What kind of food do baby possums eat
What Do Possums Eat? Can You Feed Baby Possums?
toggle
Home > Big Impact > Community
Source: Getty Images
If you find a baby possum abandoned on the side of the road somewhere, you probably shouldn’t pick them up before calling animal control. But what happens if you have no choice but to take them home to nurse them back to health? You might find yourself with an adorable conundrum on your hands. You might even find yourself wondering a few things about possum biology and behavior. For instance: can you feed baby possums? Should you feed them? And either way, what do possums eat?
Article continues below advertisement
Source: Getty Images
What kind of possum are we talking about?
If you’re from Australia, a possum is a very different animal from the one Americans keep referring to as possums. What we are talking about is the opossum, America's only marsupial, and one that possesses very few similarities to its Aussie cousin. There are 65 different species of opossum in North America, according to the Opossum Society. The most common of these many marsupials is the Virginia opossum, which is the one we shall focus on today.
Article continues below advertisement
What do possums eat?
Frankly, when it comes to the opossum, the question “what do they eat?” doesn’t really seem appropriate. It might be more appropriate to ask “what don’t they eat?” Opossums have always had a bit of a bad reputation among suburban residents for being scavengers — which, of course, they are. But that doesn’t mean we should hold it against them. Especially because their versatile diets actually help us get rid of carrion (decaying dead animal bodies).
Source: Getty Images
Article continues below advertisement
According to pest control company Terminix, opossums eat everything from dead animals to insects, rodents, birds, frogs, plants, fruit, and grain. They don’t just feed on the flesh of carrion or roadkill either. Possum diets require a high degree of calcium, which they can get from eating the skeletal remains of rodents and other dead creatures. Opossums will also eat cat food, dog food, and table scraps from our garbage cans. Unfortunately, it is this “taste for trash” that makes them more of a pest than a helper in the eyes of many.
Possum diets require a high degree of calcium, which they can get from eating the skeletal remains of rodents and other dead creatures. Opossums will also eat cat food, dog food, and table scraps from our garbage cans. Unfortunately, it is this “taste for trash” that makes them more of a pest than a helper in the eyes of many.
How do possums eat so many different things?
Opossums are scavengers by evolution and opportunity. They are nocturnal but possess poor eyesight, which doesn’t really help when it comes to trying to find food. Luckily, they make up for this with great hearing and a very keen sense of smell. This has made them fairly successful opportunists, especially when they find themselves living in and around suburban and rural communities.
Article continues below advertisement
These remarkable marsupials possess other positive traits as well — though we will admit that most of these also have to do with them finding food. Opossums don’t just find food well, they can also remember where it is located for the next time. According to Landscape Architecture Magazine, possums scored higher than rats, rabbits, cats, and dogs in laboratory tests meant to recall where food was placed. That’s why it’s so hard to get rid of possums on your own — they remember where you keep the goods!
According to Landscape Architecture Magazine, possums scored higher than rats, rabbits, cats, and dogs in laboratory tests meant to recall where food was placed. That’s why it’s so hard to get rid of possums on your own — they remember where you keep the goods!
Source: Getty Images
Article continues below advertisement
What do baby possums eat?
Adults may be great at scavenging, but baby opossums are not nearly as well-equipped. Like all marsupials, opossum mommies lack a placenta, so their young must grow and be kept in a pouch. Newborn opossums are about the size of a honey bee and will stay in their mother’s pouch for around 80 days before they are mature enough to begin scavenging on their own.
What to feed baby possums?
Once they are big enough to leave the pouch, baby possums can eat just about everything. You can feed them dog and cat food in moderation. You could also feed them insects like cockroaches, worms, slugs, and snails (one of their favorite foods). This is only pertinent if the baby is old enough, of course, and with an orphaned opossum, that isn’t always known.
This is only pertinent if the baby is old enough, of course, and with an orphaned opossum, that isn’t always known.
Article continues below advertisement
Source: Getty Images
According to the blog WildHeart, baby possums do not thrive on milk. For one, marsupial milk is very different from cow’s milk or formula. On top of that, baby possums don’t suckle like other animals, so attempting to bottle feed could cause them to aspirate and die. The point we’re trying to make here is that you, reader, are likely ill-equipped to feed or care for a baby possum on your own.
Should I feed a baby possum?
No, you really, really shouldn’t — not without some guidance, anyway, If you find a baby possum, either alone or attached to their deceased mother, you should contact your local animal control, veterinarian, or animal rescue right away. If the baby possum is alone and walking in the wilderness and you can’t help yourself, get a box with towels or old shirts, along with a wrapped heating pad or water bottle, and get them to an animal expert as quickly as possible. That is the best way to help them.
That is the best way to help them.
Advertisement
More from Green Matters
Latest Community News and Updates
Advertisement
5 Things Baby Possums Like to Eat Most (Diet, Care & Feeding Tips)
It is easy to be touched by the sight of a cute and cuddly baby possum. You may come across one who has become detached from its mother or has otherwise lost its way. If you are to help the little fur baby survive, it is important to learn a little about how to nourish and care for it.
Table of Contents
- Baby Possum Habits and Biology
- Do baby possums eat dirt?
- What do baby possums like to eat most?
- Food You Should Avoid Feeding Baby Possums
- Tips to Feed Baby Possums
- FAQ
- Summary
Baby Possum Habits and Biology
Female possums are without a placenta. They carry their babies in a pouch between 80 and 100 days until they are big enough to leave.
Possums are scavengers. A baby possum is about the size of a honey bee when it is first conceived and will not leave the mother’s pouch until it can scavenge on its own.
The possum is a nocturnal creature with poor eyesight but excellent hearing and a keen sense of smell. This gives it some advantages when trying to survive in a human habitat. Possums forage for food while humans sleep, and they are more alert to potential threats in the dark as they rely more on sound than sight.
As scavengers, possums are not very good. However, what they lack in skill they make up for in memory. Once they have a hit scavenging jackpot, they remember where it is and return to it again and again to feed.
Although possums do not hibernate, they do slow down in winter. They burrow themselves into holes that they fill with leaves or whatever else they can find to keep themselves warm. Their fur and fat reserves also help keep the chill out.
And here is a fun fact. Ever wonder where the phrase “playing possum” comes from? It refers to the fascinating defense mechanism possums used to protect themselves against predators.
When possums are frightened or harmed, they go into a kind of catatonic state. They freeze, paralyzed with fear, and sometimes lay down as though dead.
A baby possum who is left unharmed will usually recover from this state after a few hours.
Do baby possums eat dirt?
No. Possums are omnivorous and survive by eating a wide-range of foods. Dirt is not among them.
What do baby possums like to eat most?
Once a possum is mature enough to scavenge on its own, it will do so. Baby possums are not picky about what they eat. Evolution has given them the ability to make the best of what’s around.
One little known fact about possums is their high need for large amounts of calcium. It is why they will eat the remains of rodents and roadkill. Here are some of the other things that baby possums like to eat most:
Here are some of the other things that baby possums like to eat most:
- -They are especially fond of snails. They will also eat insects, including ants, cockroaches and the like.
- -Plants. If you are taking care of a possum or have spotted a few rummaging around your house (remember, they will remember where food is once they have found it), then you should keep your potted plants at an elevated level and build a fence around your garden plants.
- -Fruits and grain. Baby possums are likely to eat low-hanging fruit from trees or fruit that has fallen to the ground. But they will also climb a tree to get at the fruit.
- –Frogs. If you have any around your house, you are unlikely to be burdened by the noise they make for very long if there are possums around.
- -Dog food, cat food, and scraps. It is said that one man’s trash is another man’s treasure. The aphorism can certainly be extended to possums. They are known for rummaging around trash looking for discarded food and containers with minute quantities of food in them.

The bottom line is that baby possums will eat nearly anything they can find. Accessing source of food is not a typical problem for them. Their sharp sense of smell gives them the ability to track down the exact location of the food.
They have sharp claws that enable them to dig up the ground when necessary. Their sharp claws and long tail also give them the ability to climb trees to get what they need.
Food You Should Avoid Feeding Baby Possums
As was stated above, possums eat just about anything. However, you should take care when feeding baby possums. Unless you have the education and training, you are unlikely to be able to tell the exact age of a baby possum.
If you find it rummaging through animal remains or discarded trash, it is probably old enough to have left its mother’s pouch and scavenge on its own. However, the possum may be small enough to look like a baby in your eyes, and you may want to feed it milk.
This is the wrong thing to do. Marsupial milk differs considerably from other animal milk or formula. Additionally, possums don’t suckle like human beings. Trying to feed them like you would your own baby can cause them to aspirate and die.
Marsupial milk differs considerably from other animal milk or formula. Additionally, possums don’t suckle like human beings. Trying to feed them like you would your own baby can cause them to aspirate and die.
Here are a couple of other things you should avoid:
- Don’t feed an injured or orphaned baby possum
Feeding them the wrong kind of milk can cause a deadly and irreversible metabolic bone disease to develop in them. Feeding a malnourished and dehydrated baby possum can cause a shock to their system and kill them.
- Don’t force-feed a baby possum
If a possum is old enough to have left its mother’s pouch, it is old enough to find its own food and eat it. You can leave out scraps or even insects and slugs for it to eat. The possum will do so in its own time.
Tips to Feed Baby Possums
In general, it is best to leave a baby possum alone—even if it has been separated from its mother. Most baby possums only look tiny, fragile and helpless. In reality, they may not be as young and vulnerable as they appear.
Most baby possums only look tiny, fragile and helpless. In reality, they may not be as young and vulnerable as they appear.
In fact, any possum that seems able to get around pretty good under its own power is probably a juvenile possum. And the latter are perfectly capable of surviving on their own.
You should know that in most states it is illegal to care for possums unless you are a licensed wildlife rehabilitator. However, if you have come across a baby possum—an actual baby—that has somehow become separated from its mother, then you can offer temporary care in the form of feeding.
You should warm the infant baby possum before attempting to feed it. You must stimulate it before the feeding by lightly rubbing its genital areas with a warm and moist cotton ball.
You can feed the baby possum Esbilac over a 24-hour period. However, this should be dispensed using a dropper or syringe.
If the baby possum seems a little too large to be a baby but it seems injured, you can feed offer it water in a shallow bowl or jar lid. The possum is likely to defecate in it, so you will need to change the water often.
The possum is likely to defecate in it, so you will need to change the water often.
For more explicit guidance, watch this video:
Remember, the best place for a wounded or orphaned possum in a clinic or refuge run by a licensed wildlife rehabilitator.
FAQ
1. How long can baby possums go without food?
Like most animals, baby possums cannot survive long without food. They are unlikely to live more than a few days without proper sustenance.
2. When do baby possums eat solid food?
When they are between 3 to 5 months old.
3. Can baby possums eat cat food?
You can feed them cat and dog food in moderation.
4. Can baby possums eat apples, bananas, and other fruit?
Yes. Possums eat fruit of all kinds.
Possums eat fruit of all kinds.
5. What do baby possums eat in captivity?
If they are mature enough to eat sold food, you can feed them just about anything. Snails is among their favorite foods.
6. What do baby possums eat in the wild?
Baby possums are scavengers, and will eat anything they can find and get access to—from plants to roadkill.
7. What do baby possums eat in New Zealand?
Possums have been filmed eating the eggs, chicks, and adults of birds that are native to New Zealand.
8. What do baby possums eat in Australia?
Possums in Australia have a high tolerance for toxins in certain plants and will eat some that other animals find poisonous.
9. Can baby possums eat carrots?
Yes. They eat vegetables of every kind.
10. Can baby possums eat baby food?
Possums can eat baby food when they have started on solids.
Summary
Baby possums are adorable little creatures. But they are tougher and more resilient than other young animals. It is best to let an orphaned baby possum alone. If it seems in distress, you should follow the guidelines above to care for it, and contact a licensed wildlife rehabilitator as soon as possible.
It is best to let an orphaned baby possum alone. If it seems in distress, you should follow the guidelines above to care for it, and contact a licensed wildlife rehabilitator as soon as possible.
Who are possums?. Animal World
Who are possums?. Animal worldWikiReading
Animal World
Sitnikov Vitaly Pavlovich
Contents
Who are possums?
These small furry rat-like animals belong to the marsupial family. Female opossums have bags on their abdomens formed by folds of skin. Newborn cubs climb into these bags and stick to their mother's nipples.
Possum rat pups are born blind, hairless and completely shapeless. You can imagine how tiny they are, if they fit from 5 to 18 pieces in a tablespoon. However, their innate instinct tells them that they can only survive in the mother's pouch. Therefore, as soon as they are born, they crawl into a bag and grow there.
Until the age of one month, the rat pups do not even come out of the bag and do not tear themselves away from the nipples. But as soon as they are a month old, they already begin to look out of the bag and look around. After another three weeks, the baby opossums get out and try to run on their own. But they are still so small and helpless that they do not go far from their mother or prefer to move on her back, clinging with their tails to her tail raised up.
At three months, babies are already quite independent and no longer need maternal care. Adult opossums spend a lot of time on trees, deftly climbing from branch to branch, holding on with their paws and tail. There, in the trees, they hunt and feed.
In places where possums are found, people are accustomed to seeing how they hang, clinging to a branch with their tail, head down. Such acrobatics allows animals to free their paws with which they hold food and eat.
Opossums are omnivorous animals: they are very fond of eggs and chicken, raid orchards, do not disdain insects, lizards, adore crayfish, snails, and do not refuse other food.
This text is an introductory fragment.
Who are tadpoles?
Who are the tadpoles? In summer, tiny round creatures with a tail swim in ponds and lakes. These are the tadpoles, which were named so because they almost entirely consist of a head. But by the end of summer there are fewer and fewer tadpoles until they are no more than
Who are insectivores?
Who are insectivores? The name itself already suggests that there are animals on Earth that mainly feed on insects. In most cases, these animals are not at all similar to each other, but scientists combine them according to one common feature and refer to group
Who are the deer?
Who are the deer? All animals living on the globe belong to a particular family, group or order. Red deer belong to a large family of deer, with their branched horns, body structure, they resemble their other close relatives - reindeer and
Red deer belong to a large family of deer, with their branched horns, body structure, they resemble their other close relatives - reindeer and
Who are termites?
Who are termites? Many consider termites to be a type of ant, and they look a bit like these insects. They are called “white ants” because of their white color and because they, like ants, live in large colonies. But termites are not ants and are completely
Who are armadillos?
Who are armadillos? The very name "armadillo" evokes the image of a strong powerful animal. But you can’t say this if you look at armadillos up close and watch how they live. Armadillos got their name from three bone plates, one
Who are lemurs?
Who are lemurs? This is the name of a whole detachment of primates, which include monkeys. Lemurs can be considered relatives of monkeys, although they differ from them in many ways. Lemurs are very ancient animals, they once lived in many places on the globe, where
Lemurs can be considered relatives of monkeys, although they differ from them in many ways. Lemurs are very ancient animals, they once lived in many places on the globe, where
Who are shellfish?
Who are clams? Each living being is an amazing and unique phenomenon. On the one hand, they are all similar in the structure of organisms, they have the same internal organs. Everyone has a digestive and circulatory system, many of them have a nervous system
Who is NASA
Who are NASA National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) NASA seal NASA Emblem Motto: "For the Benefit of All" General information Creation date - July 29, 1958 National Aeronautic Administration and
Who are parasites?
Who are parasites? Sometimes you can hear from people that they don't want to live like parasites. They want to do everything themselves. Parasites live inside or outside other organisms - the so-called "hosts". All living beings live independently. But parasites live at the expense of others
They want to do everything themselves. Parasites live inside or outside other organisms - the so-called "hosts". All living beings live independently. But parasites live at the expense of others
Who are vertebrates?
Who are vertebrates? What do you think: is there anything that unites a sparrow, a shark, a python, a frog, a dog and a person? You are right if you answered this question in the affirmative, because there is such a common feature for all the above creatures. It concludes in
Who are Whigs?
Who are Whigs? The word "whig" comes from the Scottish word "wiggamore". So called poor peasants who did not want to put up with English rule in Scotland and desperately fought for their independence. By the end of the reign of King Charles II in the English Parliament
Who are the Anglo-Saxons?
Who are the Anglo-Saxons? The word "Anglo-Saxon" is often referred to the modern inhabitants of England or their descendants. However, in reality, the Anglo-Saxons are a people who lived in England many years ago. After the conquest of Britain by the Romans, it was under the dominion of
However, in reality, the Anglo-Saxons are a people who lived in England many years ago. After the conquest of Britain by the Romans, it was under the dominion of
Why do opossums carry offspring?
Why do opossums carry offspring? Opossums belong to a group of animals called marsupials. The females of this group have a pouch on the inside of their bodies in which their young develop. Interestingly, baby opossums are very small. A tablespoon holds from
So different, so similar
So different, so similar Plants, fungi, lichens, bacteria, viruses, protozoa - they are all so different from each other that at first glance it seems that there is nothing in common between them. Well, at least in one thing these organisms are similar - they are all alive
SAME
THE SAME Contrary to their name, THE SAME, a St. Petersburg beat band of the second half of the 60s, never tried to be like others, played the heavy and hard rhythm and blues of their British mod contemporaries, like them, tried to look spectacular on stage and participated
Petersburg beat band of the second half of the 60s, never tried to be like others, played the heavy and hard rhythm and blues of their British mod contemporaries, like them, tried to look spectacular on stage and participated
Opossums
Possums are distributed from the southeast of Canada (Ontario) through the eastern states of the USA to 52°S. sh. in Argentina. They are also found in the Lesser Antilles.
Opossums are small in size: body length 7-50 cm, tail 4-55 cm. The muzzle is elongated and pointed. The tail is entirely or only at the end naked, prehensile, sometimes thickened at the base with deposits of fat. The body is covered with short thick fur, the color of which varies from gray and yellowish-brown to black. The structure of the dental system, limbs, bag testifies to the primitiveness of opossums. The limbs are shortened, five-fingered; the thumb of the hind limb is opposed to the rest of the fingers and is devoid of a claw. The hind legs are usually stronger than the front ones. The dental formula is archaic: a full row of incisors (5 on the upper jaw and 4 on the lower), well-developed fangs and acutely tuberculate molars. All opossums have 50 teeth.
The hind legs are usually stronger than the front ones. The dental formula is archaic: a full row of incisors (5 on the upper jaw and 4 on the lower), well-developed fangs and acutely tuberculate molars. All opossums have 50 teeth.
Opossums - inhabitants of forests, steppes and semi-deserts; found both on the plains and in the mountains up to 4000 m above sea level. Most lead a terrestrial or arboreal lifestyle, the water opossum is semi-aquatic. Active at dusk and at night. Possum food consists of small mammals, birds and their eggs, as well as small amphibians, insects, larvae and worms. In case of need, they eat fruits. Semi-aquatic species feed on crayfish, shrimps, fish, and frogs.
Outside of the season, mating leads a solitary lifestyle. Pregnancy lasts 12-13 days, in a litter up to 18-25 cubs. The lactation period lasts 70-100 days. Some opossums carry their young in a pouch that opens backwards, but most do not. Grown up cubs travel with their mother, holding on to the hair on her back. Sexual maturity occurs at 6-8 months of age; life expectancy 5-8 years. On the whole, opossums play the same role in the New World as representatives of the insectivorous order on other continents.
Sexual maturity occurs at 6-8 months of age; life expectancy 5-8 years. On the whole, opossums play the same role in the New World as representatives of the insectivorous order on other continents.
Due to the presence of a protein antidote in the blood, many large opossums are resistant to the venom of sympatric rattlesnakes, which is considered as an adaptation for feeding on these snake species. At the same time, resistance to poison is not universal: some species of Neotropical rattlesnakes prey on opossums.
An injured or frightened opossum falls down, pretending to be dead. At the same time, his eyes glaze over, foam flows from his mouth, and the anal glands emit a secret with an unpleasant odor. This imaginary death often saves the life of the opossum - the pursuer, after sniffing the motionless body, usually leaves. Some time later, the possum "comes to life" and runs away.
Common Opossum
Common Opossum
(Didelphis marsupialis)
Distributed from southern Mexico south to northern Peru, eastern Bolivia and Paraguay.
Body length - 36-53 cm, tail - 25-33 cm. Weight - 1.6-5.7 kg.
Virginia Opossum
Virginia Opossum
(Didelphis virginiana)
Widely distributed throughout Central and North America.
Body length - 38-51 cm, weight - 4-6 kg.
White-eared opossum
White-eared Opossum
(Didelphis albiventris)
Lives in South America, in subtropics and Argentinean pampas, as well as in mountain plains, forests, forests, and Andes. height of 2,500 m above sea level, much less common in arid and semi-arid areas, common in areas of agricultural activity.
Weight - 0.5-2.7 kg.
Big-eared Opossum
Big-eared Opossum
(Didelphis aurita)
Distributed along the Atlantic coast from Brazil to Northeast Argentina and Southeast Paraguay, where it inhabits highlands of tropical forests and Paraguay.
Body length - 31-39 cm. Weight - 0.7-1.8 kg.
Guianan White-eared Opossum
Guianan White-eared Opossum
(Didelphis imperfecta)
Distributed in central and northern South America: Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Venezuela and Brazil. It lives in tropical forests at an altitude of 60 to 2550 m above sea level.
Weight - 0.5 - 2.5 kg.
Andean White-eared Opossum
Andean White-eared Opossum
(Didelphis pernigra)
Distributed in the Andes of Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia and Northwestern Venezuela. Inhabits forests, meadows and shrublands. Keeps at an altitude of 2000-3700 m above sea level.
Weight - 1.5 - 3.7 kg.
Chaco Pygmy Opossum
Chacoan Pygmy Opossum
(Chacodelphys formosa)
Known only from one individual caught in 1920 in Argentina in the Gran Chaco region.
The smallest of all members of the family. Body length about 68 mm, tail length - 55 mm.
Kalinowski's Mouse Opossum
Kalinowski's Mouse Opossum
(Hyladelphys kalinowskii)
Distributed in French Guiana, Guyana and Peru. Inhabits subtropical and tropical lowland forests.
Body length - 178-208 mm. Weight approx. 16.33 g.
Water Opossum
Water Opossum
(Chironectes minimus)
Inhabits tropical and subtropical rainforests from southern Mexico to Argentina, distributed in Central and South America - Colombia, Ecuadorean, Venezuela , Paraguay, Eastern Brazil up to the north of Argentina. Settles along reservoirs with running water. Encounters in mountainous areas are noted.
Body length - 270-400 mm, tail - 310-430 mm.
Chacoan Gracile Opossum
Chacoan Gracile Opossum
(Cryptonanus chacoensis)
Inhabits the plains and forests of Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay.
Weight - 15-40 g.
The genus (Cryptonanus) also includes: Agricola's graceful opossum (Cryptonanus agricolai), Guahiba Gracile Opossum (Cryptonanus guahybae), Red-bellied graceful opossum (Cryptonanus ignitus), Unduavian graceful opossum (Cryptonanus unduaviensis).
Bolivian Gracile Opossum
Bolivian Gracile Opossum
(Gracilinanus aceramarcae)
Distributed in subtropical and tropical forests of Bolivia and Peru.
Agile Gracile Opossum
Agile Gracile Opossum
(Gracilinanus agilis)
Distributed mainly in dry and seasonally dry forests south of the Amazon, Brazil, and Paraguay. It occurs at altitudes up to 1800 m above sea level. Leads an arboreal lifestyle.
Body length is 215 mm, of which 123 mm is on the tail. Weight - 13-22 g. Males are somewhat larger than females.
Brazilian Gracile Opossum
Brazilian Gracile Opossum
(Gracilinanus microtarsus)
Distributed in southeastern Brazil.
The genus (Gracilinanus) also includes: Tree graceful opossum (Gracilinanus dryas), Gracilinanus emilae graceful possum, Northern graceful opossum (Gracilinanus marica).
Patagonian opossum
Patagonian opossum
(Lestodelphys halli)
Distributed in southern Argentina: Patagonian pampas; in the provinces of Chubut, Mendoza, Neuquen, Rio Negro, Santa Cruz. Leads a nocturnal solitary lifestyle.
Body length - 13.3-14.5 cm, tail - 9.5 cm. Weight - 70-80 g.
Otter Opossum
Lutrine Opossum
(Lutreolina crassicaudata)
Distributed from Guiana to Northern Patagonia.
Body length approx. 30 cm, tail 35 cm.
Mexican Mouse Opossum
Mexican Mouse Opossum
(Marmosa mexicana)
Distributed in Belize, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua and Panama. Inhabits wet and dry tropical forests.
Inhabits wet and dry tropical forests.
Overall length 119-168 mm. Weight of males - 63 g, females - 46 g.
Mouse OPSSUM
Linnaeus's mouse Opossum
(MARMOSA Murina)
is widespread in Venezuela, Trinidad and Tobago, Gaean, Suriname, French Gaviania, Blovyan, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazili, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia, Brazia Keeps at considerable heights (2500 m and above).
Body length - 11-14.5 cm, tail - 13.5-21 cm.
Rufous Mouse Opossum
Rufous Mouse Opossum
(Marmosa lepida)
Distributed in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru and Suriname.
Overall length 82-120 mm. Weight - 18-42 g.
Red Mouse Opossum
Red Mouse Opossum
(Marmosa rubra)
Distributed in Southeastern Colombia, Eastern Ecuador and Eastern Peru.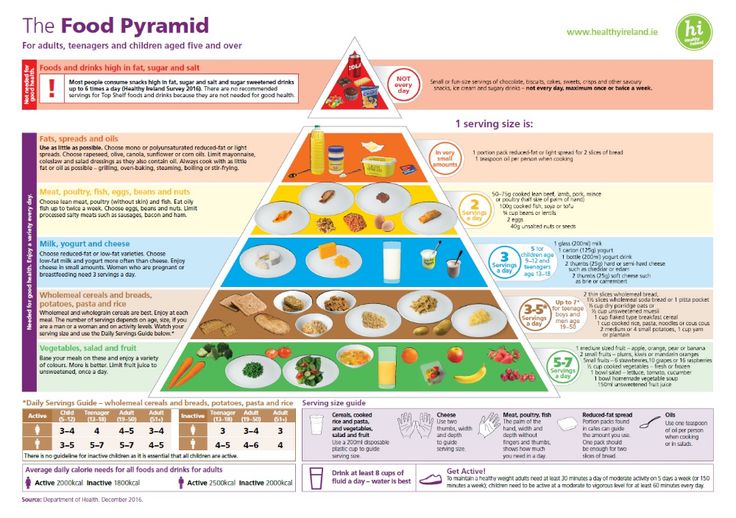 Inhabits lowland or foothill tropical forests at an altitude of 180 to 730 m above sea level.
Inhabits lowland or foothill tropical forests at an altitude of 180 to 730 m above sea level.
Overall length 128-200 mm. Weight - 59-81 g.
Guajira Mouse Opossum
Guajira Mouse Opossum
(Marmosa xerophila)
Occurs in the arid lowlands of the Caribbean in northwest Venezuela and extreme northeast Colombia. Inhabits dry, deciduous, thorny forests and shrubs.
Overall length 100-160 mm. Weight - 30-90 g.
Robinson mouse opossum
Robinson's Mouse Opossum
(Marmosa robinsoni)
Distributed in Belize, Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Peru, Trinidad and Tobago, Panama, Honduras and Venezuela.
Overall length 83-218 mm. Weight of males - 71 g, females - 44 g.
The genus (Marmosa) also includes: Anderson's mouse opossum (Marmosa andersoni), Quechuan mouse opossum (Marmosa quichua), Tyler's mouse opossum (Marmosa tyleriana).
Alston's Mouse Opossum
Alston's Mouse Opossum
(Micoureus alstoni)
Inhabits forests from Belize to Northern Colombia.
White-bellied Woolly Mouse Opossum
(Micoureus constantiae)
Inhabits the humid forests of Eastern Bolivia, Brazil (Mato Grosso state) and Northwestern Argentina
Woolly Mouse Opossum
Woolly Mouse Opossum
(Micoureus demerarae)
Distributed in Colombia, Venezuela, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, Brazil and Eastern Paraguay.
Paraguayan Woolly Mouse Opossum
Tate's Woolly Mouse Opossum
(Micoureus paraguayanus)
Inhabits the forests of the Atlantic coast of Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina.
Bare-tailed Woolly Mouse Opossum
(Micoureus regina)
Distributed in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Bolivia.
The genus (Micoureus) also includes: Small woolly mouse opossum (Micoureus phaeus).
Grayish Mouse Opossum
Grayish Mouse Opossum
(Tlacuatzin canescens)
Distributed in Mexico from the state of Sanora to Oaxaca. Inhabits mixed and tropical forests up to an altitude of 2100 m above sea level, most often found up to 1000 m above sea level.
Body length 205-350 mm.
Andean slender possum
Tschudi's Slender Opossum
(Marmosops impavidus)
Distributed in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru and Venezuela. It lives in forests at an altitude of about 2300 m above sea level, although sometimes it is found even lower (1000 m).
Body length approx. 14 cm. Weight approx. 42 g.
Gray Slender Opossum
Gray Slender Opossum
(Marmosops incanus)
Widely distributed along the east coast of Brazil, from about 10 to 25 degrees south latitude. It lives in coastal moist forests up to 800 m above sea level, as well as on continental islands. Sometimes found in drier forests, on the Brazilian plateau up to 1300 m above sea level.
It lives in coastal moist forests up to 800 m above sea level, as well as on continental islands. Sometimes found in drier forests, on the Brazilian plateau up to 1300 m above sea level.
Male body length - 270-430 mm, weight - 25-140 g. Females are slightly smaller - 240-360 mm, with a weight of 20-70 g.
White-bellied Slender Opossum
White-bellied Slender Opossum
(Marmosops noctivagus)
Distributed in the Amazon rainforests: Ecuador, Peru, Western Brazil and Bolivia. Prefers swampy watery areas.
Body length approx. 11 cm. Weight approx. 30 g.
Delicate Slender Opossum
Delicate Slender Opossum
(Marmosops parvidens)
Distributed in Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana and northern Brazil. Prefers tropical rain forests.
Body length approx. 9.9 cm. Weight approx. 15 g.
The genus (Marmosops) also includes: Narrow-headed slender opossum (Marmosops cracens), Bishop's slender opossum (Marmosops bishopi), Dorothy's slender opossum (Marmosops dorothea), Dark slender possum (Marmosops fuscatus), Handley's slender opossum (Marmosops handleyi), Panama slender Opossum (Marmosops invictus), Junin Slender Opossum (Marmosops juninensis), Neblina Slender Opossum (Marmosops neblina), Brazilian Slender Opossum (Marmosops paulensis), Pinheiros Slender Opossum (Marmosops pinheiroi).
Brown Four-eyed Opossum
Brown Four-eyed Opossum
(Metachirus nudicaudatus)
Distributed from Nicaragua south to Paraguay and Northern Argentina. Inhabits dense forests or shrubs on plains.
Body length - 25-26 cm, tail - 33 cm.
Brown possum
Sepia Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis adusta)
The habitat does not go beyond Brazil and some adjacent countries (Guiana, Venezuela, Peru).
Body length approx. 12 cm. Weight approx. 36 g.
Northern Three-striped Opossum
Northern Three-striped Opossum
(Monodelphis americana)
Distributed in Eastern Brazil from the State of Para south to Santa Catarina.
Body length approx. 11 cm. Weight approx. 20 g.
Ihering's Three-striped Opossum
(Monodelphis iheringe)
Distributed in southeastern Brazil, where it inhabits the subtropical forests of the Atlantic coast.
Body length approx. 9.1 cm. Weight approx. 110 g.
Northern Red-sided Opossum
Northern Red-sided Opossum
(Monodelphis brevicaudata)
Inhabits the forests of Brazil, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname and Venezuela.
Body length approx. 14 cm. Weight approx. 90 g.
Southern Red-sided Opossum
Southern Red-sided Opossum
(Monodelphis sorex)
Distributed in Southeast Brazil: from the state of Minas Gerais to Rio Grande duvay Sul, in the Paraguayan province Northeast Argentina.
Body length approx. 7.2 cm. Weight approx. 48 g.
Yellow-tailed opossum
Yellow-sided Opossum
(Monodelphis dimidiata)
Distributed in Uruguay, southeastern Brazil, northern and central Argentina, and southeastern Paraguay.
Body length approx. 10 cm. Weight approx. 45 g.
10 cm. Weight approx. 45 g.
Gray Short-tailed Opossum
Gray Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis domestica)
Distributed in Brazil, Bolivia, Argentina and Paraguay, where it inhabits tropical forests and grassy areas. Often found near human habitation. Forages on the ground or low vegetation.
Body length from 10 to 15 cm. Weight - 90-155 g.
Emilia's Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis emiliae)
Distributed in Bolivia, Brazil and Peru.
Body length approx. 13 cm. Weight approx. 52 g.
Pygmy Short-tailed Opossum
Pygmy Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis kunsi)
Distributed in Bolivia, Brazil and northern Argentina.
Body length approx. 7 cm. Weight approx. 11 g.
Osgood's Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis osgoodi)
Distributed in subtropical and tropical lowland forests of Bolivia and Peru.
Body length approx. 9.5 cm. Weight approx. 110 g.
Saci Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis saci)
Lives in lowland rainforests along the southern coast of the Brazilian Amazon.
Body length from the tip of the nose to the base of the tail - 9-12 cm. Tail length - 4-6 cm. Weight - 17-30 g.
Long-nosed Short-tailed Opossum
Long-nosed Short-tailed Opossum
(Monodelphis scalops)
Distributed in Southeast Brazil: in the states of Espirito de Santo Katarina. Inhabits the lowland forests of the Atlantic coast.
Body length approx. 14 cm. Weight approx. 760 g.
Amazonian Red-sided Opossum
Amazonian Red-sided Opossum
(Monodelphis glirina)
Distributed in the humid Amazonian forests from the western bank of the Xingu River (Brazil) to the west through the Manu River to Bolivia.
Overall length 151-213 mm. Weight - 24.4-79.6 g.
Hooded red-sided opossum
Hooded Red-sided Opossum
(Monodelphis palliolata)
Distributed in Colombia and Venezuela. Inhabits tropical forests at altitudes up to 2250 m above sea level.
Total length approx. 139.5 mm. Average weight - 78.84 g.
Gardner's Short-tailed Opposum
(Monodelphis gardneri)
Inhabits the mountain forests of Central Peru.
The genus (Monodelphis) also includes: Marai short-tailed opossum (Monodelphis maraxina), Reiga opossum (Monodelphis reigi), Ronald's opossum (Monodelphis ronaldi), Chestnut striped opossum (Monodelphis rubida), Southern three-banded opossum (Monodelphis theresa), Red three-striped opossum (Monodelphis umbristriata), Single-striped opossum (Monodelphis unistriata).
Gray Four-eyed Opossum
Gray Four-eyed Opossum
(Philander opossum)
Inhabits Central America north to the Yucatan Peninsula and South America to Paraguay and southern Brazil.
Body length - 27-29 cm, tail - 38-39 cm.
Anderson's Four-eyed Opossum
(Philander andersoni)
Distributed in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela. Inhabits primary and secondary lowland forests, as well as gallery forests along riverbanks and wetlands. It lives at an altitude of 200 to 1600 m above sea level.
Total length 250-350 mm. Weight - 240-600 g.
McIlhenny's Four-eyed Opossum
(Philander mcilhennyi)
Inhabits the dry tropical forests of Peru and Brazil. Also found in flooded forests of upper rivers.
Overall length 287-307 mm. Weight - 396-640 g.
Southeastern Four-eyed Opossum
Southeastern Four-eyed Opossum
(Philander frenatus)
Distributed in Brazil and Peru.
Overall length 210-285 mm. Weight - 120-130 g.
The genus (Philander) also includes: Delta four-eyed opossum (Philander deltae), Mondolf's four-eyed opossum (Philander mondolfii), Olrog's four-eyed opossum (Philander olrogi).
Elegant Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
Elegant Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
(Thylamys elegans)
Distributed in Chile, Argentina, Bolivia and Peru at an altitude of about 2500 m above sea level.
Body length - 106-121 mm, tail - 115-142 mm.
Karimi's Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
(Thylamys karimii)
It is endemic to central and northeastern Brazil.
Body length approx. 95 mm, tail length approx. 72 mm.
White-bellied Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
(Thylamys pallidior)
Distributed in Argentina and Bolivia.
Body length - 84-99 mm. Tail length - 104-113 mm.
Common Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
Common Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
(Thylamys pusillus)
Distributed in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay.
Body length from 75 to 120 mm. Tail length - 90-134 mm.
Buff-bellied Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
(Thylamys venustus)
Inhabits the forests of northern Argentina and southern Bolivia.
Overall length 195-248 mm.
Paraguayan Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
Paraguayan Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum
(Thylamys macrurus)
Inhabits the forests of Brazil and Paraguay.
Body length approx. 135 mm, tail length 140 mm.
The genus (Thylamys) also includes: Cinderella Fat-tailed Mouse Opossum (Thylamys cinderella), Argentine fat-tailed opossum (Thylamys sponsorius), Tate's fat-tailed opossum (Thylamys tatei), Pygmy fat-tailed opossum (Thylamys velutinus).
Derby's Woolly Opossum
Derby's Woolly Opossum
(Caluromys derbianus)
Inhabits the montane and lowland rainforests of Belize, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua and Panama.