this list from the Humane Society:
https://www.humanesociety.org/resources/how-find-wildlife-rehabilitator
Related QuestionsCan you touch a newborn baby rabbit?In most cases, you can gently touch a newborn baby rabbit if it’s a pet rabbit and the mother is calm.
You should not touch a newborn wild rabbit unless you are sure it has been orphaned and needs human care.
Can baby bunnies drink water?Baby bunnies will start to drink water at about 3-4 weeks old, and you can give them a very shallow bowl of water to drink from while they are small.
Babies usually rely on their mothers to show them how to drink from a water bottle, and you may need to lower the water bottle or make a little ramp to make it easier for babies to reach as they get older.
No, cow’s milk isn’t good for baby rabbits.
Mother rabbits spend less than 5 minutes a day feeding their babies, so rabbit milk is extremely nutritious and has special enzymes babies need.
Baby rabbits may not be able to digest cow’s milk, and it may not have all the nutrients they need. Instead, feed baby rabbits a Kitten Milk Replacer formula, or goat’s milk.
How long can baby bunnies go without food?At most, baby rabbits can go without food for 3-4 days.
In nature, most baby bunnies are fed only once a day, between midnight and 5 a.m.
And, unlike many animals, rabbits do not nurse their young right after their born – their mother feeds them the following night.
How do you feed a baby rabbit with a syringe?
To feed a baby rabbit with a syringe, remember that mother rabbits stand over the nest, and babies reach upright to feed.
Hold the baby rabbits upright, with the tip of the syringe pointed downward and slightly to the side of their mouths.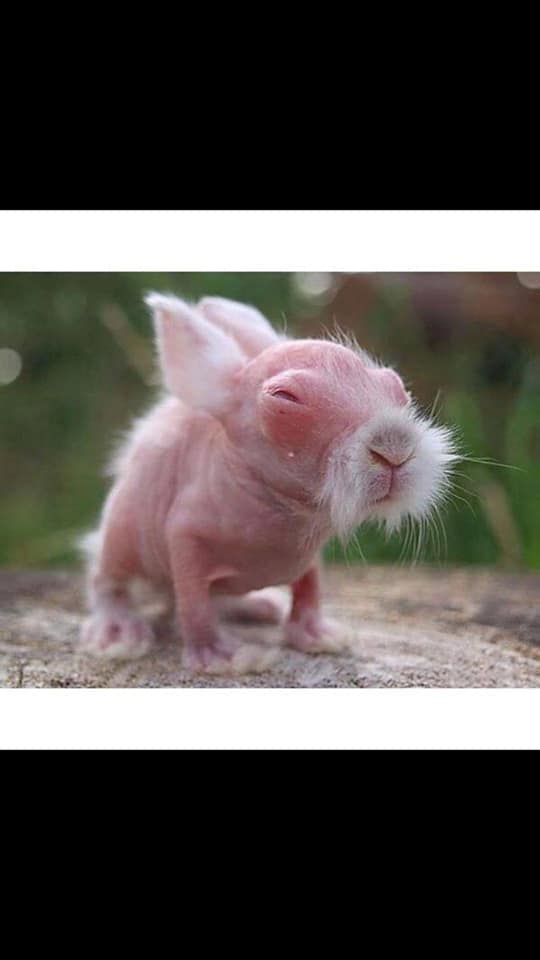
Gently squeeze the formula out into their mouths, going slowly.
Do not overfeed baby rabbits, but if they aren’t eating enough, you can offer food more frequently during the day.
Because mother rabbits spend so little time at the nest, it’s common for people to think that baby rabbits are abandoned or orphaned when they really aren’t.
For pet rabbits, don’t try to force the mother to sit or stay at the nest. If the babies have good skin tone and color, are warm and wiggling, and don’t make much noise, they are probably fine and getting all the care and food they need.
If you find a nest of wild baby rabbits, call a local wildlife center before you disturb the nest.
Baby rabbits are adorable, but not easy to care for, so it’s best left to a professional when possible.
Save for later!
28 shares
- Share
- Tweet
weekly, monthly and after jigging
Little rabbits, like all babies in the animal kingdom, need a balanced diet.
In the first days and weeks, their life is completely dependent on mother's milk. And then the whole responsibility falls on the shoulders of a person. There are several options for feeding little rabbits and how to organize their diet at different ages.
At home, the most difficult thing is the proper nutrition of young animals after birth. All the most important elements for life at first come to animals with colostrum and rabbit milk. But even if the mother does not feed the kids, you can create the most complete diet for them. Young animals after the first weeks of life, for example, at the age of 14-20 days, it is already easier to keep, but there are some nuances. So, let's find out how to feed rabbits in different periods of their lives.
Content
- 1 from birth to week
- 2 complementary foods of two -week babies
- 3 How to feed menstruation rabbits
- 4 After a junction from mother
- 5 Double -month
- 6 “Rabbits, they eat a salad together with rabbits”
- 6.
 1 6.1 6.1 6.1 Similar articles
1 6.1 6.1 6.1 Similar articles
- 6.
Birth to one week old
From the very birth, the main food of rabbits is mother's milk. If the female behaves normally, she is healthy and feeds the babies well, there is no cause for concern. During this period, the task of a person is to monitor the relationship between mother and newborn children as much as possible. Otherwise, there will be little milk and artificial feeding will be needed.
If a mother for various reasons does not feed her cubs, then improvised means will already be used. Small rabbits that are less than seven days old can be given milk or formula milk. Milk is taken from goat or cow, at the rate of 1 ml for each feeding. In total, babies eat five times a day with an 8-hour night break. The number of daily feedings is at least 3, plus one in the late evening and one in the early morning.
At the age of one week, apart from milk, nothing else is included in the diet of rabbits.

At the end of the first week, babies are already covered in down, becoming heavier, ideally they should double their birth weight. Young animals eat the same amount as at birth, however, after 7 days, you can slightly increase the amount of food for feeding. An important clarification: cow's milk is mixed 1:1 with condensed milk and so given, and goat's milk is given in its pure form. The milk mixture at home is diluted twice as concentrated as indicated on the jar.
Complementary foods for 2 week old babies
Small rabbits that are already 14 days old are fed more intensively. At this time, you need to look to see if they have enough mother's milk. If not, the babies squeak and constantly reach for the nipples of the rabbit, it is worth turning on the feeding. Like week-old babies, they are fed only milk, they do not offer other food. You also need to feed babies if they are stunted and not gaining weight.
If during this period, the female no longer feeds, then we switch to artificial feeding. The number of feedings is reduced to 3 per day. Young animals after two weeks from about 20 days will already be able to drink from a saucer, so you will not need a nipple or syringe. Strong young animals already weigh 500 grams by this age, and by 20 days already almost 600 (consider the breed). A milk ration will be necessary for rabbits at least until they are one month old.
The number of feedings is reduced to 3 per day. Young animals after two weeks from about 20 days will already be able to drink from a saucer, so you will not need a nipple or syringe. Strong young animals already weigh 500 grams by this age, and by 20 days already almost 600 (consider the breed). A milk ration will be necessary for rabbits at least until they are one month old.
From birth to three weeks, rabbits are fed only with mother's milk or are fed artificially with milk mixtures. From 17-20 days you can offer them fresh hay in small quantities, as well as a little finely grated fresh carrots.
If the children are kept together with the rabbit and feed on her milk, the transition to adult food will be smoother and more natural. The rabbits will instinctively eat what is good for them if the female leads by example.
How to feed monthly rabbits
Young rabbits after the age of 20 days and up to a month can already chew their own food. This is due to the fact that after a 20-day milestone, the teeth of the rodents will partially change, part of the milk ones will be replaced by permanent ones. For monthly pets, milk is no longer so necessary, in the diet it takes about 25%. Strengthened rabbits begin to give more hay, green mash, bran, dried wild plants. After a month, many breeders generally transfer their rabbits to an adult diet.
This is due to the fact that after a 20-day milestone, the teeth of the rodents will partially change, part of the milk ones will be replaced by permanent ones. For monthly pets, milk is no longer so necessary, in the diet it takes about 25%. Strengthened rabbits begin to give more hay, green mash, bran, dried wild plants. After a month, many breeders generally transfer their rabbits to an adult diet.
Ever since the gradual decrease in the milk content and the increase in the proportion of solid and succulent feed, babies also need clean water. The more rabbits drink, the less kidney problems they will have. Young animals must be forced to drink (from a syringe), if they do not drink themselves. Until the age of 30-45 days, it is better to compensate for the liquid not with water, but with milk, especially in winter.
After weaning from mother
After jigging rabbits from their mother (and this happens at different times, but not earlier than 20-24 days), you need to carefully monitor their digestion. Having ceased to receive part of the enzymes with milk from the mother, grown-up babies learn to digest coarser food. From the age of 20 days, the rabbits fed by their mother try a little adult food. Therefore, after jigging, the process of adaptation to coarser, juicier or green food goes naturally.
Having ceased to receive part of the enzymes with milk from the mother, grown-up babies learn to digest coarser food. From the age of 20 days, the rabbits fed by their mother try a little adult food. Therefore, after jigging, the process of adaptation to coarser, juicier or green food goes naturally.
During this period, animals are boldly given vegetables and cereals. Good soft hay is also introduced, a small amount of grass pellets (about 3% of the rabbit's weight per day). You can give young animals cooled grain brewed with boiling water, greens of wild plants, a little bran. When more than 20 days have passed since jigging, the rabbits can be completely transferred to an adult diet. In the morning they give dry food, more moist food - in the middle of the day.
Bimonthly
So, your rabbits are no longer a week, not 20 days, or even a month, but two whole - how to feed two-month-old individuals? Here the matter is small - just arrange for them the right diet with plenty of fiber. Let's have some purchased compound feed, again, hay, herbal mixtures with nettle, dandelion, fireweed and other herbs, bran.
Let's have some purchased compound feed, again, hay, herbal mixtures with nettle, dandelion, fireweed and other herbs, bran.
What about your favorite treat - vegetables? Some breeders of rabbits say that juicy food should be given only after 2 months. However, if your pets live with their mother in a cage, they will inevitably try such food sooner. Do not worry, it is important to control their nutrition after transplanting, then everything will be fine.
Video "Rabbits eat salad with a rabbit"
In this video, we can watch how already grown cubs, together with their mother, appetizingly crunch salad, which belongs just to juicy food. In small quantities, such a product will not harm, but will be useful.
How to feed rabbits at home
Proper feeding of rabbits requires balanced mixtures containing a certain norm of the necessary products and having a high nutritional value. Without observing this condition, it is impossible to achieve good growth and strong immunity in animals. By adjusting the diet of rabbits, you can improve the quality of meat and fur, increase the survival of offspring and maximize the potential of the breed.
By adjusting the diet of rabbits, you can improve the quality of meat and fur, increase the survival of offspring and maximize the potential of the breed.
- What can rabbits eat?
- Benefits of specialty foods
- Benefits of compound feed produced by MEGAMIX
- Feeding norms and rations
- Self-preparation of feed
- Nuances of feeding rabbits depending on the season
- What should not be fed to rabbits?
What can rabbits eat?
The metabolism of rodents is so intense that they need to constantly eat for the proper functioning of all body systems. If the rabbit for some reason stops eating, then during the day there is a malfunction in the digestive tract. This entails serious consequences for health, up to and including death.
Compound feed for rabbits is complete and concentrated. The first one provides all the needs of animals in calories and nutrients. The second is used as a supplement to the main diet. Young rabbits reach a commercial weight of 3.5–4.5 kg, provided that they are properly fed, at the age of 4–5 months, and an adult female brings 30 or more cubs per year. If the diet is balanced and meets the needs of the breed, the rabbit is capable of the next reproductive cycle as early as 3-5 days after birth.
Young rabbits reach a commercial weight of 3.5–4.5 kg, provided that they are properly fed, at the age of 4–5 months, and an adult female brings 30 or more cubs per year. If the diet is balanced and meets the needs of the breed, the rabbit is capable of the next reproductive cycle as early as 3-5 days after birth.
Livestock specialists have repeatedly researched the best way to feed rabbits. The diet of meat and decorative animals should include the following products:
Cereals (concentrated feed) have the highest nutritional value. They contain a large amount of protein and a minimum of water. Oats are considered the best grain, as they are well absorbed, have a positive effect on intestinal motility and reproductive functions, and do not contribute to obesity. It is used in the form of whole or crushed grains. Rye, barley and wheat are offered to rabbits in the form of crushed, mixed with other feeds.
It should be remembered that you can not give a lot of wheat, and it is better to remove the shell from barley. These grains are difficult to digest, often leading to bloating. Many farmers recommend pre-treatment of grain products: soaking, sprouting, steaming or yeasting. Sprouting allows you to increase the amount of vitamins and increase protein digestibility. Yeasting improves the digestibility of fiber, but feeding animals with such grains for more than 5 days in a row is undesirable, as it can provoke fermentation in the intestines.
These grains are difficult to digest, often leading to bloating. Many farmers recommend pre-treatment of grain products: soaking, sprouting, steaming or yeasting. Sprouting allows you to increase the amount of vitamins and increase protein digestibility. Yeasting improves the digestibility of fiber, but feeding animals with such grains for more than 5 days in a row is undesirable, as it can provoke fermentation in the intestines.
Green foods form the basis of the rabbit diet from spring to late autumn. This type of food includes: vegetable tops; fodder cabbage; wild herbs; seeded cereals and legumes. Nettle, wormwood, dandelion, couch grass, plantain, quinoa are considered the most suitable wild plants. Freshly cut greens are recommended to be slightly dried and dried in the sun. The tops of fodder and sugar beets, carrots, turnips, rutabaga, Jerusalem artichokes are also suitable as green fodder. Sugar and fodder beet tops are not recommended for young animals. It has laxative properties, therefore, along with it, animals are advised to give plant foods that have a fixing effect. For these purposes, yarrow, comfrey, branches and leaves of oak and alder are suitable. In the mass of green fodder beet tops should not be more than 30%.
For these purposes, yarrow, comfrey, branches and leaves of oak and alder are suitable. In the mass of green fodder beet tops should not be more than 30%.
The aerial part of legumes, legumes and cereals is rich in vitamins and minerals, and also contains a large amount of proteins. However, experienced rabbit breeders advise using the above plants in a mixture with other feeds, since herbs alone will not be able to provide good nutrition and can lead to bloating in animals.
The diet of rabbits should be approximately 25% roughage. These include: hay, straw, tree branches. The optimal harvesting time is in spring and summer. Such food is very important, as it creates a feeling of satiety and contains fiber necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive tract.
The main share of roughage is hay. Harvest it using the same herbs as for green fodder. Legume hay has much more plant protein than grain hay, so it is more nutritious. Haylage is under-dried hay pressed into briquettes. Rabbits eat it with gusto, and also love clean straw if it's well dried.
Rabbits eat it with gusto, and also love clean straw if it's well dried.
Juicy food (vegetables)
- Potato: high in fast digesting starch. It is recommended to give in boiled form;
- Carrots contain C and B vitamins vital for breeders, pregnant/nursing females and growing rabbits. It is the main source of carotene in winter. The daily norm for an adult animal is up to half a kilogram. Young rabbits are started on portions weighing 20–30 g.
- Cabbage contains many minerals, vitamins C and E. Helps to improve the quality of the skin and fur. Introduced into the diet of animals gradually, used both raw and boiled.
- Zucchini helps to better assimilate other foods. They are given fresh.
- Pumpkin improves coat quality and has a positive effect on milk production in lactating rabbits. It has a good effect on digestion and weight gain in animals. Offered to rabbits both raw and boiled.
- Feed and sugar beet improves metabolism and blood quality, improves immunity.
 Use raw or boiled, no more than 150–200 g for young animals and 250–300 g for adults per day. Excess beets can lead to diarrhea in animals. Table varieties are strictly prohibited.
Use raw or boiled, no more than 150–200 g for young animals and 250–300 g for adults per day. Excess beets can lead to diarrhea in animals. Table varieties are strictly prohibited. - The diet of rabbits also includes melons, watermelons, turnips, Jerusalem artichokes, and radishes. However, their nutritional value is not very high.
Processed products of legumes and oilseeds (meal, cake of soybeans, peas, beans, sunflower, hemp, flax) are sources of fatty acids necessary for the body, including essential ones.
The composition of feed mixtures necessarily introduce products of animal origin: meat and bone or fish meal. Meat and bone contains about 40% protein and 14% fat, while fish contains about 45% protein and 7% fat. Flour is mixed into wet food in small portions - 5–10 g per individual.
Also, table salt must be present in the diet of rabbits. The rabbit needs 0.5–1 gram per day. For adults, the rate is increased by 1.5–2 times. When fattening animals, the daily amount of salt is 2-3 grams per individual.
Benefits of specialty foods
Complete nutrient mixtures can be prepared independently, but this is a very time-consuming work. To produce a quality product for feeding rabbits, you need:
- crushers, crushing components to the desired size;
- stocks of various grain crops;
- meat and bone and fish meal;
- protein-vitamin-mineral complexes;
- cake.
It is important to check the quality of incoming raw materials to minimize the risk of mortality. In the process of preparing mixtures for feeding rabbits, it is necessary to know exactly how much and what components are required, and at home or in a small enterprise it is difficult to achieve proportions. Because of this, there is a possibility of an excess of some nutrients and a deficiency of others, which can lead to improper formation of rabbits and young animals.
For the storage of compound feed, it is necessary to maintain normal ventilation in the room, a humidity level of not more than 75% and a temperature of up to 25 ° C. It is desirable to place bags on lattice racks or pallets. For small farms and medium-sized farms, buying ready-made feed can be more profitable than own production. The higher cost of the product is offset by guaranteed quality and time savings.
It is desirable to place bags on lattice racks or pallets. For small farms and medium-sized farms, buying ready-made feed can be more profitable than own production. The higher cost of the product is offset by guaranteed quality and time savings.
Benefits of compound feed produced by MEGAMIX
Our compound feeds for rabbits are presented in correctly formulated complete mixtures, which contain all the necessary nutrients:
| universal | for lactating queens |
|---|---|
| Ideal for weaned rabbits and fattening animals. | Also suitable for queens and rabbits. on milk feeding. |
Feed is produced in the form of granules and packaged in convenient packages: standard bags of 25 and 40 kg or big bags for large customers. The composition of the mixtures contains only valuable components that improve productivity, strengthen the immune system, positively affect the quality of the fur and the resulting meat, increase the growth and activity of rabbits.
Thanks to our own science-intensive production, we create recipes that best meet the needs of a particular breed of animal. The quality of incoming raw materials and the final product is carefully checked against more than 280 indicators in our analytical center, accredited to the international standard. Our requirements for commercially available compound feed for rabbits are stricter than GOSTs. All products undergo mandatory certification.
The company closely cooperates with VolGAU. The effectiveness and safety of all feeds are tested in a research center. Due to this, we are able to quickly navigate the needs of customers, clearly analyze each request and select the most profitable option for the customer. Our production facilities are designed to produce up to 180 tons of products annually.
We work not only in the central regions of Russia (Moscow and nearby regions), but also organize delivery to the cities of the Urals, Western Siberia, the North Caucasus, Crimea through an extensive network of dealerships.
Feed mixtures from MEGAMIX are effective for breeding rabbits at home, on medium-sized farms or large complexes. Using them, you will provide the animals with all the necessary trace elements, vitamins and mineral supplements, get a high average daily weight gain and reduce the risk of livestock infection.
Norms and diet
For agricultural breeds (meat and fur)
In summer, one rabbit needs 40-50 grams of concentrated and roughage plus a pound of green. During preparation for mating, the amount of food increases: green for 600 grams, concentrated and coarse - 70-80 grams. For a pregnant female, you will need 550–700 grams of greenery and 70–90 grams concentrated and coarse. A lactating female needs at least a kilogram of greens per day and up to 150 grams of roughage.
In winter, the basis of the diet is succulent food (150–200 grams) plus hay (120–150 grams). The amount of rough and concentrated feed remains the same. During preparation for mating 150-200 grams of juicy, 90-100 grams of concentrated and coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A pregnant rabbit needs 200-250 grams of juicy, 100-130 grams of coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A lactating female will need 300-350 grams of juicy, 140-160 concentrated and coarse and 200-250 grams of hay.
A pregnant rabbit needs 200-250 grams of juicy, 100-130 grams of coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A lactating female will need 300-350 grams of juicy, 140-160 concentrated and coarse and 200-250 grams of hay.
Fattening of meat breeds usually occurs in autumn and winter. When fattening, the amount of concentrated feed, bran and root crops (especially boiled potatoes) is gradually increased.
In ornamental breeds, digestion works worse than in agricultural ones. They can be given the following foods.
- Hay is the main feed for ornamental breeds. It should be clean and dry and should be replaced as needed.
- Grass - it can be added to the diet in summer. It is desirable to collect grass away from roads and other sources of pollution.
- Granular food - 2 tablespoons per day.
- Vegetables and fruits - can be given little by little, in small pieces and only washed and fresh. Radishes, parsley, carrots are good. It is better to exclude beets and cabbage in order to avoid stomach problems.

A complete balanced diet for rabbits, of course, should include the main vitamins:
- A - has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous and reproductive systems in wards, improves their general physical condition;
- B1 - responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates in the body, normalizes the activity of the cardiovascular system, indirectly improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- B2 - improves the condition of the skin and fur, optimizes the general physical condition of animals;
- B5 - normalizes the digestive system;
- B6 - is responsible for the absorption of proteins and simple proteins, as well as for the enzymatic balance in the body;
- B12 - promotes the absorption of proteins, is extremely important for the health of newborn rabbits;
- C - strengthens the immune system and normalizes the digestive tract;
- D - necessary for the proper development of the eared musculoskeletal system, promotes better absorption of minerals;
- E - responsible for the development of the muscular system of pets.
 Stabilizes the work of the heart and reproductive system;
Stabilizes the work of the heart and reproductive system; - K is an essential vitamin for rabbit breeding.
Self-feed preparation
The mash is a delicacy for rabbits. The most popular recipe includes:
- boiled potatoes;
- carrots;
- oats;
- germinated wheat;
- table salt;
- bran;
- chopped hay.
The mixer is prepared using a blender or other chopper. To enrich it with biologically active substances, concentrated feed additives are added to it.
Hay is harvested using the same herbs as for green fodder. It is important to mow the plants before they bloom. The resulting raw material is dried on the street, and then allowed to lie down for some time in a well-ventilated place under a canopy (without direct sunlight).
Silage ingredients are crushed to fragments no larger than 1 cm in length. The resulting mass is placed in a sealed barrel and covered with a layer of sawdust 5 cm thick. The resulting substrate is compacted until juice appears and pressed down with a wooden circle, on which a load is placed on top. In the process of silage maturation, the barrels are stored in a moderately warm place, and then removed to a cool room.
The resulting substrate is compacted until juice appears and pressed down with a wooden circle, on which a load is placed on top. In the process of silage maturation, the barrels are stored in a moderately warm place, and then removed to a cool room.
Nuances of feeding rabbits depending on the season
The summer diet of animals should consist of cereals by 30-40%, and in winter and with intensive fattening - by 50-70%. In the summer, green food predominates in the diet of rabbits, but with the onset of cold weather, juicy food - silage and vegetables - become the main part of the menu. The owners who grow vegetables and melons on their plots give the animals various root crops, cabbage, zucchini and pumpkins. Such food contains many vitamins, but little fiber and protein; in lactating rabbits, it contributes to more intense lactation.
When planning the volume of the product harvested for the winter, farmers proceed from the calculation: 40 kg of hay for a rabbit; 10–15 kg per head of potential offspring. If there is not enough hay for all the livestock, then first of all it should be fed to females and lactating females, young animals. For adult males during the dormant period (if mating is not planned), the above product can be replaced with pea, lentil, oat or millet straw. You can’t feed it for a long time, because there are very few nutrients in the straw.
If there is not enough hay for all the livestock, then first of all it should be fed to females and lactating females, young animals. For adult males during the dormant period (if mating is not planned), the above product can be replaced with pea, lentil, oat or millet straw. You can’t feed it for a long time, because there are very few nutrients in the straw.
Branch fodder becomes a good help in winter. Timely harvested young twigs of trees contain quite a lot of vitamins. In addition, rabbits that have a constant opportunity to eat such food are much less likely to express a desire to gnaw on cages. Branches of only certain tree species are suitable for harvesting: willow, willow, maple, linden, acacia, mountain ash, poplar, aspen, ash, oak, alder. The content of nutrients in tree shoots is highest in the first month of summer.
Vitamin supplements are administered most often at the end of winter - in early spring, when there is a shortage of green and succulent fodder. To fill the need for vitamins A and D, animals are given special concentrated preparations or fish oil is added to food. At the same time, the amount of fish oil required by rabbits is calculated depending on their physiological state.
To fill the need for vitamins A and D, animals are given special concentrated preparations or fish oil is added to food. At the same time, the amount of fish oil required by rabbits is calculated depending on their physiological state.
What should not be fed to rabbits?
It is better to refrain from adding birch branches to the diet, as they can lead to kidney disease. The same can be said about the branches of cherries, sweet cherries and plums. They contain hydrocyanic acid, which is quite dangerous for the body of animals. Branches of wild rosemary, buckthorn, bird cherry, apricot and elderberry are strictly forbidden to give to rabbits.
Even beneficial plants in excess can harm rabbits. From freshly cut grass, they have bloating of the intestines. Therefore, before feeding rabbits, it must be dried in direct sunlight. As a rule, an excess of cabbage leads to intestinal upset. It is also not recommended to give dirty vegetables to rabbits. This negatively affects the work of the digestive tract.