What do you feed wild baby frogs
What Do Frogs Eat? Food List & Feeding Guide
Frogs are a very popular pet, especially with new reptile hobbyists. It is also common to see wild frogs in a garden and want to feed them.
What Do Bearded Dragons Eat? Best F...
Please enable JavaScript
What Do Bearded Dragons Eat? Best Food List and Feeding Guide
Most frogs eat a diet of only bugs, but this does not mean you can feed them any bug you find crawling around the garden! Pets and wild species have different diets from each other.
It is important to understand their diet before feeding. Many people make feeding mistakes such as feeding bugs they caught in the garden. Others feed prey that is too large, overfeed, or feed dead prey.
To avoid these mistakes, keep reading for a complete guide on what and how to feed a frog.
Table of Contents
- What Do Frogs Eat?
- What Do Baby Frogs Eat?
- How Do Frogs Hunt?
- Frog Diet
- Feeding Frogs
- How To Feed A Frog
- Adult Frog Feeding Schedule
- Baby Frog Feeding Schedule
- Frog Food
- What Can’t Frogs Eat?
- Summary
What Do Frogs Eat?
Frogs in the wild are carnivores and will eat insects (e. g. fruit flies and dragonflies), earthworms, caterpillars, beetles, crickets, grasshoppers, snails, slugs, spiders and minnows. Frogs are very opportunistic hunters. They are not really picky about their food and will eat pretty much anything that will fit into their mouths.
Small frogs eat ants, aphids, springtails, mosquito larvae and fruit flies. Larger species like the Pacman frog are also known to eat mice. Aquatic species also eat tadpoles, redworms and mosquito larvae.
Many people think frogs are insectivorous, but this is not true. An insectivore’s diets consist mostly of insects. Since they do not exclusively eat insects, they are carnivores.
Frogs are usually nocturnal hunters. They rely on the cover of darkness to keep them hidden from potential predators.
In the wild they will generally eat as often as they can. Sometimes this means eating several small prey items in a day. If they hunt a grasshopper, or small rodent, this might mean not eating for several days.
They have to find a good balance between conserving energy and using it for hunting effectively.
| Baby Frog | Frog | |
|---|---|---|
| Wild | Plant leaves and roots, mosquito larvae, water striders and other small insects | Beetles, earthworms, crickets, mosquitos, slugs, snails, ants, butterflies, moths, grasshoppers, locusts, minnows, other frogs, small rodents and birds |
| Pet | Bloodworms, redworms, brine shrimp, pinhead crickets, wingless fruit flies | Earthworms, redworms, bloodworms, crickets, mealworms, locusts, grasshoppers, hornworms, waxworms, snails and slugs, minnows and pinky mice |
What Do Baby Frogs Eat?
The diet of baby frogs is very different from adults. Food and prey they eat changes as they grow.
Most tadpoles begin their lives as herbivores and only eat plant matter like algae. As they grow they change from herbivores and become omnivores.
Babies will eat mostly ants, mosquitos, gnats, redworms, fruit flies, and other very small prey.
A challenge for feeding baby frogs is that they have very high metabolisms. This means they digest their food quickly and need to feed multiple times a day.
Growth in baby frogs requires a lot of energy. Babies are constantly on the hunt and need to feed multiple times a day. This helps them grow and increases their chances of survival.
| Tadpole | Baby Frog | |
|---|---|---|
| Wild | Algae and other soft plant matter | Plant leaves and roots, mosquito larvae, water striders and other small insects |
| Pet | Algae wafers, bloodworms and fish food | Bloodworms, redworms, brine shrimp, pinhead crickets, wingless fruit flies |
How Do Frogs Hunt?
There are two different hunting strategies that frogs use to catch their food.
For the most part wild frogs hide and wait to ambush their prey. They remain motionless, and when something tasty passes by them, they pounce.
Many people imagine frogs catching prey with a long, sticky tongue, as this is how frogs are animated in many cartoons. The reality, is quite close.
A frog will flip its tongue out and strike a nearby insect, which then becomes stuck to their tongue. Their tongue is coated in a sticky saliva that helps to trap prey. They then pull back their tongue into their mouth to swallow the prey. Most species only have teeth on the upper jaw, so prey is often swallowed whole rather than chewed.
Frogs that lack a long, sticky tongue will catch food with their front legs. They will grab onto prey with their front feet and stuff it into their mouths before it can wriggle free.
Frog Diet
The diet of a pet is different from what wild frogs eat. As you are deciding to feed a frog, you can be a bit more selective about what to feed in order to keep it as healthy as possible.
Adult pet frogs generally eat insects and other small bugs. Crickets, mealworms, hornworms, waxworms, flightless fruit flies, grasshoppers and pinky mice (for larger individuals) all should be a part of their diet.
They will only eat live prey. They are not scavengers, so they will not recognize dead bugs as something they can eat. You should not feed your frog wild-caught or dead bugs.
The most important thing is that the bugs should be no longer than the distance between the frog’s eyes. This usually measures between 1 to 2 cm for adults. Ideally, the bugs should be gut-loaded.
The same rules apply for feeding baby frogs as adults.
Be sure the prey is no longer than the distance between the frog’s eyes, offer them only live prey, and make sure they are gut-loaded.
When feeding baby frogs you will want to stick with small insects. Pinhead crickets, wingless fruit flies, and bloodworms will be your best bet. It is also easy to find this prey in local pet stores.
Feeding Frogs
An important part of feeding a frog is supplements. Frogs, like many other reptile, need a calcium supplement to keep them healthy.
Reptile calcium powder is easy to find, but make sure you get one that includes vitamin D3. This will help your frog synthesize the calcium better.
You will also want to gut-load your prey before feeding.
Gut-loading simply means to feed the prey nutritious and vitamin-rich foods in order to increase its nutritional quality before feeding them to your frog. Most pet-stores do not gut-load their insects, this is something you will need to do yourself.
Once you have selected and gut-loaded the prey and purchased a calcium supplement you are ready to feed one.
How To Feed A Frog
Now that you know what you should be feeding frogs, it is time to learn how to feed one.Knowing how to properly feed a frog will help keep it happy, healthy and enriched. It will also make meal times much safer and avoid them being injured by prey.
- Take five crickets and place them into a container you can seal.
- Sprinkle a little bit of calcium powder supplement into the container.
- Gently shake it to thoroughly coat the insects in the calcium.
- Open the enclosure.
- Use tweezers or feeding tongs to drop the insects one at a time into the tank.
- Watch your frog and wait until it has eaten the first insect.
- After it has eaten the first insect, you can drop in the next one.
- Dropping multiple insects at a time can overwhelm them, and allow some prey to escape.
- The feeding session should last for 10 to 20 minutes.
- Anything your frog does not eat within this time period should be removed from the tank.
You should not move the frog into a separate container for feeding. This can cause unnecessary stress, and may result in your frog refusing to eat.
Adult Frog Feeding Schedule
You will want to feed an adult frog every two to three days, although this can vary with their size. Smaller, higher-energy species should be fed every two days, and frogs larger than three inches can be fed three days.
Smaller, higher-energy species should be fed every two days, and frogs larger than three inches can be fed three days.
You should feed a varied diet made up of:
- Crickets
- Mealworms
- Grasshoppers
- Locusts
- Minnows
- Brine shrimp
- Pinky mice
- Fuzzy mice (for larger species)
Avoid feeding prey that is dead or larger than the width between their eyes. Also do not feed any wild-caught bugs, fruits, vegetables or human foods. All of these can be harmful.
Crickets and mealworms are generally considered staple foods, but it is good to switch them out for other insects every so often. This helps to provide a more nutritious and varied diet.
Feed your frog approximately five insects per feeding. If your frog eats all of these within 10 minutes, it is safe to offer a few more insects. Likewise, if your frog eats slowly or does not eat all the insects you offer, you can remove them.
Baby Frog Feeding Schedule
Baby frogs are not able to eat the same prey as adults. Their smaller size limits what you can safely feed them. Most people stick to:
Their smaller size limits what you can safely feed them. Most people stick to:
- Pinhead crickets
- Bloodworms
- Wingless fruit flies
Since younger frogs have a higher growth rate, they need to be fed much more frequently than adults.
You will want to feed a baby frog twice a day, offer anywhere from five to ten insects per feeding. Again, this will vary depending on the species.
It is important to have as little contact as possible during feeding. The oils in our skin can upset the mucosal layer frogs have on their skin.
Frog Food
In order to help you feed a frog, we have compiled a comprehensive list of the best foods for frogs.
Keep in mind that you should only feed bugs and prey purchased from a pet store or from a website that sells live feeders for reptiles.
You should not feed wild or dead bugs as they can infect a frog with a parasite or disease. Pet species generally have a much lower resistance to parasites than their wild siblings.
When picking from the frog food list below try and provide variation in their diet. Just feeding one type of insect is not as nutritious as a varied diet. Wild species naturally vary their diet by hunting different prey:
- Mealworms
- Crickets (excellent for any size)
- Hornworms (use as treats)
- Waxworms (use as treats)
- Wingless fruit flies
- Locusts (good for prey variation)
- Grasshoppers
- Snails and slugs
- Brine shrimp (for aquatic species)
- Bloodworms (for baby frogs)
- Minnows
- Pinky mice
- Fuzzy mice (for the African bullfrog)
Remember, when feeding frogs, avoid prey items larger than the distance between their eyes. Feeding prey that is too large could cause your frog to choke while trying to swallow the bug.
What Can’t Frogs Eat?
Frogs eat wide variety of prey, but there is also a long list of foods they cannot eat.
Unlike many lizards, Adult frogs are strictly carnivorous. This means you should not try to feed them fruits or vegetables. Feeding anything other than meat or insects could cause impaction. Impaction is a blockage in the gut which could lead to death within a few days if left untreated.
This means you should not try to feed them fruits or vegetables. Feeding anything other than meat or insects could cause impaction. Impaction is a blockage in the gut which could lead to death within a few days if left untreated.
Frogs cannot have any human foods. Things humans use to season our food (e.g. butter and spices) can be very harmful to a frog. Food made for other animals could pose a choking hazard or contain harmful additives.
Finally, you should avoid feeding any bugs you catch outside or in your house. These bugs could contain parasites and diseases or expose your frog to pesticides. They can make your frog very ill.
Here is a list of foods to avoid feeding your frog:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Human food
- Food made for other animals (e.g. kibble)
- Prey larger than the distance between the frog’s eyes
- Wild-caught bugs
Summary
You now know everything you need to know about what do frogs eat.
Frogs in the wild are carnivores. They will normally eat insects, snails, slugs, worms, caterpillars, other frogs, pinky mice, fuzzy mice, and sometimes even small birds.
You can feed a frog various insects, such as crickets, grasshoppers, and locusts, as well as mealworms, bloodworms, hornworms, waxworms, brine shrimp and minnows.
Make sure that you are only feeding prey that is no longer than the distance between their eyes. Avoid feeding human food, food made for other species, wild-caught bugs or food that is too large.
Did you find this guide helpful? Let us know in the comments!
How to Care for Baby Frogs
By Jacob Reis | Updated September 26, 2017Baby frogs require special care, especially in feeding, to survive and live to adulthood. As amphibians, they also require a habitat relative to their natural habitat to thrive.
Things You'll Need
A glass aquarium
A piece of plexiglass cut and sanded
Nontoxic aquarium sealant
Aquarium gravel
Substrate like potting soil or sand
Distilled water
Plants, logs or other hides
A water dish for dry-environment species
Crickets, worms and other insects
Reptile diet powder for insects
Building the Habitat
Step 1: Choose an Aquarium
Many toads and some frogs live in dry, arid environments and do not do well in aquatic conditions. Others require much more water. Consult a herpetologist -- a reptile scientist -- if you aren't sure about your frog. Match the frog's enclosure as closely as possible to its natural habitat and consider the adult size of your frog before deciding. Most species do well in 20-gallon aquarium tanks. Make sure to choose a secure-fitting lid as well. Baby frogs are adept escape artists.
Others require much more water. Consult a herpetologist -- a reptile scientist -- if you aren't sure about your frog. Match the frog's enclosure as closely as possible to its natural habitat and consider the adult size of your frog before deciding. Most species do well in 20-gallon aquarium tanks. Make sure to choose a secure-fitting lid as well. Baby frogs are adept escape artists.
Step 2: Add Substrate
Many semiaquatic species, like the firebellied toad, are happiest in an enclosure that is half dry land and half water. Cut a piece of plexiglass to the width of the tank and to a height equal to the length of a full-grown frog of whichever species you will own, plus one inch. Sand the top edge until it's rough but not sharp -- your frogs will climb over this from water onto dry land. Secure this plexiglass in the middle bottom of the tank with aquarium sealant. You should now have two equal sides with a piece of plexiglass between them. Layer both sides with just enough aquarium gravel to cover the glass, then build one side of the tank up with another type of substrate like sand or potting soil right to the level of the plexiglass.
Layer both sides with just enough aquarium gravel to cover the glass, then build one side of the tank up with another type of substrate like sand or potting soil right to the level of the plexiglass.
Step 3: Add Water
Use distilled water to fill the other side of the enclosure. If your frog is from a warm or tropical environment, a water heater may be necessary. Getting the temperature right is especially important for baby frogs. Use a low-power aquarium filter to keep the water clean. If you're providing a dry environment for arid-habitat species, provide a water dish at least large enough the frog to submerge itself.
Step 4: Add Plants and Hides
Frogs require places to hide. Using a hollowed-out half-log on the dry side of their tank lets them get under cover when they are tired or feeling threatened. Adding real or artificial plants to the enclosure also helps to mimic frogs' natural environment. These plants and hides also retain moisture, which will help keep humidity high for species that require it. Use a stick or long piece of bark in the water, leaning onto the plexiglass, to provide your frog with another way from water to land.
These plants and hides also retain moisture, which will help keep humidity high for species that require it. Use a stick or long piece of bark in the water, leaning onto the plexiglass, to provide your frog with another way from water to land.
Frogs receive all their necessary vitamin D3 from their diet and as such do not require full-spectrum reptile lighting. Normal lights will work fine for them.
Caring Specifically for Baby Frogs
Once froglets have absorbed their tadpole tails and become frogs, their care is very similar to that of adult frogs. The only difference is in feeding. Growing frogs require more regular feeding than adults. Feed your frogs daily, usually at dawn or in the evening, depending on the species' natural schedule.
As carnivores, frogs must be fed insects. Crickets are ideal for baby frogs, as pet stores carry them in a variety of sizes. Use insects that are not longer than your frog's mouth is wide. This will prevent choking and ensure that the insects don't harm your frog. Remove uneaten food at dawn if fed in the evening, and in the evening if fed at dawn. As your frogs grow, they can start to take larger insects, like earthworms.
This will prevent choking and ensure that the insects don't harm your frog. Remove uneaten food at dawn if fed in the evening, and in the evening if fed at dawn. As your frogs grow, they can start to take larger insects, like earthworms.
Sprinkle crickets with reptile diet powder two or three times per week to ensure that your frog gets the vitamins and minerals he needs.
Do not touch or hold your baby frog if not absolutely necessary. Not only are baby frogs' skeletal structures fragile, but many frogs absorb chemicals through their skin and may pick up anything you may have on your hands. Baby frogs are especially sensitive to outside chemicals. Observe your baby frog's behavior from outside of his enclosure instead.
Warnings
Do not house baby frogs with larger frogs. A small-enough baby can become a meal for your larger critters.
How to feed the frogs from the pond. Breeding edible frogs. Is it possible to feed a frog with live food
Frogs are poikilothermic animals, their temperature is directly dependent on the temperature of the environment. Young frogs and tadpoles tolerate cooling down to -1.1 °C, but they do not tolerate high temperatures well. Adult frogs withstand a minimum temperature of -0.4 to -0.8 °C and tolerate temperatures of +39 °C. At a temperature of +5 ° C, the reflex activity of frogs almost stops. nine0003 Pond and lake frogs overwinter in water bodies, and common frog and ground toad - on land, burrowing in sand pits, cellars, under leaves, sawdust, moss or in the ground.
Young frogs and tadpoles tolerate cooling down to -1.1 °C, but they do not tolerate high temperatures well. Adult frogs withstand a minimum temperature of -0.4 to -0.8 °C and tolerate temperatures of +39 °C. At a temperature of +5 ° C, the reflex activity of frogs almost stops. nine0003 Pond and lake frogs overwinter in water bodies, and common frog and ground toad - on land, burrowing in sand pits, cellars, under leaves, sawdust, moss or in the ground.
Frogs are harvested for laboratory needs in the autumn season. Pond and lake frogs are caught from reservoirs with nets.
Frogs in large numbers should be kept in special terrariums, which are organized in dark places and basements. Frogs should be in concrete pools filled with clean water. The water level is small (only 3-4 cm), so that the frogs can freely stick their heads above the water. Place a few stones in the pool that protrude above the water so that the frogs can climb on them. It is better if the pool is divided into sections isolated from each other. The depth of the pool and the height of the partitions between the sections is 1-1.2m. It is advisable to change the water frequently, and give the water aged in tubs. The pool from above must be covered with nets. The temperature in the terrarium should be 6-10 °C. nine0003 Small numbers of frogs can be found in enameled tubs, tubs and aquariums. To do this, you must observe the above water level and change it frequently.
The depth of the pool and the height of the partitions between the sections is 1-1.2m. It is advisable to change the water frequently, and give the water aged in tubs. The pool from above must be covered with nets. The temperature in the terrarium should be 6-10 °C. nine0003 Small numbers of frogs can be found in enameled tubs, tubs and aquariums. To do this, you must observe the above water level and change it frequently.
Dead frogs or tadpoles must be disposed of in a timely manner.
Maintenance and delivery, especially in winter, of pond, grass and lake frogs are associated with significant difficulties. In addition, more females than males are found among these frog species, making it difficult to conduct a biological test to detect early pregnancy in a hospital setting. Breeding frogs in the laboratory is impossible. Recently, instead of frogs, earth toads have been successfully used, which are easy to keep throughout the year in simple, specially built nurseries or in basements, in boxes. In addition, according to Jungfes, the ground toad has 100 males for 18.5 females. All this distinguishes them favorably from frogs and speaks of the expediency of breeding ground toads at every hospital. nine0003 Ground toads are kept in terrariums. The bottom should be covered with light porous earth and covered with pieces of moss and turf. The earth is slightly moistened. In a terrarium for toads, it is useful to arrange small ponds (puddles) or put flat dishes filled with water. It is quite possible to keep ground toads in the wild in shady places (where there are puddles), fenced with wire mesh or a concrete wall. In winter, toads are placed in cellars, boxes filled with crushed and moistened peat.
In addition, according to Jungfes, the ground toad has 100 males for 18.5 females. All this distinguishes them favorably from frogs and speaks of the expediency of breeding ground toads at every hospital. nine0003 Ground toads are kept in terrariums. The bottom should be covered with light porous earth and covered with pieces of moss and turf. The earth is slightly moistened. In a terrarium for toads, it is useful to arrange small ponds (puddles) or put flat dishes filled with water. It is quite possible to keep ground toads in the wild in shady places (where there are puddles), fenced with wire mesh or a concrete wall. In winter, toads are placed in cellars, boxes filled with crushed and moistened peat.
Fat frogs and toads harvested in autumn go without food throughout the winter. By spring, they lose weight, and in order to keep them until autumn, feeding should be established in late spring and summer. nine0003 J. Prokopich (1957), studying the issue of feeding the pond frog, showed that 96% of the captured prey are beetles, bugs, mollusks, and 4% of the contents of the stomach are plant foods. Quite often (up to 10% of cases) the phenomena of cannibalism are noted.
Quite often (up to 10% of cases) the phenomena of cannibalism are noted.
Frogs and ground toads can be fed with their natural food (earth and flour worms, mollusks, spiders, flies and other insects, small fish). You can feed with finely chopped strips of meat (including frog meat). Food must be taken with tweezers and held in front of the mouth, as frogs and ground toads only capture moving prey. If the animals refuse to take food themselves, then it is necessary to resort to force-feeding, i.e. pushing food into the mouth. Feed should be 1-2 times a week. nine0013
HOME KEEPING OF TOADS AND FROGS
If many people have toads and frogs made of metal and stone, and even with a coin in their mouth as a symbol that brings money and prosperity, then some prefer to have live real amphibians at home. Under natural conditions, toads, and they are gray and green, lead a twilight lifestyle, always avoid bright light. Toads are very useful if they are in a summer cottage or garden plot, they exterminate harmful insects, including pests such as slugs, and in very large quantities. If there is a pond on the site, and there are no frogs, you should try to attract them by laying driftwood and shards near the pond, frogs like to hide under them. Often we cannot deny ourselves the desire to have a piece of wildlife next to us all year round, so we keep frogs and toads at home. Keeping toads at home deprives them of their freedom and natural instincts. However, toads and frogs are often settled in a living corner. nine0013
If there is a pond on the site, and there are no frogs, you should try to attract them by laying driftwood and shards near the pond, frogs like to hide under them. Often we cannot deny ourselves the desire to have a piece of wildlife next to us all year round, so we keep frogs and toads at home. Keeping toads at home deprives them of their freedom and natural instincts. However, toads and frogs are often settled in a living corner. nine0013
Toads are kept in high humidity and in aquaterrariums specially equipped for their keeping. They should have enough snags, pieces of bark and stones that serve as shelter for the toads, because during the daylight hours it will be impossible to see the toad, it does not come out of the shelter. The temperature of the content should be 18-20 degrees. Toads should be fed by running live insects into the terrarium, toads eat only moving insects and invertebrates. Cockroaches, bloodworms, slugs, flies and earthworms are good food for toads. A toad needs 3-4 grams of food per day. nine0013
nine0013
The skin of toads is quite bumpy due to the many venom glands, the largest glands are located behind the eyes. These glands are the most dangerous, they can give out a poisonous secret at a distance of up to one meter. If you take a toad in your hands, the glands located on the body and legs work, you can feel this liquid, it has an unpleasant odor and a bitter taste. In the old days it was believed that they appeared precisely from this secret allocated by the toad.
Keeping frogs in a pet zoo does not differ much from keeping toads. Frogs can live in terrariums with a pond, at a temperature of 18-20 degrees, or in aquariums with created islands or stones protruding from the water, on which frogs can periodically crawl out. Only now the frogs need to create a very high humidity. If the humidity is low, the frog's skin dries out quickly, which can lead to its death. The food for frogs is the same as for feeding toads, only tubifex is to be excluded. Frogs should be kept in aquariums without fish, because fish can be excellent food for them. Keeping frogs as domestic amphibians is an occupation only for rare exotic lovers. The most popular frog for the home aquarium is the clawed frog. The homeland of such a frog is Africa, in nature, frogs live in reservoirs with stagnant water and often move overland in search of another reservoir, but they cannot live without water. The bottom of the aquarium or aquaterrarium should be covered not with sand, but with fine gravel, frogs dig in it, and the water becomes cloudy. From plants for an aquarium with frogs, it is better to use large aquatic plants with a powerful stem, otherwise the frog can damage them by simply breaking them, and it is better to place plants floating on the surface, they can also serve as islands of land for frogs. nine0013
Keeping frogs as domestic amphibians is an occupation only for rare exotic lovers. The most popular frog for the home aquarium is the clawed frog. The homeland of such a frog is Africa, in nature, frogs live in reservoirs with stagnant water and often move overland in search of another reservoir, but they cannot live without water. The bottom of the aquarium or aquaterrarium should be covered not with sand, but with fine gravel, frogs dig in it, and the water becomes cloudy. From plants for an aquarium with frogs, it is better to use large aquatic plants with a powerful stem, otherwise the frog can damage them by simply breaking them, and it is better to place plants floating on the surface, they can also serve as islands of land for frogs. nine0013
In an aquarium with frogs, you need to constantly change the water, or install filters, the frogs release a lot of organic matter, and the water quickly becomes cloudy and dirty. Compressors can be omitted, as frogs breathe when leaving the water on the islands. From above, the aquarium should be covered with glass or a grate; frogs can easily jump out of it.
From above, the aquarium should be covered with glass or a grate; frogs can easily jump out of it.
If you have a pair of frogs, they can reproduce by laying eggs. Aquarium clawed frogs can be observed laying eggs 3-4 times a year. Tadpoles emerge from the eggs, and then, after about two months, frogs develop from them. Tadpoles and frogs can be fed fish food. Frogs in an aquarium can live up to 15 years. nine0013
There are many types of frogs, but some of them are very dangerous. These are toad frogs and spadefoot frogs. It is better not to keep them at home. Frogs imported from America are even more poisonous and dangerous. The poison secreted by toads and frogs will not cause serious poisoning in humans, but getting on the mucous membranes can lead to inflammation, redness and irritation. Skin areas should be thoroughly rinsed with water immediately after exposure to the poison.
Frogs are mostly green, gray and white, with a yellow belly, but cannot be colored. Be careful, colored frogs are imported from China, these are artificially colored frogs.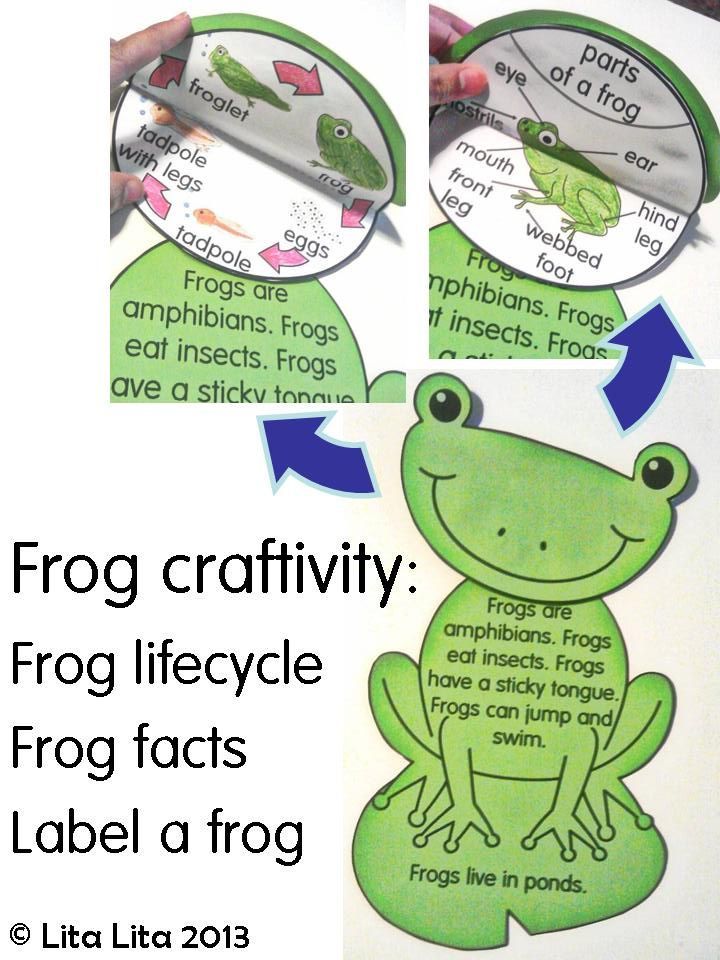 nine0013
nine0013
views: 12199
07/26/2017
Everyone knows that frog legs are considered a gourmet delicacy in France, and many fans of this dish around the world idolize their refined and delicate taste, which slightly resembles chicken.
Frog dishes adorn the menus of the most famous and respectable restaurants in Belgium, Italy, Spain, Greece, Great Britain, Holland and many other European countries.
Frogs are also in high demand in countries such as China, Vietnam, Laos, where they are bred on special farms, since frog meat is valued much higher than veal and costs an order of magnitude more expensive. In the East, no one will be surprised by the assortment of a supermarket, where, next to the hams of various animals and birds, frozen paws of these amphibians will lie.
In Peru, they even manage to add frog meat to chocolate and biscuits after drying and grinding it. It is believed that such an unusual delicacy cures anemia and helps women with infertility. nine0013
nine0013
Fried frog legs have also appeared in the menu of many Ukrainian cafes and restaurants (as a rule, they prefer to sell French or exotic cuisine). True, not every frog goes into food, but only large green ones, which are the edible species.
It is noteworthy that in many countries of the world, frog legs are equated with pike and even sturgeon caviar in terms of their biological value.
frog species nine0016
There are only five varieties of frogs in the reservoirs of Ukraine: grass frog ( lat. Rana temporaria ), moor ( lat. Rana arvalis ), quick ( lat. Rana dalmatina ), pond ( lat. Rana lessonae ) and lake ( lat. Rana ridibunda ). The first three species have a brown and brown body color, and the last two species are combined by scientists into a group of "green frogs", which, when crossed, give the very famous edible species. nine0013
For the first time a large green frog as a separate species was described by Carl Linnaeus back in 1758. It was he who gave her a name (lat. Rana esculenta), which translates as "edible frog." This hybrid species is widely represented in the reservoirs of Transcarpathia and lives in the Danube Delta.
It was he who gave her a name (lat. Rana esculenta), which translates as "edible frog." This hybrid species is widely represented in the reservoirs of Transcarpathia and lives in the Danube Delta.
During the Soviet Union, these amphibians were massively exported to France, because their value in foreign currency was three times (!) Higher than the price of expensive fish species. Every year, up to eighty tons of this first-class product were exported from the country. nine0013
At present, due to the spread of diseases and massive epidemics of birds, pigs and cattle, the demand for frog meat has increased dramatically. True, in Ukraine it still remains quite low, since the use of a frog by many residents of the country seems unusual and unnatural, therefore, today, the most promising direction is the cultivation of amphibians for export.
Description of the edible frog nine0013
When creating optimal conditions for growth and development, individual specimens of frogs can gain weight up to one and a half (!) Kilograms, but on average their weight does not exceed one kilogram.
An amphibian reaches sexual maturity at the age of three years and one female is able to lay up to fifteen thousand eggs during the year.
Frog rearing
Growing an edible species of frogs for commercial purposes is simple and technologically similar to breeding ordinary pond fish (the fattening period to obtain a marketable species is from twelve to twenty months). nine0013
To start, you need frog caviar, which can be collected in a pond during spawning, and in three or four years, the amphibian population will increase tenfold.
It is desirable to grow caviar in a closed pond with clean running water, since open ponds significantly increase the mortality rate of the population. The incubation room should be warm (it is necessary to maintain the temperature at least twelve degrees Celsius), bright and clean. It is advisable to change the water once every three or four days, while first passing it through the filter (or letting it settle), since highly chlorinated water can kill the entire population of frogs. nine0013
nine0013
Consideration must also be given to the ground. An ideal basis for an incubation pond is a mixture of earth, peat, crushed sphagnum (peat bog moss), expanded clay or charcoal (in a ratio of 3:1:1:1). Such soil will not turn sour, and harm the skin of tadpoles and young frogs.
After mass hatching of tadpoles (which grow for about
four months old), they are intensively fattened until they turn into young frogs, and then they are moved to an open pond. nine0013
It is desirable to leave the largest and healthiest frogs for subsequent breeding, thus forming a strong breeding stock of frogs.
Diet
The diet of frogs (at all stages of development) is quite varied. The food is based on small invertebrates (bloodworms, worms, caterpillars), crustaceans and insects (mosquitoes, flies, beetles). All swimming, jumping, crawling and flying small animals that a frog can swallow at one time are used. nine0013
To prevent rickets, young frogs need to be supplemented with vitamins.
Upon reaching marketable weight, the frog is slaughtered with a mallet, the skin is removed, the legs are separated, packaged and frozen. This is how they are implemented.
Frog legs in Europe range from four to six dollars, while live amphibians range from one to four dollars per kilogram (equivalent to about sixty adults). nine0013
Breeders need to remember that catching an adult frog is not easy, because it can overcome a distance of three (!) Meters from one jump, and at the same time it can knock down even an adult person. This "animal" is able to swallow a mouse, small snake or duckling.
However, the same French prefer to eat frogs of a much more modest size (weighing about one hundred grams).
Delicious frog legs are easy to make. To begin with, they are kept in cold water with lemon juice (like asparagus), and then fried in vegetable oil in breadcrumbs or batter. The dish turns out to be crispy, fragrant, tender, and small bones are not a hindrance for enjoyment.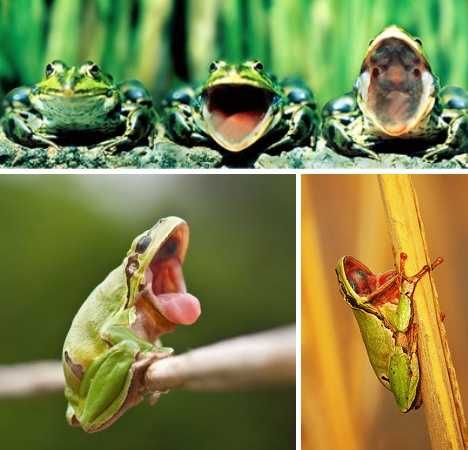 nine0013
nine0013
While working in the garden, you can often stumble upon frogs unexpectedly jumping out of the green grass or important and clumsy toads barely crawling out. Many of these animals are disgusted. Meanwhile, it should be remembered that there are benefits from frogs. They are tireless hunters for all sorts of small pests, bringing invaluable benefits.
The information in the article will allow you to get acquainted with the life of these animals, perhaps many will even feel some sympathy for these interesting creatures. nine0013
Before we know what the frog eats, let's provide a description of it.
General information about toads and frogs: differences
Toads and frogs are tailless amphibians living in water and on land. Even when leaving the water, these animals are very dependent on it. In addition to pulmonary, they also have active skin respiration, which allows amphibians to stay under water for a longer time. But dry air and prolonged exposure to the sun's rays have a detrimental effect on them. nine0013
nine0013
What does a frog eat? You can find out more about this in the article below.
Frogs and toads are closely related. Their difference lies in the fact that the skin of frogs is smoother, long strong hind legs have well-developed membranes between the fingers. All this helps the frogs to jump well and swim quickly. And the toad has dry skin covered with "warts", their paws are weak and short, allowing them to move only waddling or in short jumps. The membranes between the fingers are not developed, and therefore they swim poorly, and spend less time in the water (in fact, only during the breeding season). nine0013
It is difficult to determine what the frog eats by its structure and appearance, but it can be assumed. She has a flat back and head, and her eyes often protrude above the water surface like liquid bubbles, without betraying the animal itself. The hind legs are strong, like a spring, and the front paws, arranged like palms, are grasping. The jaws of the frog are studded with sharp, small, inward-facing teeth. A sticky tongue is located in a wide mouth. Comparing all of the above external signs, we can assume what the frog eats - mostly small aquatic inhabitants. nine0013
A sticky tongue is located in a wide mouth. Comparing all of the above external signs, we can assume what the frog eats - mostly small aquatic inhabitants. nine0013
Distribution
This family (true frogs) belongs to the order Anurans. The composition of the latter is numerous, it includes 32 genera and about 400 species. Most of them are inhabitants of the jungle (wet tropics).
The largest of the tailless amphibians is the goliath frog (3 kilograms), which lives on the coast of the Republic of Cameroon in Africa. Most recently, the smallest frog was discovered in New Guinea - the size of a little finger nail.
In central Russia, mainly varieties of the common and common toad live. They are widely distributed in Russia to Sakhalin, as well as throughout Europe and Africa (northwest). nine0013
Most of these amphibians have a modest inconspicuous coloration, but some of the outfit can be quite bright, especially for poisonous species that live mostly in the tropics.
Types of frogs and toads
Before we find out what frogs eat in a pond, as well as in other natural and domestic conditions, let's consider the most common varieties of these amphibians. Their life (toads and frogs) is closely connected with water, however, there are species that, in their adult state, mainly live and hunt only on land. nine0013
4 species of frogs live in central Russia: lacustrine, pond, herbaceous, moor. The first two species are green in color, the second are closer to brown.
Among the inhabitants of the gardens of Russia, moor and grass are more common. The first has a protective coloration that allows it to be invisible on the ground, but it is much smaller in size than grass. The second has a gray-brown or brown back with spots of different colors, and the belly is mostly light with dark spots. nine0013
In addition to the common frog, the Siberian frog also lives in Siberia. Its distinctive feature is pink spots on a brown abdomen.
Among toads, the most common are 2 types:
- common, or gray, with a dark brown back;
- green with large green spots on a light gray back.
Feeding characteristics
All types of frogs are tireless in obtaining food. What does a frog eat? It is known that the grass frog eats about 1300 insects - pests of gardens and orchards during the entire summer period. And the moored one exterminates many pests, including stinky bugs and beetles, which even birds shun. nine0013
As a rule, frogs forage during the day, and toads destroy pests mostly at night and at dusk.
What does a frog eat and how does it do it? They, like toads, are insectivorous animals. Frogs have teeth only on the upper jaw, and toads do not have them at all, so they have nothing to bite off pieces of food with. In connection with these features, food is swallowed whole by frogs and toads. They catch their prey with the help of their original tongue - long, strong and forked at the end. It is thrown out of the mouth with lightning speed in the direction of the victim, and then, due to the fact that it is sticky, it returns back with the prey already stuck. nine0013
It is thrown out of the mouth with lightning speed in the direction of the victim, and then, due to the fact that it is sticky, it returns back with the prey already stuck. nine0013
Another curious fact is that food enters the esophagus through the eyes. When blinking, the eyes sink deeper, pushing food into the esophagus.
Toads have an excellent appetite. The main food for them are invertebrates: worms, insects, bugs, spiders, caterpillars, molluscs, and so on. More than half (60%) of all insects eaten by toads are agricultural pests. Also, these animals feed on slugs. Many gardeners observe unpleasant slugs on strawberries, which usually hide in the damp ground during the day, and come out to eat soft juicy fruits of sweet ripe strawberries in the evening. It is very difficult to fight them. Just in this toads are great helpers. nine0013
Adult frog is a carnivore. The frog feeds on mosquitoes and other types of insects. For the lake, tasty prey are fish fry. As a result, fish farms suffer considerable damage. Hiding in shallow water, the frog waits for a flock of fry, and after waiting for them, it sharply opens its mouth, where a bunch of fish are involved in the flow of water. Tadpoles may also be in the mouth with fry.
Hiding in shallow water, the frog waits for a flock of fry, and after waiting for them, it sharply opens its mouth, where a bunch of fish are involved in the flow of water. Tadpoles may also be in the mouth with fry.
In the stomachs of frogs, plant remains are also often present, because part of the leaves and flowers on which their prey sat on sticks to their tongue. All this is quickly swallowed by the frog, after which it again goes for new food. nine0013
The larval stage is very similar in different frog species.
Tadpoles hatched from eggs do not have a mouth opening. The embryonic supply of nutrients ends after about seven days, when their length reaches 1.5 cm. During this period, the mouth breaks through and self-feeding begins.
The main food of tadpoles is unicellular algae. Random impurities that are absorbed by the frog's body along with the main food are mold fungi, protozoa, and other microorganisms. nine0013
The mouthparts of the tadpole are well suited for scraping off algae and are like a “beak” surrounded by fringed lips. The lower one has rough outgrowths and is larger than the upper one. Tadpoles feed during the day, being in heated water on the shallows and near the coast, forming mass accumulations (up to 10,000 pieces). Not everyone survives from them, since frog larvae serve as food for birds, fish and many other inhabitants of the reservoir.
The lower one has rough outgrowths and is larger than the upper one. Tadpoles feed during the day, being in heated water on the shallows and near the coast, forming mass accumulations (up to 10,000 pieces). Not everyone survives from them, since frog larvae serve as food for birds, fish and many other inhabitants of the reservoir.
Tadpoles turn into frogs of the year. They are pretty greedy. In the filled state, the volume of their stomach exceeds 1/5 of the total mass. nine0013
One more curious detail - with insufficient amount of animal food in the reservoir, the tadpole hibernates in the larval stage, postponing the transformation into a predator until spring.
Aquarium frogs
Especially popular among aquarists is the clawed frog, whose skin secretions have the effect of a natural antiseptic that disinfects water well. Such a frog is usually planted in an aquarium with fish that have some kind of infection. However, there must be a mesh partition between them, since the frog can eat its “patients”.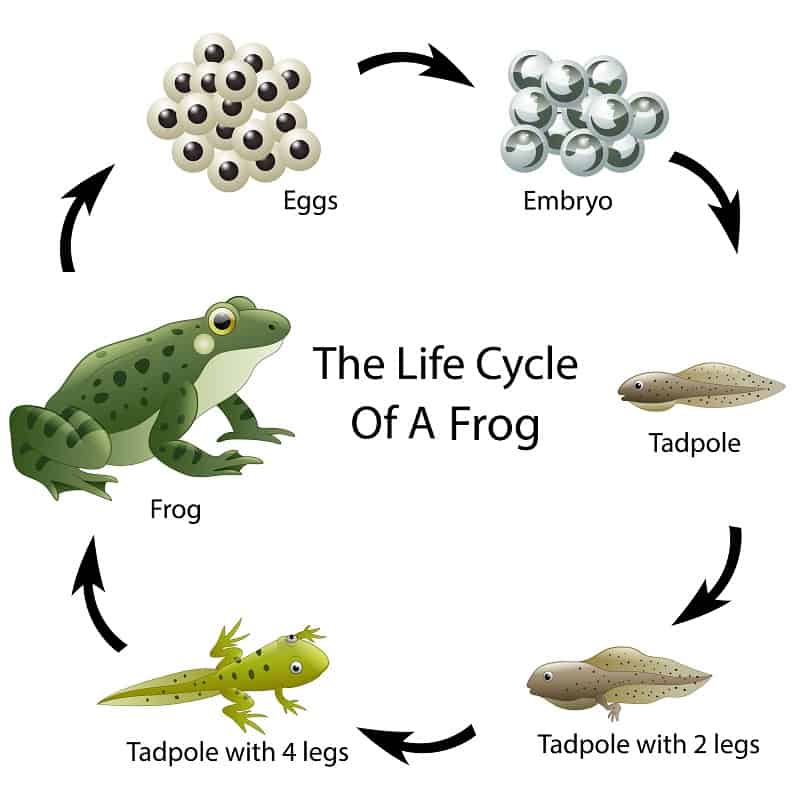 nine0013
nine0013
Usually, amphibians living in an aquarium feed on live food: earthworms, daphnia, bloodworms, etc. Due to the fact that in captivity frogs move little, they tend to become obese. They should be fed no more than 2 times a week. They may also eat thinly sliced lean meats or fish.
What do frog tadpoles eat at home? In the very first days, milk powder is suitable for them (baby formula is also good). In the second week, mixtures of insects and herbs can be introduced into the diet after a good steaming in the oven or in the sun to avoid various putrefactive processes. nine0013
Beef liver and small bloodworm are introduced in the last days of metamorphosis to strengthen the body of small frogs, but all this should be crushed to the smallest sizes.
Conclusion
Creating the animal world, nature has shown incredible ingenuity. Amphibians can be attributed to the number of amazing miracles.
They emerged from the World Ocean millions of years ago, but their connection with the water element was not interrupted.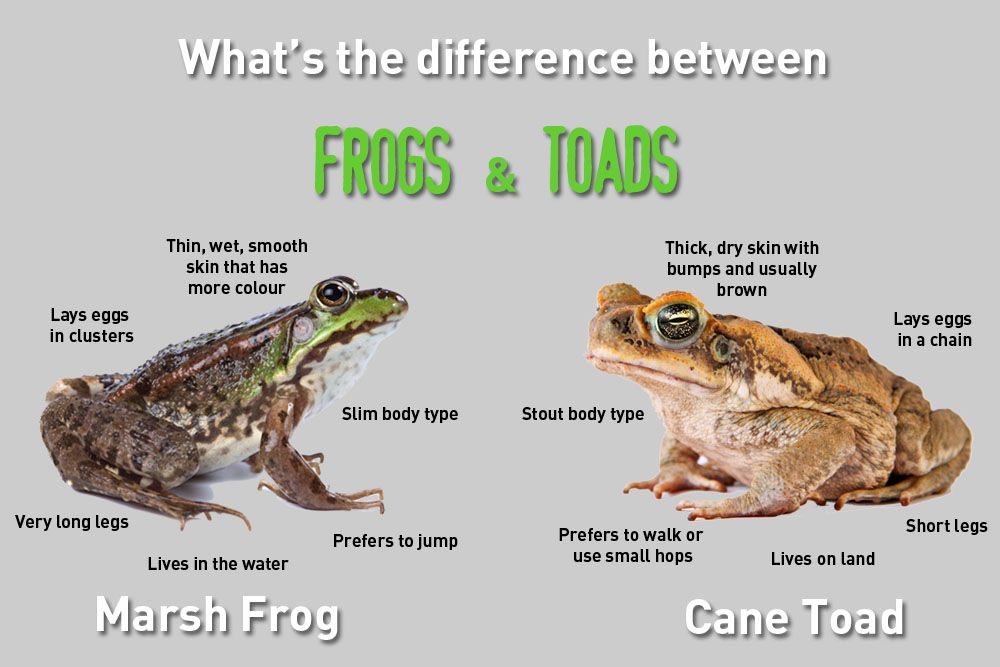 And they begin their life in the water.
And they begin their life in the water.
Frogs, leading an aquatic lifestyle, have long taken a strong place in amateur aquariums. And the touching little frogs, which are now sold in almost every pet store, cause an irresistible desire among people who are inexperienced in aquaristics to buy, as they say, "there are those two white ones and this gray one." But no matter how cute they are, let's first figure out what kind of frogs they are, what conditions they need and with whom they can live in the same aquarium.
Two types of frogs are currently kept in aquariums: the smooth clawed frog - xenopus (Xenopus laevis), which has been bred in captivity for many years, and the dwarf frog - hymenochirus (Hymenochirus boettgeri), which has become popular not so long ago. Adult frogs of these species vary greatly in size, appearance, behavior, and content. Frogs in pet stores are often kept in the same aquarium and when selling, they do not always focus on their species. nine0013
Clawed frog.
So, if aquarium frogs are white or pinkish, with red eyes, then regardless of size, they are clawed. The albino clawed frog was artificially bred at the Moscow Institute of Developmental Biology for laboratory experiments.
If a small frog is grayish, brownish or olive in color with dark spots, then to determine the species, you should pay attention to the length and thickness of its limbs, the presence of webbing between the fingers of the front paws and the pointedness of the muzzle. Wild-colored clawed frogs are more dense, they have thicker legs with bandages, like babies, a rounded muzzle, and there are no webbing on the fingers. nine0013
Hymenochirus, on the other hand, has membranes, long and slender legs, and a pointed muzzle. The size of an adult hymenochirus, as a rule, does not exceed 4 cm, while the clawed frog grows up to 10–12 cm.
These frogs also behave in different ways. They are active, strong and completely shameless. But they are clearly visible, they have large expressive faces and they have a habit of stretching out beautifully to hang in the thickness of the aquarium water. nine0013
nine0013
Hymenochiruses are calmer, quieter, slower and more delicate. They slowly crawl along the bottom, climbing on underwater objects and periodically freezing for a long time. As one amateur aptly put it, pygmy frogs resemble "meditating scuba divers." They almost do not damage plants, do not disturb fish (they simply do not have such an opportunity due to the size of their body and mouth), pollute the aquarium a little.
In a large aquarium, they are almost invisible, because they constantly hide on the bottom or in thickets of plants, and if active fish live nearby, then hymenochiruses may not keep up with food. nine0003
Aquarium frogs: maintenance and care
Both species are not too demanding on the conditions of detention. For clawed frogs, an aquarium of 20-30 liters per couple is enough, while it needs to be filled with water by half or a third. The aquarium should be closed with a lid or net. The soil is a large pebble. The aquarium is equipped with a compressor or a small internal filter, you can use a waterfall filter, but there should not be a strong current. There is no need for bright lighting.
There is no need for bright lighting.
The water temperature is about 22-25°C, xenopuses are practically indifferent to the chemical parameters of water. The exception is the content of chlorine and fluorine in the water, so it is recommended to defend it before adding it to the aquarium for at least 2-3 days. They change the water once or twice a week for 20-25%, a number of authors recommend changing less often, as it becomes cloudy.
Only hard-leaved plants may be planted, always in pots, otherwise they will be dug up immediately. Some lovers of these animals act as follows: they put a pot with a houseplant with hanging shoots next to the aquarium, and place these shoots in the aquarium. In this case, the aquarium becomes green, and the roots of the plant remain intact. nine0013
For hymenochiruses, the volume of the aquarium can be even smaller, 1-2 liters of water for such a frog is enough.
A lid is required - hymenochiruses, especially wild-caught ones, often try to escape.
They require a minimum water temperature of 24°C. A filter or compressor is desirable, but it should not be too powerful to leave areas of still, stagnant water in the aquarium.
At the bottom, it is necessary to equip small shelters under which these quivering creatures can hide. Plants are very desirable, it is good if they form dense thickets in places. It is also better to plant them in pots. It is necessary to equip the aquarium with lighting, since hymenochiruses sometimes like to rise among the thickets to the surface and bask under the lamp, sticking their head and upper body out of the water. nine0003
Feeding
Decorative aquarium frogs - both xenopuses and hymenochiruses - are preferred.
For claws, these can be mealworms, earthworms, crickets, bloodworms, fry and tadpoles. You can give pieces of liver, meat, fish, shrimp with tweezers.
Clawed frogs should not be fed tubifex, pork, fatty beef.
Hymenochirus are fed small bloodworms, live daphnia or fish. Dry and immobile frog food is usually ignored. Food for adult xenopus and hymenochirus should be given twice a week. nine0013
Dry and immobile frog food is usually ignored. Food for adult xenopus and hymenochirus should be given twice a week. nine0013
Feeding behavior of representatives of these two species of frogs also differs. Spurs have an excellent sense of smell, in addition, they have a very developed sense of touch (the receptors are pits located on the sides of the frog and resemble the lateral line of fish). Therefore, frogs are good at detecting smells and the slightest movements of water, quickly find food and greedily pounce on it.
Hymenochirus, on the other hand, usually need to bring food directly to the nose. You can teach them to feed in a certain place or according to a certain signal (for example, tapping with tweezers), but they will take a long time to get to the food, as if thinking along the way whether it is worth doing this at all. nine0013
Xenopus are extremely voracious and therefore prone to obesity, therefore, the amount of food they eat must be strictly controlled - a healthy frog must remain flat.
As for the clawed frog, knowing the peculiarities of its behavior, one can answer unequivocally - it has nothing to do in an aquarium with fish.
She will swallow everything that fits in her mouth, wipe out most of the plants, dig up the soil, raising the dregs, and move carefully placed scenery. nine0013
In addition, she does not like fresh water with a good current, and most fish will not like the swamp she is used to.
The only advantage of living together between fish and clawed frogs is that the frogs' skin mucus contains antimicrobial substances that can have a curative effect on sick fish. But at the current level of development of aquarium pharmacology, this can hardly be considered a serious argument. If you really want to do without chemistry, it is much easier to place a sick fish in a small container, where the frog had been for some time before. nine0013
Some aquarists advise keeping xenopus with Xenopus as they do well in old water and breathe atmospheric air. But why do it? A separate small aquarium with frogs will take up very little space, and everyone will be fine as a result.
But why do it? A separate small aquarium with frogs will take up very little space, and everyone will be fine as a result.
Things are not so scary with hymenochiruses. It is believed that they get along well with calm, not too large, non-predatory fish. They will not violate the beauty of the aquarium either. However, in a large aquarium, hymenochiruses spend a lot of time in shelters, so it is almost impossible to observe them, and it can be quite difficult to control the process of feeding them. nine0003
Diseases of frogs
Aquarium frogs may experience the following health problems:
In the treatment of frogs, preparations for tropical aquarium fish are usually used, choosing them according to the causative agent of the disease (anthelmintic, antifungal or antibacterial). Sick frogs are isolated. With dropsy, a puncture of the skin is often effective.
It should be known that individuals usually fall ill if they live in unsuitable conditions for them, are prone to obesity or experience prolonged severe stress. nine0013
nine0013
And finally, some interesting facts about clawed frogs:
- the clawed frog was the first vertebrate to be cloned;
- at the beginning of the 20th century, clawed frogs were used to diagnose short-term pregnancy: if a frog is injected with the urine of a pregnant woman, it starts spawning under the influence of chorionic gonadotropin;
- The clawed frog does not have a tongue, therefore, when eating prey, it helps itself with its front paws, and it cannot bend its fingers, it keeps them stretched out, as if eating with Chinese chopsticks; nine0196
- When clawed frogs accidentally entered the waters of the tropical United States, they destroyed native species of frogs there, therefore keeping clawed frogs is prohibited in some states, while in others it is limited.
Fortunately, keeping frogs is allowed in our country, so everyone can get these undemanding funny animals at home, watch and care for them, getting a lot of positive emotions and acquiring the skills of keeping an aquarium. The latter will definitely come in handy in the future, because usually everything is just beginning with frogs. nine0013
The latter will definitely come in handy in the future, because usually everything is just beginning with frogs. nine0013
Interview with a specialist: how to keep and feed freshwater aquarium frogs:
Fried cheesecakes with herbs, cheese and garlic
Fried cheesecakes with herbs, cheese and garlic
Eww! Do frogs eat it? What do amphibians eat? we make a container for insects, temperature conditions for keeping crickets, feeding crickets, how long do crickets live? how many crickets to feed frogs? photo feeding frogs toads amphibians tree frogs in captivity
For many amphibian lovers, their food causes not very pleasant feelings. Usually you can handle slippery amphibians, but many people don't like insects. In this article, we give some tips for those who would rather take an extra trip to the pet store than grow crickets in their garage or apartment.
Red-eyed Litoria (Litoria chloris)
Making a Handy Insect Container
handle insects. Sometimes such containers are sold in pet stores, but it is quite simple to make them yourself. nine0013
Sometimes such containers are sold in pet stores, but it is quite simple to make them yourself. nine0013
For frogs that feed on small crickets, a small to medium sized container is suitable for keeping crickets. If you need large insects using the same technology, make a larger container.
Related article Worms are ideal food for tailed amphibians
Take a large yogurt cup (preferably with a bottom diameter of 6 centimeters). You can try using a plastic container, but it most likely contains some kind of chemicals, as crickets often die quickly in it. So it is better to take a container made specifically for food. nine0013
Poke a few holes in the sides of the cup. You can use a pushpin for this. The holes should be large enough to allow air to pass through, but not so wide that crickets can gnaw through them and climb out. These containers can be changed every few months. Cut a hole in the lid of the cup large enough for a few crickets to crawl through. It is better if it is located closer to the wall of the glass. Then you can easily shake out a few crickets for breakfast for your pets. nine0013
It is better if it is located closer to the wall of the glass. Then you can easily shake out a few crickets for breakfast for your pets. nine0013
Make a plug for this hole. Cut it out of a piece of rubber. It should fit snugly into the hole, so that even the strongest cricket could not push it out. If you are lucky enough to buy a container with a hole in the lid, you can find another whole lid to put on top. Then all you have to do is take it off and feed the frogs through the hole.
Singing cricket
And finally, one more addition - useful, but not necessary. Cut off the edge of the sponge, rinse it well so that no chemical particles remain (even a new sponge may contain chemicals). Blot the sponge well several times and wring it out. Then take a needle and thread and sew the sponge vertically inside the cup on one side, passing the thread through the holes you made earlier. Now when you shake out dinner for your frogs, the sponge will not hang around the glass, injuring insects and blocking the hole. In addition, there are many holes under it, and to wet it, you just need to put the side of the cup under a stream of water from the tap without the risk of your crickets scatter. nine0013
In addition, there are many holes under it, and to wet it, you just need to put the side of the cup under a stream of water from the tap without the risk of your crickets scatter. nine0013
You will need to clean the container every time you want to buy more crickets. Right before going to the pet store, feed the leftover crickets to the frogs and then rinse him under very hot water. Crickets smell, and it will be very unpleasant if the glass is left dirty. If there are a few dead insects left in the container, shake them out, along with the remaining live ones, outside.
Temperature regime for keeping crickets
Crickets are recommended to be kept at a temperature of 25-30°C. But crickets smell bad, so not everyone wants them to live long in an apartment. If the house is not too hot and not too cold, then room temperature is fine for crickets. It is not recommended to keep them in the yard or in the garage if it gets cool or, conversely, too hot - above 30°C. nine0013
Feeding crickets before they become frog food
If you don't keep crickets for more than a week, you don't need to worry about feeding them. They need moisture - a sponge provides it. You can give them nutrients to keep your frogs healthy. In the pet store you can buy (although not in all) cricket food enriched with calcium, which literally stuffs insects with this useful substance. This is very, very good for the health of your charges. If you're willing to spend a couple of hundred a week on insects, then buy pellets fortified with calcium. Simply toss a few pellets into the cricket container and close it. Feed this to your crickets the day before you feed them to the frogs. Alternatively, you can give the crickets pieces of carrots and potatoes. nine0013
They need moisture - a sponge provides it. You can give them nutrients to keep your frogs healthy. In the pet store you can buy (although not in all) cricket food enriched with calcium, which literally stuffs insects with this useful substance. This is very, very good for the health of your charges. If you're willing to spend a couple of hundred a week on insects, then buy pellets fortified with calcium. Simply toss a few pellets into the cricket container and close it. Feed this to your crickets the day before you feed them to the frogs. Alternatively, you can give the crickets pieces of carrots and potatoes. nine0013
Litoria caerulea
If you are feeding your crickets a diet that does not contain calcium, dust them with calcium powder before giving them to the frogs. You need to sprinkle lightly, and not roll completely in calcium, like fish before frying.
How long do crickets live?
If you grow them yourself, they will probably last a long time. And for someone it's easier to go once a week and buy crickets for their two frogs. If you keep them in the heat or overfeed calcium, they can die quickly and you end up with a foul-smelling bunch of dead crickets. nine0013
And for someone it's easier to go once a week and buy crickets for their two frogs. If you keep them in the heat or overfeed calcium, they can die quickly and you end up with a foul-smelling bunch of dead crickets. nine0013
Related article Vermicultivation: Raising Worms at Home
Breeding Crickets at Home
If there is no suitable pet store near you, you will have to raise your own crickets. Here you can find useful information on this subject.
How many crickets to feed the frogs?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions. The easiest way to determine this is by experience. Start with three crickets per frog per feeding and see if they fill up or stay hungry. Remember that all frogs behave differently, even within the same species. Some will gorge themselves on something tasty regardless of their needs, while others will only eat when they are very hungry. nine0013
Overfeeding is bad for frogs, although some simply ignore the extra food unless they are hungry. To determine how much food your frog needs, you must first understand its character.
To determine how much food your frog needs, you must first understand its character.
You can feed frogs mealworms, moth caterpillars or grasshoppers, but they prefer crickets.
Cricket (Gryllidae)
Frogs smaller than 1 cm
If frogs are too small to swallow even the smallest cricket, they can be fed bloodworms. It is best to offer it live in a lid with a little water. Also popular food for frogs are wingless fruit flies (Drosophila). nine0013
Frogs, 1 to 3 cm
Give small two to three week old crickets daily. Their size should not exceed the width of the frog's head. The use of a calcium or vitamin supplement is recommended. Frogs really need these supplements to grow up healthy.
Related article What and how to feed amphibians?
Frogs 3 to 7 cm
Give every 2-3 days three to four weeks old crickets. You can sprinkle them with additives less often - 1-2 times a week. You can offer frogs newborn mice (if the frogs agree to eat them).