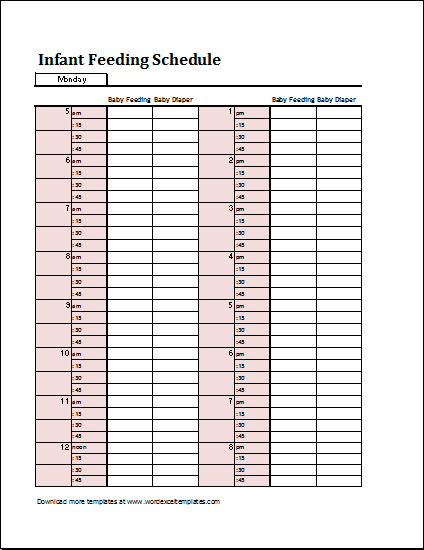
Wic feeding chart babies
California Women, Infants & Children Program
The manufacturer of Enfamil ProSobee has issued a limited voluntary recall of two batches of 12.9 oz Simply Plant-Based Powder Infant Formula manufactured between August and September 2022. Only a small number of batches are affected, and no other Enfamil ProSobee batches or other Enfamil products are impacted. For more information, visit the Enfamil’s ProSobee Recall 2023 website.
More information for WIC families on WIC temporary infant formula options can be found at the California WIC Infant Formula Options webpage. General guidance and information for California families about WIC contract formulas can be found at the WIC Contract Infant Formulas webpage.
Select language
Information on WIC Approved Temporary Formula Options
Learn More
WIC Fruits and Vegetables Benefit Increase
Learn More
COVID-19 information for WIC families
COVID-19 Vaccines are now available for everyone aged 6 months or older.
Protect yourself and your family with the latest information on COVID-19.
Learn More
How WIC Helps
WIC provides healthy foods, referrals to other services in your community, and much more!
Learn More
How can I get WIC?
If you are pregnant or have a child under 5, WIC can help
Learn More
Shopping for WIC foods
Use your California WIC Card to shop for a variety of healthy foods.
Learn More
Shop with WIC at farmers’ markets.
WIC has Farmers' Markets all over California. Find a market near you!
Learn More
Nutrition and breastfeeding
Get nutrition tips and breastfeeding support to make your parenting job easier.
Learn More
Previous Next
Give your baby the best start. WIC helps you learn how to
respond to your baby’s cries and know what to expect with
your baby’s sleep. A baby’s first year is full of changes. WIC is
here for you as you learn about feeding your baby and when
to introduce solid foods. WIC offers you tips and support to
help your little one grow healthy and strong.
WIC offers you tips and support to
help your little one grow healthy and strong.
Understanding my Baby's Cues: Getting to Know Your Baby English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Guide to Breastfeeding English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
When You Feed Me Formula English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Let your Baby Set the Pace English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Feed Me! 6 to 12 Months English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Too Soon for Solid Foods/Tips for Busy Parents English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
I Can Eat Finger Foods English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Baby Food for Me English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Playing with Your Baby English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
Time for a Cup English (PDF) | Spanish (PDF)
/ Infants
Your California WIC Card
The California WIC Card makes shopping fast and easy. Take a look at this instructional video to find out more:
Video en Español
CA WIC Customer Service
Automated Tel: 1-888-942-9675
In-Person Tel: 1-800-852-5770
Email: [email protected]
USDA/FNS Nondiscrimination Statement
Contact Us |
Report Fraud & Abuse |
CA WIC Website
© California Department of Public Health, Women, Infants and Children Program
To Top of Document
Feeding Guide: 6-12 Months - WIC South Dakota
This site requires javascript to operate correctly. Please enable it to continue.
Please enable it to continue.
On a desktop computer, hold "Ctrl" and Press "F" to search for keywords on this page.
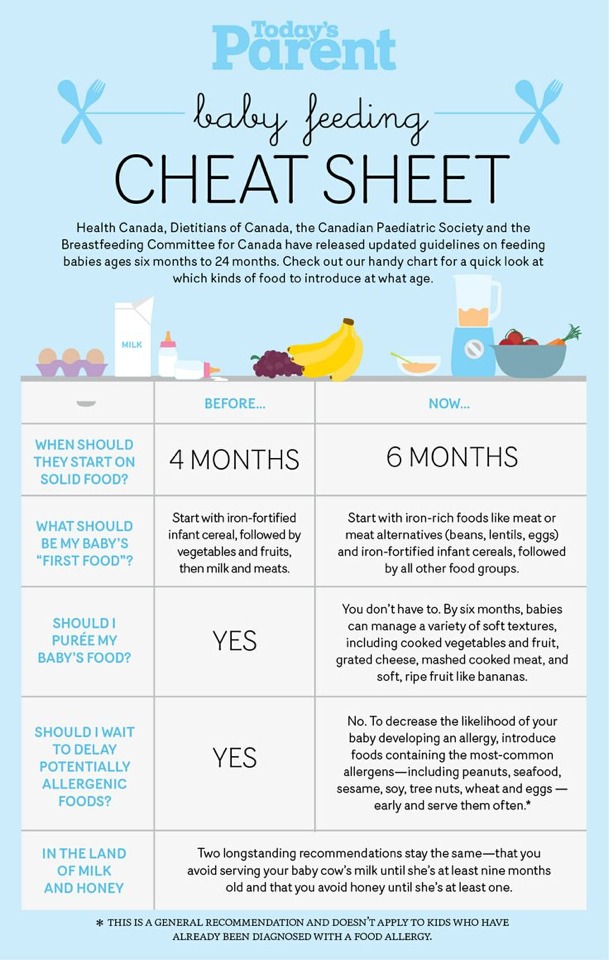
Please note: This information primarily focuses on nutrition for the healthy, full-term infant. Consult with a WIC Health Professional for more detailed and advanced information particularly for preterm, low-birth weight, special needs, or infants with medical conditions.
Breastfed Baby
It is recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics to exclusively breastfeed (no formula) through the first 6 months of life and to continue breastfeeding through 12 months of age while complementary foods are added, as mutually desired by mom and baby.
Breastmilk is still the main source of nutrition. Continue to breastfeed on demand. On average, baby will feed 3-4 times per day.
Baby will start to breastfeed less as they eat more baby food and table foods.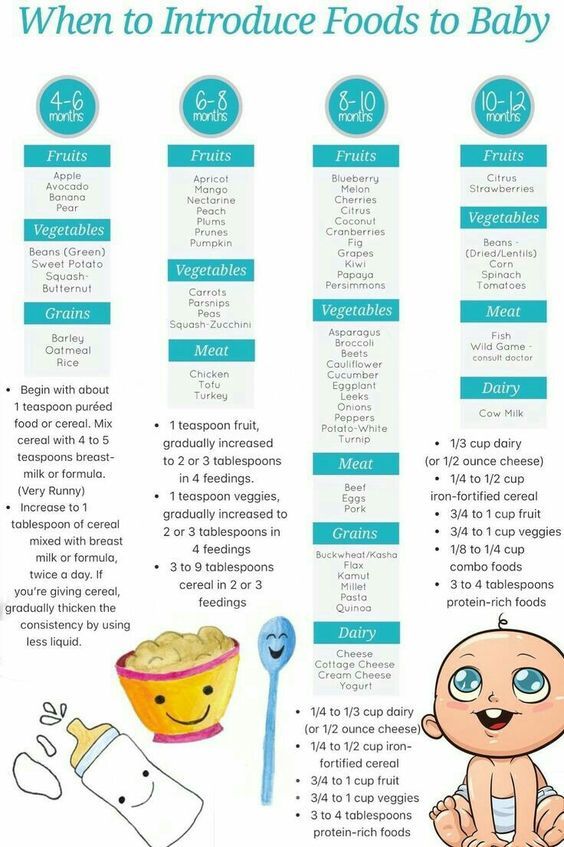 “Table foods” refers to foods the rest of the family eats at meal times. Table foods are the next step after baby has mastered baby foods and is developmentally ready for more chewing, texture, and flavor.
“Table foods” refers to foods the rest of the family eats at meal times. Table foods are the next step after baby has mastered baby foods and is developmentally ready for more chewing, texture, and flavor.
Baby food and table foods are for learning new flavors and textures as well as learning to chew and eat from a spoon, with fingers, and to start self-feeding with utensils. Let them be messy and feed themselves. It is how they learn!
- WIC does not provide solid foods until 6 months, an age most babies are developmentally ready to try solids.
- WIC provides baby food until 12 months of age.
Get more great breastfeeding information here!
Formula-fed Baby
Baby will start to consume less formula as they eat more baby food and table foods. It is important to continue providing formula through 12 months of age if not breastfeeding.
Formula is still the main source of nutrition. Continue to offer formula on demand. On average, baby will drink 24-32 ounces total per day (about 3-4 8oz bottles per day)
Baby food and table foods are more for learning new flavors and textures as well as learning to eat from a spoon, with fingers, and to start self-feeding with utensils.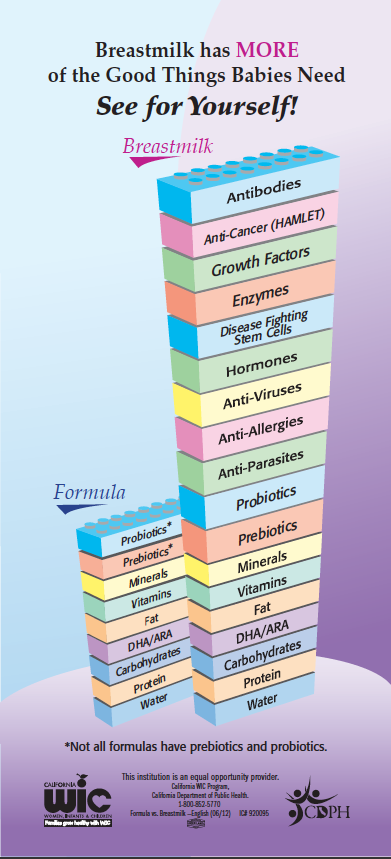
- Table foods are referring to foods the rest of the family eats at meal times. Table foods are the next step after baby has mastered baby foods and is developmentally ready for more chewing, texture, and flavor.
- Baby food is offered on your WIC package until 12 months of age.
Cow’s Milk & Other Liquids
Never give cow’s milk before 12 months. Why?
- Cow’s milk has too much protein, calcium, phosphorus, sodium, chloride, and potassium
- Cow’s milk lacks key nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin E, linoleic acid, iron, and copper
- Too much protein and minerals are hard on your baby’s kidneys, can cause dehydration, and it is hard for baby to digest.
- Cow’s milk can cause bleeding from the intestinal tract.
- Bleeding caused by cow’s milk increases your baby’s chance of becoming anemic (or low in iron).
At 12 months, whole cow’s milk can be offered until 24 months. See Feeding Guide for 1-2 year old for more information.
Water
- Water can be introduced from a cup, not a bottle at about 6 months.
- Offer a small amount of drinking water once solid foods are introduced to help babies get familiar with the taste. Just a few sips at meal times is all it takes.
- Drinking water at this age is more to practice using a cup than for nutritional needs. Let baby practice when he shows signs of readiness.
Other liquids
- Never give honey, syrup, kool-aid, pop, juice, or any sweetened drink to an infant.
- Juice is not recommended for babies less than 12 months of age.
No Honey Before 12 Months
Honey, including products that have honey cooked or baked in it, should not be fed to infants younger than 12 months due to risk of infant botulism.
- Foods cooked or baked with honey not heated to a certain temperature may still contain viable spores. When an infant eats foods with these invisible spores, the spores can produce a toxin that may cause infant botulism.
- Botulism can result in death.
- A child over 12 months can destroy the small amount of spores in honey, but an infant cannot.
Feeding Abilities
At 6-7 months, baby will:
- Use the whole hand or palm to pick up foods
At 8-9 months, baby will:
- Use their fingers to pick up foods.
- Reach for spoon to start spoon feeding themselves, may need help
- Can drink from a cup that is held or may begin to hold a cup
Introducing Food
Introduce foods around 6 months of age when showing signs of readiness.
Signs of Readiness
- Holds neck steady
- Sits without support
- Opens mouth when food is offered
- Draws in lower lip when spoon is removed from mouth
- Keeps food in mouth and swallows it
- Reaches for food showing interest
Starting solids too soon can…
- Cause choking
- Be hard for baby to digest
- Prevent baby from getting enough breast milk or formula for best growth
Food can be offered in different ways.
- Baby-Led Weaning method (also known as Baby-Led Feeding)
- Offering pureed baby foods
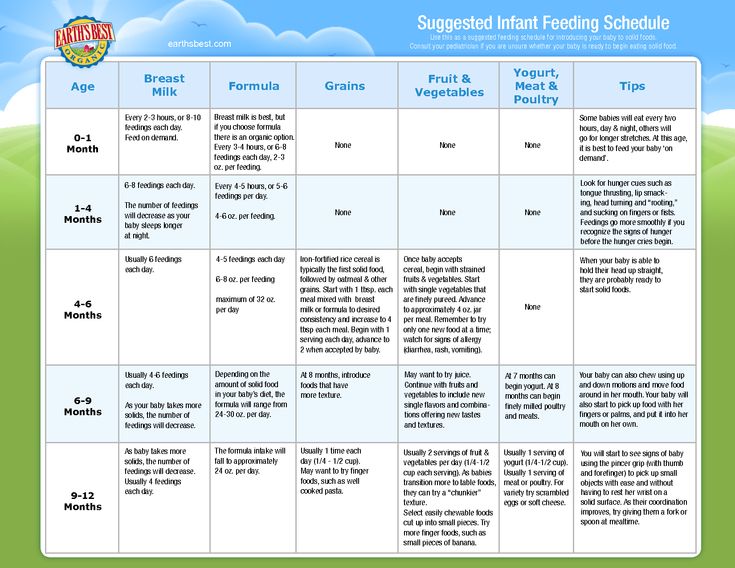
| 0-6 months | Breast Milk | 8-12 feedings on demand. Gradual decline in feedings at 4-6 months. | Feed on demand. Refrain from watching the clock. |
|
| Iron-Fortified Formula | 2-3 oz (increasing to consume around 32 oz at 6 months) | 6-8 feedings | ||
| 6-7 months | Breast Milk | Gradual decline in feedings. Continue feeding on demand. Continue feeding on demand. | Feed on demand. Refrain from watching the clock. |
|
| Iron-Fortified Formula | 6-8 oz (consuming 24-32 oz) | 3-5 feedings | ||
| Grains Infant cereal, bread, crackers | 1-2 Tbsp | 1-2 times per day | ||
| Vegetables AND Fruit Plain, strained, pureed, mashed | 1-2 Tbsp of vegetables 1-2 Tbsp of fruit | 1-2 times per day for vegetables 1-2 times per day for fruit | ||
| Protein Eggs, meat, poultry, fish, cheese/yogurt legumes; Plain, mashed, pureed | 1-2 Tbsp | 1-2 times per day | ||
| 8-12 months | Breast Milk | Gradual decline in feedings.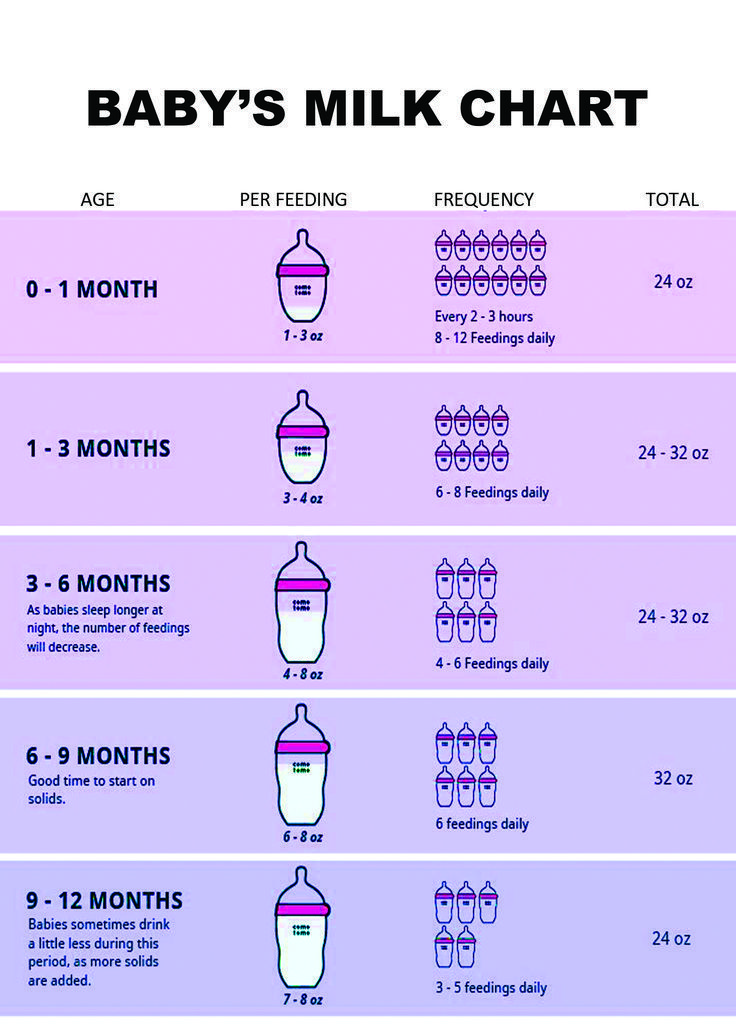 Continue feeding on demand. Continue feeding on demand. | Feed on demand. Refrain from watching the clock. |
|
| Iron-Fortified Formula | 6-8 oz | 3-4 feedings (6-8 oz each consuming 24 ounces) | ||
| Grains (Infant cereal, bread, crackers) | 2-4 Tbsp | 1-2 times per day | ||
| Vegetables AND Fruit (ground, finely chopped, diced) | 2-3 Tbsp of vegetables 2-3 Tbsp of fruit | 2-3 times per day for vegetables 2-3 times per day for fruit | ||
| Protein (meat, poultry, fish, eggs, cheese, yogurt, legumes; ground, finely chopped, diced) | 1-2 Tbsp | 1-2 times per day |
*Source: WIC Works Infant Nutrition and Feeding Manual.
Feeding Tips for the 6-12 month old
- At any time between 6-12 months, daily amounts will vary. Never force your baby to eat all his food or finish a bottle. Baby will know when he is full and done eating! Look for signs of fullness.
- Baby’s tummy is small. It is important to feed healthy foods first.
- Less healthy food choices like cookies, chips, and candy can be a choking hazard but also do not give baby what is needed for proper growth and development.
- Offer fruit for dessert. Babies do not need desserts.
- Buy plain foods. Babies do not need added salt and sugar.
- Table foods should be soft and easy to chew. See the Choking section.
- A relaxed, pleasant atmosphere is an important part of feeding children of all ages. Be patient and give them time to practice. It will be messy but have fun with it!
- Let your baby sit at the table with the family!
- Always stay with baby when he is eating.
- Offer more breast milk, formula, or water in the cup as baby gets closer to age 1.
 This will help with weaning from the bottle soon after their first birthday. See section on Weaning: Breastfed Baby and Weaning: Formula-Fed Baby.
This will help with weaning from the bottle soon after their first birthday. See section on Weaning: Breastfed Baby and Weaning: Formula-Fed Baby. - Wipe baby’s gums and teeth with a soft damp cloth after meals. This will keep baby’s gums healthy.
- Wash your hands and baby’s hands with soap before feeding. Wash the high chair with warm soapy water after baby eats.
- See section on Food Safety to learn about how to safely handle and prepare food for you and your family.
- See section on Food Allergies to learn about the newest recommendations on how to best prevent food allergies from forming in children.
Sources: Healthy Eating Research, USDA Infant Nutrition & Feeding – A Guide for Use in WIC
This post was last updated on September 1st, 2022 at 2:39 PM
This institution is an equal opportunity provider.
Kentucky formula substitutions | JPMA Inc.

New Kentucky WIC Temporary Options Due to Similac Formula Recalls:
- You can contact your WIC clinic to find out how to replace your child's formula with a large (about 30 ounce) jar of Similac Formula. If you receive eWIC benefits for a larger can, you can temporarily substitute similar formulas (Enfamil, Good Start, Kroger, Comfort, Walmart Parent Choice, Meijer, etc.) if your child's can size is not on the store shelf. .
- See TEMPORARY selection for large powder jars in the recipe table.
- To do this, you must contact your WIC clinic if your clinic has not yet changed your benefits.
- Some stores will not be able to take advantage of these benefits until Saturday, February 26th. th .
- You can contact your WIC clinic to find out how to change the size of your infant formula jars to medium (about 19-25 oz.). If you receive eWIC benefits for medium cans, you can temporarily replace them with similar formulas (Enfamil, Good Start, Kroger, Comfort, Walmart Parent Choice, Meijer, Tippy Toes, etc.
 ) if your child's cans do not fit. size. shop shelf.
) if your child's cans do not fit. size. shop shelf. - See TEMPORARY Medium Powder Jars in the formula table.
- See TEMPORARY choice for medium (20-25 oz) powder cans with soy formula
- To do this, you must contact your WIC clinic if your clinic has not yet changed your benefits.
- If you have current eWIC benefits for Similac Advance or Similac Sensitive 12.4/12.5 oz, you will be able to temporarily replace the equivalent Store branded formula. (Meijer or Walmart Parent Choice) , if your child's Similac jar size is not on the store shelf.
- See 12.4oz and 12.5oz INTERIM options. Similac Powder Cans of Formula Table.
- See TEMPORARY choice for stores Hypoallergenic powder in jars with formula
- You do not need to go to your WIC clinic to do this.
- Some stores will not be able to take advantage of these benefits until Saturday, February 26th.
- Temporarily added imported formula
- See AAP Helpful Tips for Preparing Imported Infant Formula in English and Spanish
- See Imported temporary selection formulas
Important Recall Information:
- To learn more about Similac Recall and determine if you remember the formula, visit www.
 Similacrecall.com
Similacrecall.com - If you have a Similac formula that is Not remembered, you can continue to use that formula.
- If you have Similac formula comes to mind:
- Do Do not feed recalled formula to your infant/child
- Parents and caregivers of infants who have used recalled formula and are concerned about their child's health should contact their child's physician. If your child becomes ill, you must notify your child's primary care physician and seek medical attention for your child immediately.
- Never dilute infant formula, prepare or feed infants homemade formula. Avoid buying imported mix through online sales as it can be unsafe.
- Do Do not discard the recalled formula bottle, you will need it to return to the store, Similac or clinic.
- You may return recalled opened and unopened formula cans to the store for an exchange or a refund/store credit. Contact Similac at www.
 Similacrecall.com or return your formula to a WIC clinic for a replacement benefit.
Similacrecall.com or return your formula to a WIC clinic for a replacement benefit. - If your child is on Alimentum, you may be given ready-to-drink formula or other formula by prescription.
- If your infant is on Elecare, you will need a new prescription from your doctor for the appropriate formula before WIC can change your infant/child's benefits.
- If your child is on Similac Advance, Similac Spit Up, Similac Total Comfort, or Similac Sensitive, you may be given a new pack of liquid concentrate, ready-to-eat food, a different brand of formula, or a different size jar, or you may be able to temporarily purchase store branding formula. See information above.
Infant Formula Feeding and Food Safety Tips
- Check the expiration date on the formula can and check the lot number to make sure the formula is not recalled.
- If your water comes from a cistern or well, it may not be safe for your child.
 Ask your local health department about testing your water.
Ask your local health department about testing your water. - Sterilize the water for the first 3 months. Boil water for 1 minute. Allow the water to cool to body temperature before mixing it into the formula. The water should not contain fluoride additives for the first six months.
- Wash hands, surfaces and use clean bottle to prepare concentrate and powder mixture as directed on can.
- The prepared mixture should be used immediately or stored in the refrigerator. The formula will keep up to 2 days if refrigerated.
- Never use a microwave oven to warm bottles. It can become very hot and burn the child's mouth.
- Any formula remaining in the bottle after feeding should be discarded.
- Hold your baby upright while feeding and tilt the bottle to ensure a good flow of formula.
Click here for 12 oz. small jar options
Click here to see branded hypoallergenic powder jars in store.
Click here to view medium jar formula options0006
Click here to see formula options for large cups
Click here to view imported formulas
very happy event. However, along with the joy of parents, many more questions arise. After all, it is so important that the baby grows up healthy and actively develops. One of the first such questions is usually: "How much does a newborn eat per feeding?" It would seem that feeding is such a natural process that it should not cause difficulties. However, most mothers are concerned that the baby does not have enough milk or, on the contrary, he overeats. How to strike a balance? Let's talk about it in this article.
Breastfeeding is good for both the baby and the mother:
- it helps the baby to get the substances necessary for growth, development and immunity and simply satisfy hunger;
- promotes active contraction of the woman's uterus (under the influence of sucking movements) and a faster recovery process after childbirth.

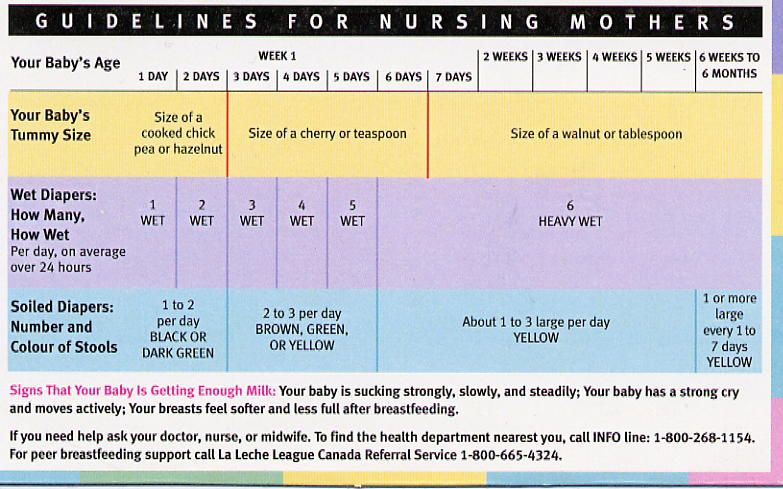
About colostrum
Newborns eat little, their sucking reflex is just developing and is beginning to be put into practice. In addition, a woman's milk is not produced immediately. In the mammary glands at the end of pregnancy and in the first hours after childbirth, colostrum is formed. This is not exactly milk, it even outwardly differs from mature milk, and in its chemical composition it is similar to blood. This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily.
Read also: Complementary foods for artificial feeding
Consumption rates
This is important!
A mother should not worry that her baby was hungry, even if she breastfed him 10 times, but it seems that he did not eat almost a drop. The size of the stomach of a newborn is very small, so only about 10 ml is eaten per feeding. Thus, for the whole day the baby can drink up to 100 ml.
Thus, for the whole day the baby can drink up to 100 ml.
On average, milk arrives 3-4 days after birth and its quantity gradually increases. The stomach of the baby also grows. This means that the amount of milk consumed also increases. So, for the first day, a newborn can drink 10 ml per feeding, for the second day - 20 ml, and for the third - 30 ml. But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist.
There is a folk way to determine the rate of consumption of breast milk. You need to multiply the number of days that have passed since the day of birth by 10. But this method is inaccurate and has no scientific confirmation.
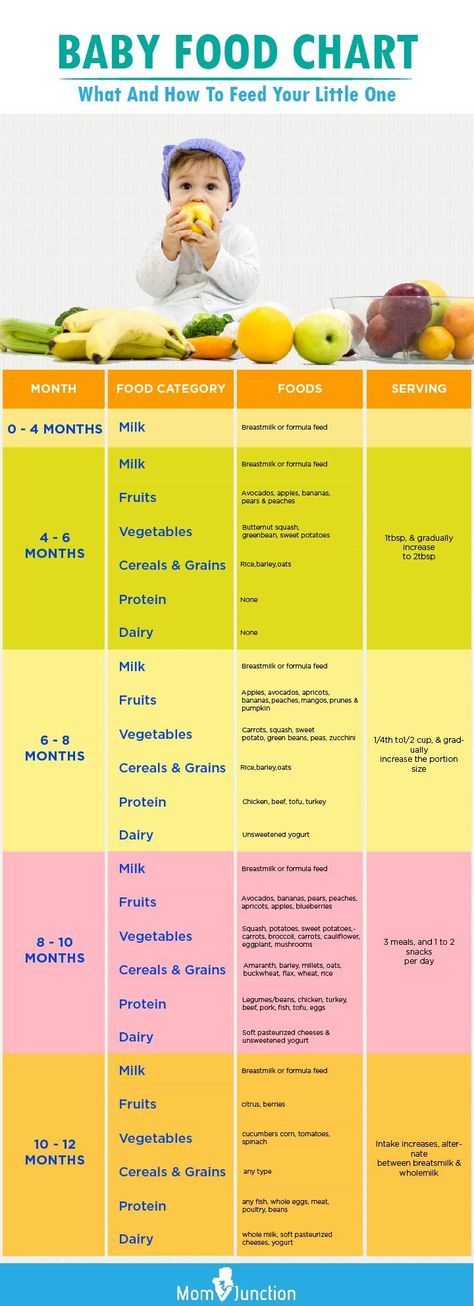
So how much should a newborn eat per feeding? The table shows the daily and one-time volume of milk by months for children under 1 year old.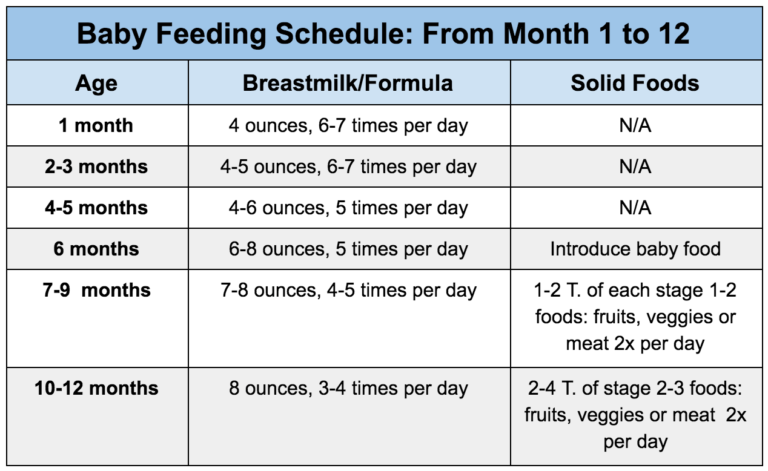
| Child's age | Molo volume for one feeding (ml) | Milk rate per day (ml) |
| 3-4 days | 9000 9000 9000 | 200-300 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 |
| 1 week | 50–80 | 400 |
| 2 weeks | 9000-1 1/6 of body weight | |
| 4 months | 180–210 | 1/6 of body weight |
| 9000 2-6 - 9000 9000 | 1/7 body weight | |
| 7–12 months | 210–240 | 1/8–1/9 body weight | 6
It is not necessary breastfeeding, complementary foods are introduced at about 6 months. This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult food.
This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult food.
How to calculate the amount eaten
In terms of measuring the amount eaten, formula feeding seems to be just perfect. Here is a bottle with a scale, here is water, here is a measuring spoon. However, in terms of its benefits, formula milk will never be compared with breast milk. And besides, making measurements is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. Babies just need to be weighed before and after feeding on a baby scale. To ensure the accuracy of the result, you need to weigh several times a day. If nothing threatens the health of the baby, he does not look thin and pale, develops according to age, and the mother has enough milk, then monthly weighing in the clinic is usually enough.
Feeding schedule
For breastfed babies, there is a rule - to put the baby to the breast on demand. Previously, it was believed that it was necessary to maintain an interval of 3 hours, but now pediatricians agree that the breaks between feedings can be 1.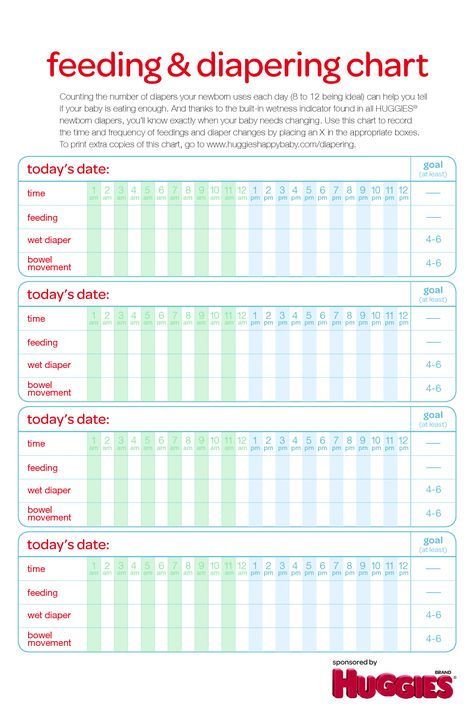 5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
Video: Does a child get enough food in the first months of life?
Author: pediatrician, Ph.D. Komarovsky E.O.
The duration of one feeding is usually 15-30 minutes. Although there are deviations from the norm. For example, a woman has a lot of milk, and the child is full in 5-10 minutes. Or, on the contrary, there is not enough milk, and the baby can suck out the remains for a long time. Some babies just enjoy suckling and use their mother's breast as a pacifier.
Things to consider
At first, mother and baby are just getting used to the changes that are taking place, so the feeding regimen may not be ideal. However, you should adhere to the following rules.
- In the first couple of weeks, a woman needs a lot of dedication, because the interests of the child in the matter of satisfying hunger come to the fore.
 You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night.
You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night. - If there is any doubt that the baby is undernourished or overeating, it is best to start monitoring the frequency of feedings. So, you need to mark the time at which the baby was really hungry, mark the intervals between feedings. This information may also be useful at the appointment with the pediatrician.
- It is impossible to establish a clear feeding regimen, as with artificial feeding, especially in the first weeks after birth. Maintaining intervals of more than 2–3 hours during the day and 3–4 hours at night is highly discouraged.
- Do not try to force feed your baby. He is still too young to realize the need for food, and is guided solely by his feeling of hunger. If the baby persistently refuses the breast, you need to try to offer him to eat a little later. If the interval is too large, it is better to contact a specialist for advice.
- It is important that your baby latch on correctly.
 His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples.
His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples. - Soothers and bottles are not recommended for breastfed babies. Such products can reduce the intensity of sucking movements.
- It is better to give the baby only one breast at a time. In the mammary gland, fore milk is formed, with which the baby quenches his thirst, and hind milk, with which he "eats up", since it is more nutritious in composition.
- Hold the baby upright for about 10 minutes after each feed. This helps to free the tummy from air and excess milk.
As a rule, with a normal feeding regimen and a sufficient amount of milk from the mother, by a month the baby's weight increases by 500–600 g. Now consider the situation when the mother does not have the opportunity to breastfeed the baby. In this case, it is necessary to choose a quality milk formula that will cover the nutritional needs. The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes).
The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes).
Consumption rates
Almost all known mixtures require 8 or 7 meals a day with an interval of 3 hours. Night feedings are also included. When the baby grows up a little, it will be possible to skip them and sleep 5-6 hours until morning. With regard to formula milk, the principle of feeding on demand is not suitable. Therefore, it is necessary to observe both the dosage indicated by the manufacturer and the regimen.
It will not be difficult to calculate how much the baby eats for feeding.
| Age | daily milk rate from body weight | |
| 10 days - 1.5 months | 9000 1/5 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 1 months | 1/6 |
| 4–6 months | 1/7 | |
| 6–8 months | 9000 | 1/9 |
For example, a baby is 2 months old and weighs 4800 grams. According to the table, we divide 4800 by 6 and get the daily rate - 800 ml of milk formula per day. To calculate the volume of one feeding, divide 800 by 6 (number of feedings per day). Thus, the child eats about 130 ml of formula at a time.
Not everyone can find the right mixture right away, but do not despair. Even with allergies, digestive problems, cow's milk protein intolerance, you can find a suitable product, but only under the strict supervision of a doctor.