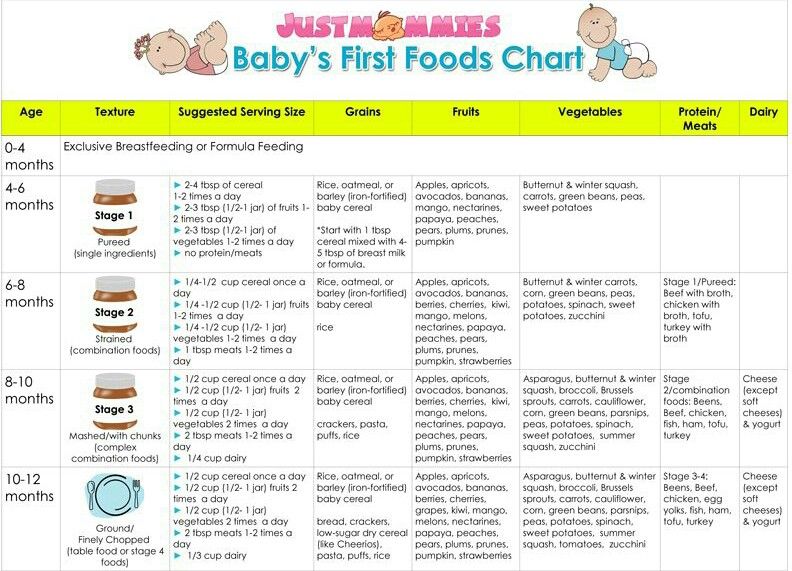
Table foods to start baby on
Best Finger Foods for Babies: The Ultimate Guide
How exciting that your baby is about to graduate from mushy foods to finger foods! This is a big step in your little one’s development. However, you may be wondering when’s the right time to start finger foods, and how to tell that your baby is ready. We’ll answer all these questions and more, plus give you a list of the best finger foods to introduce to your baby first.
Introducing Finger Foods to Your Baby
So, when can babies eat finger foods? You can start to give your baby finger foods around the time they’re able to sit up independently and can bring their hands to their mouth. This may happen between the ages of 8 months old and 9 months old, but your baby may be ready a little sooner or later than this time.
Around this time, you may also notice that your baby is developing their pincer grasp and may be making chewing motions. These are both great indications that your baby’s ready for finger foods. Moreover, using their fingers to pick up foods will further develop your baby’s fine motor skills.
Some parents who adopt the baby-led weaning approach may start offering finger foods to their infants as early as 6 months old. This method skips spoon-feeding with solid foods and instead lets your baby take the lead in self-feeding with finger foods. Some believe this approach can decrease fussiness when it comes to introducing new foods, including finger foods, to your baby. Speak to your child’s healthcare provider if this method is something you’d like to try.
Giving your baby finger foods can help your little one learn to feed themself, just one step toward gaining independence. Self-feeding can be great fun for your baby. Even if much of the food doesn’t end up in your baby’s mouth, the fact that they’re exploring this new frontier is an accomplishment to be proud of.
First Finger Foods for Your Baby
As you begin choosing finger foods for your baby, check out the following ideas:
Steamed veggies like sweet potatoes, potatoes, carrots, green beans, peas
Soft, ripe fruits like bananas, berries, peaches (peeled), mangoes (peeled)
Whole-grain breakfast cereals (without nuts, clusters, or chunks)
Whole-grain pasta (cooked well)
Whole-wheat bread
Whole-grain crackers or wafers like teething biscuits
Soft meats like chicken
Cheese (mild)
Scrambled eggs.

Be sure that any of the above finger foods are cut into small pieces. You don’t want your baby eating a piece that’s too big to swallow. And, make sure to watch them while eating.
Finger Food Safety
During this time babies are more likely to swallow foods without chewing them, whether they have a few baby teeth coming in or they have no teeth. Avoid giving any finger foods that require a grinding action to chew (this type of chewing is typically mastered around the age of 4), as these may pose a choking risk. Offer finger foods that are soft, easy to swallow, and broken or cut into pieces that your baby cannot choke on. A good rule of thumb is that soft and mushy finger foods are safe for your baby. Small, round, coin-shaped, hard, chewy, crunchy, slippery, or sticky foods may lead to choking. Here are some foods to avoid offering your baby when they start on finger foods:
Peanut butter (in chunks)
Meat (in chunks)
Cheese (in chunks)
Raw veggies (in large chunks or round shapes), including celery sticks, carrot sticks, baby carrots, cherry tomatoes, and peas
Raw hard fruit (in large chunks or round shapes), including apples, pears, and grapes
Nuts (whole)
Seeds
Popcorn
Chewing gum
Candies (hard, gooey, or sticky)
Hot dogs or meat sticks.

There are ways you can still give some of the above foods while making them easier to eat and less hazardous to swallow. For example:
Grapes or cherry tomatoes, cut in half
Creamy peanut butter spread thinly on whole-grain bread that’s cut into small squares
Hot dog, cut lengthwise and then cut into small 1/2-inch pieces.
Note on Food Allergies
Medical experts once recommended that parents avoid feeding their babies eggs, fish, and peanut butter since babies may be allergic to these foods. However, it’s now recommended that you introduce these foods early—while keeping a close watch for any reactions—since this approach can help reduce your child’s chances of developing food allergies. Before introducing peanut butter or peanut products, consult with your baby’s healthcare provider. Your baby is more likely to be allergic to these foods if
food allergies run in your family
your baby is known to have an egg allergy
your baby has eczema.

The Bottom Line
It’s time to introduce finger foods to your baby when you see that they’re able to sit up on their own, start bringing their hands to their mouth, and can use a pincer grasp to hold onto small items, like finger foods. This development happens around the age of 8 or 9 months old, but you may see it sooner or later in your baby.
In the beginning, you’ll want to introduce finger foods that are soft and easy to swallow, since babies at this age tend to swallow instead of chew even if they have a few baby teeth. Think steamed veggies and soft fresh fruits. You can also introduce whole-grain bread, crackers, cereal, or pasta if they’re cut into small pieces. Chicken, mild cheese, and scrambled eggs are also great options when served in small pieces.
Avoid hard foods like raw veggies and fruits, as well as chunks of nut butter, cheese, and meat. Whole nuts and seeds are not recommended, nor are chewing gum, candies, hot dogs, or meat sticks. All these items can pose a choking hazard.
All these items can pose a choking hazard.
Transitioning to finger foods is a big step in your baby’s development and independence. Letting your baby self-feed with finger foods may be a bit messy at first, but you’ll both get the hang of it. Learn more about developmental milestones for your 9-month-old baby.
13 Best Finger Foods for Baby
Introducing finger foods for baby is an exciting and nerve-racking time. Between the mess, possible allergies and potential choking hazards, it’s enough to give some parents white knuckles as they hover over the high chair. But while you should certainly exercise caution, there are lots of great baby finger food ideas that will make mealtime fun and nutritious, and let your growing child practice the important art of self-feeding.
In this article:
When can babies eat finger foods?
Baby finger food safety
How to introduce new finger foods for baby
Best finger foods for baby
When Can Babies Eat Finger Foods?
There’s no hard and fast rule in terms of when babies can start eating finger foods, says William Dietz, MD, PhD, director of the Sumner M.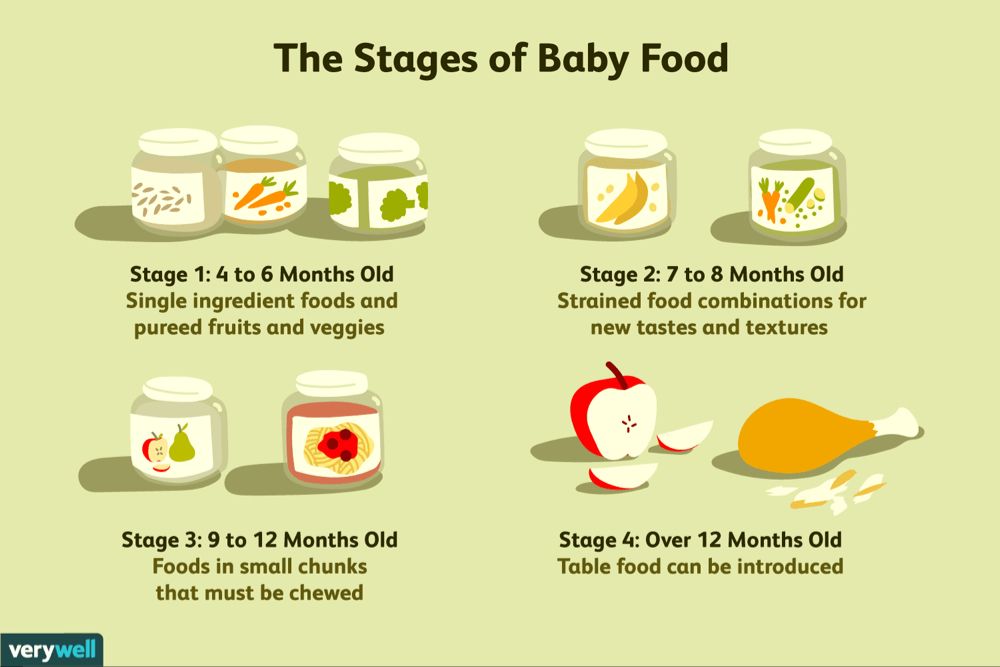 Redstone Global Center for Prevention and Wellness at the Milken Institute School of Public Health at the George Washington University in Washington, DC, and co-editor of the American Pediatric Association’s (AAP) Nutrition: What Every Parent Needs to Know. Rather than focusing on baby’s age, says Dietz, “the first indicator you should look for is that the baby is interested.” So how can you tell when baby’s interest is piqued? Reaching for the food as you’re feeding her, grabbing the bowl or spoon, putting the spoon in her mouth and fussing when she sees you eat (because she wants in!) are all signs your child may be ready. “Babies generally want to feed themselves,” Dietz says. “That’s a normal drive.”
Redstone Global Center for Prevention and Wellness at the Milken Institute School of Public Health at the George Washington University in Washington, DC, and co-editor of the American Pediatric Association’s (AAP) Nutrition: What Every Parent Needs to Know. Rather than focusing on baby’s age, says Dietz, “the first indicator you should look for is that the baby is interested.” So how can you tell when baby’s interest is piqued? Reaching for the food as you’re feeding her, grabbing the bowl or spoon, putting the spoon in her mouth and fussing when she sees you eat (because she wants in!) are all signs your child may be ready. “Babies generally want to feed themselves,” Dietz says. “That’s a normal drive.”
Being able to sit independently is another good clue that babies are physically ready to try finger foods, says Susan M. McCormack, MA, senior speech language pathologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a board-certified specialist in swallowing and swallowing disorders. If they can sit up in the high chair, then they might be ready to try their hand at finger foods.
If they can sit up in the high chair, then they might be ready to try their hand at finger foods.
Some guides suggest waiting to introduce baby finger foods until your child has mastered a pincer grasp—the ability to pick up small objects between the thumb and forefinger—but Dietz says this isn’t totally necessary. “Initially when children start to feed themselves, they don’t have a pincer grasp,” he says. “So they’re using their whole hand and putting their hand in their mouth. And that’s fine.”
If you’re waiting for your infant to sprout teeth before moving on from purees, think again. “Babies don’t need teeth to learn to eat solids and learn to chew,” McCormack says. Those strong little gums are perfectly capable of mashing up soft solids—if you’ve ever let baby teethe on your finger, then you have some idea of just how powerful they are!
Baby Finger Food Safety
When choosing the best finger foods for baby—whether you’re starting at 6 months or 9 months—experts agree that it’s best to begin with small pieces of soft food that dissolve easily.
As your infant grows and becomes comfortable eating finger foods, you can branch out, McCormack says. “As a baby develops better tongue patterns to control food pieces as well as more mature chewing, he can better ‘chew’ the foods that break apart, like pieces of fruits and vegetables. A one-year-old can also bite off pieces of food that a 6-month-old can’t.”
Avoid giving baby finger foods that are large, sticky or don’t dissolve easily, because they’re potential choking hazards, Dietz warns. He suggests steering clear of foods like hot dogs, carrots, nuts, grapes, popcorn, candy and globs of peanut butter.
Another thing to keep in mind when you’re picking out the best finger foods for babies is that a lot of adult foods—particularly snacks—can be super salty. “Often parents will doctor a food so it appeals to their tastes, and their taste may have bigger amounts of sodium than a baby’s taste,” Dietz says. When preparing food for baby, leave out the salt whenever possible. (You can always add it separately to your portion if you’re cooking for the family).
(You can always add it separately to your portion if you’re cooking for the family).
How to Introduce New Finger Foods for Baby
When babies first start on finger foods, breast milk and formula will still be their main source of nutrition, followed by purees. You should continue to spoon-feed your child initially, “but during the feeding process, they should also be allowed to feed themselves,” Dietz says. Put some finger food on her high-chair tray and let her try to get it into her mouth in between the spoonfuls of food you’re feeding her. If she gets really frustrated, go ahead and help her out.
Most important, follow your child’s cues and “let your baby be the guide,” McCormack says. If he doesn’t respond positively, take a step back and try again later. But keep in mind that babies often crinkle up their faces when they try something new, which can look like they don’t like something, Dietz says. It can take up to 20 times before they’re used to certain foods. “Parents shouldn’t force food, but they should be persistent in offering,” Dietz says.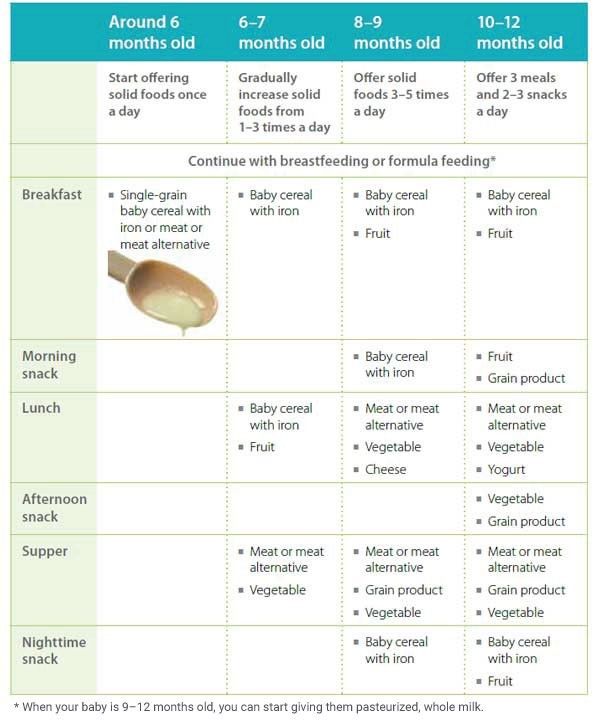
McCormack also suggests easing into finger foods by offering thicker purees with a bit of texture to them. “Try alternating bites of the smooth puree with a slightly thicker or mashed food to help your baby get used to the new textures in her mouth,” she says.
Remember, too, that this is a messy process. Parents might want to lay newspaper or an easy-to-clean vinyl tablecloth on the floor, since it’ll be a while (like, years) before your kid manages to get more food in his mouth than on the floor, Dietz advises.
Finally, never leave baby unattended while she’s eating, and keep an eye out for signs of choking. It may be tempting to hold off on introducing finger foods until your child is older, but helping baby develop this skill has multiple benefits, McCormack says, including “development of independence, fine motor skills and self-feeding skills, as well as development of oral patterns to support texture progression.” Whether you start baby finger foods at 6 or 9 months, just follow baby’s lead and let him have fun with it.
Best Finger Foods for Baby
If you’re looking for baby finger food ideas, think about options that are soft, small and easily gummed. Here are a few of the best finger foods for baby to get started—including finger foods for baby with no teeth! While the same finger foods are as appropriate for a 6-month-old as they are for a one-year-old baby, you can begin to offer slightly larger pieces that they can bite off themselves as they become more confident. Stick with these healthy options, and you’ll start baby off on the right path for healthy eating.
Image: The Bump
1. Puffs and dry cereal. Puffs and O-shaped dry cereal are some of the most popular first finger foods for good reason: They let baby practice the pincer grasp by picking up one at a time. And as McCormack explains, they also “mix well with saliva and are easy for the infant to manage in their mouth without choking.”
2. Teething biscuits and lightly toasted bread. Teething biscuits and small pieces of lightly toasted bread are another great starter finger food, since they soften quickly. Just note that some breads can turn gummy and stick in baby’s mouth; lightly toast the bread and cut into very small pieces to avoid a choking hazard. As baby gets older (around 9 to 12 months), you can offer slightly larger pieces or serve bread topped with mashed banana or avocado, or a super-thin layer of hummus or peanut butter.
Just note that some breads can turn gummy and stick in baby’s mouth; lightly toast the bread and cut into very small pieces to avoid a choking hazard. As baby gets older (around 9 to 12 months), you can offer slightly larger pieces or serve bread topped with mashed banana or avocado, or a super-thin layer of hummus or peanut butter.
3. Scrambled eggs. Doctors used to advise waiting to introduce eggs, but the AAP now recommends early exposure to potentially allergenic foods. Which is great news, since scrambled eggs are an ideal early finger food! Keep your love of runny yolks to yourself for now, however, and cook those eggs thoroughly, cut into small pieces and avoid adding salt.
4. Soft fruit. Very ripe fruit is naturally soft, making them some of the best finger foods for babies. Ripe banana, peach, watermelon, raspberries, blueberries and cantaloupe cut into small pieces are all great finger food options.
5. Avocado. A rich source of omega-3 fatty acids—which can help boost baby’s brain development—avocados are, like puffs, often one the first baby finger foods, even when your little one has no teeth. Be warned: Avocado can get messy fast, but it’s well worth it (and can result in some hilarious pics for the baby album).
Be warned: Avocado can get messy fast, but it’s well worth it (and can result in some hilarious pics for the baby album).
6. Pasta. Though recipes often recommend cooking pasta al dente, when it comes to feeding baby, you’ll want to slightly overcook it so it’s nice and soft. To start, try small pasta shapes like orzo or mini shells, or cut up fusilli or penne. Initially serve it plain, but as baby is introduced to more foods you can toss the pasta in a little butter, olive oil or low-sodium tomato sauce.
7. Tofu. Whether cooked or uncooked, tofu is a wonderful plant-based source of protein and a perfect finger food for babies. Opt for firm tofu, which is still quite soft, as opposed to soft or silken tofu, which will likely fall apart in baby’s hand and frustrate her.
8. Cooked vegetables. Though it will be a while before baby can hit the crudités platter, cooked vegetables make excellent baby finger foods. To get the most nutrients out of your vegetables, steam or roast them until soft, and, of course, cut them into small pieces. Try sweet potato, carrot, broccoli, cauliflower or beets (opt for yellow beets for less mess) to start. As baby gets bigger, you can offer steamed carrot sticks or peeled, roasted sweet potato wedges.
Try sweet potato, carrot, broccoli, cauliflower or beets (opt for yellow beets for less mess) to start. As baby gets bigger, you can offer steamed carrot sticks or peeled, roasted sweet potato wedges.
9. Cheese. If baby has shown no signs of a dairy allergy, then it’s perfectly safe to introduce soft cubes of cheese as early as 6 months. Opt for small bites of a pasteurized cheese that’s soft but not overly sticky or stinky, like Monterey Jack or cheddar.
10. Beans. Looking for more protein-rich, vegetarian baby finger foods? Try beans. Opt for canned, low-sodium beans for convenience, or soak and cook dry beans yourself to save money (they’ll freeze well too!). When first introducing beans, smash them just a bit between your fingers before serving to baby.
11. Homemade muffins. While store-bought muffins are often loaded with sugar, there are plenty of healthy muffin recipes out there. Use whole-wheat flour, sweeten with applesauce instead of sugar and add healthy ingredients like mashed banana or grated zucchini. Bake in a mini muffin tin or use a standard-size tin, and, once baked, break off into small pieces for baby.
Bake in a mini muffin tin or use a standard-size tin, and, once baked, break off into small pieces for baby.
12. Meat. After soft foods, diced chicken breast and ground beef are pediatrician-approved next-stage finger foods for baby. Just make sure they’re thoroughly cooked and cut into very small pieces.
13. Fish. Fish is another allergenic food that doctors now say can be introduced before baby is a year old. Be sure it’s thoroughly cooked, and opt for a low-mercury fish like flounder, cod or salmon. Most important, make sure to remove any tiny bones.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
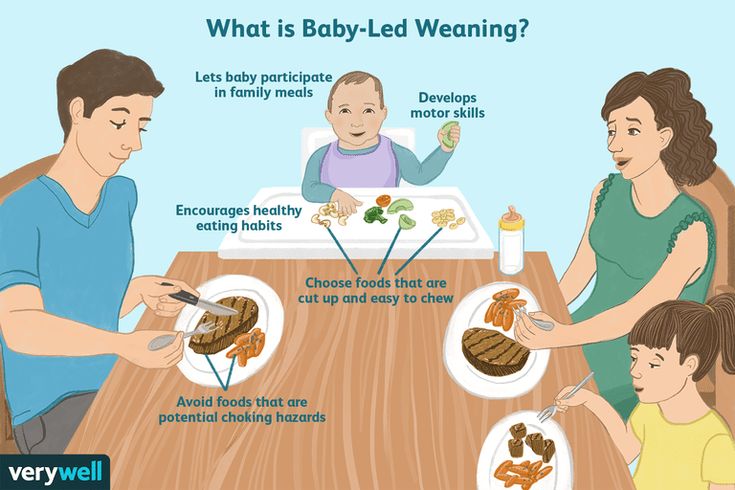
Baby-Led Weaning Basics
Why Variety Matters in Baby’s First Foods
The Dos and Don’ts of Homemade Baby Food
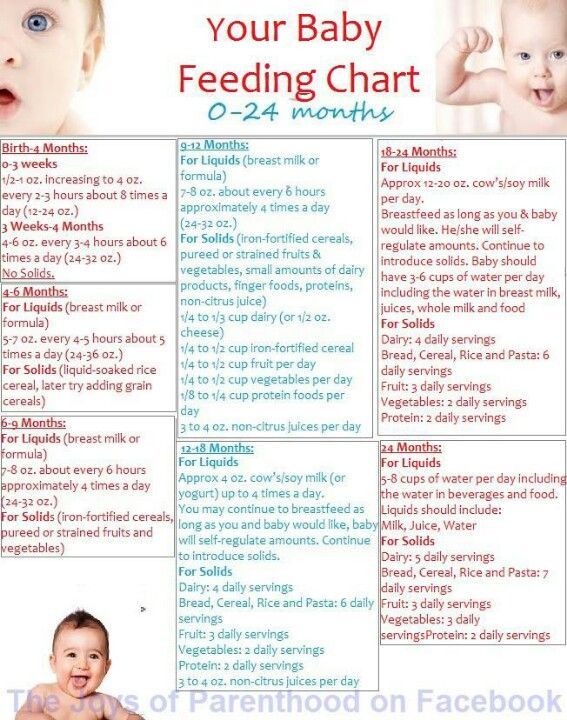
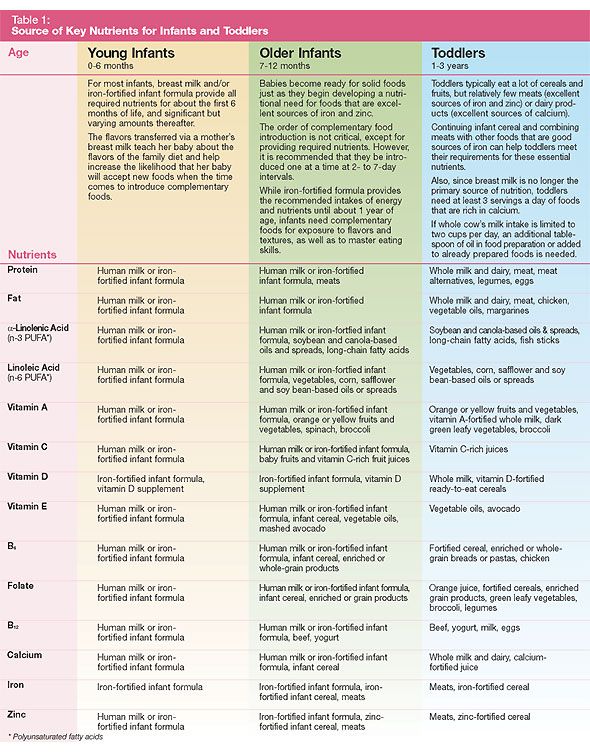
Optimal nutrition for children from 7 to 9 months
Submitted by Umeda_Ergasheva on Tue, 10/12/2021 - 18:25
Number of meals and amount of food
At this age, breast milk is still the most important food for a baby and provides half of his energy needs. Continue to breastfeed your baby on demand day and night. Solid foods cannot replace breast milk in the first year of life. There is no need for additional feeding of the child with breast milk substitutes, subsequent infant formulas (adapted milk formulas for children older than 6 months), because, being breastfed and receiving varied and timely complementary foods, the baby will be provided with all the necessary nutrients. nine0003
Continue to breastfeed your baby on demand day and night. Solid foods cannot replace breast milk in the first year of life. There is no need for additional feeding of the child with breast milk substitutes, subsequent infant formulas (adapted milk formulas for children older than 6 months), because, being breastfed and receiving varied and timely complementary foods, the baby will be provided with all the necessary nutrients. nine0003
Breastfeed after each feeding of complementary foods.
Basic recommendations for feeding your baby:
- The optimal time to introduce complementary foods is between 20 and 26 weeks of age.
- Scope: The introduction of complementary foods into the child's diet should be gradual. Start with 2-3 tablespoons, gradually increasing to 120 ml with each feeding.
- Frequency: give complementary foods 3 times a day.
- Consistency: the child should be offered food familiar to the family from the common table, mashed to a puree-like consistency.
 From about 8 months, you can start offering your baby food in pieces. nine0014
From about 8 months, you can start offering your baby food in pieces. nine0014 - Variety: try to give a variety of food at each feeding. For example: animal products (meat, eggs and dairy products), cereals (grains), root vegetables (and tubers), legumes, fruits, vegetables rich in vitamin A (carrots, pumpkin, spinach), and others (zucchini, cabbage).
- Animal products must be included in your child's diet. They should be administered as early as possible, given daily. It is necessary to grind them after sufficient heat treatment. Hard-boiled and finely chopped eggs, meat (lean beef and lamb), chicken, turkey and rabbit meat, and fish can be eaten by children even if they have no teeth. nine0014
- Foods can be mixed: purees and cereals should include a mixture of cereals, vegetables, beans, eggs, fruits, root vegetables and, if possible, rabbit meat, beef, fish, poultry. Milk can be added to cereals. Dense foods are richer in calories and vitamins - their nutritional value for a child is higher than, for example, soups.
 Children have a high need for energy and nutrients, as well as a small stomach, so the diet should include such dishes that, with a small volume, have a high nutritional value for the child. nine0014
Children have a high need for energy and nutrients, as well as a small stomach, so the diet should include such dishes that, with a small volume, have a high nutritional value for the child. nine0014 - Offer snacks (between meals) such as fruit once or twice a day.
- If your baby was exclusively breastfed, water should be started with the introduction of complementary foods. The need for water depends on the age of the child, the number of meals, the amount and type of food. Offer your child water more often, especially after meals! Let's drink it from a cup. In the first year, boiled and chilled water is recommended.
- When preparing baby food with oil or butter, use no more than half a teaspoon per day. nine0014
- Add one new meal to your child's diet every week.
- Focus on the child: be patient and actively encourage him. Don't force your baby to eat. Use a separate plate so that you can see if he ate everything that was offered.
- Observe your child and respond to his signals.
 Feed slowly and patiently, at his pace. Try different combinations of foods, flavors and textures to stimulate your child's appetite. Wait until he chews and swallows before offering another portion. nine0014
Feed slowly and patiently, at his pace. Try different combinations of foods, flavors and textures to stimulate your child's appetite. Wait until he chews and swallows before offering another portion. nine0014 - Stop feeding when the baby indicates that he has had enough.
- As the child grows older, he gradually develops the skills necessary for independent eating (taking pieces of food and putting them in his mouth, choosing food, using cutlery).
- Establish a routine for main meals and snacks. Limit feeding time to 15-20 minutes. During meals, the child should be exclusively in the high chair at the table.
nine0013 Hygiene: Hygiene (cleanliness) is essential to prevent diarrhea and other illnesses in the child. Use clean utensils and utensils when preparing food and feeding. Store food in a safe and clean place in accordance with the terms and rules indicated on them. Remember to follow the basic rules of personal hygiene - wash your hands with soap and water before preparing food and feeding the child, after using the toilet, after performing hygiene procedures and washing the child. - Observe your child and respond to his signals.
 Wash your child's hands before eating. nine0014
Wash your child's hands before eating. nine0014 Products not recommended during the first year of life:
- Med.
- Cow's (and also goat's) milk. It is not recommended to give it to children in the first year of life, since its composition does not meet the needs of infants and it can contribute to the development of anemia and allergies. To prepare cereals, you can use a small amount (diluted 1: 1 with boiled water) of cow's milk.
- Citrus fruits (lemon, orange, mandarin).
- Tropical fruits and vegetables. nine0014
- Sweets and pastries.
- Fried snacks (chips, croutons, snacks), fast foods (fast food).
- Tea, drinks carbonated and/or with a high content of sugar, dyes.
- Industrially processed meat products (sausages, sausages).
- Do not add salt, spices or food additives to baby food. If you use salt when preparing food for your child, add iodized salt.
Always think about safety: do not give your child peanuts, popcorn, small fruits or whole grapes, pieces of solid food that can choke on. nine0003
nine0003
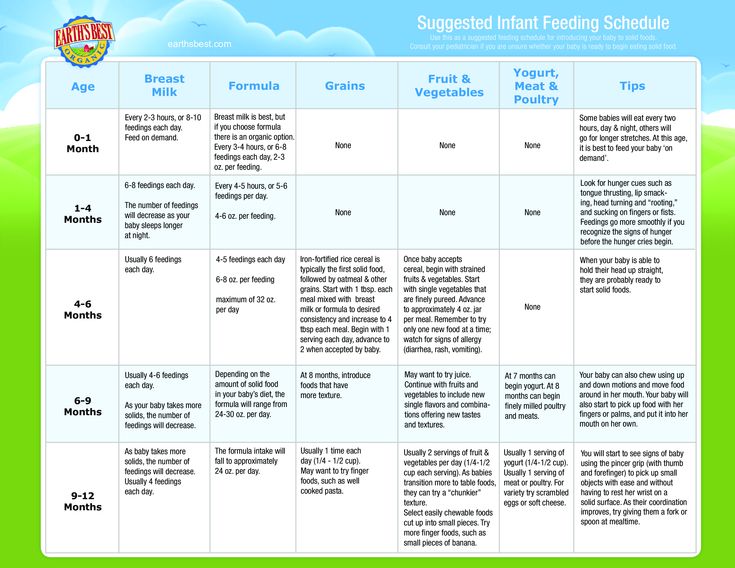
How to feed your baby
It is important that your baby has a varied diet. You can start complementary foods with thick porridge, gradually introducing any one vegetable (pumpkin, carrot, cauliflower or white cabbage) or fruit (apple, pear, plum, banana) puree into it. After that, you can move on to mashed meats (from lean beef, lamb, horse meat, pork, turkey, chicken or rabbit meat) or legumes with vegetables. The child may develop preferences for certain foods. Try to encourage your child to try different things. nine0003
- Don't limit your child's diet - he needs a variety of foods (protein, fruits and vegetables, some fat (such as vegetable oil), and cereals/cereals).
- If your child develops an allergy to any product, it should be excluded.
- If a family member has a food allergy, each new food should be introduced gradually—no more than one new food once a day for up to 7-10 days.
Off
Licensed Content
Off
Premature Content
Off
Mandatory Content
On
Weaning Tips for Babies
Search Support IconSearch Keywords
Home ›› How to Wean Your Baby
↑ Top
close communication. You are now preparing for another exciting milestone - introducing solid foods to your baby's diet. This is an exciting moment when your baby becomes more independent in eating. But, like all other stages of a child's development, this period requires a long adaptation. Like most parents, you probably want to know when to start introducing solid foods and how to introduce solid foods to your baby. nine0003
This article contains important information about introducing solid foods to your baby's diet (age-appropriate), tips for introducing complementary foods, and techniques to help you and your baby transition smoothly to the next level of nutrition.
At what age should complementary foods be introduced?
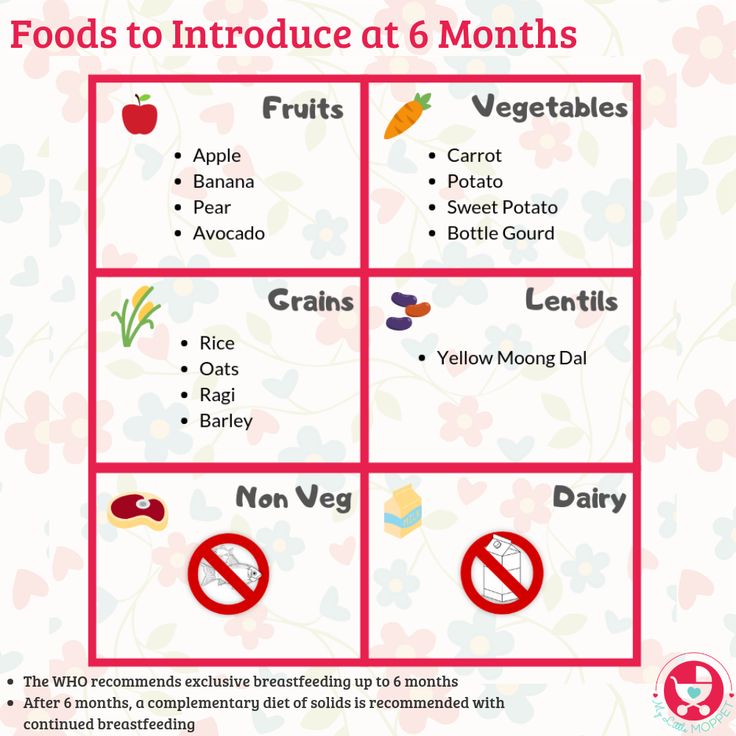
Be sure to check with your doctor when you think your child is ready to introduce new foods to their diet. There is no exact age at which complementary foods should be introduced. However, the introduction of complementary foods to children, both breastfed and bottle-fed, is recommended to start at the age of 4-6 months.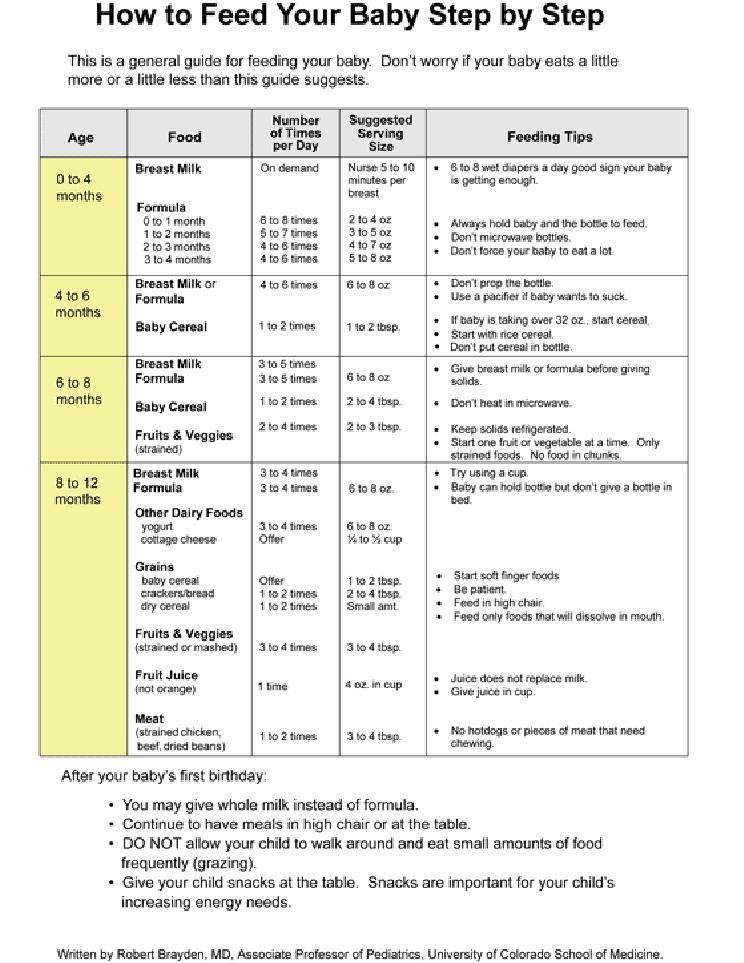 At 6 months of age, a baby's energy and mineral needs increase. However, all babies are different and some may be ready for it as early as four months. Four months is the earliest age at which complementary foods can be introduced. Until then, the baby's gastrointestinal tract is not ready to absorb any other food besides breast milk or formula. Only a doctor will be able to assess the individual readiness of each child; no matter what his decision is, it is important to continue breastfeeding, gradually introducing solid foods along with it. nine0003
At 6 months of age, a baby's energy and mineral needs increase. However, all babies are different and some may be ready for it as early as four months. Four months is the earliest age at which complementary foods can be introduced. Until then, the baby's gastrointestinal tract is not ready to absorb any other food besides breast milk or formula. Only a doctor will be able to assess the individual readiness of each child; no matter what his decision is, it is important to continue breastfeeding, gradually introducing solid foods along with it. nine0003
The doctor will try to identify key signs that your baby is ready for solid foods: [1]
- The baby can sit up without assistance or can sit on mom's lap and hold her head.
- The “spoon push” reflex, a natural reaction of rejection of food, in which the child pushes the spoon out with the tongue (the child no longer sticks out the tongue when eating), has disappeared in the baby. nine0014
- The child has an active food interest (desire to try something from the table while adults are eating).

After your baby has mastered the skills necessary for independent feeding, including holding his head well, you can begin to introduce more solid foods into the diet.
Your baby's first foods
The moment you've been waiting for is finally here: your baby is ready to try solid food! Usually the products of the first complementary foods are vegetables and cereals. nine0155
If the child is healthy, has no digestive problems and is gaining weight well, then, as a rule, weaning foods begin with the introduction of vegetables.
Monocomponent vegetable purees are good for the first feeding. Vegetables are a source of organic acids, potassium, iron, fiber. It is recommended to start vegetable complementary foods with zucchini, broccoli and cauliflower. Initially, vegetable puree should consist of one type of vegetable. Then you can make a combination of various vegetables. Start with 1 spoon, then bring the volume to 180 grams.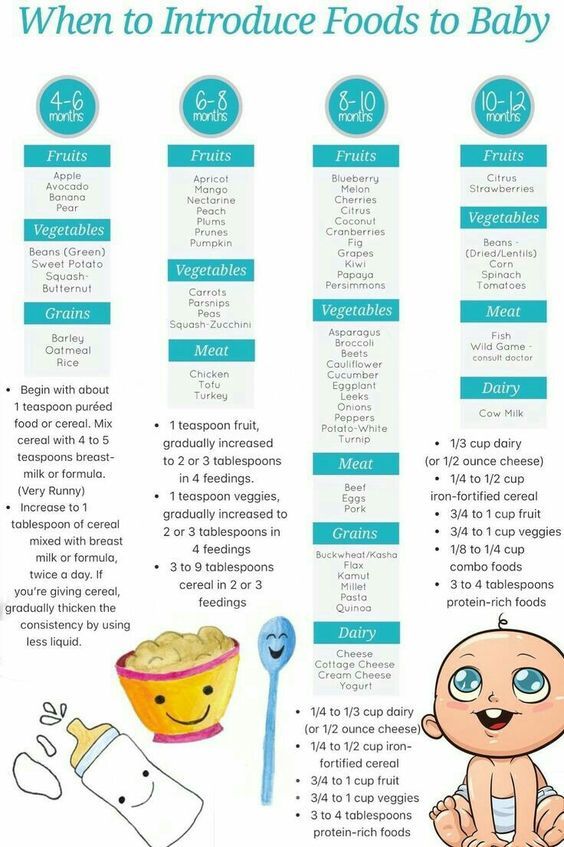 By the year, the amount of vegetable purees consumed per day is 200 grams. nine0155
By the year, the amount of vegetable purees consumed per day is 200 grams. nine0155
If the child is underweight or anemic, industrial cereals can be given as the first complementary food. As the first cereals, in order to avoid allergic reactions, it is recommended to introduce dairy-free gluten-free cereals. Mix one to two tablespoons of single-grain cereal with breast milk, or infant formula, or water. If the child is breastfed, give him complementary foods only after the main feeding, so that the child can first get enough breast milk; keep doing this until he is about
[2]
Once your child is used to their first meal, continue to introduce new foods such as fruit puree, cottage cheese, eggs, dairy products, and meat and fish purees. Before introducing each next product, you must wait three to five days to find out if the child is allergic to the previous one.
Steaming!
The inclusion of various foods in the diet is very important for the formation of taste habits in the baby.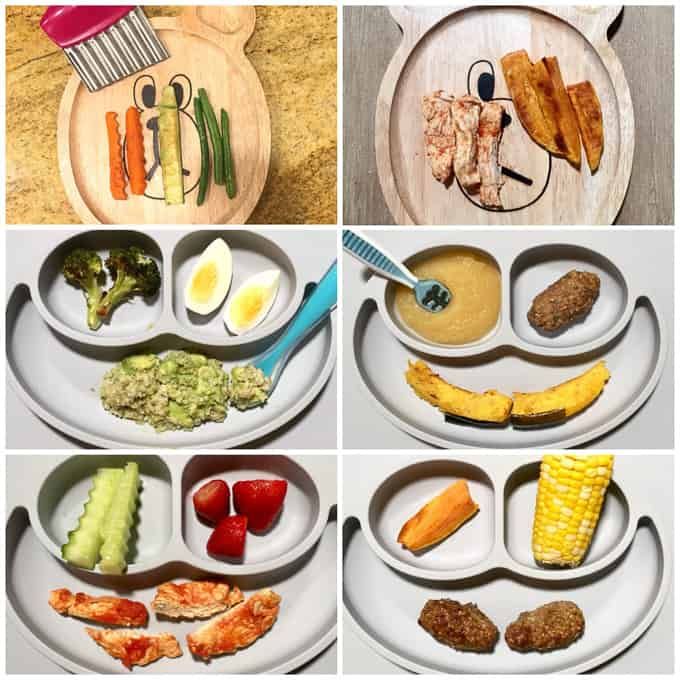 Steam a variety of healthy meals! nine0155
Steam a variety of healthy meals! nine0155
Steaming is one of the healthiest ways to prepare baby food. Steamed products are very soft and juicy, unlike fried products, which, of course, is very popular with children. And most importantly, steamed foods preserve the most important vitamins and minerals.
Make healthy cooking easy and enjoyable with the Philips Avent 4 in 1 Steamer Blender. The 4 in 1 healthy baby food maker allows you to steam and grind food in one jug. In addition, with the Philips Avent Steamer Blender, parents can make solid foods for babies of all ages, from purees to chunks. Jug with a volume of 1l. designed to cook several servings at a time. So you can prepare several meals at once to feed your baby now, and also freeze the puree for next time in a special container that comes with the steamer. The defrost and keep warm functions will help you prepare lunch or dinner for your baby even faster. nine0003
The 4 in 1 Steamer Blender also comes with a recipe booklet developed with pediatric nutritionist Emma Williams. In the brochure you will find interesting recipes for preparing tasty and fresh children's meals, as well as useful tips on the introduction of complementary foods and interesting menu ideas. Instill healthy habits in your baby from an early age for healthy development.
In the brochure you will find interesting recipes for preparing tasty and fresh children's meals, as well as useful tips on the introduction of complementary foods and interesting menu ideas. Instill healthy habits in your baby from an early age for healthy development.
In addition to the joy your child will experience from a change in diet, it is important to be aware of the various food allergies that can occur during the introduction of complementary foods. Experts recommend starting to introduce commonly known food allergens when the baby is 4-6 months old. In addition, recent studies have shown that with a later introduction of complementary foods in children, the risk of developing food allergies increases, therefore, it is necessary to introduce such foods into the baby’s diet on time and not put them off for later. The most well-known G8 food allergens include: [2] [3]
- cow's milk;
- chicken eggs;
- fish;
- seafood;
- nuts;
- peanuts;
- wheat;
- soybeans.

If you or a family member has a food allergy, be sure to consult your pediatrician for the best solution for introducing the foods listed above to your child's diet.
In addition to introducing new foods into the child's diet, it is also necessary to teach him to drink water from the age of 6 months. During the first six months of a child's life, mother's milk provides him with the necessary amount of fluid, even in hot climates. But once your baby is 6 months old, you can start giving him little by little to drink from a non-spill cup. nine0003
Check out Avent's Soft Non-Spill Training Cup from the Natural series with comfortable handles to help your child learn to drink without help. It is easy to drink from it, because the liquid begins to flow out only when the child bites or sucks on the spout of the cup. The design of the cup makes it easy to hold with little hands.
From Puree to Finely Chopped Foods
Once your child has mastered the motor skills needed to eat more solid foods, you can move on to finely chopped foods. Each child is different, but usually chopped vegetables and meat can be introduced into the diet from nine months. nine0167 [4]
Each child is different, but usually chopped vegetables and meat can be introduced into the diet from nine months. nine0167 [4]
When you introduce crushed foods into your child's diet, try to get your child to take an active part in family meals. The baby can be offered boiled vegetables, pieces of soft fruit, well-boiled pasta, or small pieces of chicken.
Remember to check that the ground food is soft and well cooked so that the child can easily grind it into mush with his mouth. Meat, for example, has a tougher structure and fibers, and therefore requires more thorough grinding compared to fruits that are delicate in texture. nine0003
With the Philips Avent 4 in 1 Steamer Blender, you can customize your food consistency from puree to chunks. Also, the recipe book that comes with the double boiler will allow you to easily choose the right recipe for the age of the child.
Tips on how to start introducing solid foods to your baby
Here are the main recommendations for introducing complementary foods to infants.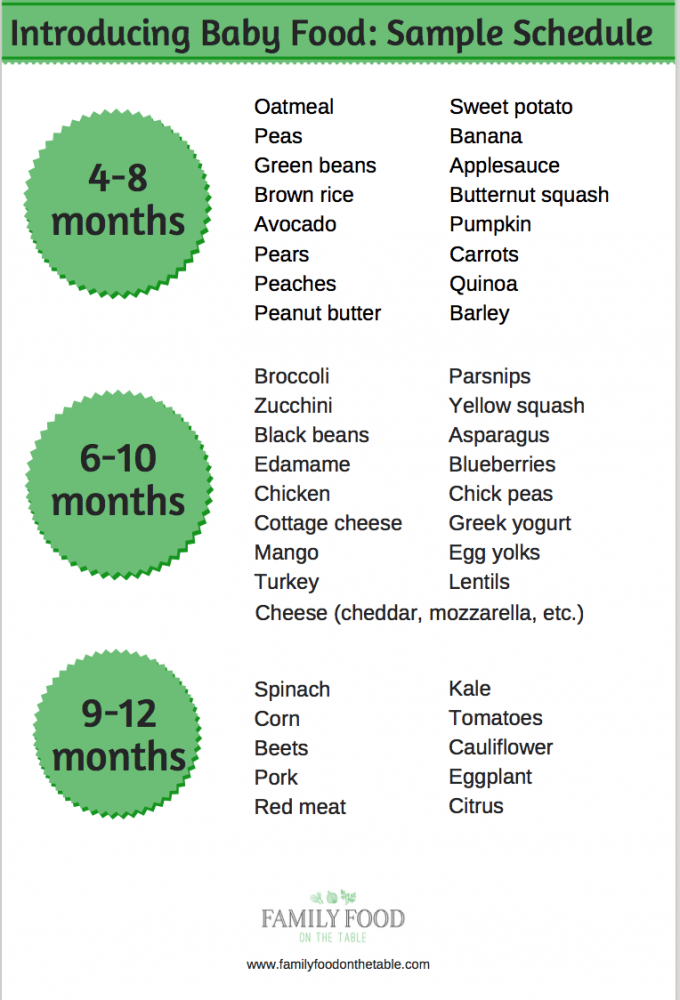 As you introduce solid foods into your child's diet, we also recommend following other tips to help your child get used to the new food: [1]
As you introduce solid foods into your child's diet, we also recommend following other tips to help your child get used to the new food: [1]
- Offer food only when the child wants it. In a quiet environment or when other family members are having lunch, offer your baby a new food if he wants to try it.
- Introduce a new product in small portions in the morning. A new product should be administered in the morning to monitor possible reactions to the product. Remember that the introduction of new foods into the diet should not be considered a complete meal for the child. It is only about giving the child the opportunity to taste different foods, as well as to get a feel for their structure, gradually increasing their portions as the baby grows older. nine0014
- Offer your child a new product only when they are healthy. Do not introduce new foods when the child is sick or during the vaccination period.

- If the child does not like the product, postpone the tasting until a later date. This is a new experience for your baby, associated with new tastes and sensations. Therefore, do not be discouraged and do not worry if the child did not like the food the first time! Simply postpone taking this product until a later time. nine0014
- Never leave your child alone with food. Although the child is already taking the first steps in independent nutrition, this does not mean that he can be completely independent.
- Do not give your child foods that are too hard or slippery, rounded or choking. These precautions will prevent the child from suffocation. Any rounded foods, such as grapes or carrots, should be cut into two or four pieces.
Goodbye liquid diet!
Proper weaning is an unforgettable experience for you and your baby. Complementary foods are very different from breastfeeding and bottle feeding, and you will certainly feel a sense of pride as your baby matures.