Do i feed my baby after vomiting
How to Know Whether You Should
Your baby just threw up all the milk they’ve chugged down so far, and you’re wondering if it’s OK to continue feeding. How soon should you feed your baby after vomiting?
It’s a good question — just about every parent has likely pondered this. Spit-up is almost a rite of passage for babies (and parents). Baby vomiting is also common and can happen for many reasons. Most of the causes aren’t serious.
The short answer — because you may have a very fussy baby on your hands and want to get back to them ASAP — is yes, you can usually feed your baby after they vomit all over your favorite sweater, sofa throw, and rug.
Here’s just about everything you need to know about feeding your baby after vomiting.
Baby vomit and spit-up are two different things — and they can have different causes. Spitting up is common in babies under the age of 1 year. It typically happens after feeding. Spit-up is usually an easy flow of milk and saliva that dribbles from your baby’s mouth. It often happens with a burp.
Spit-up is normal in healthy babies. It can happen for several reasons. About half of all babies 3 months and under have a type of acid reflux called infant reflux.
Spit-up from infant reflux is especially bound to happen if your baby has a full stomach. Being careful not to overfeed a bottle-fed infant can help. Spitting up typically stops by the time your baby is a year old.
On the other hand, vomiting is typically a more forceful throwing-up of milk (or food, if your baby is old enough to eat solids). It happens when the brain signals the muscles around the stomach to squeeze.
Vomiting (like gagging) is a reflex action that can be triggered by a number of things. These include:
- irritation from a viral or bacterial infection, like the stomach bug
- fever
- pain, such as from a fever, earache, or vaccination
- blockage in the stomach or intestines
- chemicals in the blood, like medicine
- allergens, including pollen; very uncommon in babies under 1 year
- motion sickness, such as during a car ride
- dizziness, which might happen after being twirled around too much
- being upset or stressed
- strong smells
- milk intolerance
Vomiting is also common in healthy babies, but it might mean that your baby has caught a bug or is feeling a bit under the weather.
Too much vomiting can cause dehydration and even weight loss in very serious cases. Milk feeding can help prevent both of these. Offer your baby a feeding after they’ve stopped throwing up. If your baby is hungry and takes to the bottle or breast after vomiting, go right ahead and feed them.
Liquid feeding after vomiting can sometimes even help settle your baby’s nausea. Start with small amounts of milk and wait to see if they vomit again. Your baby might vomit the milk right back up, but it’s better to try than not.
If your little one is at least 6 months old and doesn’t want to feed after throwing up several times, offer them water in a bottle or a spoon. This can help prevent dehydration. Wait a short while and try feeding your baby again.
In some cases, it’s better not to feed a baby right after vomiting. If your baby is throwing up because of an earache or fever, they may benefit from medication first.
Most pediatricians recommend pain medications like infant Tylenol for babies in their first year. Ask your doctor about the best medication and dosage for your baby.
Ask your doctor about the best medication and dosage for your baby.
If giving pain medication based on your doctor’s advice, wait about 30 to 60 minutes after doing so to feed your little one. Feeding them too soon might cause another bout of vomiting before the meds can work.
Motion sickness isn’t common in babies under the age of 2 years, but some babies may be more sensitive to it. If your baby vomits from motion sickness, it’s better not to offer a feeding afterward.
You’re in luck if your baby likes to nod off in the car. Wait until you’re out of the car to feed your baby milk.
Baby vomiting can be worrying, but it usually goes away by itself — even if your baby has the stomach bug. Most babies with gastroenteritis don’t need medical treatment. This means that most of the time, you’ll have to bravely wait out your baby’s vomiting.
But sometimes, throwing up is a sign that something’s not right. You know your baby best. Trust your gut and call their doctor if you feel your little one is unwell.
In addition, take your baby to a doctor immediately if they’ve been vomiting for 12 hours or longer. Babies and children can dehydrate quickly from too much vomiting.
Also call your baby’s pediatrician if your baby can’t hold anything down and has signs and symptoms of being unwell. These include:
- constant crying
- pain or discomfort
- refusal to feed or drink water
- diaper that hasn’t been wet for 6 hours or longer
- diarrhea
- dry lips and mouth
- crying without tears
- extra sleepiness
- floppiness
- vomiting blood or fluid with black flecks (“coffee grounds”)
- lack of smile or response
- vomiting green fluid
- bloated tummy
- blood in bowel movements
You won’t usually have any control over when or how much your baby vomits. When it happens on occasion, repeat this mantra to help you cope: “Healthy babies sometimes vomit.”
However, if your baby often vomits (or spits up) after feeding, you may be able to take some preventative steps. Try these tips:
Try these tips:
- avoid overfeeding
- give your baby smaller, more frequent feeds
- burp your baby often between feeds and after feeds
- prop up your baby so they’re upright for at least 30 minutes after feeding (but don’t prop your baby up for sleep or use anything to position them in their crib or elevate their mattress)
If your baby has a tummy bug and is old enough to eat solid foods, avoid feeding solids for about 24 hours. A liquid diet can help the stomach settle after a bout of vomiting.
Vomiting and spit-up are common in healthy babies. In most cases, you can milk feed shortly after your baby vomits. This helps to prevent your baby from getting dehydrated.
In some cases it’s best to wait a little while before trying to feed your baby again. If you’re giving your child medication like pain and fever relievers, wait a bit so the meds don’t come back up.
If your baby is vomiting a lot or seems otherwise unwell, call your pediatrician immediately. If you’re unsure if your baby’s vomiting or spit-up is cause for concern, it’s always best to check with your doctor.
If you’re unsure if your baby’s vomiting or spit-up is cause for concern, it’s always best to check with your doctor.
Vomiting (0-12 Months)
Is this your child's symptom?
- Vomiting (throwing up) stomach contents
- Other names for vomiting are puking, barfing and heaving
Causes of Vomiting
- Viral Gastritis. Stomach infection from a stomach virus is the most common cause. Also called stomach flu. A common cause is the Rotavirus. The illness starts with vomiting. Watery loose stools may follow within 12-24 hours.
- Food Allergy. Vomiting can be the only symptom of a food reaction. The vomiting comes on quickly after eating the food. Uncommon in infants, but main foods are eggs and peanut butter.
- Coughing. Hard coughing can also cause your child to throw up. This is more common in children with reflux.
- Serious Causes. Vomiting alone should stop within about 24 hours.
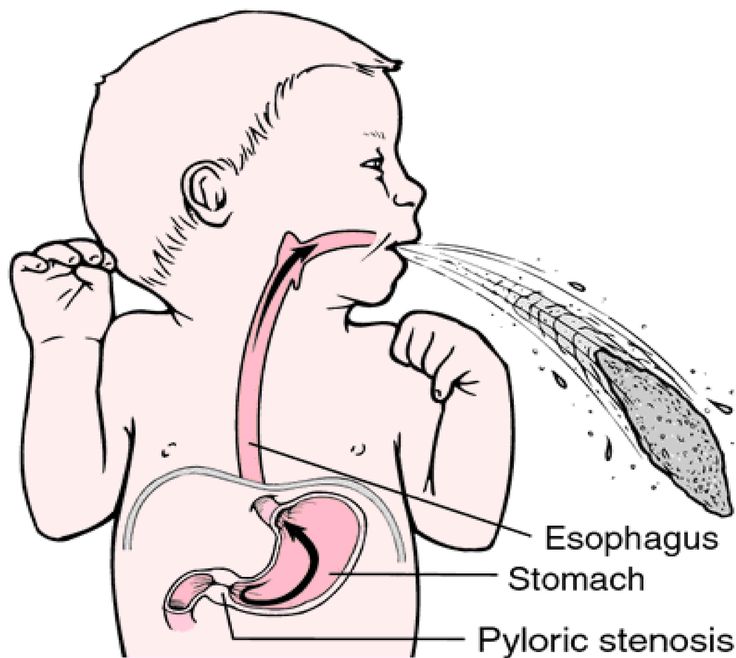
 If it lasts over 24 hours, you must think about more serious causes. An example is a kidney infection. A serious cause in young babies is pyloric stenosis. See below for more on this.
If it lasts over 24 hours, you must think about more serious causes. An example is a kidney infection. A serious cause in young babies is pyloric stenosis. See below for more on this.
Pyloric Stenosis (Serious Cause)
- The most common cause of true vomiting in young babies.
- Onset of vomiting is age 2 weeks to 2 months
- Vomiting is forceful. It becomes projectile and shoots out.
- Right after vomiting, the baby is hungry and wants to feed. ("hungry vomiter")
- Cause: The pylorus is the channel between the stomach and the gut. In these babies, it becomes narrow and tight.
- Risk: Weight loss or dehydration
- Treatment: Cured by surgery.
Vomiting Scale
- Mild: 1 - 2 times/day
- Moderate: 3 - 7 times/day
- Severe: Vomits everything, nearly everything or 8 or more times/day
- Severity relates even more to how long the vomiting goes on for.
 At the start of the illness, it's common for a child to vomit everything. This can last for 3 or 4 hours. Children then often become stable and change to mild vomiting.
At the start of the illness, it's common for a child to vomit everything. This can last for 3 or 4 hours. Children then often become stable and change to mild vomiting. - The main risk of vomiting is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much fluid.
- The younger the child, the greater the risk for dehydration.
Dehydration: How to Tell
- The main risk of vomiting is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much water.
- Vomiting with watery diarrhea is the most common cause of dehydration.
- Dehydration is a reason to see a doctor right away.
- Your child may have dehydration if not drinking much fluid and:
- The urine is dark yellow and has not passed any in over 8 hours.
- Inside of the mouth and tongue are very dry.
- No tears if your child cries.
- Slow blood refill test: Longer than 2 seconds. First, press on the thumbnail and make it pale. Then let go. Count the seconds it takes for the nail to turn pink again.
 Ask your doctor to teach you how to do this test.
Ask your doctor to teach you how to do this test.
When to Call for Vomiting (0-12 Months)
Call 911 Now
- Can't wake up
- Not moving
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Dehydration suspected. No urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth and no tears.
- Stomach pain when not vomiting. Exception: stomach pain or crying just before vomiting is quite common.
- Age less than 12 weeks old with vomiting 2 or more times. Exception: normal spitting up.
- Vomited 3 or more times and also has diarrhea
- Severe vomiting (vomits everything) more than 8 hours while getting Pedialyte (or breastmilk)
- Head injury within the last 24 hours
- Weak immune system. Examples are sickle cell disease, HIV, cancer, organ transplant, taking oral steroids.
- Vomiting a prescription medicine
- Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old.
 Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.
Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen. - Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- All other infants (age less than 1 year) with vomiting. See Care Advice while waiting to discuss with doctor.
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Vomiting
- What You Should Know About Vomiting:
- Most vomiting is caused by a viral infection of the stomach.

- Vomiting is the body's way of protecting the lower gut.
- The good news is that stomach illnesses last only a short time.
- The main risk of vomiting is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much fluid.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Most vomiting is caused by a viral infection of the stomach.
- Formula Fed Babies - May Give Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) for 8 Hours:
- If vomits once, give half the regular amount of formula every 1 to 2 hours.
- If vomits formula more than once, offer ORS for 8 hours. If you don't have ORS, use formula until you can get some.
- ORS is a special fluid that can help your child stay hydrated. You can use Pedialyte or the store brand of ORS. It can be bought in food stores or drug stores.
- Spoon or syringe feed small amounts. Give 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 mL) every 5 minutes.
- After 4 hours without throwing up, double the amount.
- Return to Formula. After 8 hours without throwing up, go back to regular formula.

- Breastfed Babies - Reduce the Amount Per Feeding:
- If vomits once, nurse half the regular time every 1 to 2 hours.
- If vomits more than once, nurse for 5 minutes every 30 to 60 minutes. After 4 hours without throwing up, return to regular nursing.
- If continues to vomit, switch to pumped breastmilk. (ORS is rarely needed in breastfed babies. It can be used if vomiting becomes worse).
- Spoon or syringe feed small amounts of pumped milk. Give 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 mL) every 5 minutes.
- After 4 hours without throwing up, return to regular feeding at the breast. Start with small feedings of 5 minutes every 30 minutes. As your baby keeps down the smaller amounts, slowly give more.
- Pumped Breastmilk Bottle-Fed Infants - Reduce the Amount per Feeding:
- If vomits once and bottle-feeding breastmilk, give half the regular amount every 1-2 hours.
- If vomits more than once within last 2 hours, give 1 ounce (30 mL) every 30 to 60 minutes.

- If continues to vomit, give 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 mL) every 5 minutes. Only if not tolerating breastmilk, switch to ORS (e.g., Pedialyte) for every 5 minutes for a few hours.
- After 4 hours without vomiting, return to regular feedings. Start with 1 ounce (30 mL) every 30 minutes and slowly increase as tolerated.
- Stop All Solid Foods:
- Avoid all solid foods and baby foods in kids who are vomiting.
- After 8 hours without throwing up, gradually add them back.
- If on solid foods, start with starchy foods that are easy to digest. Examples are cereals, crackers and bread.
- Do Not Give Medicines:
- Stop using any drug that is over-the-counter for 8 hours. Reason: Some of these can make vomiting worse.
- Fever. Mild fevers don't need to be treated with any drugs. For higher fevers, you can use an acetaminophen suppository (such as FeverAll). This is a form of the drug you put in the rectum (bottom).
 Ask a pharmacist for help finding this product. Do not use ibuprofen. It can upset the stomach.
Ask a pharmacist for help finding this product. Do not use ibuprofen. It can upset the stomach. - Call your doctor if: Your child vomits a drug ordered by your doctor.
- Try to Sleep:
- Help your child go to sleep for a few hours.
- Reason: Sleep often empties the stomach and removes the need to vomit.
- Your child doesn't have to drink anything if his stomach feels upset and he doesn't have any diarrhea.
- Return to Child Care:
- Your child can return to child care after the vomiting and fever are gone.
- What to Expect:
- For the first 3 or 4 hours, your child may vomit everything. Then the stomach settles down.
- Vomiting from a viral illness often stops in 12 to 24 hours.
- Mild vomiting and nausea may last up to 3 days.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Vomits clear fluids for more than 8 hours
- Vomiting lasts more than 24 hours
- Blood or bile (green color) in the vomit
- Stomach ache present when not vomiting
- Dehydration suspected (no urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth, and no tears)
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 10/24/2022
Last Revised: 09/21/2022
Copyright 2000-2022 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Diet for child vomiting, food menu after vomiting
How to feed a child after vomiting and diarrhea? This question is asked by all parents, since food poisoning happens periodically to everyone. No one is 100% protected from them. Even when preparing food on your own, you cannot be sure of the quality of the products and that the baby will not eat something in kindergarten or school, and even with dirty hands. In this article, we told you what you can eat after a child vomits, when you need to start eating, what foods you can eat, and which ones should be discarded for a while.
Causes of vomiting and diarrhea
Vomiting and diarrhea are common symptoms in children of different age groups. They can be signs of a functional failure in the body, an inflammatory or infectious process, intoxication or poisoning.
They can be signs of a functional failure in the body, an inflammatory or infectious process, intoxication or poisoning.
Any episode of nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea in a child requires parental attention. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the baby, try not to miss any other symptoms.
- Food poisoning. It can develop due to the consumption of stale and poor-quality food, as well as due to the child's failure to follow the basics of personal hygiene. Poisoning is manifested by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, increased formation of gases in the intestines, and abdominal pain. This state can proceed without temperature.
- Intestinal infection (salmonellosis, dysentery, rotavirus infection, etc.). These diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms that can even be found in fresh foods. For example, the source of salmonellosis are eggs, dairy or meat products. Intestinal infection is manifested by profuse watery diarrhea, which may be streaked with blood, mucus, nausea, severe abdominal pain and fever.
 If left untreated, severe dehydration develops.
If left untreated, severe dehydration develops. - Acetonemic syndrome is a condition in which the level of ketone bodies in the blood rises. This disease develops in children under 7 years of age. A characteristic symptom is the smell of acetone from the baby's mouth and from his urine.
- Child overheating, heatstroke or sunstroke. This condition can be manifested by vomiting, tachycardia, and one-time diarrhea may occur. Children under 6 years of age are more sensitive to the influence of the sun and high temperatures. Due to the high sweating, they develop an electrolyte failure and rapid fluid loss.
- Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis). These pathologies were previously considered more "adult". But over the past 10-20 years, their age category has changed dramatically. Poor quality food, ecology, chemicals "rejuvenated" these diseases. For example, cases of chronic gastritis in a baby at the age of 4 years or pancreatitis at 2 years old are not uncommon.

- Food intolerance, food allergy. For example, a baby's digestive system may not be able to digest dairy products or gluten. Most often, such individual characteristics are detected in a child at an early age, and parents, knowing about them, carefully compose the diet.
The child may vomit from a feeling of disgust for something or during crying, a nervous experience. Children under 5 years of age often vomit against the background of high temperature with SARS and influenza. It is necessary to monitor the condition of your baby, try to understand the cause of the symptoms that have arisen in him.
Basic nutrition rules for diarrhea and vomiting
Diet after vomiting in a child is not required if this symptom is due to disgust, crying or SARS. In all other cases, it is necessary to draw up a specific menu for the child after vomiting and carefully monitor his diet.
Feeding a child with vomiting and diarrhea, according to the latest WHO protocols, can be started as early as the first day of illness. Scientists have proven that hunger does not contribute to a quick recovery. However, eating with nausea and with a complete lack of appetite is also not worth it. Thus, it is possible to provoke a repeated vomiting attack.
Scientists have proven that hunger does not contribute to a quick recovery. However, eating with nausea and with a complete lack of appetite is also not worth it. Thus, it is possible to provoke a repeated vomiting attack.
Here are some general guidelines to follow when thinking about what to eat after your baby has vomited:
- Feed your baby often. Breaks between meals should not exceed 3 hours. If the child is under 3 years old, he should eat every 2 hours. Food should be given in small portions. A single amount of food should not exceed the volume of the child's fist.
- All food and drink must be at neutral (room) temperature. Hot, cold can irritate the gastric mucosa, cause nausea, abdominal pain.
- All nutrition after vomiting and diarrhea should not only be dietary and light, but also meet the energy needs of the baby's body. The child needs energy to recover.
- Do not force a child to eat if he is sick on the first day of illness.
 But you can't go hungry for a long time. You can feel sick from hunger and irritation of the stomach walls with hydrochloric acid.
But you can't go hungry for a long time. You can feel sick from hunger and irritation of the stomach walls with hydrochloric acid. - Eating during vomiting is strictly contraindicated, you can start feeding the baby only after it stops. If he vomits, begin to give a little to drink table water. It is best to drink it in a sip every 5-10 minutes. This mode of drinking will help start the digestive system, will not allow dehydration to increase.
- The best way to cook baby food is in a double boiler. It can also be boiled or stewed. All dishes should not be spicy or very salty. Spices, seasonings and flavor enhancers are prohibited.
What to eat when vomiting and diarrhea
Food on the first day of illness is very limited. In case of poisoning, you can feed the baby only with rice water, dried white bread or biscuit simple cookies. You can also eat oatmeal cooked to a slimy consistency.
In case of acute gastritis, pancreatitis or intestinal infection, you can start eating only after the permission of your doctor.
- Low-fat chicken broth made from the loin. You can add some carrots, salt to it.
- Boiled lean chicken, turkey or rabbit.
- Oven- or microwave-baked apples.
- Dried white bread.
- Biscuits.
- Boiled potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini.
- Bananas.
- Low-fat varieties of hard cheese, cottage cheese, dairy products.
- Buckwheat, oatmeal, rice porridge.
- Boiled eggs, steam omelet.
A small amount of refined vegetable oil can be added to ready meals. Butter, margarine, mayonnaise should be discarded for the period of diet therapy.
In addition to food, special attention should be paid to feeding the baby. The liquid is necessary to reduce the intoxication syndrome and to normalize the water and electrolyte balance.
Give your child plain table water to drink after vomiting and diarrhea. Then he can drink alkaline mineral water, such as Borjomi, black sweet tea, compote.
What not to eat
- Milk (other than breast milk) is a forbidden food product in case of digestive tract malfunction. You can start drinking milk only after 2 weeks.
- Fatty meats and fish, as well as broths cooked on their basis.
- Chocolate, flour confectionery, fresh bread.
- All sausages, pates.
- Meat offal.
- Shop semi-finished products.
- Carbonated drinks, coffee, cocoa.
- Juices (store-bought and freshly squeezed).
- Various sauces, tomato paste.
- Cabbage, garlic, onion.
- Citrus and exotic fruits.
- Fat varieties of hard cheese and fermented milk products.
- Fried, fatty, smoked, spicy.
How to choose and buy baby products
Baby food should be safe first and foremost. A weakened children's body is very sensitive to any toxins, preservatives, and low-quality products can cause an exacerbation of the disease or re-food poisoning.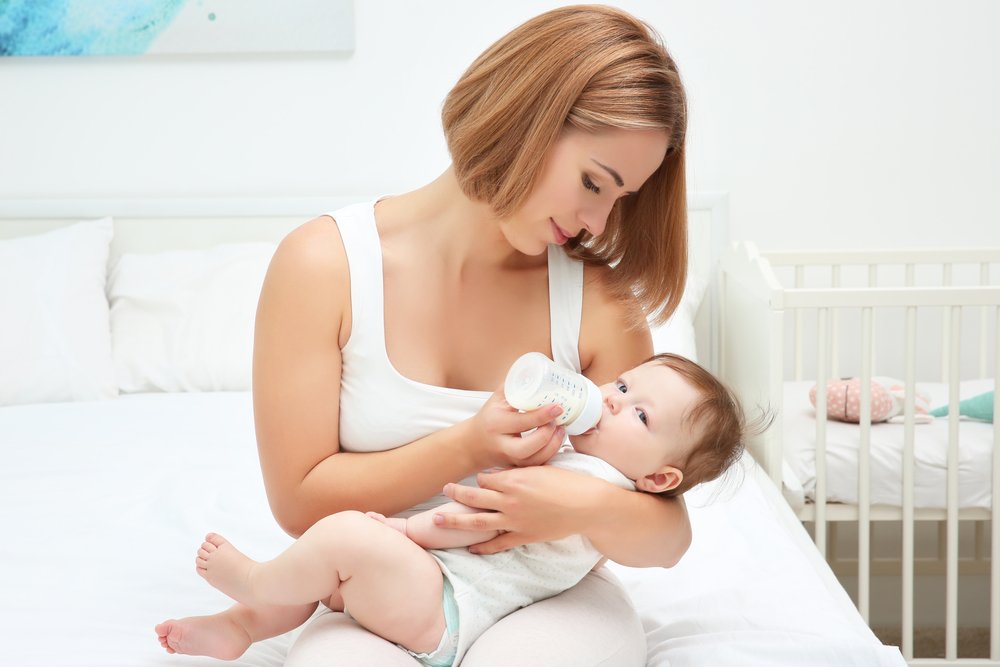
- Buy all products only at official points of sale (shops, markets). Spontaneous bazaars are dangerous places where the goods are not checked and controlled by no one.
- Please check the date of manufacture before purchasing any product. When purchasing meat or fish, do not hesitate to smell it.
- Do not buy ready-made meals for your baby at a cookery or restaurant. Only by preparing food on your own, you can safely give it to your child, without doubting the quality of the products and the cleanliness of the hands preparing the dish.
- Avoid frozen and prepared foods. There is nothing useful left in them. For example, meat becomes useless when frozen, its structural proteins are destroyed and cannot provide the body with the necessary amino acids.
Nausea, diarrhea and vomiting are symptoms that you should always watch out for. Dietary nutrition is a necessary component in the treatment of diseases of the digestive tract, which can be manifested by these symptoms.
Do not try to self-medicate, consult a doctor about the list of allowed and prohibited foods for your child. You can eat a little already in the first day, after the onset of the disease.
All food you give your child must meet his daily energy needs and be safe for his body.
Feeding a child after vomiting: what can and cannot be eaten?
After poisoning, the baby needs special nutrition. This will help him recover faster, improve his well-being. To contribute to a speedy recovery, you need to know what you can feed the child after vomiting, and what is forbidden to give. The principles of nutrition depend on the age that has passed since the time of poisoning. It is necessary to prepare food in special conditions.
Nutrition during vomiting
Poisoning is not the only cause of the gag reflex. But in childhood, in most cases, it leads to rejection of food, diarrhea.
What else causes not eating in childhood:
- intestinal infections;
- gastritis, ulcer;
- reflux;
- head injury, high intracranial pressure;
- sun and heat stroke;
- appendicitis;
- CNS diseases;
You need to know what you can eat after a child vomits. But already during it, help should be provided.
But already during it, help should be provided.
Nutrition during an acute condition:
- An important component of first aid is the observance of the drinking regimen. Diarrhea and fever increase fluid loss from the body. The balance needs to be restored. In this case, you can not force the baby to drink large amounts of water. This will lead to increased vomiting. You need to drink often and in small sips. The optimal break between fluid intake is every half an hour.
- Too cold or hot liquid is poorly absorbed by the body. Refrigerator water or just brewed tea won't keep you hydrated.
- Do not make tea sweet. Sweets should be avoided.
- In addition to water, it is useful to drink unsweetened dried fruit compotes.
- Regidron or Humana helps to restore the balance.
Important! It is not recommended to feed the baby during vomiting.
Feeding after vomiting in the first days
It will be right to find out what to feed the child after vomiting, depending on the time elapsed after it.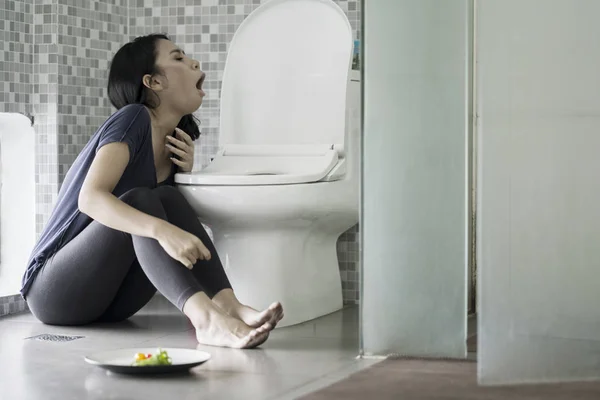 On the first day, the body is not ready to accept heavy food. But gradually you need to restore the old nutrition. This must be done correctly so as not to disrupt digestion.
On the first day, the body is not ready to accept heavy food. But gradually you need to restore the old nutrition. This must be done correctly so as not to disrupt digestion.
Important! If there is bile or an admixture of blood in the vomit, you should immediately consult a doctor!
First day
Feeding the child after vomiting on the first day, when the symptom of poisoning has not yet passed, should be minimal. The kid will not show initiative in eating, as there will be no appetite. Observing the principles of nutrition in the first day, you need to take into account the desires of the baby.
How to feed a baby on the first day of poisoning:
- On the first day, be sure to keep the amount of water you drink. Vomiting with diarrhea helps to remove pathogenic organisms from the body. Along with this, a person loses a lot of fluid and substances necessary for normal functioning. Doctors say that no liquid can replace clean drinking water. But children willingly use juices and compotes.
 It is not recommended to give sugar on the first day. Rosehip broth is not sweet, it will also remove nausea.
It is not recommended to give sugar on the first day. Rosehip broth is not sweet, it will also remove nausea. - For the first 6-7 hours, the minor should drink a moderate amount of water. Only then slowly reduce it. It is recommended to add salt to the drink.
- It is on the first day that Regidron or analogues are used.
- After 6 hours, you can include food in the diet. Receptions should be 5-7, but in small portions.
- The kid is given biscuit cookies, puree soup, a baked apple. It is forbidden to eat raw vegetables, thick cereals, dairy products. You can not drink fruit juices, even natural ones.
The second day after vomiting
The second day after the rejection of food is accompanied by relief of the baby's well-being. There is an appetite. There is an opportunity to diversify the food. But parents still need to follow the diet. The body is not ready to return to the previous diet.
How to feed a child on the second day in case of poisoning and vomiting:
- On the second day they give liquid porridge.
 Rice or wheat.
Rice or wheat. - From fruit, apples are allowed, but must be pureed. Vegetables are cooked only. Carrots or broccoli.
- In addition to biscuits, the patient is given white bread crackers. It is recommended to soften them before feeding the baby.
- It is still allowed to drink compotes from dried fruits, rosehip broth. It is recommended to give chamomile tea, it soothes, has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Important! The day after the exacerbation, appetite begins to improve. This is a sign that he is on the mend. If in the future the baby does not show a desire to eat, consult a doctor.
The third day after vomiting
The menu of the third day is diverse, the choice of food depends on the causes of indigestion. You don't have to give up on the diet.
What to give the child on the third day after vomiting:
- Natural fruit juice is introduced into the diet. The purchased product should be with a minimum amount of additives.
- You can not return to the usual amount of food. With each dose, the portions are increased gradually.
- If the cause of the symptom is not poisoning, the child is given low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt. It is important that the dairy product is of high quality.
- Kashi is given in liquid form. Milk is added if there is no poisoning poisoning.
- Soups are given on a vegetable basis. They may contain small amounts of grains.
- Kissels are added to the drink. It is important that they are not acidic, as they will irritate the gastric mucosa.
- Fish and meat are given boiled. It is recommended to take low-fat varieties.
Dried fruit compotes remain on the menu. It is a source of essential vitamins. It is allowed to make kissel from rose hips.
Fourth and fifth days
The fourth and fifth days after vomiting gradually return the baby to the previous diet. By this time, the stomach is ready to accept heavier food. These are ordinary soups, rice, buckwheat, fresh fruits and vegetables.
These are ordinary soups, rice, buckwheat, fresh fruits and vegetables.
How to feed a baby on the fourth and fifth days after poisoning:
- 4 days after the acute period, the amount of food should be enough to satisfy the patient's hunger. Portions are the usual size.
- The food should be lean. Any kind of meat and fish is stewed or boiled.
- From drinks, sweet tea, ordinary compotes are allowed. But it is better to refuse sweet soda. It irritates the mucous.
Baby still needs close monitoring. The baby should be given as much food as he needs. But it is important not to lead to overeating.
How to prepare food for a child after vomiting
What is important is what to feed a child with diarrhea and vomiting, and how to prepare food.
It should be as light, safe, useful as possible:
- Food should be cooked without spices. A moderate amount of salt is allowed, it retains water in the body, which is necessary for recovery.

- Food must not be fried. The optimal processing method is boiling, baking, steaming. In this case, the heat treatment should be sufficient. The child's body is weakened and susceptible to pathogens.
- Wash fruits and vegetables well before feeding them. It is recommended to remove the skin.
- In the first days, the products are ground with a blender or other available method.
- The temperature should be comfortable and close to body temperature.
Important! Dishes must be fresh.
What foods can you eat?
What can a small child eat in case of poisoning and vomiting:
- Cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice).
- Lean meats.
- Lean fish.
- White bread.
- Processed vegetables.
- Banana and apple fruit.
- After 3 days kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese, more fatty milk (if there was no diarrhea).
- Tea, rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote.

What foods are not allowed
When poisoning occurs, you need to eat foods that are well absorbed. Most of them can immediately be excluded from the list.
What not to feed the baby:
- Pearl barley, barley groats, millet porridge, legumes.
- Pasta.
- Fatty meat, lard, sausages.
- Smoked products, preserves.
- Raw vegetables and fruits.
- Cookies, cakes, rolls.
- Chocolate and other sweets.
- Fast food.
Peculiarities of feeding children up to a year
How to feed a child after a year with vomiting and after vomiting is easier to decide. What about babies under 12 months old? At this age, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Nutrition will depend on the type of feeding.
How to feed a child up to a year:
- When breastfeeding, the breast is given more often than before. But in small portions. This will aid in better absorption.
- If it is necessary to switch to a mixture, changes are made gradually.
- Complementary foods are refused or portions are reduced.
- Formula-fed 7 meals in small portions.
Doctor Komarovsky's advice
Doctor Komarovsky also answered mothers' questions about what to feed the child immediately after poisoning and vomiting. He claims that the babies are on a special diet. If the condition is accompanied by fever, swelling and other symptoms, you should go to the doctor. In any case, hospitalization is required at the age of 3 years.
Nutrition advice:
- Do not give food during vomiting.
- Drink small portions (2-3 sips), but often.
- Drinking temperature - room temperature.
- Add salt water, rosehip tea, dried fruit compote to the diet.
- Take Enterosgel.
In case of vomiting, it is necessary to prepare dietary food for the child. It is based on a special drinking regime, the exclusion of heavy and irritating food. It is necessary to increase portions gradually. Under the age of 3 years, with vomiting, a doctor's consultation is required.
It is necessary to increase portions gradually. Under the age of 3 years, with vomiting, a doctor's consultation is required.
Feeding a child after vomiting: what is possible, not possible
Vomiting in a child most often occurs due to food poisoning, but infectious diseases can also provoke it: scarlet fever, rotavirus.
There are other causes of vomiting: head injuries, severe stress, stomach diseases.
In case of repeated vomiting of the child, it is necessary to see a doctor, otherwise dehydration of the body can lead to undesirable consequences, up to death. The correct diet after vomiting is also important.
What to give immediately after vomiting
If a child starts vomiting, it is better not to feed him for the first day. The digestive system needs time to recover.
But, if this is a one-time vomiting that appeared due to severe stress, the diet may not be changed. When vomiting, a person loses a lot of fluid, especially if it is accompanied by diarrhea.
It is important to make up for this loss. How to properly solder when vomiting:
- Do not force your baby to drink a lot of water. Drinking must be fractional and frequent. A child can drink just a few sips, this will be enough.
- Do not give him too cold or hot drinks, the temperature of the liquid should be the same as body temperature. Then the liquid will be well absorbed and dehydration will not begin.
- Do not put sugar, jam or other sweets, even honey, in your drink. If the baby refuses to drink water, give him juice to drink, but before that, dilute it with water so that it becomes transparent.
- Solder with solutions for oral rehydration: Regidron, Hydrovit, Gastrolit, the drug is prescribed by a doctor, mineral water without gas, dried fruit compote, weak tea, rosehip broth.
Day 2 Diet
Do not force your child to eat if he does not want to. You need to feed only if there is an appetite. Your body will tell you when it is ready to eat.
The diet is selected depending on the cause of vomiting. Diet is always individual.
We will tell you about the rules of nutrition common to all diseases. But you will receive exact recommendations only from your doctor.
Features of nutrition
If this is poisoning or rotavirus infection, the child's digestive tract may suffer. To restore their work, observe the following rules:
- Do not force your baby to eat, do not ask him to eat everything on the plate if he does not want to.
- He should eat little, but often, every 2 or 2.5 hours, 5-6 times a day.
- The first days he is allowed only liquid or semi-liquid meals.
- Do not give your child hot or cold food.
- Prohibited are dishes that contain aggressive components that damage the mucous membrane.
What to feed
On the 2nd day, if the patient is already better, he does not suffer from vomiting, feed him buckwheat or rice porridge. Porridge should be liquid and boiled. It is better to cook them in water or milk diluted with water. Well, if the cereal is ground, then it will not irritate the stomach.
Porridge should be liquid and boiled. It is better to cook them in water or milk diluted with water. Well, if the cereal is ground, then it will not irritate the stomach.
During the recovery period
The recovery period of a child's body depends on the type of disease, its severity, and the immune system. But usually after 2 weeks after the onset of the disease, the child returns to the usual diet. Until that time, you will have to follow a strict diet.
It is advisable to feed your baby only liquid or semi-liquid foods. Boil food, bake, or stew, steam. Do not give your baby fried foods. All pickles, marinades, canned food, any sauces, spices, food with dyes are prohibited.
What to feed the baby:
- Soups. Vegetarian soups are best, but low-fat meat broths are also allowed. Add grated cereals to them. All vegetables should be finely chopped. Put vegetables without coarse fiber in the soup: carrots, potatoes, cauliflower, zucchini.
 You can add meatballs, quenelles.
You can add meatballs, quenelles. - Kashi. Only liquid and boiled. Boil on water, you can add 1/3 of milk. Corn, millet, barley and barley porridges are not allowed. Grate buckwheat and rice. You can put a piece of butter in the porridge.
- Meat and fish, preferably in the form of a soufflé.
Nuances of nutrition for children under one year old
If a child under one year old falls ill, you need to show him to the pediatrician. The doctor will not only prescribe the necessary medications, but also discuss the feeding regimen with you. If the baby is breastfed, he needs to be breastfed much more often than before. In this case, the milk will come in small portions, which is why it is better absorbed.
Sometimes the doctor advises to give up breastfeeding for a while and switch to lactose-free formulas. But even then it is impossible to abruptly transfer the child to the mixture, the transition should be gradual.
And it is better to do this only on the recommendation of a doctor, in case of emergency, otherwise it will be difficult to return to natural feeding later.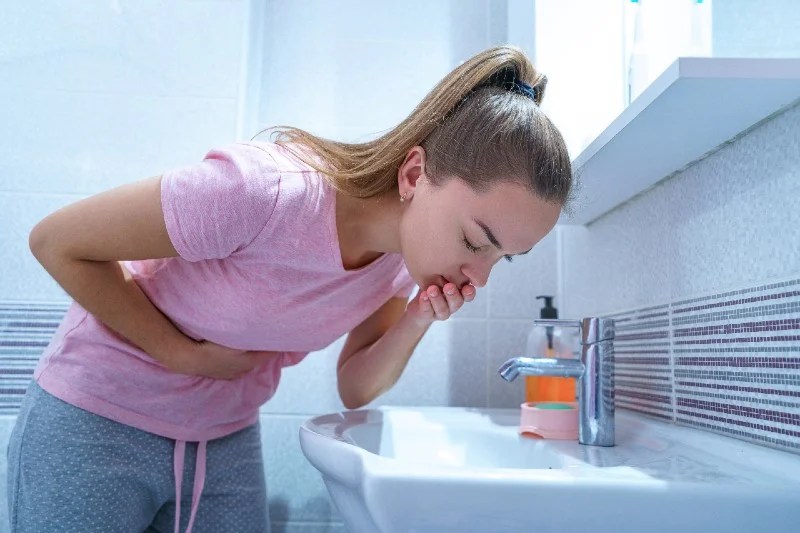
It is better to refuse complementary foods during the period of illness, but when the baby gets better, it can be introduced in small portions.
If the child is bottle-fed, he should eat more often, about 7-8 times a day if the condition is moderate, and 5-6 times a day if he feels better. The amount of the mixture, respectively, is reduced, it is better to check the exact numbers with the doctor.
What foods can you eat
To quickly restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to choose foods that promote its healing:
- cereals, but not all, oatmeal, buckwheat and rice are allowed;
- lean meat: chicken, rabbit soufflé;
- marine lean fish;
- bread - only white, dried, you can cracker;
- cooked vegetables: boiled beets, carrots, cauliflower or broccoli;
- bananas and baked apples;
- fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt, in 2-3 days - cottage cheese;
- it is useful to drink compotes from dried fruits, fruit jelly, tea with rose hips, weak slightly sweetened tea.

What foods are prohibited
The child's menu during this recovery period is not very diverse, many foods are prohibited:
It would be difficult for a healthy child to follow this diet. But if the baby has suffered a serious illness or has been poisoned, he will probably have a poor appetite, so it will not be difficult to persuade him to eat right.
A therapeutic diet will provide the child with all the necessary nutrients, unload the gastrointestinal tract as much as possible, and help him recover faster.
If you abandon the diet, there is a high risk of developing chronic inflammation of the digestive organs, later you will have to treat the child's stomach.
Diet after vomiting in children
Hello, moms and dads! Today I wrote an article about the features of the diet after vomiting in children. After all, many still do not know about the diet of a little man after poisoning ...
A child's nutrition requires a particularly careful approach, since the child's body is not yet able to fully process many new products for him, as well as low-quality or stale products. If a child vomits, then the body is fighting and rejecting unacceptable food. As a rule, during such a period, it greatly weakens, and parents need to think about the right diet.
Feeding in case of poisoning
The diet after vomiting in children should be carefully thought out in a complex way, since the work of many organs is disrupted and requires restoration. During poisoning, vomiting may be accompanied by diarrhea and rising temperature, which together lead to significant fluid loss.
Therefore, the child needs to be provided with plenty of fluids throughout the day. It can be a rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote or herbal tea.
It can be a rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote or herbal tea.
Until the vomiting finally stops, this will be enough. Of course, you should consult with your doctor to determine the cause of poor health (food poisoning, nervous stress, bactericidal infection that has entered the body, concussion, etc.). From food, it is worth limiting yourself to soaked crackers or dry cookies.
Diet for the second day
After the first day, when the vomiting finally stops, the child should be fed little by little, even if he does not want to and is capricious. After the experience, the baby may simply be afraid to eat something so that vomiting does not happen again. But parents should set him up for the fact that it is necessary to eat a little bit in order to restore strength.
From the diet it is necessary to exclude heavy foods that a weakened child's body cannot cope with, namely: meat, fish, fruit juices, sausages, smoked meats, pastries, carbonated water, sweets, vegetable and sunflower oil.
Legumes, vegetable salads (fresh or pickled), oranges, corn, cheese, eggs, fatty foods, whole milk are not recommended for the first few days.
During the diet after vomiting in children, it is planned to take in small proportions such products as one-day kefir, baked apples, bananas, yogurts without additives, sugar-free cereals (except for millet, eggs, barley), boiled carrots and broccoli.
It is also necessary to continue drinking plenty of water. You can purchase medical solutions at a pharmacy, such as Glucosolan, Rihydron, etc., but take them strictly according to the instructions. Daily portions of these drugs are calculated based on the weight of the child.
If "overdone" vomiting may recur.
During the first days, all food is prepared for the child in such a way as not to injure the lining of the stomach. Therefore, it is boiled, steamed, but by no means fried. Porridge from cereals is brought to full boil. All food is crushed or rubbed through a sieve. Rice and hercules decoctions are especially useful during this period. It is undesirable to give hot food, which can injure the stomach.
Rice and hercules decoctions are especially useful during this period. It is undesirable to give hot food, which can injure the stomach.
Diet after vomiting in children on the second or third day
When your baby is a little stronger and appetite starts to return, the number of small meals can be increased up to 7-8 times a day.
During this period, foods such as minced boiled meat (protein helps to remove toxins from the body), cottage cheese, but not more than 30 g, vegetable puree, baked or steamed dishes are introduced into the diet.
Chicken broth with a small amount of homemade croutons will help the child recover.
On the third day, steamed fish or meat cutlets are gradually included in the diet, and rice or buckwheat is served as a side dish. Rich sources of carbohydrates are baked apples, which must be included in the diet.
The best enveloping effect for the walls of the stomach will create kissel, so it is a good product in the diet.
Features of nutrition of infants after vomiting
If the baby, in addition to breast milk, receives artificial complementary foods, it is better to refuse it for the time of feeling unwell.
When he is fully bottle-fed, buckwheat or rice milk formulas are fine.
Children from six months and beyond can cook porridge in water with buckwheat in a ratio of 1:1, and, starting from 8 months, gradually give vegetable puree, meat soufflé, provided that vomiting has already stopped.
Gag reflex in babies can be caused by teething. As a rule, vomiting is short or single. The first days the child needs to be given food in small portions, dividing it into 7-8 meals. Be sure to include dried fruit compote in your diet, which will restore the balance of potassium in the body. You can give rice porridge, diluted milk.
A child's vomiting diet may vary in length depending on the cause of the malaise. A longer and more scrupulous approach requires feeding a child after a serious food poisoning.
In any case, before engaging in self-treatment and self-formation of a diet, it is worth consulting a doctor and, if necessary, passing the appropriate tests.
Please note that vomiting may be caused by a child's intolerance to certain foods, such as dairy. In this case, they should be completely excluded.
Diet during and after vomiting in a child, what can and cannot be fed / Mama66.ru
A child's nutrition should be approached very responsibly. Toddlers react sharply to food that is offered to them for the first time. If products of dubious quality penetrate into the children's stomach, serious consequences for the body can occur. When a child vomits, this means that the internal defense is working: the body is trying to rid the stomach of harmful elements.
Help for a child should be comprehensive. After the vomiting reaction is stopped, parents must decide for themselves the natural question: how to feed the child after vomiting. There was a malfunction of the internal organs. In this case, it is required to support a weak body and restore normal digestion.
In this case, it is required to support a weak body and restore normal digestion.
Feeding during vomiting
When adults detect vomiting reactions in a child, they often state that he has diarrhea (diarrhea), which is accompanied by an increase in the baby's body temperature.
This is a signal that the child is losing a lot of fluid. You can fill its deficiency by providing the patient with plenty of water. In other words, a diet for diarrhea and vomiting begins with drinking plenty of water.
During the first 24 hours, you need to drink the baby in an alternating mode:
- herbal and black tea;
- rosehip decoction;
- mineral or lightly salted water;
- dried fruit compote.
On the second day, it is recommended to start feeding the baby if the vomiting has stopped.
It is important for parents to take into account that the diet depends on the causes of vomiting. If there was a non-compliance with the diet or the child suffered some kind of stress, then after two days you can return to the usual food for the child.
In case of food poisoning or disorders of the nervous system, nutrition should be taken more seriously. It is possible that the advice of a doctor will come in handy.
Read more: How to stop vomiting in a child →
Nutrition after vomiting in the first days
When vomiting was stopped, the question arises - can the baby eat? Here, experts are extremely unanimous: it is necessary to eat.
How foods affect the baby's stomach
At first, to restore the body, the child needs a sparing diet. Children's stomach is not ready to take regular food right away. Parents are encouraged to think about how difficult to digest foods do not get into the weakened food tract. These include:
- meat and fish dishes;
- fruit juices;
- grapes, pears, plums;
- any sweets;
- fresh baked goods and all flour products;
- raw vegetables;
- fats in the form of sunflower and butter;
- millet, barley and pearl barley;
- sausages and smoked products;
- carbonated water.

On the first day, an abundance of drink is a powerful weapon against malaise: boil rose hips, prepare weak, slightly sweetened tea, or make a medical saline solution. It can be Glucosolan, Oralit or Regidron. For every kilogram of body weight, a child can be given no more than 170 g of solution. Servings should be 1-2 teaspoon, otherwise there is a risk of resumption of vomiting.
The work of the stomach will improve quickly if the child is offered to eat in small portions:
- bananas;
- baked apples;
- dried fruit decoction;
- boiled broccoli and carrots;
- plain yoghurts;
- kefir without oxidation.
Features of cooking for a child after vomiting
The main task of the products that the child consumes 24–48 hours after vomiting is to be well absorbed and not irritate the mucous membrane of the child's stomach. For this purpose, food for the baby is crushed with a blender or with a strainer.
Cereals should be brought to a boiled state, for small children they can be rubbed into jelly. Rice and hercules decoctions will have a beneficial effect on the work of the child's gastric tract. Puree and any kind of porridge should not contain sugar. The most valuable is freshly prepared food.
All food that parents give the child to eat in the very first days after vomiting is stewed, boiled, or steamed. Hot food is extremely undesirable, however, like cold food, the delicate walls of the stomach can be injured.
And don't forget: a child won't want to eat right away.
Diet mode
After 48 hours, you can enter the children's menu:
- Vegetable puree.
- Liquid or semi-liquid dishes (fat-free soups).
- Foods rich in protein (chopped boiled meat).
- Baked or steamed dishes.
Do not force your child to eat against his will!
The child should eat at least 7 times a day every 2. 5 hours. Any amount of food eaten by the baby can be regarded as the norm. Every day the child's appetite will improve.
5 hours. Any amount of food eaten by the baby can be regarded as the norm. Every day the child's appetite will improve.
Return to a normal diet occurs 4-5 days after the end of vomiting. Diet and a sparing diet require a cycle of 2-3 weeks after the illness.
Peculiarities of nutrition of children under one year old
Children who are breastfed with complementary foods do not need additional nutrition during vomiting. Formula-fed babies digest rice and buckwheat mixtures in milk well.
Six-month-old children benefit from porridge made from buckwheat and rice. They should be boiled in water and milk in a ratio of 1: 1. Complementary foods are allowed to be included in the menu of babies at the end of vomiting: this should be done gradually. The nutrition of a child at the age of 7-8 months implies the presence, in addition to cereals, meat soufflé, vegetable puree, airy cream soup.
Parents will act very wisely if they trust the needs of the child himself, and will not put pressure on him in terms of the quality and quantity of food. Let the baby eat as much as he wants and what he wants.
Let the baby eat as much as he wants and what he wants.
Irina Khubetsova,
especially for Mama66.ru
How to feed a child after vomiting: diet and nutrition rules .
The reflex removal of undigested or partially digested foods with gastric juice through the mouth or nose is called vomiting.
Doctors have been studying this reaction for many years and have come to the conclusion that it is a protective ability to get rid of dangerous, excess food with the help of a gag reflex. The famous doctor Komarovsky noticed: a person needs vomiting, you should not be afraid of it.
At temperature, poisoning, it is accompanied by acute diarrhea. Dehydration of a weakened child's body is inevitable.
Doctors identify several main causes that cause vomiting in a one-year-old baby. Particular attention should be paid to the signs of a reaction (what kind of food you ate, medications taken, possible stresses, injuries, illnesses), then inform your doctor. The most common causes are:
The most common causes are:
- food poisoning;
- excess food;
- unfamiliar food;
- fever;
- concussion;
- teething;
- use of seasonings and hot spices in the diet of an infant;
- stress;
- antibiotic treatment.
What to do in case of vomiting in a baby
In a single case of nausea, vomiting, a special diet that restores immunity is not required. With the help of a reflex, the small stomach gets rid of harmful toxic substances that accumulate in the intestinal tract. If the attacks are repeated, vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea, the parent must know and take the necessary measures to help.
The first obligatory action for nausea (from 2 times a day) in children is to call an ambulance doctor at home. The doctor will determine the cause, prescribe the appropriate treatment. Before the ambulance arrives, the baby is soldered with liquid to prevent dehydration.
Antiemetics should not be taken. The body is cleansed of pathogenic microflora, it cannot be prevented. Do not forcefully try to feed, the baby will agree to eat when the attack stops.
The body is cleansed of pathogenic microflora, it cannot be prevented. Do not forcefully try to feed, the baby will agree to eat when the attack stops.
List of drinks recommended by doctors for vomiting, diarrhea:
- meat, vegetable broth;
- dried fruit compote;
- still mineral water;
- rice water;
- sweet tea;
- kissel.
To give a baby a drink, pour liquid into a bottle. Frequent portions are given to drink. When he refuses to suck from a bottle, drink from a teaspoon 2-3 tablespoons of liquid every 10 minutes.
Poisoning: causes and consequences
Food poisoning - intoxication of the digestive tract by eating spoiled or improperly cooked food. This type of infection is the most common case among one-year-old children.
Infection is not spread by eating fresh, edible, properly prepared foods. Observing proper care for the baby, personal hygiene, eating fresh vegetables and fruits washed in warm water with soap, the infection will not bother the baby. If the rules are not observed, harmful microorganisms enter the body with food:
If the rules are not observed, harmful microorganisms enter the body with food:
- staphylococci;
- E. coli;
- proteus;
- Klebsiella.
When they enter the immature microflora of a child's body, pathogens spread rapidly, causing intoxication, salmonellosis, dysentery, escherichiosis, and other dangerous infections. Diseases are dangerous, without appropriate treatment lead to adverse consequences.
Symptoms of poisoning
Vivid symptoms of child poisoning:
- sharp pains in the stomach;
- sudden deterioration in well-being;
- pale complexion;
- diarrhea;
- fever;
- nausea;
- frequent vomiting.
The baby is very sick, diarrhea appears. The temperature may rise or fall. The described symptoms require an immediate examination by a doctor. Symptoms may occur at normal temperatures.
When the disease is exacerbated, children have no appetite, Dr. Komarovsky recommends constantly giving the baby water-salt solutions, compotes, kissels to drink.
Komarovsky recommends constantly giving the baby water-salt solutions, compotes, kissels to drink.
When restoring digestion, the properties of products to be absorbed by the body are taken into account. The wrong diet will lead to indigestion.
Restorative Diet for Children
Breastfed infants under one year of age should not receive complementary foods. Mother's milk is an easily digestible product containing vitamins and microelements necessary to restore digestion. Resume the introduction of complementary foods after complete recovery.
A bottle-fed one-year-old baby is more difficult to properly feed after vomiting. In the early days, products that create a positive microflora in the body and are quickly absorbed in the intestinal tract are acceptable. In a year, you can not feed the baby with solid food that can irritate the intestinal mucosa.
Liquid, semi-liquid vegetable broths, low-fat meat pates for baby food. Milk porridge from rice, buckwheat, fat-free cottage cheese, vegetable puree. You can feed a child with a banana, a baked apple, fresh kefir, boiled carrots, dried fruit compote. Dried fruits are a good substitute for sweets.
You can feed a child with a banana, a baked apple, fresh kefir, boiled carrots, dried fruit compote. Dried fruits are a good substitute for sweets.
The baby's menu to restore digestion
Food from the menu is divided into 7 meals, after vomiting the child does not eat everything at a time. You need to feed after 2-3 hours. When a child refuses to eat, you can not force. It is better to drink sweet tea.
- For breakfast - liquid oatmeal, kefir.
- Baked apple for afternoon snack.
- At lunch, buckwheat porridge and chicken broth, jelly.
- First dinner. Low-fat baby cottage cheese, banana. Sweet tea.
- Second dinner. Semi-liquid rice porridge with boiled fish, egg, kefir.
- At the end of the day offer low-fat yoghurt with breadcrumbs.
The menu is expanded depending on the taste needs of the child. Prohibited foods for a child during a recovery diet:
- sausages;
- smoked products;
- canned food;
- legumes;
- fruit juices;
- raw fruits, vegetables;
- fatty meats, lard;
- fried;
- sunflower, cream fats.

Diarrhea Diet
Feeding an infant with diarrhea should not contain food that relaxes the gastrointestinal tract. Beetroot is a strong laxative vegetable, it should not be used. Products are excluded from food: prunes, potatoes, desserts, freshly squeezed juices, chocolate and sweets. Milk, milk mixtures will aggravate the situation.
In case of diarrhea, the child should be fed rice liquid milk-free porridge, breadcrumbs soaked in water. Soup in white broth will help restore digestion. Banana contains potassium, the fruit should be included in the daily diet.
It is forbidden to feed fresh fruits to babies. Baked apples, on the contrary, are recommended after diarrhea, nausea. After kefir, the microflora improves.
Doctors recommend taking bifidobacteria after poisoning to restore beneficial intestinal flora.
Rules of nutrition
During the recovery diet, the regime changes fundamentally. Food is consumed in small portions every 2-3 hours. Refuse cold and hot. The portion size does not exceed the size of a fist. The mode helps the stomach digest food faster and does not burden the liver and pancreas.
Refuse cold and hot. The portion size does not exceed the size of a fist. The mode helps the stomach digest food faster and does not burden the liver and pancreas.
Frequent consumption of liquid in the form of compotes, jelly, yogurt, sweet tea will restore the water balance in the body and help the stomach recover. Adhere to diet should be 10-14 days.
After graduation, the child should not be allowed to eat forbidden food. It is necessary to introduce the usual diet gradually, one species every two days, observing the condition of the child.
If he experiences discomfort from the product, do not give it again.
In order to memorize what foods were introduced, what the child has a negative reaction to, start a notebook and write down all observations there. The reaction of the body to the introduced products is diverse.
You can find out that the food is not suitable for the baby by colic, rashes on the face, liquid or, on the contrary, excessively hard stools.
It is worth temporarily abandoning such food, and introducing food that is light in composition and consistency.
Basic rules for helping with frequent vomiting and diarrhea in a baby
Call a doctor home while he is traveling, give first aid. At a temperature, give an antipyretic, with a fever, the baby should be crushed 1/2 tablet of Drotaverin, mixed with water and given to the baby.
After 10 minutes offer to drink mineral water, follow the diet for two weeks after the appointment of the treatment. Recommendations will help you recover without negative consequences for a tiny organism.
Diet after vomiting
Vomiting is a defense mechanism of our body. It can appear due to disorders in the digestive tract, nervous system or taking medications. Vomiting can be one-time or have a prolonged character.
One of the most common causes of the gag reflex is food poisoning. When a person has eaten poor-quality or spoiled food, the stomach throws it out with the help of vomiting. Regardless of what exactly caused the gag reflex, the stomach needs to be rested and given time until the appetite returns.
Regardless of what exactly caused the gag reflex, the stomach needs to be rested and given time until the appetite returns.
Vomiting very often leads to dehydration. Due to a violation of the water balance, a malfunction occurs in the body. That is why it is so important to observe the drinking regimen. Natural water should be drunk in small sips every twenty minutes. Preference is given to mineral water without gas, which includes salts.
Drinking a large amount at one time can make the situation worse. Water with gas will irritate the stomach even more. What can be said about milk? During vomiting, it is absolutely not worth drinking it, this can cause a new wave of nausea and vomiting.
Vomiting diet is the main treatment. It helps to restore the water-salt balance, create gentle conditions in the intestines, and also provide the body with the necessary vitamins. The duration and severity of the diet directly depends on the cause that caused vomiting. So what can you eat after vomiting? What to feed the child? How soon can you return to your normal diet? We will find out the answers to these and other questions in this article.
Basic recommendations
First of all, you should find out for what reason the vomiting appeared, whether it is accompanied by an upset stomach or is this an isolated case. If it is accompanied by painful pains in the stomach, this may indicate an infectious process in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
For nausea and vomiting, water is the most important thing the body needs
The human body needs a sufficient intake of natural water. The liquid will help to quickly remove from the body those substances that provoked the disease. Try to drink water little by little. If after that there was no recurrence of nausea and vomiting, then drying, bagels or crackers without sugar and any additives.
A little later, it is allowed to eat a little broth on lean meat, but without skins and fat. It is best to use chicken breast. In addition to water, you can drink decoctions of herbs, diluted juices from green apples, weak teas. Rice broth will help to quickly get rid of the unpleasant feeling of nausea.
Sometimes people have a strong desire to eat something salty. This may indicate a lack of chloride and sodium ions. In this case, dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and drink it. You can make up for the lack of potassium with the help of cabbage broth, rosehip tincture or a weak broth of prunes and raisins.
The following recipe will help to enrich your body with a lot of vitamins and minerals: two carrots and potatoes are poured with a liter of boiling water and boiled. The resulting broth is filtered, salt is added to taste and taken 100 ml every half an hour. If the attack of nausea is accompanied by painful sensations in the abdomen, prepare a drink from starch.
Pour a tablespoon of the product into a glass of warm water. Such a solution envelops the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, relieves irritation and relieves pain.
It is strictly forbidden to consume foods that can adversely affect the work of the stomach, for example, pickles, marinades, jams, spicy, fatty, fried. This can cause the contents of the stomach to vomit again, and repeated vomiting has more serious consequences.
This can cause the contents of the stomach to vomit again, and repeated vomiting has more serious consequences.
Self-made pudding from berries will help the stomach cope with the disease. The starch contained in it will help to stop the inflammatory reaction. Beneficial effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and oatmeal. Only you need to cook it with water, not milk.
Do not also eat bakery products and fresh bread, this can further destroy the microflora of the stomach during the illness. Only wholemeal gray bread and some homemade noodles in lean broth are allowed. Eat as little oil and fat as possible. Such products are digested for a long time and therefore will irritate the walls of the stomach even more.
Green tea with mint will help to get rid of the urge to vomit
The following medicinal plants will help relieve irritation, disinfect the digestive tract and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues:
- chicory;
- chamomile;
- St.
 John's wort;
John's wort; - elecampane;
- flax seeds.
If the unpleasant symptom was caused by eating spoiled food, the diet after vomiting should include the following:
- liquid mucous porridges in water;
- rice and porridge;
- dried fruit compotes;
- white bread croutons;
- steamed meatballs.
Fatty, spicy, smoked foods can cause vomiting again, so they should not be consumed.
The "black list" for poisoning includes the following products:
- vegetable and animal fats;
- eggs;
- fresh vegetables, fruits and berries;
- whole milk;
- fermented milk products;
- onion, garlic;
- spices, spices, sauces, ketchup;
- alcoholic beverages;
- coffee.
What can you eat after vomiting?
It is not only the right choice of products that is important, but also the way they are prepared. It is best to cook food for a couple, boil, bake, stew. It is strictly forbidden to fry food, especially using a large amount of fat.
It is best to cook food for a couple, boil, bake, stew. It is strictly forbidden to fry food, especially using a large amount of fat.
Ready meals should be thoroughly ground and served pureed. It is recommended to twist the meat twice. Do not rush while eating, chew everything thoroughly. Try not to eat hot or cold foods, it will be more comfortable for the stomach to process food that comes in a warm form.
Salty food irritates the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, so try to reduce your salt intake
Nutrition after vomiting may include the following foods:
- beets, carrots, marrows;
- bananas;
- cereals with a small addition of milk and butter: buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, semolina;
- fish, chicken and turkey meat;
- cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir;
- boiled eggs, steam omelets;
- crackers, biscuits, toasted bread;
- rose hip decoction.
Consider a sample diet menu that can be followed by both an adult and a child. The only difference is in the portion sizes. The following will be a diet for one day:
The only difference is in the portion sizes. The following will be a diet for one day:
- Breakfast. Oatmeal on the water and a steam omelet. Green tea.
- Snack. Homemade yogurt and banana puree.
- Lunch. Mashed potatoes and turkey meatballs. Berry jelly and biscuit cookies.
- Afternoon snack. Fish baked in the oven. Dried fruits compote.
- Dinner. Rice porridge and steamed vegetables. Still mineral water.
Vomiting with bile can be caused by poisoning, but this symptom also indicates the development of diseases of the liver, pancreas and biliary tract. The gag reflex is accompanied by the appearance of unpleasant bitterness in the mouth. To determine the cause and further tactics, it is important to undergo an examination.
What to feed a child after vomiting?
Children usually react strongly to food they are given for the first time, and this can cause a gag reflex. Infectious processes can also cause an unpleasant symptom. During an attack of nausea, there is no appetite, so parents should not force-feed the child.
During an attack of nausea, there is no appetite, so parents should not force-feed the child.
On the first day the child should be given these drinks alternately:
- herbal and black tea;
- rosehip decoction;
- mineral water without gas;
- pharmaceutical saline solutions;
- lightly salted water;
- dried fruit compote.
At first, the child needs a sparing diet to restore the stomach. The following products will help speed up the recovery of the gastrointestinal tract: baked apples, bananas, boiled carrots and broccoli, dried fruit decoction, homemade yogurt, low-fat kefir. Food for a child of 5 years old should be crushed in a blender.
First, the child is given rice and buckwheat porridge. After a few days, you can give baby curds, vegetable puree, fruit juices. Parents should clearly understand what foods will be difficult for the baby's stomach: meat and fish, grapes, plums, pears, sweets, fruit juices, baked goods, some cereals: barley, pearl barley, millet, fats, raw vegetables and fruits.
Do not give food until vomiting stops
How to eat if vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea? The appearance of diarrhea indicates that the intestines are also involved in the pathological process. After each act of defecation, the child should be given liquid, as in this case the risks of dehydration double.
In case of diarrhea, whole milk should be excluded, it is better to give fermented milk products to the child. At the same time, do not forget that one-day kefir has a laxative effect, which can further aggravate the situation. Cottage cheese, eggs and rice, on the contrary, have a binding property.
Foods rich in fiber should be excluded from the diet:
- white cabbage;
- legumes;
- radish;
- cucumbers;
- greens.
Separately, it should be said about vomiting in infants. If this happens, then you should not stop breastfeeding, but on the contrary, you need to do it even more often. Mother's milk is well absorbed and helps to replenish the lost fluid. If the baby is bottle-fed, you should continue to give the usual mixture.
Mother's milk is well absorbed and helps to replenish the lost fluid. If the baby is bottle-fed, you should continue to give the usual mixture.
So, vomiting is an unpleasant symptom that signals various diseases and they are not always associated with the work of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, the gag reflex occurs due to poisoning. Diet plays a big role in the process of recovery and restoration of the digestive tract.
Due to the eruption of the contents of the stomach, a large amount of fluid is lost, so patients should drink more. If your child is vomiting, do not force him to eat when he is sick. Be sure to undergo an examination and follow the recommendations of a specialist in everything!
Food poisoning is an uncomfortable condition that knocks a person out of his usual life for several days. Proper nutrition, supported during the recovery period, will help you quickly return to a healthy and active state.
Basic nutrition rules
The recovery period requires adherence to certain food intake rules:
- The first day after poisoning is the most difficult for the body.
 At this time, it is better to refuse to eat food, with the exception of low-fat broths.
At this time, it is better to refuse to eat food, with the exception of low-fat broths. - The poisoned person drinks heavily. You can drink herbal teas, rice water, mineral water, rehydron and other electrolyte solutions. But it is necessary to focus on clean drinking water.
- The liquid is drunk in small sips, little by little, so as not to provoke new vomiting.
- If there is an acute feeling of hunger, you can eat a soft cracker or a small piece of dried wholemeal bread.
If you neglect them, continuing to eat in the usual way, you can cause a recurrence of unpleasant symptoms of poisoning.
The food will include light food that does not burden the stomach. It is important to choose well-digestible foods. A sparing diet is maintained for 5-10 days.
If a person consumes relatively solid food, it is thoroughly chewed or pre-crushed. Porridges are cooked exclusively on water, cutlets are steamed. Also, food should not be too cold or hot.
Nutrition after rotavirus poisoning
A diet for rotavirus infection, or intestinal flu, is a must, as it helps to eliminate symptoms as quickly as possible and alleviate the patient's condition. The most important thing is to start proper nutrition from the very first day of the disease so that the amendment comes as quickly as possible. First of all, with such a disease, it is necessary to support the body, preventing dehydration.
All the symptoms of this unpleasant disease strive to push moisture out of the body, and without it we cannot exist!
That is why, first of all, you need to start drinking water, preferably slightly salted. Due to a sharp disruption of the digestive tract, most of the enzymes that usually break down food cease to be produced, which is why it is important to switch to the most gentle mode, in combination with taking drugs like mezim, activated charcoal and others. In addition, it is useful to take probiotics - if not in the form of a medicine, then at least in the form of dairy products. So, what can you eat after rotavirus poisoning:
So, what can you eat after rotavirus poisoning:
- fat-free or low-fat kefir, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, yoghurt;
- vegetables, steamed or boiled;
- viscous cereals on the water - oatmeal, semolina, rice;
- Steamed or oven-cooked omelet.
The diet is not very varied, but it will not be necessary to observe it for long: only in the days of the acute course of the disease. The diet after rotavirus infection allows the gradual introduction of other foods, especially those that do not have a laxative effect.
Approved Products
There is a list of foods that you can eat during the recovery period without fear for your health:
- rice and buckwheat - cereals contribute to the restoration of strength, are prepared exclusively on a water basis without milk, in the form of cereals;
These products are easily digestible, do not irritate the stomach and do not overload it with unnecessary work.
From drinking pure water, non-carbonated mineral water, not strong green tea, decoctions of strengthening herbs (decoction of St. John's wort, wild rose, black currant, blueberries), jelly are allowed.
Pregnant women who are not lucky enough to get poisoned while carrying a child should strictly follow a diet and be careful with the food they eat, adding to it, among other things, berry fruit drinks.
What can not be eaten?
There is a whole list of products that are strictly not recommended to be consumed during illness. They provoke peristalsis, irritate the intestinal mucosa, aggravate diarrhea. And consequently - adversely affect the condition of a sick person. What to avoid:
- fresh pastries - white bread, rolls, any products made from fine flour;
- pasta;
- wheat, barley, barley groats;
- whole milk and all preparations made from it;
- sour milk, especially fatty. Regarding this type of product, restrictions apply only to the acute period.
 When the condition improves, low-fat kefir and cottage cheese should be introduced little by little;
When the condition improves, low-fat kefir and cottage cheese should be introduced little by little; - vegetables and fruits, raw;
- fatty meats and fish;
- preservation, smoked and spicy dishes;
- fried and fatty foods;
- sauces, mayonnaises, ketchups;
- any mushrooms;
- sweets, candies, chocolates, rich pastries;
- coffee and strong black tea;
- alcoholic beverages of any strength.
All of the above are delicious foods that are loved by almost everyone. But don't despair, it won't last forever. After recovery, they gradually return to the diet. The diet after a rotavirus infection is not as strict as in the acute period and during recovery, but nevertheless ... In order to avoid deterioration and the return of unpleasant symptoms (nausea, vomiting and diarrhea), you need to adhere to certain nutritional principles for at least 10-14 days .
The whole point is that during the illness the intestinal mucosa suffers. The period of recovery of epithelial cells is approximately two weeks. If at this time a load is placed on a fragile organ, the condition may worsen.
The period of recovery of epithelial cells is approximately two weeks. If at this time a load is placed on a fragile organ, the condition may worsen.
Recommended adult diet
For the first week, an adult is advised to follow a certain sparing diet, which prevents new stomach cramps and vomiting. It is not advisable to eat on the first two days, and the diet on the following days looks like this:
| Breakfast | Second breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | |
| Third day | Semolina porridge on the water, jelly, two croutons; | Biscuits or other dry biscuits, blackcurrant decoction; | Small portion of boiled cod, low-fat chicken broth; | 40g rice porridge and lean chicken breast, steamed; |
| Fourth day | Rusks, tea, cottage cheese casserole; | Rosehip decoction, banana puree; | Buckwheat porridge with oven-baked fish cutlets; | Mashed potatoes with water, grated carrots - 50g; |
| Fifth day | Kissel, curd pudding; | Baked apples, crackers - 2 pieces; | Soup with rice and vegetables; | Jacket potatoes, two boiled eggs, steamed; |
| Sixth day | Dry biscuits without creams and fillings, tea, semolina soufflé; | Kissel, baked pear; | Oven-baked chicken, barley; | Pumpkin puree soup; |
| Seventh day | Buckwheat, grated carrots, tea; | Small portion of cottage cheese casserole; | Chicken noodle soup, baked pumpkin salad; | 50g.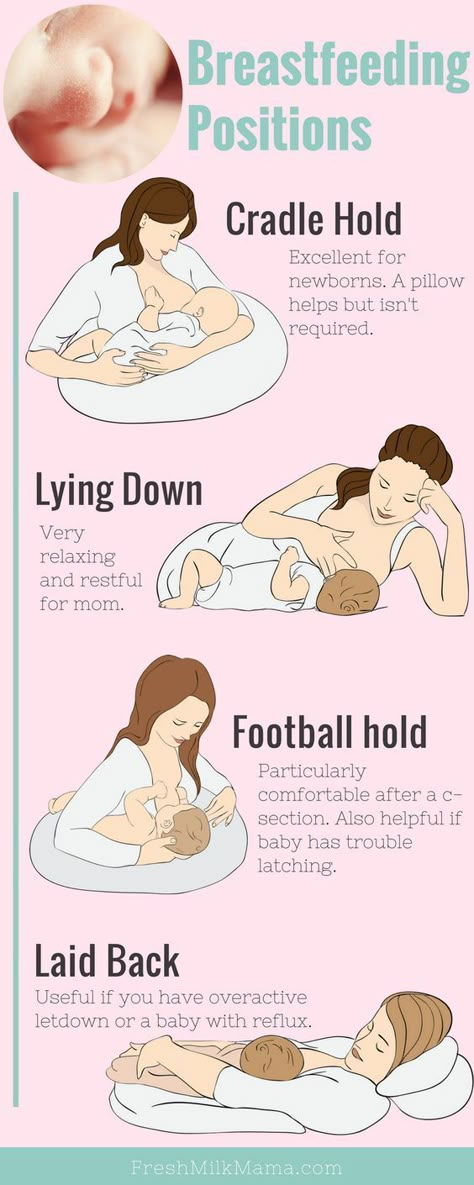 turkeys, mashed potatoes; turkeys, mashed potatoes; |
Starting from the sixth day, it is not necessary to strictly follow the menu - it is allowed to supplement it with other usual light dishes. The main thing is to listen to your own body, to observe the sensations experienced. If any symptoms of poisoning reappear, it is worth returning to strict adherence to the diet.
Diet for children
The most acute question of what to eat after poisoning is when the child had to face this unpleasant illness. At first, cereals of a very liquid consistency, light soups, small portions of rabbit and chicken are suitable.
You can not limit the flow of nutrients into a growing body, make it feel hungry.
Children, even after severe food poisoning, may begin to be mischievous and demand their favorite sweets. In this case, parents can diversify the child's diet, consisting of foods allowed during the recovery period, so that the child does not even realize that his diet is limited.
Rice and oatmeal porridges are allowed. To diversify meat dishes, in addition to steamed cutlets and boiled meat, you can cook meatballs from turkey or fish. From the third day after poisoning, broccoli can be added to the soup to increase its satiety.
The rigidity of the diet is directly proportional to the consequences of poisoning - this must be remembered when compiling a diet.
If by the fourth day the child is completely tired of eating cereals, you can cook him a steamed omelet. As a dessert, you can offer him compote with vanilla cracker.
Diet for alcohol intoxication
The same recommendations apply to the elimination of the consequences of alcohol poisoning. It is necessary to maintain the water balance in the body with the help of abundant drinking, to refrain from eating on the first day.
It is necessary to complicate the diet and supplement it with new products gradually, starting with broths and light cereals, using decoctions of herbs, lean meat. The amount of proteins and carbohydrates does not change, but fats must be reduced.
The amount of proteins and carbohydrates does not change, but fats must be reduced.
Prevention of rotavirus poisoning
How not to get sick at sea? Always wash your hands with soap before eating. If you can't wash your hands, use wet antibacterial wipes or liquid with antiseptic properties. You should also wash your hands after using the toilet, contact with animals, cutting raw food. In the summer, do not eat on the street in dubious establishments, especially all sorts of meat pies, pasties, etc. If you buy ice cream, but it has melted, you should not use this either. Avoid milkshakes in the heat.
When swimming in the sea, do not dive or swallow water, especially when the water temperature exceeds 25 degrees.
In spite of the salt, there are a lot of pathogenic microorganisms in the water. After swimming in the sea and playing in the sand, you need to wash your hands and face with clean water (you can take it with you to the beach in a bottle). Do not buy food on the beach, especially from sellers who walk along the beach with trays in the heat. It can be spoiled and it is not known who, where and when it was prepared. Eat fruits and vegetables in season and wash them thoroughly before eating.
Do not buy food on the beach, especially from sellers who walk along the beach with trays in the heat. It can be spoiled and it is not known who, where and when it was prepared. Eat fruits and vegetables in season and wash them thoroughly before eating.
It is advisable to eat food immediately after preparation. The longer it stays at room temperature (and in summer the room temperature is quite high), the more microbes multiply in it. Put the leftover food in the refrigerator, and when it's time to eat, reheat it thoroughly. Don't drink tap water, buy bottled water. Cook meat and fish at a temperature of at least 70°C.
Properly selected nutrition after poisoning plays an important role in the recovery and restoration of the digestive system and the whole organism as a whole. In this article, we examined in detail what you can eat after poisoning and diarrhea, and what foods it is better to refuse, we will make an indicative menu. On the features of nutrition after poisoning in children, also read on our website.
Why do we need a diet?
Diet after poisoning is necessary for complete recovery and for the prevention of complications of the disease. It helps to restore the following violations in the body.
- Inflammation of the gastric mucosa. It is this organ that suffers first in case of poisoning. Poor quality or poisoned food causes inflammation of its walls.
- Violation of the level of electrolytes, lack of proteins, failure in blood pH. Together with vomiting and diarrhea, the body loses a large amount of proteins and trace elements. Properly selected nutrition eliminates this problem.
- Failure of the pancreas. Chronic pancreatitis most often develops in children with poisoning. The pancreas is the main organ involved in digestion. It produces most of the enzymes that digest what is eaten.
- Liver damage. For example, a diet for alcohol poisoning makes it possible for this organ to rest, since it is through it that all alcohol passes and is neutralized.
 This organ is affected in the first place and when poisoned by mushrooms, poisons.
This organ is affected in the first place and when poisoned by mushrooms, poisons. - Failure of the kidneys. They suffer from dehydration. Most toxins and poisons are excreted by the kidneys. In case of poisoning with mushrooms, alcohol surrogates, chemicals, renal failure may develop.
- Alcohol intoxication. A diet after alcohol poisoning helps to neutralize alcohol and cleanse the body of it.
Is it necessary to eat in the first days after poisoning
Previously, it was believed that you can eat after poisoning only on the 3rd day. According to new medical protocols and recommendations, fasting after poisoning is dangerous and harmful to the body. Nutrition is part of the treatment, and with it you can:
- Replenish the nutrients, fluids, electrolytes and minerals that a person has lost due to vomiting and diarrhea.
- Restore the stomach, protect its walls from the irritating effect of hydrochloric acid.
- Provide the body with all the necessary nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates).

Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regimen. Together with vomiting and diarrhea, the patient loses a very large amount of fluid, and dehydration develops. An adult after food poisoning should drink at least 2.5-3 liters of liquid per day in case of poisoning.
The list of what you can eat after poisoning for an adult and a child is not particularly different. The exception is infants. Their diet is breast milk, which does not need to be abandoned.
Please note that in case of mushroom poisoning, you must immediately call an ambulance and be treated in the intensive care and toxicology department. The possibility of nutrition with this poisoning is discussed with the attending physician.
Basic rules of diet after poisoning
Drinking and eating after poisoning and vomiting should be started on the first day of the disease. During the first week, you need to adhere to nutrition, with the help of which the digestive system and the body will recover:
- Eat often and in small portions.
 Breaks between meals should not exceed 3 hours. The optimal single serving size is the size of the palm of your hand. If you don’t feel like eating at all, you can reduce its volume, but you can’t starve.
Breaks between meals should not exceed 3 hours. The optimal single serving size is the size of the palm of your hand. If you don’t feel like eating at all, you can reduce its volume, but you can’t starve. - Food and drink should be at room temperature. Cold and hot foods will irritate the stomach lining.
- Steam, boil or simmer foods. Fried and smoked foods should be discarded during the recovery period.
- If you have chronic diseases of the digestive system, for example: gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, then when compiling a diet, you need to take into account their features.
- It should be clarified with the attending physician what should not be eaten after stomach poisoning. The list of prohibited products may be individual. When prescribing a diet, the doctor takes into account concomitant diseases and the patient's condition.
Please note that in the first days after food poisoning, it is best to observe bed rest, rest, and avoid physical exertion.
What can you eat on the first day
On the first day, the list of what you can eat after poisoning is very limited. On the first day, it is necessary to fight dehydration and loss of electrolytes, protect the walls of the stomach from toxins and hydrochloric acid.
Drink alkaline non-carbonated drinks. It can be weak sweet black tea, sweet compote, mineral water, decoction of chamomile or St. John's wort. It is better to refuse acidic drinks, they can increase intoxication and inflammation of the stomach. Drink 1 glass of liquid every hour.
On the first day of food poisoning you can eat:
- Toasted white bread. It is best to dry it at home. Store-bought salted crackers are contraindicated.
- Boiled rice porridge without salt and oil. When preparing it, you need to add water twice as much as usual (for one glass of rice - 4 glasses of water).
- Biscuits. Only the simplest cookies will do, without additives, fillings.
- Bananas. Choose ripe, unspoiled fruits. You can eat half a banana at a time, you can chop it in a blender, and mix it with rice porridge.
- Boiled oatmeal, slimy consistency. It envelops the stomach, relieves its irritation.
Diet for day 2
The next day, after poisoning, the diet can be slightly diversified and expanded. The following products can be added to the menu:
- Boiled lean chicken or turkey. It is better to eat it without a side dish, separately. On the second day after poisoning, you can have quite a bit of meat, 100-150 grams. It is necessary to replenish the body's needs for proteins and amino acids.
- Eggs. It is better to eat them in the form of a steamed omelette, or boiled hard boiled.
- Baked apples, pears. This dish has a lot of fiber and pectins, which will stimulate intestinal motility.
- Vegetable soup with vegetable oil, which may include carrots, potatoes, zucchini.
Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regimen. On the second day, it is recommended to drink water and tea with lemon. The fact is that along with vomiting, the body loses a large amount of hydrochloric acid, and alkalosis may develop. Alkalosis is a pathological condition in which alkalization of the blood occurs, an increase in its pH. It can be corrected in case of poisoning with acidified drink.
On the second day, it is recommended to drink water and tea with lemon. The fact is that along with vomiting, the body loses a large amount of hydrochloric acid, and alkalosis may develop. Alkalosis is a pathological condition in which alkalization of the blood occurs, an increase in its pH. It can be corrected in case of poisoning with acidified drink.
Diet for the first week
In case of food poisoning, a sparing diet should be followed for 1 week. On the third day, and in the next 4 days, you can expand your menu with the following dishes:
- Dairy products. You can eat low-fat cottage cheese, drink fermented baked milk, kefir, yogurt. These products will restore the intestinal microflora, improve its work.
- Boiled or baked fish. It is best to choose low-fat varieties of sea fish.
- Low-fat chicken broth. This dish will help restore lost trace elements, fatty acids.
- Baked and boiled vegetables. You can cook them in the form of a dietary vinaigrette (without mayonnaise and beans).

- Buckwheat, millet porridge, pasta.
If you find it difficult to live without coffee, you can drink it already on the 3rd day, but only with milk. Drinking coffee is best after a meal, so that it does not irritate the stomach lining.
The table below shows an example of a menu that you can navigate during the first week after poisoning (except for 1.2 days):
- Curd;
- Biscuits;
- Coffee with milk and sugar.
- Baked apple;
- Compote.
- Chicken broth;
- Buckwheat porridge with vegetable oil;
- Berry juice.
- Tea with lemon and sugar;
- Sandwich with boiled chicken breast and white bread;
- Baked fish with boiled carrots and potatoes;
- Still water with lemon.
What is strictly prohibited in case of poisoning
With food poisoning, the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus is inflamed and irritated, the intestinal microflora is disturbed. Any errors in nutrition can cause diseases such as gastritis, cholecystitis, duodenitis. For the most rapid recovery and recovery, during the first week after poisoning, certain types of food should be abandoned. The following foods should not be eaten during poisoning, and within a week after it:
Any errors in nutrition can cause diseases such as gastritis, cholecystitis, duodenitis. For the most rapid recovery and recovery, during the first week after poisoning, certain types of food should be abandoned. The following foods should not be eaten during poisoning, and within a week after it:
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke irritates the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, can provoke peptic ulcer and the development of malignant neoplasms.
- Alcoholic spirits, including alcohol-based drugs.
- Carbonated sweet drinks, store-bought and fresh juices.
- Fatty, fried and smoked foods, offal, chips, nuts, chocolate, sweets.
- Fresh fruits, vegetables. They can increase the fermentation processes in the intestines, and cause flatulence and bloating. Vegetables and fruits can be baked or boiled.
- Legumes, including chickpeas, beans, peas.
- Black bread.
- Sweet pastries.
- Salo, butter.
- All types of cabbage.

- Garlic, onion, spices.
This list can be expanded by your doctor. For example, if a patient has diabetes, he should not add sugar, honey to his tea, and eat biscuits and bread.
Nutrition in case of poisoning is an important component of treatment. To find out exactly what you can eat with poisoning and diarrhea for a specific person, as well as find out the list of prohibited foods, contact your doctor. The diet should be followed during the first week. The first 2 days, the diet is limited and sparing. Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regimen. The amount drunk should not be less than two liters per day.
How to introduce new foods and exit the diet
Diet after poisoning lasts about 2 weeks. After the end of this period, you should not immediately pounce on the products that you miss. One new dish and product can be introduced per day.
A sudden change from dietary intake can cause pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) and disruption of the stomach and intestines.
Get a notebook and write down in it the new foods that you have introduced into your diet, note in it the body's reaction to them. If something causes stomach pain, heartburn, diarrhea - discard them.
Dietary nutrition is the main component of the treatment of poisoning. It is necessary to restore the digestive system, replenish proteins and trace elements in the body. The diet is made by the attending physician. You can start eating on the first day after poisoning. Throughout the entire period of treatment, you need to limit smoking and completely abandon coffee and alcoholic beverages. After the end of the diet, you need to get out of it correctly, introduce new foods gradually, slowly, monitor the body's reaction to them.
Children's vomiting is usually very scary for parents. In most cases, there is nothing to be afraid of, vomiting is a mechanism developed by the body to protect against the introduction of toxic substances through the walls of the stomach and intestines. It can be one-time, or it can be repeated several times. In any case, even with small similar manifestations, you need to show the child to a specialist who examines him, prescribes treatment, and gives advice on how to feed the child after vomiting.
It can be one-time, or it can be repeated several times. In any case, even with small similar manifestations, you need to show the child to a specialist who examines him, prescribes treatment, and gives advice on how to feed the child after vomiting.
Possible causes of vomiting in children
After vomiting - the main drink!
If the child's condition does not inspire concern, and the vomiting was not gushing, but single and not very strong, you can try to stabilize his condition on your own. Possible causes of child vomiting may include:
- Head injury. This condition, which threatens the life of the child, may be accompanied by fainting.
- Concussion.
- Food poisoning. Accompanied by high fever, diarrhea.
- Bacterial infection of the stomach and intestines.
- Temperature increase in acute respiratory infections, SARS.
- Gastrointestinal disorders (gastritis, duodenal ulcer and stomach ulcer).
 The vomit may be streaked with blood. Additionally, there are pains in the abdomen.
The vomit may be streaked with blood. Additionally, there are pains in the abdomen. - Pylorospasm in newborns.
- Unfamiliar food, excessive use of spices and food additives, sweets.
- Eruption of milk teeth.
It is imperative to find out the cause of vomiting in order to avoid complications. Particular attention is given to infants, newborns and children with chronic diseases. Symptoms such as vomiting of bile and blood, frequent pulse, pale skin, a combination of vomiting and diarrhea, constant drowsiness or excessive overexcitation, refusal of the breast and strong crying in the infant make one fear serious consequences. In these cases, you should immediately seek emergency medical attention.
Recovery of digestion immediately after vomiting
Vomiting is a wake-up call!
This unpleasant phenomenon is accompanied by such side effects as a violation of the water-salt balance and the loss of a large amount of fluid by the body. Before feeding the child, you need to restore this balance, if medical tactics do not provide for other measures. Before bringing these indicators back to normal, feeding may be inappropriate, and even harmful to children's health.
Before feeding the child, you need to restore this balance, if medical tactics do not provide for other measures. Before bringing these indicators back to normal, feeding may be inappropriate, and even harmful to children's health.
It is recommended to replenish the lost fluid and additionally take preparations containing salt, soda, calcium, glucose to replenish lost nutrients. These can be drugs such as Regidron, Glucosolan, Oralit. Water-salt solutions prepared from them give 1-2 tsp each. babies, older children - 1-2 tbsp. spoons at a time. Required volume:
- Children under one year old - 150-200 ml per kg of body weight per day.
- Children over one year old - 120-170 ml per kg of body weight.
It is better to drink sweet tea, rosehip decoction, non-carbonated mineral water, rice decoction, dried fruit compote. If the child does not show appetite, these measures can be dispensed with for the next 5-6 hours.
Recommended meals and diet
Severe vomiting may be a symptom of rotavirus infection
The most important thing is not to force-feed the child. Abstinence from food is one of the methods for the speedy rehabilitation of the body after suffering vomiting. The child is offered food every 2-2.5 hours, the total number of meals can be up to 6-7 times. Portion size also changes compared to the usual diet, servings become smaller.
Abstinence from food is one of the methods for the speedy rehabilitation of the body after suffering vomiting. The child is offered food every 2-2.5 hours, the total number of meals can be up to 6-7 times. Portion size also changes compared to the usual diet, servings become smaller.
After 3-5 days it is possible to return to the previous amount of food if there are no more problems with vomiting. A sparing diet and diet should be followed for 1-3 weeks after vomiting. Basic dietary requirements for children:
- foods must be easily digestible,
- rich in protein and vitamins,
- contain the minimum amount of fats and carbohydrates,
- be rich in minerals.
Diet after vomiting should be discussed with your pediatrician or doctor. You need to start with fermented milk products without aromatic and flavoring additives, at least on the first day of the problem. If a child has a desire to gnaw a cracker from white bread, this is not forbidden to him.
The next day, offer him liquid buckwheat, oatmeal or rice porridge cooked in milk diluted with water. After 1-2 days, children are given weak chicken broth with wheat bread croutons, jelly. A little later, mashed soups, steamed meat and fish cutlets, meatballs are introduced into the diet.
Preferred meats - chicken, rabbit.
Fish must be lean. Garnish for meatballs and cutlets can be rice or buckwheat. It is better to use olive or refined corn, sunflower oil in small quantities. It is better to temporarily refrain from using butter, replacing it with melted butter. It is allowed to use baked apples, which are an indispensable source of carbohydrates for the child's body.
Kissel can be considered a good product for dietary nutrition after vomiting due to its enveloping effect on the gastric mucosa. Additionally, you can offer:
- boiled carrots, broccoli,
- banana puree or fresh bananas,
- one-day kefir,
- oil-free mashed potatoes,
- yoghurts without additives.

Carbohydrates can stimulate fermentation processes, thereby creating a load on the stomach. Animal fats put an additional burden on the liver, and it already has to cope with intoxication products. In addition, additional enzymes are needed for the digestion and breakdown of fats, and the child's body already works in an increased load mode after vomiting.
But proteins, on the contrary, activate fat and cholesterol metabolism. They relieve the liver of an additional load, help to remove products of toxic damage and fats. This is due to the formation of lipotropic substances, the source of which are proteins. Vitamins and trace elements should replenish the lost supply of these substances resulting from dehydration as soon as possible.
Infant nutrition
Vomiting as a symptom of food poisoning
The best food for infants, and especially for newborns, remains mother's milk. It perfectly stabilizes the condition of the stomach and intestines in uncomplicated conditions. Formula-fed and mixed-fed infants under 6 months of age may receive their usual food, as long as it has not caused vomiting due to allergies or incompatibilities.
Formula-fed and mixed-fed infants under 6 months of age may receive their usual food, as long as it has not caused vomiting due to allergies or incompatibilities.
Infants over 6 months of age who are receiving complementary foods may begin refeeding after vomiting with buckwheat or rice porridge. They are prepared on a mixture of milk and water in equal quantities.
After 2 days, you can add a few teaspoons of freshly prepared cottage cheese to the diet. Vegetable puree and fruit juice are introduced after 3-4 days very carefully, starting with a small amount.
Meat soufflé or boiled meat puree is introduced into the children's diet by the end of the first week of the sparing period.
Food handling and preparation rules
The preparation of food for children with the consequences of vomiting requires special care. Products must be fresh, all dishes are prepared in such a way that they can be eaten immediately. All products are thoroughly washed under running water, cut and cleaned on various cutting boards. Food is served warm; food from the refrigerator or very hot food should not be offered to the child.
Food is served warm; food from the refrigerator or very hot food should not be offered to the child.
Meals are only steamed or boiled in weak meat broth, in water. If vomiting was caused by problems with the gastric mucosa, the products must be crushed with a blender or rubbed through a sieve. The groats are very boiled soft, and for infants, boiled groats are ground into jelly.
Prohibited products
Severe and frequent vomiting is a reason to call a doctor!
It is absolutely unacceptable to give fried, smoked, marinated dishes to children after vomiting. Fresh wheat bread is replaced with crackers or dried croutons. It is not recommended to feed children after vomiting such products:
- Fresh and pickled vegetable salads.
- Legumes: beans, peas.
- Sweets: chocolate sweets, caramel, lollipops, marshmallows, marmalade.
- Dishes from millet and pearl barley.
- Freshly squeezed juices and juices from sour berries and fruits.












