What age to feed baby yogurt
Can Babies Have Yogurt: Answers for Parents
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Mekeisha Madden Toby on December 17, 2018
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Babies and yogurt
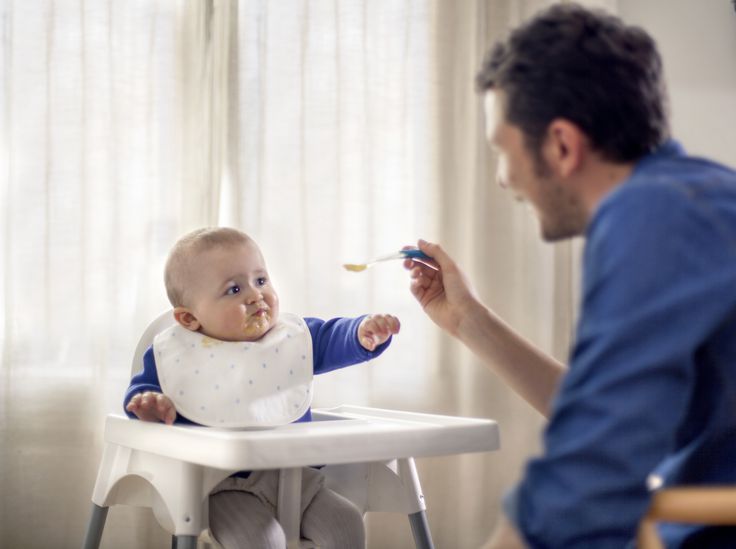
It’s exciting when your baby makes the leap from breast milk and formula to solids, and one of those exciting new foods is yogurt.
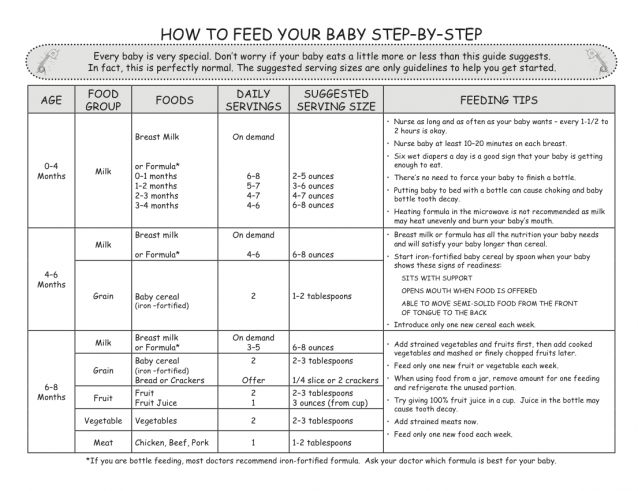
If you’re wondering if your baby can have yogurt, most experts agree that 6 months is a good age to begin eating the creamy and yummy concoction. This is a good age because it’s around this same time that most babies are starting to eat solid food.
Once you decide to feed your baby yogurt, other questions will arise such as the best recipes to try, and if Greek yogurt is a wise choice. Possible allergic reactions are something to consider as well.
Why yogurt is good for babies
It’s good for babies 6 months and older to eat yogurt because it’s nutritional and beneficial. Yogurt also may make tummies — big and small — happy.
There are three main benefits to yogurt. The first is that yogurt is a quick, easy to find, and convenient source of protein.
The second is the presence of probiotics. Much of these will not colonize the intestines so in that way, yogurt fine-tunes the immune system that lines the intestines and may help little bodies begin to recognize friendly versus harmful bacteria.
The third reason is that yogurt has less lactose than whole milk. Babies still retain the enzyme to break down lactose, so that’s not as important as it is for adults with lactose intolerance.
The Greek yogurt conundrum
Greek yogurt is all the rage. It’s high in protein and usually contains less sugar than traditional flavored yogurts.
A lot of parents also turn to frozen or refrigerated Greek yogurt as a teething solution because it’s easy to eat and soothing. It also contains some of the nutrients that babies need when teething pain and tummy troubles decrease their appetites for other solid foods.
As an added bonus, Greek yogurt is strained more than regular, store-bought yogurt. This means that one of the proteins that causes allergic reactions (whey) and the lactose levels are lower in Greek yogurt, making it easier to digest than whole milk, which is not recommended for babies under one year.
If you do choose to go with Greek yogurt, opt for plain. Greek yogurt with fruit or sweeteners and flavoring can be high in sugar and can cause unhealthy weight gain. It’s also best not to add honey until the baby is older than 12 months, to avoid botulism poisoning.
That said, there are pediatricians and nutritionists who caution against Greek yogurt and yogurt in general because of milk allergies and lactose intolerance. So if you’re worried, check with your doctor first.
Yogurt allergies
Allergic reactions to yogurt occur when babies have milk allergies, if the yogurt is made with cow’s milk.
Some telltale signs are:
- a rash around the mouth
- itching
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- swelling
- fussiness
If you spot any of these signs, stop feeding your baby yogurt and contact a doctor.
Even with milder symptoms, as is the case with most new foods introduced into a baby’s diet, it’s always best to wait three days after the initial feeding to look for signs of an allergic reaction.
Yogurt recipes and preparation
Leena Saini, who authors the blog Masala Baby: Global Cuisine for Tiny Taste Buds, encourages moms to feed babies yogurt because it’s served to babies all over the world.
Yogurt can be served in baby oatmeal and rice cereal (instead of mixing in milk as the box usually directs you to do), or added to simple mashed fruits or homemade applesauce for a protein and calcium boost.
In India, babies and children commonly drink lassi, a yogurt drink mixed with fruit and spices such as cardamom or rosewater, says Saini.
Karin Knight and Tina Ruggiero, authors of the book The Best Homemade Baby Food on the Planet, recommend yogurt for babies because it’s high in protein and contains calcium, potassium, vitamin B-12, and magnesium. Knight is a registered nurse and Ruggiero is a registered dietician.
Banana yogurt pudding recipe
One recipe the pair suggests is Yummy in My Tummy Banana Yogurt Puddin’. To make, sauté 2 to 4 tablespoons of bananas in a frying pan with 1 teaspoon of butter. Add that to 2 tablespoons of plain yogurt. Blend the mixture, chill it, then serve.
Add that to 2 tablespoons of plain yogurt. Blend the mixture, chill it, then serve.
Black bean avocado yogurt recipe
Another dish to consider once a baby is eating mixed foods is black beans with avocado and yogurt. The recipe consists of 1/4 cup of black beans, 1/4 avocado, 1/4 cup of plain yogurt, and 2 teaspoons of vegetable oil. Combine all the ingredients in a blender or food processor and serve.
Once the baby is 1 year and older, a nice cool treat is frozen plain or frozen plain Greek yogurt blended or topped with fresh fruit such as bananas, strawberries, or blueberries, and served in a waffle cone or waffle bowl.
Takeaway
Yogurt is a healthy snack for all ages. Once your baby is old enough to start eating solid food, yogurt can be incorporated into their diet.
If you notice your baby showing signs of lactose intolerance or an allergic reaction after eating yogurt, contact your pediatrician.
Mekeisha Madden Toby is a Los Angeles–based journalist.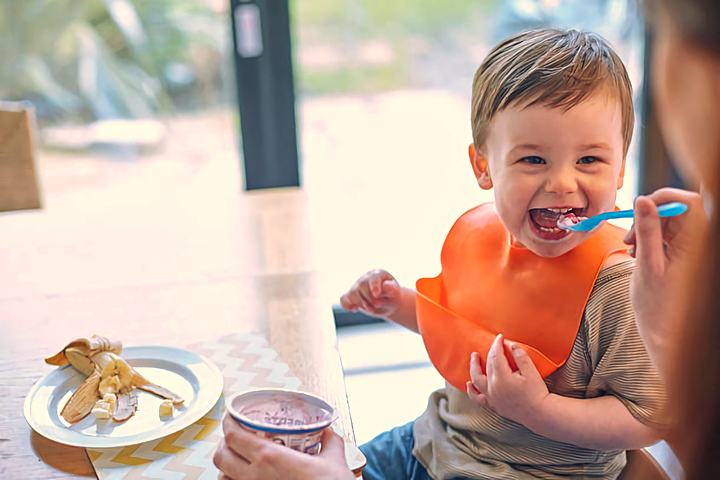 She has been honing her craft professionally since 1999, also writing for Essence, MSN TV, The Detroit News, Mom.me, People Magazine, CNN.com, Us Weekly, The Seattle Times, San Francisco Chronicle, and more. The Detroit native, wife, and mother holds a bachelor of arts in journalism from Wayne State University.
She has been honing her craft professionally since 1999, also writing for Essence, MSN TV, The Detroit News, Mom.me, People Magazine, CNN.com, Us Weekly, The Seattle Times, San Francisco Chronicle, and more. The Detroit native, wife, and mother holds a bachelor of arts in journalism from Wayne State University.
Last medically reviewed on December 18, 2018
- Parenthood
- Baby
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Food allergy reactions. (2009).
healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Food-Allergy-Reactions.aspx - Marette A, et al. (2014). Yogurt consumption and impact on health: focus on children and cardiometabolic risk.

ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24646821 - Starting solid foods. (2018).
healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/Switching-To-Solid-Foods.aspx
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Dec 18, 2018
Written By
Mekeisha Madden Toby
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
When can babies eat yogurt, and which baby yogurt is best?
Most babies can start eating yogurt as soon as they start eating solids – around 4 to 6 months. Yogurt is an excellent choice for one of your baby's first foods because it contains calcium, protein, and vitamins. The best option is plain, unsweetened, pasteurized yogurt (regular or Greek) made from whole milk and containing "live cultures."
What kind of yogurt is best for babies?
Nearly all flavored and fruit-on-top yogurts, even products marketed for babies, contain added sugar, which can contribute to tooth decay and obesity. The USDA guidelines recommend that children under 2 years old get no added sugar from their diet. Choosing plain yogurt is the easiest way to avoid added sugar.
The USDA guidelines recommend that children under 2 years old get no added sugar from their diet. Choosing plain yogurt is the easiest way to avoid added sugar.
To see whether a product has added sugar, check the nutrition label. Look at the line under "Total Sugars" to see how much of the sugar in a product is added sugar. (All yogurt contains some natural sugar in the form of lactose.)
Yogurt made from whole milk is best for babies and toddlers because they need the calories and fat in full-fat dairy products. Don't offer your child reduced-fat or fat-free yogurt before age 2 unless your healthcare provider advises it.
Greek yogurt is strained for a rich, creamy texture, and has twice as much protein as regular yogurt, making it another good choice for babies. Plus, it's often easier to find Greek yogurt in sugar-free varieties.
Is yogurt healthy for babies?
In addition to being a good source of calcium and protein, some types of yogurt contain live cultures, also known as probiotics. These are living microorganisms (bacteria) used to convert milk to yogurt, or added to yogurt afterward. They promote the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut, which researchers believe may help with digestion.
These are living microorganisms (bacteria) used to convert milk to yogurt, or added to yogurt afterward. They promote the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut, which researchers believe may help with digestion.
How can you tell whether yogurt has this good bacteria? The product label should state that the yogurt contains live or active cultures, which means the organisms haven't been destroyed by heat during processing. However, a label that says "made with active cultures" does not mean that the yogurt still contains living cultures, only that the yogurt was made with them (as all yogurt is).
It can be hard to tell if a yogurt contains a significant amount of beneficial bacteria. One way is to look for the Live & Active Cultures seal by the International Dairy Foods Association. This seal identifies products that contain at least 100 million live and active cultures per gram. But participation in the program is voluntary, so a product without the seal isn't necessarily short on cultures.
You may wonder why it's okay for babies to eat yogurt, when drinking cow's milk isn't recommended until a baby is at least 12 months old.
Advertisement | page continues below
Actually, a little bit of cow's milk, like the amount in the occasional serving of yogurt, won't hurt your baby. It's just not a good replacement for the breast milk or formula that still makes up most of their diet for the first year.
That's because babies can't digest cow's milk as easily or completely as breast milk or formula. And cow's milk doesn't have the ideal proportion of fats and nutrients that your baby gets from breast milk or formula.
For more information, see our article on when and how to introduce cow's milk to your child.
Yogurt allergies in babies
If your baby has been diagnosed with a milk allergy or shows signs of a food allergy (such as eczema), don't give them yogurt until you've checked with your healthcare provider.
Otherwise, as with any new food, wait at least three days after introducing yogurt before giving your baby another new food.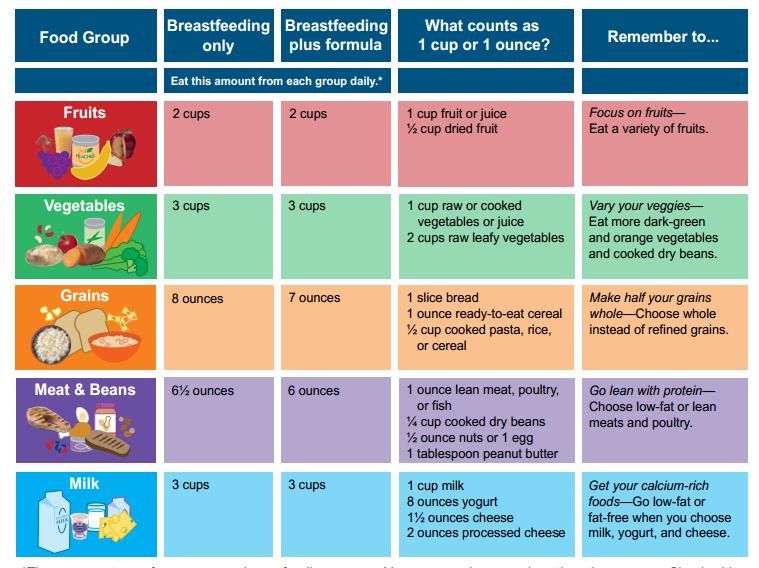 That way, if your baby has an allergic reaction, it will be easier to tell what caused it.
That way, if your baby has an allergic reaction, it will be easier to tell what caused it.
Common symptoms of an allergic reaction include itchy red spots or patches, swelling around the lips or eyes, or vomiting within two hours of eating the recently introduced food. If you notice any of these symptoms, don't give your baby any more of the food until you've checked in with your provider.
Lactose intolerance – which is different from a milk allergy – is very rare in babies. Even if your child becomes lactose intolerant, it may be fine for them to eat yogurt. The production process breaks down much of the lactose, making yogurt more easily tolerated than other dairy products.
Yogurt recipes for babies
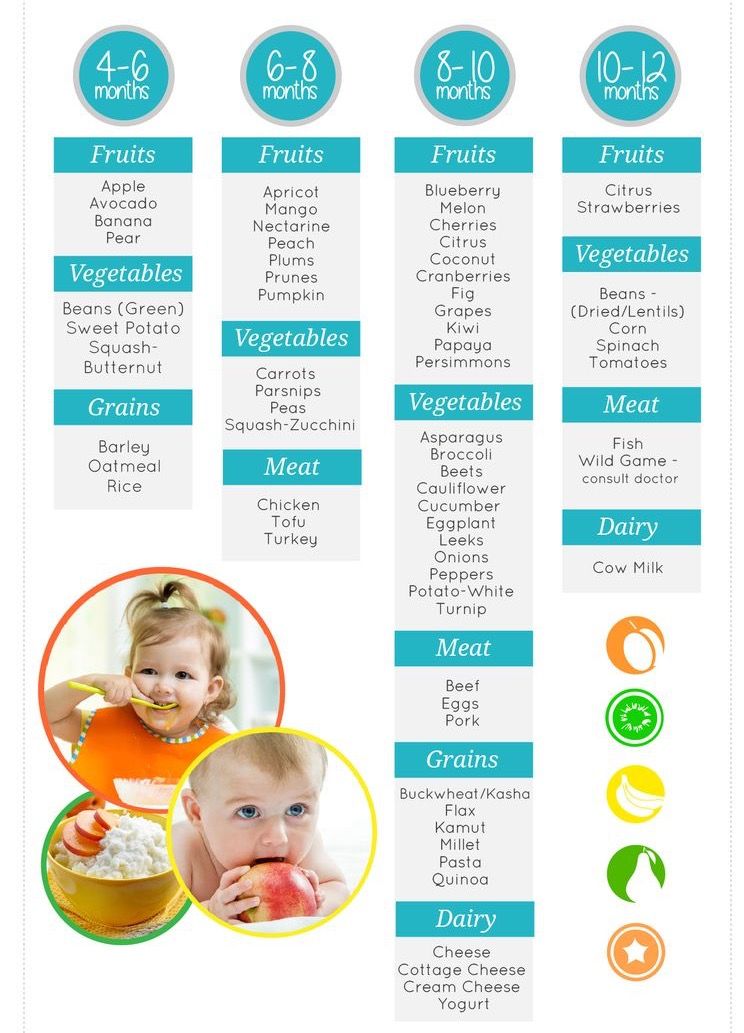
Your baby may not be a fan of plain yogurt, so try adding flavor (and nutrients) by mixing in fruit or vegetables. For babies who are new to solids, start with pureed fruit and cooked, pureed vegetables. For older babies, you can add soft fruit and cooked vegetables chopped into small pieces. Mashed avocado, applesauce, oatmeal, and wheat germ are also good additions.
Mashed avocado, applesauce, oatmeal, and wheat germ are also good additions.
Never give honey to a baby younger than 12 months because it may contain bacteria that can cause botulism in children that age.
Try these baby food recipes with yogurt:
- Yogurt and berry swirl
- Baby guacamole
- Tropical fruit salad
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
From what age can a child be given kefir
6-12 months
Article
0 reviews
It is allowed to give kefir to a child not earlier than from 8 months, and this age refers to kefir intended specifically for baby food
2 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
Where to start
It is allowed to give kefir to a child no earlier than 8 months, and this age refers to kefir intended specifically for baby food, since ordinary kefir is a product that is not adapted for baby food and is not recommended for children of the first year life.
Healthy snack for baby
Gerber® fruit and cereal bars - a convenient snack format for a child over one year old: contains from 46% fruit in the composition; no added sugar or starch. nine0003
To learn more
Kefir should be introduced gradually, starting with 10–15 ml (2–3 tsp), over 10–14 days, increasing the amount of kefir to the amount of one feeding of your child (150–200 ml). The maximum amount of kefir that your child drinks should not exceed 200 ml. For example, you started administering kefir to a breast-fed child at the age of 8 months. On the first day, give him 15 ml (3 tsp), on the second day you can increase the volume to 30 ml, on the third day the amount of kefir will be 50-60 ml, at the end of the first week - reach 90-100 ml. It is better to start the introduction of kefir not at the last feeding, but at an afternoon snack in order to carefully monitor the reaction to a new product. It is optimal if in 8-9 months the amount of kefir will be 100-120 ml, and only by the year can be increased to a maximum volume of 200 ml. By increasing the amount of kefir in feeding, you will reduce the volume of breast milk, up to the complete replacement of the volume of feeding with complementary foods.
By increasing the amount of kefir in feeding, you will reduce the volume of breast milk, up to the complete replacement of the volume of feeding with complementary foods.
Healthy and tasty!
After you make sure that the child tolerates kefir well, i.e. there are no changes in the skin and intestines, you can add fruits, berries and vegetables to kefir to form a variety of flavors. If kefir for baby food contains probiotics (bifidus and lactobacilli), this increases its benefits for your child. nine0003
Important!
Kefir is a high-quality and healthy fermented milk food product, provided it is introduced in moderation in a timely manner and special adapted products are used.
Latest Reviews
Average Customer Rating
0 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 0
- four 0 nine0043 3 0
- 2 0
- 1 0
Recommended Articles
6-12 months
Article
By-products are very important products
0 reviews
What are by-products? These include the heart, liver, kidneys, brains, tongue, lung. Let's say right away: young children are not given a lung, kidneys and brains. Therefore, we will talk about the rest of the by-products that are considered valuable for baby food. nine0003
Let's say right away: young children are not given a lung, kidneys and brains. Therefore, we will talk about the rest of the by-products that are considered valuable for baby food. nine0003
6-12 months
Article
Arachidonic acid (ARA): what are the benefits for children?
0 reviews
In the first years of life, the child's body actively grows and develops.
6-12 months
Article
Immunity Boosting Products
Oh, that mysterious capacious word "immunity"! Pediatricians attribute numerous catarrhal childhood diseases to his immaturity, saying that, they say, immunity will get stronger and the child will stop getting sick. nine0003
6-12 months
Article
Seafood and baby: compatible?
0 reviews
Seafood is marine life other than fish, i. e.: seaweed, shrimp, squid, lobster, spiny lobster, crabs, krill, scallops, oysters, etc.
e.: seaweed, shrimp, squid, lobster, spiny lobster, crabs, krill, scallops, oysters, etc.
6-12 months
Article nine0003
Jelly and jelly in the diet of a child
0 reviews
Jelly is a gelatinous mass obtained from broths and sweet drinks by adding gelling agents, most often gelatin. Should I give my child jelly and jelly? There are different opinions on this matter.
6-12 months
Article
Drink cow's milk for health? nine0017
0 reviews
Now there is a lot of talk about the dangers of cow's milk for babies, and it is on it that our grandmothers and mothers grew up. Is cow's milk really so harmful, and what exactly is its negative impact? When is it worth introducing cow's milk into a child's diet, and how to do it right?
6-12 months
Article
Products containing iron nine0017
0 reviews
A complete and balanced nutrition according to the main ingredients allows you to satisfy the physiological need of the child's body for trace elements. Let's look at the list of foods containing iron.
Let's look at the list of foods containing iron.
6-12 months
Article
nuts
What do you need to know about nuts and when can you give them to your baby?
nine0002 6-12 monthsArticle
Eggs: how much, when, what?
After a year, we introduce egg white into the child's diet. Thus, the child can eat a whole egg in one of the meals. And here a lot of questions arise. Which eggs are preferable, chicken or quail; is it possible to eat eggs daily and in what quantity; and also in what form they should be served. Do we know?
6-12 months
nine0002 ArticleDoes a child need cholesterol?
0 reviews
Cholesterol plays an important role in a number of physiological processes in the body of children.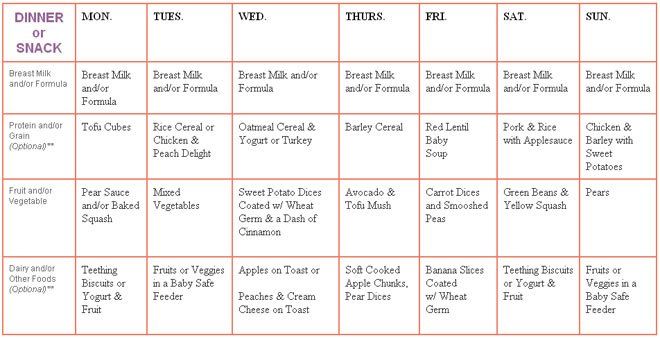
6-12 months
Article
Why is cow's milk not good for babies?
Cow's milk, which occupies a worthy place in the diet of adults and older children, is categorically not recommended for infants, even in the form of fermented milk products and in a diluted form. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Proper nutrition is the basis of future health
During the first 1000 days of a baby's life, optimal nutrition largely determines the growth and development of the child in the present and future. A balanced diet, which contains the most important macro and micronutrients, is an important investment in a child's future health.
6-12 months
Article nine0003
Yogurt in the baby's diet
0 reviews
Children's yoghurts are a source of protein, calcium and other trace elements (iron, magnesium, zinc, iodine) and vitamins B, A, E and C, have a lower acidity compared to kefir. Thanks to lactic acid bacteria, yogurt is easily digested and absorbed. This product improves bowel function and strengthens the immune system. When to introduce yogurt into the baby's diet? Which yogurt do you prefer? nine0003
Thanks to lactic acid bacteria, yogurt is easily digested and absorbed. This product improves bowel function and strengthens the immune system. When to introduce yogurt into the baby's diet? Which yogurt do you prefer? nine0003
6-12 months
Article
Antioxidants: what are the benefits and what foods contain
0 reviews
Antioxidants are very important substances for human health: they reduce the action of free radicals that can damage body cells, and thus reduce the risk of developing various diseases.
6-12 months
Article
Herbal teas in baby food
0 reviews
Herbal teas in baby food
6-12 months
Article
Chocolate for children: good or bad?
Chocolate in Latin means "food of the gods". It deserves such a name, because it has many useful properties. But can you give chocolate to children? And from what age? nine0003
It deserves such a name, because it has many useful properties. But can you give chocolate to children? And from what age? nine0003
6-12 months
Article
selenium for babies
0 reviews
Selenium is an essential element, i. vital. It plays a key role in the body's antioxidant defense system. This means that it protects the cells of our body from damage and death.
6-12 months
Article nine0003
The need for iron in children. Complex of vitamins and iron Iron +
0 reviews
Iron is one of the most important trace elements for the human body. It is part of a variety of tissue proteins, enzymes that provide metabolism in cells.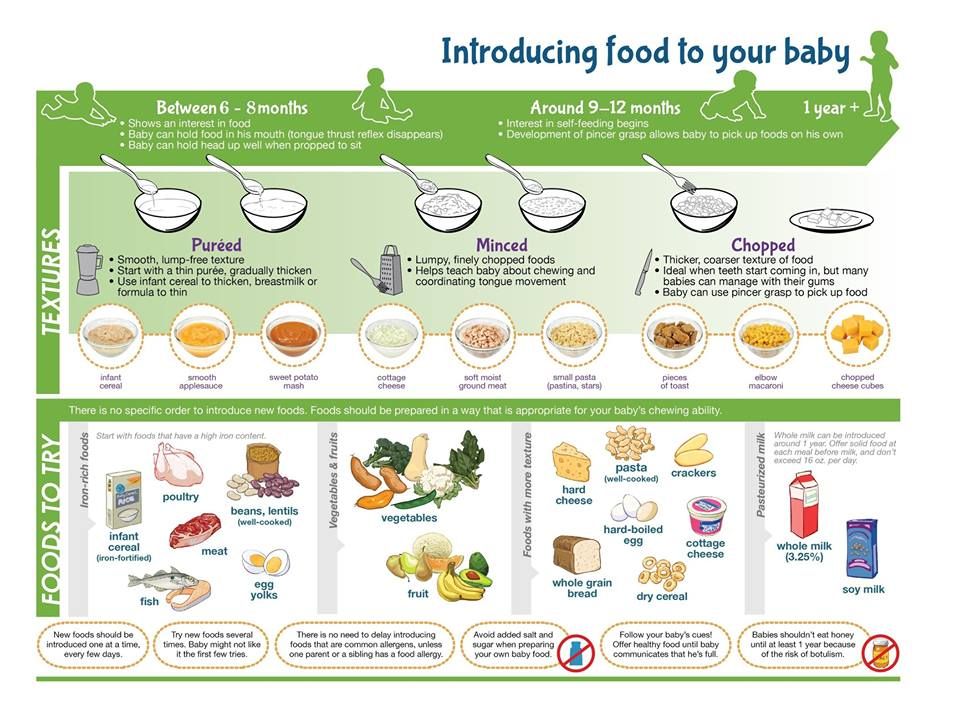 The most important function of iron is participation (in the composition of hemoglobin) in the delivery of oxygen to all tissues of the body.
The most important function of iron is participation (in the composition of hemoglobin) in the delivery of oxygen to all tissues of the body.
6-12 months
Article
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) for children: what are the benefits?
0 reviews
It is important for every mother that her child is healthy, active, learns something new well and develops intellectually. Children are characterized by curiosity, a desire to explore the world, they quickly pick up the behavior and vocabulary of their parents.
Join the Club nine0013
We know that being a mother is not only unlimited happiness, but also a great responsibility. We will help you!
Register
Still haven't found what you need?
Try our new search.
Search
When can kefir be given to a child? nine0250
— Fermented milk products improve digestion and strengthen the immune system. Kefir contains B vitamins, proteins, enzymes and amino acids necessary for healthy development and growth, as well as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which have a good effect on the balance of microflora.
Pediatricians recommend giving yogurt to a baby in the second half of life:
- with artificial feeding - from 7-8 months;
- when breastfeeding - from 8 months. nine0053
- Breastfed babies can be offered yogurt no earlier than eight months. At the same time, by the year and up to three years, the volume of kefir in the children's diet can be 200 ml per day. nine0044
- Formula-fed children can be given kefir from seven months. And by the year, its normal volume is also brought up to 200 ml per day.
But some gastroenterologists argue that it is better to delay this moment until 11-12 months due to the immaturity of the enzymatic system.
— What are the consequences for parents who introduce kefir into their child's diet too early?
- Symptoms can be very diverse: from a disorder of the baby's gastrointestinal tract (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, colic) to allergic reactions, when you need to immediately remove a specific fermented milk product from the diet. Sometimes in such cases, an elimination diet lasting 5-6 months is prescribed. Then fermented milk products are given again and look at the reaction of the child's body. nine0003
Sometimes in such cases, an elimination diet lasting 5-6 months is prescribed. Then fermented milk products are given again and look at the reaction of the child's body. nine0003
In addition, with early lactic acid supplementation, a child may experience kidney failure due to acid and mineral salts, which are part of kefir.
- What is the difference between special children's kefir and "adult"?
- If we are talking about biokefir, then this product contains a lot of living microorganisms (lacto- and bifidobacteria). It can be given to a child as complementary foods, alternating with regular kefir, if these products are tolerated normally. You can also offer a child sour-milk mixtures, which differ from kefir in low acidity and are additionally enriched with vitamins. These products can also be alternated with kefir. nine0003
— How to introduce kefir into complementary foods for a child: should it be offered gradually and according to what scheme?
- Of course, like any other new product, kefir is introduced gradually, starting with a teaspoon, and preferably at lunchtime, in order to track the possible adverse reaction of the baby.
- Which yogurt is better for children under one year old: ready-made from the store or cooked at home? How to make kefir for babies at home?
- It is better to give preference to kefir bought in a store. An industrial product is inspected, tested and processed under certain conditions. Homemade kefir is “kinder”, our grandmothers will say, but everyone has different cooking methods and conditions. With the same mistress, even the percentage of fat content in milk no one will ever be able to track. Therefore, it is better not to start the first feeding with homemade kefir. nine0003
— What should parents pay attention to when buying yogurt for a child?
- First of all, the expiration date is important. Kefir retains its beneficial properties for only three days, then nothing but alcohol remains in it. With a specific smell, it is better not to take risks and abandon the dubious product. Before choosing a lactic acid product, it is advisable to read about its composition on the package - the fewer obscure words, that is, additives, the better. The most useful products are not always on the shelves of stores. nine0003
Kefir retains its beneficial properties for only three days, then nothing but alcohol remains in it. With a specific smell, it is better not to take risks and abandon the dubious product. Before choosing a lactic acid product, it is advisable to read about its composition on the package - the fewer obscure words, that is, additives, the better. The most useful products are not always on the shelves of stores. nine0003
— Diarrhea after yogurt in a child is not uncommon. What should parents do if the baby has an upset gastrointestinal tract on kefir?
- This product is discontinued immediately: for one to three months. If the allergic reaction is severe, the doctor may prescribe an elimination diet and appropriate therapy. After the product is canceled, the child must be shown to the pediatrician, especially if the baby's reaction to the introduction of kefir is accompanied by one or more symptoms: on the part of the skin - bright redness, swelling, itching, peeling, and on the part of the gastrointestinal tract - disorders, constipation or diarrhea and other signs food allergies. nine0003
nine0003
— Is it possible to replace kefir with other fermented milk products?
— Complementary foods can be started with other fermented milk products. For example, the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences recommends fruit purees with goat curd for complementary foods. This product is also available in the MAMAKO ® line. It is suitable for babies who do not want to drink kefir because of its consistency. A child may not like liquid kefir, but he is happy to eat cottage cheese. The goal - getting all the vitamins and minerals from fermented milk products - will be achieved in any case. nine0003
Acquaintance with fermented milk products is better to start with children's adapted ready-made kefir. Purchased baby kefir has low acidity, and it is enriched with vitamins. The product is included in the children's diet gradually, starting with one teaspoon, during the day, since the work of the baby's gastrointestinal tract will change in any case.