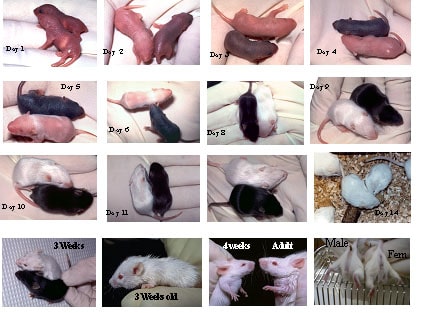
What to feed a baby mouse with fur and closed eyes
What Do Baby Mice Eat if Their Eyes Are Closed?
By Tom Ryan | Updated September 26, 2017When a mouse is born, he can’t do much to defend himself -- he’s blind and deaf, and therefore unable to navigate his environment or find his own food. Fortunately, his mother is there to take care of him. If she doesn’t assume responsibility for feeding him, someone else has to, or he won’t survive.
Litter Size
Just like larger mammals like dogs and cats, mice give birth to litters. A female mouse typically gives birth to a litter of five or six babies, though she can actually give birth to more than a dozen. It’s her responsibility to care for the babies when they are born, because the males don’t do anything to help raise the young. Because the gestation period is so short and a female can breed again immediately, she can give birth to as many as 10 litters per year -- quite a few little mouths to feed.
Blind Dependency
When the baby mice are born, they’re completely deaf and blind -- they won’t be able to see or hear for more than a week. This means that during that period -- and afterward -- the mother is solely responsible for feeding her young. They feed at her teats, which they find by feeling their mother’s warm body blindly.
Nursing a Mouse
If a mother abandons her young or dies, they need to be fed, either by a foster mouse, a foster rat or human hand-feeding. Mothers already nursing babies of their own are typically willing to take on fosters -- rats make especially-willing foster mothers for mice. By removing the mouse or rat mother from her babies and then rubbing her natural babies in your hands with the orphans, you make the two litters indistinguishable to her.
Though they are tiny, baby mice have big appetites -- the babies eat about once every two hours, so if you take on feeding duties yourself, you have to diligently monitor the time. It takes a baby mouse about five minutes of feeding to get his fill of milk or formula.
Weaning
Even after the babies open their eyes, they continue relying on their mother for food. They can see and hear when they are about 10 days old, but their mother feeds them until they are about three weeks old. By this time, their teeth have started to grow in and they can be weaned off of the teat and onto solid foods. By the time the babies are four weeks old, they’re completely independent.
They can see and hear when they are about 10 days old, but their mother feeds them until they are about three weeks old. By this time, their teeth have started to grow in and they can be weaned off of the teat and onto solid foods. By the time the babies are four weeks old, they’re completely independent.
References
- Animal Control Technologies Australia: Mouse Biology
- Kid Cyber: Animals: Mice
- American Fancy Rat and Mouse Association: Caring for Rat & Mouse Orphans
Photo Credits
Writer Bio
Tom Ryan is a freelance writer, editor and English tutor. He graduated from the University of Pittsburgh with a degree in English writing, and has also worked as an arts and entertainment reporter with "The Pitt News" and a public relations and advertising copywriter with the Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh.
Orphaned Mouse Care | Chip Chloe Squirrel
What should I do if I find an orphaned baby mouse?
Determine if the mouse/mice are indeed orphaned. If you have accidentally destroyed a nest with babies in it, build a makeshift nest using any of the nest remains in a small shallow container, and place it near the original nest site and leave it undisturbed for an hour or two to see if the mother returns to retrieve and relocate her babies. If any of the babies have already died, if they are lethargic or cold to the touch, or if you find one baby wandering alone, chances are that they have been orphaned.
If you have accidentally destroyed a nest with babies in it, build a makeshift nest using any of the nest remains in a small shallow container, and place it near the original nest site and leave it undisturbed for an hour or two to see if the mother returns to retrieve and relocate her babies. If any of the babies have already died, if they are lethargic or cold to the touch, or if you find one baby wandering alone, chances are that they have been orphaned.
Always wash your hands thoroughly after handling mice.
The risk of contracting disease is rare but increases if you live in the southwestern United States.
When you find an abandoned mouse, there are a few essential steps that should be immediately taken.
(Please note - these instructions are also applicable for other small rodents like orphaned voles and rats)
The first priority is to get the baby warmed up before attempting to feed it anything. Baby mice with their eyes closed (and even for a week after eyes open) are unable to maintain their own body temperature without a supplemental heat source. Make a small nest using t-shirt material, flannel or fleece and place it in a secure container with ventilation (a reuseable Tupperware with vented lid works well) and place it on a heating pad set on low. Make sure it doesn’t have an ‘auto shutoff’. If you don’t have a heating pad, you can fill an old sock with rice, corn or another grain and microwave it for 30 seconds to use as a heat source (use good judgement to make sure it’s not too hot – you’re trying to mimic the mother mouse’s body temperature). This will need to be rewarmed every couple of hours to maintain the warmth.
Make a small nest using t-shirt material, flannel or fleece and place it in a secure container with ventilation (a reuseable Tupperware with vented lid works well) and place it on a heating pad set on low. Make sure it doesn’t have an ‘auto shutoff’. If you don’t have a heating pad, you can fill an old sock with rice, corn or another grain and microwave it for 30 seconds to use as a heat source (use good judgement to make sure it’s not too hot – you’re trying to mimic the mother mouse’s body temperature). This will need to be rewarmed every couple of hours to maintain the warmth.
While the mouse is warming up, use ahnow.org to locate wildlife rehabilitators in your area who may be able to assist in raising the mouse. Leave messages with as many as possible because you may not get a return call for several hours or days. Orphaned mice are VERY difficult to raise and require feedings every 2-3 hours around the clock for several weeks. Rehabilitators are already equipped with the proper tools, formula and knowledge to properly rehabilitate orphaned wildlife but they are very busy and usually overloaded with animals to care for, so be prepared to transport your mouse to them.
After warming, the mouse needs to be hydrated within a few hours of being found. Plain Pedialyte is the best option, but you can also make your own makeshift hydration solution by dissolving 1 tablespoon of sugar and 1 teaspoon of salt in 1 cup of warm water. The best tools for feeding mice are small syringes with pointed rubber nipples (example here), but you probably won’t have those on hand, so you can try dipping the tip of a tiny paintbrush in the fluid and allowing the mouse to lick it off. Get as much fluid into the mouse as you can (0.2-0.5 mL), every 2 hours for the first 4-6 hours.
Mice with their eyes closed need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate after each feeding/hydration session. Gently rub the genital area with a q-tip or tissue in a motion that mimics the mother mouse licking the area. Moistening the q-tip in warm water may help. Do this for about 10 seconds, and if no results, try again after feeding some more. You may not see any poop for the first few times, but you should hopefully see a few drops of urine unless they’re very dehydrated.
If you are unable to locate a wildlife rehabilitator after multiple attempts:
Baby mice can’t go too long without being fed, so if you’re not able to locate a rehabber within about 6-8 hours of finding the babies, you will eventually need to transition them from the hydration solution to a suitable formula. After 2 feedings of the hydration formula, you can start to feed watered-down formula, gradually making the formula to water ratio stronger over the next 3-4 feedings (for example, start with 5 parts water to 1 part formula powder, then 4:1, then 3:1 and finally 2 parts water to 1 part formula powder). For babies under 1 week old, I like to keep the ratio at around 3:1 or 2.5 parts water to 1 part formula so it's easier on their digestive systems. Acceptable formulas are: Goat’s Milk Esbilac Puppy Milk Replacer, Fox Valley brand formulas (20/50 squirrel formula; Puppy Formula), or if none of those are available, you can make homemade formula (3 tbsp goat’s milk, 3 tbsp plain yogurt, 2 tbsp heavy cream, 1/2 egg yolk. If you can't find goat’s milk, double the yogurt.)
If you can't find goat’s milk, double the yogurt.)
Powdered formulas are preferred because you can mix a fresh batch each day for the needed amount, in comparison with liquid formulas which must be used within three days. Please contact me for advice if you are having trouble locating suitable options. DO NOT FOLLOW OTHER ONLINE RECIPES FOR MIXING YOUR OWN FORMULAS WITHOUT GUIDANCE FROM A LICENSED REHABILITATOR – these can result in severe malnutrition and issues like bloat that can lead to death.
Baby mice need to be fed as often as once every two hours depending how old they are. (This chart can help to estimate age.) This means that you must be prepared for some sleepless nights. A good goal is to feed every 3 hours around the clock, and for the mouse to ingest between 0.3mL – 0.5mL per feeding (up until eyes open) and up to 1mL for eyes-open babies until they gradually wean at 3 weeks of age.
You can use the same method of dipping a tiny paintbrush into the formula and allowing the mouse to suck it off. However – this is a very difficult method of feeding small mice and usually results in the mouse not getting enough food at each feeding. Please try to order the proper syringes and small pointed nursing nipples for the best results.
However – this is a very difficult method of feeding small mice and usually results in the mouse not getting enough food at each feeding. Please try to order the proper syringes and small pointed nursing nipples for the best results.
After warming formula, gently hold the mouse between your fingers, with your index finger near the head, ready to prevent it from lunging forward and falling. Carefully and consistently apply pressure to the syringe plunger to administer 1 drop at a time and ensure that the baby is suckling and swallowing the formula.
TIP: Mice like their formula WARM and it cools very quickly in such a small syringe so it’s recommended to fill 2 syringes and have one sitting in a cup of hot water so you can swap back and forth regularly while the other one keeps warm.
Be careful not to allow any formula to enter their lungs. You can check this by observing that no milk is bubbling from their nose. If milk enters their lungs, aspiration pneumonia may occur. The best way to avoid this is to keep the mouse upright when feeding it, never allowing it to rest on its back. If you do see a bubble form, flip the baby to a head-down position to prevent any more liquid from entering its lungs and wipe the nose with a tissue to absorb any liquid.
The best way to avoid this is to keep the mouse upright when feeding it, never allowing it to rest on its back. If you do see a bubble form, flip the baby to a head-down position to prevent any more liquid from entering its lungs and wipe the nose with a tissue to absorb any liquid.
Overfeeding is also dangerous and can lead to bloat. Check to ensure that they are well fed by the emergence of a white patch in the middle of their belly, a milk belly. This should recede before the next feeding. If you are seeing a full milk belly when the time comes for the next feeding, wait an extra half hour, and water down the formula to a 50:50 water to formula ratio for one feeding. If your mouse experiences diarrhea, it is also likely a result of being overfed. If this happens, or if your mouse is looking bloated, it’s ok to substitute Pedialyte/electrolyte solution for one or two feedings until the condition resolves.
Make sure to gently massage your baby’s abdomen and rectal area after each feeding to assist food in moving through the digestive tract and to help the baby eliminate waste. It’s almost impossible to reverse the effects of bloat once too much formula has backed up in the digestive tract, and this can lead to a painful death.
It’s almost impossible to reverse the effects of bloat once too much formula has backed up in the digestive tract, and this can lead to a painful death.
Baby mice begin to open their eyes at around 10-12 days of age. They may need a larger enclosure at this point (acrylic kritter keepers work well), but still keep using the heating pad on low under the nest portion of their tank. At this point, you can begin to add some dry oats into their nest and they will start to nibble on these within 1-2 days. Once they start nibbling solids, they will no longer require a nightly feeding – they can last from midnight to 6am without formula.
You can start to introduce other soft solids like spinach and other greens, fruit and crushed nuts. At three weeks of age, the babies will also no longer require the syringe for feedings and may begin to feed from a dish (jar lids work well as shallow dishes). Gradually make the switch from the syringe to a dish by leaving a dish of formula available between meals and spacing out feeding times to every 4-5 hours.
You can begin integrating foods such as baby food, fresh fruits and veggies, seeds and commercial mouse foods. Make sure to add a shallow dish of fresh water.
Mice are often very messy eaters, so after they finish their meals, it will be necessary to clean them up and replace soiled cage bedding often. Plain paper towels make for easy clean up when used to line the cage. Alternatively you can use an unscented shredded paper bedding made for rodents.
By this point, your babies will be getting more active so you can move them to a larger tank – a large acrylic kritter keeper or 10 gallon tank with a tight fitting screen lid are best. A wheel for exercise and some places to hide and things to chew on are also good for enrichment.
Mice can be released at about 4 weeks of age – about 1 week after weaning. However, it’s often better to keep them for an extra week if possible to allow them to put on some more weight. To begin acclimating for release, ensure that the weather is consistently above 50 degrees Fahrenheit and that there are at least 3-4 days with no rain forecasted*. A suitable release location should be an area with plenty of underbrush for shelter and nearby food and water sources.
A suitable release location should be an area with plenty of underbrush for shelter and nearby food and water sources.
It’s good to move their cage outdoors in a protected area at least a full day before release so they can adjust to the outdoor smells and sounds. Secure the lid so no predators can intrude overnight. Mice should be released at dusk since this is when they are most active. Gently tilt the tank on its side and gradually open the screen cover. Continue to place food and water at the release location for at least a week, if not longer, while they establish a nesting site nearby.
*If the mice are old enough for release but it’s too cold outside or if heading into the winter months, you may need to overwinter the mice until spring. Please visit the Adult Mouse Care page for further instructions.
What mice feed their cubs. Where mice live in the wild
House mice are rodents that live in people's homes. In the photo, the house mouse looks like ordinary mice. Is there a difference between them?
Is there a difference between them?
Because house mice have adapted so well to living with humans, they have been able to spread throughout the world, thus becoming one of the most common mammals. Mice are also pets and model organisms for laboratory research. nine0005
Appearance of the house mouse
The house mouse is a long-tailed small rodent with a body length of 6.5 to 9.5 cm. In relation to body length, the tail is less than 60%.
Upper tail covered with ring-shaped horny scales and short sparse hairs. The weight of an adult is from 12 to 30 grams. The ears are small and rounded. The skin has a brownish-gray or dark color. The color of the abdomen is from white to ash-gray. Desert mice have a light yellowish-sand color and a white belly. nine0005
Domesticated mice are variegated, blue-gray, yellow, black or white. Females have five pairs of nipples. The house mouse has no sexual dimorphism.
Distribution of the house mouse and its subspecies
The house mouse is a cosmopolitan species and lives almost everywhere. It is absent only high in the mountains, Antarctica and the Far North. The main factors that limit the distribution of house mice are high humidity and low temperatures. On the territory of Russia, the house mouse is not found in the mountain tundra, in the interfluve of the Lena and Yenisei, in Taimyr, in most of northeastern Siberia. nine0005
It is absent only high in the mountains, Antarctica and the Far North. The main factors that limit the distribution of house mice are high humidity and low temperatures. On the territory of Russia, the house mouse is not found in the mountain tundra, in the interfluve of the Lena and Yenisei, in Taimyr, in most of northeastern Siberia. nine0005
Presumably the home of the house mouse is North Africa, Western Asia or North India. In Western Asia, the house mouse is known in fossil form. Throughout the world, the house mouse has spread along with humans.
About one hundred and thirty subspecies of the house mouse have been described so far. They are grouped into four main subspecies.
1.M.m. castaneus - lives in Southeast Asia;
2.M.m. bactrianus - lives in Asia with the exception of the South-East region; nine0022 3. M.m. domestic - common in Australia, America, Europe and most of Africa;
4.M.m. musculus - lives in Eastern Europe, starting from the territory of Poland and further eastward, occupying most of Russia.
It has long been believed that the Japanese subspecies M.m. molossinus is the fifth "major" subspecies, however according to recent studies it is a hybrid between M.m. castaneus and M.m musculus.
Interestingly, in ancient Rome, mice and rats were considered the same species, so rats were simply called big mice. nine0005
House mouse lifestyle
House mice live in a wide variety of biotopes and landscapes, including anthropogenic ones. In general, it can be argued that house mice are very closely related to humans and are a synanthropic species. The house mouse often settles in outbuildings and residential buildings. In the north of their range, mice make seasonal migrations. At the end of the summer period or at the beginning of autumn, animals begin to massively migrate to the so-called "feeding places", which include warehouses, grain and vegetable stores, as well as residential buildings. In autumn, the range of migrations can reach up to five kilometers. Often, house mice hibernate in stacks, haystacks and forest belts. nine0005
Often, house mice hibernate in stacks, haystacks and forest belts. nine0005
In spring, house mice leave their wintering grounds and return to their natural habitat, gardens, orchards and fields. In the south of the range, in semi-deserts and deserts, they often live outside human habitation throughout the year. Under such conditions, house mice gravitate towards various water bodies and oases.
In their natural habitat, the house mouse prefers soft, not too dry soils. In them they dig small holes with a simple device. The length of the hole reaches one meter, and the nesting chamber is located at a depth of 20-30 centimeters and has from one to three entrances. In winter, mice often deepen their burrows up to 50-60 centimeters. The diameter of the nesting chamber is from ten to twenty-five centimeters. Inside the chamber, the animals arrange bedding using soft plant rags. Often, house mice occupy burrows belonging to other rodents: gerbils, mole rats, voles. Cracks in the ground and natural voids are also used for housing.![]() nine0005
nine0005
House mice settled near people equip their dwellings in the most protected and secluded places. Most often they live in attics, in household waste, garbage heaps and under the floor. To arrange nests, house mice use any available material: artificial fibers, feathers, scraps of fabric, paper.
Under natural conditions, house mice are nocturnal and twilight. But living next to a person, they adjust the daily regimen depending on the nature of human activity. Under artificial lighting, a house mouse can maintain round-the-clock activity, reducing it only during those periods when people are active themselves. The activity of the house mouse in this case has a polyphasic character: within one day there can be fifteen to twenty periods of wakefulness lasting from twenty-five minutes to one and a half hours. Like many other members of the mouse family, house mice gravitate towards constant routes when moving. nine0005
Such routes are easy to follow due to the visible piles of dust and droppings that are held together by urine.
The house mouse is a very nimble, mobile animal. They run fast enough, reaching speeds of up to 13 km / h, jump well, climb and are good swimmers. However, they rarely leave their nest. Under natural conditions, each mouse has its own individual area. In males, it reaches 1200 sq.m, and in females - up to 900 sq.m. However, if the population is dense enough, mice prefer to settle in family groups that consist of one dominant male, as well as several females with their offspring, or small colonies. nine0005
Relations within the colony are hierarchical. In relation to each other, adult males are quite aggressive. In contrast, females show aggression much less frequently. Skirmishes are rare within the family group, and as a rule they come down to expelling the grown offspring.
House mouse food
Under natural conditions, the house mouse is a typical seed-eater. It feeds on the seeds of cultivated and wild plants. Preference is given to seeds of Compositae, legumes and cereals. nine0005
nine0005
The diet of the house mouse also includes carrion, insects and their larvae. The green parts of plants are also eaten, which, depending on how accessible drinking water is, can account for up to a third of the food consumed. Every day, a house mouse consumes up to three milliliters of water. If the relative humidity of the air was about thirty percent, and the food was exceptionally dry, then during the experiment, laboratory mice died of dehydration on the 15-16th day.
With great desire, mice eat dairy products, chocolate, meat or grain. Under natural conditions, under the condition of an excess of food, stocks are made.
House mouse breeding
The house mouse is extremely fertile. If conditions are favorable (for example, in stacks and heated rooms), then it can breed throughout the year. Under natural conditions, the breeding season lasts from March to November. Re-entry into estrus is observed in females already 12-18 hours after the birth of offspring. During the year, a house mouse can bring from five to fourteen offspring. Each litter has three to twelve cubs. nine0005
During the year, a house mouse can bring from five to fourteen offspring. Each litter has three to twelve cubs. nine0005
Pregnancy lasts about twenty days (19-21). Cubs are born naked and blind. After about ten days, their bodies are completely covered with hair. After two weeks of life, their eyes open, and at the age of three weeks they become independent and capable of settling. The house mouse reaches puberty at the fifth to seventh week of life.
It should be noted that males, trying to attract a female, emit ultrasonic calls at 30-110 kHz. In their complexity, these cries are comparable to the singing of birds. The house mouse easily interbreeds with the mound mouse, which lives, for example, in the Black Sea region. nine0005
The offspring from such crosses is quite normal and viable. A number of zoologists consider the mound mouse to be a subspecies of the house mouse.
House mouse enemies
The house mouse has many enemies, primarily predators. These are birds of prey, snakes, large lizards, mongooses, small representatives of the mustelid family, foxes, cats, crows, and even.
These are birds of prey, snakes, large lizards, mongooses, small representatives of the mustelid family, foxes, cats, crows, and even.
Serious competition for house mice is that they often kill and even partially eat their small relatives. nine0005
At the same time, mice can act as predators themselves, which is generally unusual for them.
Once upon a time, mice were accidentally brought to the island of Gof, located in the South Atlantic, and they took root there. Since they had no natural enemies on the island, they multiplied very quickly and now their population is estimated at 0.7 million individuals. It should also be noted that these island mice are three times larger than their mainland counterparts. They unite in groups and attack bird nests with them, eating chicks. nine0005
It must be said that Gough Island is the most important colony of sea birds, among which we can mention such birds as Schlegel's typhoon and. These birds do not nest anywhere else. However, despite the fact that albatross chicks can reach a height of one meter and weigh 250 times more than the mice of this island, they practically do not move and are unable to protect themselves.
However, despite the fact that albatross chicks can reach a height of one meter and weigh 250 times more than the mice of this island, they practically do not move and are unable to protect themselves.
As a result, the mice literally gnaw through the bodies of the chicks and inflict deep wounds on them. According to scientists, mice destroy over a million chicks on this island every year. nine0005
House mouse lifespan
Under natural conditions, the life expectancy of these rodents is a year and a half. However, in captivity, they can live up to three years. The life expectancy record is almost five years (1819 days).
House mouse sense organs
The sense organs of these rodents are very well developed. True, the eyesight of a house mouse is quite weak.
Like most other rodents, they are farsighted. They also have very acute hearing. The range of frequencies perceived by them is very wide - up to 100 kHz. For comparison, the upper human threshold is 20 kHz. In low light, the house mouse is perfectly oriented with the help of vibrissae. The role of smell is extremely high in the life of mice, which is necessary both for searching for food and for recognizing relatives. nine0005
In low light, the house mouse is perfectly oriented with the help of vibrissae. The role of smell is extremely high in the life of mice, which is necessary both for searching for food and for recognizing relatives. nine0005
Each mouse has sweat glands on its paws, with which they automatically mark the territory. If the mouse is very frightened, then a substance is released into the urine that causes fear and flight in other animals. Moreover, the smell is quite stable, and lasts up to a quarter of a day, informing other mice about the insecurity of this place.
Moreover, if the signal substance was left by the male, then all individuals react to it, while only females react to the female's mark, while males ignore it. nine0005
House mouse and man
House mice are pests and carriers of a number of dangerous infections such as plague, etc. At the same time, mice play a very important role as laboratory animals. On July 1, 2013, a monument to a laboratory mouse was even erected in Novosibirsk for its contribution to experimental medicine and genetics.
If you find an error, please highlight the text and press Ctrl+Enter .
Description of the field mouse nine0113 :
- Body length not exceeding 12 cm, excluding tail. The thin tail makes up 70% of the body length.
- Body oblong. Hind feet are elongated, protrude forward when running.
- Long muzzle, small round ears, oblong nose.
The fur is hard, coarse, short. Colors can be different - gray, brown, ocher or beige. A straight line of black or brown shade runs along the spine. The color of the abdomen is white. At the base of the hairline has a dark shade. Small spots may be present on the chest. nine0005
The vole mouse has unique teeth , a pair of long incisors on the lower jaw grow throughout her life. To prevent their excessive growth, and they grow at a rate of 1-2 mm per day, the mouse is forced to continuously grind them on solid objects.
As for weight, the average animal does not weigh more than 20 grams.
Photo
Distribution of animals
This representative of the fauna is widely distributed in Europe. Also, animals can be found in China, Mongolia, Denmark, Finland, Korea, Taiwan. In the Russian Federation, the rodent is common in Primorye, Siberia, and the Urals. Often settles on the hills, climbs low into the mountains. nine0005
Occurs near the Black and Azov Seas. Does not like desert forest-steppes and continuous forests. Perfectly takes root in moist interfluves .
Prefers overgrown meadows with small hollows, collective farm arable lands, sunny edges of deciduous forests and, of course, kitchen gardens. It can be found in greenhouses, greenhouses, cellars, barns, abandoned utility sheds, and even in residential areas.
IMPORTANT! With the onset of the autumn period, rodents move into stacks, haystacks, straw bales. nine0005
Reproduction
The breeding season of the vole mouse is from early spring to mid-autumn.![]() In one season, the animal is able to bring 3-4 offspring . In rare cases, up to 5-6. Bearing cubs lasts 21-23 days. In one litter, 5-7 babies are usually born.
In one season, the animal is able to bring 3-4 offspring . In rare cases, up to 5-6. Bearing cubs lasts 21-23 days. In one litter, 5-7 babies are usually born.
Babies are born helpless and blind, but they develop very rapidly :
- 12-14 days after birth, they begin to see clearly.
- 30 days after birth become independent. nine0117
- Juveniles are capable of giving birth as early as 90-105 days after birth.
How long does a field mouse live? The life expectancy of a field mouse can reach 7 years, but in the wild, animals live, as a rule, for a year or two.
Now imagine how fast rodents can breed in just one summer season, provided there is plenty of food and sun.
Lifestyle
In summer and spring field mice are active in the evening and at night. In autumn and winter, they can be active during the day. They do not hibernate in winter. nine0005
How vole mice hibernate :
- Natural hiding places or earthen passages can be used as minks.

- Their burrows reach 3-4 m in length and have 2-4 exits, one of which leads to a watering hole.
- Dwellings must have a nesting chamber and 2-3 pantries in which winter supplies are stored.
- Storerooms are located at a depth of 0.5-1 m.
IMPORTANT! Rodents living in swampy areas do not dig holes. They build nests. The main material is grass. Such dwellings are usually located on high bushes. nine0005
Distinctive features
Vole mice have their own, distinctive features from other rodents :
- Depending on the habitat (eastern and western), individuals have different colors and sizes.
- Differs from other rodents in the presence of a flat strip along the spine.
- Unlike mice, it has a larger body size.
- Differs from the Dahurian hamster in a longer tail.
- Unlike pied, it has a longer puberty period - about 100 days. nine0117
- Compared to other rodent subspecies, the field mouse has an underdeveloped pinna.
- Field mice have coarser fur. And adults often have soft spines, like hedgehogs.
- Field mice belong to the mobile subspecies. They are characterized by seasonal feeding movements.
- May be common in swampy areas. At the same time, they use grass nests as burrows.
It is very common for mice to be mistaken for other types of mammals that look like voles. nine0112 The most common species of rodents in appearance resembling mice :
- . Despite this name, this animal actually belongs to the mouse family, but differs from voles in its large size.
- . Lives underground and belongs to the hamster family.
As well as rodents from the family of mice-voles:
- and . Outwardly similar to mice, but have a number of distinctive features.
- . Forest inhabitants, differing from the field in the color of the fur coat. nine0117
- . This species lives in colonies and is able to make significant, up to 15 kg, stocks for the winter.

What harm is done to a person?
Voles can cause significant damage to both crop storage areas and plants in the fields. They can damage the vegetables planted in the garden and spoil the preparations for the winter in the cellar.
Moreover, these rodents are carriers of fatal infections for humans such as leptospirosis, tularemia, tick-borne typhoid fever. nine0005
Methods of struggle and protection
The main difficulty in the fight against field mice is that they live in places hidden from human eyes. This means that it is rather problematic to catch or poison them. Therefore, the first priority in the fight against voles is the need to find and destroy their habitat . You can do this in the following ways.
Drive mice out of the area
nine0113 :
- Mow long grass, dry leaves and weeds. You also need to get rid of branches and piles of plant debris. All of these are great places to build burrows.

- Fruits that have fallen from the tree should not be left on the site, as they are an easily accessible source of nutrition.
- Digging up the site can help get rid of burrows and underpasses.
- To prevent rodents from spoiling fruit trees, a fine-mesh net is dug into the ground around the trunks. The same can be done around the perimeter of the entire site. nine0117
We use repellers
The use of special repeller devices can speed up the process of expelling voles from your territory. They are installed around the perimeter of the site and provide protection from moisture.
Using mousetraps
Ordinary mousetraps can also help in the fight against mice. Experienced gardeners recommend installing these devices on the site in early spring and late autumn , since it is at this time that mice reproduce most actively. In order not to harm pets, mousetraps can be covered with a box, this will not stop mice in pursuit of bait. nine0005
nine0005
Using poisons
In late winter and early spring, the use of poisons is very effective. At this time, the mice are hungry and not very picky about food. Poisons are placed directly in the burrows.
How to get rid of field mice in the house?
If you have mice in your home, use time-tested, traditional methods :
- Mousetraps. At the same time, do not forget about safety measures so that people and pets do not suffer. nine0116 Repellers. Special devices are safe for people and pets, but have a negative effect on mice.
- Poisons can be used with all precautions.
- Cat. The most effective, proven and safe "remedy" for mice. If you don't have a cat at home, borrow it from friends for a while.
Thus, it is quite possible to get rid of mice on the plot or in the house. It is enough to create unbearable living conditions for them. And so that voles do not reappear, prevention is needed - keeping the site clean, timely cleaning of plant debris and food waste. nine0005
nine0005
Video
In the video you can see what field mice look like:
In the wild, mice only mate during the warm season. In winter, females do not estrus, and males do not care for a partner. At home, rodents are ready to mate all year round. Fans of these animals should know how mice breed so as not to harm their pets.
Mating rodents
Allows females to become fertile already on the 28-50th birthday. But the cubs of the decorative animal are born fatter and in greater numbers. Therefore, the breeder should not mate a female that has not reached the age of two months. nine0005
Interesting!
Obese animals are unable to reproduce. Animals preparing for mating should be fed greens and sprouted grains so that they do not become overweight.
If a person keeps one pair of mice, then the male and female live in different cages. They are planted next to each other when it is time for mating games. The female herself will “tell” about her readiness for reproduction. Her behavior changes as follows:
The female herself will “tell” about her readiness for reproduction. Her behavior changes as follows:
- she can become restless and a little aggressive;
- the female arches her back and raises her ass;
- male courtship is not rejected.
At home, the mouse becomes ready for fertilization 14 hours after birth. Wild mice do not breed as actively.
The estrous cycle in mice lasts, on average, five days. It consists of four phases:
- The epithelium of the vagina is located low and has a small thickness.
- After 50-60 hours, the number of epithelial cells increases.
- Estrus begins, the duration of which is 10-18 hours.
- The top layer of the epithelium is separated. The last phase lasts 24-30 hours.
Mating takes place during a fast estrus period.
Mice should not breed too frequently. Enough twice a year. Otherwise, the body of the female will weaken, and she will not be able to give strong offspring. Also avoid impregnating the mouse while she is feeding the babies. nine0005
Also avoid impregnating the mouse while she is feeding the babies. nine0005
Pregnancy
Mice gestate for 17-24 days. In the second half of pregnancy, the mouse rounds, and the owner can feel the mice in her tummy.
Care should be taken to ensure that a pregnant female can build a cozy place for newborn cubs. To do this, put paper, dry grass, pieces of cloth in a cage.
A pregnant mouse needs careful care:
- plenty of food. In the first half of gestation, mice - by a third, and in the second - by half. nine0117
- The cage with the animal must not be touched or rearranged.
- It is desirable to provide the animal with peace - less petting and picking up.
Note!
The male does not take part in rearing the offspring, so he is separated from the female before giving birth. Although some breeders claim that the "daddy" helps in childbirth - and it can be removed after the mice are born.
Pregnant mice often develop toxicosis, which causes death of the pet. The following signs of the disease are distinguished:
The following signs of the disease are distinguished:
- muscle spasms;
- drooping eyelids;
- salivation;
- ruffled and dull coat.
Mouse toxicosis is not treatable. Therefore, for this period, the female should be provided with access to fresh food and water and less likely to disturb her.
Childbirth
Before the expected date of birth, the mouse cage must be washed and disinfected, and fresh hay should be placed in its nest. Mice are born mainly at night, and the process itself can take two hours. nine0005
Note!
New breeders often wonder how many mice are born at one time. A well-cared for female is able to give birth to many babies - about 14 pieces. But on average, she can give birth to 5-9 mice.
The squeak of the cubs notifies the owner of the completion of childbirth. You can't touch the mice right away. The mother may not like the foreign smell, and she will refuse the offspring or kill him. But it is necessary to remove the stillborn.
But it is necessary to remove the stillborn.
If there are no contractions on the expected day of delivery, do not contact the veterinary clinic for help. It is necessary to observe the state of the mouse. A healthy female behaves as follows:
- she eats well;
- actively moving;
- coat and eyes shine.
It is worth panicking if the contractions go on for a long time (10-15 minutes) and there are no cubs. In this case, you need to call a veterinarian.
Babies are born naked, with closed ears and eyes.
Rodent breeders need to know how mice breed. So it will be possible to get strong offspring and maintain the health of the female. Decorative ones may experience complications in childbirth, which a doctor can handle. nine0005
A mouse is a small animal that belongs to the class of mammals, order of rodents, family of mice (lat. Muridae).
Mouse - description, characteristics and photo. What does a mouse look like?
The length of the body of a mouse covered with short fur, depending on the species, ranges from 5 to 19 cm, and doubles with the tail. These rodents have a rather short neck. On the pointed muzzle, small black beady eyes and small semicircular ears are visible, allowing mice to hear well. Thin and sensitive whiskers growing around the nose, give them the ability to perfectly navigate the environment. In mice, unlike, there are no cheek pouches. nine0005
These rodents have a rather short neck. On the pointed muzzle, small black beady eyes and small semicircular ears are visible, allowing mice to hear well. Thin and sensitive whiskers growing around the nose, give them the ability to perfectly navigate the environment. In mice, unlike, there are no cheek pouches. nine0005
Mouse paws are short with five prehensile toes. The surface of the tail is covered with keratinized scales with sparse hairs. The color of the mouse is usually characterized by gray, brown or red tones, however, there are variegated and striped individuals, as well as white mice. Animals lead an active lifestyle in the evening or at night. They communicate with each other using a thin squeak.
Types of mice, names and photos.
The mouse family includes 4 subfamilies, 147 genera and 701 species, the most common of which are:
- (lat. Apodemus agrarius) reaches a size of 12.5 cm, not counting the tail, which can be up to 9 cm long.
 grey. The habitat of the field mouse includes Germany, Hungary, Switzerland, Poland, Bulgaria, the southern part of Western Siberia and Primorye, Mongolia, Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula and certain territories of China. This species of mice lives in wide meadows, in dense thickets of shrubs, city gardens and parks, and the shelter suits both in minks and in any natural shelters. In flooded areas, nests in bushes. Depending on the season, the diet may consist of seeds, berries, green parts of plants and various insects. The field mouse is the main pest of grain crops. nine0117
grey. The habitat of the field mouse includes Germany, Hungary, Switzerland, Poland, Bulgaria, the southern part of Western Siberia and Primorye, Mongolia, Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula and certain territories of China. This species of mice lives in wide meadows, in dense thickets of shrubs, city gardens and parks, and the shelter suits both in minks and in any natural shelters. In flooded areas, nests in bushes. Depending on the season, the diet may consist of seeds, berries, green parts of plants and various insects. The field mouse is the main pest of grain crops. nine0117
- (lat. Apodemus flavicollis) has a reddish-gray color and a light belly (sometimes with a small speck of yellow). The body size of adults reaches 10-13 cm, the tail has approximately the same length. The weight of the mouse is about 50 grams. This species of mice is widely distributed in the forests of Russia, Belarus, Moldova, Bulgaria, Ukraine, the Caucasus, the northern provinces of China and Altai.
 Yellow-throated mice settle on open edges in tree hollows or dug minks, but they can also live in stony placers. Their diet includes both plant and animal foods. Eating young seedlings of fruit trees, they cause significant harm to nurseries. nine0117
Yellow-throated mice settle on open edges in tree hollows or dug minks, but they can also live in stony placers. Their diet includes both plant and animal foods. Eating young seedlings of fruit trees, they cause significant harm to nurseries. nine0117
- Grass mouse (Nilotic grass mouse) (lat. Arvicanthis niloticus) is one of the largest representatives of the mouse family and can reach 19 cm in length, and together with the tail - 35 cm. The weight of individual large individuals exceeds 100 g. The fur of the back and sides has a dark gray or grayish brown coloration with individual hard and prickly bristles of a darker shade. The color of the belly is light grey. This species of mice is most common in African countries, where they live in bushes, forests and savannahs. As a refuge, grass mice choose abandoned termite mounds or dig holes on their own, but on occasion they can penetrate into human habitation. The basis of the diet of mice is plant foods.
 nine0117
nine0117
- (lat. Micromys minutus) is one of the smallest rodents in the world. The body length of an adult animal does not exceed 7 cm, the tail is 6.5 cm, and the weight of the baby does not exceed 10 g. The back and sides are monophonic and have a reddish-brown or brown color, in contrast to the light gray, almost white belly. The muzzle of baby mice is short and blunt, with small ears. The distribution range of this species of mice stretches from west to east from the northwestern provinces of Spain to Korea and Japan, in the south to Kazakhstan, China and the northern regions of Mongolia. The mouse lives in forest and forest-steppe zones, in meadows with tall grass. In the summer, mice use nests twisted in the grass as a refuge, and winter in minks, haystacks, residential or outbuildings of a person. The basis of the diet of baby mice is the seeds of cereals and legumes, as well as small insects. Often they settle near granaries, causing great harm to agriculture.
 nine0117
nine0117
- (lat. Mus musculus) is the most common species on the planet from the rodent family. The body length of an adult mouse does not exceed 9.5 cm, and together with the tail - 15 cm. The weight of the mouse is 12-30 g. The color of the fur on the sides and back is gray with a brown tint, and on the abdomen from light gray to white. Individuals living in desert areas have a sandy color. The muzzle of the mouse is sharp with small rounded ears. The area of distribution of this species of mice does not include only the territory of the Far North, Antarctica and high mountain regions. House mice live in all types of landscapes and natural areas, very often they penetrate into household and residential buildings of a person. Under natural conditions, minks dig on their own, although they can also occupy dwellings abandoned by other rodents. They feed on seeds and succulent green parts of plants, and when they enter a person’s house, they consume everything that gets into their teeth - from bread and sausages to paraffin candles.
 nine0117
nine0117
- (lat. Lemniscomys striatus) is a small rodent: body length 10-15 cm, intermittent stripes of light colors are visible along the back and along the sides. Under natural conditions, striped mice rarely live more than 6-7 months, in captivity they live two to three times longer. The menu of these individuals includes mainly vegetable “dishes”: root crops, non-hard seeds, juicy fruits, and occasionally small insects.
- (akomis) (lat. Acomys) is a rather cute representative of the mouse family, the owner of huge eyes and the same big ears. The size of the spiny mouse, together with the tail, is 13-26 cm, the back of the animal is covered with thin needles, like a normal one. An amazing feature of these animals is regeneration: in case of danger, the mouse is able to shed a piece of skin, leaving the attacker at a loss. The skin is quickly restored without harm to the individual. The spiny mouse lives in Asia, is found in Cyprus and Africa.
 In food, it focuses on plant foods; this animal is often kept as a pet. nine0117
In food, it focuses on plant foods; this animal is often kept as a pet. nine0117
Where does the mouse live?
The area of distribution of mice covers almost all climatic zones, zones and continents of the globe. Mouse representatives can be found in tropical thickets, coniferous or deciduous forests, steppe expanses and deserts, on mountain slopes or in swampy areas. Mice also live in people's homes.
Mice can make nests from grass stalks, occupy abandoned burrows, or dig complex systems of underground passages. Unlike species that live in swamps, mountain, steppe, and forest mice are poor swimmers. nine0005
What does a mouse eat?
The basis of the diet of mice is plant foods: grass seeds, fruits of trees or shrubs and cereals (oats, barley, millet, buckwheat). Mice that live in swampy areas, in wet and flooded meadows, feed on leaves, buds or flowers of plants and shrubs. Some species of mice prefer protein supplement as insects, worms, beetles, spiders
The mouse does not fall into hibernation and can move under the snow cover without appearing on the surface.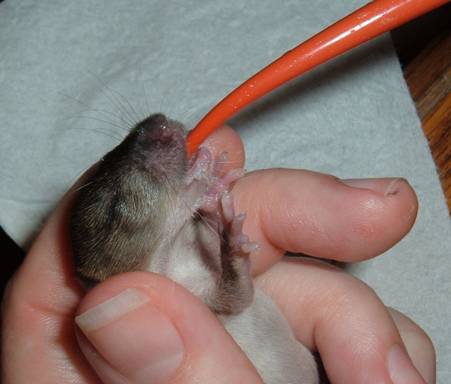 To survive the cold, she has to create solid food stocks in pantries arranged near the entrance to the mink. nine0005
To survive the cold, she has to create solid food stocks in pantries arranged near the entrance to the mink. nine0005
Fried cheesecakes with herbs, cheese and garlic
Fried cheesecakes with herbs, cheese and garlic
House mouse. Photo of house mice. House mouse What kind of litter do wild house mice have
- Rodentia Bowdich, 1821 = Rodents
- Family: Muridae Gray, 1821 = Mouse
Childbirth and development in mice
- nine0003
Pregnancy in house mice lasts an average of 22 days (20-26 days) and it proceeds easily and without complications. Usually, in mice, the fetuses in the uterus are located with their heads towards the exit from uterus and pathology of childbirth does not happen, and cases of death from childbirth among mice are very rare. Childbirth usually occurs at night. There are usually five to nine mice in one litter. It is interesting that the female already a day after giving birth, comes into heat and she is ready again to mate and may become pregnant again. In a female, lactation and pregnancy can sometimes occur simultaneously. nine0005
In a female, lactation and pregnancy can sometimes occur simultaneously. nine0005
Therefore, almost every female house mouse can give up to 10-11 litters in a row. But such intensity of reproduction greatly depletes it. For this reason, no more than nine litters are allowed to produce good offspring.
Normally kept female mice are quite rare cases of birth stillborn babies. The reason for this may be a lack of vitamins and minerals. in feed, as well as some infections. But mice born normal, sometimes die soon after birth due to some reason. This may be the lack of milk in the female, an underdeveloped instinct of motherhood, or stress, due to which the female tries to hide the mice, dragging them around the cage, as a result of which they die. Sometimes it happens that mice are born underdeveloped, as they lag behind in growth in the embryonic period, which is most often associated with insufficient and poor-quality nutrition of the female during pregnancy. nine0005
Since such mice, as a rule, die, the cases of the birth of weak litters serve as a signal of problems associated with the diet or feeding of animals. And here the death of offspring in closely related breeding of mice is almost never observed. Sometimes mice of smaller sizes than normal can be born, but, as As a rule, they quickly gain the desired body weight.
And here the death of offspring in closely related breeding of mice is almost never observed. Sometimes mice of smaller sizes than normal can be born, but, as As a rule, they quickly gain the desired body weight.
Mice are born naked and with closed eyes and ears. The average weight of newborn mice is about 1-2 g, with a body length of about 3 cm. Mice are born helpless and hardly move. In newborn mice, determine the sex, i.e. it is almost impossible to distinguish between females and males. But at a later age, males become larger than females. nine0005
During this period, it is necessary to maintain a high milk production of the female. AT the cage should always have good quality milk and fresh water. Newborns grow fast. Their mass doubles on the fourth or fifth day, the linear dimensions of the body increase. On the third or fifth day after birth the ears of the mice open, the body begins to become covered with hair. First teeth - lower the incisors erupt on the eighth day, and the upper ones on the 14th day after birth. AT At two weeks of age, mice open their eyes and begin to see. the world around them. Mice crawl out of the nest at about the third week of life and from this time they begin to consume food on their own. A mass of mice in this age averages about 8-8.3 years.
AT At two weeks of age, mice open their eyes and begin to see. the world around them. Mice crawl out of the nest at about the third week of life and from this time they begin to consume food on their own. A mass of mice in this age averages about 8-8.3 years.
Weaned shortly thereafter, 20-25 days after birth young from females and mother's milk. At the same time, if the female at this time lactation and pregnancy proceed at the same time, then weaning of young animals should be produce at least a day or two earlier than the deadline. And right there at jigging it is advisable to seat males and females in different cages in order to avoid them mating. And the mice after weaning from mother's milk continue to quickly grow, reaching by the age of one month, depending on gender, 11-12 g, their length the body is about 6 cm, and the tail is about 5 cm. And only by six to seven months in white mice, growth and development ends and stabilization occurs body weight and linear dimensions. By this time, young house mice already weigh about 25-30 g. In the future, the body weight of adult mice may change in depending on the quantitative and qualitative indicators of feeding and depending also on the conditions of keeping mice. nine0005
By this time, young house mice already weigh about 25-30 g. In the future, the body weight of adult mice may change in depending on the quantitative and qualitative indicators of feeding and depending also on the conditions of keeping mice. nine0005
The house mouse (Mus musculus) got its name because the vast majority of these rodents spend their entire lives in human housing and utility buildings. This is a typical synanthrope animal. But in summer it can be found in gardens, vegetable gardens, grain fields and stacks of straw.
In ancient times, house mice were distributed only in the south of Europe and Asia, but to the extent of human settlement, they penetrated far to the north and are now found in all areas of the continents. The main condition for settling the dwelling of house mice - food supply, temperature conditions - are of secondary importance. nine0005
Appearance of the house mouse
The house mouse is a small rodent with a body size of about 90 mm, a tail shorter than the body, and rounded ears. The color of the hairline of the back is one-color - dirty gray with a reddish tinge, the belly is whitish or light gray. This coloring makes these rodents, which are nocturnal, almost invisible. Sometimes there are reddish or intensely dark-colored, in which the belly is lighter in color.
The color of the hairline of the back is one-color - dirty gray with a reddish tinge, the belly is whitish or light gray. This coloring makes these rodents, which are nocturnal, almost invisible. Sometimes there are reddish or intensely dark-colored, in which the belly is lighter in color.
Habitat and nutrition of house mice
The house mouse lives mainly in the walls, under the floor, in the attics of houses, where they feel comfortable. Having settled in natural conditions, they dig shallow, uncomplicated burrows with two or three entrance holes. Nests are lined with pieces of paper, rags, dry herbs, weeds. They feed on a wide variety of food products that are sought in the premises. Under natural conditions - exclusively
grains and seeds of agricultural crops, giving preference to oilseeds (sunflower, hemp). nine0005
Reproduction and fertility of the house mouse
The house mouse breeds in warm rooms, with enough food, throughout the year. Pregnancy of the female lasts 20 days. For a year there are 5 or more offspring, fourteen kids in each. Newborn babies are blind, they begin to see clearly only on the 9th day. However, they develop rapidly, 20 days after birth they can live independently, and at the age of two months they are already able to reproduce.
For a year there are 5 or more offspring, fourteen kids in each. Newborn babies are blind, they begin to see clearly only on the 9th day. However, they develop rapidly, 20 days after birth they can live independently, and at the age of two months they are already able to reproduce.
Harm from mice
The exceptional fecundity of the house mouse and unpretentiousness to the conditions of existence contributed to the fact that
it became one of the most harmful rodents that cause great losses, both in housing and in granaries and food compositions. It is no less dangerous as a carrier of pathogens of many serious infectious diseases.
In the field, an important factor in the fight against house mice is high agricultural technology, which creates unfavorable conditions for its reproduction. In addition, house mice become prey to animals that feed on them (weasels, steppe ferrets, foxes, owls). If there is a rat's dwelling next to the house mouse hole, the number of house mice decreases, and gradually they completely disappear. Rats are crowding out the house mouse. nine0005
Rats are crowding out the house mouse. nine0005
Below you can watch a video about the dangers of house mice and how to protect yourself from the dangerous infections that they carry.
Which has spread throughout the planet, becoming one of the most common mammals. This happened due to their ability to coexist next to a person.
Habitat
The house mouse, the photo of which is presented in this article, is actually a wild animal. It got its name for living near a person. House mice in the world live everywhere, with the exception of permafrost, Antarctica and highlands. The Latin name of the animal is Mus musculus, while a 3rd word is added to it, demonstrating the habitat, for example, house mice that live in southeast Asia are Mus musculus castaneus. In our country, house mice also live almost everywhere: Krasnodar Territory, Rostov Region, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Astrakhan, etc. The only exceptions are the regions of the Far North. nine0005
Lifestyle
The house mouse lives in various biotopes and landscapes, including anthropogenic landscapes. It is very closely associated with people and often inhabits outbuildings and residential buildings. In the north, they carry out seasonal migrations. For example, at the end of summer, the animals begin to massively move to warm places: grain and vegetable stores, residential buildings, and warehouses. The range of such migrations can reach 5 km. Often they winter in stacks, in haystacks and forest belts. In the spring they leave their "winter apartments", returning to gardens, kitchen gardens, and fields. In the south of the range, they often live all year round without human habitation. In this place, house mice are tied to various reservoirs, oases. nine0005
It is very closely associated with people and often inhabits outbuildings and residential buildings. In the north, they carry out seasonal migrations. For example, at the end of summer, the animals begin to massively move to warm places: grain and vegetable stores, residential buildings, and warehouses. The range of such migrations can reach 5 km. Often they winter in stacks, in haystacks and forest belts. In the spring they leave their "winter apartments", returning to gardens, kitchen gardens, and fields. In the south of the range, they often live all year round without human habitation. In this place, house mice are tied to various reservoirs, oases. nine0005
In nature, they are nocturnal and twilight animals, but in human habitation they adjust their daily routine to the life of people. Sometimes, under artificial lighting, they remain active around the clock, reducing it only during the period of active activity of people. At the same time, the activity of animals is polyphasic, there are up to 20 periods of wakefulness per day, which last up to 90 minutes. Like many other mice, they follow fixed routes when moving, creating conspicuous paths with small piles of dust and droppings held together by urine. nine0005
Like many other mice, they follow fixed routes when moving, creating conspicuous paths with small piles of dust and droppings held together by urine. nine0005
House mice are very nimble, mobile animals; they run, jump, climb and even swim well. But they do not often move away from their nest. Each mouse in nature has an individual area: males up to 1200 m2 and females up to 900 m2. But with large animals, they settle in small family groups or colonies, consisting of the main male, several females with their children. Hierarchical relations are always established among the members of this colony. Males are quite aggressive relative to each other, females show aggression much less often. Clashes are very rare within family groups, they mainly consist in the expulsion of offspring, which has already grown up. nine0005
Description
House mice are long-tailed, small rodents with an oval body, small head, beady eyes and rounded ears. The tail is covered with sparse hairs and ring-shaped scales. Animals that live in nature are of the zonal type of color, in this case the hair at the base of the tail is brownish-brown, the middle is fawn, while the tip is painted in a pale gray tint. The abdomen is colored much lighter - to white. At the same time, which were bred by selective breeding, they have a huge range of colors: black, white, blue-gray, yellow, as well as colors that combine several shades. White mice are albinos, since they practically do not synthesize melanin, which is responsible for the coloring of tissues. Breeders also bred tailless, long-haired, short-tailed, hairless, satin and curly mice. nine0005
Animals that live in nature are of the zonal type of color, in this case the hair at the base of the tail is brownish-brown, the middle is fawn, while the tip is painted in a pale gray tint. The abdomen is colored much lighter - to white. At the same time, which were bred by selective breeding, they have a huge range of colors: black, white, blue-gray, yellow, as well as colors that combine several shades. White mice are albinos, since they practically do not synthesize melanin, which is responsible for the coloring of tissues. Breeders also bred tailless, long-haired, short-tailed, hairless, satin and curly mice. nine0005
Character
House mice are curious, lively, cunning, intelligent, but very shy animals. Unexpected noise or harsh sounds frighten them. They don't like being alone either. Without communication and attention, house mice yearn and begin to run wild. Females are excellent mothers, and males show paternal feelings for their offspring only if there are no other males in the cage.
Relations with other pets
House mice are pets that can be dangerous to dogs, cats, rats and birds. nine0005
Attitude towards children
They can be started in those families in which the children are 10 years old. They want to have a "own" animal, although there is no experience in caring for it. Many are interested in the question: "Do house mice bite or not?" It is worth noting that they are not aggressive, although they can bite until they have time to adapt to the owners and the environment, therefore, it is first necessary to help children get to know the animal, as well as tame it. Very young children with these miniature, at the same time nimble and dexterous creatures should not be left alone. nine0005
Training
House mice are among the most intelligent animals among rodents, while decorative varieties quickly get used to their owners and are perfectly tamed if they are given enough attention, while talking affectionately and softly. They are able to remember their nickname. Mice quickly begin to recognize the aroma of the person who brings food, and they will meet him with a cheerful squeak. Animals can be trained to respond to various whistles and various commands, for example, “Come!”, “Serve!”, “Home!” nine0005
They are able to remember their nickname. Mice quickly begin to recognize the aroma of the person who brings food, and they will meet him with a cheerful squeak. Animals can be trained to respond to various whistles and various commands, for example, “Come!”, “Serve!”, “Home!” nine0005
It is worth noting that scientists have been studying house mice for a long time. Kotenkova E.V. (Doctor of Biological Sciences), for example, devoted a lot of time to this issue, writing several scientific papers about their behavior, as well as their role in ancient mythology.
Diet
The main diet of house mice is cereals and seeds. They are happy to eat wheat, oats and millet, uncooked pumpkin and sunflower seeds. They can also be given dairy products, white bread, egg white pieces, and boiled meat. The green parts of various plants can make up a third of the animal's diet with a normal amount of water. At the same time, mice prefer cabbage and dandelion leaves, slices of cucumber, beets and carrots, green grass from succulent feed. Mice need up to three milliliters of water during the day. In summer, they can feed on insects, as well as their larvae. Mice have a very high metabolism, so they always have food in the feeder. nine0005
Mice need up to three milliliters of water during the day. In summer, they can feed on insects, as well as their larvae. Mice have a very high metabolism, so they always have food in the feeder. nine0005
The mouse can be kept at home in a small-mesh metal cage, as well as in a special organic glass container with a lid. It is necessary, as mice are great high jumpers. The terrarium or cage should be spacious enough, as the animals are very active and need movement. In the form of bedding, strips of uncolored paper or shavings are used. A house (a jar, a box, a pot, etc.) is installed in the cage, in which the mice will arrange a nest, a drinking bowl, a feeder, put a piece of chalk, as well as other devices for playing. For this, ladders, levels, shelters, branches are suitable, it is also desirable to put a wheel for running. nine0005
The terrarium or cage is placed as far as possible from windows, radiators, air conditioners and doors, as animals do not like temperature fluctuations, direct sunlight and drafts. The best air temperature is 20°C with an air humidity of 55%. Every day, garbage and leftover food are removed from the cage, feeders and drinking bowls are washed. The litter is changed three times a week, at least once a month it is necessary to carry out disinfection and complete cleaning of the terrarium or cage. Mice feces have an unpleasant pungent odor. At the same time, females smell much weaker than males. nine0005
The best air temperature is 20°C with an air humidity of 55%. Every day, garbage and leftover food are removed from the cage, feeders and drinking bowls are washed. The litter is changed three times a week, at least once a month it is necessary to carry out disinfection and complete cleaning of the terrarium or cage. Mice feces have an unpleasant pungent odor. At the same time, females smell much weaker than males. nine0005
In the terrarium, it is desirable to install pieces of large tree branches directly with bark (birch, willow, mountain ash) so that the animals can grind their incisors on them. It should be borne in mind that lilacs are poisonous for these animals. Wooden toys can also be placed in the cage, with which the animal will play, grinding off the incisors. With well-organized housing, house mice do not need walks. If the animal does go for a walk, then the place for its walks must be limited by the hands of the owner or the table. It must be remembered that various house plants are poisonous for mice, including aralia, yucca, feces, etc.
These mice are evening and nocturnal animals, they can interfere with sleep by noise and various sounds, although they mostly adapt to human mode.
The destruction of such mice is caused by the damage they bring to human stocks, as well as equipment and household appliances.
Wild house mice, which have been fought for centuries by man, are able to eat almost anything. As a result, food, candles and soap, wiring, etc. become eaten in the house.
Animals in warehouses gnaw grain, destroy crops of various root crops, eat stocks of cereals, in addition, they significantly pollute the house with the products of their vital activity. They actively excrete their waste, therefore even a small population can cause great harm. So, the animals do not eat the bulk of the grain, but rather pollute it.
In addition, brownies, we will find out below) are carriers of a huge number of pathogens of various diseases. They can transmit E. coli, helminth eggs to a person, cause plague, and blood-sucking insects very often live on them, including fleas and ticks, which pass with pleasure to humans.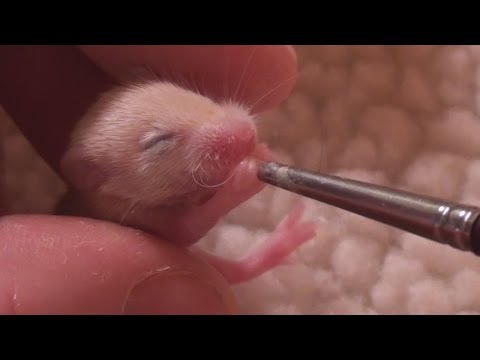 nine0005
nine0005
Therefore, house mice can cause significant harm. How to get rid of them, unfortunately, not everyone knows. The professional destruction of animals is becoming the main activity for suburban areas, private houses, catering organizations, as well as various types of institutions. This service can be ordered in specialized companies, or in the old fashioned way, use a mousetrap.
A bit of history
In nature, white mice are periodically born - albinos, which are almost impossible to survive, because they are very noticeable, and also instantly become prey. But in ancient times in Crete they were kept in the form of living amulets that bring good luck. They were also kept in temples, where they were specially cared for by ministers. 4,000 years ago in ancient Egypt, mice were bred and kept, paying close attention to the colored species. The Egyptians attributed supernatural abilities to them, in addition, depicted them on their clay vessels. nine0005
In the period of Ancient Rome and in the Middle Ages, healers used mice and rats for medicinal potions, while in Asia they are still specially bred for such purposes. With the development of veterinary medicine and experimental medicine, mice and rats began to be used for various studies as laboratory animals. It is believed that decorative and laboratory mice originate from white, spotted and black fighting mice, described in the book in 1787 edition. It tells about the animals that were used for fighting at that time. They were brought by English merchants from Japan. Subsequently, mice formed a special line of house mice, while decorative breeds began to be bred as pets. nine0005
With the development of veterinary medicine and experimental medicine, mice and rats began to be used for various studies as laboratory animals. It is believed that decorative and laboratory mice originate from white, spotted and black fighting mice, described in the book in 1787 edition. It tells about the animals that were used for fighting at that time. They were brought by English merchants from Japan. Subsequently, mice formed a special line of house mice, while decorative breeds began to be bred as pets. nine0005
Today, in various countries of Western Europe and America, there are Clubs of mouse lovers, the main purpose of which is to breed new varieties of these animals. Most often, individuals of various colors are obtained: gray, white, red, brown, purple or pinkish, with spots. Special exhibitions with expert evaluation are held there.
But in our country, decorative mice are less known than in the countries of America and Europe, but among animal fans they are becoming more and more popular every year. In the clubs of lovers of various rodents, special sections of decorative mice have been created, nurseries have been opened that are engaged in selection and breeding work, and exhibitions are held where house decorative mice are exhibited along with other small animals. nine0005
In the clubs of lovers of various rodents, special sections of decorative mice have been created, nurseries have been opened that are engaged in selection and breeding work, and exhibitions are held where house decorative mice are exhibited along with other small animals. nine0005
A mouse is a small animal that belongs to the class of mammals, order of rodents, family of mice (lat. Muridae).
Mouse - description, characteristics and photo. What does a mouse look like?
The length of the body of a mouse covered with short fur, depending on the species, ranges from 5 to 19 cm, and doubles with the tail. These rodents have a rather short neck. On the pointed muzzle, small black beady eyes and small semicircular ears are visible, allowing mice to hear well. Thin and sensitive whiskers growing around the nose, give them the ability to perfectly navigate the environment. In mice, unlike, there are no cheek pouches. nine0005
Mouse paws are short with five prehensile toes. The surface of the tail is covered with keratinized scales with sparse hairs. The color of the mouse is usually characterized by gray, brown or red tones, however, there are variegated and striped individuals, as well as white mice. Animals lead an active lifestyle in the evening or at night. They communicate with each other using a thin squeak.
The surface of the tail is covered with keratinized scales with sparse hairs. The color of the mouse is usually characterized by gray, brown or red tones, however, there are variegated and striped individuals, as well as white mice. Animals lead an active lifestyle in the evening or at night. They communicate with each other using a thin squeak.
Types of mice, names and photos.
The mouse family includes 4 subfamilies, 147 genera and 701 species, the most common of which are:
- (lat. Apodemus agrarius) reaches a size of 12.5 cm, not counting the tail, which can be up to 9 cm long. grey. The habitat of the field mouse includes Germany, Hungary, Switzerland, Poland, Bulgaria, the southern part of Western Siberia and Primorye, Mongolia, Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula and certain territories of China. This species of mice lives in wide meadows, in dense thickets of shrubs, city gardens and parks, and the shelter suits both in minks and in any natural shelters.
 In flooded areas, nests in bushes. Depending on the season, the diet may consist of seeds, berries, green parts of plants and various insects. The field mouse is the main pest of grain crops. nine0117
In flooded areas, nests in bushes. Depending on the season, the diet may consist of seeds, berries, green parts of plants and various insects. The field mouse is the main pest of grain crops. nine0117
- (lat. Apodemus flavicollis) has a reddish-gray color and a light belly (sometimes with a small speck of yellow). The body size of adults reaches 10-13 cm, the tail has approximately the same length. The weight of the mouse is about 50 grams. This species of mice is widely distributed in the forests of Russia, Belarus, Moldova, Bulgaria, Ukraine, the Caucasus, the northern provinces of China and Altai. Yellow-throated mice settle on open edges in tree hollows or dug minks, but they can also live in stony placers. Their diet includes both plant and animal foods. Eating young seedlings of fruit trees, they cause significant harm to nurseries. nine0117
- Grass mouse (Nilotic grass mouse) (lat. Arvicanthis niloticus) is one of the largest representatives of the mouse family and can reach 19 cm in length, and together with the tail - 35 cm.
 The weight of individual large individuals exceeds 100 g. The fur of the back and sides has a dark gray or grayish brown coloration with individual hard and prickly bristles of a darker shade. The color of the belly is light grey. This species of mice is most common in African countries, where they live in bushes, forests and savannahs. As a refuge, grass mice choose abandoned termite mounds or dig holes on their own, but on occasion they can penetrate into human habitation. The basis of the diet of mice is plant foods. nine0117
The weight of individual large individuals exceeds 100 g. The fur of the back and sides has a dark gray or grayish brown coloration with individual hard and prickly bristles of a darker shade. The color of the belly is light grey. This species of mice is most common in African countries, where they live in bushes, forests and savannahs. As a refuge, grass mice choose abandoned termite mounds or dig holes on their own, but on occasion they can penetrate into human habitation. The basis of the diet of mice is plant foods. nine0117
- (lat. Micromys minutus) is one of the smallest rodents in the world. The body length of an adult animal does not exceed 7 cm, the tail is 6.5 cm, and the weight of the baby does not exceed 10 g. The back and sides are monophonic and have a reddish-brown or brown color, in contrast to the light gray, almost white belly. The muzzle of baby mice is short and blunt, with small ears. The distribution range of this species of mice stretches from west to east from the northwestern provinces of Spain to Korea and Japan, in the south to Kazakhstan, China and the northern regions of Mongolia.
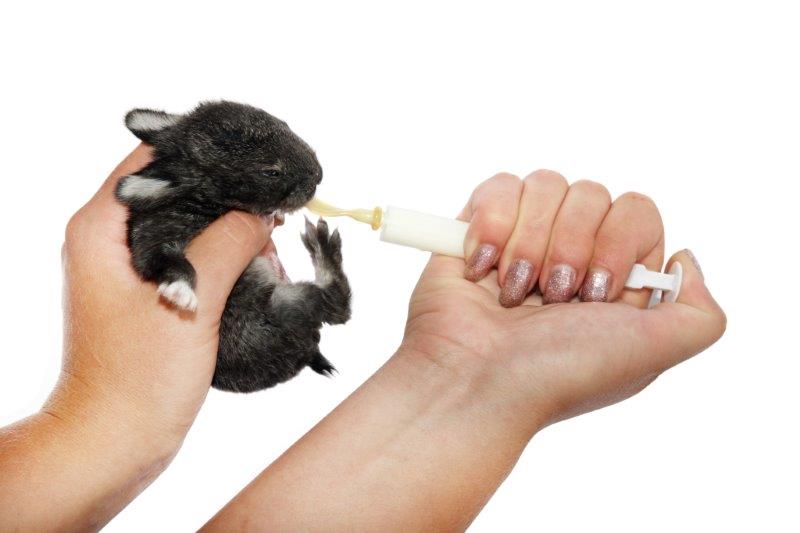 The mouse lives in forest and forest-steppe zones, in meadows with tall grass. In the summer, mice use nests twisted in the grass as a refuge, and winter in minks, haystacks, residential or outbuildings of a person. The basis of the diet of baby mice is the seeds of cereals and legumes, as well as small insects. Often they settle near granaries, causing great harm to agriculture. nine0117
The mouse lives in forest and forest-steppe zones, in meadows with tall grass. In the summer, mice use nests twisted in the grass as a refuge, and winter in minks, haystacks, residential or outbuildings of a person. The basis of the diet of baby mice is the seeds of cereals and legumes, as well as small insects. Often they settle near granaries, causing great harm to agriculture. nine0117
- (lat. Mus musculus) is the most common species on the planet from the rodent family. The body length of an adult mouse does not exceed 9.5 cm, and together with the tail - 15 cm. The weight of the mouse is 12-30 g. The color of the fur on the sides and back is gray with a brown tint, and on the abdomen from light gray to white. Individuals living in desert areas have a sandy color. The muzzle of the mouse is sharp with small rounded ears. The area of distribution of this species of mice does not include only the territory of the Far North, Antarctica and high mountain regions.
 House mice live in all types of landscapes and natural areas, very often they penetrate into household and residential buildings of a person. Under natural conditions, minks dig on their own, although they can also occupy dwellings abandoned by other rodents. They feed on seeds and succulent green parts of plants, and when they enter a person’s house, they consume everything that gets into their teeth - from bread and sausages to paraffin candles. nine0117
House mice live in all types of landscapes and natural areas, very often they penetrate into household and residential buildings of a person. Under natural conditions, minks dig on their own, although they can also occupy dwellings abandoned by other rodents. They feed on seeds and succulent green parts of plants, and when they enter a person’s house, they consume everything that gets into their teeth - from bread and sausages to paraffin candles. nine0117
- (lat. Lemniscomys striatus) is a small rodent: body length 10-15 cm, intermittent stripes of light colors are visible along the back and along the sides. Under natural conditions, striped mice rarely live more than 6-7 months, in captivity they live two to three times longer. The menu of these individuals includes mainly vegetable “dishes”: root crops, non-hard seeds, juicy fruits, and occasionally small insects.
- (akomis) (lat. Acomys) is a rather cute representative of the mouse family, the owner of huge eyes and the same big ears.
 The size of the spiny mouse, together with the tail, is 13-26 cm, the back of the animal is covered with thin needles, like a normal one. An amazing feature of these animals is regeneration: in case of danger, the mouse is able to shed a piece of skin, leaving the attacker at a loss. The skin is quickly restored without harm to the individual. The spiny mouse lives in Asia, is found in Cyprus and Africa. In food, it focuses on plant foods; this animal is often kept as a pet. nine0117
The size of the spiny mouse, together with the tail, is 13-26 cm, the back of the animal is covered with thin needles, like a normal one. An amazing feature of these animals is regeneration: in case of danger, the mouse is able to shed a piece of skin, leaving the attacker at a loss. The skin is quickly restored without harm to the individual. The spiny mouse lives in Asia, is found in Cyprus and Africa. In food, it focuses on plant foods; this animal is often kept as a pet. nine0117
Where does the mouse live?
The area of distribution of mice covers almost all climatic zones, zones and continents of the globe. Mouse representatives can be found in tropical thickets, coniferous or deciduous forests, steppe expanses and deserts, on mountain slopes or in swampy areas. Mice also live in people's homes.
Mice can make nests from grass stalks, occupy abandoned burrows, or dig complex systems of underground passages. Unlike species that live in swamps, mountain, steppe, and forest mice are poor swimmers. nine0005
nine0005
What does a mouse eat?
The basis of the diet of mice is plant foods: grass seeds, fruits of trees or shrubs and cereals (oats, barley, millet, buckwheat). Mice that live in swampy areas, in wet and flooded meadows, feed on leaves, buds or flowers of plants and shrubs. Some species of mice prefer protein supplement as insects, worms, beetles, spiders
The mouse does not fall into hibernation and can move under the snow cover without appearing on the surface. To survive the cold, she has to create solid food stocks in pantries arranged near the entrance to the mink. nine0005
Mice , under favorable conditions of keeping and feeding, are able to breed throughout the year. Puberty in mice occurs at the age of 30-35 days after birth, that is, long before the end of growth. Males tend to mature at a later date and are able to fertilize females throughout their lives.
It is believed that the working qualities of the male are the highest up to one and a half years of age. Fluctuations in the degree of sexual activity depend on the usefulness of feeding and the physical health of the animal. A visible external sign of male sexual maturity is the movement of the testes into the scrotum, which is well expressed in mice, as well as the manifestation of sexual activity. In females, the onset of puberty is determined by the appearance of estrus. The phases of estrus are determined by taking a swab from the vagina. They are well studied and are of interest in the special breeding of mice. The total duration of a normal cycle in white mice ranges from three to nine days. Its duration can be affected by a change in the duration of individual phases, the ambient temperature. At lower temperatures, the cycle lengthens. During estrus, some changes occur in the uterus - the mucous membrane swells, its folding increases. nine0005
Fluctuations in the degree of sexual activity depend on the usefulness of feeding and the physical health of the animal. A visible external sign of male sexual maturity is the movement of the testes into the scrotum, which is well expressed in mice, as well as the manifestation of sexual activity. In females, the onset of puberty is determined by the appearance of estrus. The phases of estrus are determined by taking a swab from the vagina. They are well studied and are of interest in the special breeding of mice. The total duration of a normal cycle in white mice ranges from three to nine days. Its duration can be affected by a change in the duration of individual phases, the ambient temperature. At lower temperatures, the cycle lengthens. During estrus, some changes occur in the uterus - the mucous membrane swells, its folding increases. nine0005
In the first mating, the female is allowed at the age of two or three months, and the males a little later.
In this case, strong and viable young animals are obtained. Mating occurs at any time of the day. It is known that the female is ready to mate three hours before ovulation. Covered females are initially kept together with other individuals, and then placed in separate cages, provided with improved nutrition, milk is introduced into the diet, and the presence of water in the drinkers is strictly monitored. Visible signs of pregnancy in females are observed in the second half of the term. The female's belly increases, she becomes inactive, builds a nest. The duration of pregnancy is 20-26 days (average 22 days). It flows easily. Childbirth occurs, as a rule, at night, complications do not happen. In one litter, there can be from five to nine mice. 20-24 hours after giving birth, the female comes into heat and is ready to become pregnant again. Sometimes lactation and pregnancy can occur at the same time. In practice, a female mouse can give 10-11 litters in a row. But it exhausts her. To obtain good offspring, no more than nine litters are allowed.
Mating occurs at any time of the day. It is known that the female is ready to mate three hours before ovulation. Covered females are initially kept together with other individuals, and then placed in separate cages, provided with improved nutrition, milk is introduced into the diet, and the presence of water in the drinkers is strictly monitored. Visible signs of pregnancy in females are observed in the second half of the term. The female's belly increases, she becomes inactive, builds a nest. The duration of pregnancy is 20-26 days (average 22 days). It flows easily. Childbirth occurs, as a rule, at night, complications do not happen. In one litter, there can be from five to nine mice. 20-24 hours after giving birth, the female comes into heat and is ready to become pregnant again. Sometimes lactation and pregnancy can occur at the same time. In practice, a female mouse can give 10-11 litters in a row. But it exhausts her. To obtain good offspring, no more than nine litters are allowed. Cases of death from childbirth among mice are very rare. Usually, in mice, the fetuses in the uterus are located with their heads towards the exit from the uterus and there is no pathology of childbirth. There are also rare cases of stillborn cubs being born in normally kept females. This happens with a lack of vitamins, trace elements and some infections. nine0005
Cases of death from childbirth among mice are very rare. Usually, in mice, the fetuses in the uterus are located with their heads towards the exit from the uterus and there is no pathology of childbirth. There are also rare cases of stillborn cubs being born in normally kept females. This happens with a lack of vitamins, trace elements and some infections. nine0005
It is easy to confuse with stillborn mice that were born normal, but died due to some reasons immediately after birth: lack of milk in the female, insufficiently developed maternal instinct, or stress, due to which the female tries to hide the mice by dragging them around the cage , resulting in their death. Sometimes mice are born underdeveloped, lagging behind in growth in the embryonic period. This is due to the malnutrition of the female during pregnancy. These mice usually die. Cases of the birth of weak litters serve as a signal of a violation of the balance of the diet of animal feeding. With closely related breeding of mice, the death of offspring is not observed.