Wegmans baby food
EWG's Food Scores | Wegmans Baby Spinach
EWG Overall Score Breakdown
The product score is based on weighted scores for nutrition, ingredient and processing concerns. Generally, nutrition counts most, ingredient concerns next and degree of processing least. The weighted scores are added together to determine the final score.
Lower concern
Higher concern
Lower concern
Higher concern
Read our full methodology
Considers calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, sodium, protein, fiber and fruit, vegetable and nut content to differentiate between healthful and less healthful foods. For more information on nutrition concerns, read our full methodology.
Good source of naturally occurring iron []
Contains fruit, vegetables, beans or nuts as a primary ingredient []
The nutrition factors used for scoring Wegmans Baby Spinach
Positive factors
Fruit, vegetable, bean or nut content
Protein content
Fiber content
Omega-3 fatty acids
Negative factors
Calorie density
Sugar/low-calorie sweetener content
Sodium content
Saturated fat content
Trans fat content
Considers food additives, pesticides, hormones, antibiotics and contaminants like mercury and BPA, which can affect human health and the environment. For more information on ingredient concerns, read methodology.
On EWG's Dirty Dozen list for pesticide residues []
This product has some contamination concerns:
- Pesticide Residues from Spinach
This contaminant is of moderate concern in food. Learn why.
Estimates how much the food has been processed. Considers many factors, chief among them, modification of individual ingredients from whole foods and number of artificial ingredients. For more information on processing concerns, read our full methodology.
Product has been classified as having no processing concerns
Products with no processing concerns identified are generally whole foods without additives.
Please note that EWG obtains the displayed images of products from third parties and that the product's manufacturer or packager may change the product's packaging at any point in time. Therefore, EWG assumes no responsibility for the accuracy of images presented.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nutrition Facts for Wegmans Baby Spinach • MyFoodDiary®
WegmansBaby Spinach
Fresh
Nutrition Facts
Serving Size 2 cups = 85g
Amount Per Serving
20
Calories
% Daily Value*
0%
Total Fat 0g
0% Saturated Fat 0g
Trans Fat 0g
0%
Cholesterol 0mg
3%
Sodium 70mg
1%
Total Carbohydrate 3g
7%
Dietary Fiber 2g
Total Sugars 0g
0%
Includes 0g Added Sugars
Protein 3g
0% Vitamin D 0mcg
6% Calcium 80mg
10%
Iron 1. 8mg
8mg
10% Potassium 470mg
31% Vitamin A 275mcg
27% Vitamin C 24mg
*
The % Daily Value (DV) tells you how much a nutrient in a serving of food contributes to a daily diet. 2,000 calories a day is used for general nutrition advice.
1 Net Carbs Per Serving
Add to Food Diary
Burn 20 Calories
3.7 minutes Walking at 17 min/mile
150-pound adult. No incline or extra weight carried.
Burn 20 Calories
3 minutes Weight training
150-pound adult. Moderate effort.
Burn 20 Calories
1.4 minutes Cycling at 18 mph
150-pound adult. No significant wind or incline.
Burn 20 Calories
1.1 minutes Running stairs
150-pound adult. Moderate pace.
Burn 20 Calories
1.7 minutes Running at 10 min/mile
150-pound adult. No incline.
No incline.
Previous Next
Top Wegmans Items
| WegmansWatermelon 2 cups | |
| WegmansRoasted Brussels Sprouts 4 oz | |
| WegmansRoasted Cauliflower 4 oz | |
| WegmansRoasted Potatoes w/ Garlic & Rosemary 4 oz | |
| WegmansPeachRaw 1 medium | |
| WegmansBlueberriesRaw 1 cup | |
| WegmansRoasted Baby Potatoes 4 oz | |
| WegmansAhi Tuna Sashimi StyleRaw 4 oz | |
| WegmansRoasted Butternut Squash 4 oz |
Not Signed In
You must be logged into your account in order to add items to your food diary.
Sign In
or
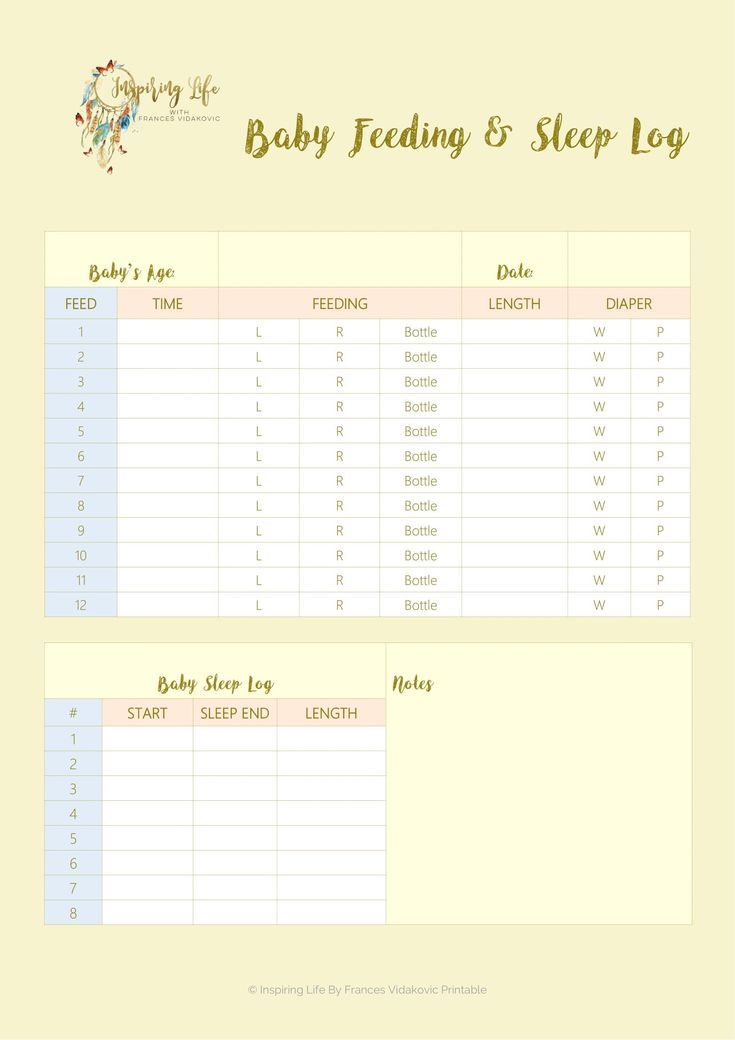
Rings. baby food or not?, - 12053
In the list by which the development of the child is determined, there is such an item - “development of fine motor skills”. Having read and watched foreign videos on how to develop fine motor skills, we got down to business. Following the recommendations of foreign pediatricians, they learned to take and eat with their hands special rings (for children under one year old). These rings are so arranged that once in the mouth they instantly become soft and the child cannot choke on them. The result was on the face. The neuropathologist who came to us for an examination (at 8-9months), was pleasantly surprised by our success. He said that motor skills are developed, well, just very well, not for his age. But then a problem arose - where to get these rings themselves. The strategic reserves brought from abroad were coming to an end, and I rushed to look for something similar in the domestic market. Here is what I found
Here is what I found
Composition 1 (domestic manufacturer) Glazed rings of 4 types Start TU U15.6-00378537-004:2006. "Snidanki dry grains" Ingredients: corn groats, oatmeal, sugar, wheat flour, rice groats, invert syrup, natural honey, palm oil, salt, barley malt, lecithin, corn oil, baking soda, flavor identical to natural "honey"
Vitamins: A, D3, E, B1,2,6,12,9 (folic acid), 5 (pantothenic acid), PP, C, biotin
Minerals: Zinc, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, selenium.
Nowhere is it indicated - for baby food or not. The phone of the manufacturer does not answer, only a fax.
Composition 2 (domestic manufacturer) Corns, fruit rings TU U15.6-00378537-004:2006. "Snidanki dry grains"
Ingredients: corn grits, sugar, wheat, wheat flour, salt, baking soda, natural dye "carmine", natural identical flavor "strawberry"
Vitamins: B1,2, PP Minerals: no
But the compositions of foreign production
Composition 3 (for children under one year old) Gerber. Graduates puffs (www.gerber.com) Rice flour, wheat flour, wheat starch, sugar, oatmeal, dried peach puree, di- and tri-calcium phosphate, peach juice concentrate, natural peach and vanilla flavors, lecithin, mixed tocopherols (for freshness when stored), annatto extract for color. What is annatto (annatto), I did not understand, judging by the context, perhaps some kind of plant. Can someone tell me
Graduates puffs (www.gerber.com) Rice flour, wheat flour, wheat starch, sugar, oatmeal, dried peach puree, di- and tri-calcium phosphate, peach juice concentrate, natural peach and vanilla flavors, lecithin, mixed tocopherols (for freshness when stored), annatto extract for color. What is annatto (annatto), I did not understand, judging by the context, perhaps some kind of plant. Can someone tell me
Vitamins: E Minerals: calcium, iron, zinc.
Composition 4 (after a year) Multi-grain toasted cereal, Wegmans Barley flour without hulls, oatmeal, wheat flour, corn flour, malt sugar, rice flour, sugar, calcium diphosphate, salt, calcium carbonate, sunflower oil, caramel color , trisodium phosphate, annatto extract (for color), mixed tocopherols (for storage freshness). Vitamins: A, C, D, E, thiamine, riboflavin, niacin (PP), B6, 12, 9, 5, Minerals: calcium, iron, zinc, phosphorus
Now let's analyze the following compositions: Unlike foreign rings intended for baby food for children up to a year (composition 3) and after (composition 4), our rings contain artificial flavors (identical to natural) and one of the samples (composition 2) is a dye . Composition according to the content of cereals, salt, soda, etc. practically does not differ. There are only minor nuances. There are practically no vitamins in Gerber for children under one year old (probably calculated according to the daily dose, taking into account the fact that the child consumes vitamins with breast milk or an adapted mixture). In imported rings for children after a year (composition 4), the amount of vitamins increases, which is probably right, since children, as a rule, are no longer breast-fed or formula-fed.
Composition according to the content of cereals, salt, soda, etc. practically does not differ. There are only minor nuances. There are practically no vitamins in Gerber for children under one year old (probably calculated according to the daily dose, taking into account the fact that the child consumes vitamins with breast milk or an adapted mixture). In imported rings for children after a year (composition 4), the amount of vitamins increases, which is probably right, since children, as a rule, are no longer breast-fed or formula-fed.
In search of a description of TU U15.6-00378537-004:2006. "Snidanki dry grains" found that the products of this manufacturer do not contain GMOs. It pleases, if, of course, the truth!
http://www.stand.lutsk.ua/downloads/GMO/results_03.11.pdf position 37. I did not find a description of the TU itself, but I really wanted to read what this product is intended for. I will search further. If I find it, I'll post it here. But I found an interesting site where you can see the composition of many products http://epipoka. inf.ua/
inf.ua/
In addition, I found that another similar product was produced according to the same TU
RINGS "JUMP" 4 CEREAL Producer: OAO "Cerealia Foods", Ukraine. Jump rings 4 cereals Ingredients: corn grits, sugar, oatmeal, rice grits, semolina, salt, soda. Please note there are no additives! But this product, despite the fact that it was produced in Ukraine, was not found on our shelves (including the Internet). It turned out that OJSC "Cerealia Foods" is a Swedish company that produces in Ukraine, but sells only in Russia, since the owner of the trademark is a Russian citizen.
http://www.pr-info.ru/Apressclip102009.html It's a shame!
Thus, I draw the following conclusions: children under one year old should not be given rings from our counters. After a year you can start, but not very often. We really like these rings. We even have special containers - non-spill cups with silicone petals so that you can eat "on the go" and not sow all over the apartment
With the right of parents and having information, you can make your choice
If someone tells me similar rings with a "normal" composition that can be bought in Ukraine, I will be grateful
Impossible Foods: the history of the artificial meat manufacturer
Contents The Vision of Impossible Foods
We live in an age of plant-based meat. This market is expected to be worth $85 billion by 2030.
This market is expected to be worth $85 billion by 2030.
If the trend continues, conventional meat consumption will fall by 33% by 2040.
Now Impossible Foods burger is indistinguishable from meat: it is just as juicy and tasty and sizzles in the pan. But its production requires 96% less land and 87% less water, while creating 89% less carbon emissions.
Impossible Foods products are already available at Walmart, Lidl and Burger King. If earlier alternative meat was a curiosity, now it is becoming one of the basic components of the menu. As of the beginning of 2020, plant-based alternatives accounted for only 2% of packaged meat retail sales, but their share is growing, also due to the pandemic.
Meat supply disruptions, rising prices, and consumer fears that beef and chicken can spread disease are the cause.
In an interview with the Wall Street Journal, Impossible Foods CEO Pat Brown said that for conventional meat consumers, now is the perfect time to try something new.
In the summer of 2020, Impossible Foods has added a new product - Impossible Sausage. Now there are plans to enter the market of alternative dairy products. Unlike other herbal counterparts, Impossible milk will completely imitate cow's milk.
In early 2021, the company announced that it was studying the baby food market and conducting test launches in American schools.
America's Meat Trouble
Impossible Foods CEO and Founder Pat Brown was a professor at Stanford University and is known as a pioneer in the field of genetic mapping. However, his ambitions were greater. In 2009, he went into the Sabbatical for 18 months. His goal was to understand how to change the meat industry - in his view, it represents the most serious threat to the environment.
13-18% of greenhouse gas emissions come from livestock, and a third of the world's land is allocated for their cultivation. Livestock also contribute significantly to deforestation, soil erosion, biodiversity loss, and pollution through sewage and fertilizers.
By the end of his sabbatical, Brown came to the conclusion that people would never give up meat solely for the sake of nature. The only way to reduce its use would be the free market. And for this it was necessary to create an analogue of meat based on plants.
Alternative meats
Veggie burgers have been on store shelves since the 1990s. However, they were positioned as a product for vegetarians. Impossible Foods never aimed to reach an audience that had already given up meat.
In 2019, Impossible Foods CEO Brown stated, “The only consumer we care about is the die-hard meat eater.”
The main problem is that a person depends on meat. We are genetically attracted to protein and fat calories. So right after Brown formally founded Impossible Foods in 2011 and raised $3 million in a seed round, he began biochemical research to understand what meat tastes like.
Researchers have come to the conclusion that it's all about blood, or more specifically, an iron-containing molecule called heme. It took the first year to develop non-meat heme (based on yeast that produces heme during fermentation). Thanks to this, Impossible Foods received another $75 million to create a burger.
It took the first year to develop non-meat heme (based on yeast that produces heme during fermentation). Thanks to this, Impossible Foods received another $75 million to create a burger.
During tests, more than 1,500 consumers could not distinguish between an alternative product and a meat product. The scientists themselves conduct "a minimum of 100 internal" tastings a week to control the quality of the product.
From Silicon Valley to Burger King
The Impossible Burger was born in 2016 after five years of research and hundreds of iterations. The final version consists of soy and potato protein, fermented yeast based heme, sunflower and coconut oils, methylcellulose (often used in jam and ice cream) as a binder, and food starch (a common ingredient in canned soups).
The company primarily targets gourmets, chefs and celebrities. Investments from Jay-Z and Serena Williams caused a stir. The first establishment to feature Impossible Burger on the menu was Nishi, David Chang's New York-based Italian restaurant.
The name of the famous chef and founder of the Momofuku network could not fail to attract attention. Now the media was talking about plant-based burgers with the "Approved by David Chung" label.
In 2018, Impossible Burger appeared in chain restaurants such as Applebees, Cheesecake Factory and Hard Rock Cafe.
According to Nielsen and the Good Food Institute, from 2016 to 2017 only. plant-based meat sales rose 8.1%.
Trust in alternative burgers grew. They first appeared on the menus of niche chains such as Umami Burger and Bare Burger. In April 2018, they finally hit the mass market through the White Castle chain. Deals followed with Little Caesars, Qdoba, Red Robin, Little Caesars and Disney Parks, and by early 2019In 2018, a large-scale campaign was launched in partnership with Burger King - Impossible Whopper.
2019 hamburger shortage
Impossible Foods had 25 employees at launch and 125 by the end of 2017. But that wasn't enough to keep up with the demand. To triple production, the team worked 12 hour shifts.
But that wasn't enough to keep up with the demand. To triple production, the team worked 12 hour shifts.
The shortage ended when the company began to cooperate with a large manufacturer. It looks like it paid off: during the pandemic, Impossible Foods did not face a shortage of products
In a way, the limited supply story was actually helpful. She has demonstrated customer loyalty. The owners of Ruby's in New York recall that diners could stop by for an Impossible Burger and refuse to dine if only Beyond Food was available.
Retail entry
By September 2019, Impossible Foods had overcome the supply disruption and began shipping its raw food to retail stores for customers to cook at home.
Meat alternatives appeared in 27 Gelson's supermarkets in Southern California, followed a week later by Wegmans and Fairway Markets on the US East Coast. In the following years, burgers were already on the shelves of Walmart, Krogers, Safeway and other major US chains.
Text photo: Steve Heap / Shutterstock
The company now has almost 600 employees. Impossible Foods convenience foods are sold in 8,000 grocery stores and nearly 20,000 restaurants in the US, Hong Kong, Macau and Singapore.
In January 2021, the company announced the launch of its own online store on the Goldbelly platform.
The terms 'steak', 'sausage' and 'burger'
Correct naming is one of the key challenges that alternative food brands must solve. In 2018, the US Cattlemen's Association asked the US Department of Agriculture to clarify the definitions of the terms "meat" and "beef" so that plant-based producers cannot use them as names.
While this issue remains a matter of debate in the US, the European Parliament recently confirmed the right to use the names 'steak', 'sausage' and 'burger' for plant-based alternatives.
To promote their interests, the big meat companies turned to the infamous lobbyist Richard Berman. He bought entire pages in the New York Times, the Wall Street Journal, the New York Post, and the Chicago Tribune to run ads critical of plant-based meats. During Super Bowl 2019years broadcast a video with children who can hardly spell the names of various ingredients. One of them was methylcellulose, a flavorless thickener that is used in canned food and is certified harmless.
He bought entire pages in the New York Times, the Wall Street Journal, the New York Post, and the Chicago Tribune to run ads critical of plant-based meats. During Super Bowl 2019years broadcast a video with children who can hardly spell the names of various ingredients. One of them was methylcellulose, a flavorless thickener that is used in canned food and is certified harmless.
In response, Impossible Foods ran a parody video in which children said the word "turd". This was a reference to studies that found the presence of feces in beef products.
At the same time, Impossible Foods faces serious competition from forward-thinking meat producers who are trying to add plant-based alternatives to their range. Tyson, Smithfield, Nestle and Perdue already make these products and place them alongside chicken wings and ground beef.
Some environmentalists believe that the food system should be simplified, not complicated. For example, nutritionist Diana Rogers draws attention to the long list of ingredients in Impossible Foods and calls their activity greenwashing.
"Beyond Burger and all meat substitutes are just another version of food made from cheap, raw ingredients that are heavily processed and labeled as cleaner, healthier, and healthier," she says.
The biggest problem for vegetable protein
However, the main factor holding back the herbal analogues market is the price. Real meat is very cheap. This is due to a number of factors, including the subsidies received by the agribusiness and the lack of environmental legislation.
Impossible Meat has a solution. Brown says he wants to achieve price parity with meat products and then beat them. In the coming years, he plans to launch at least one product that will cost the same or even less than the meat counterpart.
The company started with wholesale discounts so food chains and restaurants can sell Impossible Meat products at low prices.

 2010. "Dietary Reference Intakes Tables and Application." Accessed April 8, 2014: link
2010. "Dietary Reference Intakes Tables and Application." Accessed April 8, 2014: link