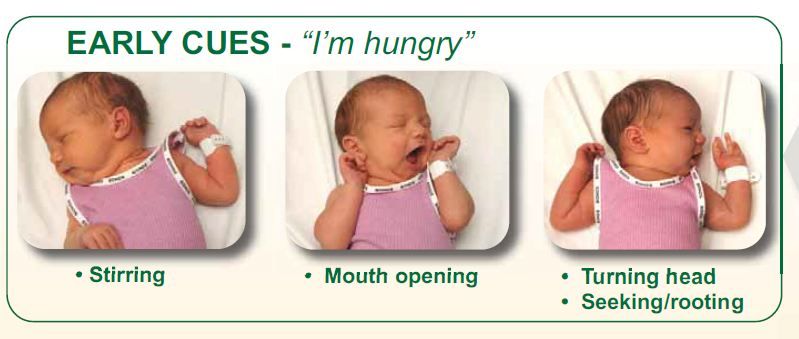
Things not to feed your baby
Foods to avoid giving babies and young children
Salt
Babies should not eat much salt, as it's not good for their kidneys.
Do not add salt to your baby's food or cooking water, and do not use stock cubes or gravy, as they're often high in salt.
Remember this when you're cooking for the family if you plan to give the same food to your baby.
Avoid salty foods like:
- bacon
- sausages
- chips with added salt
- crackers
- crisps
- ready meals
- takeaways
Sugar
Your baby does not need sugar.
By avoiding sugary snacks and drinks (including fruit juice and other fruit drinks), you'll help prevent tooth decay.
Saturated fat
Do not give your child too many foods that are high in saturated fat, such as crisps, biscuits and cakes.
Checking the nutrition labels can help you choose foods that are lower in saturated fat.
See more on food labels.
Honey
Occasionally, honey contains bacteria that can produce toxins in a baby's intestines, leading to infant botulism, which is a very serious illness.
Do not give your child honey until they're over 1 year old. Honey is a sugar, so avoiding it will also help prevent tooth decay.
Whole nuts and peanuts
Whole nuts and peanuts should not be given to children under 5 years old, as they can choke on them.
You can give your baby nuts and peanuts from around 6 months old, as long as they're crushed, ground or a smooth nut or peanut butter.
If there's a history of food allergies or other allergies in your family, talk to your GP or health visitor before introducing nuts and peanuts.
See more on food allergies in babies and young children.
Some cheeses
Cheese can form part of a healthy, balanced diet for babies and young children, and provides calcium, protein and vitamins.
Babies can eat pasteurised full-fat cheese from 6 months old. This includes hard cheeses, such as mild cheddar cheese, cottage cheese and cream cheese.
Babies and young children should not eat mould-ripened soft cheeses, such as brie or camembert, or ripened goats' milk cheese and soft blue-veined cheese, such as roquefort. There's a higher risk that these cheeses might carry a bacteria called listeria.
There's a higher risk that these cheeses might carry a bacteria called listeria.
Many cheeses are made from unpasteurised milk. It's better to avoid these because of the risk of listeria.
You can check labels on cheeses to make sure they're made from pasteurised milk.
But these cheeses can be used as part of a cooked recipe as listeria is killed by cooking. Baked brie, for example, is a safer option.
Raw and lightly cooked eggs
Babies can have eggs from around 6 months.
If the eggs are hens' eggs and they have a red lion stamped on them, or you see a red lion with the words "British Lion Quality" on the box, it's fine for your baby to have them raw (for example, in homemade mayonnaise) or lightly cooked.
Hens' eggs that do not have the red lion mark should be cooked until both the white and yolk are solid. So should duck, goose or quail eggs.
So should duck, goose or quail eggs.
Avoid raw eggs, including uncooked cake mixture, homemade ice creams, homemade mayonnaise, or desserts that contain uncooked egg that you cannot confirm are red lion stamped.
Rice drinks
Children under 5 years old should not have rice drinks as a substitute for breast milk or infant formula (or cows' milk after 1 year old) as they may contain too much arsenic.
Arsenic is found naturally in the environment and can find its way into our food and water.
Rice tends to take up more arsenic than other grains, but this does not mean that you or your baby cannot eat rice.
In the UK, there are maximum levels of inorganic arsenic allowed in rice and rice products, and even stricter levels are set for foods intended for young children.
Do not worry if your child has already had rice drinks. There's no immediate risk to them, but it's best to switch to a different kind of milk.
There's no immediate risk to them, but it's best to switch to a different kind of milk.
Raw jelly cubes
Raw jelly cubes can be a choking hazard for babies and young children.
If you're making jelly from raw jelly cubes, make sure you always follow the manufacturers' instructions.
Raw shellfish
Raw or lightly cooked shellfish, such as mussels, clams and oysters, can increase the risk of food poisoning, so it's best not to give it to babies.
Shark, swordfish and marlin
Do not give your baby shark, swordfish or marlin. The amount of mercury in these fish can affect the development of a baby's nervous system.
Further information
For more information and advice about babies and food, see:
- food allergies in babies and young children
- your baby's first solid foods
- baby and toddler meal ideas
Foods to Never Feed Your Baby (3 Months of Age to 1 Year)
According to the CDC, you can start introducing solid foods to your baby at around 6 months old. As long as they are receiving a balanced diet and a variety of nutrient-enriched foods, most vegetables, fruits, proteins, and grains. When it comes to more allergenic foods, it is best to introduce them after other baby-friendly foods. Always consult your pediatrician with concerns.
As long as they are receiving a balanced diet and a variety of nutrient-enriched foods, most vegetables, fruits, proteins, and grains. When it comes to more allergenic foods, it is best to introduce them after other baby-friendly foods. Always consult your pediatrician with concerns.
Growing babies soon start to show interest in trying new foods, and it's normal to want to introduce them to new tastes and textures. But not all foods are safe for your baby. Here is a list of foods you should avoid feeding your baby during the first year of growth.
More: Can You Eat Thanksgiving Turkey While Pregnant?
Pureed Foods vs Finger Foods
Babies are typically introduced to solid foods around six months of age. For newborns and babies less than six months old, solid foods may pose a choking hazard. So for young babies, many parents will turn to baby pureed foods. Pureed foods are softer than finger foods and easier on a baby’s digestive system. However, some parents turn to baby-led weaning which can also be a great option to introduce your little one to solid foods.
Honey
Infants under a year old should not be fed any form of honey (raw, baked, or cooked). Honey is bad for babies because it can harbor Clostridium botulinum, which can produce botulinum spores. These spores secrete toxins that can lead to muscle weakness, poor sucking, a weak cry, constipation, decreased muscle tone, and even paralysis in young infants. An infant's intestinal tract isn't strong enough to fight off these spores and toxins.
Infant botulism can be prevented by avoiding raw honey and avoiding contact with soil contaminated with the same C botulinum spores. This is rare and mostly found at agricultural sites in Utah, California, or Pennsylvania.
Cow's Milk
Stick to breast milk or formula until your child's first birthday. A child under the age of one can't digest the enzymes and proteins in cow's milk, and certain minerals in it can cause damage to your baby's kidneys. This is also true for certain dairy products such as cottage cheese. Also, unlike breast milk or formula, cow's milk doesn't provide all the proper nutrients for a growing infant. So if you are breastfeeding or if you are bottle feeding with breast milk or infant formula then keep doing so.
Also, unlike breast milk or formula, cow's milk doesn't provide all the proper nutrients for a growing infant. So if you are breastfeeding or if you are bottle feeding with breast milk or infant formula then keep doing so.
Egg Whites
Don't feed egg products to a child under the age of one, to avoid an allergic reaction or allergies in the future. While the proteins in egg yolks are seldom a source of allergens, the proteins in egg whites may cause allergic reactions. By the age of five, a child normally outgrows the potential for an allergic reaction to egg whites.
Citrus
Avoid feeding citrus fruits and juices to your baby for the first couple of months. These foods are high in Vitamin C and acid, which can cause an upset tummy and/or acid reflux in your baby. Remember, their digestive system is still developing.
Seafood/Shellfish
Another potential allergen for babies is seafood, and particularly shellfish. Talk to your pediatrician before feeding your baby boneless fish -- even tuna. Do not give any sort of shellfish (such as shrimp, clams, swordfish, mackerel, or crabmeat) to your baby until it's been discussed.
Do not give any sort of shellfish (such as shrimp, clams, swordfish, mackerel, or crabmeat) to your baby until it's been discussed.
Wheat
Due to allergens in wheat, it is best to wait until your baby is one, two, or even three years old before introducing it into your baby's diet. If you have checked with your pediatrician and are sure that your baby hasn't had an allergic reaction to rice, oats, or barley, you may try introducing wheat at the age of eight or nine months.
Large Chunks of Food
It is widely recommended that you feed your child breast milk or formula for the first four to six months. Once you start baby on solids, pea-sized foods are safest, to prevent choking. Make sure that vegetables are diced and cooked up soft, and cut fruits into quarters to avoid them getting stuck in your child's throat. Meats and cheese should also be cut into very small pieces or shredded.
Soft, Sticky Foods
While most soft foods are good for young babies, some soft foods should be avoided. Sticky foods like jellies and marshmallows should not be fed to a baby before six months as these foods can get stuck in a baby’s throat and block the child’s airway.
Sticky foods like jellies and marshmallows should not be fed to a baby before six months as these foods can get stuck in a baby’s throat and block the child’s airway.
Small, Hard Foods
Foods like whole nuts, popcorn, whole grapes, raw vegetables, raisins, candies, dried fruits, seeds, or any other small, hard food should not be given to a baby. They are all choking hazards and can easily become lodged in your baby's throat. Any food you give your baby should be diced into small bits and cooked until soft.
Fruits
Below is some insight on certain fruits that many parents have questions about feeding their baby.
- Strawberries and raspberries: Many berries are packed with vitamin C and are good for babies and young children. The American Academy of Pediatrics that you hold off introducing these fruits until after they have tried other solids first.
- Pineapple: Pineapple is considered a safe food for your baby to eat. However, it is a firm fruit and should be sliced into thin strips since it can be a choking hazard when cubed.
- Melon: Watermelon is a good example of a first fruit you can offer to your baby. It is soft, easy to chew, and full of vitamins. It is made up of mostly water so it is also great for hydration.
- Papaya: This is a superfood that is super healthy and great for your baby. The recommendation is to wait to introduce it to your little one until they are 7 or 8 months old.
Vegetables
Vegetables are healthy options for kids, but when is the right age for babies to start eating their veggies? Here is a list of veggies and produce that parents have questions about. You can find below whether or not they are safe to give to your baby.
- Spinach: Believe it or not, raw spinach is full of nitrates. This is not to be confused with synthetic nitrates but is still not good to give much to little ones. It is recommended that if you give them spinach, make sure it is cooked and pureed.
- Lettuce: This can be hard for your baby to chew, so it's best to wait until they are between 9 months and 1 year old.

- Peas: Green peas are a great starter food. They are easy to pick up, offer a new texture, are small enough to avoid choking and can be pureed.
- Onions: Many parents add cooked onions to homemade baby food. They are full of vitamin C and can be introduced between 6 and 8 months old.
- Garlic: If you cook frequently then you know that garlic can add a whole new flavor to certain foods. You can cook down and add a small amount to your baby's food between 6 and 8 months old.
- Sweet Potatoes: This is another great first solid. Soft, cooked sweet potato cut into chunks is perfect for a 6-month-old.
- Potatoes: These are considered starchy vegetables so even though they are safe to give to your baby, you will want to do it in moderation.
Meats
Introducing meat to your baby's diet can happen after starting solids, which is usually around 6 months. Poultry and lean beef are fine to give your little one in small amounts. Below are two types of meat that should be avoided.
Below are two types of meat that should be avoided.
- Hotdogs: Hotdogs are a choking hazard. It is not recommended to give them to young children under 4 years of age. When they are old enough, they can be thinly sliced or minced.
- Bacon: It is best to wait until after your baby's first birthday to give them any bacon. It is full of synthetic nitrates and possible carcinogens. It is generally considered unhealthy and should be offered rarely.
Fruit Juice
Most juices are full of added sugar. Since babies are generally still drinking from bottles under 1 year old, it is not advisable to put fruit juice in them. It is known to cause tooth decay. Offer your baby a little water after 6 months if you are looking to give them something besides breast milk or infant formula.
What About Peanut Butter?
Experts previously believed that introducing peanut butter or any sort of nut product at an early age could lead to nut allergies. Times have changed and many pediatricians encourage the introduction of peanut butter to children between 6 and 8 months after they have tried a few solid foods with no issues. The AAP recommends talking with your pediatrician about introducing nut products to your baby, once he is eating solid foods. If your baby doesn't have any food allergies or risk factors, your doctor will probably advise feeding him a thin layer of creamy (not chunky) peanut butter on a cracker or bread, or foods that have peanut butter in them. Never give whole peanuts or nut pieces to a child under age 4 because of the choking risk.
Times have changed and many pediatricians encourage the introduction of peanut butter to children between 6 and 8 months after they have tried a few solid foods with no issues. The AAP recommends talking with your pediatrician about introducing nut products to your baby, once he is eating solid foods. If your baby doesn't have any food allergies or risk factors, your doctor will probably advise feeding him a thin layer of creamy (not chunky) peanut butter on a cracker or bread, or foods that have peanut butter in them. Never give whole peanuts or nut pieces to a child under age 4 because of the choking risk.
If your child is at high risk for a peanut allergy or other food allergies (because of family history or if he has an existing food allergy or eczema), your doctor might recommend doing allergy testing before introducing nut products or feeding your child nut products at the doctor's office in case of an allergic reaction.
Breastfeeding Products | products for breastfeeding |
There are many baby care products, accessories and clothes on the market. But which ones are really necessary for breastfeeding? More on this in our helpful list.
But which ones are really necessary for breastfeeding? More on this in our helpful list.
Share this information
If you are planning to breastfeed, the right kit will make it so much easier. However, it is not so easy to understand which accessories are really needed for this, and which ones can be dispensed with. To help you, we have divided the whole breastfeeding period into several stages, as your needs are likely to change over time. In addition, we asked breastfeeding moms for tips and tricks on the most useful nursing accessories.
Breastfeeding supplies for the early days
The first few days after your baby is born can be stressful, so it's best to prepare ahead of time. Here are some things you're sure to need, whether you're staying in the hospital for a few days or heading straight home:
- nursing bras, nursing night bras and nursing tops;
- nursing nightgowns or pajamas;
- breastfeeding pillow;
- disposable or reusable bra pads;
- diapers;
- nipple remedy for dry skin and cracks;
- shapers* for flat or inverted nipples;
- book on breastfeeding;
- contacts of a lactation consultant, supervising doctor or hotline.

If you are having trouble breastfeeding, your lactation consultant or healthcare provider may recommend the following accessories:
- Nursing pads* if your baby cannot latch on or your nipples are sore. Do not use nursing pads for a long time. If you have any problems or pain, contact your lactation consultant or your healthcare provider.
- Breast pump** to relieve symptoms of breast swelling and/or stimulate milk production.
- Some mums like to use the cooling hydrogel pads* which provide relief in the first days after delivery, especially when milk begins to flow.
Nursing Tips
“Pillows help a lot to support your back, legs and arms. I also need bra pads in case of milk leaks, a nursing bra and loose tops for quick access to the breasts (I converted regular quality bras into nursing bras that better support the breasts). And we also used a sling all the time,” advises Zaria, a mother of two from South Africa.
“Hydrogel pads were my number one product. They were given to me in the first days of breastfeeding, so I never had sore or cracked nipples. I highly recommend hydrogel pads and buy them for anyone who plans to breastfeed,” shares her experience Camilla, a mother from Australia.
“You absolutely need someone to bring you something to drink. I kept forgetting to prepare myself a glass of water before feeding!” says Meg, mother of two from France.
Thermos to drink hot while sitting in bed. Delicious food and light snacks. My mother-in-law cooked me amazing beef stew and delicious pancakes (I had to eat well!). A pillow to put the baby on because I didn't have the strength to hold it. A comfortable chair, a nightlight for feeding at night and a pillow to sit on (I had stitches - not a pleasant feeling!) ”advises Felicia, a mother of two from the UK.
“A caring spouse, girlfriend or grandmother to bring tea and anything else you might need while you sit and feed. And also an e-book to read with one hand!” says Julie, a mom from Spain.
And also an e-book to read with one hand!” says Julie, a mom from Spain.
Initial Breastfeeding Supplies
You and your baby will likely get comfortable with breastfeeding in the first couple of weeks. Feeding will occur frequently and take a long time. Here are some tools that will make your life easier and make breastfeeding more comfortable as your milk production begins to stabilize:
- feeding chair;
- breastfeeding mobile application;
- disposable or reusable bra pads;
- breast milk collection pads*;
- Large stock of healthy snacks, drinks and ways to pass the time.
Sooner or later you will get bored with the comfort of home and want to start walking with your baby. For tips on breastfeeding outside the home, see our article on breastfeeding in public.
Tips for breastfeeding moms
“For me, the most useful things were breastfeeding bras, disposable bra pads and large diapers to wipe up leaking milk, cover the baby or cover the chest. With cracked nipples, I saved myself with lanolin cream, and loose tops and cardigans made the feeding process easier, ”says Tatiana, mother of three children from Switzerland.
With cracked nipples, I saved myself with lanolin cream, and loose tops and cardigans made the feeding process easier, ”says Tatiana, mother of three children from Switzerland.
“I find the most useful accessory to be a good quality U-shaped breastfeeding pillow. I also had a rocking chair, in which, at a certain inclination, it was very convenient for me to feed the child. To relax, I always listened to music,” says Violeta, a mother from Romania.
“A sports water bottle that doesn't leak, even when open, so you can put it next to you on a sofa or bed. And also an application to track feedings and remind me which breast I fed last time, ”says Francesca, a mother from the UK.
“Breast milk collection pads that are placed inside a bra to collect leaking milk. I had an overabundance of milk, that was the only way I was saved, ”says Lisa-Maria, a mother of two from Switzerland.
“I really liked the D-ring feeding cover to cover my baby and not distract him when feeding outside the house. The slightly rocking chair turned out to be a great alternative to outrageously expensive rocking chairs. Reusable bra pads, in my opinion, perfectly absorb milk, and diapers, as it turns out, can be used in a thousand ways. I regret that I didn’t buy the Medela Easy Expression bustier, it would have been much easier to pump with it!” says Camilla, a mother from Australia.
The slightly rocking chair turned out to be a great alternative to outrageously expensive rocking chairs. Reusable bra pads, in my opinion, perfectly absorb milk, and diapers, as it turns out, can be used in a thousand ways. I regret that I didn’t buy the Medela Easy Expression bustier, it would have been much easier to pump with it!” says Camilla, a mother from Australia.
Breastfeeding accessories for pumping
During breastfeeding, you may need a breast pump to express your milk. The right type of breast pump depends on the individual case and how much milk you want to get. If you plan to express milk regularly, you may also need:
- steam sterilizer, cold water sterilizer, or microwave sterilization bags;
- breast milk storage bags;
- bustier top for hands-free pumping;
- cool bag.
Advice for breastfeeding moms
“At first, when I thought my breasts were about to explode, I used the Medela Electronic Breast Pump** just to get rid of excess milk without overstimulating my breasts. He made my life a lot easier,” says Tatiana, a mother of three from Switzerland.
He made my life a lot easier,” says Tatiana, a mother of three from Switzerland.
“I used a Medela Freestyle Dual Electronic Breastpump** to increase my milk supply and fixed it with an Easy Expression bustier to keep my hands free. It turned out to be a wonderful decision,” says Amy, a mother from the UK.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RC No. FZ 2010/07352 dated 07/19/2010
** RC No. FZ 2010/06525 dated 03/17/2021
Breastfeeding in public places | Tips for breastfeeding moms
Open breastfeeding in public takes some getting used to. Here are some tips to help you and your baby feel more confident
Share this information
The beauty of breastfeeding is that everything you need is always at your fingertips: you can feed your baby wherever you are, and the milk temperature will always be just right. But while there's nothing more natural than breastfeeding, the very idea of breastfeeding in front of everyone, especially the first time, can be a little unsettling. Whether you are worried about what others will think or not, our tips will help you prepare for this event.
Whether you are worried about what others will think or not, our tips will help you prepare for this event.
1: Rehearse
If you are embarrassed by the prospect of breastfeeding your baby for the first time in a public place, practice in front of a mirror at home to imagine how you will look from the outside. You will surely notice that the chest is not so open at the same time: it is blocked by the head of the child.
First, try breastfeeding in public in a friendly environment. In the company of other mothers or in a cafe with a friend, you will obviously be more comfortable than alone in the train or in a noisy shopping center.
2: Dress comfortably
When it comes to comfortable clothing for breastfeeding in general and in public places in particular, there are many options. If breastfeeding is going well and you intend to continue, it's worth picking up a few pieces of nursing clothing that will make feeding easier.
“I had a very comfortable nursing shirt. It was possible to discreetly feed the child in it even in winter, since nothing had to be removed. Just put the baby on the slit in the T-shirt and you're done. You can feed anywhere and anytime!” says Caroline, mother of two from France.
It was possible to discreetly feed the child in it even in winter, since nothing had to be removed. Just put the baby on the slit in the T-shirt and you're done. You can feed anywhere and anytime!” says Caroline, mother of two from France.
However, it is not necessary to buy special nursing clothes - you can just wear two regular T-shirts. “I solved the problem with a stretch blouse that I wore under a loose top. When it was necessary to feed the child, I pulled the jacket under my chest and lifted the top. He covered my chest, and the jacket - my stomach. So it was possible to feed discreetly anywhere, while not freezing and not showing anyone your tummy that sagged after childbirth,” recalls Suzanne, a mother of two children from the UK.
Other handy options are tops and dresses with buttons or front zips, with straps or side slits. You can also try wraparound styles, collar collars or shawl collars.
“Wrap-around cardigans have been a lifesaver when I have to feed in public,” says Natalie, a UK mom. - I just untied one floor and covered my baby's head with it during feeding or when she cried. And you didn’t have to carry anything with you to disguise.”
- I just untied one floor and covered my baby's head with it during feeding or when she cried. And you didn’t have to carry anything with you to disguise.”
3: Know your surroundings
Before you go anywhere with your baby, make a list of good feeding places in advance so you don't have to rush around looking for them at the last minute. Shopping malls, department stores and children's clothing stores often have mother and baby rooms where you can feed your baby in peace and quiet, sitting on a comfortable chair, or use the changing table. Many cafes and hotel restaurants also try to create comfortable conditions for nursing mothers.
“If you're worried, look ahead for breastfeeding friendly places so you know where to go if you need to. Feeding in public can be difficult at first, but over time it gets better and better. And then you do it so quickly and imperceptibly that people around you don’t even realize that you are breastfeeding a baby, ”says Rachel, a mother from the Maldives.
Other potentially suitable locations are fitting rooms in department stores, furniture stores, community centers, libraries, museums, and parks. Ask around moms you know - they can probably share their experience about suitable feeding places nearby.
“In the UAE, children under the age of two are legally allowed to breastfeed. Breastfeeding is highly encouraged here, shopping malls have dedicated facilities for breastfeeding, and mothers who breastfeed in public places like restaurants are treated with respect,” says Fay, mother of two from the UAE.
4: Try a breastfeeding cape
Some moms prefer to cover themselves and their baby with a cape when breastfeeding in public. The choice here is huge - from simple shawls and ponchos to special capes and aprons with a rigid semicircular hole on top, which allows you to watch the baby during feeding. There is a solution for every taste. And you can also feed your baby in a sling or carrier - this is both convenient and shelters you from prying eyes.
“I recommend buying a carrier,” says Caroline, mother of two in the US. “With a little practice, you can feed on the go, without looking up from other things.”
However, the last word often rests with the baby. Some babies do not tolerate any capes when feeding, and someone, on the contrary, is distracted if he is not covered. “Both of my babies didn’t like it when I tried to cover them with a shawl during feeding, so I just had to rely on their heads to cover their breasts enough,” recalls Esther, mother of two from the UK.
5: Know your rights
Breastfeeding in all public places is legal in many countries. Moreover, there are laws aimed at protecting breastfeeding mothers. If you are not sure if there are such laws in your country, search the Internet for information. The best place to start is with the websites of government and health agencies. Or try asking your doctor. You can also ask familiar mothers, friends and relatives about their own experiences. The answers may surprise you.
The answers may surprise you.
"Breastfeeding is widely accepted in Australia, and it's quite normal to sit bare-chested in a cafe while a nice waiter takes your order for a fat-free latte!" says Amy, mother of two from Australia.
If someone is upset that you are breastfeeding your baby in a public place, politely remind them of your rights. If you believe that asking you not to breastfeed in a store, cafe, or similar establishment violates your rights, you can file a formal complaint—if you are willing and supported by local law.
“One day I decided to breastfeed my baby in a diner after I had eaten myself, and I did it right at the table because they didn't have a feeding room. A confused junior manager was sent to me asking if I could move to the women's room for this. I replied that no - do they eat there? Then I was asked to move to a side booth. But I refused here and didn’t budge until we were done!” recalls Maya, a mother of two from Spain.
“My advice is don't worry! I was worried at first, but I regularly had to breastfeed my baby in public places, both in the city and in the countryside.