3 month old baby bottle feeding schedule
3- and 4-month-old feeding schedules
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby Names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
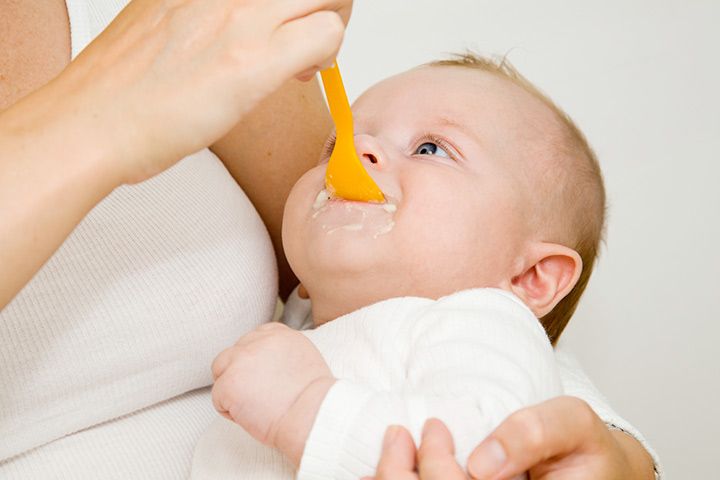
At 3 and 4 months old, babies are still eating frequently throughout the day but are capable of going for longer stretches at night. Breastfeeding parents can expect their baby to continue to eat often, anywhere from eight to 12 times a day. If you're formula-feeding your little one, they'll be ready for 4- to 6-ounces bottles six to eight times a day. As your baby grows out of the newborn stage, you may notice them starting to develop a more predictable schedule for feeding, sleep, and play.
Photo credit: iStock.com / Hiraman
At 3 and 4 months old, your baby may be naturally falling into a schedule. You can encourage them by adding more consistency to their days. Keep their naptimes, mealtimes, and bedtime routine about the same from day to day. Babies are awake and alert more now, making it a good time to start getting them on a more predictable schedule.
It can be a big help to see what other moms and dads are doing. Below, you'll find several sample schedules based on those of real parents and reviewed by a pediatrician on our Medical Advisory Board.
As you're creating a schedule for your baby, here are a few things to keep in mind:
- The schedule for a formula-fed baby may look different than the schedule for a breastfed baby. At 3 to 4 months old, your formula-fed baby will have around 32 ounces of formula each day over five to eight feedings of 4 to 6 ounces each. (See whether your baby is getting enough formula.)
- If you're breastfeeding, your baby will eat five to eight times a day, every two or three hours. (Here's how to tell whether your baby is getting enough breast milk.
 )
) - By focusing on longer feedings every three to four hours during the day, you can start encouraging your baby to sleep for longer stretches at night. Babies can go through the night without a feeding as early as 3 months, but it more commonly happens later, around 5 or 6 months
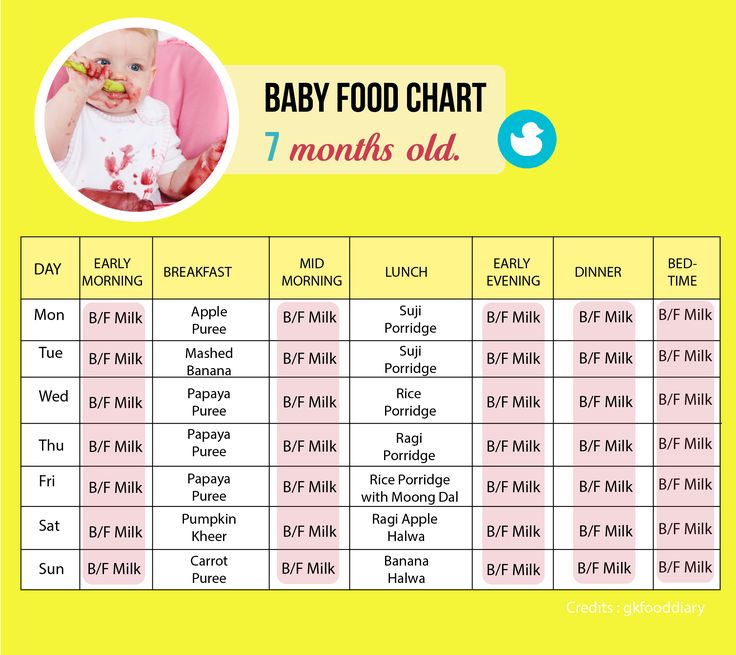
Sample 3-month-old feeding schedule
7 a.m.: Nurse.
8 a.m.: Daycare drop off; playtime.
9:45 a.m.: 4 ounces of expressed breast milk.
10 a.m.: Naptime. (Mom pumps at work.)
12 p.m.: Playtime.
Advertisement | page continues below
12:45 p.m.: 4 ounces of expressed breast milk.
1:30 p.m.: Naptime. (Mom pumps again.)
2:30 p.m.: Playtime.
4 p.m.: 4 ounces of expressed breast milk. (Mom pumps again.)
4:30 p.m.: Naptime.
5:15 p.m.: Daycare pickup.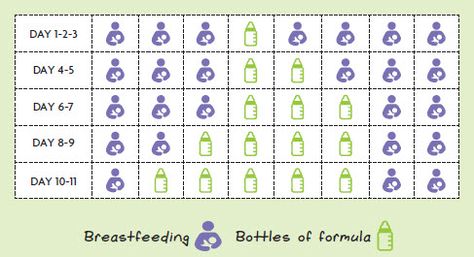
5:45 p.m.: Playtime.
6:30 p.m.: Nurse.
6:45 p.m.: Playtime and tummy time.
7:30 p.m.: Nurse, then bedtime routine.
12 a.m.: Nurse.
4 a.m.: Nurse.
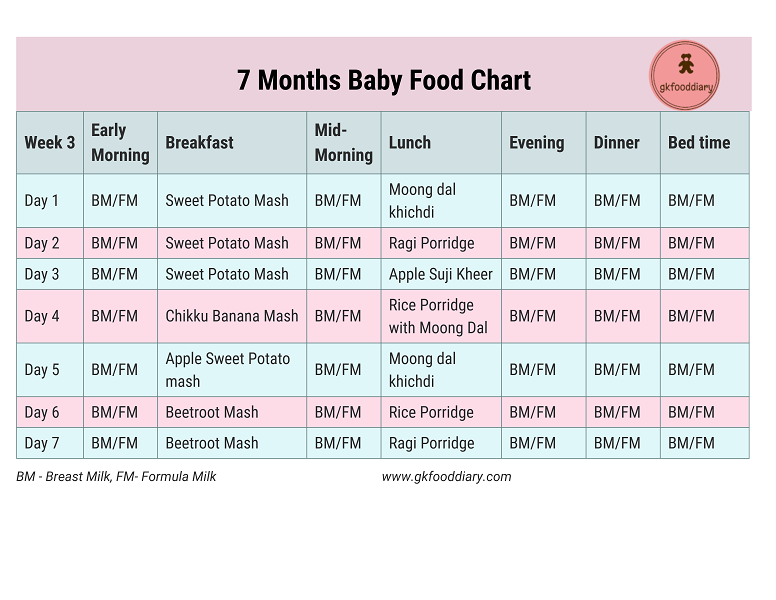
Sample 4-month-old feeding schedule
5 a.m.: Nurse, then back to sleep.
7 a.m.: Nurse and back to sleep again.
9 a.m.: Wake up.
10 a.m.: Nurse, then tummy time and playtime.
12 p.m.: Naptime.
2 p.m.: Nurse.
2:30 p.m.: A walk in the stroller.
3 p.m.: Short nap.
4 p.m.: Nurse.
5 p.m.: Playtime.
7 p.m.: Bedtime routine – bath, read a few books and sing a lullaby.
7:30 p.m.: Nurse and bedtime.
1 a.m.: Nurse, then back to bed.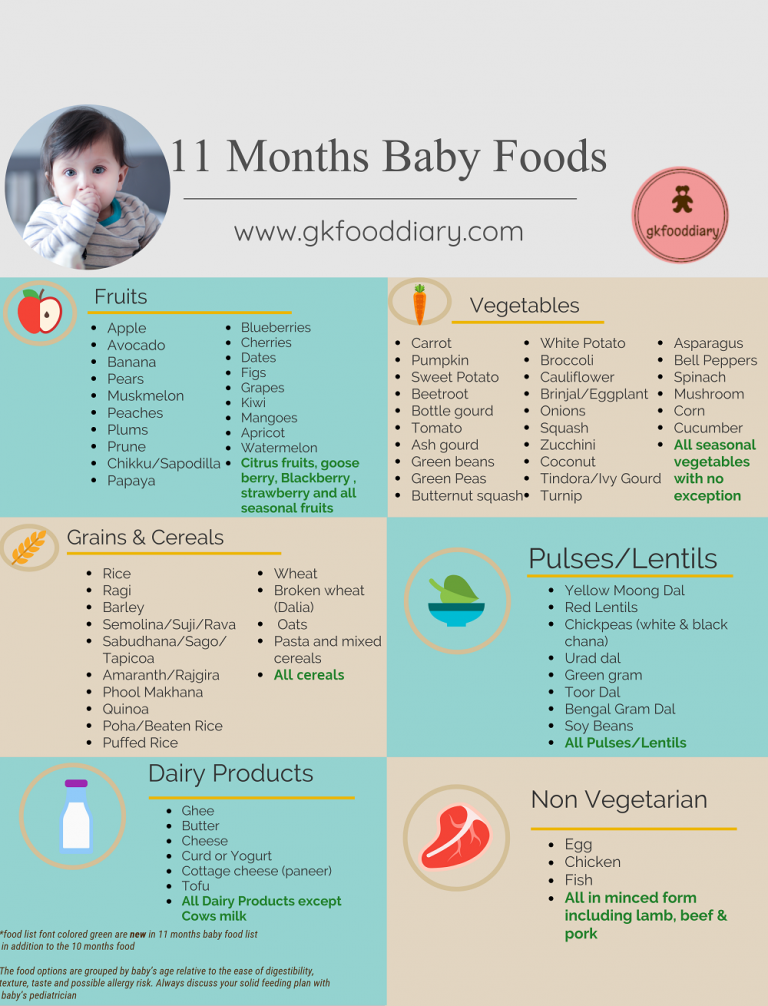
Tips for feeding your 3- or 4-month-old
You may be breastfeeding exclusively, pumping and breastfeeding, exclusively pumping, formula-feeding, or supplementing with formula. No matter how you're feeding your 3- to 4-month-old baby, here are some tips for helping it go smoothly.
- If you're breastfeeding, continue to nurse or pump often to keep your milk supply up. Offer both breasts at each feeding to keep signaling to your body that it needs to make enough milk to keep up with your baby's hunger.
- It's hard to overfeed a breastfeeding baby, but at 3 to 4 months it's also okay to encourage them to go for slightly longer stretches between meals. By focusing on longer feedings, you can fill their belly and try to avoid your baby "snacking" all day long.
- Eat plenty of nutritious foods to keep yourself fueled for feeding your baby. Breastfeeding moms need more calories (450 to 500 extra calories each day), and dieting can decrease your milk supply.
- If your baby is nursing exclusively but you're ready to introduce a bottle, it can sometimes be a challenge.
 Here are some tips for giving your breastfed baby a bottle.
Here are some tips for giving your breastfed baby a bottle. - If you're exclusively pumping and you notice a sudden drop in milk supply, try power pumping. The idea is to pump frequently over an hour to increase supply. One commonly suggested power pumping schedule is pump for 20 minutes, rest for 10 minutes, pump for 10 minutes, rest for 10 minutes, pump for 10 minutes. You can power pump once or twice a day.
- Practice paced bottle feeding if your baby is drinking formula or breast milk from a bottle. By feeding your baby in a more upright position and taking regular breaks to burp them, you allow them more control over how quickly and how much milk or formula they drink.
- Keep your bottle-fed baby safe from foodborne illness by practicing safe bottle feeding. Wash your bottles thoroughly between feedings and be sure you're storing formula safely. Expired or compromised formula can be dangerous for babies, so double-check the label before feeding your baby from a new container of formula.
Learn more:
- Your 3-month-old baby's growth and development
- Your 4-month-old baby's growth and development
- 3-month-old sleep guide
- 4-month-old sleep guide
- When can my baby start sleeping through the night?
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Mary Sauer
Mary Sauer is a freelance parenting and health writer living in Kansas City. She is a mom of four and loves to hike with her kids, read, and knit. Cooking a complicated meal her kids probably won't eat is one of her favorite pastimes.
Advertisement
Tips for the First Year
Every baby may get hungry on their own unique schedule. That said, most infants in the first months of life will eat every 2-4 hours, depending if they are nursing or drinking formula. Once they eat solids, they’ll gradually drink less.
Eat, sleep, pee, poop, repeat. Those are the highlights of a day of the life of a brand-new baby.
And if you’re a new parent, it’s the eating part that may be the source of many of your questions and worries. How many ounces should your baby take? Do you wake a sleeping baby to eat? Why do they seem hungry all the time? When can your child start solids?
How many ounces should your baby take? Do you wake a sleeping baby to eat? Why do they seem hungry all the time? When can your child start solids?
Questions abound — despite Grandma’s insistence, the answers have changed since you were a tot. It’s now recommended that newborns, even formula-fed ones, eat on demand (consider it good preparation for the teenage years) and that babies wait to start solid foods until they’re 4 to 6 months old.
On day one of life, your baby’s stomach is the size of a marble and can only hold 1 to 1.4 teaspoons of liquid at a time. As your baby gets older, their stomach stretches and grows.
It’s hard (or impossible, really) to know how much milk your baby is taking in while breastfeeding. But if you’re bottle feeding due to any number of valid reasons, it’s a bit easier to measure.
Here, from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), a typical feeding schedule for bottle-fed babies.
| Age | Ounces per feeding | Solid foods |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 2 weeks of life | . 5 oz. in the first days, then 1–3 oz. 5 oz. in the first days, then 1–3 oz. | No |
| 2 weeks to 2 months | 2–4 oz. | No |
| 2–4 months | 4-6 oz. | No |
| 4–6 months | 4–8 oz. | Possibly, if your baby can hold their head up and is at least 13 pounds. But you don’t need to introduce solid foods yet. |
| 6–12 months | 8 oz. | Yes. Start with soft foods, like one-grain cereals and pureed vegetables, meats, and fruits, progressing to mashed and well-chopped finger foods. Give your baby one new food at a time. Continue supplementing with breast or formula feedings. |
Every baby is unique — but one thing that’s pretty consistent is that breastfed babies eat more frequently than bottle-fed ones. That’s because breast milk is easily digested and empties from the stomach a lot quicker than formula.
Breastfed babies
There’s no rest for the weary. According to La Leche League International, you should begin nursing your baby within 1 hour of birth and provide about 8 to 12 feedings daily in the first few weeks of life (yeah, we’re exhausted for you).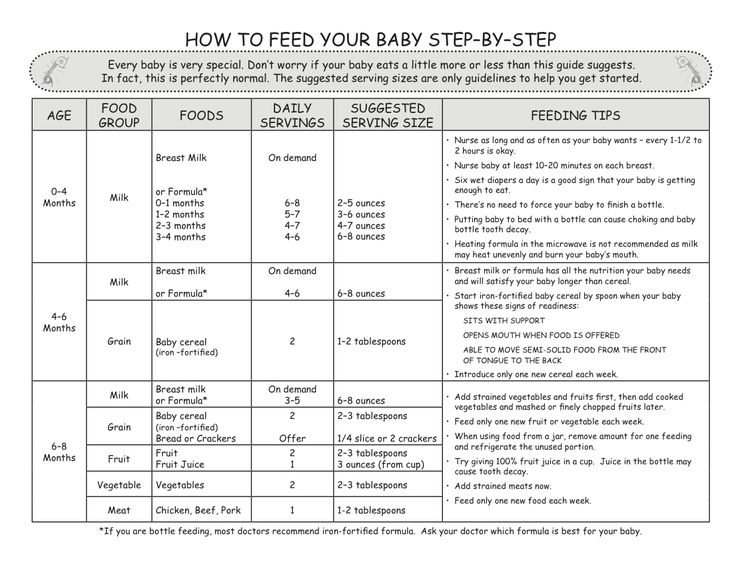
At first, it’s important not to let your baby go more than 4 hours without feeding. You’ll likely need to wake them up if necessary, at least until breastfeeding is well established and they’re gaining weight appropriately.
As your baby grows and your milk supply amps up, your baby will be able to take in more milk in less time at one feeding. That’s when you might start to notice a more predictable pattern.
- 1 to 3 months: Your baby will feed 7 to 9 times per 24 hours.
- 3 months: Feedings take place 6 to 8 times in 24 hours.
- 6 months: Your baby will feed around 6 times a day.
- 12 months: Nursing may drop to about 4 times a day. The introduction of solids at about 6 months helps to fuel your baby’s additional nutritional needs.
Keep in mind that this pattern is just one example. Different babies have different paces and preferences, along with other factors that influence the frequency of feedings.
Bottle-fed babies
Like breastfed babies, bottle-fed newborns should eat on demand. On average, that’s about every 2 to 3 hours. A typical feeding schedule may look like this:
On average, that’s about every 2 to 3 hours. A typical feeding schedule may look like this:
- Newborn: every 2 to 3 hours
- At 2 months: every 3 to 4 hours
- At 4 to 6 months: every 4 to 5 hours
- At 6+ months: every 4 to 5 hours
For both breastfed and bottle-fed babies
- Don’t give liquids other than formula or breast milk to babies under a year old. That includes juices and cow’s milk. They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup.
- Don’t add baby cereal to a bottle.
- It can create a choking hazard.
- A baby’s digestive system isn’t mature enough to handle cereal until about 4 to 6 months of age.
- You could overfeed your baby.
- Don’t give your baby any form of honey until after their first birthday. Honey can be dangerous for a baby, occasionally causing what’s called infant botulism.

- Do adjust your expectations based on your baby and their unique needs. Premature babies are likely to follow feeding patterns according to their adjusted age. If your baby has challenges like reflux or failure to thrive, you may need to work with your doctor on the appropriate feeding schedule and amount they should be eating.
Schedules are the holy grail of every parent. Your child will naturally start to fall into a feeding pattern as their tummy grows and they can take in more breast milk or formula at one sitting. This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
For now, though, focus on learning your baby’s hunger cues, such as:
- rooting around your chest, looking for a nipple.
- putting their fist in their mouth
- smacking or licking their lips
- fussing that can escalate quickly (don’t wait until your baby’s hangry to feed them)
Once your baby is a few months old, you may be able to introduce a sleep/feed schedule that works for you.
Let’s say, for example, your 4-month-old wakes every 5 hours for a feeding. That means if you feed at 9 p.m., your baby wakes around 2 a.m. But if you wake and feed the baby at 11 p.m., just before you go to bed, they may not rouse until 4 a.m., giving you a decent chunk of nighttime winks.
In general, if your baby seems hungry, feed them. Your baby will naturally eat more frequently during growth spurts, which typically occur around 3 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Some babies will also “cluster feed,” meaning they’ll feed more frequently during certain periods and less at others. For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
Worried about overfeeding? While this isn’t really possible to do with an exclusively breastfed baby, you can overfeed a baby who’s taking a bottle — especially if they’re sucking on the bottle for comfort. Follow their hunger cues, but talk to your pediatrician if you’re worried your little one may be overeating.
Follow their hunger cues, but talk to your pediatrician if you’re worried your little one may be overeating.
Your baby is probably ready for solids if they’re 4 to 6 months old and:
- have good head control
- seem interested in what you’re eating
- reach for food
- weigh 13 or more pounds
Which food to start with? The AAP now says it doesn’t really matter much in what order you introduce foods. The only real rule: Stick with one food for 3 to 5 days before offering another. If there’s an allergic reaction (rash, diarrhea, vomiting are common first signs), you’ll know which food is causing it.
As your baby grows, move from pureed baby food to ones that have more texture (for example, mashed banana, scrambled egg, or well-cooked, chopped pasta). This generally happens around 8 to 10 months of age.
Your supermarket offers a variety of baby food products, but if you want to make your own, keep it sugar and salt free. Additionally, at this stage, don’t feed your baby anything that could be a choking hazard, including:
- hard foods, such as popcorn or nuts
- hard, fresh fruits, like apples; cook to soften or chop into very small pieces
- any meat that isn’t well cooked and very well chopped (this includes hot dogs)
- cheese cubes
- peanut butter (though talk to your pediatrician about this one — and the benefits of introducing diluted peanut butter before the age of 1)
As your baby nears their first birthday, they should be eating a variety of foods and taking in about 4 ounces of solids at each meal. Continue to offer breast milk or formula. By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
Continue to offer breast milk or formula. By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
Oh yeah, and buy some stock in a company that makes stain-fighting laundry detergent. It’ll pay for college.
Babies aren’t cookie cutter. Some will gain weight easily, while others will have problems. Things that can affect a baby’s weight gain include:
- having a birth defect like a cleft lip or palate, which creates problems feeding
- having a milk protein intolerance
- being premature
- being fed with a bottle versus the breast
A 2012 study of more than 1,800 babies found that the infants who were fed with a bottle — regardless of whether the bottle contained breast milk or formula — gained more weight in the first year than babies who nursed exclusively.
Your baby’s doctor is the best one to advise you on a healthy weight range for your baby.
How, when, and what to feed a baby are top worries of every parent — but there’s good news: Most babies are pretty good judges of when they’re hungry and when they’re full — and they’ll let you know it.
You just need to present them with the right choices at the right time and pay attention to their cues. If you have any questions or concerns, your pediatrician is there to help you along the way.
newborn diet on IV, how to properly feed a baby with formula from a bottle
The desire for a child to grow up strong and healthy is natural for mothers. And the health of a newborn begins with proper nutrition. Mother's milk has always been considered the best option for feeding - the most healthy and nutritious food for infants. However, in some cases, breastfeeding is not possible. And then mixtures come to the aid of mothers.
Contents: Hide
- In what cases is the transition to artificial feeding
- How to choose a mixture of
- Basic artificial feeding rules
- The main errors for artificial feeding
In what cases is required the transition to artificial feeding 9,0002 Medical medical contrasts to breastfeeding.
 There are a number of diseases in which breast milk is prohibited. On the mother's side, these are HIV, an open form of tuberculosis, dangerous infections, and a serious state of health. On the part of the child, these are leucinosis, galactosemia, and individual food intolerance. It is not necessary to take tests after hearing the terrible names of diseases. All newborns are checked in maternity hospitals for their presence. But allergies are not so easy to identify. Many newborns have skin rashes and redness, which may be due to a reaction to an aggressive environment. Only a strict diet for the mother can help here, so that her milk does not contain allergens, monitoring the baby and consulting a doctor.
There are a number of diseases in which breast milk is prohibited. On the mother's side, these are HIV, an open form of tuberculosis, dangerous infections, and a serious state of health. On the part of the child, these are leucinosis, galactosemia, and individual food intolerance. It is not necessary to take tests after hearing the terrible names of diseases. All newborns are checked in maternity hospitals for their presence. But allergies are not so easy to identify. Many newborns have skin rashes and redness, which may be due to a reaction to an aggressive environment. Only a strict diet for the mother can help here, so that her milk does not contain allergens, monitoring the baby and consulting a doctor. Lack of lactation or its complete cessation. This is the second objective reason for transferring a child from breast milk to formula. Lactation does not always come in the right amount and it can be increased. It happens that milk disappears a few days after the birth of the crumbs. This often depends on the individual characteristics of the mother's body. So that the child does not starve, he is first transferred to mixed, and then completely to artificial feeding.
This often depends on the individual characteristics of the mother's body. So that the child does not starve, he is first transferred to mixed, and then completely to artificial feeding.
Insufficient nutritional value of mother's milk. Usually this problem can be solved without resorting to the transition to IoT, but this is not always possible. A woman may have a lot of milk, but it will be like water in both color and consistency. In such cases, doctors give advice to the mother on nutrition in order to increase the fat content of milk and its usefulness. If the milk remains watery, the child stops eating, cries of hunger, loses weight. The only way out in this situation is the transition to the mixture.
Impossibility of regular feeding. Children who, for a number of reasons, are separated from their mother for long periods of time are transferred to artificial feeding: the woman is in a hospital, going to work or study, business trips, etc. If the break in breastfeeding is one-time, then restoring lactation and breastfeeding is still possible . However, more often in such cases, breastfeeding has to be abandoned.
However, more often in such cases, breastfeeding has to be abandoned.
Mother's personal wish. Unfortunately, there are cases when a woman, having every opportunity to breastfeed her baby, refuses to breastfeed for various subjective reasons. In this case, lactation is interrupted, and the baby is transferred to the mixture.
Read also: Newborn weight gain by month
How to choose a formula
If you are going to transfer your baby to artificial feeding, then the first thing you will encounter will be the choice of nutrition. Today there are a large number of different mixtures: adapted and non-adapted, dairy and sour-milk, dry and liquid. There are mixtures against regurgitation, hypoallergenic, for premature babies, etc. How to choose the optimal replacement for mother's milk from such a variety?
- Make your choice only after consulting a pediatrician. The doctor will examine the baby and give all the necessary recommendations.
- Monitor your child.
 When adapting to a new diet, the child may have small rashes, but they disappear if the body begins to absorb the mixture normally. The baby eats with appetite, he has a normal stool and no colic. Otherwise, the mixture must be changed.
When adapting to a new diet, the child may have small rashes, but they disappear if the body begins to absorb the mixture normally. The baby eats with appetite, he has a normal stool and no colic. Otherwise, the mixture must be changed. - If it is necessary to replace the mixture with a thicker formula (anti spit up), choose the same brand of food that was previously used.
- Consider the age of the baby. All mixtures have a gradation by months of life.
- Prefer adapted formulas, they are usually easier to digest
Basic rules for artificial feeding save you a lot of problems.
1. Choose proven blends. This applies not only to the choice of brand, but also to the packaging itself. Look at its integrity, check the expiration date.
2. Observe the storage conditions for opened packaging at home (in a dry and cool place, but in no case in the refrigerator, the mixture must not become damp). Remember that the open mixture is stored for three weeks. After this period, it can no longer be used.
After this period, it can no longer be used.
3. Strictly follow the instructions when preparing meals. It is indicated on the packaging. Water for the preparation of the mixture must be purified and boiled. The optimal temperature for preparing the mixture is 36–37 °C. You can cook food right in the bottle. This is quite convenient, since baby bottles have a volume scale that makes it easier to calculate the right amount of scoops. The mixture must be stirred until completely dissolved, and then cooled to an acceptable temperature so that the baby can drink without burning himself. You can check if the milk is hot by dropping it on your wrist - there the skin is most tender and sensitive. If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child.
4. Sterilize baby dishes. Baby bottles and nipples should be thoroughly rinsed using a special brush so that no food residue remains. You can use children's dishwashing detergents. Do not wash bottles with common cleaning products that you are used to using, no matter how good they are. After washing, be sure to place the dishes in boiling water. This helps to kill harmful bacteria. It is recommended to sterilize children's dishes during the entire first year of a baby's life. Then you can limit yourself to just a thorough wash.
After washing, be sure to place the dishes in boiling water. This helps to kill harmful bacteria. It is recommended to sterilize children's dishes during the entire first year of a baby's life. Then you can limit yourself to just a thorough wash.
5. Hold the bottle in a semi-vertical position when feeding. The milk should completely fill the nipple. This prevents the child from swallowing air. After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in a column for several minutes to avoid spitting up.
6. Monitor the amount of formula consumed and the feeding schedule. Maintaining a balance is extremely important for the healthy and full development of the baby.
- Calculate the amount of formula to be prepared based on the baby's weight. It is body weight, and not the age of the crumbs, that is the main indicator when calculating the daily nutritional intake. You can find out the required volume of the mixture for feeding either at a pediatrician’s appointment, or on your own (it is recommended to use Maslov’s caloric method when calculating).

- Observe breaks between feedings. During the day they should be 3.5 hours, at night - 6. Try not to break the schedule.
- Give your child water. Supplementation with water is a necessity for artificial feeding. Water should be given somewhere in the middle of the interval between feedings or 10-15 minutes after it. Avoid supplementation before meals.
Major mistakes in artificial feeding
Overfeeding. The desire to feed the child is understandable, but in the case of mixtures, feeding must be approached strictly. On artificial feeding, the child is normally gaining weight very well. Excess body weight is an additional burden on the body and health problems. Even an adult can find it difficult to cope with problems from being overweight. What to say about the tiny weak body of a newborn? Follow the diet and control the daily milk intake. Fortunately, you can always see how much the child ate.
Unreasonable mixture change. If the child eats the current mixture well, then it is not necessary to change it. The baby will have to go through a difficult period of adaptation again, and it’s not a fact that his body will accept new food just as well.
The baby will have to go through a difficult period of adaptation again, and it’s not a fact that his body will accept new food just as well.
Use of old mix. The child's food must be fresh. If the child has not finished eating, then literally after half an hour the milk can only be poured out. Milk mixtures are an excellent environment for the life of pathogenic bacteria.
Pet milk feeding. Do you think this is a more natural option than artificial mixtures? This is an erroneous opinion. For a child under one year old, cow or goat milk, even boiled, is strictly prohibited. The composition of such milk is very different from that of women, which can lead to the development of allergies, diseases, problems with the skeletal system in the baby.
If you have any doubts about your baby's nutrition, please consult neonatologists and paediatricians. Do not rush to make decisions without expert advice. After all, nothing is more important than your baby's health.
#Nutrition for babies up to a year
How to bottle feed
Feeding your baby is not only an important process for his healthy growth and development, but also a way to establish close emotional contact with the child and build trusting and loving relationships. The transition from breastfeeding to bottle feeding should be carried out after the mother and the child are fully prepared for this. We are talking about both the moral aspect, and about choosing the right bottle and getting adults the necessary skills so that eating brings only positive emotions and benefits to the baby. In this article, we will talk more about how to properly bottle feed your baby and where to start.
How to prepare your baby for bottle feeding
If this method of feeding is a completely new experience for the baby, or if parents decide to bottle feed their baby from a very young age, slow flow nipples should be preferred. So you protect the child from the possibility of choking while eating. Over time, you can gradually switch to bottles with nipples, which would provide faster and more intense feeding.
So you protect the child from the possibility of choking while eating. Over time, you can gradually switch to bottles with nipples, which would provide faster and more intense feeding.
Feeding bottle selection and daily care
All baby accessories should be kept clean and sterilized regularly and thoroughly.
There are several ways to sterilize dishes:
- select the appropriate mode when using the dishwasher;
- or place the bottle and teat in a vessel of boiling water for 5 minutes.
Before using this method of cleaning the bottle, make sure that the material it is made of can be exposed to high temperatures. Since some types of plastic contain various chemicals in their composition, after sterilization they can become dangerous for their little user. For this reason, experts recommend choosing glass bottles.
The need for thorough cleansing of everything that the baby will touch is caused by the fact that in the first months of life, the child's immune system is just beginning to strengthen. Before sterilizing the teat, it can be cleaned with dishwashing detergent. There are special products for washing children's dishes, without a strong odor and with a safe composition.
Before sterilizing the teat, it can be cleaned with dishwashing detergent. There are special products for washing children's dishes, without a strong odor and with a safe composition.
How to bottle feed your baby
Before starting a meal, mom or dad should wash their hands well with soap and warm running water. Particular attention should be paid to the area between the fingers and under the nails. The hand washing process should take at least 20 seconds. And after carrying out this hygienic procedure, hands should be wiped dry with a paper towel or clean towel.
The next step is to prepare for the meal. If you plan to fill the bottle with formula, then dilute it with water in accordance with the instructions in the instructions. Improper proportions can lead to dehydration or bloating. It should also be remembered that for the preparation of the mixture you need to use only clean drinking water.
Breast milk is the most beneficial for a newborn. Despite this, pediatricians advise breastfeeding babies for as long as possible. Even if the mother is ready to give up breastfeeding, milk can be expressed into a bottle and gradually accustom the baby to the nipple. If, for one reason or another, the mother does not have the opportunity to feed herself, then the only alternative is feeding with a special mixture.
Despite this, pediatricians advise breastfeeding babies for as long as possible. Even if the mother is ready to give up breastfeeding, milk can be expressed into a bottle and gradually accustom the baby to the nipple. If, for one reason or another, the mother does not have the opportunity to feed herself, then the only alternative is feeding with a special mixture.
In the first six months after birth, cow's or goat's milk or its substitute in the form of soy milk should not be included in the baby's diet. Valid options for supporting healthy development of a newborn are breast milk or formula milk only.
What temperature should the bottle filler be? Under no circumstances should the bottle be heated on the stove or in the microwave. If the temperature of the bottle and its filling exceed 37°C, the baby may be burned. It is recommended to use special bottle warmers. If this is not possible, then use the following method:
- put a saucepan on the stove with a little water;
- bring the water to a boil, then remove the pan from the heat;
- place a bottle of milk in a vessel and heat it up to 37◦С;
- check the temperature with a pre-cleaned thermometer or a special device for measuring the temperature of foodstuffs.

You can also check the temperature of the ready-to-use bottle as follows:
- turn the bottle over;
- drip several times into your wrist area.
In this way, you can check not only the temperature of the milk or formula, but also how well the liquid flows out of the bottle. If you have to shake or squeeze the bottle hard to drip, the nipple is blocked and needs to be cleaned out. If, on the contrary, the filler pours out when the bottle is turned over, this means that the nipple is damaged and another nipple should be used to feed the baby, having previously sterilized it.
How to bottle feed your baby lying down
There are several techniques for feeding your baby. However, it is the feeding of the child lying down from the bottle that young parents consider the most comfortable. It is worth noting that eating in this position will only be safe when the baby's head is slightly raised. Otherwise, the child may simply choke.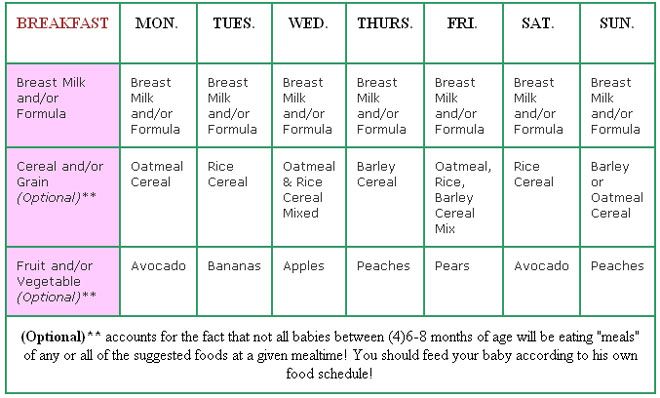 In the prone position, the child should be placed on his arm bent at the elbow. After feeding, you should place the baby in an upright position, taking him in your arms and putting his stomach to your chest.
In the prone position, the child should be placed on his arm bent at the elbow. After feeding, you should place the baby in an upright position, taking him in your arms and putting his stomach to your chest.
Make sure that the feeding bottle is closed correctly: the ring at the connection of the nipple to the bottle must not be too tight. Air must enter the bottle, otherwise a vacuum will be created there, which, in turn, will complicate the consumption of food for the child.
How to bottle feed without spitting up
Since the newborn is not able to fully control the process of feeding, along with milk, he can also take in air. This may be the reason that at one meal the child could not master the planned portion. In view of this, it is recommended to take small breaks during feeding.
As soon as you notice that the baby has stopped sucking on the pacifier, is tired or thoughtful, pick him up and press his face to you, holding his head and back. To help burp excess air, you can make a light massage between the shoulder blades, pat on the back or pope.
To help burp excess air, you can make a light massage between the shoulder blades, pat on the back or pope.
The air will quickly rise up and the baby will burp it without any extra effort. However, you should be prepared for the fact that, along with the air, part of the consumed mixture or milk may also return. Therefore, before taking the baby in your arms, cover yourself with a diaper, because it will be easier to wash it than clothes.
Never leave your baby alone with the bottle or let him fall asleep while using it. After eating, mom or dad must help their child burp. This will help to avoid colic, bloating and other manifestations of stomach discomfort.
Where to buy baby accessories
Without too much modesty, we can say that the online store I Love Mommy is one of the best places to buy nursing products. Our catalogs feature products from world-famous brands, the quality of which you will not have to doubt for a minute. Bottles, baby dishes, pacifiers, baby bibs - all this and much more you can buy for your son or daughter from us at affordable prices in just a few minutes.