What do you feed a baby alligator
Alligator Facts | FWC
- Home
- Wildlife & Habitats
- Wildlife Conservation
- Alligator Management Program
- Alligator Facts
Alligator management programs implemented by FWC emphasize the conservation of alligator populations for their ecological, aesthetic, and economic values while providing for public use and safety.
Facts and Information
Expand/Collapse Legal Status
The American alligator is classified by the US Fish and Wildlife Service as similarity of appearance to a threatened taxon. This listing provides federal protection for alligators but allows state-approved management and control programs. This listing has been adopted by the State of Florida. Alligators can be legally taken only by individuals with proper licenses and permits.
Expand/Collapse Food Habits
Alligators are opportunistic feeders. Their diets include prey species that are abundant and easily accessible. Juvenile alligators eat primarily insects, amphibians, small fish, and other invertebrates. Adult alligators eat rough fish, snakes, turtles, small mammals, and birds. Go to the following links for more information:
- Diet and Condition of American Alligators in Three Central Florida Lakes
Expand/Collapse Size
Female alligators rarely exceed 10 feet in length, but males can grow much larger. The Florida state record for length is a 14 foot 3-1/2 inch male from Lake Washington in Brevard County. The Florida record for weight is a 1,043 pound (13 feet 10-1/2 inches long) male from Orange Lake in Alachua County.
The Florida state record for length is a 14 foot 3-1/2 inch male from Lake Washington in Brevard County. The Florida record for weight is a 1,043 pound (13 feet 10-1/2 inches long) male from Orange Lake in Alachua County.
Expand/Collapse Reproduction
Nearly all alligators become sexually mature by the time they reach approximately 7 feet in length although females can reach maturity at 6 feet. A female may require 10-15 years and a male 8-12 years to reach these lengths. Courtship begins in early April, and mating occurs in May or June. Females build a mound nest of soil, vegetation, or debris and deposit an average of 32 to 46 eggs in late June or early July. Incubation requires approximately 63-68 days, and hatching occurs from mid-August through early September.
Expand/Collapse Survival
About 1/3 of alligator nests are destroyed by predators (mainly raccoons) or flooding. The average clutch size of an alligator nest is 38. For nests that survive predators and flooding, an estimated 24 live hatchlings will emerge. Only 10 alligator hatchlings will live to one year. Of these yearlings, 8 will become subadults (reach 4 feet in length). The number of subadults that reach maturity (6 feet in length) is approximately 5. These estimates are for a growing alligator population. As a population matures (and has a higher percentage of large alligators), the survival rate would be expected to be lower, in part due to a higher rate of cannibalism.
Expand/Collapse Mortality
Eggs: Alligator eggs are susceptible to drowning, being crushed by the female, predation, and other less common calamities. Raccoons are the primary predator, although hogs, otters, and bears have been reported to depredate nests.
Raccoons are the primary predator, although hogs, otters, and bears have been reported to depredate nests.
Juveniles: Small alligators are eaten by a variety of predators including raccoons, otters, wading birds, and fish; however, larger alligators may be their most significant predator.
Adults: Cannibalism, intraspecific fighting, and hunting by humans are probably the most significant mortality factors.
Diseases and Parasites: Very little information is available in the scientific literature on wild alligator diseases and parasites. They are not believed to be a significant problem for wild alligators.
Expand/Collapse Distribution
Alligators occur from southeast Oklahoma and east Texas on the western side of their range to North Carolina and Florida in the east. They prefer fresh water lakes and slow-moving rivers and their associated wetlands, but they also can be found in brackish water habitats.
They prefer fresh water lakes and slow-moving rivers and their associated wetlands, but they also can be found in brackish water habitats.
Native Range of the American Alligator
Courtesy of US Geological Survey, Nonindigenous Aquatic Species Program.
Expand/Collapse Thermoregulation
Alligators are ectothermic -- they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. Alligators control their body temperature by basking in the sun, or moving to areas with warmer or cooler air or water temperatures. Alligators are most active when temperatures are between 82° to 92° F (28° to 33° C). They stop feeding when the ambient temperature drops below approximately 70° F (21° C) and they become dormant below 55° F (13° C). Alligators are dormant throughout much of the winter season. During this time, they can be found in burrows (or "dens") that they construct adjacent to an alligator hole or open water, but they occasionally emerge to bask in the sun during spells of warm weather. The article at this link contains information about thermoregulation in Everglades alligators.
During this time, they can be found in burrows (or "dens") that they construct adjacent to an alligator hole or open water, but they occasionally emerge to bask in the sun during spells of warm weather. The article at this link contains information about thermoregulation in Everglades alligators.
Expand/Collapse Evolution
The most recent evidence indicates that crocodilians (which includes alligators) and dinosaurs evolved from a common ancestor that existed subsequent to the common ancestor that they share with other reptiles. So, even though alligators are classified as reptiles along with lizards, snakes, and turtles, they are actually more closely related to birds, whose direct ancestors were dinosaurs!
Expand/Collapse The Heart of an Alligator
While most reptiles have 3-chambered hearts, the heart of alligators, and all crocodilians, has 4 chambers, a trait shared with mammals and birds. The advantage of a 4-chambered heart is that oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood are separated, which results in more efficient respiration needed for the high metabolism of endothermic (warm-blooded) animals, and enables different pulmonary (lung) and systemic blood pressures, but is seemly over-complex for ectothermic (cold-blooded) crocodilians. The single ventricle of the 3-chambered reptile heart allows some mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood, which may help regulate their metabolic state. Crocodilians have evolved a shunt between the left and right aorta (immediately above the ventricles) to facilitate the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Crocodilians also have a valve in the pulmonary artery that, when closed, forces deoxygenated blood to recirculate through the left aorta, which increases mixing. This increased mixing helps crocodilians transition to a lower metabolic state, and enables them to dive for extended periods.
The advantage of a 4-chambered heart is that oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood are separated, which results in more efficient respiration needed for the high metabolism of endothermic (warm-blooded) animals, and enables different pulmonary (lung) and systemic blood pressures, but is seemly over-complex for ectothermic (cold-blooded) crocodilians. The single ventricle of the 3-chambered reptile heart allows some mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood, which may help regulate their metabolic state. Crocodilians have evolved a shunt between the left and right aorta (immediately above the ventricles) to facilitate the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Crocodilians also have a valve in the pulmonary artery that, when closed, forces deoxygenated blood to recirculate through the left aorta, which increases mixing. This increased mixing helps crocodilians transition to a lower metabolic state, and enables them to dive for extended periods.
Some scientists have hypothesized that the complex heart structure of crocodilians might indicate that they evolved from endothermic (warm-blooded) ancestors.
Go to the external links below for more information.
- The Physiological and Evolutionary Significance of Cardiovascular Shunting Patterns in Reptiles
- How long can a crocodile stay underwater?
Expand/Collapse Eye-Shine
The tell-tale eye-shine of an alligator (and other nocturnal vertebrates) is caused by a layer of cells called the tapetum lucidum (a Latin phrase meaning "bright carpet"). This structure is located beneath the photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) in the retina and reflects light back into these cells to increase the amount of light detected, which improves an alligator's vision in low light conditions. In alligators this eye-shine is red, but it can be different colors in other species. For more information, see the documents at the links below.
- Texas Parks and Wildlife: Eyeshine
- Wikipedia: Tapetum lucidum
Fish and Wildlife Research Institute
FWC Alligator Research Publications
How to Feed Baby Alligators
By Laura Bramble | Updated November 01, 2017Warnings
Do not go near baby alligators in the wild. Mothers will stay with their young for up to two years, so a mother alligator could be nearby and think you are threatening her young. In this case, she will attack you.
Keep pets and any other kinds of food away from your hatchling and young gator. Alligators are not overly particular about what they eat and will eat whatever is handy.
Do not put small pebbles in your hatchling enclosure; use only larger natural rocks that have been sterilized by boiling.
 Your baby alligator will probably eat some and they could get lodged in her digestive system, which could result in illness or death.
Your baby alligator will probably eat some and they could get lodged in her digestive system, which could result in illness or death.Feeding a baby alligator in the wild is not recommended.
Caring for baby alligators, or hatchlings, requires special knowledge, and you must carefully consider what will happen to your pet once it reaches an unmanageable size. Because alligators grow about a foot a year until they reach maturity, it will not be long until you have a pet that is able to do significant damage to you, your family and your home. It is illegal to keep alligators as pets in many states, and many of those where it is legal require you to have the proper permits or licenses. You can successfully feed your pet baby alligator by using common sense and following a few important guidelines.
Choose foods such as small fish, insects, crawfish, small mice and frogs. Alligators eat whole food in the wild, so do not feed your hatchling a steady diet of meat pieces. They need the calcium and other nutrients found in whole food.
They need the calcium and other nutrients found in whole food.
Use unfrozen, raw and preferably live food to feed your hatchling or young gator. They have sensitive digestive systems and cannot handle cooked or frozen foods. Thaw any frozen or partially frozen food first before feeding it to the hatchling.
Feed your hatchling every other day; juveniles every three or four days. Alligators will eat as much and as often as you let them, so keep to a strict schedule. Overfeeding will lead to gout.
Use a utensil to feed your hatchling so that both you and the baby get used to not associating your hands with food. This will help prevent confusion, which could be deadly later on.
Set up a feeding routine and schedule. Feed your hatchling at the same time of day, using the same method and in the same location. While you cannot “train” an alligator, you can keep him calm by keeping things predictable.
References
- Care Sheet for Alligators and Crocodiles
- Crocodilian Captive Care F.
 A.Q’s
A.Q’s - Louisiana Alligator Advisory Council
Tips
- Keep pets and any other kinds of food away from your hatchling and young gator. Alligators are not overly particular about what they eat and will eat whatever is handy.
- Do not put small pebbles in your hatchling enclosure; use only larger natural rocks that have been sterilized by boiling. Your baby alligator will probably eat some and they could get lodged in her digestive system, which could result in illness or death.
- Feeding a baby alligator in the wild is not recommended.
Warnings
- Do not go near baby alligators in the wild. Mothers will stay with their young for up to two years, so a mother alligator could be nearby and think you are threatening her young. In this case, she will attack you.
Photo Credits
Conan Exiles Pet Feeding on Shadowflowers mysterngame
Conan Exiles / Guides
Author: Administration
Contents
updated: added Siptah's pets
Finally got around to making a complete table of all pets and shadowflower food with the maximum percentage of appearance of top animals.
Here is the main pet and bladehorn guide, a link to the food list has also been added to it.
Below I have collected for you all the cubs and what to feed them to get an alpha hybrid. These feeds are produced from a combination of Shadowbloom (flower) and common food (resources) in cooking (cook's stove).
Shadowblooms are obtained by gathering meat from bosses in the Midnight Grove dungeon of the Jabbaal Saga. Or prey from the corpses of werewolves summoned from the seal of Jabbaal Saga.
In the "Shadowflower Food" column, I have indicated the required ingredient in parentheses if it is not obvious from the name of the food.
The "% growth" column is the maximum chance of the appearance of the animal you need.
Table of maximum % with indication of feed
| Cubs | Food with shade flower | % growth | Result | Produces: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lovenok | Ideal clipping with a tennol of (exotic meat) | 75 25 | Lev Large Lion | Navigation |
| Scorpio egg | Blood Demon Blood with Tenum Flows | 15% 9000,000% 30% 9000% 9000% | Hand Scorpio (A) manual scorpion (b) manual scorpio (C) Hand scorpion (D) | Dung |
| Elephant | Vegetable fibers with shade | 76% 12% 12% | Elephant Alpha Elephant | Manure |
| Bear cub | Honey with shadow flower | 70% 30% | Bear Big bear | Dung |
| Camel | Vegetable fibers with shade flower | 100% | Camel | Manure |
| Baby Crocodile | Perfect Tenderloin with Shadeflower (Exotic Meat) | 70% 30% | Crocodile Large crocodile | Dung |
| Baby gazelle | Vegetable fibers with shade flower | 100% | Gazelle | Manure |
| Frostwolf | Fatty Meat with Shadeflower (Raw Pork) | 50% 50% | Wolf Big Wolf | 3 |
| Jaguar Baby | Shadowflower Perfect Tenderloin (Exotic Meat) | 70% 30% | Jaguar Large Jaguar | Manure |
| Publi locusts | Human meat with tenesuating | 52% 19% 14% 9000 10% | ||
| Locust Hatchling | Corrupted Shadowflower Seasoned Meat (abyss flesh) | 48% 24% 14% 14% | Green locust Yellow location orange locust Queen of locust | Pile 90% 9000% 9000% 9000% 9000 9000 |
| Strass Ponus | mountain berries with a tenum of Desert berries with a tenum of | 10% 45% 45% | Strescen Red ostrics | Manure 80% Feathers 20% |
| Panther Panthers | raw hard meat with a tenum (exotic game) | 70% 30% | Panther Large Panther | Navigation |
| Stonehorn | Stonehorn Breeding Guide | |||
| Baby Rhino | Shadeflower Bark | 70% 15% 0% 15% | Rhino Black Rhino White Rhino Big Rhino | Dung |
| Publosysh rhino | Plant fibers with a tenum of | 75% 0% 15% 19% | Nosorog Black nosorog 9000 | |
| Saber Tooth Cub | Fat Meat with Shadeflower (Raw pork) | 70% 30% | Sabertooth Large sabertooth | Manure |
| Publiknik Publika | Juicy mollusks with a tenum of (exotic mollusk) | 48% 0% 24% 14% 14% | Green shell -pavers 9000 2 000 violet gover shell Large shell | Manure |
| Chitnel Kitolva | Fat larva with a tenum of insects with a tenum of | 60% 25% 15% | Green whales 9000% 9000% | |
| Cubeen spider | Blood Demon Blood with Tenum Flower | 0% 0% 60% 9000%
20% | Gray spider 9000 Green spider Black Widow Scarlet Widow Corrupted Spider | Dung 90% Ichor 10% Corrupted Spider gives 50% of their manure and 9004 50% of their manure and 9004 9004 |
| Spotted Hyena Cub | Raw Stringy Meat with Shadeflower | 70% 30% | Spotted Hyena Large Dung Hyena | |
| Striped Hyena Cub | Raw Stringy Meat with Shadowflower (Small game) | 70% 30% | Striped hyena Big hyena | Dung |
| Tiger Cub | Raw Tough Meat with Shadeflower (Exotic Game) | 70% 30% | Tiger Big Tiger | Dung |
| Piglet | Shadeflower Smoke Mushrooms | 70% 30% | Boar Large Boar | Manure |
| Wolf Cub | Perfect Tenderloin with Shadeflower (Exotic Meat) | 70% 30% | Wolf Big Wolf | 9 Dung |
| Baby Salamander | Perfect Tenderloin with Shadowflower (Exotic Meat) | 70% 30% | Salamander Big Salamander | 3 |
| Komodo Baby | Shadowflower Perfect Cut (Exotic Meat) | 70% 30% | Komodo Big Komodo | Manure |
List of food with shade for Siptah pets
| Earth Wolf Cub | Shadowflower Perfect Tenderloin (Exotic Meat) | Carrion Earth Wolf Large carrion dirt wolf | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Baby Crested Lizard | Perfect Tenderloin with Shadeflower (Exotic Meat) | Crested Lizard Large Crested Lizard | 75 9040 2 | ||
| Wild puppy | Flesh of the abyss | Wild dog - Variant A Large wild dog - Variant A | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Wild Puppy | Small Game | Wild Dog - Variant A Large Wild Dog - Variant A | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Wild puppy | Human flesh | Wild dog - Variant B Large wild dog - Variant B | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Wild puppy | Wild game | Wild dog - Variant B Large wild dog - Variant B | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Wild puppy | Exotic game | Wild dog - Variant C Large wild dog - Variant C | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Wild puppy | Raw pork | Wild dog - Variant C Large wild dog - Variant C | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Wild puppy | Exotic meat | Wild dog - Variant D Large wild dog - Variant D | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Island Lynx | Raw Tough Meat with Shadeflower (Exotic Game) | Island Lynx Large Island Lynx | 75 25 | ||
| Baby Jaguar | Raw Tough Meat with Shadeflower (Exotic Game) | Jaguar Large Jaguar | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Cougar Cub (puma) | Raw Tough Meat with Shadowflower (Exotic Game) | Cougar Large Cougar | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Forest Claw Hatchling (Tiger) | Raw Tough Meat with Shadowflower (Exotic Game) | Red Forest Claw Large Red Forest Claw | 75 2 | ||
| Baby Turtle | Exotic Shellfish | Small Tortoise Tortoise Big turtle | 50 30 20 | 4 | |
| Siptah Rhino Cub | Bark with Shadeflower | Siptah Rhino Siptah Large Rhino | 69 31 | ||
| Siptah Pelican Nestling | Shadeflower Smoke Mushrooms | Siptah Pelican Large Siptah Pelican | 75 25 | 4 | |
| Shaggai grub | Honey+ Shaggai Queen Jelly (beehive grown) | Shaggai Drone Shaggai Warrior | 75 25 | specify |
Tagsconan exilesfeeding petsshadowcolorshadecolor Conan Exilesfeeding pet
Crocodile cubs: various facts
Crocodile is one of the most dangerous predators of our planet. Representatives of most species are smart, cunning and very strong. It is not surprising that these animals have always aroused increased interest among both scientists and people far from the scientific world who are simply interested in nature.
Representatives of most species are smart, cunning and very strong. It is not surprising that these animals have always aroused increased interest among both scientists and people far from the scientific world who are simply interested in nature.
Our article will tell you about how these powerful predators are born, what dangers they will face before they take the top positions in the food chain.
Name
Let's start with the simplest. Do you know the name of a baby crocodile? Note that a special name for newborns and young animals does not always exist. If in doubt, it is better not to invent words, but to get by with a “cub”.
Spotted hyena. Description, habitat
In Africa, the inexperienced traveler faces many dangers at every turn. This...
Modern dictionaries and reference books advise using the word "crocodile" exclusively in oral speech. For writing, simply "cub", "crocodile" or "little crocodile" is more suitable.
Breeding of crocodiles
Most of the amphibians and reptiles that inhabit the tropics begin to look for a mate on the eve of the onset of the rainy season. Crocodiles are no exception.
Crocodiles are no exception.
Males arrange fights, which often end in the death of one of the rivals. The most aggressive and strong, having won, begin to look for girlfriends. By the way, the mating season is the only period during which individuals of different sexes are in contact with each other.
Mating occurs in water. The process is quite lengthy, and throughout its duration, partners replace each other. As a result, several males fertilize one female, just as each male mates with several partners.
Baby animal - wild and domestic
The cat takes care of babies from their very birth. She feeds, licks and practically does not...
After the process is completed, the males disperse, and the females begin to plan the construction of nests. It is not uncommon for a crocodile to build several hiding places in order to choose the best one. The nest should be near water, but without the risk of flooding.
Clutch usually contains 40 to 80 eggs. With a huge mass and seeming sluggishness, a crocodile can carefully lay all the testicles without damaging them. During the laying of eggs, the female seems to fall into a trance: the pupils dilate, the ear gaps are covered, she practically does not notice everything that is happening around. But as soon as the masonry is ready, there is no trace of detachment. During the protection of the nest, the reptile turns into an aggressive defender, ready to repulse anyone.
With a huge mass and seeming sluggishness, a crocodile can carefully lay all the testicles without damaging them. During the laying of eggs, the female seems to fall into a trance: the pupils dilate, the ear gaps are covered, she practically does not notice everything that is happening around. But as soon as the masonry is ready, there is no trace of detachment. During the protection of the nest, the reptile turns into an aggressive defender, ready to repulse anyone.
The sex of future crocodile cubs depends on the ambient temperature: at a temperature of 31.7 to 35.4 degrees, males are born, and in other cases, females.
The egg maturation period is approximately 3 months. During this time, the excavated nest, camouflaged with leaves and watered by heavy rains, becomes very dense, so it is not easy for newborns to get out of it. As soon as they are born, they begin to make noise, calling for help from their mother.
What a baby crocodile looks like
The babies of some animals are very difficult to identify because they are so unlike their parents.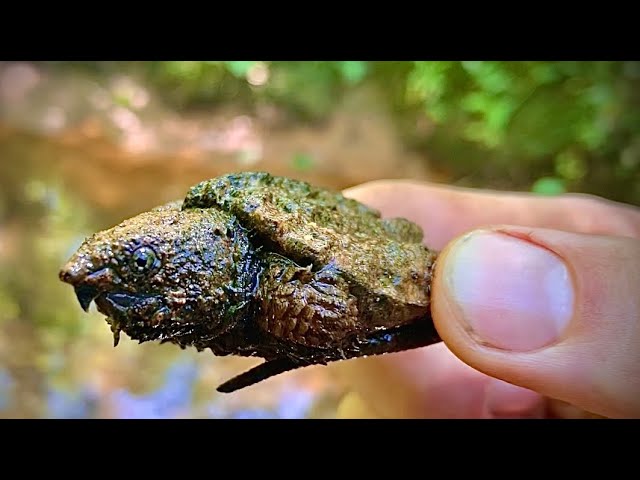 But in this case, things are different: crocodile cubs are smaller copies of moms and dads. In length, they reach about 30 cm, and, like in adults, 2/3 of the body is occupied by the head. Even newborns have teeth.
But in this case, things are different: crocodile cubs are smaller copies of moms and dads. In length, they reach about 30 cm, and, like in adults, 2/3 of the body is occupied by the head. Even newborns have teeth.
The length of a crocodile: the maximum dimensions known to science...
Many aspects of the structure of predatory reptiles are known to science. For example, weight, length of crocodiles, their...
But the kids look pretty cute: they have big shiny eyes, clumsy thin paws, iridescent spots in the sun. In appearance, they are completely defenseless, and in fact they are not yet able to stand up for themselves.
Birth and childhood
Hearing the cries of babies, the crocodile rakes the nest, freeing them. Scientists have repeatedly recorded how a female crocodile carries cubs in a mouth dotted with powerful teeth. She does this very carefully, without causing any harm to the children.
At this time, a caring mother should not be disturbed, because all her attention is focused on her offspring.