What to feed a baby fawn
Wildlife First Aid - How to Feed Baby Deer (Fawns)
Baby fawns go through two containers of milk a day. All goat milk or a fawn replacement milk should be used. Some Walmart stores carry goat milk; Tractor Supply stores carry a wildlife replacement milk that will include fawns on the back label.
A newborn fawn is the size of two Chihuahuas. It's important to add seven drops of lactate as well to the formula. If you have a young fawn, do not add anything solid.
When
they are the size of the deer in the photos below, add
some solid food to the formula such as baby rice or baby
cereal.
Mix it well with water until it has a pudding-like consistency.
Deer love sweet tastes, and bananas are always a good
source of sweetness. For older deer, you can add a banana,
but be sure to beat it with a fork until it liquefies.
You can put it into a blender or use a mixer and stir
it up -- but make sure the banana seeds don't clog the
nipple.
| The hole in this nipple is too large! |
Also, be sure that the hole in the nipple
is not too large so the liquid cannot be drunk too quickly. If they drink too fast, they will give themselves a stomachache
along with having digestive problems.
If they drink too fast, they will give themselves a stomachache
along with having digestive problems.
Before feeding, heat up the formula. You don't want to feed deer cold formula. Then give it to the deer before everybody else eats it. (Ingrid said that as one of her cats was sampling the formula to be sure it was just right.)
Use a funnel to pour the mixture into
baby bottles (two per fawn per feeding).
There
should
be
two feedings a day. Be sure to heat the liquid. It must
be given very warm.
It must
be given very warm.
When feeding, keep the bottles high because that's how they would eat from the mother as she stands up
They go through it quickly.
You can pull and push back and forth as you feed, because that's what the mother does.
Also take a warm wet cloth and wipe the genital area to help stimulate the bowels. If they are not kept regular, they will get diarrhea or become constipated.
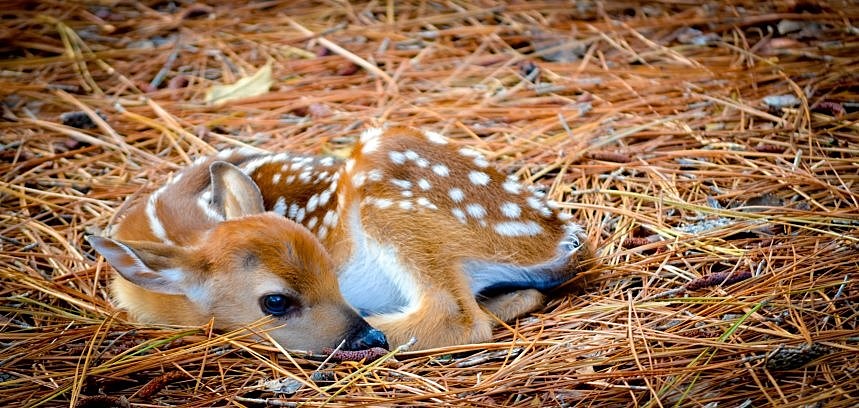
The deer in the photo are not that young,
more like two months old. By the way, these guys
are not related.
By the way, these guys
are not related.
If they're older, you can chop up carrots or apples and just stick the pieces in their mouth. When deer go from formula to other foods, it's a big move.
FURTHER NOTES:
Unless you actually see a dead doe, leave the fawn alone. Fawns are rarely orphaned. The mother will often run if you approach, and return to the fawn after you leave; the fawn can't run, and will typically freeze and try not to be seen.
Be sure to contact an animal rehabilitator
promptly if you are dealing with a young fawn, because
they imprint quickly, and once imprinted, are problematic
to
release into
the wild.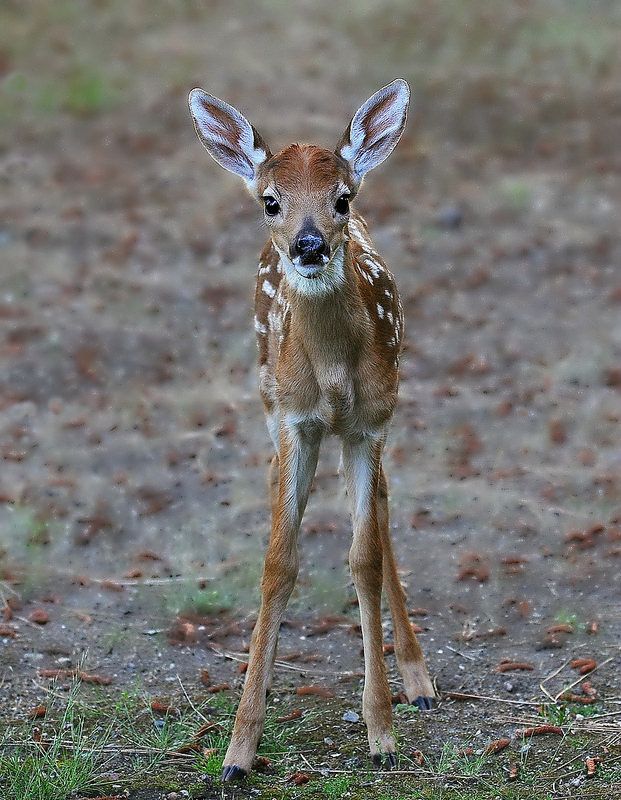
Wildlife Watch / Rehabilitator Hotline: 877-WILD-HELP |
SEE ALSO:
The R.O.C.K. column is each issue of the
Wildlife Watch Binocular.
Back to First Aid Index
What Do Fawns Eat? - AZ Animals
More Great Content:
The word fawn refers to more than just a color, or a behavior; it’s also what we call a baby deer. Members of the Cervidae family—which includes elk, moose, reindeer (caribou), red deer, roe deer, white-tailed deer, key deer, fallow deer, and mule deer, among others—are known as fawns until they reach one year of age.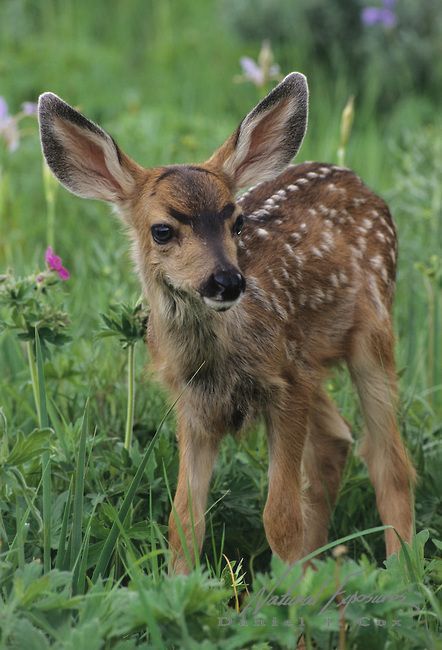 Fawns are characterized by their long spindly legs, oversized ears, tan bodies, and white spots.
Fawns are characterized by their long spindly legs, oversized ears, tan bodies, and white spots.
Here, we’ll learn more about what fawns eat, how they transition from mother’s milk to greens, and how long it takes them to mature. Then, we’ll explore the ways that wildlife rescue organizations feed and rehabilitate these small deer.
The Fawn’s Favorite Foods
Fawns eat milk for the first several months of life, gradually weaning onto grasses, leaves, and twigs.iStock.com/randimal
Fawns eat exclusively mother’s milk for the first two weeks of life. They are herbivores, and once weaned will eat primarily leaves, twigs, and other greens.
Fawns weigh between 4-8 pounds at birth. By drinking only mother’s milk, which is rich in fat, sugar, and protein, they double in weight in the first two weeks of life. After one month they will have tripled their birth weight. Once they’re a couple of weeks old, they start nibbling on tender grasses and new shoots, but just enough to get their ruminant, four part stomach started.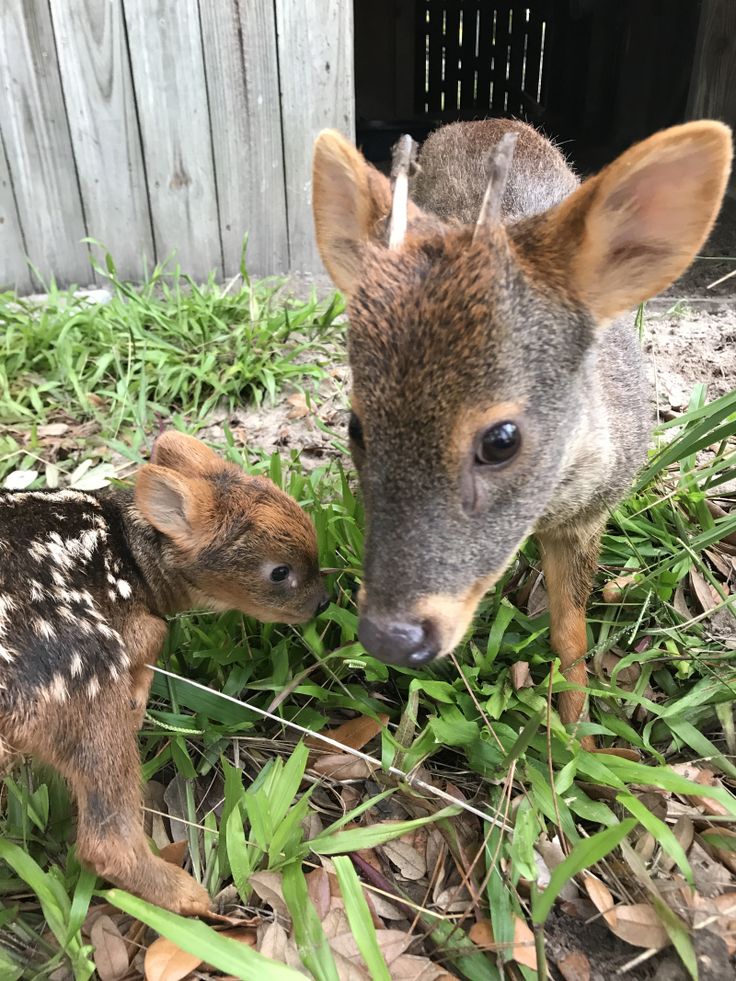
A Complete List of Foods that Fawns Eat:
- Mother’s milk
- Grasses
- Leaves
- Twigs
- Sedges
- Forbs
- Shrubs
- Trees
- Young roots and tubers
- Berries
- Fruit
- Lichen & fungi (in the winter)
What Do Wild Fawns Eat?
Wild fawns are completely dependent on their mothers for the first several weeks of life. The mother feeds the fawn around eight times a day, allowing it to nurse until it’s had its fill.
Fawns eat a lot of milk; between 10-20% of their body weight every day. When the mother is not feeding the fawn, she leaves it in an area with thick, low to the ground growth, where the fawn hides until the mother returns.
Wild fawns are nearly odorless, and since they don’t move or make a sound while the mother is gone, they are very hard for predators to find. They have to be; until the fawn is about a month old, it isn’t able to run from predators.
Fawns rely so much on this undetectability that they actually can’t expel waste, the smell of which would give away their location, without stimulation.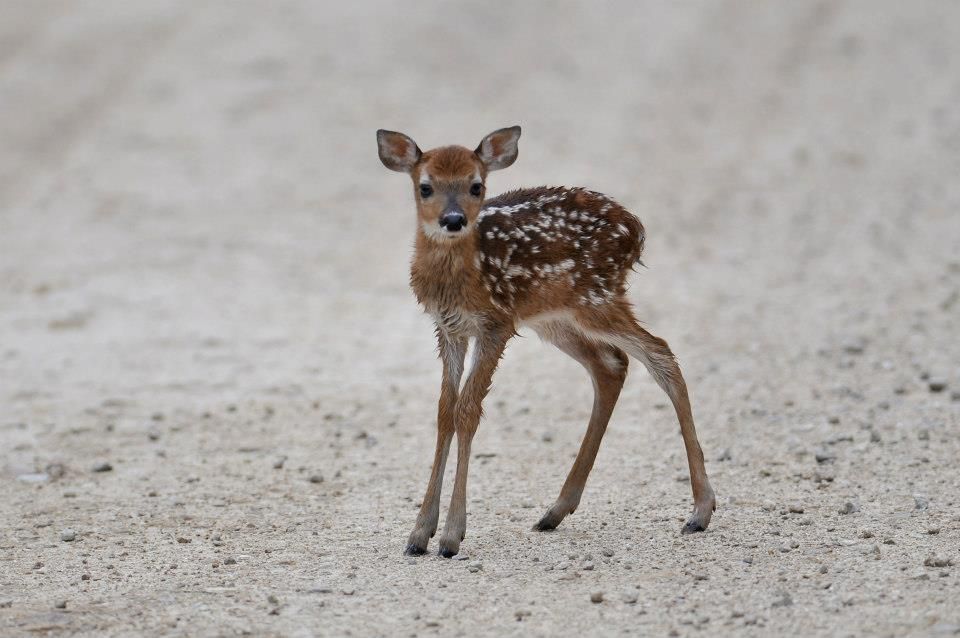 The fawn won’t urinate or defecate until either they, or the mother, licks their genital region to stimulate the processes. The mother then immediately eats the waste, further ensuring that her fawn will remain undetectable by predators and survive to adulthood.
The fawn won’t urinate or defecate until either they, or the mother, licks their genital region to stimulate the processes. The mother then immediately eats the waste, further ensuring that her fawn will remain undetectable by predators and survive to adulthood.
Surviving Through the Winter
Fawns eat young grasses and shoots as early as two weeks of age.iStock.com/nearandfar
Fawns are normally born in the spring months between April and June. The earlier they are born, the better chance they have at surviving through the next winter. At just three weeks old they start venturing out with their mother to nibble on tender grasses. They gradually replace more and more of the milk in their diet with greens like twigs, leaves, and young shoots. By the time they are 3-4 months old they are almost fully weaned.
Fawns won’t stop ‘nursing’ from their mother’s just because they’re weaned though; they have been observed ‘nursing’ well into their first winter, long after the mother has stopped providing milk. Scientists think this behavior may act as a bonding agent between the mother and fawn, or it may simply be a way for the weaned fawn to derive comfort.
Scientists think this behavior may act as a bonding agent between the mother and fawn, or it may simply be a way for the weaned fawn to derive comfort.
What Do Captive Fawns Eat?
Many people find lone fawns, seemingly abandoned or motherless, and mistakenly ‘rescue’ them. As we’ve learned, these fawns are almost certainly not far from their mothers, and should be left alone unless they are visibly injured or distressed. Regardless, many wildlife rescue organizations exist that know how to care for fawns, and eventually rehabilitate them to the wild.
Fawns have very high nutritional needs, and if the wildlife organization cannot immediately return them to their mother, it’s up to them to meet these needs. Captive fawns eat either goat milk or a milk substitute. Dairy milk is not recommended as the fawns have a hard time digesting it.
But caretakers often take the fawn’s nutrition a step further by feeding them fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens. Fawns are fond of sweet things like fruit, and will happily eat bananas, strawberries, berries, oranges, pears, watermelons, and apples.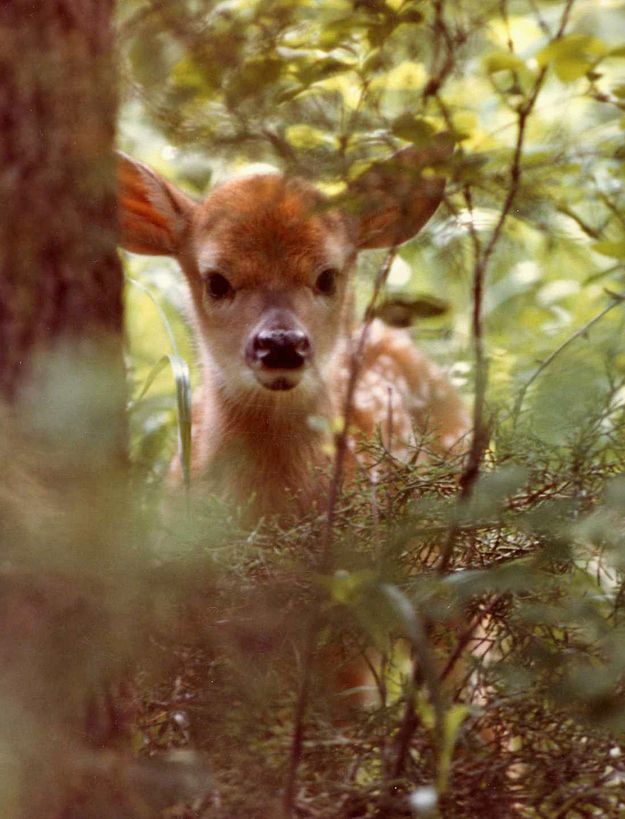 They can also be fed vegetables like carrots, and starches like corn, barley, and wheat.
They can also be fed vegetables like carrots, and starches like corn, barley, and wheat.
Though these foods make excellent treats for fawns, their primary food for the first 3-4 months of life should be milk. As they begin eating more solids, they should be fed on a mix of grasses, forbs, and shoots, in addition to their treats, in order to meet all of their nutritional requirements.
Do Fawns Need to Drink Water?
Fawns eat forbs, including wild thistle, during the spring and summer, and lichens and fungi in the winter.iStock.com/twildlife
Though the moisture content of mother’s milk is very high, fawns still have to drink water. This is the case for both wild and captive fawns. In northern climates, where the air turns cold and the leaves fall from the trees, weaned fawns survive largely on lichen and fungi. They get some moisture from these foods, but have also been observed eating snow to get all the water they need.
iStock.com/JNevitt Share this post on:
About the Author
Brandi Allred
Brandi is a professional writer by day and a fiction writer by night. Her nonfiction work focuses on animals, nature, and conservation. She holds degrees in English and Anthropology, and spends her free time writing horror, scifi, and fantasy stories.
Her nonfiction work focuses on animals, nature, and conservation. She holds degrees in English and Anthropology, and spends her free time writing horror, scifi, and fantasy stories.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Nursing of young ungulates
Nursing of red deer (red deer) in artificial conditions
I must say right away that my personal experience in this area is not very great - we (so far) raised only one baby red deer to its feet. But at the very beginning we faced a huge problem - we could not find information anywhere that would help us out. Actually, that's why I came up with the idea to write a short guide for those who still have to enter in the search engines "how to feed a red deer cub."
First you need to determine the age of the animal. Our Yashik came to us through second hands, so only a veterinarian could reliably determine his age - 6-7 days. So, how does a red deer cub look like at a week of age:
So, how does a red deer cub look like at a week of age:
Height at the withers: 64 cm
It still does not stand very well on its legs, they are slightly curved with the letter X. Often “cries”.
Teeth: back (if I may say so) not yet, front 8 (now Yasha is already 2 months old, but the front is gone), they are all below. 2 in the center are very large and funny :o) the rest are quite small.
Weight: 10-12 kg (but this is taking into account that he was fed incorrectly all his first week)
By the way, it will be useful to understand who is in front of you - red deer or spotted deer. They are often confused. The red deer is larger (against our 65 at the withers - 45-50 in the sika deer, weight approx. 4-6 kg). The head is large, the ears are elongated. I would compare them with the length of the nose from the tip to the eyes. The deer has a neat muzzle with VERY large round ears. Now as for the coloring. It should be noted that everyone has spots. In deer, they are located along the ridge and will come off after the first molt in October, while in spotted deer they are all over the body and will remain for life.
In deer, they are located along the ridge and will come off after the first molt in October, while in spotted deer they are all over the body and will remain for life.
In red deer the spot under the tail is yellow and small, dimly outlined. In a deer, on the contrary, it is white, wider and strikingly different in color from the general background.
And now the most important thing - about feeding. Or is it more correct to say feeding .
Golden rule: don't overfeed. Feeding and deer and deer is a fractional milk supply. We gave cow's milk (necessarily boiled!) With the addition of water and infant formula "Malyutka 1" (one - that is, from birth).
Mixture: 1 liter of milk, 8 measuring spoons of formula, 0.5 liters of water. For the first 2 weeks, you need to feed 8-10 times a day, 100 g of the resulting mixture. It is better to use a bottle with a simple (not the most expensive) elongated nipple. By the way, because of the structure of the jaws, the deer did not recognize the Aventa's nipple so respected by the mothers. Of course, it is better to warm up to 36-38 degrees. You can check the temperature in the same way as for children - a drop on the bend of the elbow.
Of course, it is better to warm up to 36-38 degrees. You can check the temperature in the same way as for children - a drop on the bend of the elbow.
After the second week, give about 150 ml of water during the day between feedings. Once a day, we gave lightly salted (1 teaspoon without top per liter of boiled water). Now we feed 8 times a day, 250 ml each.
At the age of three weeks, a red deer was drunk with a five-day course of the Vetom-2 probiotic (I won’t say why exactly “2”, but that’s how we were determined in the veterinary clinic). Dilute one sachet in 200 ml of water, divide in half and give twice a day one hour after feeding (so you will need 5 sachets)
Month. At this age, you can transfer from a baby bottle to a cow bottle (for feeding calves - sold in veterinary stores). No, of course, you can continue to drink from a small one, but it will be tiring - you need to fill it several times for one meal or have 4 at once. At the same time, we began to feed Yashechka with Kormilak whole milk substitute. Its cost in Primorsky Krai ranges from 1900 to 2400 for a 25 kg bag. This amount is enough for about 2 months. The first days we add kormilak to cow's milk, but we cancel the infant formula (i.e. it turns out 1 liter of milk + 0.75 ml of water + 100 g of kormilak), then (well, say, on the fifth day) we give pure kormilak, i.e. . at the rate of 1:9, as written on the package. I weighed a plastic container on a culinary scale, it turned out to be 200 gr, i.e. almost 2 liters of water. At the age of one to two months, his daily intake increased from 2.5 to 4 liters of formula per day, and the frequency of feeding decreased from 6 to 4 times.
Its cost in Primorsky Krai ranges from 1900 to 2400 for a 25 kg bag. This amount is enough for about 2 months. The first days we add kormilak to cow's milk, but we cancel the infant formula (i.e. it turns out 1 liter of milk + 0.75 ml of water + 100 g of kormilak), then (well, say, on the fifth day) we give pure kormilak, i.e. . at the rate of 1:9, as written on the package. I weighed a plastic container on a culinary scale, it turned out to be 200 gr, i.e. almost 2 liters of water. At the age of one to two months, his daily intake increased from 2.5 to 4 liters of formula per day, and the frequency of feeding decreased from 6 to 4 times.
Grass . I wondered for a long time when to start feeding with grass. But everything turned out to be easier - Yashichek himself reached for the raspberries. And off we go. Most of all he liked dandelions, grapes, raspberries. Then come beets, ash leaves, currants. And he also loves berries terribly: o) Honeysuckle, strawberries, currants, raspberries, irga - everything goes with a bang. At the same time, the apples directly spits out. You can give pureed vegetables as a substitute for grass.
At the same time, the apples directly spits out. You can give pureed vegetables as a substitute for grass.
Faeces. Normally, he is like a goat - balls. Our pet had diarrhea at first. Wrong food - diarrhea, did not boil the bottle - diarrhea, overfed - diarrhea again. What to do. Give less food and carefully monitor the sterility of dishes.
Dehydration On the second day of life at my house, the veterinarian diagnosed us - Yashka refused to eat, could hardly stand on his feet. He was given a dropper in the neck (do not do it without a specialist!) with saline through a butterfly 4-ku, 200 ml + half a bottle of glucose. He almost immediately got to his feet, but it was impossible to feed, it was possible to give saline in the evening and replace one meal with it the next day. In general, having a doctor in the family, on the second day we were ready to repeat the drip on our own, but, fortunately, it was not necessary. In order to prevent, see above, drink salted water daily.
Arrangement places. Here, of course, the more the better. Yasha had to live in an open chicken pen, 3x8. The size, frankly, is not great. Net height 3.5 meters. It is necessary to make a small canopy, 1.1-1.2 m high, with a roof and without one wall - so that it can enter freely, cover the floor with hay, which needs to be changed regularly (because they defecate, most often, under themselves).
General recommendations. The life of these small, defenseless creatures is in your hands. Therefore, it is important to decide what will happen to them when they are ready to exist on their own: do you intend to give it to the zoo / zoo / safari park or plan to release it into wildlife. The permissible frequency of contact with the animal depends on this. If he is destined for the fate of a wild beast, then do not allow strangers to approach him, i.e. he should know only those 1-2 people who care about him. But you need to remember that even with this option, it is vital for him, no matter how pathetic it may sound, closeness and warmth, a sense of security - when you feed him, do not be lazy to stroke and talk - he will soon begin to recognize your voice. If you are not going to let go into the wild, then you need to hug the first 3-4 weeks as often as possible - you yourself will see how it calms him down.
If you are not going to let go into the wild, then you need to hug the first 3-4 weeks as often as possible - you yourself will see how it calms him down.
Nursing of young ungulates. "I breastfeed a deer because it is like my own baby" Understand who is in front of you
For 5-6 months, antler deer are in a pasture that provides them with high-quality vitamin and cheap feed. During this period, antlers are cut down, calving takes place, young animals are grown, preparations are underway for the rut, the rut. All production indicators of reindeer breeding mainly depend on the quality and quantity of fodder reserves of the park. Proper use of pastures and proper care of them make it possible to fully provide the antler deer with the necessary feed.
In winter 90,004 antler deer are fed hay from seeded and wild grasses. The favorite hay of antler deer is from small-leaved forbs, harvested during the period of mass flowering. Straw is eaten by antler deer poorly, and therefore it is fed along with hay or in a flavored form. Branch food is eaten by antler deer willingly, especially branches of oak, linden, lispedecia, willow and other hardwoods. Branches of shrubs and deciduous trees 1-2 cm thick, harvested in June-July and dried in the shade, are also highly nutritious food. Silage from seeded and wild herbs is well eaten by antler deer in winter and spring. Antler deer eat root and tuber crops well, but they must be carefully cleaned from the remnants of the earth and fed in crushed form. Cake, grain feed and compound feed are given to deer only in crushed form, and bran is mixed with other feed or wetted. Mineral feeds (feed salt and chalk) are mixed with other feeds.
Branch food is eaten by antler deer willingly, especially branches of oak, linden, lispedecia, willow and other hardwoods. Branches of shrubs and deciduous trees 1-2 cm thick, harvested in June-July and dried in the shade, are also highly nutritious food. Silage from seeded and wild herbs is well eaten by antler deer in winter and spring. Antler deer eat root and tuber crops well, but they must be carefully cleaned from the remnants of the earth and fed in crushed form. Cake, grain feed and compound feed are given to deer only in crushed form, and bran is mixed with other feed or wetted. Mineral feeds (feed salt and chalk) are mixed with other feeds.
Feeding marals.
In October, marals are transferred from the pasture to winter keeping in winter roads. Here the herd is divided into sex and age groups, and each group, in turn, into subgroups, depending on the fatness of the deer.
Daily Value feeding is established depending on fatness and taking into account biological cycles. For males, three feeding periods are established: the first period (August - September) - preparation for the rut and the rut, the males are on the best pastures and are additionally fed 1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day; the second period (October - December) - after the rut, the males are kept in winter houses and fed to them with 5–10 kg of coarse, 5–10 kg of succulent and 1 kg of concentrated feed; the third period (March - May) - the growth of antlers, males are fed 3-7 kg of coarse, 10-12 kg of succulent and 1-1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day.
For males, three feeding periods are established: the first period (August - September) - preparation for the rut and the rut, the males are on the best pastures and are additionally fed 1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day; the second period (October - December) - after the rut, the males are kept in winter houses and fed to them with 5–10 kg of coarse, 5–10 kg of succulent and 1 kg of concentrated feed; the third period (March - May) - the growth of antlers, males are fed 3-7 kg of coarse, 10-12 kg of succulent and 1-1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day.
For females establish two feeding periods: the first - the first half of pregnancy until February, they are fed 8 kg of coarse, 4 kg of succulent and 0.5 kg of concentrated feed per day per head; the second - the second half of pregnancy after February, females are fed 4–7 kg of coarse, 4–5 kg of succulent and 0.5–1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day.
Sika deer feeding.
In winter, spotted deer are divided into two groups: one group consists of males from 2.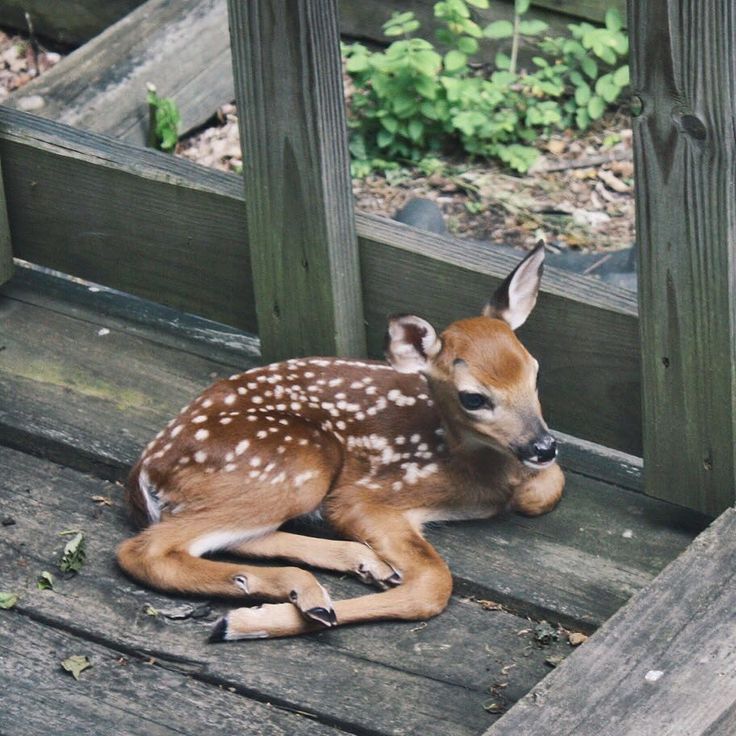 5 years and older and calves up to 1 year old, they are kept in reindeer herds; the second group - females and young animals older than 1 year, they are kept in parks. Livestock is placed in reindeer herds in December and the males are kept until the cutting of antlers and calves until May 15th. For males set three feeding periods: the first period (August - October) - preparation for the rut, the rut, the males are on the pasture and additionally they are fed 1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day; the second period (November - December) - after the rut, males are fed 2-3 kg of coarse, 5-10 kg of succulent and 1 kg of concentrated feed; the third period (April - May) - the growth of antlers, males are fed 2-3 kg of coarse, 4 kg of succulent and 1.2 kg of concentrated feed per head per day.
5 years and older and calves up to 1 year old, they are kept in reindeer herds; the second group - females and young animals older than 1 year, they are kept in parks. Livestock is placed in reindeer herds in December and the males are kept until the cutting of antlers and calves until May 15th. For males set three feeding periods: the first period (August - October) - preparation for the rut, the rut, the males are on the pasture and additionally they are fed 1.5 kg of concentrated feed per head per day; the second period (November - December) - after the rut, males are fed 2-3 kg of coarse, 5-10 kg of succulent and 1 kg of concentrated feed; the third period (April - May) - the growth of antlers, males are fed 2-3 kg of coarse, 4 kg of succulent and 1.2 kg of concentrated feed per head per day.
For females establish two feeding periods: the first period - the first half of pregnancy until February, they are fed 2–3 kg of coarse, 4–5 kg of succulent and 0.5 kg of concentrated feed per day per head; the second period - the second half of pregnancy after February, females are fed 1. 5 kg of coarse, 2 kg of succulent and 0.6 kg of concentrated feed per day per head.
5 kg of coarse, 2 kg of succulent and 0.6 kg of concentrated feed per day per head.
Hiding among plants and bushes is a normal behavior of roes and deer. With the onset of the season of wild plants, many reached into the forest for the gifts of nature - wild garlic and ferns. Whole squadrons of pickers plow burnt areas and open glades in search of tasty and healthy vegetation. But it happens that not wild plants become their trophy, ... but newborns found in the same glades.
The fact is that in May-June, young animals appear in ungulates. Usually female roe deer give birth to two cubs, rarely one or three, and for a week the roe deer stay where they were born, hiding in the grass.
Hiding among plants and bushes
Hiding among plants and bushes is a normal behavior of roe deer and fawns. Mother always walks somewhere nearby, she comes, guards them, feeds them. In the meantime, they are dependent, they hide, so they never need to be picked up, ”this is the unequivocal opinion of all zoologists and conservationists.
We repeat, no, it is not lost or abandoned, you just happened to see a hidden roe deer, and the mother looks at you anxiously from behind a bush. It is impossible to pick up and carry away the young animals from the found place, since the parents will most likely not find their cubs in the future.
It is forbidden to touch and stroke the animal - the returned mother will smell your smell and her behavior towards her own child can be arbitrarily unpredictable.
For persuasiveness, we cite as an example an excerpt from the story of Viktor Korkishko, a well-known researcher of the Far Eastern taiga, about the “rescue” of roe deer and deer.
“.. A newborn baby almost immediately gets on his feet and is soon able to walk. But it is very risky to accompany the mother everywhere - there are too many who want to eat roe meat, starting with poachers, ending with predators and even stray dogs. Therefore, the roe deer spends the first days of life alone.
Mom feeds him at night, and for the day she goes to feed herself and, in case of danger, takes the enemy away from her child. This continues for several weeks, until the roe deer becomes as frisky as the mother, and can not keep up with her if danger threatens. And until that time, he lies in the grass, hiding, not moving.
In Primorye during this period there are usually endless drizzling rains with cold fogs.
Therefore, roe deer are very cold alone and some of them die in cold years. It is good if the mother gave birth to twins and the company is a brother or sister. But even in this case, they lie "below the grass, quieter than the water." Only when they are very hungry, in the late afternoon, the roe deer begin to squeak plaintively. By screaming, their mother finds them.
Danger threatens the roe deer from the most unexpected side. Often he becomes a victim of overly compassionate people who do not know the peculiarities of roe deer life. Having found a lonely roe deer, people think that the mother has abandoned him, and out of compassion they take the baby away, not knowing what pain they inflict on the mother, who watches from the bushes how her child is carried away.
And having taken the cub, people most often do not know what to do with it - feeding a roe deer is a big problem. So they are trying to place the orphans in the reliable hands of the employees.”
The story of red deer rescue
Such “rescue” stories are repeated from year to year. For example, during the past year, employees of the Udege Legenda park took three roe deer and one red deer from the residents for keeping in a recreational enclosure. Two roe deer were already adults, the other two cubs were fed almost from birth. Their lives were saved, but the main law of nature was violated - they did not become wild animals. They have grown too trusting of humans, they do not know what a predator is, what food is better and where to look for them at different times of the year.
Therefore, remember: As much as you want to pet, help, rescue, or protect a small living creature, the best thing you can do is to leave, leaving the cub in place. And only if you are absolutely sure that the mother is dead, you can take it. Getting out of a newborn wild animal is a whole science that the park staff did not comprehend of their own free will, but managed to do it. But for those who are already faced with the need to raise a weakened deer / roe deer on their feet, we have written a short guide to nursing a deer cub in captivity.
And only if you are absolutely sure that the mother is dead, you can take it. Getting out of a newborn wild animal is a whole science that the park staff did not comprehend of their own free will, but managed to do it. But for those who are already faced with the need to raise a weakened deer / roe deer on their feet, we have written a short guide to nursing a deer cub in captivity.
Red deer rearing in artificial conditions
Red deer rearing in artificial conditions (personal experience of a park employee) I must say right away that my personal experience in this area is very small - we (so far) raised only one. But at the very beginning we faced a huge problem - we could not find information anywhere that would help us out. Actually, that's why I came up with the idea to write a short guide for those who still have to enter in the search engines "how to feed a red deer cub."
First you need to determine the age of the animal
Our Yashik came to us through second hands, so only a veterinarian could reliably determine his age - 6-7 days. So, what does a wapiti cub look like at a week of age:
So, what does a wapiti cub look like at a week of age:
Height at the withers: 64 cm
It still does not stand very well on its legs, they are slightly curved with the letter X. Often “cries”.
Teeth: back (if I may say so) not yet, front 8 (now Yasha is already 2 months old, but the front is gone), they are all below. 2 in the center are very large and funny: o) the rest are quite small.
Weight: 10-12 kg (but this is taking into account that he was fed incorrectly all his first week)
Understand who is in front of you
By the way, it will be useful to understand who is in front of you - a red deer or a spotted deer. They are often confused. The red deer is larger (against our 65 at the withers - 45-50 in the sika deer, weight approx. 4-6 kg). The head is large, the ears are elongated. I would compare them with the length of the nose from the tip to the eyes. The deer has a neat muzzle with VERY large round ears. Now as for the coloring. It should be noted that everyone has spots. In deer, they are located along the ridge and will come off after the first molt in October, while in spotted deer they are all over the body and will remain for life.
In deer, they are located along the ridge and will come off after the first molt in October, while in spotted deer they are all over the body and will remain for life.
In red deer the spot under the tail is yellow and small, dimly outlined. In a deer, on the contrary, it is white, wider and strikingly different in color from the general background.
And now the most important thing - about feeding. Or, more accurately, breastfeeding.
Golden rule: do not overfeed.
We gave cow's milk (necessarily boiled!) with the addition of water and baby formula "Malyutka 1" (one - ie from birth).
Proportions: 1 liter of milk, 8 measuring spoons of the mixture, 0.5 liters of water. For the first 2 weeks, you need to feed 8-10 times a day, 100 g of the resulting mixture. It is better to use a bottle with a simple (not the most expensive) elongated nipple. By the way, because of the structure of the jaws, the deer did not recognize the Aventa’s nipple so respected by mothers. Of course, it is better to warm up to 36-38 degrees. You can check the temperature in the same way as for children - a drop on the bend of the elbow.
Of course, it is better to warm up to 36-38 degrees. You can check the temperature in the same way as for children - a drop on the bend of the elbow.
After the second week, give about 150 ml of water during the day between feedings. Once a day, we gave lightly salted (1 teaspoon without top per liter of boiled water). Now we feed 8 times a day, 250 ml each.
At the age of three weeks, the red deer was drunk with a five-day course of probiotic Vetom-2 (I won't say why “2”, but that's how we were determined in the veterinary clinic). Dilute one sachet in 200 ml of water, divide in half and give twice a day one hour after feeding (so you will need 5 sachets)
Month.
At this age, you can transfer from a baby bottle to a cow bottle (for feeding calves - sold in veterinary stores). No, of course, you can continue to drink from a small one, but it will be tiring - you need to fill it several times for one meal or have 4 at once. At the same time, we began to feed Yashechka with a whole milk substitute Kormilak.
Its cost in Primorsky Krai ranges from 1900 to 2400 for a 25 kg bag. This amount is enough for about 2 months. The first days we add kormilak to cow's milk, but we cancel the infant formula (i.e. it turns out 1 liter of milk + 0.75 ml of water + 100 g of kormilak), then (well, say, on the fifth day) we give pure kormilak, i.e. . at the rate of 1:9as written on the package. I weighed a plastic container on a culinary scale, it turned out to be 200 gr, i.e. almost 2 liters of water. At the age of one to two months, his daily intake increased from 2.5 to 4 liters of formula per day, and the frequency of feeding decreased from 6 to 4 times.
- Grass. I wondered for a long time when to start feeding with grass. But everything turned out to be easier - Yashichek himself reached for the raspberries. And off we go. Most of all he liked dandelions, grapes, raspberries. Then come beets, ash leaves, currants. He also loves berries terribly: o) Honeysuckle, strawberries, currants, raspberries, irga - everything goes with a bang.
 At the same time, the apples directly spits out. You can give pureed vegetables as a substitute for grass.
At the same time, the apples directly spits out. You can give pureed vegetables as a substitute for grass. - Faeces. Normally, he is like a goat - balls. Our pet had diarrhea at first. Wrong food - diarrhea, did not boil the bottle - diarrhea, overfed - diarrhea again. What to do. Give less food and carefully monitor the sterility of dishes.
- Dehydration on the second day of life at my home was diagnosed by a veterinarian - Yashka refused to eat, could hardly stand on his feet. He was given a dropper in the neck (do not do it without a specialist!) with saline through a butterfly 4-ku, 200 ml + half a bottle of glucose. He almost immediately got to his feet, but it was impossible to feed, it was possible to give saline in the evening and replace one meal with it the next day. In general, having a doctor in the family, on the second day we were ready to repeat the drip on our own, but, fortunately, it was not necessary. In order to prevent, see above, drink salted water daily.

- Site arrangement. Here, of course, the more the better. Yasha had to live in an open chicken pen, 3x8. The size, frankly, is not great. Net height 3.5 meters. It is necessary to make a small canopy, 1.1-1.2 m high, with a roof and without one wall - so that it can enter freely, cover the floor with hay, which needs to be changed regularly (because they defecate, most often, under themselves).
- General recommendations. The life of these small, defenseless creatures is in your hands. Therefore, it is important to decide what will happen to them when they are ready to exist on their own: do you intend to give it to the zoo / zoo / safari park or plan to release it into wildlife. The permissible frequency of contact with the animal depends on this. If he is destined for the fate of a wild beast, then do not allow strangers to approach him, i.e. he should know only those 1-2 people who care about him. But you need to remember that even with this option, it is vital for him, no matter how pathetic it may sound, closeness and warmth, a sense of security - when you feed him, do not be lazy to stroke and talk - he will soon begin to recognize your voice.
 If you are not going to let go into the wild, then you need to hug the first 3-4 weeks as often as possible - you yourself will see how it calms him down.
If you are not going to let go into the wild, then you need to hug the first 3-4 weeks as often as possible - you yourself will see how it calms him down.
Reindeer diet.
Reindeer food depends on the season. In the summer they feed on grass, cereals and ... mice - yes, yes! Not that they are specially hunted for them, but if some frivolous mouse gapes on a tussock, the deer will grunt it along with the grass and will not even notice. And also tasty food for them - mushrooms. The peoples of the North do not eat mushrooms precisely because deer do.
So the Sami thinks: Why am I, a man, going to eat reindeer food? I'm not a deer! And there are so many mushrooms that sometimes the whole tundra around seems to be covered with a solid carpet of bright boletus caps. So deer will not be left without food in the summer.
But in winter, when there is neither grass nor mushrooms in the tundra, deer hunt moss from under the snow. This is the only food available in the winter cold. Deer have an excellent sense of smell, and they smell reindeer moss even under a meter layer of snow, and they know how to get it from this great depth. And what can you do: winter in these parts lasts nine months, so we had to adapt. They dig the snow with their front legs so deep that sometimes only one back is visible in a feeding deer.
Deer have an excellent sense of smell, and they smell reindeer moss even under a meter layer of snow, and they know how to get it from this great depth. And what can you do: winter in these parts lasts nine months, so we had to adapt. They dig the snow with their front legs so deep that sometimes only one back is visible in a feeding deer.
Yagel is a lichen.
In the past, the Sámi used to keep their reindeer near their dwellings in the winter - a very small herd of three to five heads. And they prepared reindeer moss for them for the winter. In the summer it is quite simple, since you do not need to dig up plants from under the snow - you gathered an armful, put it in a shed, and let it dry for yourself. Before giving it to deer, reindeer moss was soaked in a bucket of water, and it became like fresh. And since deer love salt, salted fish heads were also thrown there. It turned out such a venison salad - reindeer moss with salted fish. Yummy!
Berry picking in the north.
And deer are very fond of berries that grow in the tundra in swamps: cloudberries, blueberries, lingonberries, cranberries. We humans are also not averse to eating such berries, so I will tell you how they are harvested.
For harvesting cranberries and lingonberries, there are special tools similar to a scoop with a scallop. With these combs, the berry is, as it were, combed out from the bumps: r-r-time - and I have already collected a whole glass of cranberries! But cloudberries have to be picked by hand, each berry separately - it is very tender. But deer do not need all these complexities and adaptations. After all, unlike humans, they are not afraid to get stuck in a swamp and calmly walk through it, nibbling berries.
Information from the book about reindeer.
Reindeer grazing
Reindeer grazing.
Reindeer walk in the summer by themselves, and no one looks after them at all. This is called free grazing. They roam in small groups of 3-5 individuals along the seashore, where the wind drives away annoying insects from them. and nibbling young grass.
and nibbling young grass.
Such reindeer self-sufficiency is very convenient for a person: you don't need to look after them or feed them. And in autumn, instinct makes them go to warmer places, deep into the Kola Peninsula. So they rush to the south with trampled thrones, along their thousand-year-old routes. This is where the shepherds lie in wait for them. They know all these paths well and gradually gather deer into herds, which are driven to winter pastures. Such herds may not be very large, or they may simply be gigantic. And then their distillation to pasture is an impressive sight.
Imagine: ten thousand deer are walking, powerful snowmobiles accompany them from all sides, and helicopters fly from above. As if a whole army is on the offensive - with equipment and aircraft!
For the winter, reindeer can be placed in a large corral, or you can do without it. Then the reindeer herders constantly go around the herd and make sure that the deer do not disperse. This way of grazing is called guarding. This, of course, is because deer are guarded. And the Sami herd their most reindeer much easier. Here is a hut in the pasture in which shepherds live. Deer calmly graze nearby, extracting reindeer moss from under the snow. And the shepherds only go around the herd from time to time: they look to see if anyone has strayed.
This way of grazing is called guarding. This, of course, is because deer are guarded. And the Sami herd their most reindeer much easier. Here is a hut in the pasture in which shepherds live. Deer calmly graze nearby, extracting reindeer moss from under the snow. And the shepherds only go around the herd from time to time: they look to see if anyone has strayed.
Deer antlers
Discarded deer antlers - food for the inhabitants of the tundra.
All the deer in the world have large beautiful antlers only in males, and only in reindeer do females wear them.
But here's the question: if thousands of deer shed their antlers every year, why should the whole tundra be littered with them? But this, of course, is not the case. In winter, the discarded horns are eaten in the tundra by all living creatures: mice, arctic foxes. Yes, the deer themselves are not averse to nibbling their antlers, sometimes right on each other's heads! Well, what can I get lost, since they are so useful! And in the summer, tourists come to the tundra, who are also happy to pick up discarded horns. They will bring it home, hang it on the wall - it is immediately clear that the person has been in the tundra.
They will bring it home, hang it on the wall - it is immediately clear that the person has been in the tundra.
- 43.51 Kb
B winter period lichens do not provide deer body with protein, minerals substances, vitamins. Due with that, eating in the snowy period lichens, the deer always strives eat plants that are partially or completely preserved snow in green condition. AT total stock of forage grasses preserved on pastures in winter, dominated by rags, i.e. dry brown shoots and leaves, and only 5-10% of the total supply green fodder grasses account for live green shoots. In green parts of wintering plants is preserved about 50% protein, and in rags - 35-40%. In winter, most sedges and grasses, constituting the main mass of snow reserves, contains 5-6% protein (absolutely dry matter). With sufficient providing snowy greens food for deer is preserved average fatness throughout the entire winter period.
Winter green feed includes about 80 plants, but essential for deer are only a few types: individual species of sedge, cereals, herbs and horsetail. Some sedges (water, swollen, roundish, vilyui) and cotton grass (vaginal, narrow-leaved) retain under snow up to 50% of ground organs in green condition. Deer eat and browned dry parts of these plants, and in some sedge species - and rhizomes. In those areas where cotton grasses are widespread, they make up to 90% deer diet. Young cottongrass shoots contain up to 4.5% mineral substances and up to 20% protein. In winter time nutritional value of sedge decreases, but the ash content is still sufficient great. Therefore, they are valuable as a source enrichment of the body of a deer with salts.
Some sedges (water, swollen, roundish, vilyui) and cotton grass (vaginal, narrow-leaved) retain under snow up to 50% of ground organs in green condition. Deer eat and browned dry parts of these plants, and in some sedge species - and rhizomes. In those areas where cotton grasses are widespread, they make up to 90% deer diet. Young cottongrass shoots contain up to 4.5% mineral substances and up to 20% protein. In winter time nutritional value of sedge decreases, but the ash content is still sufficient great. Therefore, they are valuable as a source enrichment of the body of a deer with salts.
Cereals nutritionally superior to sedges. Their green mass is preserved under the snow by 25-30%, and aftertaste - by 50%. Highest value have a sinuous pike, a squat fescue, sheep's fescue, yellow arctoila. Only some types of forbs have quite important in the nutrition of deer in the winter time. This is a cat's paw and northern linnaeus. Rhizomes are well eaten by deer three-leaf watch and marsh cinquefoil.
Horsetails willingly eaten by deer as in green as well as in a browned state. Greatest practical value for reindeer herding how winter-green fodder has marsh horsetail and reed, as well as wintering and Komarova.
Extant the remains of green plants, although they have lower nutritional value than in summer, but compared to the main food of deer - moss - contain 3-4 times more protein, 2-3 times more minerals and richer in vitamins. Presence under the snow such plants is important because it allows you to replenish the body deer protein, minerals and vitamins.
Summer green fodder. Green plants as the main pasture food of northern deer provide the body with all the necessary nutrients and vitamins. In summer, when choosing food, deer have a wide range of plants: from 318 types of fodder reindeer plants 268, or 84%, are summer food.
Most willingly deer eat cereals, sedges, foliage shrubs - various types of willows and dwarf birch. Especially valuable for them in the feed regarding plants such as watch, mountaineer, ragwort, lagotis, astragalus, bluegrass, foxtail, reed grass, arctophila, horsetail. The most valuable are the leaves of the tundra willows and dwarf birch. deer always very picky in the choice of food. They are usually do not touch dented or broken plants, but choose and bite individual leaves and tops of stems and shoots favorite, freshest, youngest plants. From the range available on the pasture deer usually chooses those plants that are in the leafing phase throwing out shoots, budding and flowering, always preferring fresh young greens. A plant of the same species is eaten reindeer more or less willingly depending on from the phase of its development. Since spring, deer willingly they eat sedges and grasses, but after flowering, when the leaves and stems coarsen, edibility these plants is drastically reduced. autumn, when, with the onset of a cold snap, the foliage shrubs fall off. Meaning of monocots plants in the diet of deer increases again.
The most valuable are the leaves of the tundra willows and dwarf birch. deer always very picky in the choice of food. They are usually do not touch dented or broken plants, but choose and bite individual leaves and tops of stems and shoots favorite, freshest, youngest plants. From the range available on the pasture deer usually chooses those plants that are in the leafing phase throwing out shoots, budding and flowering, always preferring fresh young greens. A plant of the same species is eaten reindeer more or less willingly depending on from the phase of its development. Since spring, deer willingly they eat sedges and grasses, but after flowering, when the leaves and stems coarsen, edibility these plants is drastically reduced. autumn, when, with the onset of a cold snap, the foliage shrubs fall off. Meaning of monocots plants in the diet of deer increases again.
Shrubs. Of great importance in the diet of deer are leaves of shrubs, especially willows and birches. Leaf nutritional content shrubs represent a large fodder value. Deer eat them all the time. growing season up to leaf fall. In some areas of reindeer husbandry, the share shrub fodder accounts for up to 80% all food eaten in the summer. Willows and birches widespread in reindeer breeding areas.
Leaf nutritional content shrubs represent a large fodder value. Deer eat them all the time. growing season up to leaf fall. In some areas of reindeer husbandry, the share shrub fodder accounts for up to 80% all food eaten in the summer. Willows and birches widespread in reindeer breeding areas.
By nutrition comes first willows: gray, shaggy, spear-shaped.
Grey, or gray, willow widespread in the tundra, forest-tundra and mountainous regions; forms extensive thickets in floodplains and in low places of the tundra. East from the Lena River, this willow is less common. Gray willow leaves are readily eaten by deer throughout the summer, until leaf fall, they remain tender, fall off late. Gray willow reaches 1.5 m in height, has dark brown branches with gray hairy summer shoots, leaves narrowed at both ends, entire-extreme, dense gray felt above, bluish below. Flower earrings develop later leaves.
Hairy willow , except for the Far East, found throughout river valleys along the watersheds. deer eating leaves and young shoots. Reaches 1.1 m in height, branches are thick, knotty, old - brown color, young - gray felt. blooms before the leaves bloom. Leaves usually hold on to the snow.
deer eating leaves and young shoots. Reaches 1.1 m in height, branches are thick, knotty, old - brown color, young - gray felt. blooms before the leaves bloom. Leaves usually hold on to the snow.
Spear willow - widespread shrub, found as thickets in valleys rivers (forms thickets along rivers and streams), as well as among the tundra on the watersheds. bushes reach 1.8 m in height; dark brown branches young shoots are yellowish, pubescent. The leaves are thin, with a finely serrated edge, dull green. Blooms before leaves appear.
Large importance in deer nutrition depending on from the region there are also willows such as iron, wood, loparsky, beautiful, Krylova, Sakhalin, Korean.
Leaves birches bloom later than at the willows, but they get rough earlier. As a result, in the second half growing season palatability them is reduced. birch leaves are characterized high nutrient content and minerals, while the greatest importance in the diet of deer have dwarf birch, skinny, Midendorf.
Birch dwarf often found in southern tundra and forest tundra, enters the forest zone. Widespread in Western regions of the Far North, east of Yenisei, its arrays are thinning. Leaves her fine are eaten by deer.
Mushrooms. In the regions of the Far North with pasture keeping deer is of no small importance as a feed product I have some hat mushrooms (boletus, boletus, goat, flywheel, russula, etc.). deer greedily eat mushrooms that appear in the tundra and forest-tundra from the second half summer and autumn. Even in early winter, deer dig out from under the snow dried or slimy remains of mushrooms.
Mushrooms contain significant amounts of nitrogenous substances (up to 45% of absolutely dry matter), from 9 to 17% carbohydrates and 5-10% ash. Mushrooms are rich and vitamins; they contain significant the amount of vitamin A, vitamins are found in them from group B, vitamins C, D and PP. For mushrooms high fiber content, mostly in the range of 20-30%, and mushroom fiber is poorly digested. Mushrooms contain 84 to 93% water. Mushrooms increase the digestibility of other feeds due to the high content of enzymes. The reasons deer's predilection for eating mushrooms not studied. This is supposed to be explained the presence in rough a significant amount nitrogenous substances and vitamins.
Mushrooms contain 84 to 93% water. Mushrooms increase the digestibility of other feeds due to the high content of enzymes. The reasons deer's predilection for eating mushrooms not studied. This is supposed to be explained the presence in rough a significant amount nitrogenous substances and vitamins.
Yield mushrooms depends on weather conditions and fluctuates over the years from 10 to 100 kg/ha. More mushrooms in the taiga zone and forest-tundra, in arctic and mountain there are fewer of them in the tundra.
Concentrated stern. Deer eat various grains foods rich in carbohydrates (cereal grains). With success, you can feed oats to deer, barley, corn and other cereal grains crushed or crushed. Deer willingly eat grain products bran, rye flour, crackers, baked bread etc. Digestibility and nutritional value grain feed for deer on average not have significant differences compared to with other farm animals.
Good eaten and used by northern deer animal feed - fish and meat and bone meal. Especially deer willingly eat fishmeal, which more often than other feeds it is used for top dressing.
Especially deer willingly eat fishmeal, which more often than other feeds it is used for top dressing.
Fish flour is highly valued in reindeer herding because she is local feed and contains in a small volume all missing in the winter pasture forage elements needed for food. Feeding with fishmeal stimulates the eating of reindeer moss. Nutritious the dignity of fishmeal for deer is assessed at 75-80 feed units. per 100 kg of feed, with the content 43-45% digestible protein.
Suitable use to feed deer meat and bone meal prepared in areas of development of marine fishery of the Magadan region from waste zhirotopny production, meat and bones sea animal.
For deer feeding can be used and compound feed. Horse feeding compound feed leads to rapid decrease in deer performance, because his body is not adapted to the digestion of this type of feed; chewing gum and stomach activity (rumen) when fed with this compound feed are violated. The deer is forced more often and chewing coarse parts of food longer, which stay longer in the stomach. When feeding mixed fodder, the deer requires about twice as much drinking water (up to 3-4 liters per day) than when feeding reindeer moss. Adding 1kg feed per 2kg reindeer moss provides complete nutrition deer and does not cause disruption digestive tract.
When feeding mixed fodder, the deer requires about twice as much drinking water (up to 3-4 liters per day) than when feeding reindeer moss. Adding 1kg feed per 2kg reindeer moss provides complete nutrition deer and does not cause disruption digestive tract.
Nutritious the dignity of compound feed is assessed for deer at 60-66 feed units per 100kg of feed, i.e. it is somewhat lower than according to tabular data for others farm animals.
Concentrated feed matters for feeding riding reindeer during periods of tense transport work. deer fast get used to eating concentrates, especially for fishmeal.
Coarse stern. Hay is eaten by deer significantly worse than fresh green fodder. When giving deer eat plenty of hay a day about 0.3-0.5 kg, in rare cases up to 1 kg. eatability hay depends on its botanical composition and cleaning times. Deer prefer small grass hay from legumes, cereals and herbs, harvested no later than the flowering period. The reason for the poor eating of hay by deer lies in the inability of his stomach to the processing of large masses of dry rough fodder. Deer do not eat hay cut better than hay, leaving a lot of food in the remnants, but hay flour is eaten completely.
Deer do not eat hay cut better than hay, leaving a lot of food in the remnants, but hay flour is eaten completely.
Nutritious the dignity of hay for deer is assessed 40-50 feed units per 100 kg of feed, and willow leaf hay 74 feed units in the presence of 5-8% digestible protein.
B mixtures with reindeer moss digestibility and nutritional value of hay rise somewhat.
B as roughage with success birch brooms can be used and willows. Deer willingly eat brooms, harvested at the end of June-July. Dry them in the shade, store in germs. Per head per day give 0.3-0.5 kg.
Mineral stern. When fed with reindeer moss and consumed snow instead of drinking water, the deer often mineral starvation occurs. That's why mineral supplements are needed. In some areas (Karelian ASSR) insufficiency mineral nutrition causes winter disease of 7-8 month old calves - appears weakness and then paralysis of the hind limbs.
Dacha salt, ash with the addition of trace elements (copper sulfate and cobalt chloride) prevents disease.
From mineral feed the greatest value have salt and bone meal. Salt is essential give to all deer in winter, during the feeding period lichen food. Adding salt improves deer appetite, makes them search for grazing more intensively feed. When fertilizing with salt, it slightly increases digestibility of lichen food and digestibility of nitrogenous substances. Eventually deer receiving table salt in winter usually remain satisfactory by spring fatness, and the pregnant uterus gives stronger, normally developed offspring.
Salt fed to deer in a hammer form (table salt) or rock salt (lick). Can be used brine - the brine that remains after salting fish. The brine contains nitrogenous substances. He's being frozen and set in the form of blocks, which animals lick. Deer should be given salt at the rate of at least 5-6g per head per day. At a minimum, salt should be given during the most difficult pasture period - from February to May.
Description of work
Reindeer get their food in the harsh conditions of the Arctic, where snow cover makes access to food difficult, and the nutritional characteristics of food do not always satisfy the needs of the body. This is the reason for the specialization of nutrition according to the seasons on those feeds in which at other times there are no fats, vitamins and salts, as well as the reason for sharp fluctuations in the size of muscle mass and the content of salts and vitamins in the body. Having subjugated the reindeer, man took care of satisfying his needs. The better a person knew them, the more successfully he bred deer and received more products. The folk school of reindeer husbandry is largely the science of how to feed the reindeer. In this direction, she has accumulated a number of observations that are also of theoretical interest
This is the reason for the specialization of nutrition according to the seasons on those feeds in which at other times there are no fats, vitamins and salts, as well as the reason for sharp fluctuations in the size of muscle mass and the content of salts and vitamins in the body. Having subjugated the reindeer, man took care of satisfying his needs. The better a person knew them, the more successfully he bred deer and received more products. The folk school of reindeer husbandry is largely the science of how to feed the reindeer. In this direction, she has accumulated a number of observations that are also of theoretical interest
Contents
Introduction…………..……………………………………………………3 …………………..4
Nutrient requirements………………7
Nutritional assessment. Feed digestibility……..8
Feed characteristics……………………………….…10
Conclusion………………………………………………….……19
List Literature………………………………….………...20
Beautiful, graceful, graceful and intelligent animals - reindeer - live in the northern polar latitudes. Reindeer food is not available everywhere, so they have to spend a lot of time and effort looking for it. Deer are able to walk hundreds of kilometers in summer - to the north, and in winter - to the south, in order to feed themselves and their offspring.
Reindeer food is not available everywhere, so they have to spend a lot of time and effort looking for it. Deer are able to walk hundreds of kilometers in summer - to the north, and in winter - to the south, in order to feed themselves and their offspring.
We will try to find out together with you what basic and pasture food saves animals from starvation in the harsh conditions of cold latitudes in summer and winter.
Deer feeding habits
Unfamiliar with the natural conditions of the tundra, it may seem that the natural world of this region is very poor. This is not so, therefore, large animals, the basis of the diet of which is plant food, manage to provide themselves with everything they need on their own.
Their main food in summer is leaves of willow, dwarf birch, and other plants, as well as grass and berries. It has been noticed that deer are picky about greens - they will not eat wilted branches with dry leaves, but will choose young and juicy leaves. They even eat mice. Deer do not specifically hunt for them, but if a mouse gapes, it will most likely be eaten along with a bunch of juicy grass. Deer graze in groups of three to five individuals where there is lush grass - most often on the sea coast.
They even eat mice. Deer do not specifically hunt for them, but if a mouse gapes, it will most likely be eaten along with a bunch of juicy grass. Deer graze in groups of three to five individuals where there is lush grass - most often on the sea coast.
In autumn, deer find cotton grass, cloudberries, fallen acorns, and sorrel. Mushrooms are considered a favorite delicacy of reindeer. Most they find right away, but in order to feast on flywheels, in early winter they have to dig up the snow.
In winter, when there is neither grass nor mushrooms, animals feed on reindeer moss, digging snow up to a meter thick with their hooves, they find lichens and eat them up to ten kilograms a day. In addition to reindeer reindeer, they eat lichens from branches and tree trunks with pleasure, drinking sea water and eating algae. So that such a monotonous diet does not lead to vitamin deficiency in winter, because the winter period here lasts almost nine months, deer are given bone meal, table salt and other feeds that satisfy their needs for vitamins, minerals and microelements.
For free-ranging animals, finding salt sometimes becomes a real problem, therefore, in order to find shale emissions, deer go on many kilometers of wandering.
Yagel is an amazing plant that grows in most of the natural tundra zone. This is a soft moss of light color, it sometimes grows in height up to 40 centimeters. It grows slowly, so pastures are quickly eaten up and herds of deer roam again and again in search of food. It is thanks to its chemical composition that deer do not get sick, and endure the harsh winter cold.
Animals can gnaw their discarded horns, which is not considered something out of the ordinary. Moss moss does not satisfy the body's needs for protein and salt, so animals eat lemmings, bird eggs and even their chicks.
Feeding reindeer kept in paddocks
Representatives of northern peoples keep deer as pets, so they worry about what animals will eat in winter. They prepare reindeer reindeer moss in the summer and store it in dry sheds.