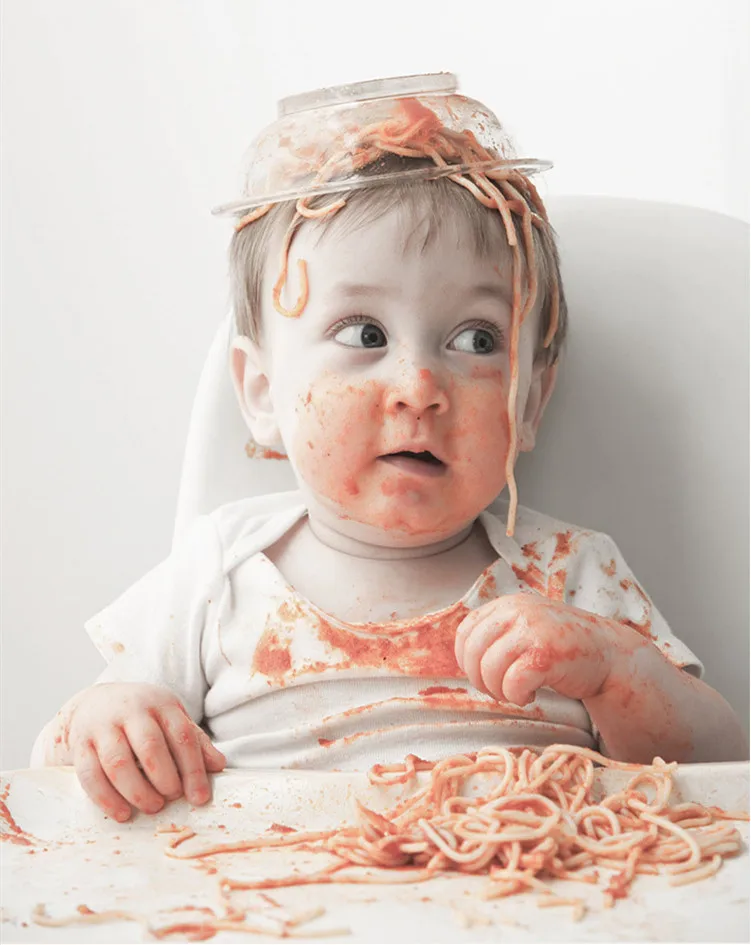
When babies eat food
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods.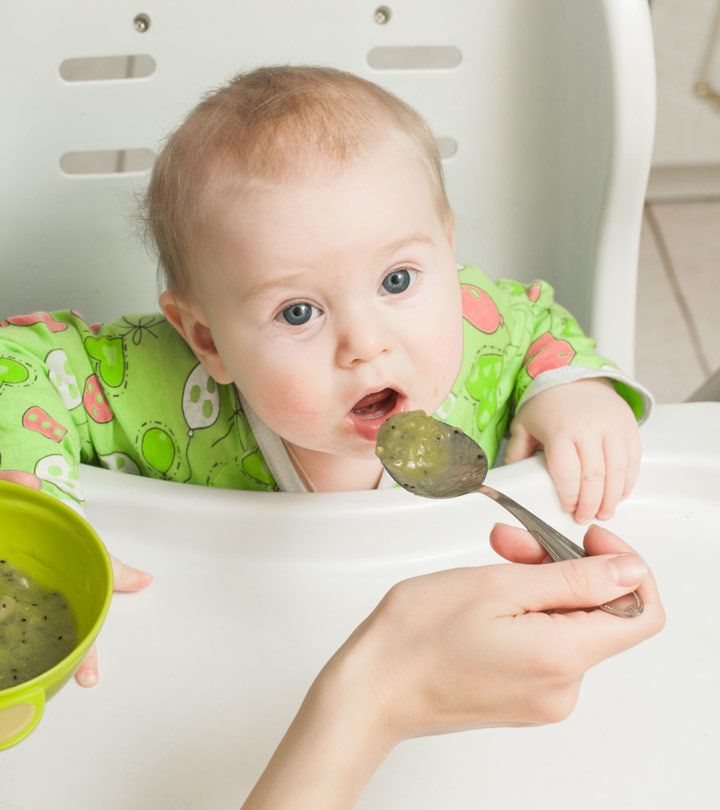 But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula.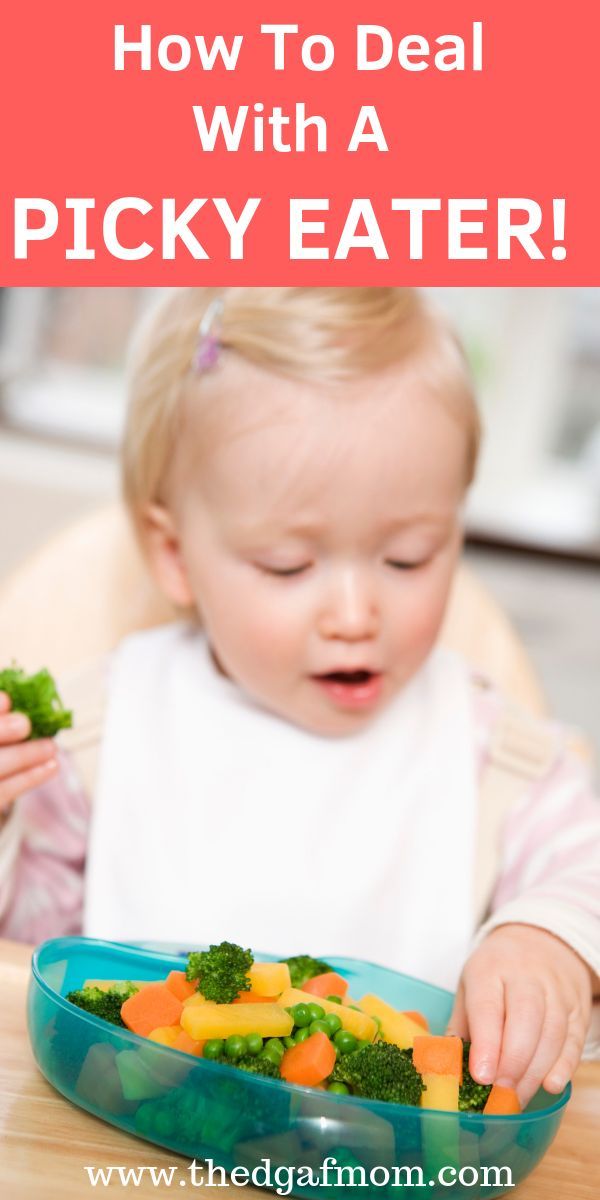 Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula.
 It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese. - foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.
- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods.
 (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
(Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.) - After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.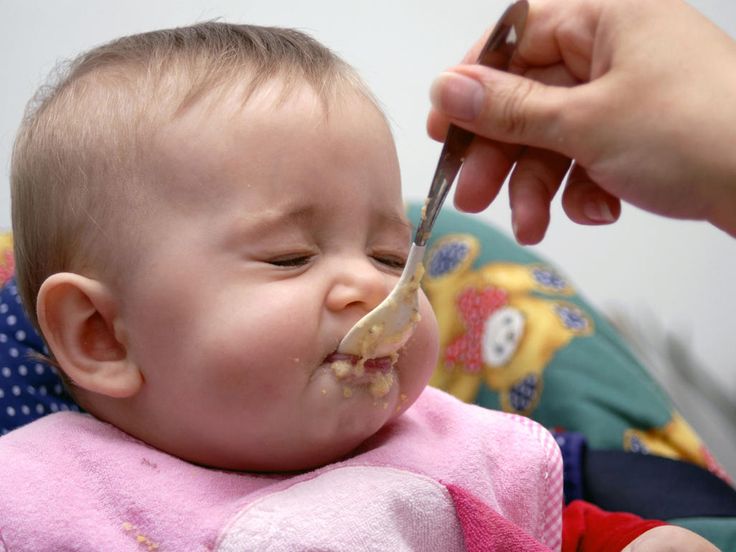
What time do children start eating on their own?
Many mothers and fathers are often interested in: what time do children start eating on their own? There is no single answer to this question, everyone is individual. But it is important for parents to know: how to discern the first impulses for independence in time, at what age you can give the baby a spoon, how to teach him to eat without outside help, and what accessories will help the baby master this difficult science.
What time do children start eating by themselves with a spoon?
It depends on the character and development of the child, as well as on his parents. Some children already in the year flatly refuse to be fed with a spoon. But there are those who start eating on their own only at the age of 3, when they come to kindergarten (in a team, children involuntarily imitate others and the learning process goes faster). In large families, children learn self-service skills at an earlier age.
But overprotection hinders the development of the baby. If an overly caring mother tries to do everything for the child, then he will not strive to eat himself, even if he can do it. If parents are too much in favor of accuracy, and porridge smeared on the table causes them stress, then the learning process can slow down. After all, the baby feels the mood of adults, and prefers not to experiment at the table. The lack of independence can also be associated with an unwillingness to grow up. For example, another baby has appeared in the family, and the child, feeling that they are paying less attention to him, tries to “stay small”, wants his mother to take him in her arms more often, feed him from a spoon, etc.
From the age of 7 months a child usually learns to pick up and hold objects between thumb and forefinger, such as a dryer or a piece of bread. The child can be offered a spoon when he is already receiving complementary foods and sits well in the highchair. At first, the baby will only try to take the spoon in his hands and play with it, but later he will try to use it for its intended purpose. For drinking to a baby up to a year, a drinking mug is convenient.
At first, the baby will only try to take the spoon in his hands and play with it, but later he will try to use it for its intended purpose. For drinking to a baby up to a year, a drinking mug is convenient.
At 12 months the child still does not hold the spoon correctly, but he knows how to bring it to his mouth, and part of the contents can reach the goal. Closer to two years, coordination improves significantly, the baby is capable of more precise movements and misses less and less. The kid can already hold a regular mug, but only with two hands.
From the age of 2 years a child can eat by himself with a spoon, although he does not always do it sloppy. He already holds a mug with one hand and knows how to use a fork.
From the age of 3 years the baby becomes more dexterous and accurate, his fingers are getting stronger, and his movements are more and more confident. It is quite possible to give him a non-sharp children's knife, having previously shown how to use it.
Accessories to help children learn to eat on their own
Buy a baby plate with a suction cup so that the dishes do not run away from the child. It’s good if the child’s favorite character is drawn at the bottom of the plate. To see the picture, the baby will try quickly and eat all the food to the end.
The non-spill cup is the best option when switching to adult dishes. Choose a model with two handles, it is more convenient for your baby to hold. An additional advantage is the presence of a rubber stand, which gives the cup stability.
A special anatomically shaped spoon with a rounded non-slip handle and a curved fork with rounded teeth are best suited for babies up to a year old.
Paper napkins or towels should always be at hand. This teaches you to be careful, helps to avoid the temptation to wipe your hands on clothes.
It's good if a grown child eats at a common table. He will be able to watch adults, copy their actions. To do this, the baby will need a special chair that can be attached to a large table (for example, high chairs from IKEA, “growing” Stokke Tripp Trapp, Kotokota, KidFix, etc.)
Buy your baby a soft silicone bib, oilcloth or apron. This will help parents save their nerves and spend less time on laundry and cleaning.
How to teach a baby to eat without the help of adults?
If, during feeding, the baby seeks to take away the mother's spoon and tries to eat by himself, then “the time has come”. Use this moment!
At first, it is difficult for the baby to eat liquid food on his own, such as soup. And he probably wants to take pieces of fruit or pasta with his hands. Therefore, the ideal food for the first workouts is porridge or vegetables, which must first be kneaded with a fork.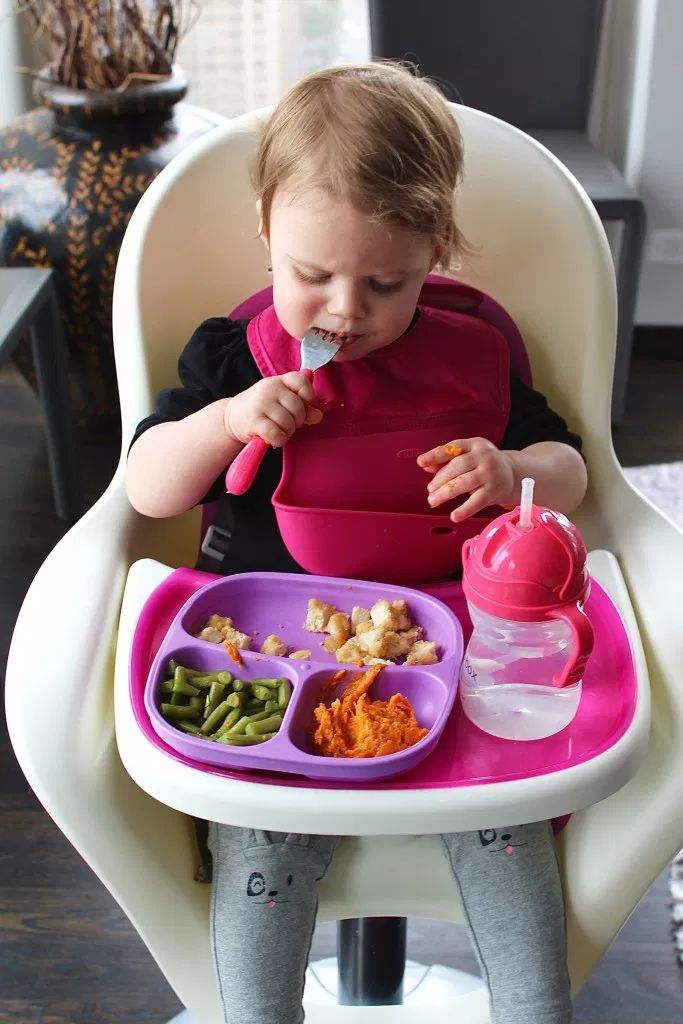
The game will be a good help in learning. You can train the skill in the sandbox. Help the baby to scoop up the sand with a spatula, carefully pour it into the mold, make a cake. Buy a set of toy dishes, let the child feed dolls and teddy bears with a small spoon. This improves coordination, develops fine motor skills and will help him handle real cutlery.
At the beginning of training, one spoon should be in the hands of the mother, and the second - in the child. She feeds the baby, and the baby is only trying to collect food himself and send it to her mouth. Thus, the baby will not remain hungry and at the same time will gradually improve his skills.
Support the child at this stage of growing up, do not scold for mistakes and praise for successes. The main thing is patience and confidence that everything will work out.
What should I do if my child refuses to eat from a spoon? Doctor Komarovsky tells
How to teach a child to eat with a spoon on his own? Mom's Experience
Table Etiquette for the Littlest Ones
How Montessori Educators Help Toddlers
Learn Keep SpoomTatyana Petulko
share
Twit
Class
Share
We are in social networks
We love to see children grow and develop at their own pace and without limits. Six months later, they are already starting to introduce new foods into your diet They drank only milk. With the introduction of the new diet, they have already started a different way of eating , but we still need to know when kids eat alone.
It will take a few months for your child to catch the first cutlery and use it for food.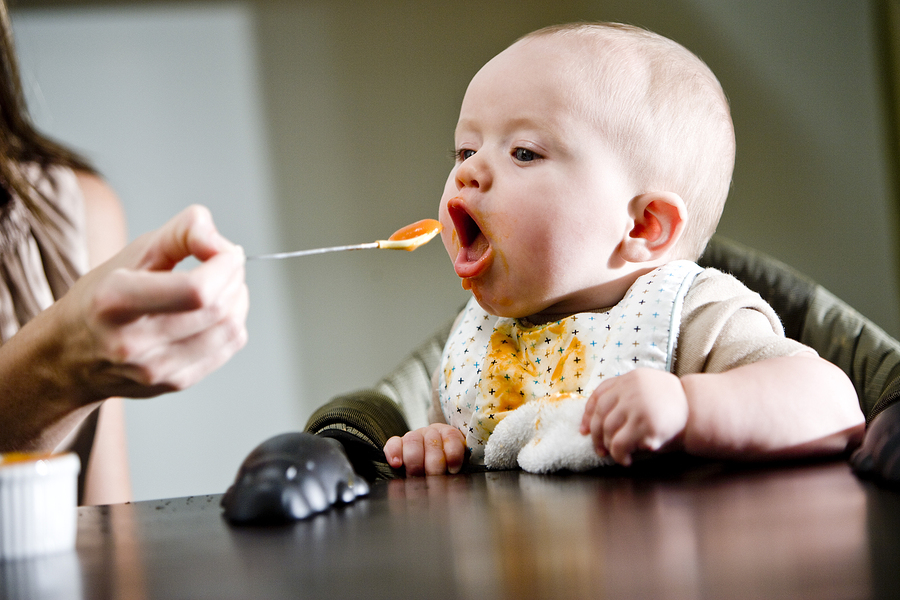 They will first like to get to know the food, they will play with it and put it in their mouth. Later, they would use a spoon or fork to go to , gradually copying his skills.
They will first like to get to know the food, they will play with it and put it in their mouth. Later, they would use a spoon or fork to go to , gradually copying his skills.
Index
- 1 At what age can children eat alone?
- 2 In the first two years of life
- 3 From the age of three
- 4 From the age of 5
At what age can children eat alone?
There is no exact age to determine when children can start giving birth. are independent of their diet. From 12 months and up to 26 and 28 months They are already starting to learn their first skills, you can take silverware and do some tricks. When they turn two they can hold cutlery with more safety without parental assistance.
The best way to learn is to leave the child alone in front of meals and cutlery. Make sure the food is safe so he doesn't make a big mess, and that he's himself without fear of handling a spoon or fork.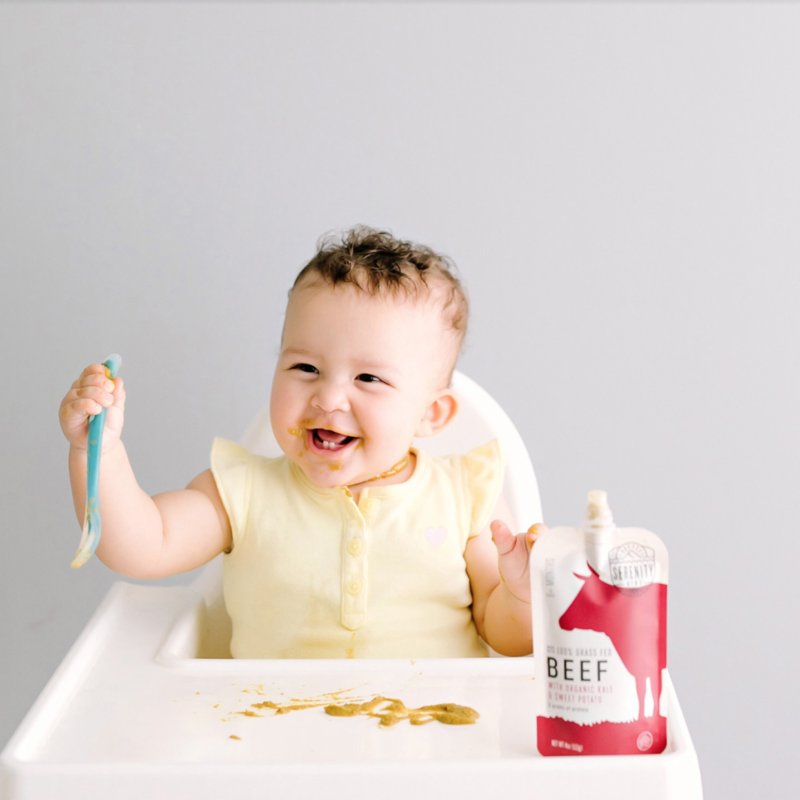 may not be safe to use at first and will use 's hands as your best tool to catch food. You will be able to take a spoon and put it in your mouth, where you will try to insert some of what you have collected, but without much success. When eating, it is better to place the child closer to the parents so that learn to imitate how the elders do it.
may not be safe to use at first and will use 's hands as your best tool to catch food. You will be able to take a spoon and put it in your mouth, where you will try to insert some of what you have collected, but without much success. When eating, it is better to place the child closer to the parents so that learn to imitate how the elders do it.
In the first two years of life
Child will become interested in food and the best test is to try to catch him with your hands. If he is offered cutlery, he will use it, but it will still be awkward. Some children will be able to use them firmly, but with some mistakes. Even if you don't use them perfectly, you can Offer a fork to start It will take a little longer to eat, but it's worth looking at as it is part of your learning and growth.
Likes food And he will have no problem trying what he thinks his parents eat, although he will have a craving for certain foods.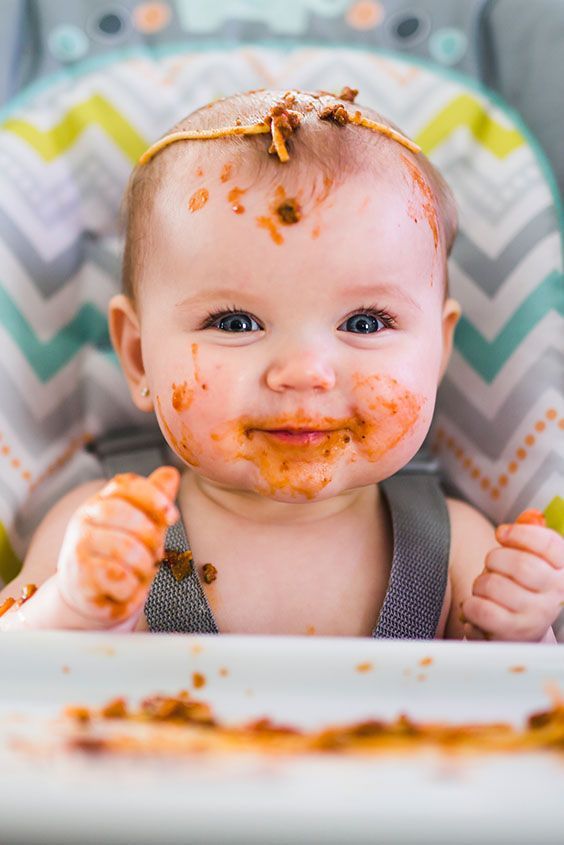 For two years now, has been able to hold a cup and drink without spilling content. Before that, I could only use specialized closed glasses to drink from the spout.
For two years now, has been able to hold a cup and drink without spilling content. Before that, I could only use specialized closed glasses to drink from the spout.
From the age of three
The child is older and you can eat almost everything. You can already include 9 in your diet0109 solid and fleshy food. You may still find it difficult to introduce new foods into your diet because you refuse to try new flavors. The child is already starting to chew with his mouth closed usually use cutlery . It may be difficult for you to sit the whole evening, it will not be easy, but little by little.
Not all children don't want to try new food, some of them will be open to try different textures and colors . Now they can even use knives adapted to their age and handle glasses or small jugs with a handle.
At 4 years old, children begin to be curious about food and some will go to the kitchen to see how they are being prepared.










