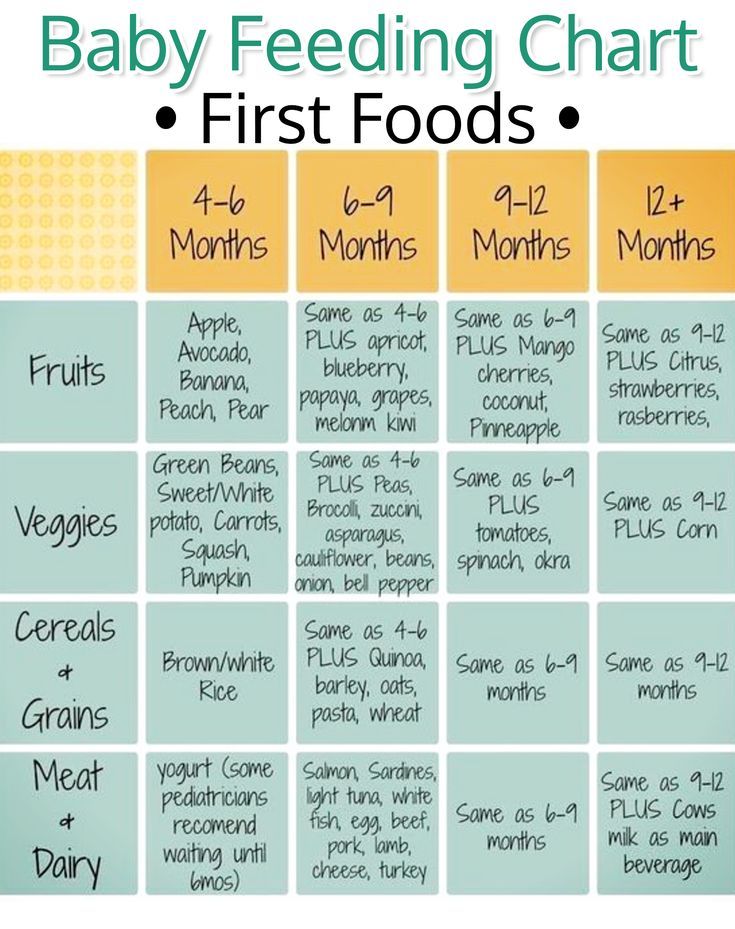
When to start feeding baby 3 times a day
Your baby's first solid foods
When to start introducing solid foods
Introducing your baby to solid foods, sometimes called complementary feeding or weaning, should start when your baby is around 6 months old.
At the beginning, how much your baby eats is less important than getting them used to the idea of eating.
They'll still be getting most of their energy and nutrients from breast milk or first infant formula.
Giving your baby a variety of foods, alongside breast or formula milk, from around 6 months of age will help set your child up for a lifetime of healthier eating.
Gradually, you'll be able to increase the amount and variety of food your baby eats until they can eat the same foods as the rest of the family, in smaller portions.
If your baby was born prematurely, ask your health visitor or GP for advice on when to start introducing solid foods.
Why wait until around 6 months to introduce solids?
It’s a good idea to wait until around 6 months before introducing solid foods because:
- breast milk or first infant formula provide the energy and nutrients your baby needs until they're around 6 months old (with the exception of vitamin D in some cases)
- if you're breastfeeding, feeding only breast milk up to around 6 months of age will help protect your baby against illness and infections
- waiting until around 6 months gives your baby time to develop so they can cope fully with solid foods – this includes solid foods made into purées, cereals and baby rice added to milk
- your baby will be more able to feed themselves
- your baby will be better at moving food around their mouth, chewing and swallowing it – this may mean they'll be able to progress to a range of tastes and textures (such as mashed, lumpy and finger foods) more quickly, and may not need smooth, blended foods at all
Signs your baby is ready for solid foods
There are 3 clear signs which, when they appear together from around 6 months of age, show your baby is ready for their first solid foods alongside breast milk or first infant formula.
They'll be able to:
- stay in a sitting position and hold their head steady
- co-ordinate their eyes, hands and mouth so they can look at the food, pick it up and put it in their mouth by themselves
- swallow food (rather than spit it back out)
The following behaviours can be mistaken by parents as signs that their baby is ready for solid foods:
- chewing their fists
- waking up in the night (more than usual)
- wanting extra milk feeds
These are all normal behaviours for babies and not necessarily a sign that they're hungry or ready to start solid food.
Starting solid foods will not make your baby any more likely to sleep through the night. Sometimes a little extra milk will help until they're ready for solid foods.
Get tips to help your baby sleep well
How to start solid foods
In the beginning your baby will only need a small amount of food before their usual milk feed.
Do not worry about how much they eat. The most important thing is getting them used to new tastes and textures, and learning how to move solid foods around their mouths and how to swallow them.
They'll still be getting most of their energy and nutrients from breast milk or infant formula.
There are some foods to avoid giving to your baby. For example, do not add sugar or salt (including stock cubes and gravy) to your baby's food or cooking water.
Babies should not eat salty foods as it's not good for their kidneys, and sugar can cause tooth decay.
Tips to get your baby off to a good start with solid foods:
- Eating is a whole new skill.
 Some babies learn to accept new foods and textures more quickly than others. Keep trying, and give your baby lots of encouragement and praise.
Some babies learn to accept new foods and textures more quickly than others. Keep trying, and give your baby lots of encouragement and praise. - Allow plenty of time, especially at first.
- Go at your baby's pace and let them show you when they're hungry or full. Stop when your baby shows signs that they've had enough. This could be firmly closing their mouth or turning their head away. If you're using a spoon, wait for your baby to open their mouth before you offer the food. Do not force your baby to eat. Wait until the next time if they're not interested this time.
- Be patient and keep offering a variety of foods, even the ones they do not seem to like. It may take 10 tries or more for your baby to get used to new foods, flavours and textures. There will be days when they eat more, some when they eat less, and then days when they reject everything. Do not worry, this is perfectly normal.
- Let your baby enjoy touching and holding the food.
 Allow them to feed themselves, using their fingers, as soon as they show an interest. If you're using a spoon, your baby may like to hold it or another spoon to try feeding themselves.
Allow them to feed themselves, using their fingers, as soon as they show an interest. If you're using a spoon, your baby may like to hold it or another spoon to try feeding themselves. - Keep distractions to a minimum during mealtimes and avoid sitting your baby in front of the television, phone or tablet.
- Show them how you eat. Babies copy their parents and other children. Sit down together for family mealtimes as much as possible.
Texture progression
Once you've started introducing solid foods from around 6 months of age, try to move your baby on from puréed or blended foods to mashed, lumpy or finger foods as soon as they can manage them.
This helps them learn how to chew, move solid food around their mouth and swallow.
Some babies like to start with mashed, lumpy or finger foods.
Other babies need a little longer to get used to new textures, so may prefer smooth or blended foods on a spoon at first.
Just keep offering them lumpy textures and they'll eventually get used to it.
Safety and hygiene
When introducing your baby to solid foods, it's important to take extra care to not put them at risk.
Key food safety and hygiene advice:
- always wash your hands before preparing food and keep surfaces clean
- cool hot food and test it before giving it to your baby
- wash and peel fruit and raw vegetables
- avoid hard foods like whole nuts, or raw carrot or apple
- remove hard pips and stones from fruits, and bones from meat or fish
- cut small, round foods, like grapes and cherry tomatoes, into small pieces
- eggs produced under the British Lion Code of Practice (stamped with the red lion) are considered very low risk for salmonella and safe for babies to eat partially cooked
Always stay with your baby when they're eating in case they start to choke.
Choking is different from gagging. Your baby may gag when you introduce solid foods.
This is because they're learning how to deal with solid foods and regulate the amount of food they can manage to chew and swallow at one time.
If your baby is gagging:
- their eyes may water
- they might push their tongue forward (or out of their mouth)
- they might retch to bring the food forward in their mouth or vomit
Equipment checklist
- High chair. Your baby needs to be sitting safely in an upright position (so they can swallow properly). Always use a securely fitted safety harness in a high chair. Never leave babies unattended on raised surfaces.
- Plastic or pelican bibs. It's going to be messy at first!
- Soft weaning spoons are gentler on your baby's gums.

- Small plastic bowl. You may find it useful to get a special weaning bowl with a suction base to keep the bowl in place.
- First cup. Introduce a cup from around 6 months and offer sips of water with meals. Using an open cup or a free-flow cup without a valve will help your baby learn to sip and is better for their teeth.
- A messy mat or newspaper sheets under the high chair to catch most of the mess.
- Plastic containers and ice cube trays can be helpful for batch cooking and freezing small portions.
Find out more:
- tips to help your baby enjoy new foods
- children's food: safety and hygiene
- foods to avoid giving babies and young children
- how to stop a child from choking
- baby and toddler safety
Feeding your baby: from 0 to 6 months
Breast milk is the best food your baby can have during their first 6 months of life.
It's free, always available and at the perfect temperature, and is tailor-made for your baby.
First infant formula is the only suitable alternative if you do not breastfeed or choose to supplement breast milk.
Other milks or milk substitutes, including cows' milk, should not be introduced as a main drink until 12 months of age.
"Follow-on" formula is not suitable for babies under 6 months, and you do not need to introduce it after 6 months.
Babies do not need baby rice to help them move to solid foods or sleep better.
When using a bottle, do not put anything (such as sugar or cereals) in it other than breast milk or infant formula.
Vitamins for babies
It's recommended that breastfed babies are given a daily supplement containing 8.5 to 10 micrograms (µg) of vitamin D from birth, whether or not you're taking a supplement containing vitamin D yourself.
Babies having 500mls (about a pint) or more of formula a day should not be given vitamin supplements.
This is because formula is fortified with vitamin D and other nutrients.
All children aged 6 months to 5 years should be given vitamin supplements containing vitamins A, C and D every day.
Find out more:
- benefits of breastfeeding
- how to make up baby formula
- vitamins for children
Feeding your baby: from around 6 months
When they first start having solid foods, babies do not need 3 meals a day. Babies have tiny tummies, so start by offering them small amounts of food (just a few pieces, or teaspoons of food).
Pick a time that suits you both, when you do not feel rushed and your baby is not too tired.
Start offering them food before their usual milk feed as they might not be interested if they're full, but do not wait until your baby is too hungry.
Allow plenty of time and let your baby go at their own pace.
Keep offering different foods, even foods your baby has already rejected.
It can take 10 tries or more before your baby will accept a new food or texture, particularly as they get older.
Your baby will still be getting most of their energy and nutrients from breast milk or first infant formula.
Breast milk or infant formula should be their main drink during the first year. Do not give them whole cows' (or goats' or sheep's) milk as a drink until they're 1 year old.
You can continue breastfeeding for as long as you both want.
Introduce a cup from around 6 months and offer sips of water with meals. Using an open cup or a free-flow cup without a valve will help your baby learn to sip and is better for their teeth.
Using an open cup or a free-flow cup without a valve will help your baby learn to sip and is better for their teeth.
First foods
You might want to start with single vegetables and fruits.
Try mashed or soft cooked sticks of parsnip, broccoli, potato, yam, sweet potato, carrot, apple or pear.
Include vegetables that are not sweet, such as broccoli, cauliflower and spinach.
This will help your baby get used to a range of flavours (rather than just the sweeter ones, like carrots and sweet potato) and might help prevent them being fussy eaters as they grow up.
Make sure any cooked food has cooled right down before offering it to your baby.
Foods containing allergens (such as peanuts, hens' eggs, gluten and fish) can be introduced from around 6 months of age, 1 at a time and in small amounts so you can spot any reaction.
Cows' milk can be used in cooking or mixed with food from around 6 months of age, but should not be given as a drink until your baby is 1 year old.
Full-fat dairy products, such as pasteurised cheese and plain yoghurt or fromage frais, can be given from around 6 months of age. Choose products with no added sugar.
Remember, babies do not need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water).
Finger foods
As soon as your baby starts solid foods, encourage them to be involved in mealtimes and have fun touching, holding and exploring food.
Let them feed themselves with their fingers when they want to. This helps develop fine motor skills and hand-eye co-ordination.
Your baby can show you how much they want to eat, and it gets them familiar with different types and textures of food.
Offering your baby finger foods at each meal is a good way to help them learn to self-feed.
Finger food is food that's cut up into pieces big enough for your baby to hold in their fist with a bit sticking out.
Pieces about the size of your own finger work well.
Start off with finger foods that break up easily in their mouth and are long enough for them to grip.
Avoid hard food, such as whole nuts or raw carrots and apples, to reduce the risk of choking.
Examples of finger foods include:
- soft cooked vegetables, such as carrot, broccoli, cauliflower, parsnip, butternut squash
- fruit (soft, or cooked without adding sugar), such as apple, pear, peach, melon, banana
- grabbable bits of avocado
- cooked starchy foods, such as potato, sweet potato, cassava, pasta, noodles, chapatti, rice
- pulses, such as beans and lentils
- fish without bones
- hardboiled eggs
- meat without bones, such as chicken and lamb
- sticks of pasteurised full-fat hard cheese (choose lower salt options)
Baby-led weaning
Baby-led weaning means giving your baby only finger foods and letting them feed themselves from the start instead of feeding them puréed or mashed food on a spoon.
Some parents prefer baby-led weaning to spoon feeding, while others do a combination of both.
There's no right or wrong way. The most important thing is that your baby eats a wide variety of food and gets all the nutrients they need.
There's no more risk of choking when a baby feeds themselves than when they're fed with a spoon.
Find out more:
- help your baby enjoy new foods
- drinks and cups for babies and young children
- food allergies in babies and young children
- foods to avoid giving babies and young children
Feeding your baby: from 7 to 9 months
From about 7 months, your baby will gradually move towards eating 3 meals a day (breakfast, lunch and tea), in addition to their usual milk feeds, which may be around 4 a day (for example, on waking, after lunch, after tea and before bed).
As your baby eats more solid foods, they may want less milk at each feed or even drop a milk feed altogether.
If you're breastfeeding, your baby will adapt their feeds according to how much food they're having.
As a guide, formula-fed babies may need around 600ml of milk a day.
Gradually increase the amount and variety of food your baby is offered to ensure they get the energy and nutrients they need.
Try to include food that contains iron, such as meat, fish, fortified breakfast cereals, dark green vegetables, beans and lentils, at each meal.
Your baby's diet should consist of a variety of the following:
- fruit and vegetables, including ones with bitter flavours, such as broccoli, cauliflower, spinach and cabbage
- potatoes, bread, rice, pasta and other starchy foods
- beans, pulses, fish, eggs, meat and other non-dairy sources of protein
- pasteurised full-fat dairy products, such as plain yoghurt and cheese (choose lower salt options)
As your baby becomes a more confident eater, remember to offer them more mashed, lumpy and finger foods.
Providing finger foods as part of each meal helps encourage infants to feed themselves, develop hand and eye co-ordination, and learn to bite off, chew and swallow pieces of soft food.
Remember, babies do not need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water).
Feeding your baby: from 10 to 12 months
From about 10 months, your baby should now be having 3 meals a day (breakfast, lunch and tea), in addition to their usual milk feeds.
Around this age, your baby may have about 3 milk feeds a day (for instance, after breakfast, after lunch and before bed).
Breastfed babies will adapt their milk consumption as their food intake changes.
As a guide, babies fed infant formula will drink about 400ml daily.
Remember that formula-fed babies should take a vitamin D supplement if they're having less than 500ml of formula a day.
All breastfed babies should take a vitamin D supplement.
By now, your baby should be enjoying a wide range of tastes and textures.
They should be able to manage a wider range of finger foods, and be able to pick up small pieces of food and move them to their mouth. They'll use a cup with more confidence.
Lunches and teas can include a main course, and a fruit or unsweetened dairy-based dessert, to move eating patterns closer to those of children over 1 year.
As your baby grows, eating together as a family encourages them to develop good eating habits.
Remember, babies do not need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water).
Feeding your baby: from 12 months
From 12 months, your child will be eating 3 meals a day containing a variety of different foods, including:
- a minimum of 4 servings a day of starchy food, such as potatoes, bread and rice
- a minimum of 4 servings a day of fruit and vegetables
- a minimum of 350ml milk or 2 servings of dairy products (or alternatives)
- a minimum of 1 serving a day of protein from animal sources (meat, fish and eggs) or 2 from vegetable sources (dhal, beans, chickpeas and lentils)
Your child may also need 2 healthy snacks in between meals.
Go for things like:
- fresh fruits, such as apple, banana or small pieces of soft, ripe, peeled pear or peach
- cooked or raw vegetable, such as broccoli florets, carrot sticks or cucumber sticks
- pasteurised plain full-fat yoghurt
- sticks of cheese (choose a lower salt option)
- toast, pitta or chapatti fingers
- unsalted and unsweetened rice or corn cakes
The World Health Organization recommends that all babies are breastfed for up to 2 years or longer.
You can keep breastfeeding for as long as it suits you both, but your child will need less breast milk to make room for more foods.
Once your child is 12 months old, infant formula is not needed and toddler milks, growing-up milks and goodnight milks are also unnecessary.
Your baby can now drink whole cows' milk. Choose full-fat dairy products, as children under 2 years old need the vitamins and extra energy found in them.
From 2 years old, if they're a good eater and growing well, they can have semi-skimmed milk.
From 5 years old, 1% fat and skimmed milk is OK.
You can give your child unsweetened calcium-fortified milk alternatives, such as soya, oat or almond drinks, from the age of 1 as part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Children under 5 years old should not be given rice drinks because of the levels of arsenic in these products.
Find out more:
- what to feed young children
- foods to avoid giving babies and young children
- drinks and cups for babies and young children
- vitamins for children
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
For information and advice you can trust, sign up for weekly Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails.
When Should A Baby Eat Solids 3 Times A Day? It Takes Some Time
Life
by Cat Bowen
Starting your baby on solid foods can be daunting. After all, everyone seems to be giving advice, but there doesn't seem to be any consensus. Your mom says one thing, Google says something else, and your pediatrician has just given you an entirely new set of guidelines. Once you've figured out when to start food and what kind of solids to feed your baby, you'll need more answers. Like, when should a baby eat solids three times a day?
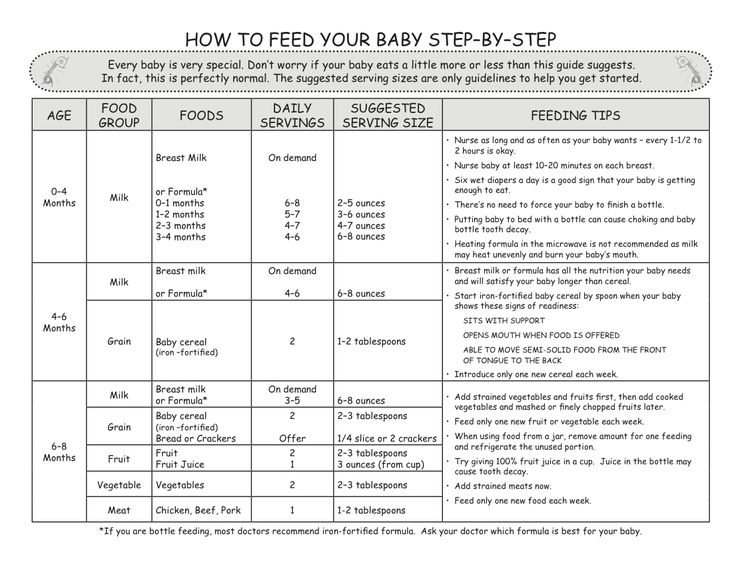
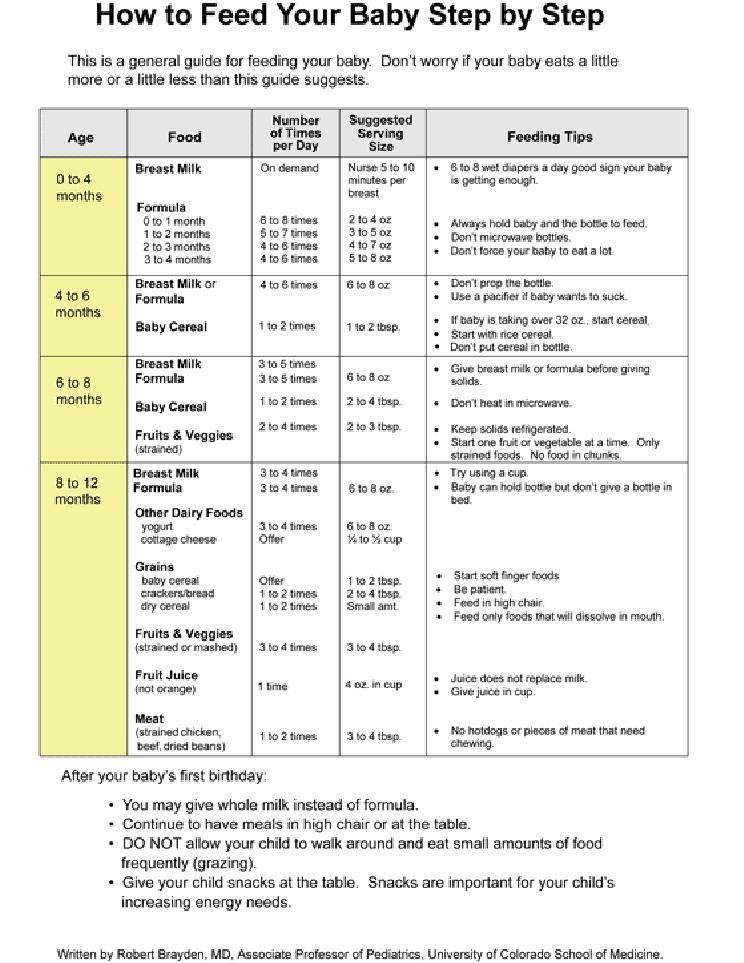
According to The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), it's recommended that you don't start your baby on solid food until at least 6 months of age. The AAP wrote that you should start your baby on an iron-fortified cereal or oatmeal, mixed with breast milk or formula to begin. Experts have found that it's best to start with one feeding of just a few tablespoons of food per day for the first week or two; your baby is new to this eating solid foods thing, and there's a bit of a learning curve.
It's like learning to eat raw oysters for adults (or my 9-year-old). It's not the simplest of foods to get the hang of, but once you settle into it, you can slurp down a dozen blue points without looking sideways. That's what your baby is learning to do — how do they move this thick food around their tiny mouth and get it in the right direction to swallow?
According to Kaiser Permanente Hospitals, you should continue with breast milk or formula for at least one year, in addition to solids. However, the amount of food and number of meals should increase in the six month period between introducing solids and weaning.
So when should your baby eat solids three times a day? According to Kaiser Permanente, after the first week of one meal a day, your baby will be ready for two meals of iron-fortified cereals. Although the AAP noted that some babies will not like the cereal, and if that's the case, it's fine to move onto other puréed foods. By about 7 months, according to Kaiser, your baby will be ready to have a few tablespoons of food at breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
According to Neumors Health System, by 8 months of age, your baby is ready for three meals and two snacks per day. According to Kaiser, this should be primarily fruits and vegetables with whole grains and protein. (I found it interesting that they suggest starting with lamb before beef or poultry, and now I can't stop picturing a baby chowing down on a gyro.)
It's actually pretty serious though. Researchers with the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that the foods babies eat early in life become foundational tastes, developing their palates, and influencing their eating behaviors for a lifetime, so it's important to try to develop those tiny, often picky palates by offering them new and interesting textures and tastes, all while keeping it healthy and nourishing.
Who knows? You may have an adventurous eater on your hands who's the first in your family to actually try the oysters. Just remember, your little one will continue to get the bulk of their nutrition from their breast milk or formula until they are at least 1-year-old. Not to worry though, by the time your baby tries oysters, they'll have that eating part down and will definitely be eating at least three times per day.
Not to worry though, by the time your baby tries oysters, they'll have that eating part down and will definitely be eating at least three times per day.
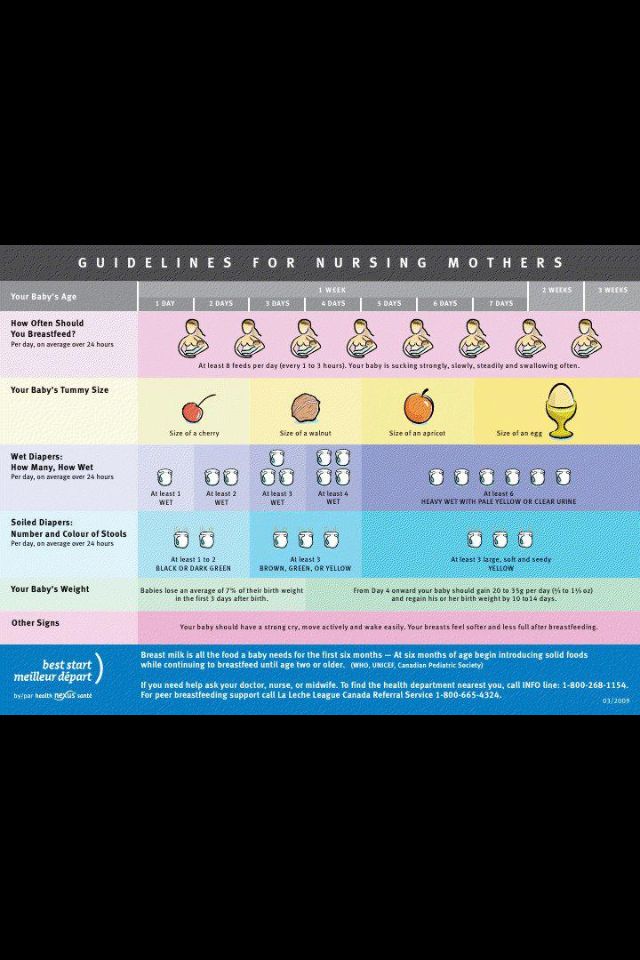
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding necessary for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk.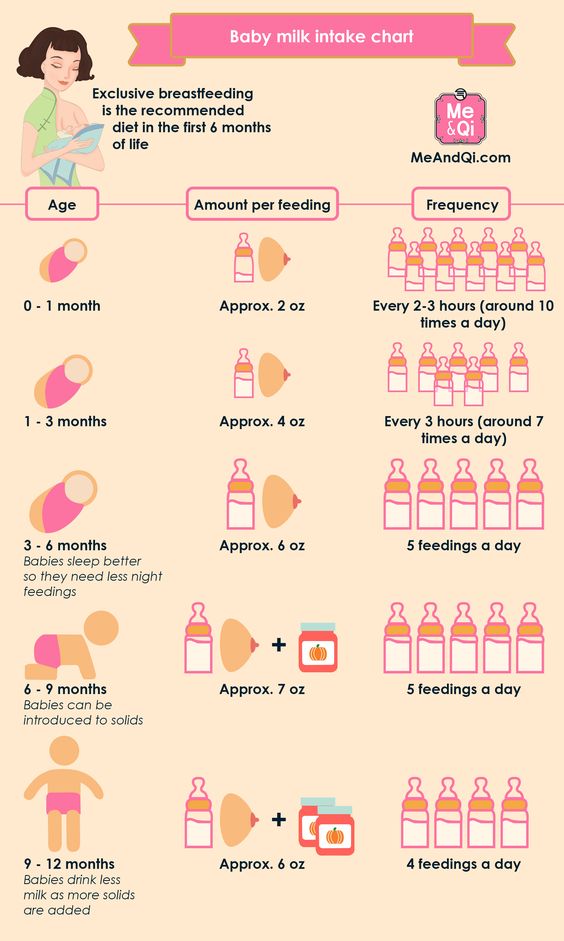 This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes.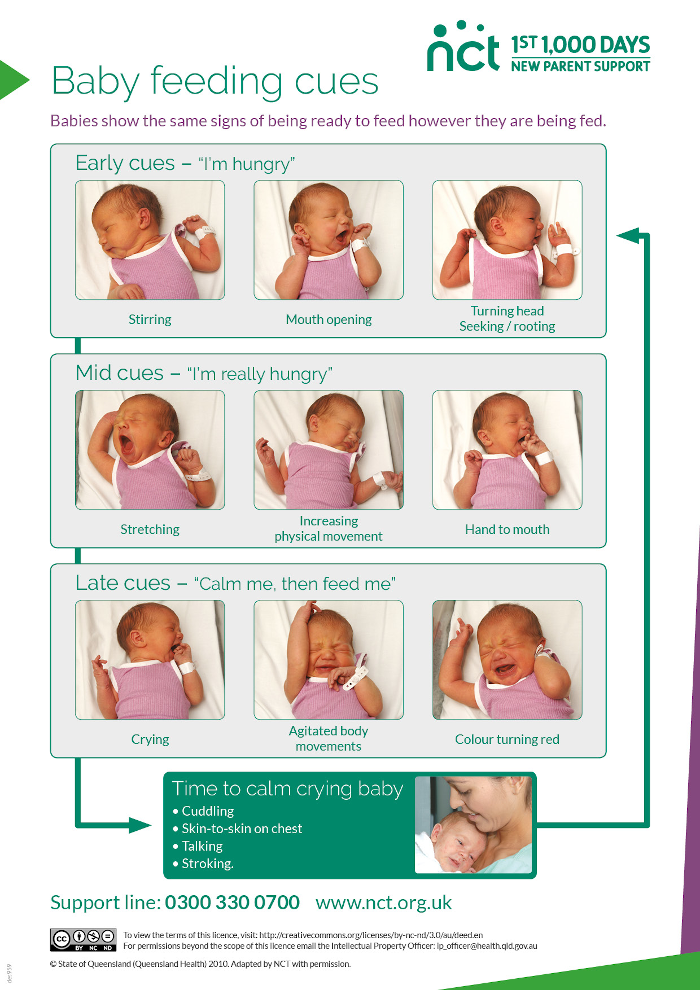 And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
This whole process is biologically justified. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with breast in mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
The daytime naps of a one-month-old infant feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2. 5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for suckling. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person deliberately harming an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook.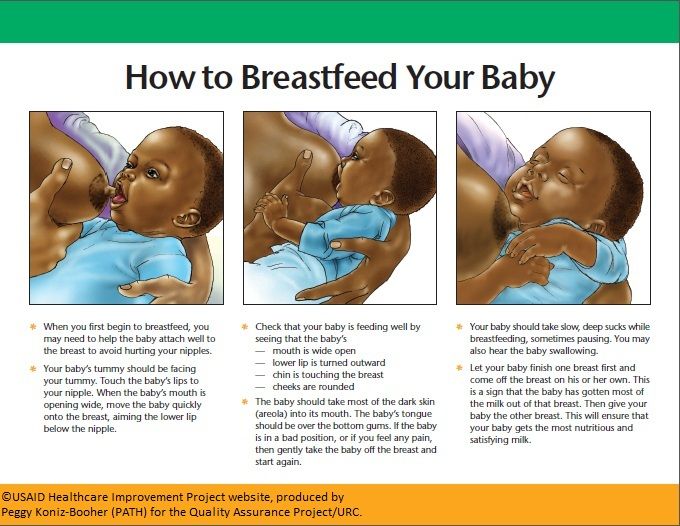 For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed noticeably less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen. And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
- At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.
- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications.
 At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.
At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness. - At seven months, the frequency of application is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times.
 The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times. - In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
- Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons.
 The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours. - At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast. The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
- At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.
 e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down. - At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking. The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Moms who don't think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when breastfeeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is wrong. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking back at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.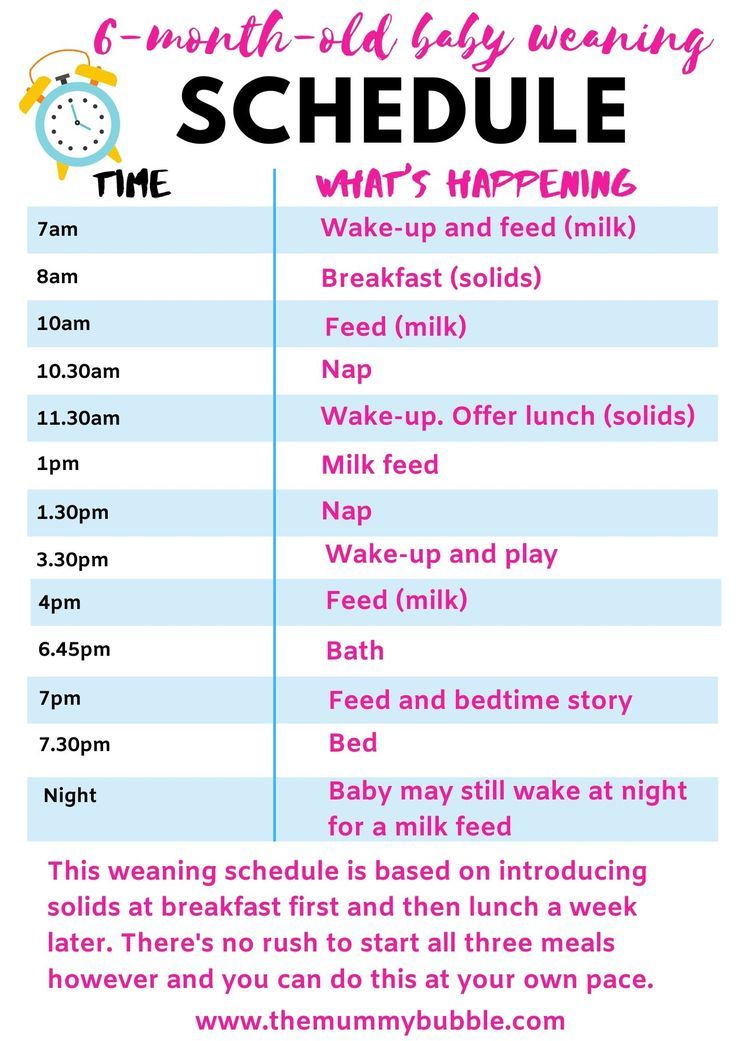
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when I advise mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists.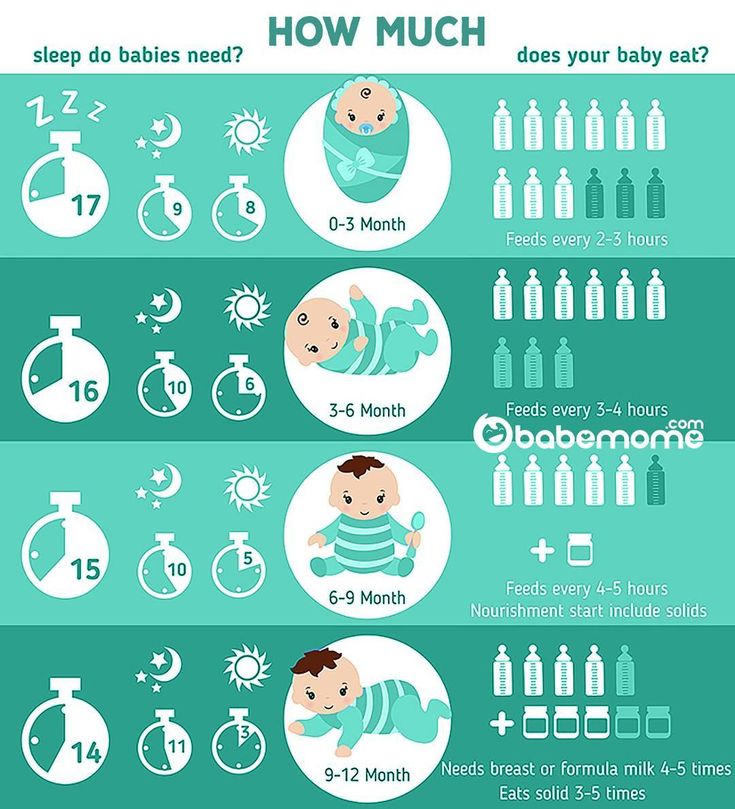 These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
Breastfeeding is important not only for the baby, it is also important for the mother. During on-demand feeding, the woman's feelings change, a stronger attachment to the baby is formed, the woman becomes more sensitive to the needs of the baby. Deeper affection and understanding are not only preserved in infancy. They persist for life. For clarity, imagine what happens to a woman’s feelings if she tries to “withstand” a child, endures his crying, anxiety. What happens to a woman if she uses the recommendation from one very popular parenting book: "Go to the child if he cries for more than 15 minutes"? Speaking in abstract terms, humanity is interested in reviving the practice of breastfeeding. The revival of this practice is impossible without mothers realizing the true reasons for the child's need for attachment to the breast.
Lilia Kazakova, pediatrician,
Head of Breastfeeding and Child Care Counselors
Child nutrition 0-1.
 5 years
5 years Child nutrition is one of the most important topics that every mother faces. How long to breastfeed, where to start complementary foods, how to feed a one-year-old baby?
Ashikhmina Olga Vladimirovna, a specialist in the cabinet for raising a healthy child at the Children's Polyclinic No. 1, tells about the nutrition of a child aged 0 to 1.5 years.
Speaking about the nutrition of a child under 1.5 years old, I would like to divide the topic into several parts: breastfeeding and complementary foods.
When it comes to breastfeeding, healthcare professionals today are doing their best to maintain and encourage breastfeeding (LF).
The WHO Declaration "Protect, Promote, Support Breastfeeding" proclaims 10 principles of breastfeeding.
10 principles of breastfeeding:
1. Strictly adhere to the established rules of breastfeeding and regularly communicate these rules to medical personnel and women in labor.
2. Train medical staff in the necessary skills for breastfeeding.
3. Inform all pregnant women about the benefits and techniques of breastfeeding.
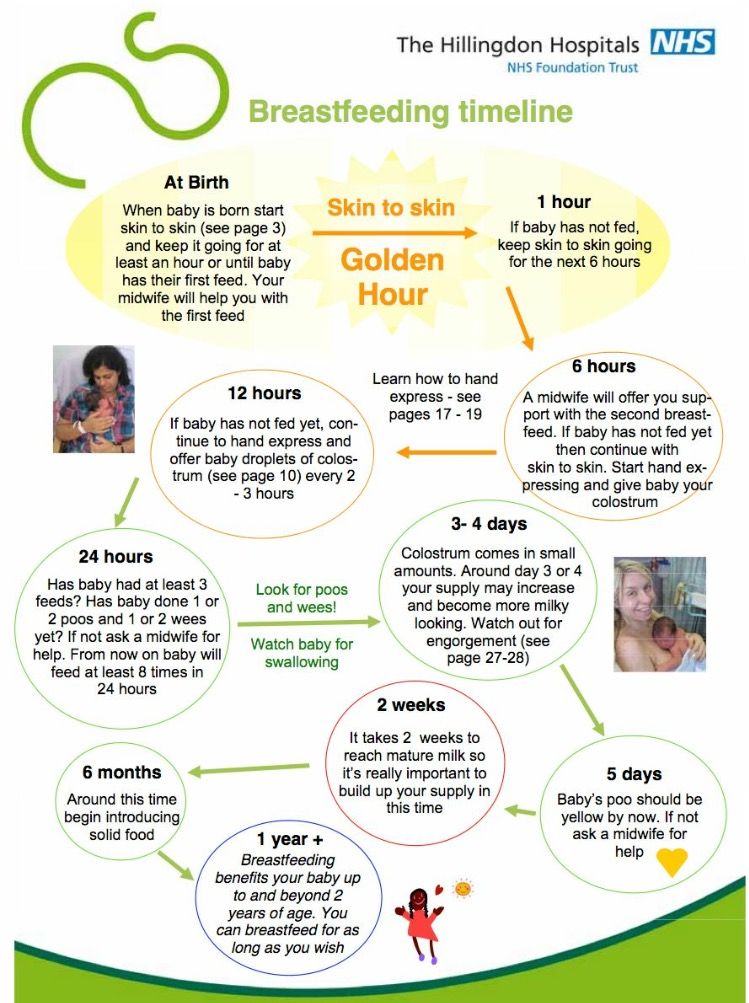
4. Help mothers initiate breastfeeding within the first half hour after delivery.
5. Show mothers how to breastfeed and how to maintain lactation, even if they are temporarily separated from their children.
6. Give newborns no food or drink other than breast milk, unless medically indicated.
7. Practice having the mother and newborn side by side in the same room around the clock.
8. Encourage breastfeeding on demand, not on schedule.
9. Do not give breastfeeding newborns any sedatives or devices that mimic the mother's breasts (nipples, etc.)
10. Encourage the establishment of breastfeeding support groups and refer mothers to these groups after discharge from the hospital or hospital.
From the birth of a baby, medical workers are ready to help mothers with breastfeeding and child care. The patronage service, which visits newborns for examinations, actively advocates for the support of breastfeeding and is always ready to advise the mother on feeding the baby.
Experts advise to feed the baby not according to the schedule, but at the request of the baby. At first, feeding can be up to 10-12 times a day. After a month, the mother can switch to the regime - once every 3 hours, including feeding at night.
If the baby constantly requires the breast and eats for a long time, it is necessary to check whether the baby is properly attached to the breast. On this issue, a woman can always contact a pediatrician or a healthy child's office. The specialist weighs the baby before and after feeding and determines how much milk the baby receives and, if necessary, tells how to properly attach the baby to the breast.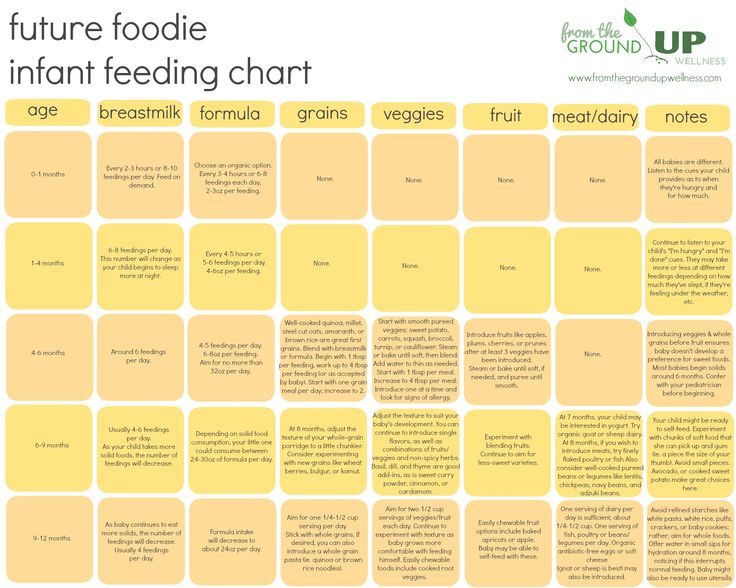
What affects the amount of milk a mother has? One factor is nutrition. A nursing woman should eat a varied diet at least 6 times a day. Favorably, a nursing woman is influenced by walks in the fresh air, physical activity. And, of course, as far as possible, it is important for a nursing woman to protect herself from stress as much as possible. Stress negatively affects lactation.
How long should I breastfeed my baby? Breastfeeding, according to pediatricians and neonatologists, must be maintained in the first year of a baby's life. At the same time, it is important to understand that in addition to milk, the child needs other food, which will form the taste habits of the baby, develop social skills.
Complementary foods
From 4 to 6 months, it is necessary and necessary to introduce complementary foods into the baby's diet. Why from 4 to 6 months? This is the so-called window of tolerance.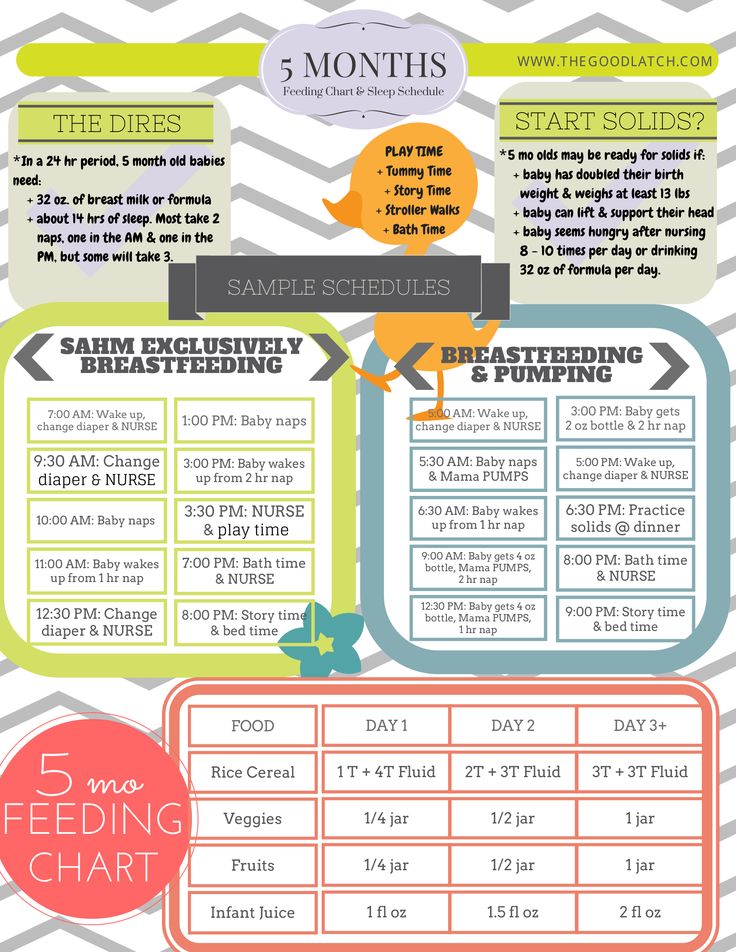 Products introduced into the diet during this period are well tolerated by young children.
Products introduced into the diet during this period are well tolerated by young children.
Complementary foods are given to the child in the morning before breastfeeding, sitting in the mother's arms, starting with 1 teaspoon. For 7 days, bring up to 100-150 g of the product. For a whole week we give the same product, constantly increasing its quantity.
Meals for children of the first year of life are boiled in water or steamed, crushed with a blender and given to the child in liquid form, moreover, salt, sugar and spices are not added.
If a child develops an allergy to a certain product, we cancel it and introduce another product after 2-3 days.
Complementary foods begin with the introduction of vegetables or cereals. Underweight children with unstable stools start with cereals. Porridges are not milk based, gluten free. Complementary foods are introduced from three cereals - buckwheat, rice, corn.
For overweight children with constipation, it is recommended to start complementary foods with vegetable purees. 3 weeks - 3 vegetable purees - from cauliflower, broccoli and zucchini.
Meat puree is introduced into the artsion from 6 months: first turkey and rabbit, then beef, chicken is introduced last.
Fruit puree is introduced from 6-6.5 months. Yolk from 7 months to ¼ boiled yolk, protein is not introduced at 1 year of age.
From 8 months old cottage cheese is added to the diet, from 8 months and 1 week - kefir, fish puree from 8 months and 2 weeks - lean fish is given instead of meat puree once a week.
Bread can be introduced into the diet from 8 months. Vegetable oil with vegetable puree, butter in porridge, 0.5 tsp each. into porridge.
Fruit juice can be introduced no earlier than 9-10 months.
It is important to introduce one new food per week to monitor the child's response to a particular food.
Do not introduce new products during vaccinations or when the baby is unwell.
From 8-9 months thicker food with small pieces can be included.
By the age of 1, breastfeeding continues, but only 2-3 times a day.
Nutrition from 1 to 1.5 years
Photo taken from ru.freepik.com
After 1 year, cheese can and should be introduced. Cottage cheese in such large quantities as before is not needed - 2-3 times a week is enough. Egg white is introduced into the diet 2-3 pieces per week.
At this age, we can start feeding our baby soups cooked in the second broth. We cook boneless meat, after boiling the broth is drained and filled with water. This broth can be given to a one-year-old child - it is less fat than the first.
At this age, the child can be given beets, cook borscht.
Closer to 1.5 years, we introduce salads into the diet - cucumber and tomato, beets and carrots.
By the age of 1.5, a fairly varied diet and now we can make a daily menu for him - breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea and dinner.
I would like to note that complementary foods are a very important social component in a child's life. Complementary feeding is not only the introduction of food, it is teaching the child hygiene skills - we teach the baby to wash his hands before eating, sit on a chair at the table, hold a spoon on his own. For a toddler, these are important social skills that will come in handy later in kindergarten.
Daily ration for a child aged 12-18 months
If we talk about the child's daily menu for the day. At 1-1.5 years, the daily diet may look like this:
Breakfast:
- Milk porridge - 150 ml
- Fruit - 30 g
- Fruit tea - 120 ml
Lunch:
- Vegetable salad with herbs and vegetable oil - 40 ml
- Vegetable puree soup - 120 g
- Meat soufflé - 50 g
- Boiled potatoes - 50g
- Compote - 100 g
Snack:
- Sour milk drink - 120 ml
- Curd - 30 g
- Fruit - 120 ml
Dinner:
- Vegetable stew - 120 g
- Chicken cutlet - 70 g
- Bread - 30 g
- Water/herbal tea - 100 ml
Before bed:
Infant formula - 200 ml
The subject of nutrition and feeding of the baby is inexhaustible.