What food gives baby gas while breastfeeding
Foods that may cause gas in breastfed babies
When you breastfeed, the foods you eat also nourish your baby. That means a well-balanced diet with plenty of fresh fruit, veggies, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean protein is good for both of you. Eating a range of different foods may even help your baby enjoy a wide variety of flavors for years to come.
However, if you have a very fussy and gassy breastfed baby, you may wonder whether certain foods in your diet – especially those that tend to make you gassy – are to blame. Here's what you need to know about foods that may cause gas in breastfed babies.
Food sensitivities and gas in breastfed babies
Some moms swear that when they eat foods such as dairy products, broccoli, cabbage, bananas, eggs, or garlic, their babies are gassy and fussy for up to the next 24 hours. While there are few quality studies on the topic, the evidence suggests that a small number of babies may be sensitive to dairy products in a breastfeeding mother's diet, resulting in excessive gas.
The research on infant sensitivity to other foods is less clear – although you may find that symptoms such as gas and colic improve when you avoid eating certain foods that you've linked to stomach troubles in your baby.
Keep in mind that people of all ages get gas, no matter what they eat. Gas is simply a part of how the digestive process works. It happens when gut bacteria break down food in the intestine, as well as when you swallow air.
Infants tend to have more gas than older children and adults, and that's normal. Babies' immature digestive systems aren't yet efficient at breaking down the food they eat. Because they're still getting the hang of eating, they also swallow more air – and what goes in one end comes out the other. Plus, babies don't hesitate to let it rip when they're gassy.
If your breastfed baby doesn't seem bothered by gas, there's no need to adjust your diet. Usually, breastfeeding moms can eat a wide range of foods without problems. Foods to avoid when you're breastfeeding (or limit) typically include high-mercury fish, some herbs, alcohol, caffeine, and chocolate.
Food allergies in breastfed infants
A small number of breastfed babies – about 2 to 3 percent – have a true allergic reaction to a food in Mom's breast milk, usually a cow's milk allergy.
It's possible that other allergenic foods in a breastfeeding mom's diet – such as eggs, wheat, fish, peanuts, and other nuts – could cause an allergic reaction in babies, although there's not much quality evidence.
Babies with a food allergy usually have not only gas but severe colic, skin rashes, vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty breathing that lasts a few hours after they eat. If you notice any of these symptoms in your baby, call your doctor right away, since severe food allergies can be life-threatening.
If anyone in your close family has a food allergy, talk to your doctor about whether it's a good idea to avoid certain foods while breastfeeding.
Foods that may cause gas in breastfed babies
The most likely culprit for a gassy breastfed baby is dairy products in your diet, which include:
- milk
- cheese
- yogurt
- pudding
- ice cream
- any prepared food that contains milk products, casein, whey, or sodium caseinate
Other potentially allergenic foods – including eggs, wheat, peanuts, soy, fish, and tree nuts – might cause gas and other symptoms. However, the few studies that have been done have come to conflicting conclusions. There's no guarantee that eliminating these foods from your diet will help with your baby's gas.
However, the few studies that have been done have come to conflicting conclusions. There's no guarantee that eliminating these foods from your diet will help with your baby's gas.
Anecdotally, some moms say other foods that commonly cause gas in adults, such as broccoli, cabbage, beans, cauliflower, garlic, or spicy foods, make their breastfed babies gassy or irritable. You may find that your baby's gas improves when you eliminate a suspect food from your diet.
Does broccoli cause gas?
Some people get more gas when they eat cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli. This is because the stomach and small intestine don't entirely digest certain carbohydrates, notably fiber, found in broccoli. When these carbs reach the large intestine, they get digested by gut bacteria that in turn produce gas.
Just because broccoli causes gas in you, however, doesn't mean it necessarily will in your breastfeeding baby – so there's no reason to avoid it just in case. The fiber that causes gas in you doesn't pass into your breast milk. And there's no good evidence suggesting that cutting broccoli out of your diet will reduce gas and fussiness in your baby.
And there's no good evidence suggesting that cutting broccoli out of your diet will reduce gas and fussiness in your baby.
That said, some moms have linked broccoli to gas in their babies. If you do notice that your baby seems gassier and fussy every time you eat broccoli, you may want to try eliminating it from your diet to see if your baby's gas improves.
Know that once your baby starts eating solids, they may have gas when you feed them broccoli for the same reason you do. Nevertheless, it's a good idea to expose your baby to many flavors, including broccoli, as often as possible when they're little. That way they'll learn to enjoy these healthy foods at a young age. Start with very small portions and gradually increase the amount you serve, which helps reduce or even eliminate noticeable gas problems for many people.
Does cabbage give you gas?
Cabbage is another high-fiber cruciferous vegetable that can cause gas in adults and babies who eat solids. Again, the fiber reaches the large intestine intact, where it's broken down by naturally-occurring gut bacteria that produce gas.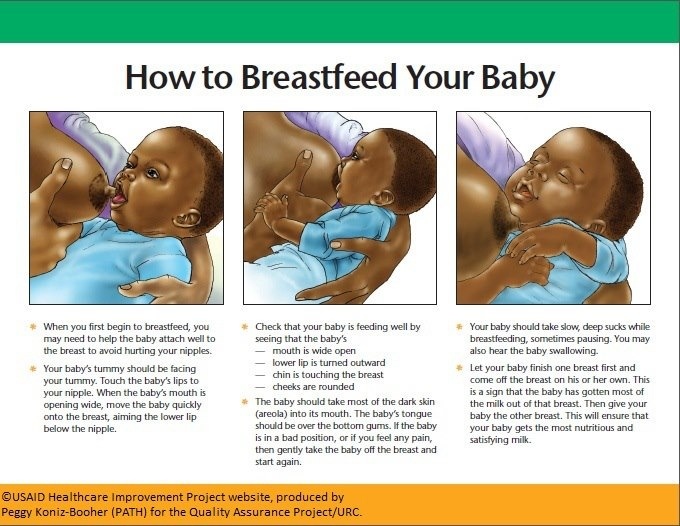
Just as with broccoli, there's no reason to systematically avoid cabbage while you're breastfeeding just because it gives you gas. But if your baby seems gassy and fussy every time you eat cabbage, you may want to avoid it to see if your baby's stomach troubles improve.
Do bananas cause gas?
Fruits including bananas, apples, peaches, pears, and dried fruits can cause excessive gas, especially in people with gastrointestinal (GI) disorders including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). That's because these fruits contain fructose, a type of sugar their GI systems poorly digest. Fruits with high-fiber skin, like apples and pears, tend to cause more gas than bananas.
Research shows that fructose can pass through breast milk. And children can have IBS, especially if a parent has the condition. IBS causes other symptoms beyond gas, including abdominal pain as well as constipation and/or diarrhea. If your baby has these symptoms and you're concerned it's IBS, talk to their doctor. They may suggest an elimination diet for you and possibly probiotic drops for your baby.
They may suggest an elimination diet for you and possibly probiotic drops for your baby.
Do eggs cause gas?
Eggs are actually less likely to cause gas than many other foods. However, when they do, the gas tends to be stinky.
Egg allergies, on the other hand, are one of the most common food allergies in children and can occur as early as infancy. Children who are allergic to eggs have other symptoms, including skin rashes, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or trouble breathing, in the hours after eating.
Research suggests that breastfed infants are unlikely to experience food allergies from allergenic foods that their moms eat. But if you think your baby has a food allergy – and especially if they have any other symptoms after you eat eggs or other allergenic foods – talk to their doctor.
Does garlic make babies gassy?
Garlic commonly causes gas for people with IBS and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). It's a high-FODMAP food, meaning it contains certain sugars – in this case, fructans – that people with these conditions have a hard time digesting, causing gas and other GI symptoms like constipation and diarrhea.
There's no evidence proving that the gas-causing properties of garlic make it into your breast milk. But you may want to consider eliminating garlic from your diet if it seems to cause tummy troubles in your baby.
Strong flavors like garlic can make your breast milk taste and smell different, although this usually doesn't make babies fussier. In fact, research has found that babies whose moms eat garlic extract tend to feed for longer and prefer more flavors in breast milk, which may ease the transition to solid foods.
What to do if your breastfed baby is gassy
For the most part, baby gas isn't something to be concerned about. In the vast majority of cases, a little gas is completely normal and doesn't bother most babies. Chances are you can eat what you want without upsetting your baby's tummy.
However, you may want to try one of the following tactics if your gassy breastfed baby seems to be uncomfortable or colicky, cries for no discernable reason, or consistently has a challenging witching hour.
Check for latching problems
Many newborns struggle to find a good breastfeeding latch. If your baby isn't latching on well, they'll swallow more air, resulting in gas. A poor latch may also make your nipples sore, bruised, red, or cracked. If you think your baby might not be latching properly, talk to their doctor and consider visiting a lactation consultant.
Manage oversupply
If you have an abundance of milk, your baby may be suffering from lactose overload. This happens if your baby gets a lot of foremilk, which has lots of lactose, and less hindmilk, which is high in fat to slow the digestive process. As a result, the enzyme in your baby's system that digests lactose becomes overwhelmed and can't do its job. Babies with lactose overload may also be fussy at feedings and have loose, green, explosive stools.
To ensure your baby is getting enough fatty hindmilk, allow your baby to nurse for as long as they want on the first breast. Your baby may only nurse a little – or possibly not at all – on the second breast. It's a good idea to talk to a lactation consultant to make sure oversupply is the problem before you try nursing on only one side, so you don't inadvertently cause your milk supply to drop.
It's a good idea to talk to a lactation consultant to make sure oversupply is the problem before you try nursing on only one side, so you don't inadvertently cause your milk supply to drop.
Keep the air out
The more air your baby swallows during feedings, the gassier they'll be. Try to feed your baby before they start crying, because babies swallow air when they're upset. Also burp your baby after (and even during) every feeding.
Talk to your pediatrician about probiotics
Gas is partly a byproduct of certain bacteria in the intestines. Some evidence suggests that giving breastfed babies probiotics to feed healthy bacteria in the gut can help ease colic (which is commonly thought to be linked to gas). Talk to your doctor about whether it might be helpful to give your baby infant probiotic drops.
Try an elimination diet
Still concerned that your baby might have a food sensitivity? You don't need to severely limit your diet (which can lead to nutritional deficiencies, especially when you're breastfeeding) or avoid all foods that are gas-forming for you.
Instead, take notes on your diet and your baby's gassiness and look for patterns. Then eliminate one potentially problematic food at a time for two to three weeks to see what happens. If your baby is sensitive to that food, you should see an improvement within a week. (Though babies with true food allergies will need at least a month for symptoms to resolve.) After a week, try the food again to see how your baby responds.
If you decide to eliminate one or more foods from your diet, talk to a registered dietician and/or a lactation consultant. They can evaluate the situation and help ensure you're meeting your nutritional needs. In most cases, you should be able to return to your normal diet when your baby is around 6 months of age.
Foods to Eat or Avoid When Breastfeeding
Reviewed by Poonam Sachdev on June 26, 2022
It’s a good source of protein. Some, like salmon and tuna, also give you omega-3s, which your body needs. But what about mercury and other contaminants? You can have cooked seafood twice per week. Each serving can be up to 6 ounces, which is the size of two decks of cards. Choose types that are lower in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, and trout. Avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, which have high levels of mercury.
Each serving can be up to 6 ounces, which is the size of two decks of cards. Choose types that are lower in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, and trout. Avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, which have high levels of mercury.
Love hot sauce? Most babies can handle it and other fiery foods in your diet. But if your little one is gassy or colicky and gets diarrhea every time you sprinkle red pepper flakes over your pizza, cut back on the heat for a few weeks to see if that helps.
They’re full of flavor. But some herbs may affect how much milk your body makes. For instance, eating a lot of parsley could curb lactation. And too much sage and peppermint may cut your milk supply. For some nursing moms, even peppermint-flavored toothpaste and candies are a problem.
It’s rarely a problem. But see how your baby does. Tell your pediatrician if your tot gets skin problems, has trouble breathing after breastfeeding, or has other symptoms.
As refreshing as your cup of chai or Earl Grey may be, it has some downsides. It’s got caffeine, which can affect your sleep – and your baby’s. It may also make it harder for your body to absorb iron, which you need for energy. If you drink hot or iced tea, try not to sip it when you eat foods that are rich in iron, such as lean meat; dark, leafy greens; and fortified breakfast cereals.
It’s got caffeine, which can affect your sleep – and your baby’s. It may also make it harder for your body to absorb iron, which you need for energy. If you drink hot or iced tea, try not to sip it when you eat foods that are rich in iron, such as lean meat; dark, leafy greens; and fortified breakfast cereals.
What if you aren’t allergic, and you want to prevent your baby from developing an allergy? Sorry, but there’s no proof that you can do that by skipping specific foods. Cutting certain foods out of your diet may make the skin condition eczema less likely for your little one. Ask your doctor or pediatrician for advice.
Breastfeeding can make you thirstier than you usually are. If that’s the case, drink a glass of water every time you breastfeed. But no matter how parched you feel, don’t go for regular sodas or fruit drinks, which give you calories without nutrition.
It's best for your baby if you don't have any booze at all. But if you do choose to drink, don’t breastfeed until the alcohol has completely cleared your milk. For 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of liquor, wait at least 3 hours. Pumping doesn’t speed that up.
For 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of liquor, wait at least 3 hours. Pumping doesn’t speed that up.
Common culprits include beans, broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts. Bloating, burping, and passing gas are normal. But if your baby is gassy or has colic, avoid these foods for a few weeks to see whether they relieve the symptoms.
Both have caffeine. You’ll also find it in energy drinks and cola. If you’re lost without your latte, limit yourself to 2-3 cups per day of the brewed kind. Or you could switch to decaf.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Getty
2) Getty
3) Getty
4) Getty
5) Getty
6) Getty, iStock
7) Getty
8) Getty
9) Getty
10) Getty
SOURCES:
Mayo Clinic.
The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
La Leche League.
The American Academy of Pediatrics.
U.S. Department of Agriculture.
© 2022 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
Flatulence in children: help and treatment
Increased gas formation is a problem that accompanies almost all babies in the first weeks of life. This is due to the fact that the baby's body is just being formed. Adapting to life outside the mother's belly is not an easy task.
This is due to the fact that the baby's body is just being formed. Adapting to life outside the mother's belly is not an easy task.
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months Read more
Intestinal flatulence is often confused with baby colic. From a medical point of view, there is no “equal” sign between these phenomena, from a practical point of view, they are, in general, one and the same. When a child is worried about flatulence, he becomes naughty, cries loudly, kicks his legs and refuses to eat. The baby is worried about sharp pains in the abdomen. Premature babies suffer from them more often than those born at term. Their digestive system is even more immature, and the musculature of the walls of the stomach and intestines is very poorly developed. Like colic, bloating begins to bother babies from birth, but significantly decreases (or completely disappears) by 3-4 months, when the child gets stronger.
Causes of flatulence in infants
Aerophagy. This is the name of the swallowing of air during feeding. The child may take the nipple or breast incorrectly, cry during feeding, rush, the mother may hold the bottle incorrectly. As a result, the baby “grabs” air, which enters the intestines and causes the formation of gases. Therefore, it is very important to establish the correct feeding process.
Immaturity of microflora. The baby is still very small, his body is just learning to work, the microbiocenosis (microflora) has not formed. Flatulence will pass with age. If the problem is tormenting an older baby, pay attention to the child's reaction to complementary foods or changing the mixture. If the baby is unwell, consult a doctor to alleviate his condition.
Diet of a nursing mother. Gas in the baby's intestines can be caused by foods that the mother ate. A nursing woman needs to be more careful about her diet. It is worth using dairy products, fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, cabbage, yeast bread, pastries, nuts with caution. It is better to avoid carbonated drinks altogether.
It is worth using dairy products, fresh fruits and vegetables, legumes, cabbage, yeast bread, pastries, nuts with caution. It is better to avoid carbonated drinks altogether.
Delayed bowel movements. Under such conditions, gases accumulate, this gives the baby more and more discomfort.
How to help a baby with flatulence?
Help the baby empty the intestines. Effective massage of the tummy (make circular movements around the navel clockwise), gymnastics (press the baby’s legs bent at the knees to his tummy, then straighten them), a warm bath will help (it’s good to add a decoction of chamomile or string). If mild methods don't work, you can use an enema or a gas tube. Remember that you need to act very carefully!
With flatulence, children's teas with medicinal herbs - fennel, chamomile, dill, anise and cumin help. You can buy dill water in the pharmacy in the drug production department (keep in mind that it is stored in the refrigerator and no more than 10 days).
To prevent gas formation, make sure that the baby eats in a calm environment, not distracted, not in a hurry. Before feeding the baby, it is useful to put it on the tummy for 5 minutes (this is a kind of massage). After the baby has eaten, hold it with a “column” so that excess air comes out with a burp.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
3.79 14
Power supplyShare:
You may be interested
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
Foods that cause colic in newborns
The baby cannot fall asleep, at first glance he cries for no reason, behaves anxiously. All this causes anxiety among young parents, who cannot immediately guess what is the main reason for such behavior. And the answer may lie on the surface. It’s just that mom didn’t follow a diet and allowed herself foods that cause colic in babies. As a result, the baby develops intestinal spasms, pain, which means that the little one begins to cry and spin. To prevent this from happening, the mother should monitor her diet by excluding foods that cause colic in children from the menu.
As a result, the baby develops intestinal spasms, pain, which means that the little one begins to cry and spin. To prevent this from happening, the mother should monitor her diet by excluding foods that cause colic in children from the menu.
Foods that can cause colic in a newborn
In your daily diet, avoid foods that cause colic in newborns. These include:
- Whole milk. The lactose contained in the composition refers to a substance that causes colic in newborns due to gas formation. This product is poorly absorbed by the baby's body and can cause, in addition to bloating, allergic reactions. In your diet, it is better to replace milk with kefir, curdled milk, fermented baked milk.
- Spicy sauces. Ketchup, mayonnaise, mustard cause intestinal irritation, which causes colic in newborns, so it is not recommended to include these products in the menu of a nursing woman.
- Black bread. The enzymes that make up the composition lead to gas formation.
 When breastfeeding, this product is best replaced with whole grain bread.
When breastfeeding, this product is best replaced with whole grain bread. - Legumes. Lentils, corn, beans, peas are foods that cause colic in newborns. Instead, it is better to include other protein-rich foods in the diet of a nursing mother. For example, cottage cheese, soy cheese, low-fat fish.
- Raw vegetables and fruits. Flatulence causes fiber, and some fruits can cause an allergic reaction. Therefore, any vegetables and fruits should be heat treated.
- Sweets. Chocolate, sweets are among those products that cause colic in children. So it is better to give up your favorite delicacies. Carbonated drinks. Not only Fanta or Coca-Cola can cause colic in newborns, but also ordinary sparkling mineral water. So you should accustom yourself to drinking weak tea or herbal decoctions.
How to make a menu to save a newborn from colic
Knowing what foods cause colic in babies, any woman can make the right menu for herself. May include:
- Lean fish and meat.

- Cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk.
- Buckwheat, rice, wheat groats.
- Baked vegetables and fruits.
It is important to consider not only what foods cause colic in newborns, but also to understand what can cause gas. In this regard, it is necessary:
- There are products separately without mixing them.
- Drink more clean water.
- Eat in small portions.
- Avoid exotic foods.
In order to increase the protective properties of the child's body, it is necessary to gradually introduce new foods into the diet. After all, the baby should prepare for nutrition not only with mother's milk. And at this stage it is very important to reduce the formation of colic. For this purpose, you can give the baby the drug "Kolikid", which is shown to children from the first months of life. The active ingredient simethicone gently eliminates gas formation in the stomach of the baby, without penetrating into the bloodstream and not being absorbed by the body.











