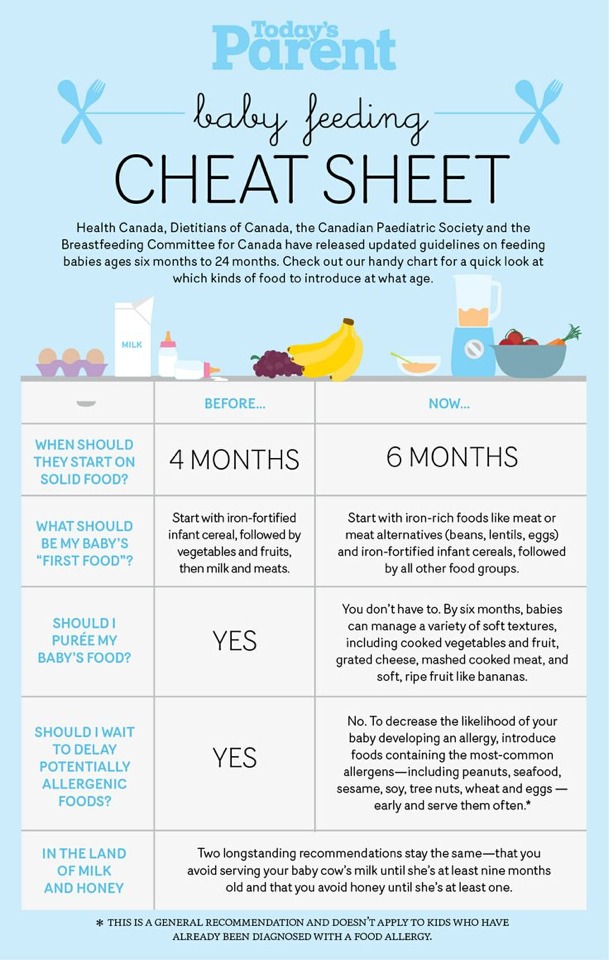
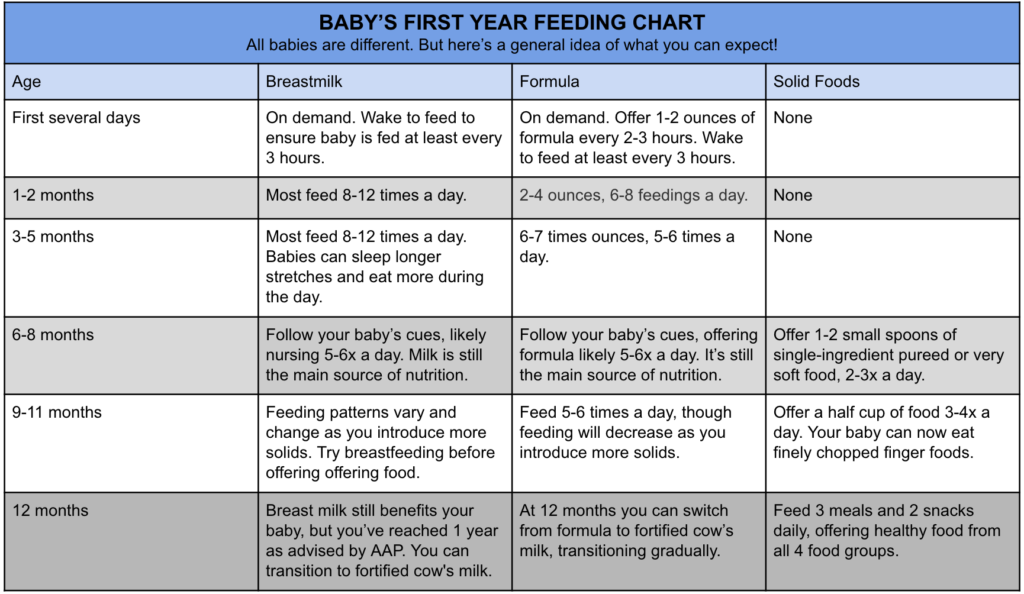
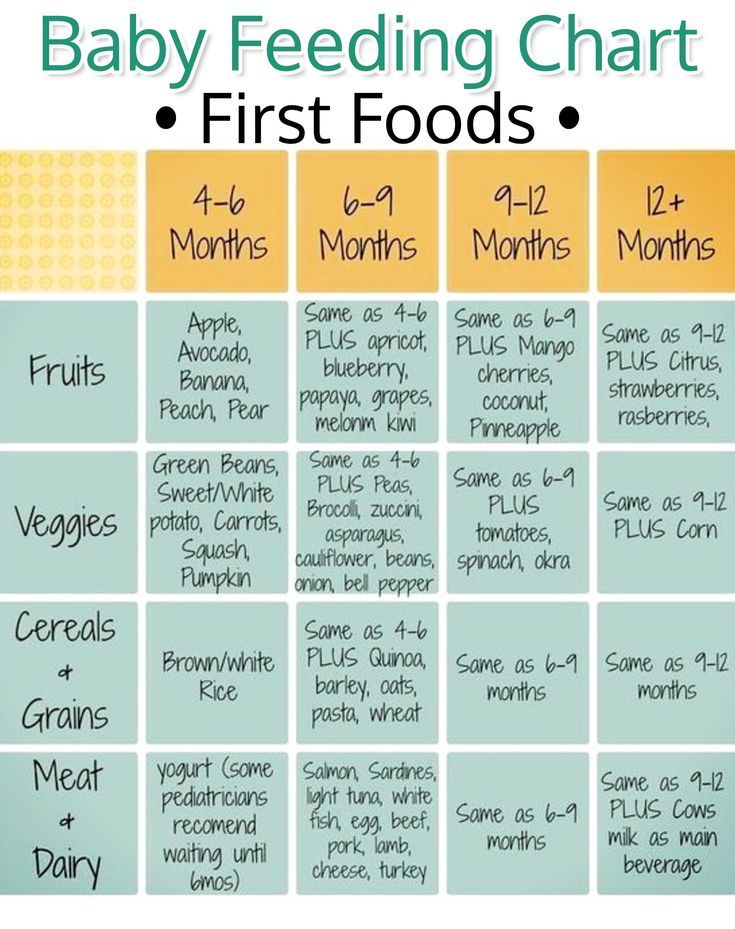
Baby age food guide
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.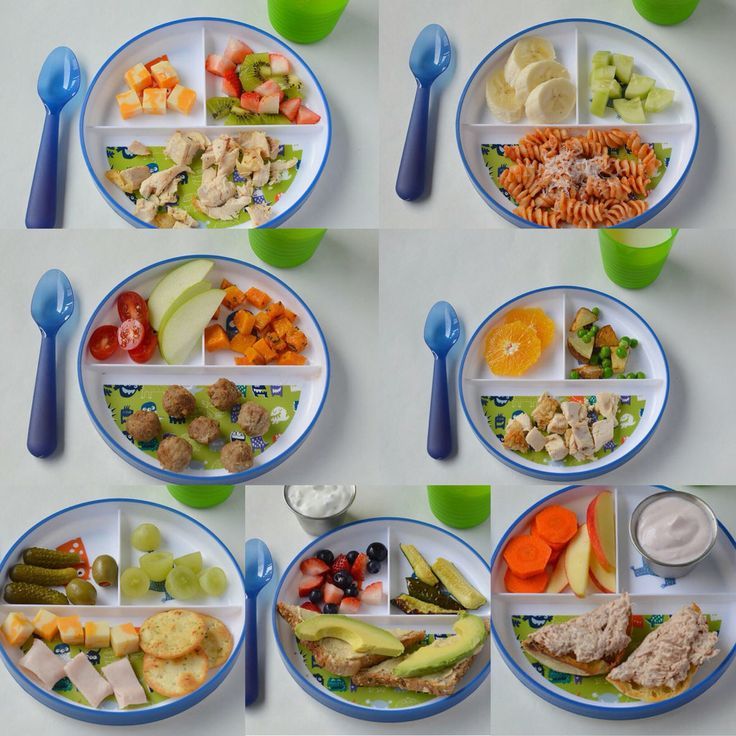
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
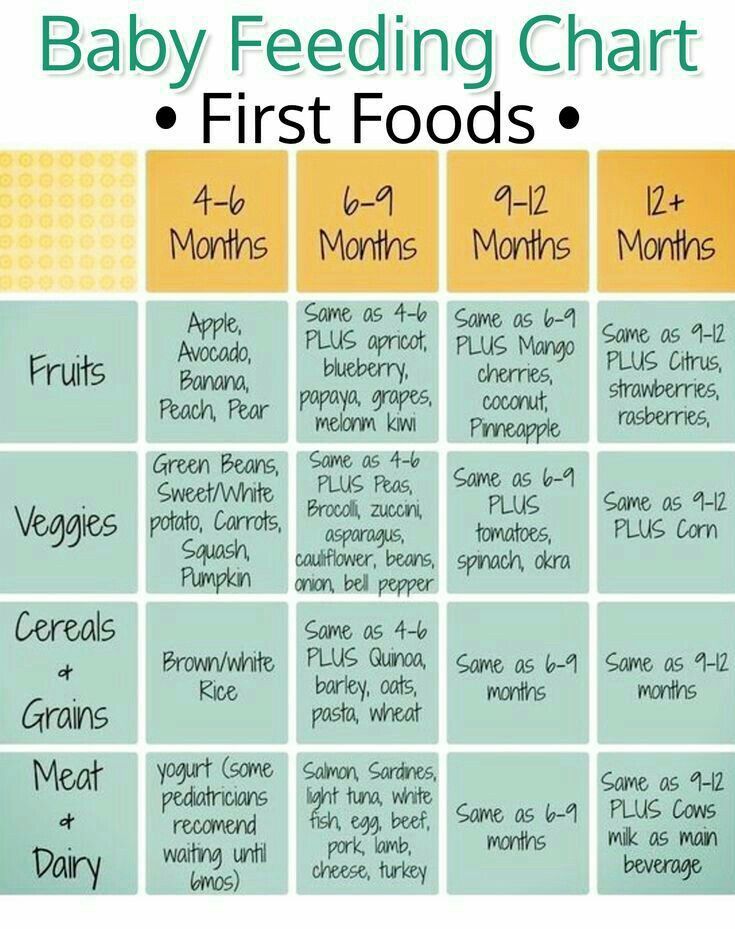
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Introducing solids: why, when, what & how
Solid foods: why babies need them
As babies get older, they need solid food to get enough nutrients for growth and development. These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
For the first 6 months of life, babies use iron stored in their bodies from when they were in the womb. They also get some iron from breastmilk and/or infant formula. But babies’ iron stores go down as they grow. By around 6 months, babies need to start having solid food.
Introducing solids is also important for helping babies learn to eat, giving them experience of new tastes and textures from a range of foods. It develops their teeth and jaws, and it builds other skills that they’ll need later for language development.
Signs that it’s time to introduce solids
Signs your baby is ready for solids include when your baby:
- has good head and neck control and can sit upright when supported
- shows an interest in food – for example, they look at what’s on your plate
- reaches out for your food
- opens their mouth when you offer them food on a spoon.
Most babies start to show these signs by around 6 months, although this can vary.
It’s recommended not to introduce solids before 4 months.
If your baby is nearing 7 months of age and hasn’t started solids, you might like to get some advice from your child and family health nurse or GP.
The best times of day to introduce solids
When you’re first introducing solids, it’s good to offer solids when you and your baby are both happy and relaxed.
This is often after a feed of breastmilk or formula. Babies will still have room in their tummies for a taste of new foods after a feed of breastmilk or formula. But if they’re really hungry before a feed, they just want the breastmilk or formula that they know satisfies their hunger.
As time passes, you’ll learn when your baby is hungry or full, not interested or tired.
Signs of hunger include your baby:
- getting excited when they see you getting their food ready
- leaning towards you while they’re sitting in the highchair
- opening their mouth as you’re about to feed them.

Signs your baby is no longer interested include:
- turning their head away
- losing interest or getting distracted
- pushing the spoon away
- clamping their mouth shut.
Your baby’s appetite can vary from day to day.
How much food to offer when introducing solids
When you’re first introducing solids, try offering 1-2 teaspoons of food once a day. At first, your baby might have only a small taste and probably won’t swallow much.
As your baby grows, you can increase the amount according to your baby’s appetite and signs.
By 12 months, your baby should be eating around 3 small meals a day, plus breastmilk or infant formula.
The right textures for first foods
When your baby is ready for solids, first foods might be smooth or finely mashed, depending on what baby likes. Over the next weeks and months, your baby can move on to roughly mashed or minced foods and then chopped foods. All foods should be very soft.
All foods should be very soft.
Your baby needs a variety of food textures. This helps your baby learn how to chew, and chewing helps with speech development and self-feeding. It also helps to prevent feeding difficulties as your baby develops. Babies can chew even before they get their first teeth.
By the time your baby is 12 months old, they should be eating the same foods that the rest of the family is eating. But you might still need to chop some foods into smaller pieces and cook vegetables until they’re soft.
To prevent choking, always supervise babies and young children while they’re eating solid food. Avoid nuts, take special care with pieces of meat and check fish for small bones, because these are choking hazards. And if your baby can move around, make sure baby is sitting down while they’re eating. If you sit with your baby while they’re eating, baby is less likely to move around.
Types of food to offer when introducing solids
All new foods are exciting for your baby.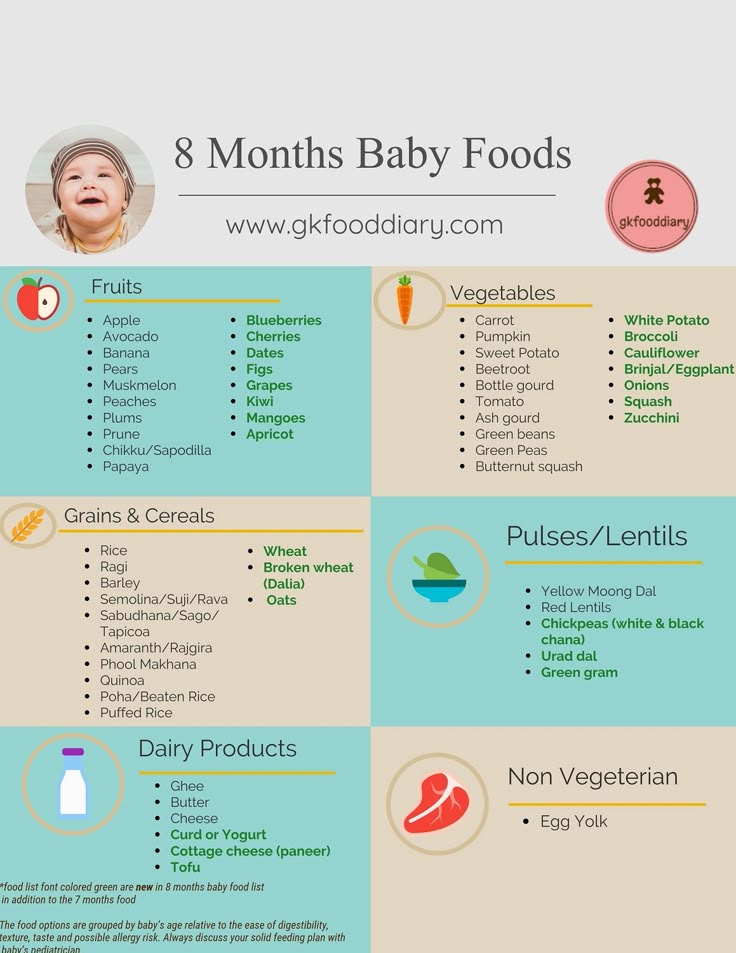
The key is to include iron-rich foods of the right texture in your baby’s first foods. Iron-rich foods include:
- iron-fortified infant cereal
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- cooked tofu and legumes
- mashed, cooked egg (avoid raw or runny egg).
To these iron-rich foods, you can add other healthy foods of the right texture like:
- vegetables – for example, cooked potato, pumpkin, sweet potato, carrot, broccoli or spinach
- fruit – for example, banana, apple, pear, melon or avocado
- grains – for example, oats, bread, rice and pasta
- dairy foods – for example, yoghurt and full-fat cheese.
You can introduce any number of new foods at a time and in any order. When you offer your baby a variety of foods, they can try plenty of new tastes and get a range of nutrients.
Read our tips for introducing solid foods to learn how to get your baby interested in new foods and manage mealtime mess and play.
Breastmilk and infant formula while introducing solids
You should keep breastfeeding or using infant formula until at least 12 months.
When you start introducing solids, breastmilk or infant formula should still be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Over the next few months, your baby will start having more solids and less milk or formula. The rate that this happens will vary.
By around 9 months, babies have generally developed enough chewing and swallowing skills to move from having milk before solids to having milk after solids.
Here are some signs that your baby is getting enough nutrition from both solids and breastmilk or formula during this time. Your baby:
- has plenty of wet nappies – at least 6-8 wet cloth nappies or 5 very wet disposables in 24 hours
- is alert and mostly happy after and between feeds
- is gaining weight at about the right rate – your child and family health nurse will weigh your baby at your regular check-ups.

From 12 months onwards, solids should be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Your baby doesn’t need infant formula after 12 months, but you can keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
If solid food replaces breastmilk and/or infant formula too quickly, babies can miss out on important nutrition. If you have any concerns about your baby’s feeds or weight, talk to your midwife, child and family health nurse, lactation consultant or GP.
Introducing water
Once your baby has reached 6 months, you can start to offer baby cooled, boiled water in a cup at mealtimes and at other times during the day. This is so your baby can practise drinking from a cup, but baby still doesn’t really need fluids other than breastmilk or formula at this age.
Once your baby has reached 12 months, you can offer fresh tap water without boiling it.
Foods and drinks to avoid while introducing solids
There are some foods to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- Honey until 12 months – this is to avoid the risk of infant botulism.

- Raw or runny eggs and foods containing raw eggs like home-made mayonnaise until 12 months – bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies.
- Reduced-fat dairy until 2 years – babies need full-fat dairy for growth.
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods until 3 years – these are choking hazards.
There are some drinks to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- pasteurised full-fat cow’s milk as a main drink until 12 months
- dairy alternatives like soy, goat’s, sheep’s, rice, oat, almond and coconut milk until 2 years, unless your GP or child and family health nurse has recommended these for a particular reason
- unpasteurised milks at all ages
- tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened drinks at all ages
- fruit juice – this should be limited at all ages (whole fruits are better because they have fibre and help babies develop chewing and feeding skills).
Your baby doesn’t need added salt or sugar. Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introducing solids
Introducing allergenic foods early can reduce the risk of your child developing food allergy. Allergenic foods are foods that might cause allergies.
All babies, including babies with a high allergy risk, should try solid foods that might cause allergies from around 6 months of age. These foods include well-cooked egg, peanut butter and other nut butters, wheat (from wheat-based breads, cereals and pasta) and cow’s milk (but not as a main drink).
Once you’ve introduced an allergenic food, it’s a good idea to regularly include it in your baby’s diet.
It’s a good idea to get advice from your GP, child and family health nurse, dietitian, paediatrician or allergy and immunology specialist for the following reasons:
- Your baby already has a food allergy.
- Your baby has severe eczema.
- Your family has a history of food allergy and you’re concerned about starting solids.
- You’re worried about reactions to foods.
how to choose and what kind of baby food is better?
The ideal "baby food" for an infant is breast milk. However, not all mothers can breastfeed their baby, usually this is due to the health of the mother or child. It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk. Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
In this article, we will talk about what foods for babies are and how to choose the best baby food.
Legislation under "baby food" means food products that meet the physiological needs of the body of a child under 14 years of age. And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia created the National Program for feeding children in the first year of life and the National Program for optimizing the nutrition of children from one to three years old [2]. They describe recommendations regarding what formula to feed the baby from birth, how to introduce complementary foods and expand the baby's diet. These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages.
First you need to figure out what kind of baby food is[3]. Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Infant formula. There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3). The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3). The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
- In the initial mixtures, the amount of protein is reduced to 1.2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins.
- After six months, the baby's need for protein increases, mother's milk changes its composition. And babies on artificial feeding begin to be fed with a more nutritious mixture of formula 2. Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself. Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished.

- A child's diet changes after one year - he is already able to eat a variety of solid foods. However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.
Complementary foods As we have already noted, it is introduced when the baby is four to seven months old. This interval is called the "critical window" and is considered optimal for the initiation of complementary foods for several reasons:
- The baby needs a wider range of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients. In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula.
- At this age, the child develops an interest in food, and it is necessary to offer him the right foods to develop his taste.
- During this period, the risk of developing a food allergy to a new product is lower.

- Timely introduction of complementary foods prevents the risk of micronutrient deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia.
Usually the first food is vegetable puree or monocomponent gluten-free cereals, dairy or dairy-free. Over time, cereals containing gluten, supplements from fruits and berries, and also consisting of several cereals are added. A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
From the age of 12 months, complementary foods already make up the majority of your baby's diet. At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals.
Information
During the first feeding, the baby's eating habits are laid, and it depends on the parents how correct they will be. Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Domestic doctors are concerned about such irrational nutrition of young children - due to the wrong approach to nutrition, many babies experience a deficiency of vitamins and an excess of fast carbohydrates.
How to choose baby foods
Finding the right foods for your baby is not an easy task. Store shelves are bursting with boxes, jars and bottles, and manufacturers write on every second package that the baby will be healthy, strong and cheerful after feeding. Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
However, products for children differ in their properties. It is necessary to select food so that by the end of the first year of life the baby has actively developed chewing skills and an interest in independence, and the diet of complementary foods is reasonably varied.
For children from one to three years of age, the diet should be even more varied. It is important that the child receives daily something new from the main food groups: dairy, vegetables and fruits, meat and fish, cereals, butter and vegetable oil. Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health.
When organizing the nutrition of a child from the moment of introduction of complementary foods and up to three years, a mother needs not only to know what can be fed, but also to consider what foods should not be included in the diet. Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
- any mushrooms, vegetables and fruits in a marinade;
- pickles, preserves in tomato sauce;
- commercial juice concentrates, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea;
- various condiments - mustard, ketchup, hot sauces, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise;
- products containing flavors, industrial colors, including chewing gum;
- margarine and refractory fats - lamb, pork;
- chocolates, sweets and other sweets.

To choose the right baby food, you need to know exactly what you should pay attention to and what you don't need to worry about.
When choosing mixtures, it is important to check:
- Absence of palm oil. Formula manufacturers may use palm oil (more specifically palm extract) because, like breast milk, it is rich in palmitic acid. However, in human milk, palmitic acid is in the beta position, while in palm oil it is in the alpha position. Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5].
- Protein ratio. Breast milk protein is primarily whey proteins and casein. A child needs both types of protein, while proteins are easily digested, which cannot be said about casein.
 If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool.
If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool. - The presence of additional functional elements in the composition - lutein, nucleotides, pre- and probiotics. The task of lutein is to protect vision from ultraviolet rays. Nucleotides are low molecular weight compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in the intestines. And pre- and probiotics in the composition of infant formulas help to establish comfortable digestion.
When choosing complementary foods, pay attention to:
- Age appropriate. It is important that in the diet of a child under three years of age who receives complementary foods, special children's products predominate - in their composition the components are selected taking into account the age-related needs of the baby's body. It is impossible at an early age to transfer children to "adult" foods like pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and so on.

- Fortified products. It is important that the composition contains vitamins and minerals. The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies.
- For a varied diet. The menu for a baby up to six months is quite monotonous. But as they grow older, the baby needs more various nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- For the individual reaction of the baby. If the child is already receiving complementary foods, then it is worth introducing a new product only after the previous one has been fully introduced. If the baby is allergic to the product, then it should be administered carefully, carefully checking the reaction of the body.
Ingredient safety testing is optional. Of course, the content of any "chemistry" in the product for feeding a child, whether it be a mixture or complementary foods, is unacceptable.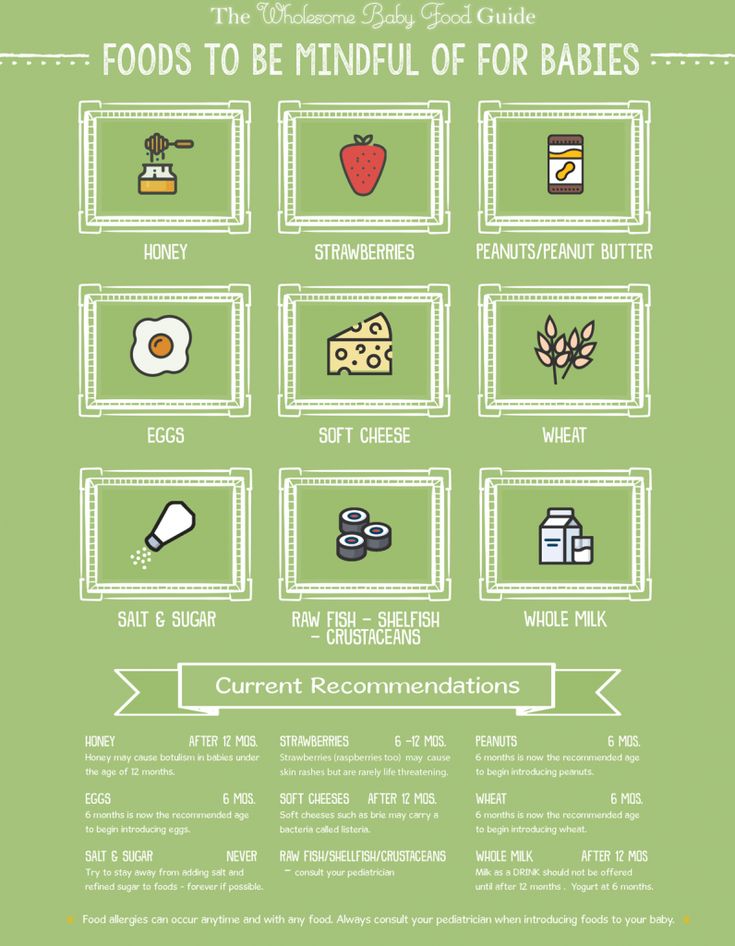 There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
Note
Baby food in jars (usually mashed potatoes) has a short shelf life after opening because it does not contain preservatives. However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food.
Features of the choice of dairy products
It is necessary to choose dairy products for babies, following the doctor's recommendations. The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the organism. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
Goat milk baby food may be a suitable option for young children with a predisposition to allergies. Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed.
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, other dairy products will appear in the baby's diet. Unadapted fermented milk drinks, such as kefir, yogurt, biolact, can be introduced into the diet from eight months and in an amount not exceeding 200 ml. Also during this period, it is recommended to give cottage cheese - no more than 50 g per day, but according to indications, it can also be prescribed from the age of six months. Whole milk cannot be used as the main food, and it is advised to introduce it into the diet of babies no earlier than a year (in the amount of 100-150 ml per day) [8]. As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
To choose the best baby food, it is necessary to take into account the health of the baby, his tastes, as well as individual reactions of the body. Therefore, before going to the store, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will not only tell you which baby food to choose, but also give recommendations on how to make the child's diet balanced and healthy.
Baby Nutrition Guide: Birth to Year
Helping your baby gain weight during the first year of life can be quite challenging. Here's what you need to know about baby food , about the weight of the child, how to comply with medical recommendations, as well as how to keep the child healthy and happy, will be told by a very popular women's site about beauty and health among girls.
Newborn (1 to 4 weeks)
Now your baby is more fragile than ever. Don't worry if your baby has lost a couple of hundred grams after birth - most babies experience this. A healthy baby gains weight again in 10-12 days and will soon return to its birth weight.
Baby should eat: Breast milk or formula. Call your doctor if you think your baby is having an allergic reaction to breast milk, as he may react to what you eat or be sensitive to formula ingredients.
1 month
From now until the age of 6 months the baby will grow by about 2-3 cm per month and gain about 150-200g per week. If you do not have problems with feeding, then the child will gain weight steadily.
If you do not have problems with feeding, then the child will gain weight steadily.
Baby should eat: Breast milk or formula. Feeding times are not precise and it is not possible to determine how much milk a baby will eat per breastfeed. Children at this age should eat 8 to 12 times a day or every 2-3 hours.
2 months
The child should gain weight steadily every week. In some cases, babies don't get enough milk or can't suckle properly. If you are experiencing any of these difficulties or problems with lactation, visit your pediatrician and learn how to make sure your baby is eating enough.
Baby should eat: Breast milk or formula. Don't start introducing grains or baby food until your baby is 4 months old. Feeding food too early can lead to digestive problems in the baby.
3 months
At this stage, the child will move from the standard increase of 200g. As a result, the baby will gain about a kilogram this month, as well as in all subsequent months up to 7 months.
Baby should eat: Breast milk or formula. This is probably the last month your baby will use breast milk or formula as a main source of nutrition, as he will also get the nutrients he needs from grains and other foods later on.
4 months
Around this age, the child begins to show signs that he is ready for more solid foods. Some of these signals are: he can hold his head, sit with support, and show interest in what you are eating. The transition from liquid to solid food should be gentle, so don't force your baby to eat if he's not ready.
That being said, don't confuse spitting out cereal with disgust. This is a normal habituation process that will end around 7 months of age.
Baby should eat: Breast milk or formula and fruits and vegetables. Children who enjoy eating fruits usually do not have aversion to vegetables either. Start introducing different types of baby foods, including grains. Soon, your baby will begin to erupt teeth so that he can cope with the new, harder food. Teething will begin at about 6 months of age. The two lower front teeth, and then the two upper ones, will give your baby a charming smile.
Teething will begin at about 6 months of age. The two lower front teeth, and then the two upper ones, will give your baby a charming smile.
5 months
Before 5-6 months, the baby should weigh twice as much as at birth. Just at this time, a physical examination is scheduled, so you can consult a doctor about your child's weight.
6 months
Starting at six months, the baby will grow about 1 centimeter per month and gain about 100 grams per week.
The child should eat: Fruits and vegetables, then gradually add meat puree. Diarrhea and rashes are indicators of food sensitivity, so pay attention to how your child reacts to different foods. You can also continue to breastfeed or give formula to your baby.
7 months
The baby's weight will again increase steadily by about 1 kg per month. If the child is gaining less than 500 grams or more than 3 kg, you should contact your pediatrician and get advice on proper baby food and weight management.
Baby should eat: Keep giving your baby chopped fruits, vegetables, and meats. Your child should now be able to handle thicker foods, so leave small pieces of fruit and vegetables for him to nibble on.
8-9 months
To maintain normal weight, offer your child small snacks such as scrambled eggs, steamed vegetables or small pieces of bread every 3-4 hours. Children who snack occasionally are more likely to eat healthy and gain weight.
The child should eat: Baby cereal, soft fruits like kiwi or banana, and soft (or shredded) vegetables and meat.
10 months
When your baby starts to move actively, his weight may decrease. At this age, the child will probably crawl a lot and try to get to his feet with the help of chairs, tables, your leg or something else. This mobility burns a lot of calories, so don't expect your baby to gain more than 0.5-1kg this month.
The child should eat: Try introducing green vegetables, harder fruits such as diced or julienned apples into the child's diet.