Taste bud organic baby food
Taste Bud Development in Babies
Feeding your baby through the first year of their life is an exciting journey - introducing them to new textures, tastes, and flavors as they grow. But as they move from the newborn stage to a one-year-old, their taste preferences and taste buds undergo some major changes. Knowing about these changes will help you feed them the way that works best for them as they grow.
Parents often wonder, when do babies get taste buds? The truth is that babies are born with a sense of taste - they actually develop taste buds in the womb. Your baby absorbs the flavors of the mother’s food choices during pregnancy through amniotic fluid. And as your baby grows, their sense of taste changes and they can distinguish different flavors.
That explains why their preferences for foods seem to shift - it’s a natural process. For example, babies around 4-7 months are pretty open to trying most new foods, but toddlers are notoriously picky eaters.
Looking at the timeline of baby taste bud development can help clue you into what your baby wants and needs to be eating during the first year of life.
Babies are born with a surprisingly sensitive sense of taste - they may even have more widely distributed taste buds than adults. With taste buds on the back of the tonsils, the back of the throat, and the tongue, newborns can tell the difference between sweet and bitter flavors.
They naturally prefer sweeter tastes like breastmilk and are exposed to new flavors through breastmilk as well. That means breastfeeding is a great chance to introduce your baby to new tastes early on.
3 to 6 MonthsIn this stage, babies begin to use their tongues more to explore the world. This phase is full of curiosity and also caution for parents, as you need to be quite careful of what your baby is picking up and putting in their mouth!
Babies at this age are beginning to explore more textures as well as different tastes. They also develop the ability to taste salty flavors, though that doesn’t mean giving them added salt is a good idea. They now have a pretty complete range of taste buds, and are able to taste sweet, salty, savory, bitter, and sour flavors.
They now have a pretty complete range of taste buds, and are able to taste sweet, salty, savory, bitter, and sour flavors.
This stage is often both exciting and frustrating - babies develop the ability to pick up solid foods by themselves around eight months, and so they can begin to feed themselves and explore new foods. Babies will love some foods right away and eat them happily.
But experiencing new tastes and textures after six months of breastmilk and formula can also be a little overwhelming for new eaters. Babies at this stage will often reject foods the first few times out of surprise, but don’t stop offering them - it can take up to eight tries to successfully introduce your baby to a new food.
Do Babies Inherit Preferred Tastes?Parents can hope - or worry - that their baby will inherit their food preferences or dislikes. If you’re a picky eater, you might worry that your baby will be one as well. And adventurous eaters often want to raise children with the same attitude towards food.
But truthfully, your baby’s taste preferences are affected by many different factors. Babies tend to prefer foods they were exposed to in the womb and during breastfeeding, but they also lean towards liking foods they’re exposed to often.
And of course, babies base a lot of their reactions to foods on how their parents react to them. If you make a face every time you encounter broccoli, your baby will pick up on that and probably do the same. Modeling positive behaviors is helpful when raising healthy eaters.
Helping Your Baby Enjoy Different FoodsIf you want to encourage your baby to eat and enjoy a wide variety of foods, that’s a great goal! There are a few steps you can take to help your baby explore different foods.
Letting babies explore foods at their own pace is important - pushing them to eat foods they don’t enjoy out of a desire to broaden their palate could actually backfire. But don’t let one negative reaction put you off. Introducing a food repeatedly can help babies get used to a new flavor or texture slowly.
Exposing your baby to a wide variety of foods, including different textures and tastes, is very important. That’s why at Tiny Organics, we aim to introduce your child to their first 100 flavors - evidence shows that children who are exposed to a wider variety of fruits and vegetables earlier have a higher intake of them as they grow. That’s how we help you raise a healthy eater for life!
REVIEW - Tiny Taste Buds - M&S Baby Food
We have recently been putting the M&S Tiny Taste Buds Range to the test.
My daughter Erin was a bit of a fussy eater and always had been even from the early weaning days. Some days getting her to eat anything was a challenge, and since the teeth started to make an appearance this only got worse! As a first time mum, I found myself getting quite worked up and anxious about the quality of food that she eats, having often spent hours in the kitchen making a yummy dinner only for her to turn it away. As a result, I often purchased pouches and jars, as she appeared to enjoy these much more than my own home made food!!!
Before feeding Erin anything bought off the shelf I always tasted it first to make sure it tastes like ‘real’ food and as such have became quite fussy about which products I would buy.
As a big lover of M&S Food (and a massive fan of the dine in for 2!) I was really excited to learn that Marks and Spencer had launched their own new range of baby and toddler meals – M&S Tiny Taste Buds. A brand that I trust, we were really keen to check it out!
Table of Contents
About Tiny Taste BudsThe Tiny Taste Buds range provides healthy, balanced meals for each stage of your baby’s weaning which have been specifically tailored to the nutrition needs of your baby to support their growth and development.
Using only the highest quality organic ingredients, Tiny Taste Buds products use foods from each of the key food groups to help introduce new tastes and textures, with the aim of helping your child develop positive eating habits for the future.
All of the Range is categorised as Eat Well – made from 100% organic ingredients with no added sugar or additives and are low in salt.
The range is suitable for babies from 6 months as follows:
Stage 1 – from around 6 months – with a smooth texture for babies just beginning their weaning journey. These first tastes include flavours such as organic vegetable root medley, organic banana porridge, organic fruity mango dessert and organic pea, broccoli, and parsnip with pear. Portions are 120/130g pouches.
These first tastes include flavours such as organic vegetable root medley, organic banana porridge, organic fruity mango dessert and organic pea, broccoli, and parsnip with pear. Portions are 120/130g pouches.
Stage 2 – from 7 months and for babies who are more established with weaning, the stage 2 foods are gently mashed to introduce texture. These next stage flavours include organic creamy chicken and sweetcorn, organic super green veg and salmon with cheese sauce, and organic cottage pie with sweet potato. Portions are 130g pouches.
Stage 3 – from 10 months features tiny yummy chunks, to help develop tastes and encourage chewing. These meals include organic sweet potato and beef casserole with rice, organic mighty meat pasta, organic basil and tomato chicken with rice, organic Italian bean ragu. Portions are 190g pots.
Stage 4 – 12 months + is for babies/toddlers learning to feed themselves with bite size chunks to chew. These meals feature organic supergreen vegetable risotto, organic chunky vegetable and chicken casserole. Portions are 200g pots.
These meals feature organic supergreen vegetable risotto, organic chunky vegetable and chicken casserole. Portions are 200g pots.
Tiny Taste Buds also support Great Ormond Street one of the world’s leading children’s research hospitals with the broadest range of dedicated, children’s healthcare specialists under one roof in the UK. Marks and Spencer are generously donating £500,000 towards vital research to help children with nutrition and allergy related conditions.
Prices range from 99p to £1.99
Our ExperienceWe trialled the range of Stage 3 foods from Tiny Taste Buds with my daughter Erin who is 11 months at the time of testing.
The packaging is bright and appealing, with a cartoon image of a baby surrounded by vegetables on the front of the packet.
They stage 3 pots are small enough in size to be able to pop into a changing bag, so perfect for out on the go.
On reading the choice of recipes, the options sounded really appetising, with a good combination of foods combined in one dish. A lot of the baby foods on the market can be somewhat limited in their flavours, so it was good to see something a little bit different, or a slight twist on a more traditional dish.
A lot of the baby foods on the market can be somewhat limited in their flavours, so it was good to see something a little bit different, or a slight twist on a more traditional dish.
The meals can be warmed using the microwave (40 seconds on full power) or heated in hot water for 5 minutes. We don’t have a microwave at home, but it was very quick and simple to heat up the pot in a bowl, and I simply left on the side to heat up whilst getting Erin in her chair.
The texture of the food is just right for her age group – with small lumps that encourage chewing without chunks too large for her to handle. Erin still has a habit of spitting out larger squares of foods so the smaller size pieces was preferable! You can visually see the range of ingredients within the dish, and it smelled lovely, without the slightly synthetic smell that is sometimes prevalent in pre packaged baby food!
As for the taste test, both Erin and us as her parents gave the dishes a try, and my other half quite happily polished off the small amount that Erin had left – waste not want not! Lol
Her personal favourite was the organic mighty meat pasta, which is a little like a spaghetti bolognaise only with more substantial pasta pieces. At 190g per portion, she would generally eat around 3/4 of the dish, with a few finger food pieces alongside it. Erin does however have a reasonably small appetite, and therefore other babies may quite happily polish off the lot!
At 190g per portion, she would generally eat around 3/4 of the dish, with a few finger food pieces alongside it. Erin does however have a reasonably small appetite, and therefore other babies may quite happily polish off the lot!
Overall we were really impressed with the quality and flavours within the range of Tiny Taste Buds foods, and I would happily serve them to Erin again.
Pros:
- Great combination of flavours with organic ingredients and no added salt or sugar.
- Meals that we would happily enjoy ourselves
- Attractive design and packaging.
- Easy to prepare and serve, and can be eaten directly from the bowl, reducing the need for washing up!
- Perfect size to pop into your changing bag for feeding out and about.
- Supporting Great Ormond Street – a fantastic cause for children.
Cons:
- Depending on the size of your child’s appetite, some of the food may get wasted. Although the food can be kept refrigerated for 24 hours, this is only if its not been heated up.
 So unless you decant into another bowl and heat up a small amount a time, it could prove an expensive way to feed your child. For those with a more “normal” appetite or who don’t like to supplement their meals with finger food this shouldn’t be a problem.
So unless you decant into another bowl and heat up a small amount a time, it could prove an expensive way to feed your child. For those with a more “normal” appetite or who don’t like to supplement their meals with finger food this shouldn’t be a problem. - With prices starting at 99p (1.79 for stage 3 products), there are obviously some cheaper options on the market, however, for an occasional treat or meal for when out and about, I personally don’t mind paying a little extra for high quality organic ingredients.
You can learn more about the full range of M&S Tiny Taste Buds foods and their collaboration with Great Ormond Street on the M&S website here
Choosing a mixture - The First Izmailovo Clinic of Dr. Bandurina
The task of transferring an infant to artificial feeding is not an easy one, and therefore the approach must be serious. The most important points in this situation are considered to be:
- The right choice of infant formula.

- Learn how to administer it correctly by studying the feeding norms.
Choosing food for the baby
Everyone has long been accustomed to artificial feeding of children, since it has been used since ancient times, and given the modern pace of life, when a woman gave birth to a child, and after a month or two continues her work and career, it has become the norm. There were times and situations in life when parents simply did not have access to breast milk. Such an extremely important problem was solved in different ways. Everything depended on various factors, ranging from the well-being of the family, and ending with the achievements of scientific and technological progress in a given period of time.
So, the parents of babies got out of the situation with the lack of breast milk in different ways:
1. They resorted to the services of a breadwinner. Only wealthy parents could afford it. Sometimes neighbor babies were fed by women who had excess milk.
2. Replaced breast milk with other foods not suitable for small children due to digestion difficulties. For example, chewed bread, animal milk (cow, goat), etc. This was done in extreme cases or in very poor and large families.
Many are familiar with the legend that the founders of Rome were suckled by a she-wolf. But this beautiful story had a happy ending, which cannot be said about cases from real life. The result of feeding babies with animal milk was frequent deaths, various diseases of children. Because such milk is not very suitable for the child in terms of its constituent components, because of this it is poorly digested by the child's body.
But the problem of child feeding has always been relevant, and all the time new ways of feeding babies were invented and appeared. For example, milk began to be diluted with decoctions of cereals. Most often used rice water, oatmeal or buckwheat. Milk was made tastier with sugar and cream. A decoction of cereals gave milk nutrition and richness, and sugar added flavor. At the age of six months, children were boiled porridge in milk, grinding some cereals for this, for example, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal.
At the age of six months, children were boiled porridge in milk, grinding some cereals for this, for example, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal.
Invention and use of baby food as a substitute for breast milk
Humanity owes this to Henry Nestle, who in the 19th century invented powdered baby food, identical in composition to mother's milk. Five or six years later, such baby food was used to feed young children in seventeen countries around the world. This food was the founder of modern baby food, as we see it and know it now.
The success of the invention of Henry Nestle was stunning, but he did not stop repeating that at the first stage of life for the baby, the best food is mother's milk. Today, the World Health Organization uses this principle as a fundamental rule for the nutrition of newborns. Over time, the formula of baby food will improve and look more and more like mother's milk. Everything invented is immediately launched into production and in a short time appears on the shelves of specialized stores for children's goods.
Today, the buyer can choose from a selection of formulas for children from zero to twelve months of age among fifty types of food items. But here new problems and questions appear - how to make the right choice so as not to harm the health of the child, which brand to give preference to, which flavoring additives will not cause adverse reactions, and in general, is it possible to believe what the manufacturer indicates on the label or packaging of infant formula. After all, food should be not only healthy, but also tasty. Not so long ago, scientists agreed that infants develop a taste and preference for food very quickly, like an adult.
Basic rules for choosing baby food:
1. Consult a pediatrician. They should understand baby food and understand who, what is more suitable.
2. When choosing, take into account the age and physiological parameters of the baby. It is strictly forbidden to feed a child with food that does not suit him according to age criteria. For example, your baby is six months old, and the mixture is recommended for children from one year old. This can harm the health of the baby.
3. Carefully study everything that is written on the food box. If you have questions about the composition or anything else, seek help from a pediatrician or infant formula specialist.
Classification of breast milk substitutes for healthy babies
Baby food can be divided into three categories:
- These are formulas for babies in the first months of life and up to six months. First of all, they must be highly adapted and close in composition to mother's milk. They should not irritate the intestines, and it is very sensitive in babies during this period of life, and a complex of nutrients must also be present, since the mixture is the only source of all the nutrients for the child at the initial stage of life.
- This is a follow-up meal. Nutrition for children from six months to one year. The mixtures are designed taking into account the increased risk of intestinal infections.
They contain bifidobacteria. These bacteria have a beneficial effect on the formation of intestinal microflora, and, accordingly, high immunity.
- This food is for children of the age category 1-3 years old. The composition of such complementary foods is fully selected according to the needs of the child's body.
Mixing ingredients
All infant formula contains an adapted protein. To get it, manufacturers use cow's milk, sometimes goat's, but this is extremely rare. There is much more such protein in artificial nutrition than in mother's milk, and it puts a lot of stress on the kidneys. The protein can have a heterogeneous composition, which includes both casein and whey protein. Casein is very poorly digested by the baby's digestive system. Whey protein is more gentle and well accepted by the child's body. The amino acids of whey protein are identical to the amino acids of mother's milk.
In terms of numbers, the ratio of proteins and casein in the nutrition of the first degree is 60 to 40. These are very high figures. Nutrition of the second and third degree has different indicators, in which the protein gradually decreases, and casein increases. This is directly related to changes in the child's body associated with growth and development. The highest quality infant formula has a ratio of 70 to 30, no matter what grade the infant formula belongs to.
These are very high figures. Nutrition of the second and third degree has different indicators, in which the protein gradually decreases, and casein increases. This is directly related to changes in the child's body associated with growth and development. The highest quality infant formula has a ratio of 70 to 30, no matter what grade the infant formula belongs to.
Every meal contains fat. Their presence is very important, therefore, on the packages of most mixtures there is a table of fats. You should always pay attention to her. Cow's milk is identical to mother's milk in terms of the presence of fats, but these fats differ in their structural formula. Unsaturated fats are present in cow's milk, while polyunsaturated fats dominate in mother's milk. The difference is large and obvious. Children benefit more from unsaturated fats, so manufacturers use plant-based fats in baby food.
Fats are a source of energy, vitality, an indispensable building material - they are part of the cell membrane. Linolenic acid is the building block of the body's nervous system. For the proper development of the brain, organs of vision, arachidonic, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids are needed. They have a positive effect on the body's immune system. These acids are in the composition of mother's milk and are absent in the milk of animals, whether it be a cow or a goat.
Linolenic acid is the building block of the body's nervous system. For the proper development of the brain, organs of vision, arachidonic, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids are needed. They have a positive effect on the body's immune system. These acids are in the composition of mother's milk and are absent in the milk of animals, whether it be a cow or a goat.
How well infant formula will be tolerated depends on the amount of carbohydrates in it. Mom's milk is much sweeter and tastier than cow's milk. This is due to the lactose content. Lactose is a source of energy and a platform for the growth of bifidobacteria, which are necessary to support the baby's immune system. In order for lactose to be properly absorbed, special enzymes are needed. In their absence, the fermentation process begins in the intestines of the child, causing severe discomfort in the baby.
Many babies suffer from colic and pain in the tummy. In case of problems with the intestines, children's doctors, in addition to drugs, often prescribe fermented milk mixtures to children. They contain a high content of bifidobacteria, which contribute to the maintenance of the body's immune system. A healthy immune system is the key to a healthy baby. Also, bifidobacteria contribute to the good absorption of lactose, which is very important.
They contain a high content of bifidobacteria, which contribute to the maintenance of the body's immune system. A healthy immune system is the key to a healthy baby. Also, bifidobacteria contribute to the good absorption of lactose, which is very important.
Some infant formulas contain maltodextrin. It is more complex than lactose and other sugar-containing components, but at the same time it is more gentle for the intestines and does not cause fermentation processes, does not contribute to bloating and normalizes children's stools. Despite the multifunctionality, it is easily digested and has a sweetish aftertaste.
When choosing food for your baby, you should remember some things:
1. The sweetness of the food should be in moderation, especially for mixtures of the first degree.
2. A diet with lactose is better than a diet with regular sugar or glucose.
3. The presence of lactoalbumin is good for the baby. Lactoalbumin is a special category of protein. It helps to digest lactose, which means it promotes the growth of bifidobacteria, which, in turn, support the child's immunity.
It helps to digest lactose, which means it promotes the growth of bifidobacteria, which, in turn, support the child's immunity.
Benefits of trace elements and vitamins
It's no secret that animal milk is less fortified than mother's milk. Therefore, when developing artificial baby food, manufacturers enrich it with vitamins and microelements.
Baby food should give the baby all the necessary vitamins and other useful substances. Useful components include vitamins such as: A, E, K, PP, lecithin, biotin, choline. Among the necessary minerals: magnesium, iodine, zinc, selenium, copper, manganese, iron. The presence of vitamins and minerals should be balanced, according to the needs of the child's body.
There is a special table of the ratio of vitamin and minerals. For example, in order to absorb iron, you need vitamin C, and for the absorption of calcium, you need the right proportion of phosphorus. Calcium is very important in the development of the child's body, and calcium requires a certain amount of vitamin D, which is produced with the help of sunlight.
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to a disease called rickets. This disease is manifested by excessive sweating and general restlessness of the child, as well as underdevelopment of muscle tissue and abnormal development of bones in general. That is why any high-quality baby food contains the daily intake of vitamin D. The daily dose of vitamin D, according to the established standards of the World Health Organization, is four hundred units.
In addition to the vitamin and mineral complex, infant formulas contain essential components. This group of substances is necessary for the proper development and growth of the baby. Essential components enter the body only with food, they are not produced independently. A representative of essential substances is taurine, which is necessary for the development of the brain and vision. Especially the baby needs taurine in the first months of life. Proper metabolism needs L-carnitine. Nucleotides are required for the development of the nervous system. To provide antioxidant protection to the baby, selenium is needed, but not in excess, otherwise you can harm the baby. Organic selenium is used in high-quality baby food - it is more beneficial.
To provide antioxidant protection to the baby, selenium is needed, but not in excess, otherwise you can harm the baby. Organic selenium is used in high-quality baby food - it is more beneficial.
Another unfamiliar but important indicator is found in baby food. This is the osmolarity of the mixture. It determines the saturation of baby food with mineral and low molecular weight components. The osmality of infant formula should not exceed 280 mOsm/L. When the norm is exceeded, there is a load on the kidneys of the child.
Medical and special baby food
In addition to standard baby formulas, special and medical formulas are also produced. Special nutrition is intended for children with physiological characteristics. Physiological features are considered frequent regurgitation, colic and other concerns. Such food contains a special type of dietary fiber that promotes the digestion of food. Dietary fiber has a positive effect on the microflora of the stomach, eliminating colic and fermentation of food. Dietary fibers have the property of thickening the mixture, and carob gluten helps in this. Among other things, this diet contains beneficial nutrients.
Dietary fibers have the property of thickening the mixture, and carob gluten helps in this. Among other things, this diet contains beneficial nutrients.
For premature babies and children born with insufficient body weight, a separate nutrition line has been developed. These mixtures are more caloric, and the presence of protein and fat content is identical to that of mother's breast milk.
Partially hydrolysed nutrition is formulated to prevent allergic reactions. They are based on hydrolyzed proteins. Such nutrition is prescribed for babies who are at risk, but do not suffer from allergies and other irritations. Hydrolyzed proteins contribute to the development of tolerance, or rather, the processing of proteins. Highly hydrolyzed nutrition solves the problem of allergies in the baby. The usual protein in such baby food is replaced with soy, but this does not affect the quality of the mixture.
Feeding with special nutrition or therapeutic mixtures is permissible only with the appointment or recommendations of a children's doctor. In terms of taste, such nutrition differs significantly from standard mixtures and mother's milk.
In terms of taste, such nutrition differs significantly from standard mixtures and mother's milk.
There is also a line of formulas that is made for babies with intolerance to an amino acid called phenylalanine.
Babies with intestinal problems need to eat mixtures where there is no lactose or its low content.
No matter how technologies develop in the vector of production of infant formula, breast milk remains the best and most useful at a certain stage in a baby's life. This proven fact should not be neglected by any mother, because first of all you need to think and take care of the baby, and then about yourself.
Health programming and the role of nutrition in the formation of healthy lifestyle habits. XVIII Russian Congress "Innovative Technologies in Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery". Satellite symposium of JSC PROGRESS
At the symposium of JSC PROGRESS, dedicated to topical issues of forming healthy lifestyle habits in children, leading experts in the field of pediatrics and baby nutrition considered the main factors influencing the formation of healthy eating and sleep habits, discussed the quality and safety of baby food.
Professor, MD E.S. Keshishyan
Ph.D. E.A. Pyrieva
Professor, MD I.N. Zakharova
Child's sleep: from physiology to psychology
Head of the Scientific Department of Neonatology and Pathology of Young Children, Scientific Research Clinical Institute of Pediatrics named after V.I. Yu.E. Veltishcheva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elena Solomonovna KESHISHYAN, at the beginning of her speech, emphasized that in our country, sleep problems in a young child are one of the most common reasons parents turn to a pediatrician.
In the period from the first to the third (fourth) month of life, the child has not yet formed sleep receptors, but there is a change in excitation and inhibition of cells with a certain rhythm. Feeding, a feeling of satiety leads to inhibition of cells, the child falls asleep. However, in some cases, a clear change in the rhythm of "sleep - wakefulness" is disturbed. Children become restless, cry a lot. At this age, the nervous system is immature, and excitation works better than inhibition. Often, in a newborn, anxiety increases with the onset of evening or changes in weather conditions.
At this age, the nervous system is immature, and excitation works better than inhibition. Often, in a newborn, anxiety increases with the onset of evening or changes in weather conditions.
From the point of view of evidence-based medicine, there is no reason to assert that hypoxia, the method of delivery (caesarean section), the formation of intracranial blood flow, and liquorodynamic disorders affect the child's sleep rhythm disturbance. During the first months of life, sleep cycles are uneven in duration and depend on the individual characteristics of the child's nervous system.
From the fourth month, the period of wakefulness increases. The child continues adaptive processes, including the formation of sleep rhythms (biological clock). But it is at this time that due to intestinal colic, usually occurring at night, sleep becomes more restless. For children, the alternation of deep and superficial phases of sleep is typical. At this age, the regulation of the change in the work of cells begins. Differentiation of cells of excitation and inhibition occurs. Depending on which phase of sleep prevails - slow or fast, the child has problems falling asleep. He cannot sleep, bends over, screams, falls asleep, then wakes up again. In this case, there are no pathological symptoms. Difficulties in falling asleep may be associated with overexcitation from new impressions and information. In addition, the child, if he is not put to bed at the first sign of drowsiness, is very overworked and cannot fall asleep.
Differentiation of cells of excitation and inhibition occurs. Depending on which phase of sleep prevails - slow or fast, the child has problems falling asleep. He cannot sleep, bends over, screams, falls asleep, then wakes up again. In this case, there are no pathological symptoms. Difficulties in falling asleep may be associated with overexcitation from new impressions and information. In addition, the child, if he is not put to bed at the first sign of drowsiness, is very overworked and cannot fall asleep.
Parents are worried about the child waking up at night. From the point of view of physiology, these are also the consequences of the formation of relationships between the phases of sleep. Infrequent nocturnal awakenings are considered normal for infants and young children. In a child with a predominant superficial phase, as a result of an increase in brain activity, sleep becomes more sensitive, so any rustle can wake up a baby. Over time, the duration of sleep phases changes.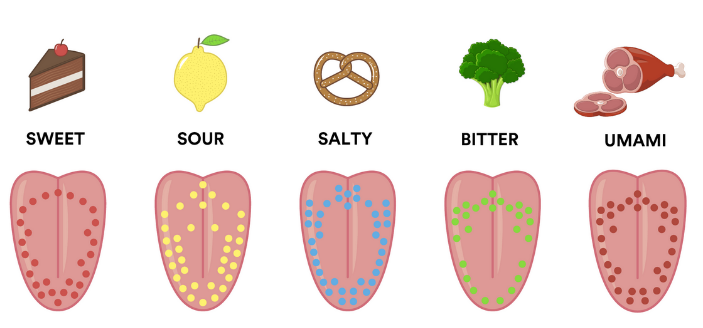 The period of fast sleep, accompanied by eye movements, decreases and the period of slow sleep increases, which is due to the ongoing maturation of the central nervous system. The gradual decrease in the need for sleep in children is associated with the characteristics of physical development. Often after six months of life, restless sleep, screaming in a dream, falling asleep in uncomfortable positions are noted.
The period of fast sleep, accompanied by eye movements, decreases and the period of slow sleep increases, which is due to the ongoing maturation of the central nervous system. The gradual decrease in the need for sleep in children is associated with the characteristics of physical development. Often after six months of life, restless sleep, screaming in a dream, falling asleep in uncomfortable positions are noted.
Undoubtedly, restless sleep significantly affects the normal growth and development of young children, and also reduces the quality of life of their parents. How can you help a family in such a situation?
Sleep disorders in children require special attention, as they affect physical and mental development and reduce the ability to learn. Today, the issues of pharmacotherapy of sleep disorders in childhood are practically not considered in international clinical guidelines and specialized literature. Some drugs are prohibited for use due to the high risk of side effects on the developing brain of a child. When organizing the sleep of a child under one year old, special attention should be paid to the formation of sleep rituals. Sleep problems arise when the regime is set incorrectly, when the time and place of bedtime vary from day to day. Preparations for bed should start at the same time and include a series of sequential activities that stimulate sleep every day: a relaxing bath, calm music, reading a fairy tale, putting down your favorite toy, a kiss goodnight.
When organizing the sleep of a child under one year old, special attention should be paid to the formation of sleep rituals. Sleep problems arise when the regime is set incorrectly, when the time and place of bedtime vary from day to day. Preparations for bed should start at the same time and include a series of sequential activities that stimulate sleep every day: a relaxing bath, calm music, reading a fairy tale, putting down your favorite toy, a kiss goodnight.
An important component of preparing for sleep in young children is breastfeeding, not only to satisfy the feeling of hunger, but also to achieve emotional comfort and tranquility. For artificially fed children, various night formulas of baby food have been developed. A wide selection of cereals of the FrutoNyanya line, intended for preventive and therapeutic nutrition, allows you to choose the best complementary foods for each child, including at bedtime. FrutoNyanya before bedtime cereals are available in packs of 200 and 500 ml and are intended for children older than six months. FrutoNyanya cereals are nutritious, milk and cereals included in their composition provide the baby with a long feeling of fullness.
FrutoNyanya cereals are nutritious, milk and cereals included in their composition provide the baby with a long feeling of fullness.
Summing up, Professor E.S. Keshishyan noted that the task of parents is to create a safe and sleep-friendly environment for the child, to form a reflex and the correct rhythm of sleep.
Foods for young children. Reboot 2.0
As the head of the laboratory of age-related nutrition of the Federal Research Center (FRC) of Nutrition and Biotechnology, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor Ekaterina Anatolyevna PYRYEVA, emphasized, rational nutrition of young children not only provides optimal growth parameters, development and prevention of alimentary-dependent diseases, but and forms the correct eating behavior throughout the subsequent life. Proper nutrition of children should contribute to maintaining health in the long term. According to the interdepartmental strategy for the formation of a healthy lifestyle of the population, the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases for the period up to 2025, it is necessary to ensure healthy nutrition from the earliest age stages.
On the basis of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "Federal Research Center for Nutrition and Biotechnology", an All-Russian interregional multicenter study of the state of nutrition at the age of six months to three years was conducted with the participation of 42 subjects of the Russian Federation. During the study, the nutrition of children of the first year of life and early age was evaluated. Early introduction of complementary foods (from three months) occurred only in 5% of the population, later - in 15%. More distant dates for the introduction of milk and fruit juices were registered in comparison with the previously existing practice. The average time for the introduction of milk as an independent product was 15.94 ± 7.6 months, fruit juice - 11.93 ± 8.3 months.
In 40% of the population, late introduction of dishes of complex consistency was observed. Indeed, many parents grind complementary foods to a puree state for a long time, not allowing the child to acquire chewing skills in a timely manner. In the first year of life, parents add sugar to complementary foods in 29% of cases, and salt in 41%. In most cases, vegetable and fruit purees are introduced as the first course of complementary foods.
In the first year of life, parents add sugar to complementary foods in 29% of cases, and salt in 41%. In most cases, vegetable and fruit purees are introduced as the first course of complementary foods.
The main problems begin after the child is transferred to a common table and he gets acquainted with such industrial food products as pastries, sweets, chocolate, pickles, smoked meats, fast food and carbonated drinks. Inadequate diet leads to excessive consumption of saturated fats, salt (more than half of the children's population of the Russian Federation), high consumption of added sugars (65% of children). In turn, there is a low consumption of milk and dairy products (38%), meat and poultry (18%), fish (74%) and vegetables and fruits (29–35%). This also negatively affects the organization of nutrition for children of preschool and school age, since taste habits are formed in the first years of life.
In this regard, it is necessary to constantly improve the principles of rational nutrition and promote their observance at all stages of a child's life. Optimizing the nutrition of young children should begin with following the recommendations of nutritionists. First of all, in children of the first year of life, the intake of sugar and salt with food should be controlled and their addition to complementary foods should be avoided. These requirements are reflected in the draft National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation 2019d. The use of industrial products that meet high quality and safety requirements has been confirmed.
Optimizing the nutrition of young children should begin with following the recommendations of nutritionists. First of all, in children of the first year of life, the intake of sugar and salt with food should be controlled and their addition to complementary foods should be avoided. These requirements are reflected in the draft National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation 2019d. The use of industrial products that meet high quality and safety requirements has been confirmed.
Currently, the following trends are observed in the production of food for young children:
- reduction in added sugars, salt;
- expansion of flavor diversity (new flavor combinations), use of food ingredients with functional properties;
- release of organic products;
- release of alternative products.
It should be noted that taste diversity at the early stages of a child's development serves as a prevention of eating disorders in subsequent periods of life 1 .
Over the past five years, there has been a 100% increase in the production of alternative products. These are products in a popular format that have useful qualities and contribute to the development of the right nutrition stereotypes: crackers, bars, grain and vegetable chips, etc.
Specialists of PROGRESS JSC have developed a sugar-free recipe for fruit, fruit-milk, fruit-cereal purees and desserts. In addition, the company produces cereals, fermented milk products (Biolact) without sugar, with the addition of prebiotic components.
It's no secret that most parents prefer sweeter-tasting foods for their children. In this aspect, programs to teach parents the principles of a healthy lifestyle, in particular a healthy diet, are of particular importance, and this applies to all family members.
In recent years, organic products have gained popularity all over the world. Its market in developed countries is rapidly growing and developing. Baby food is a product that requires special approaches to the quality of raw materials. This is primarily due to the physiological characteristics of early childhood: insufficient maturity of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) (high permeability of the intestinal wall, enzymatic immaturity), immune system, antioxidant protection, etc. During periods of active growth, the child's body is especially sensitive to adverse environmental factors .
This is primarily due to the physiological characteristics of early childhood: insufficient maturity of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) (high permeability of the intestinal wall, enzymatic immaturity), immune system, antioxidant protection, etc. During periods of active growth, the child's body is especially sensitive to adverse environmental factors .
Even small amounts of pesticides obtained from food adversely affect the health of young and young children. Pesticides have a negative impact on cognitive development, endocrine, immune, reproductive systems, and contribute to the development of atopic dermatitis. Russian legislation contains requirements for the quality and safety of baby food products, in particular with regard to the content of pesticides.
Studies of the practical aspects of the use of organic products in pediatric practice have shown the optimal tolerance of these products and a decrease in the frequency of atopic reactions. When eating organic products in children of the first two years of life, a lower incidence of atopic dermatitis was recorded 2 . Meanwhile, not everything is so simple. The evidence base of research on the undeniable benefits of organic products is insignificant. In addition, questions arise regarding the assessment of nutritional value. The content of nutrients in products depends on a number of factors: the geographical location of the area, climate and soil features, food supply, storage characteristics, and so on. No less important is the nutrient composition - the content of antioxidants (vitamins C, E, beta-carotene) and safety indicators (heavy metals, pesticides). Without a doubt, further research on the clinical effectiveness of organic products is required to promote them on the market.
Meanwhile, not everything is so simple. The evidence base of research on the undeniable benefits of organic products is insignificant. In addition, questions arise regarding the assessment of nutritional value. The content of nutrients in products depends on a number of factors: the geographical location of the area, climate and soil features, food supply, storage characteristics, and so on. No less important is the nutrient composition - the content of antioxidants (vitamins C, E, beta-carotene) and safety indicators (heavy metals, pesticides). Without a doubt, further research on the clinical effectiveness of organic products is required to promote them on the market.
In 2020, a law regulating the production of organic products will come into force in our country. The concept of organic products will appear in the law, the norms for the production, storage, transportation, labeling and sale of organic products will be regulated.
JSC PROGRESS, one of the first Russian manufacturers of baby food, brought domestically produced organic products to the Russian market. Under the FrutoNyanya brand, a line of organic fruit purees is produced, in the production of which only organic raw materials are used. The products are certified according to European standards and requirements for organic products. The PROGRESS company follows high quality and safety standards and uses only high-quality raw materials grown without the use of pesticides and GMOs for the production of baby food.
Under the FrutoNyanya brand, a line of organic fruit purees is produced, in the production of which only organic raw materials are used. The products are certified according to European standards and requirements for organic products. The PROGRESS company follows high quality and safety standards and uses only high-quality raw materials grown without the use of pesticides and GMOs for the production of baby food.
In addition, PROGRESS is actively introducing new types of baby food products. As an alternative to confectionery products for children over 12 months old, under the FrutoNyanya brand, natural sweets "Fruit Pieces" and "Fruit Octopussy" are produced from fruit and berry juice, puree, pectin, dietary fiber, without added sugar, preservatives and dyes. To ensure the taste diversity and convenience of consumers, the company is constantly expanding its range of products. Thus, ready-made vegetable cream soups and pates for children are sold under the FrutoNyanya brand.
The accumulated data show that in order to improve the effectiveness of children's nutrition, joint efforts of representatives of science, the nutrition industry and pediatric practice are required, as well as the improvement of the regulatory framework. Until recently, when organizing the nutrition of young children in Russia, they were guided by the National Program for Optimizing the Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life, adopted in 2011. In accordance with them, fruit juice, vegetable puree, porridge, from six months - meat, cottage cheese , yolk, and from eight months - non-adapted fermented milk products.
New domestic recommendations for the appointment of complementary foods were prepared in 2019. Now, vegetable puree and porridge are named as the first component of complementary foods, taking into account new knowledge about the role of carbohydrates in the formation of taste preferences. Familiarity with fruit juice, as well as with fermented dairy products, has been pushed back to eight months of life. The new document recommends not adding salt and sugar to complementary foods. “I would like to hope that this document will soon be approved at the legislative level and acquire the status of a regulatory document,” E.A. Pyrieva in conclusion.
The new document recommends not adding salt and sugar to complementary foods. “I would like to hope that this document will soon be approved at the legislative level and acquire the status of a regulatory document,” E.A. Pyrieva in conclusion.
The taste of a child: what it depends on and how to raise him
According to the head of the Department of Pediatrics of the Russian Medical Academy of Continuing Professional Education, Honored Doctor of Russia, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Irina Nikolaevna ZAKHAROVA, back in the 19th century. Physiologist Adolf Fick described four fundamental tastes - bitter, sweet, sour and salty. The sensation of sweet is created by sugars, glycerin, proteins, amino acids. The same taste bud detectors G-proteins are responsible for recognizing bitterness and sweetness. Bitterness is felt as a danger signal, as many bitter foods are toxic. The standard of bitterness is quinine. At 1980, the umami taste was identified, which is characteristic of foods with a high content of glutamic acid. "Umami" - the taste of glutamates and nucleotides (Parmesan and Roquefort cheeses, walnuts, broccoli, tomatoes). Scientists discovered L-glutamate receptors in the human tongue, after which they recognized “umami” as the fifth main taste, separating it from salty. Today, carriers of "umami" are food additives E600-E699.
"Umami" - the taste of glutamates and nucleotides (Parmesan and Roquefort cheeses, walnuts, broccoli, tomatoes). Scientists discovered L-glutamate receptors in the human tongue, after which they recognized “umami” as the fifth main taste, separating it from salty. Today, carriers of "umami" are food additives E600-E699.
In the East, one more taste is added - hot (red and black pepper, radish and mustard). But so far it has not been possible to find receptors that recognize this taste, so it is not classified as the main one. The tart (due to the astringent components of tannins), fatty, metallic taste of unclotting blood, the cooling taste of menthol, which affects cold receptors, are considered minor tastes.
The formation of taste involves taste receptor cells located on the mucous membrane of the tongue, soft palate, oropharynx, larynx and upper third of the esophagus. The "sensors" of pressure around the root of the teeth and taste buds are also important. In addition, taste buds are located in the stomach, intestines and pancreas.
The center of taste sensations is located in the postcentral gyrus and the islet of the cerebral cortex, the parahippocampal gyrus and the hippocampus.
As you know, the perception of shades of taste is inextricably linked with the olfactory system. Moreover, to feel the taste of any substance in the mouth, it needs 25 times more than for recognition by olfactory receptors. Each taste bud contains several dozen taste cells. Cilia located on their surface provide recognition, amplification and transformation of taste signals. Substances dissolved in saliva enter the taste bud, bind molecules dissolved in saliva, and trigger a cascade of biochemical reactions. The released neurotransmitter stimulates the taste nerve, and electrical impulses are sent to the brain.
It is believed that a molecule of a substance that causes a taste sensation can only bind to its receptor. If there is no receptor or it does not work, the substance will not cause any taste sensation.
Young children have more taste buds, a sharper taste, they are more picky about food. In older people, many taste buds die off, so food often seems bland to them. There is an effect of getting used to the taste - over time, the sharpness of sensation decreases. At the same time, addiction to sweet and salty develops faster than to bitter and sour. Bitter addiction increases the sensitivity to sour and salty, and sweet adaptation sharpens the perception of other tastes.
A person recognizes bitter, sweet taste and “umami” with the help of receptors discovered in 1999 belonging to the GPCR (G-protein-coupled receptors) family, coupled with G-proteins that are inside the cell and are excited when interacting with receptors. In addition to taste substances, GPCRs can recognize hormones, neurotransmitters, odorants, and pheromones.
Obviously, the formation of a child's taste habits is influenced by genetic factors, social and cultural traditions.
J. A. Menella et al. (2005) studied the amino acid sequence of the TAS2R38 gene. It has been established that human sensitivity to bitter taste is due to the difference in amino acids in the 49th position. A study involving 143 children showed that a third of children are homozygous for the amino acid alanine and are not sensitive to bitter taste, and 2/3 of the children are either heterozygous or homozygous for proline amino acid and highly sensitive to bitter taste 3 .
A. Menella et al. (2005) studied the amino acid sequence of the TAS2R38 gene. It has been established that human sensitivity to bitter taste is due to the difference in amino acids in the 49th position. A study involving 143 children showed that a third of children are homozygous for the amino acid alanine and are not sensitive to bitter taste, and 2/3 of the children are either heterozygous or homozygous for proline amino acid and highly sensitive to bitter taste 3 .
Thus, taste is a multimodal sensation. For its perception, the information brought together from taste and heat receptors, from mechanical sensors of teeth and chewing muscles, olfactory receptors must reach the central cerebral cortex, medulla oblongata, hypothalamus and reach the taste zone of the cerebral cortex.
The formation of the taste of the baby begins in utero, continues against the background of breast or artificial feeding and the introduction of complementary foods. The fetus learns to distinguish smells and tastes by swallowing up to 450 ml of amniotic fluid. During the study, pregnant women were offered candy with anise ten days before giving birth, and then the newborns were observed in the first four days of life. Children whose mothers ate anise sweets clearly distinguished this smell and turned their heads in its direction. According to other studies, the same effect is observed with garlic, carrots and alcohol.
During the study, pregnant women were offered candy with anise ten days before giving birth, and then the newborns were observed in the first four days of life. Children whose mothers ate anise sweets clearly distinguished this smell and turned their heads in its direction. According to other studies, the same effect is observed with garlic, carrots and alcohol.
Taste preferences depend on family food traditions, customs of the country in which a person grew up. Of course, people taste the same substance in different ways, and the threshold of taste sensitivity is different for different people. Sometimes it seems that a person himself chooses which food to prefer, in extreme cases, he eats what he was used to in childhood. But scientists are increasingly inclined to believe that genes make the choice for a person.
The nature of nutrition at an early age affects not only physical, but also emotional development. Without a doubt, breastfeeding of children in the first months of life is preferable to artificial, since it has a positive effect on the overall psychophysiological development, the development of taste preferences. Babies who are breastfed in the first months of life are better at eating fruit later on because the diet of breastfeeding mothers contains more fruit 4 . Children receiving hydrolyzate at the age of four or five are less active, less sociable and more shy than at the age of seven. Among children receiving a standard formula, a similar dependence is not observed 5 .
Babies who are breastfed in the first months of life are better at eating fruit later on because the diet of breastfeeding mothers contains more fruit 4 . Children receiving hydrolyzate at the age of four or five are less active, less sociable and more shy than at the age of seven. Among children receiving a standard formula, a similar dependence is not observed 5 .
Complementary foods play an important role in the formation of taste in children. Their diversity forms the correct eating behavior of the child. At the same time, food intake is influenced by factors such as appearance, smell, taste and texture. New complementary foods should be introduced gradually. Acceptance of a new taste usually requires 8–10 attempts to introduce a new dish, on average, acquaintance with a new taste occurs after 12–15 “meetings”. Parents should understand that the initial rejection of an unfamiliar dish is a common occurrence. The dish must be offered again. Often a “successful acquaintance” follows a refusal.
Professor I.N. Zakharova emphasized that the expansion of the child's diet should begin with monocomponent industrial products. The Russian company PROGRESS produces a wide range of complementary foods under the brand name FrutoNyanya. Complementary foods based on fruits and vegetables, meat and grains of the FrutoNyanya trademark, made from natural ingredients without the use of GMOs, dyes, flavors, preservatives, thickeners and sugar, are characterized by high quality, safety, good tolerance and hypoallergenicity.
Among the products of the FrutoNyanya line is fruit and cereal puree in a convenient soft pouch package. Puree is made from fruits (apple, peach, pear) and high quality cereals without the use of preservatives, dyes, artificial additives.
Fruit purees "FrutoNyanya" of the "Organic" product line are made from organic raw materials that have the appropriate certificates. In the production of organic raw materials, PROGRESS JSC strictly complies with clear requirements regarding the cultivation and production of environmentally friendly products. The soil is not treated with chemicals harmful to health before and after planting, only natural fertilizers and open soil are used, exclusively manual picking and sorting of ripe fruits. Raw materials intended for the production of baby food undergo a multi-level quality control system.
The soil is not treated with chemicals harmful to health before and after planting, only natural fertilizers and open soil are used, exclusively manual picking and sorting of ripe fruits. Raw materials intended for the production of baby food undergo a multi-level quality control system.
The FrutoNyanya line includes one-component meat purees (veal, beef, turkey, chicken, rabbit, lamb and pork), meat purees with offal. The composition of FrutoNyanya puree from beef with tongue includes beef, beef tongue, rice groats, vegetable oil, concentrated lemon juice, drinking water. Puree does not contain salt, preservatives, dyes, flavors and starch. Designed for children over eight months old.
In conclusion, Professor I.N. Zakharova emphasized that the right choice of foods introduced into the diet of young children as complementary foods not only ensures optimal growth and development, but also shapes the taste.
Conclusion
A wide selection of FrutoNyanya products (PROGRESS JSC) allows you to choose the best complementary foods for each child.