Starting food for 6 month old baby
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
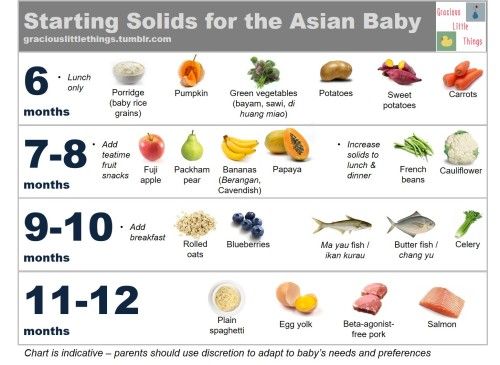
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
When can I start giving my baby peanut butter?
Log in | Register
Tips & Tools
Tips & Tools
Listen
Español
Text Size
Question
Amanda Cox, MD, FAAAAI
Answer
Many parents have questions and concerns about when peanut butter can be safely introduced, because it is the leading cause of fatal and near-fatal food allergic reactions in the United States.
New Guidelines on the Introduction of Allergenic Foods:
For many years, experts thought that the best way to fight peanut allergy was to avoid peanut products in the first years of life. At the time, it was thought that delaying introduction would possibly prevent the development of other allergic conditions, especially eczema. However, more recent guidelines show that there is no benefit to delaying the introduction of allergenic foods. In 2015, an important study showed that early introduction and regular feeding of peanut prevented the development of peanut allergy in infants at "high risk" for peanut allergy (meaning infants who had severe eczema and/or an egg allergy).
Advice to Parents:
Start solids with a few foods that are of low allergy risk—for example, infant cereal, puréed bananas, or puréed prunes. Give your baby one new food at a time, and wait at least 2 to 3 days before starting another. After each new food, watch for any allergic reactions such as diarrhea, rash, or vomiting.
 If any of these occur, stop using the new food and consult with your child's pediatrician.
If any of these occur, stop using the new food and consult with your child's pediatrician.If there is no special reason to be concerned that your baby is at increased risk for food allergies, after a few first foods have been tolerated, you can start to introduce the more highly allergenic foods (milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanut, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish). It is important that these—and all foods—are in forms and textures appropriate for infants. For instance, while whole cow's milk is not recommended before 1 year of age; you may introduce processed dairy products such as whole milk yogurt or Greek yogurt mixed with a fruit that your baby has already had in his or her diet.
If your baby has or had severe, persistent eczema or an immediate allergic reaction to any food— especially if it is a highly allergenic food such as egg—he or she is considered "high risk for peanut allergy." You should talk to your child's pediatrician first to best determine how and when to introduce the highly allergenic complementary foods.
 Ideally peanut-containing products should be introduced to these babies as early as 4 to 6 months. It is strongly advised that these babies have an allergy evaluation or allergy testing prior to trying any peanut-containing product. Your doctor may also require the introduction of peanuts be in a supervised setting (e.g., in the doctor's office).
Ideally peanut-containing products should be introduced to these babies as early as 4 to 6 months. It is strongly advised that these babies have an allergy evaluation or allergy testing prior to trying any peanut-containing product. Your doctor may also require the introduction of peanuts be in a supervised setting (e.g., in the doctor's office). Babies with mild to moderate eczema are also at increased risk of developing peanut allergy. These babies should be introduced to peanut-containing products around 6 months of age; peanut-containing products should be maintained as part of their diet to prevent a peanut allergy from developing. These infants may have peanut introduced at home (after other complementary foods are introduced), although your pediatrician may recommend an allergy evaluation prior to introducing peanut.
Babies without eczema or other food allergies, who are not at increased risk for developing an allergy, may start having peanut-containing products and other highly allergenic foods freely after a few solid foods have already been introduced and tolerated without any signs of allergy.
 As with all infant foods, allergenic foods should be given in age- and developmentally-appropriate safe forms and serving sizes.
As with all infant foods, allergenic foods should be given in age- and developmentally-appropriate safe forms and serving sizes.
Choking Prevention:
Whole peanuts themselves are choking hazards and should not be fed to babies. They can block the air passages, and if whole or partially chewed peanuts are inhaled into the lungs, they can cause a severe and possibly fatal chemical pneumonia. Avoid whole peanuts until your child is old enough to be counted on to chew them well (usually at least 4 years and up).
A good way to introduce peanut in infancy would be mixing and thinning-out a small amount of peanut butter in cereal or yogurt. Dissolving peanut butter puffs with breast milk or formula and feeding it by spoon is another good option.
Remember:
The highly allergenic foods should initially be given to your baby in small tastes at home, and the amount can gradually be increased in a developmentally appropriate manner if there are no signs of intolerance or allergic symptoms.
NOTE: The AAP recommends breastfeeding as the sole source of nutrition for your baby for about 6 months. When you add solid foods to your baby's diet, continue breastfeeding until at least 12 months. You can continue to breastfeed after 12 months if you and your baby desire. Check with your child's doctor about vitamin D and iron supplements during the first year. Remember that each child's readiness for solid foods depends on his own rate of development.
Additional Information & Resources:
Working Together: Breastfeeding and Solid Foods
Sample Menu for an 8 to 12 Month Old
Infant Allergies and Food Sensitivities
Peanut Allergies: What You Should Know About the Latest Research
- The Effects of Early Nutritional Interventions on the Development of Atopic Disease in Infants and Children: The Role of Maternal Dietary Restriction, Breastfeeding, Hydrolyzed Formulas, and Timing of Introduction of Allergenic Complementary Foods (AAP Clinical Report)
Amanda Cox, MD, FAAAAI
Amanda Cox, MD, FAAAAI is an Assistant Professor of Pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Allergy and Immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York and a practicing pediatric allergist at Jaffe Food Allergy Institute. She is a former president of the New York Allergy & Asthma Society and a fellow of the American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology where she serves on the Adverse Reactions to Foods Committee. Dr. Cox is a contributing writer to The Pediatrician's Guide to Feeding Babies and Toddlers and has written several book chapters and review articles in the area of food allergy.
She is a former president of the New York Allergy & Asthma Society and a fellow of the American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology where she serves on the Adverse Reactions to Foods Committee. Dr. Cox is a contributing writer to The Pediatrician's Guide to Feeding Babies and Toddlers and has written several book chapters and review articles in the area of food allergy.
- Last Updated
- 3/17/2019
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to mixed or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.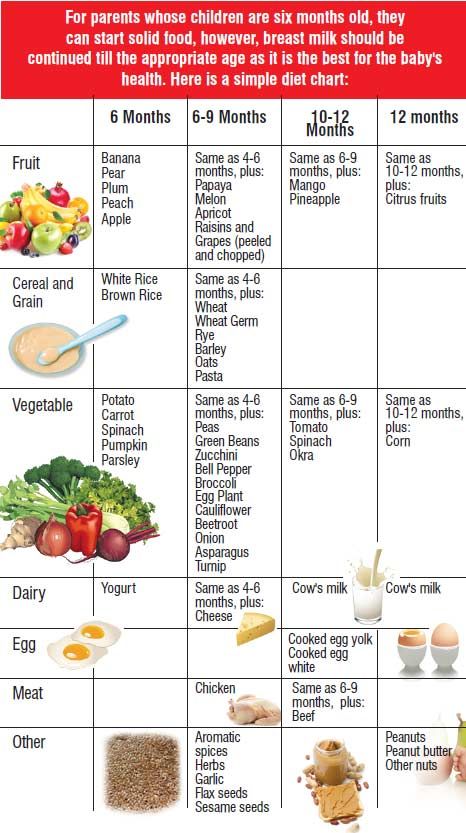
If the first complementary food is introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually “dilute” this product with a new one.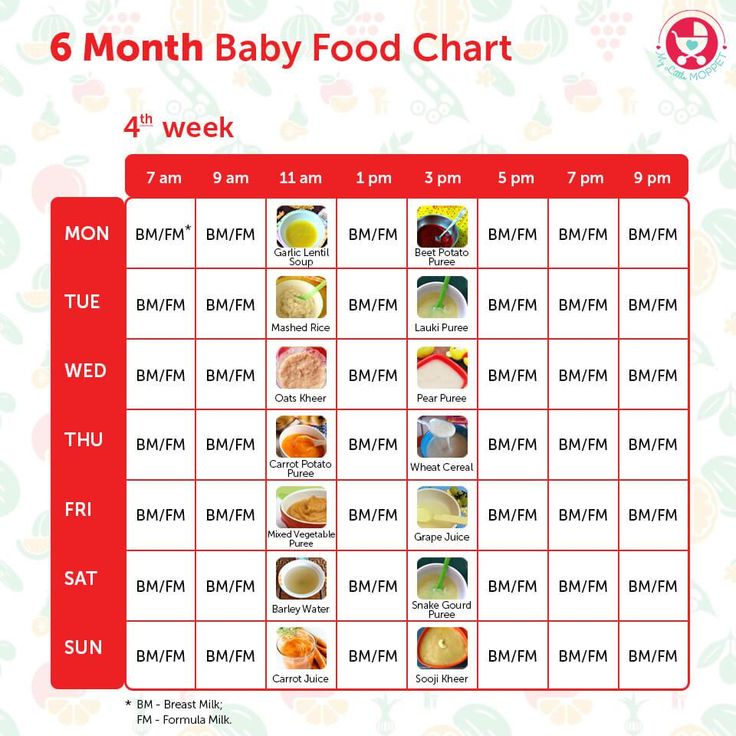 For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. The materials were prepared by the staff of the Healthy and Sick Child Nutrition Laboratory of the National Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of Russia and are based on the recommendations given in the National Program for Optimizing the Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation, approved at the XV Congress of Pediatricians of Russia (02.2009d.) Pediatricians around the world, including experts from the World Health Organization, unanimously believe that the introduction of complementary foods should be carried out in the interval of 4-6 months. Early introduction of complementary foods (up to 4 months). fraught with the development of allergic reactions and indigestion. Late introduction of complementary foods, from 7 months, can lead to a deficiency in the child's diet of essential nutrients, an iron deficiency state at the age of 9-10 months, eating disorders, delayed development of chewing skills and swallowing of thick foods. With the normal development of the child and the absence of signs of iron deficiency anemia, complementary foods can be introduced from 6 months. This applies to both formula-fed and breast-fed babies. Signs that a baby is ready to breastfeed include It is important to remember that a child’s lack of teeth and the ability to sit are not signs of a baby’s unpreparedness for eating thick foods. It is very important to understand the main goals of the introduction of complementary foods: In no case should the introduction of complementary foods be of a violent nature, since this will not only not contribute to the development of a child’s food interest, but can also lead to a complete refusal of the baby from complementary foods, which will destroy the main goals of complementary foods. The first product of complementary foods, regardless of the start date of the introduction of complementary foods and the type of feeding of the baby (breast or artificial), should be energy-intensive foods: porridge, or vegetable puree. If the child has a liquefied or unstable stool, and there is also a lack of body weight, then it is better to choose porridge as the first complementary food. After 3-4 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g) If the child has a tendency to constipation, then it is better to choose vegetable marrow puree as the first complementary food, which can have a mild laxative effect on the child's stool. Starting from the 3-4th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g) The first cereals can be buckwheat, rice or corn. The first vegetable puree can be zucchini, broccoli, or cauliflower. Later, kohlrabi, potatoes, green beans, white cabbage, green peas, celery can be introduced into the diet. The third type of complementary foods can be fruit puree from apples, pears or bananas. Later, you can introduce mashed apricot, peach. For starters, fruit puree may not be given to the child separately, but it is better to mix it with cereal or vegetables so that the child does not begin to prefer the sweet taste of fruits. When the amount of fruit puree reaches 50 g or more, it can also be given separately, for example, after the child has eaten porridge or cottage cheese. Juices should not be the first feeding, in addition, they can not be introduced into the baby's first year of life at all, given their sweet taste and low nutritional value. The introduction of a new product should be gradual. Important! If on the 5-7th day of the introduction of a new product, the baby still cannot eat 100-150 ml of porridge or puree at once, then this amount can be divided into 2 doses, for example, give 100 ml of porridge in the morning and 50 ml in the evening. From the second week of the introduction of a new product, one milk feeding can be completely replaced with complementary foods. If we start complementary foods with vegetable puree, then the schedule might look something like this: 2 weeks From the second week, you need to start introducing dairy-free porridge. 3 week From the third week, you need to start introducing meat puree, which is most convenient to add to vegetable puree 4 week From the fourth week, you can introduce fruit puree, which is most convenient to add to porridge I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VMS 
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk 
Complementary foods at 6 months | Useful tips from the Tyoma brand


How to start introducing complementary foods at 6 months of age?
What products are better to give preference to at 6 months?
Kashi
 They must be dairy-free and can be diluted with water or breast milk, or the mixture that the baby eats. Later, you can introduce oatmeal and millet porridge
They must be dairy-free and can be diluted with water or breast milk, or the mixture that the baby eats. Later, you can introduce oatmeal and millet porridge Vegetables
Fruit
Juices

Basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods from 6 months
How to start the introduction of a new product?

Approximate weekly feeding schedule
 Vegetable oil 5 g Supplementary feeding with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml
Vegetable oil 5 g Supplementary feeding with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml