When do babies go longer between feedings
Breastfeeding after one month: What to expect
Do you know when your breast milk supply settles down? Or how your baby’s breastfeeding frequency and duration change as he gets bigger and more active? Find out in our guide to breastfeeding after one month
Share this content
Congratulations – you’ve made it through the first crazy month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk is now fully mature,1 your supply is beginning to calm down, and your breasts won’t leak as much, or at all, any more. Don’t worry, you’re not losing your supply – your breasts are just getting more efficient at making and storing milk.2 At six weeks, you’ll start seeing your baby’s first gorgeous gummy smiles, and by two months you’ll have 500 to 600 feeds under your belt. Hopefully any latch issues will be resolved, and now it’s a case of maintaining breastfeeding and enjoying the convenience and ongoing health benefits.
When does breastfeeding frequency slow down?
The range of ‘normal’ breastfeeding for babies aged one to six months is wide – some only feed four times in 24 hours, while others have 13 feeds a day.3
“After he’s about one month old, your baby will begin taking bigger volumes of milk at a feed and may start to go longer between feeds,” explains internationally renowned lactation consultant Cathy Garbin. “His stomach is growing so he can take larger feeds, plus your mature milk keeps him fuller for longer.”
Feeds can last anything from 12 minutes to nearer an hour – there really is that much variability between babies!3 But if your baby is gaining weight and has a feeding pattern that fits into these ranges, you have no cause for concern.
Amazingly however, no matter how often your baby feeds, he’ll consume roughly the same quantity of milk per day at one month old as he will at six months, when you start introducing solid foods.4
“Having said that, you’ll invariably get some days when he wants to feed a bit more or less, especially if he’s not feeling well, and you should just go with it,” says Cathy.
Does my baby really only need breast milk for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk provides your baby with everything he needs for the first six months of life – if he’s exclusively breastfed, he doesn’t even need water!5 In fact, his digestive system is not able to cope with solid foods until around six months, and he won’t be able to drink cow’s milk until he’s a year old.
Breastfeeding throughout this stage also prepares your baby for the exciting milestones ahead. It exercises his mouth muscles and helps develop his jaw and align his teeth,6,7 which are all important for eating and talking. And because the flavour of your breast milk can be influenced by what you eat or drink, it means your baby can experience new tastes before he even starts solids.8
Not only that but if he gets ill, your body will produce antibodies that go into your breast milk to help fight off the infection.9 This means it will continue to protect him as he grows and gets more active over the months to come.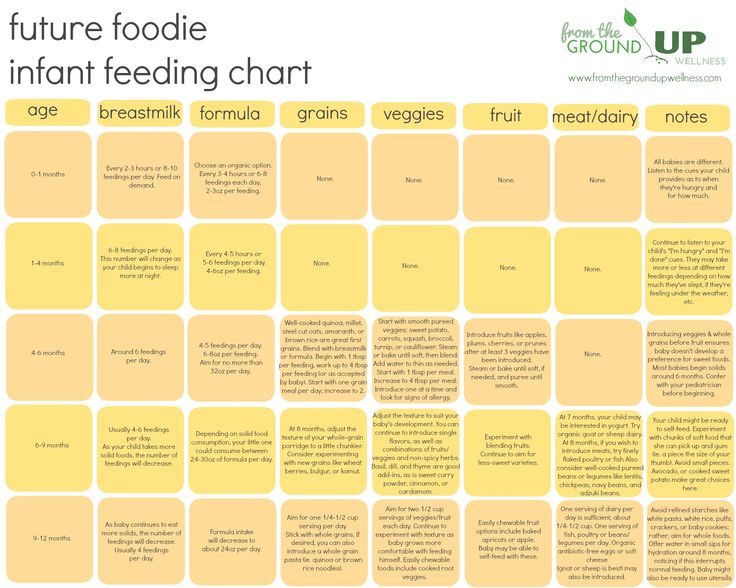
Once you hit your stride, carrying on breastfeeding is also incredibly convenient, as Claudia, mum of two, UK, discovered: “Not having to sterilise loads of bottles, make up formula, cart it all around, then heat it up, made breastfeeding the easy option – especially as my babies got a bit older and we went out more.”
When will my breastfed baby sleep through the night?
It’s normal for all babies to wake during the night. The majority of one- to six-month-old babies consume a fifth of their daily milk intake at night, so these feeds are important to ensure they get enough calories.3
“Really, it depends on what you call sleeping through the night,” says Cathy. “If your baby goes to bed at midnight and wakes up at 05:00, some people call that sleeping through and it’s certainly better than waking every two hours! I’ve known breastfed babies who’ve gone to bed at 19:00 and woken at 07:00 from six weeks, but plenty of others continue to wake frequently. Every child is different.”
Every child is different.”
A study of more than 700 babies in Wales showed that almost 80% woke at least once a night between six and 12 months, and 25% woke three times or more. There was no difference in frequency between breastfed or formula-fed babies.10
So, if you’re going to be waking up anyway, at least breastfeeding is a convenient option! As Minette, mum of two, Australia, agrees: “At night you barely have to wake up – just let your body and baby go on automatic pilot. No planning, measuring or sterilising. It’s all ready and at the right temperature in your boob. Perfect for me.”
My baby has started waking up more – is he hungry?
At around four months, your baby’s sleep patterns may change as he starts to cycle between periods of deep and light sleep, just like an adult. As a result, he may start waking more frequently at night. “At this four-month stage you may be dealing with a sleep issue not a feeding issue,” says Cathy. “It can wear you out, but try to go with the flow and ride through it.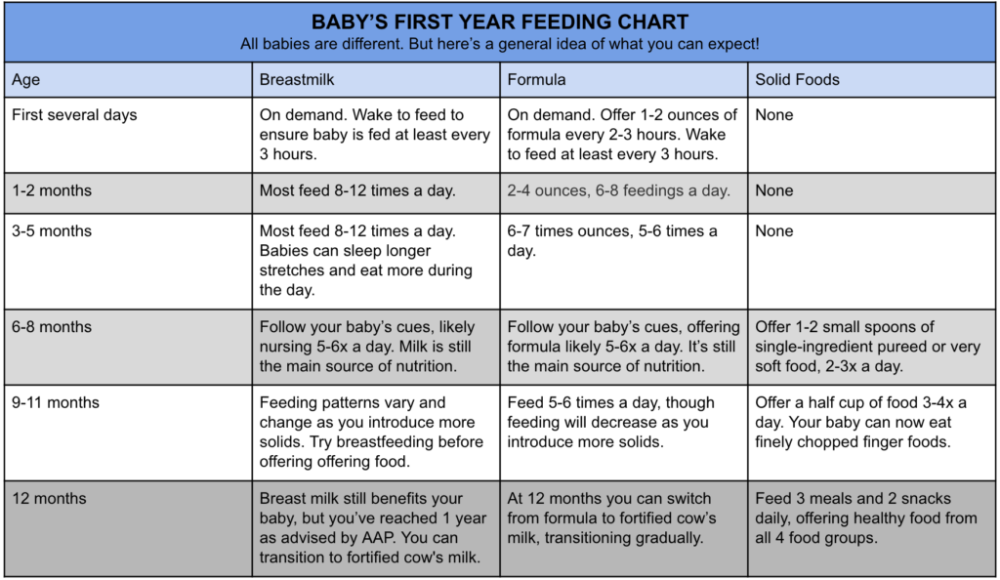 ”
”
Some people refer to this as the ‘four-month sleep regression’ but a more apt word is progression. While it may feel like a step back, your baby is approaching an important developmental phase. He’s learning rapidly, becoming more aware of the world, gaining better depth-perception, and perhaps starting to experience separation anxiety. Crying for you when he wakes, feeding and being close to you is a way of seeking reassurance.11–13
Don’t be tempted to give a ‘top-up’ of formula or introduce solids early in a bid to make your baby sleep longer. Your breast milk contains hormones that cause drowsiness and help both of you relax. And studies show mums who breastfeed actually get more sleep each night than those using formula or mixed feeding.14
How will teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething often starts from about four months. Your baby might become fussy and pull off your breast, crying with discomfort, if his gums are sore, which can be frustrating.
However, breastfeeding can also be soothing. A study showed babies who are breastfed during immunisations cry less and recover more quickly from the pain,15 and this calming effect could also help your baby while he’s teething.
An unwanted side effect may be that your baby starts to use your breast to try out his new teeth.“Occasionally some babies will have a little game and bite their mum playfully. If this is about to happen, you might notice a subtle change in your baby during the feed – he’ll have to move his tongue out of the way before he bites,” says Cathy. “It’s not usually a big problem and might only happen for a couple of feeds. Just stop the feed, tell him gently that it’s not good to bite, and he’ll soon cotton on.”
How can I continue breastfeeding if I’m away from my baby?
There may be occasions while you’re still exclusively breastfeeding during the first six months when you need to leave your baby for a couple of hours – or even longer if you have to return to work or go away for a day or two.
Don’t feel like you have to give up breastfeeding at this point. You can still continue giving your child the benefits of breast milk by pumping milk that can be fed to him while you’re not there, as Cathy explains:
“Express milk for a couple of days beforehand, taking small quantities – maybe 40 to 60 ml (1.4 to 2.1 fl oz) at a time – so you have a bank ready for whoever will be caring for your baby. By taking small amounts, you won’t affect your milk supply.
“If you’re returning to work, talk to your employer to get a plan in place. Many mums breastfeed their baby at night and do the first and last feeds. Then they express at lunchtime to ease any discomfort and provide milk for the next day.
“It’s usually much easier than people think it’s going to be, and many workplaces are set up for it these days,” she adds. “Breast pumps are efficient and will help you manage this juggling act easily.”
Natalie, mum of one, US, describes her routine: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes, and sometimes again before I go to work to get my supply going and have that connection. I pump twice at work for the next day (he has two bottles of breast milk while I’m at work) and then hurry home for his evening feed. At the weekends, I don’t pump and he goes back to just breastfeeding.”
I pump twice at work for the next day (he has two bottles of breast milk while I’m at work) and then hurry home for his evening feed. At the weekends, I don’t pump and he goes back to just breastfeeding.”
Can I continue breastfeeding after introducing solids?
When your baby is showing an interest in food and sitting up unsupported, at around six months, he’s ready for you to start introducing solid foods. However, this doesn’t have to be the end of breastfeeding, as Cathy explains: “Your baby’s stores of iron, built up during pregnancy, have been used by six months and he needs to start getting more,” she says.
“Introduce foods around this time, but remember breastfeeding will remain more important as a source of calories and nutrients until your baby is around eight to nine months old. He’ll be eating a lot more food by that point, but you may still be giving breastfeeds four to five times a day, depending on your baby. By the time he gets to 12 months, you could be breastfeeding anywhere between two and six times a day. All babies are individuals and he could still be getting half his calories from breast milk.”
All babies are individuals and he could still be getting half his calories from breast milk.”
And don’t forget, your breast milk can also be added to your baby’s first solid foods, such as cereals and purees, so he can experience a familiar flavour at meals. If possible, use it freshly expressed (not defrosted) and mix in just before serving, so the live components and nutrients are not destroyed.16
You may feel social pressure to stop at six months, but the longer you breastfeed or express, the more benefits there are for you both.
How long can I keep breastfeeding for?
“The World Health Organization recommends giving toddlers breast milk alongside solid foods until they turn two and beyond, as it still has a vital role in supporting the immune system,” says Cathy. “It’s also an important way to offer emotional support when they’re feeling overwhelmed or poorly.”
At eight months old, you may be giving your baby four feeds a day but after he’s a year old, you could be feeding as little as twice a day.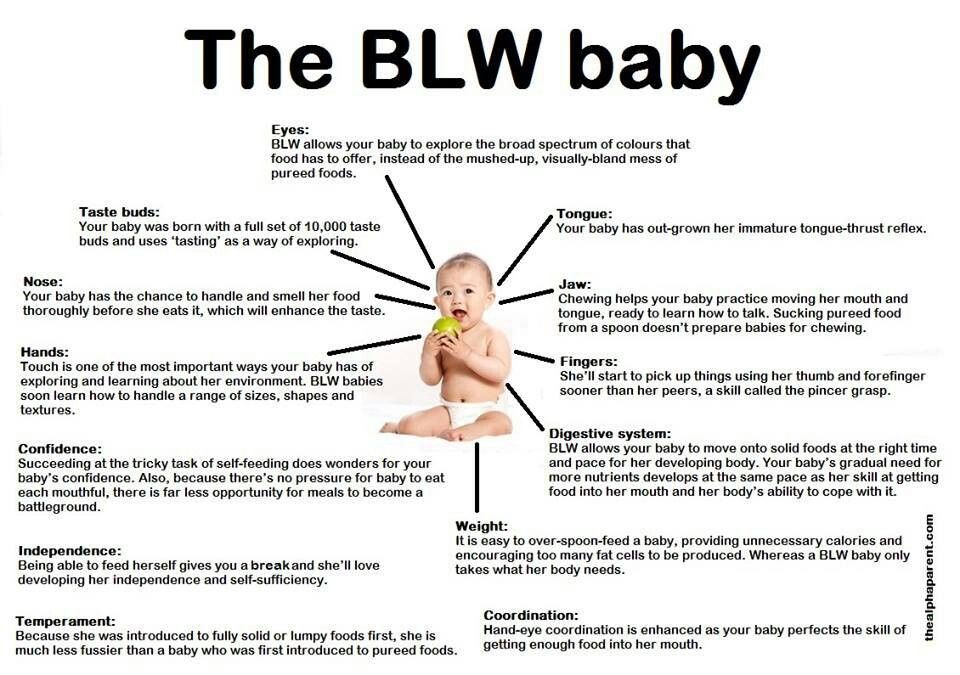 You can find a pattern that works for you both and fits into your lifestyle, as Jane, mum of two, US, found. She breastfed her children until they were around the age of two: “I’d feed when I was around in the evenings and at weekends, when they wanted to feel close to me,” she says. “It was a great help when they were sick, and my go-to method of comforting.”
You can find a pattern that works for you both and fits into your lifestyle, as Jane, mum of two, US, found. She breastfed her children until they were around the age of two: “I’d feed when I was around in the evenings and at weekends, when they wanted to feel close to me,” she says. “It was a great help when they were sick, and my go-to method of comforting.”
“As my son grew older and became more adventurous, he’d often come back to me to nurse, as if to ground him and allow him to recharge,” remembers Amy, mum of two, Canada. “When he encountered bumps and bruises along the way, breastfeeding was a great comfort to him.”
If you breastfeed your baby into toddlerhood, other people may comment that he’ll never want to stop. But, given the freedom to choose, toddlers often self-wean between the ages of two and four years.17
“I never set out to breastfeed for so long but am still feeding my four-year-old and 22-month-old,” says Susannah, mum of two, UK. “I feed my youngest before and after work and pump during work trips. My eldest has a little comfort feed before bed or when she’s upset – it’s a great way to reconnect. When I’m exhausted or feeling touched out, I focus on the amazing health benefits and comfort I’m giving them. I’m now planning to follow infant-led weaning and let them stop when they’re ready.”
My eldest has a little comfort feed before bed or when she’s upset – it’s a great way to reconnect. When I’m exhausted or feeling touched out, I focus on the amazing health benefits and comfort I’m giving them. I’m now planning to follow infant-led weaning and let them stop when they’re ready.”
Find out more about what you can expect, along with lots of support and advice, in Breastfeeding challenges after the first month
References
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet, Gynecol, & Neonatal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-21.
3 Kent JC et al. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3):e387-395.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.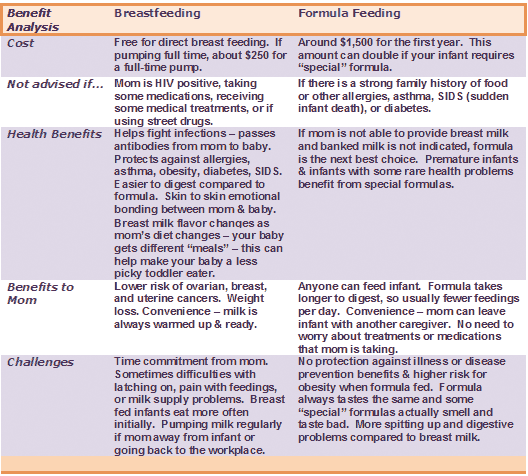
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
6 Victora CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med. 2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb]
[Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb]
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [cited 2018 Feb]
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb]
14 Kendall-Tackett K et al. The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
15) Harrison D et al. Breastfeeding for procedural pain in infants beyond the neonatal period. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;10.
16 Czank C et al. Retention of the immunological proteins of pasteurized human milk in relation to pasteurizer design and practice. Pediatr Res. 2009;66(4):374.
17 Weaning from the breast. (2004). Paediatr Child Health, 9(4):249–253.
Breastfeeding and Returning to Your Workplace | Nutrition
Many parents have questions about expressing breast milk when returning to their workplace after having a baby. Whether returning to work from maternity leave or starting a new job after having your baby, you may be working from home, at a work site, or some combination of the two. Below you will find common questions with information and resources to help you prepare to return to your workplace. The Office on Women’s Healthexternal icon provides additional information.
Whether returning to work from maternity leave or starting a new job after having your baby, you may be working from home, at a work site, or some combination of the two. Below you will find common questions with information and resources to help you prepare to return to your workplace. The Office on Women’s Healthexternal icon provides additional information.
What are my rights as a breastfeeding employee?
The federal Break Time for Nursing Mothers Provisionexternal icon of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act requires employers to support breastfeeding employees by providing:
- A reasonable break time to express breast milk for 1 year after your child’s birth.
- A private, non-bathroom space to express breast milk.
This law applies to most hourly employees and some salaried employees (nonexempt workers) who are covered by the Fair Labor Standards Actexternal icon. Most states also have laws that protect breastfeeding employees.
For breastfeeding people who work in settings with higher risk of potential exposure to COVID-19, such as health care settings, they should wear a mask while breastfeeding or expressing milk in the workplace.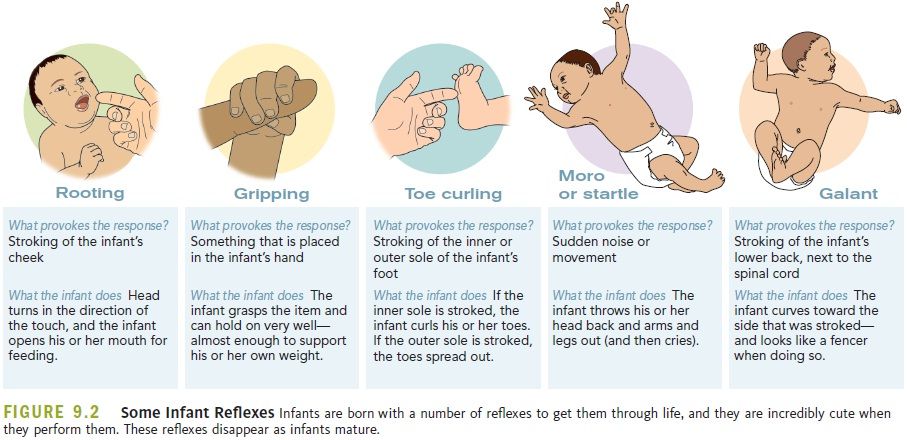 Learn more at Care for Breastfeeding People.
Learn more at Care for Breastfeeding People.
How do I talk with my employer about my needs as I return to work?
If you work outside your home, talk with your employer before you return to your workplace about expressing breast milk during work hours. Having this conversation early will help make sure a plan is in place.
Talk with your employer about:
- Where there is a private, non-bathroom space to express breast milk.
- Where breast milk can be stored (eg, refrigerator, insulated cooler).
- Where pump parts can be cleaned.
- What times are best for you during your work schedule for expressing milk.
The timing and length of breaks needed to express milk and clean breast pump parts may change from day to day and over time. It may be helpful to discuss this with your employer since they may not be familiar with the process of expressing milk or cleaning pump equipment.
Some bras and pumps are designed to be used hands-free! This allows you to collect milk for your baby while doing other things.
How should I clean my breast pump kit parts at my workplace?
For best practices on cleaning pump kit parts, visit CDC’s FAQ page on cleaning breast milk pump parts.
What if I don’t have time to wash pump parts or have access to a sink and water to wash parts?
Careful cleaning of your breast pump parts after every use is important to prevent germs from contaminating the milk you feed your baby. Cleaning breast pump parts at work may require creative solutions depending on your workplace. Here are some ways that you might handle these challenges:
- Bring multiple breast pump kits to your workplace so that a clean kit can be used for each pumping session. Take used parts home after work and wash them all at once.
- If you have access to a microwave, rinse parts and then use steam bags made for cleaning breast pump parts. Some pump parts should not be steamed in the microwave, so be sure to check the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Learn how to hand express directly into milk collection containers.

Can I store my pump parts in the refrigerator between pump sessions while at my workplace?
The CDC and most breast pump manufacturers recommend cleaning pump parts after every use to help protect babies from germs.
More information about storing pump parts in the refrigerator between pumping sessions can be found on CDC’s FAQ page on breast pump cleaning.
Where can I store breast milk at my workplace?
- In the refrigerator: Expressed breast milk is a food and may be stored alongside other foods in any refrigerator that is appropriate for food storage.
- In an insulated cooler: You can store and carry freshly expressed milk in an insulated cooler bag with frozen ice packs for up to 24 hours. Once you get home use the milk right away, store it in the refrigerator, or freeze it.
Always label breast milk containers with your name and the date you expressed the milk. You can also label your cooler with your name and contact information.
How can I pump and store breast milk if my work requires travel?
For detailed information about travel, visit Travel Recommendations for Nursing Families
What else might help me continue breastfeeding after returning to work?
- Practice using your pump or hand expressing breast milk before returning to work so you are comfortable with the process.
- Build a supply of frozen breast milk before returning to work.
- Think about how much breast milk you will need to leave at home or at childcare for your baby before your first day back at work.
- Think about how often you will need to pump or express breast milk while at work to have enough for your baby while you are apart.
- Once breastfeeding is going well, practice bottle feeding your breast milk so your baby will be used to a bottle while you are away at work. If your baby is having trouble taking a bottle at first, try having another adult feed your baby with the bottle.
 You can also try different types of bottles and nipples.
You can also try different types of bottles and nipples.
Top of Page
- Break times and spaces to express milkexternal icon
- Helpful tips for pumping breast milkexternal icon
- General breast milk storage
- Breast milk storage at work
- FAQs on breast pump cleaning
- Types of employers that provide breastfeeding support in the workplaceexternal icon
- Traveling with Children | Transportation Security Administration (tsa.gov)external icon
The prosecutor explains - Prosecutor's Office of the Perm Territory
Prosecutor explains
- November 19, 2020, 02:10
Is an employer required to give a working mother time to feed her child if she is on parental leave and does not work full time?
Text
Share
Many employers assume that if the mother of a child under one and a half years old goes to work part-time and is on parental leave, they should not give her nursing breaks.
In accordance with Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working women with children under the age of one and a half years are provided, in addition to a break for rest and food, additional breaks for feeding the child (children) at least every three hours, lasting at least 30 minutes each .
If a working woman has two or more children under the age of one and a half years, the duration of a break for feeding is set at least one hour.
At the request of a woman, breaks for feeding the child (children) are added to the break for rest and nutrition, or in a summarized form are transferred both to the beginning and to the end of the working day (work shift) with a corresponding reduction in it (her).
Breaks for feeding the child (children) are included in working hours and are payable in the amount of average earnings.
Thus, it does not matter whether the mother went to work full-time/part-time, whether she is on parental leave, and it does not matter the type of feeding (breastfeeding or not), a break for feeding must be provided .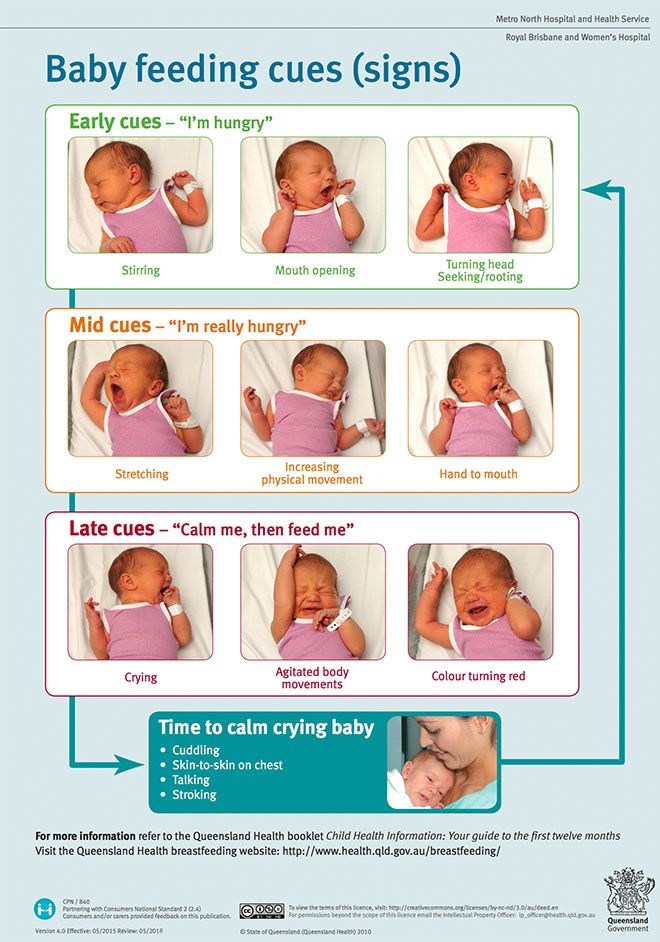
(prepared by Zh.S. Burkova, Senior Assistant Prosecutor of the Yusvinsky District)
Is an employer obliged to provide a working mother with time to feed her child if she is on parental leave and does not work full time?
Many employers assume that if the mother of a child under one and a half years old goes to work part-time and is on parental leave, they should not give her nursing breaks.
In accordance with Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working women with children under the age of one and a half years are provided, in addition to a break for rest and food, additional breaks for feeding the child (children) at least every three hours, lasting at least 30 minutes each .
If a working woman has two or more children under the age of one and a half years, the duration of a break for feeding is set at least one hour.
At the request of a woman, breaks for feeding the child (children) are added to the break for rest and nutrition, or in a summarized form are transferred both to the beginning and to the end of the working day (work shift) with a corresponding reduction in it (her).
Breaks for feeding the child (children) are included in working hours and are payable in the amount of average earnings.
Thus, it does not matter whether the mother went to work full-time/part-time, whether she is on parental leave, and it does not matter the type of feeding (breastfeeding or not), a break for feeding must be provided .
(prepared by Zh.S. Burkova, Senior Assistant Prosecutor of the Yusvinsky District)
Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as amended with Comments and latest amendments for 2022
New edition Art. 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Working women with children under the age of one and a half years are provided, in addition to a break for rest and food, additional breaks for feeding the child (children) at least every three hours, lasting at least 30 minutes each.
If a working woman has two or more children under the age of one and a half years, the duration of the break for feeding is set at least one hour.
At the request of a woman, breaks for feeding the child (children) are added to the break for rest and meals, or in a summarized form are transferred both to the beginning and to the end of the working day (work shift) with a corresponding reduction.
Breaks for feeding the child (children) are included in working hours and are payable in the amount of average earnings.
Commentary on Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Russian legislation, Article 258 of the Labor Code, establishes breaks for feeding a child for women who have children under the age of one and a half years and continue to work, without linking it with breastfeeding children. Breaks are also provided for artificial feeding.
Breastfeeding breaks are provided if the woman does not use parental leave. The fact that another family member is on parental leave does not deprive the mother of the right to a break.
Nursing breaks can be granted not only to mothers, but also to guardians and adoptive mothers. In addition, Article 264 of the Labor Code gives the right to a break to a father or guardian who is raising a child without a mother.
In addition, Article 264 of the Labor Code gives the right to a break to a father or guardian who is raising a child without a mother.
In accordance with part 1 of article 258 of the Labor Code, breaks for feeding a child are provided at least every three hours of continuous work of at least 30 minutes, and if there are two or more children under the age of one and a half years - one hour each. The first break may not be provided three hours after the start of the work shift, but earlier, based on the time of the previous feeding.
Part 1 of article 258 of the Labor Code establishes a minimum duration of a break of 30 minutes. In addition, when determining the duration of the break, one should take into account the state of health of the mother and child, the remoteness of the place of residence of the family (or the location of the child during the mother's work) from the place of work, and other circumstances affecting the feeding regimen. In addition, the duration of the breaks may be extended based on a medical opinion. The time of breaks for feeding a child, on the basis of paragraph 3 of Article 258, can be summarized and added either to a break for rest and food, or to the beginning or end of the working day (shift).
The time of breaks for feeding a child, on the basis of paragraph 3 of Article 258, can be summarized and added either to a break for rest and food, or to the beginning or end of the working day (shift).
The desired break arrangements are indicated on the woman's or other person's application. This applies to breaks, both ordinary and attached to a break for rest and food, or transferred to the beginning or end of the working day.
If, due to the conditions of work, it is impossible to provide breaks, the woman, at her request, must be transferred to another job.
The time of breaks for feeding the child is included, in accordance with part 4 of article 258 of the Labor Code, in working hours. During this time, a woman retains her average earnings, which, in accordance with paragraph 7 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is included in the expenses of the organization when calculating income tax.
Another commentary on Art. 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. ILO Convention N 103 provides that if a woman is breastfeeding her child, she has the right to interrupt work for this purpose for one or more breaks per day, the duration of which is established by the legislation of the country.
ILO Convention N 103 provides that if a woman is breastfeeding her child, she has the right to interrupt work for this purpose for one or more breaks per day, the duration of which is established by the legislation of the country.
Russian legislation establishes broader guarantees and grants the right to breastfeeding breaks to all women with children under the age of one and a half years and who continue to work, not associating it only with breastfeeding, so breaks are also provided for artificial feeding.
2. Breastfeeding breaks are provided if the woman does not use parental leave. If another member of the family is on vacation, actually caring for the child, this does not deprive the mother of the right to a break.
3. Nursing breaks are provided for both mothers and guardians and adoptive mothers. The father or guardian who is raising a child without a mother also has the right to a break (see Article 264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and commentary thereto).
4. As a general rule, breaks for feeding a child are provided at least every three hours of work lasting at least 30 minutes, and if there are two or more children under the age of one and a half years - one hour each.
When scheduling work with breaks, it must be taken into account that the purpose of these breaks is to ensure the most favorable diet for the child. Therefore, the first break can be provided not three hours after the start of the work shift, but earlier, based on the time of the previous feeding.
Part 1 Art. 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the minimum duration of a break. Based on the state of health of the mother and child, the remoteness of the place of residence of the family (or the location of the child during the mother's work) from the place of work, other circumstances affecting the feeding regimen, the duration of the breaks can be increased. In this case, the duration of the breaks is determined on the basis of a medical report.
5. In contrast to the rules provided for in art. 169 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part 3 of Art. 258 gives women the opportunity to sum up the breaks and add them either to a break for rest and food, or to the beginning or end of the working day (shift). Since this is a woman's right, the consent of the employer is not required for such summation.
Second difference art. 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation from Art. 169 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is in the order of providing breaks. Previously, such a procedure was established by the employer together with the elected trade union body, taking into account the wishes of the woman. Now, the law does not require any special approvals and breaks are provided in the order indicated in the application of a woman or other person entitled to breaks. This applies not only to regular breaks, but also to breaks attached to a break for rest and food or transferred to the beginning or end of the working day.











