Baby arching back after feeding
Causes, Solutions, and When to Worry
By now you’ve likely learned to recognize the various types of crying your baby has. You can distinguish between the I’m-so-hungry cry and the get-me-out-of-this-soggy-diaper cry. Your finely tuned ear may also pick up the I-need-attention and cuddle-me-now cries.
Sometimes crying is accompanied by expressive body movements, including an arched back. Back or spine arching — like a bow or doing the cat pose in yoga — is common in babies. Babies arch their backs for many reasons.
In some cases, an arched back along with other symptoms can signal a health condition. But if your baby arches their back without any other symptoms, chances are they’re just a natural at yoga. Let your baby’s pediatrician know about the back arching, just to be on the safe side.
Here’s what to look for and what your baby might be trying to tell you.
Gassiness
Gassiness can be common in a baby’s brand new digestive system. Some babies can have bouts of fussiness that last for several day or weeks. This is sometimes labeled generically as colic.
Colic can start when your baby is only 4 to 6 weeks old and cause crying for hours at a time. Fortunately, babies usually outgrow colic by the time they’re 4 months old.
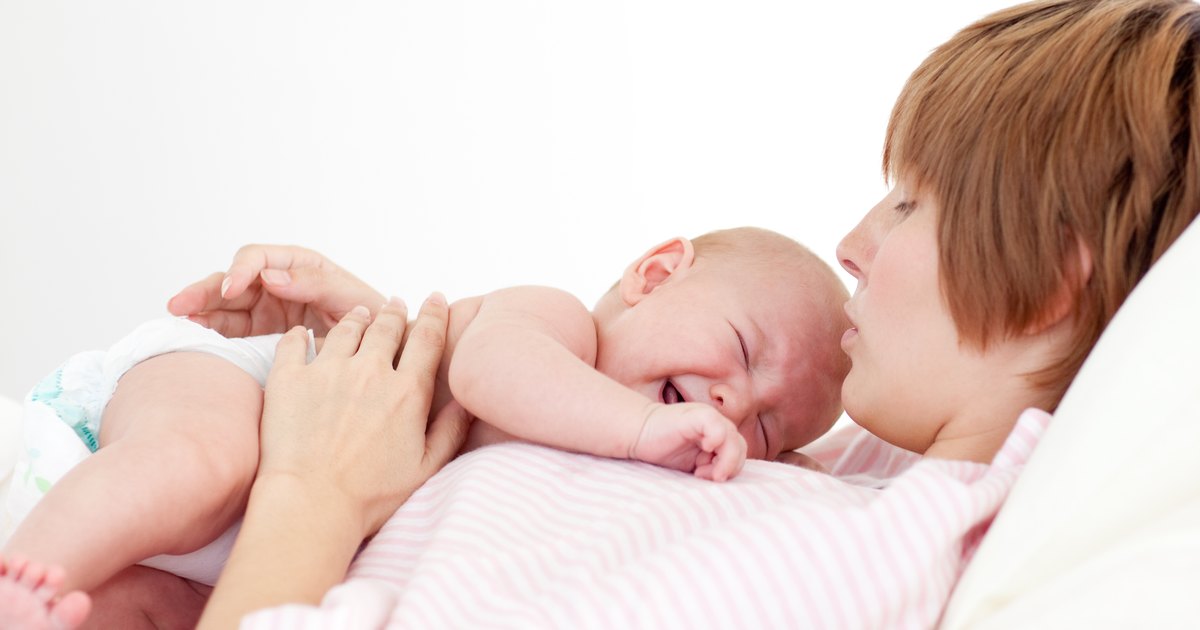
Your baby might arch their back when they have gas or an upset stomach. This could be because arching the back stretches the stomach a bit and might make them feel a little better. You might notice that your baby arches their back after feeding, when trying to poop, and even while lying down.
Baby reflux
Reflux, or gastroesophageal reflux, is common in babies right from birth to about 18 months of age.
Babies reflux happens because the round muscles that pinch both ends of the stomach closed don’t yet work properly in these new little humans. If your baby is premature, they might have more reflux.
Your (very healthy) baby can have reflux several times a day. It’s usually completely normal and nothing to worry about. But, sometimes if they’re spitting up and seem to have other symptoms, they may arch their back.
It’s usually completely normal and nothing to worry about. But, sometimes if they’re spitting up and seem to have other symptoms, they may arch their back.
Similar to when babies have colic, they might arch their back because it helps bring down the feeling that come with reflux. You might notice this during and after feeding, while your baby is lying down, and even while they’re fast asleep.
Body language
Sometimes your baby might arch their back because they don’t want to be held or fed. This kind of body stiffening could be a sign to put them down or change position.
Some babies have strong back muscles and this may be the easiest way — other than crying — for their body to tell you what they want. Your little independent one may use the “back arch method” to get out of unwanted cuddles up to the age of 2 years! (Don’t take it personally, mom and dad.)
Startle reflex
Most babies have a startle reflex (also called the Moro reflex) when they hear a sudden or loud noise. It might also happen if they feel like they’re falling or if they’re moved suddenly.
It might also happen if they feel like they’re falling or if they’re moved suddenly.
Startling may make a baby suddenly straighten their legs forward and throw back their arms. Their head may also jerk backwards, making their back arch. The startle reflex usually goes away by the time baby is 2 to 4 months old.
Rollover attempts
As your little one gets used to tummy time, they’re also building stronger back and neck muscles. They’ve learned to lift their head and realize that the more they can move, the more they can look around. This is exciting!
So your baby may arch their back during tummy time or while they’re lying down on their side or back to get into a better position to explore. Some babies arch their backs when they’re trying to roll over or move forward. You’ll probably see their eyebrows go up as they wiggle every muscle they can.
Temper tantrums
Your little angel might have a head start on the terrible twos. Some babies arch their backs and throw their heads back when they’re upset or frustrated. This can happen while they’re lying down, sitting down, standing — or even cradling in your arms. A baby in the heat of a tantrum may also cry, whine, and thrash about.
This can happen while they’re lying down, sitting down, standing — or even cradling in your arms. A baby in the heat of a tantrum may also cry, whine, and thrash about.
Just about anything might set off a temper tantrum. Your little one may be hungry and not getting what they ordered from you — their short-order cook — immediately. Or they may be finished feeding and want to go play. Or your baby might be frustrated because they can’t express their needs to you.
No matter what the reason for a tantrum, it can be alarming when your baby arches their back and throws their head backwards. They can hurt themselves — and bump you squarely in the face.
If your little one gets into the habit of this, look for warning signs like crying or being upset first.
Related: Help! Why is my toddler angry and what can I do to help them?
Seizures or seizure-like movements
Although it sounds serious, seizures in newborn babies aren’t the same as seizures or epilepsy in older children and adults. Your baby may have seizures — or seizure-like movements and behaviors that are mistaken for seizures — that begin in the first week of life.
Your baby may have seizures — or seizure-like movements and behaviors that are mistaken for seizures — that begin in the first week of life.
A seizure can last for a few seconds. Your baby might suddenly be very quiet and look like they are very stiff or frozen. Or they may still be able to move their hands by rotating their wrists.
Some babies may arch their backs during what appears to be seizure-like behavior. It can happen at any time, usually when your baby is awake or just drifting asleep.
Newborn seizures are uncommon, but may happen because a baby’s brain is still growing and the nerves can get their wires crossed. One rare type of newborn seizures can run in families. Some babies with this rare genetic type of seizure disorder may have them often, while others have them once in a while or not at all. These baby seizures usually stop completely by the time your child is 6 to 9 months old.
Nerve damage
Your baby’s delicate neck and back can get sprained in a difficult delivery. Sometimes, the nerves between the neck and shoulders can get damaged.
Sometimes, the nerves between the neck and shoulders can get damaged.
Erb’s palsy is a condition that happens to about 1 out of every 1,000 newborns. It happens when the neck nerves are weak because of too much stretching during birth. The weaker nerves lead to weaker muscles in the neck and shoulder.
This may cause back arching in your baby, because they can move their back muscles and other strong muscles better than their neck muscles. However, back arching alone isn’t a sign of this condition. It would come with other symptoms — in particular, decreased movement in one shoulder and arm.
Most babies with Erb’s Palsy and other nerve damage from birth recover completely. Your baby’s pediatrician may recommend daily exercises to help make the neck and shoulder muscles stronger.
Newborn jaundice
Almost 60 percent of newborns have jaundice. This condition might make your baby look a bit yellow. It happens because a new baby’s tiny liver is not yet working properly, which causes too much bilirubin in the blood. This chemical is left over from when your body breaks down blood.
This chemical is left over from when your body breaks down blood.
Babies have the most bilirubin when they are 3 to 5 days old. Normally, the liver kicks in and clears up the bilirubin by the time your baby is a couple of weeks old.
Sometimes, the jaundice gets worse instead of better. In rare cases, too much bilirubin, causing severe jaundice, can cause a kind of brain condition called kernicterus.
Arching the back is a classic sign of brain damage from kernicterus in babies who have or have had very high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms include:
- high pitch crying
- floppiness or stiffness
- hard to wake up or not sleeping at all
- not feeding well
This serious condition only happens if the jaundice isn’t treated and bilirubin levels get very high. If your baby is diagnosed with kernicterus, they can still be treated by a specialist doctor.
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is a group of muscle control conditions. It usually happens when there is brain damage while your baby is still in the womb. About 1 in 323 children worldwide have a type of cerebral palsy.
About 1 in 323 children worldwide have a type of cerebral palsy.
Signs of this condition might show up while your little one is a baby or toddler. Signs include muscle floppiness, strong reflexes, and stiffening (like arching the back). Babies with cerebral palsy may also have trouble swallowing and moving their eyes. Some babies with this condition may also be more likely to have seizures.
Sandifer syndrome
Sandifer syndrome is a rare movement condition almost always associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It starts in babies or small children. Once the baby is treated for GERD (or it goes away on its own), this condition goes away.
Sandifer syndrome causes serious back arching in babies that can last for up to 3 minutes. It causes a frozen kind of back arching that can sometimes be mistaken for a baby seizure.
Back arching from this syndrome can happen about 10 times a day, usually after your baby has eaten. During back arching your baby will also stretch their legs out backwards and be very stiff. Other symptoms of Sandifer syndrome include:
Other symptoms of Sandifer syndrome include:
- tilting the head to one side
- nodding head movements
- poor feeding
- vomiting
- problems with eye movements
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) typically show several signs. This sometimes includes repetitive motions like back arching, but remember that back arching is much more often due to other causes.
Autistic children may show symptoms around the time they are a year old (or earlier), but most kids aren’t diagnosed until they’re about 3 years old.
A newborn or a baby that is only a few weeks to a few months old will likely not show signs of this condition. If your child is on the autism spectrum, they’ll likely have several other signs along with back arching.
By the end of the first year, an autistic baby may show characteristic traits that are more common, like:
- not smiling spontaneously at parents or caregivers
- not using eye contact to communicate
- not gesturing (waving or pointing) on their own
Later on your child may show other repetitive motions, such as:
- stiffening their arms
- flapping their hands
- walking on their toes
In most cases, your baby’s back arching will go away on its own as they learn to roll over and control their body better, outgrow the startle reflex, and get more comfortable with people around them.
If there’s a health problem that’s making your little one arch their back, treating the underlying condition will solve the back arching. For example, treating common baby problems like gassiness and acid reflux will take care of the back stretching.
For normal gassiness and baby reflux you can try simple, low risk home remedies like:
- prop your baby upright after feeding
- avoid overfeeding
- give smaller feeds more often
- use a smaller bottle and nipple size to stop air-gulping if this seems to be an issue
- thicken breast milk or formula with a tiny bit of infant cereal (check with your pediatrician first as this can have risks)
If your little angel is throwing their head backwards and arching their back in a toddler temper tantrum, gentle behavior training may help stop this. Teaching your child how to express themselves in a less dramatic way might help. Ask your pediatrician for recommendations.
Some babies with seizures will naturally outgrow them. Other more serious causes of back arching may need physical therapy, medications, surgery, or other medical treatment.
Other more serious causes of back arching may need physical therapy, medications, surgery, or other medical treatment.
Sometimes gassiness and fussiness can start to be accompanied by other symptoms that won’t go away, and acid reflux might be a sign of a more serious health condition. Call your child’s pediatrician urgently if your baby:
- is crying for 3 hours or longer
- is arching their back and showing other signs of pain
- throws up every time you feed them
- is irritable during feeding
- refuses to feed
- isn’t gaining weight or has lost weight
- isn’t wetting their diaper
Look for symptoms of brain or nerve problems along with back arching. Contact your child’s doctor or go to urgent or emergency care right away if your baby experiences:
- sudden difficulty latching or feeding
- weak sucking
- difficulty swallowing
- high-pitched cry
- seizures
- bulging or swollen soft spots on the head
- stiffness
- floppiness
- strange head or neck posture
- jerking movements
- muscle spasms
If your baby’s got back (arching), you probably don’t have to worry. Babies arch their backs for many reasons — or for no reason at all. In a happy, comfortable, healthy baby, back arching likely has no cause and is just one of those things they do.
Babies arch their backs for many reasons — or for no reason at all. In a happy, comfortable, healthy baby, back arching likely has no cause and is just one of those things they do.
This common baby movement can also be a sign of other underlying health problems — sometimes serious. If you notice your baby is arching their back, look for other symptoms. Let your pediatrician know what you notice. Make sure you take your new bundle of joy to all their regular check-ups.
Baby Arching Back: Why Do Babies Arch Their Backs?
Does your little one keep arching their back? If so, you might be curious to know why babies do this. Maybe you notice your baby arching their back when crying, or while sleeping. Or maybe there’s no pattern at all and your baby is simply a casual acrobat! Read on to learn more about this curious movement, including why it happens and when it could be cause for concern.
Why Do Babies Arch Their Backs?
A baby who is arching their back may be doing so for a number of reasons, and very few are cause for concern. Babies and newborns most often arch their backs while they’re crying, and sometimes when nursing, eating, sleeping, or working on motor development. It’s typically just an expressive movement, a way to communicate, or a reflexive motion in reaction to something.
However, if back arching accompanies certain symptoms, it could indicate a health condition. We’ve rounded up the most common reasons why babies arch their backs along with guidance on when you do and don’t need to contact your child’s healthcare provider.
Babies and newborns most often arch their backs while they’re crying, and sometimes when nursing, eating, sleeping, or working on motor development. It’s typically just an expressive movement, a way to communicate, or a reflexive motion in reaction to something.
However, if back arching accompanies certain symptoms, it could indicate a health condition. We’ve rounded up the most common reasons why babies arch their backs along with guidance on when you do and don’t need to contact your child’s healthcare provider.
Gas and Reflux
A gassy baby can also be a back-arching baby! When you’re feeding your little one, they may eat too fast or swallow air, which can cause gas. And because gas can lead to an upset stomach and discomfort, your child may move around, arching their back or pulling their legs up to find some relief.
Similarly, if your infant or baby is arching their back while nursing, or perhaps when eating solid foods, it could be a sign of reflux. Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is when your baby’s food comes back up through the esophagus after feeding.
Gassiness and GER are nothing to worry about unless they’re prolonged or accompany other symptoms. For example, if your baby is crying and arching their back after eating, it could be a sign of a food allergy or sensitivity. And if GER lasts more than 12 to 14 months, it could be a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and may require some feeding adjustments or medical intervention.
If you’re going through quite a few diapers these days, download our Pampers Club App to start earning rewards on all your diapers and wipes purchases. Do you know the right diaper size for your baby? Take the quiz below to find out!
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is when your baby’s food comes back up through the esophagus after feeding.
Gassiness and GER are nothing to worry about unless they’re prolonged or accompany other symptoms. For example, if your baby is crying and arching their back after eating, it could be a sign of a food allergy or sensitivity. And if GER lasts more than 12 to 14 months, it could be a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and may require some feeding adjustments or medical intervention.
If you’re going through quite a few diapers these days, download our Pampers Club App to start earning rewards on all your diapers and wipes purchases. Do you know the right diaper size for your baby? Take the quiz below to find out!
Building Muscles and Motor Skills
As your baby progresses beyond the newborn stage, you’ll start to see more and more movement. Your little one is busy working on developing muscle strength and control—especially in the back and neck muscles—which they need to master motor skills and reach important development milestones, like sitting up.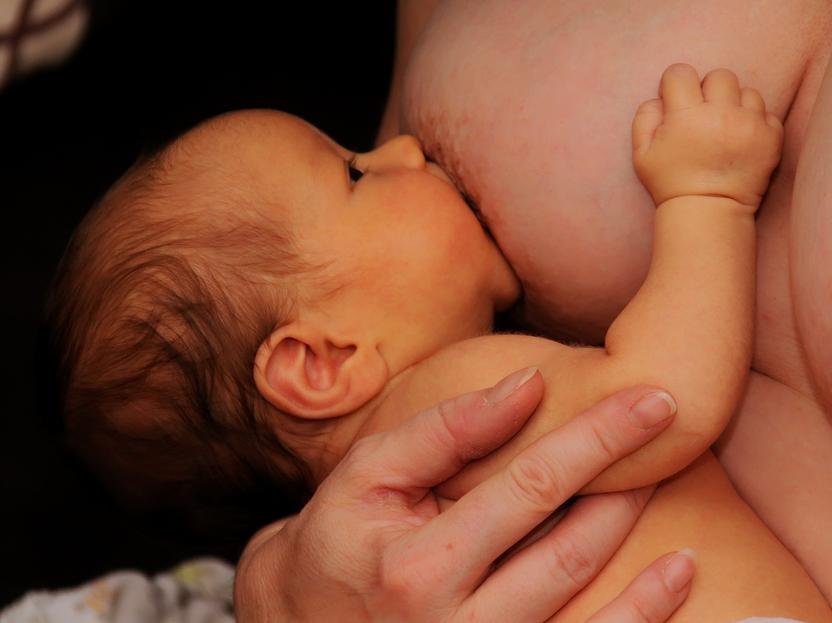 Arching the back may be part of this exciting process.
For example, at around 4 months or a little later, your baby may start trying to lift their chest, which involves pushing up on the arms and arching the back. These infant pushups help build upper body strength and balance, which your baby needs to stay stable and upright when sitting. You might also see your baby arching their back while they rock on their stomach, kicking their legs and doing a swimming motion with their arms—all of this is to prepare for rolling over and sitting up.
You can help your baby practice their moves and build those essential muscles by including tummy time in your daily routine. Always make sure to stay close to your baby during tummy time sessions. To learn more about the benefits of tummy time, watch the video below.
Arching the back may be part of this exciting process.
For example, at around 4 months or a little later, your baby may start trying to lift their chest, which involves pushing up on the arms and arching the back. These infant pushups help build upper body strength and balance, which your baby needs to stay stable and upright when sitting. You might also see your baby arching their back while they rock on their stomach, kicking their legs and doing a swimming motion with their arms—all of this is to prepare for rolling over and sitting up.
You can help your baby practice their moves and build those essential muscles by including tummy time in your daily routine. Always make sure to stay close to your baby during tummy time sessions. To learn more about the benefits of tummy time, watch the video below.
Being Overstimulated or Colicky
Babies cry often and for different reasons—they could be bored or tired, hungry or uncomfortable. Crying is how they communicate. And when babies cry because they’ve become overstimulated, they may arch their back at the same time. It’s common for colicky babies to arch their backs during crying spells, too.
Here are a few things that babies may be reacting to or experiencing when they’re crying and arching their backs:
Crying is how they communicate. And when babies cry because they’ve become overstimulated, they may arch their back at the same time. It’s common for colicky babies to arch their backs during crying spells, too.
Here are a few things that babies may be reacting to or experiencing when they’re crying and arching their backs:
Too much stimulation. Babies do need breaks from play and interaction. Babies have a stimulation threshold, and yours may have reached theirs when they start crying, arching the back, and looking away. Your baby is letting you know it’s time for a break, such as a nap.
Colic. One of the signs of colic in babies is an arching back. Colic is when an otherwise healthy baby cries for more than three hours a day during at least three days a week, for three or more weeks. If your baby has colic, you may notice them arching their back, straightening their arms and legs, crying or screaming for extended periods, or clenching their fists.

Sleeping, Nursing, Eating, and Teething
Sometimes babies or newborns arch their backs while doing everyday things, like nursing or sleeping, or while going through the teething stage. Here is additional insight on what it means when your baby arches their back in these situations:
Sleeping. Sometimes, you may notice your baby arching their back while sleeping. Your baby could be moving around or stretching in a stage of light sleep or could be arching the back to relieve gas. Remember to always put your baby down to sleep on the back, as this is the safest way for babies to slumber.
Nursing and eating. Arching the back relates to gas and reflux, as your baby might eat too much too fast. If your little one gets gassy a lot, try using a slow-flow baby bottle designed to limit the amount of air swallowed, which can help prevent gas and reflux.
Teething.
 Teething can cause swollen and tender gums that may make your baby a little fussy and uncomfortable. If your baby is crying and/or arching their back while teething, try massaging their gums or letting them chew on a teething toy made with hard rubber.
Teething can cause swollen and tender gums that may make your baby a little fussy and uncomfortable. If your baby is crying and/or arching their back while teething, try massaging their gums or letting them chew on a teething toy made with hard rubber.
What to Do and When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
By now, you probably understand that a newborn or older baby arching their back is natural, normal, and typically not a cause for concern. However, if your baby is arching their back because of discomfort or pain, it could be related to a health condition. There are a few things you can do at home to help your baby, but if this movement accompanies more serious symptoms, it’s best to contact your child’s healthcare provider to rule out any medical issues that may require treatment.
In the chart below, you’ll find a few home remedies to help you with issues causing your baby to arch the back. However, if you notice any of the serious symptoms listed, contact your child’s healthcare provider.
When babies arch their backs, it’s mostly related to normal development or common conditions that you and your child’s healthcare provider can manage from home. However, there are some additional, more complicated issues that could cause your baby to arch their back, so consult the provider when:
any of the serious symptoms listed above occur
your baby appears to be in pain
your baby exhibits odd behavior or a change in behavior
you have any questions or concerns.
Usually, back-arching isn’t something to worry about, but it’s always best to double-check with your child’s healthcare provider.
The Bottom Line
You may be asking yourself, “Why does my baby boy or girl arch his or her back?”—and you’re not the only parent wondering about this curious little behavior! You may notice your baby or newborn arching their back when tired, hungry, uncomfortable, or upset. Other reasons include your little one having gas or reflux, or wanting to show off new back muscle skills.
This behavior isn’t typically something to worry about but be sure to contact your child’s healthcare provider with any questions or concerns. Together, you can explore why your baby arches their back and determine if any medical intervention or treatment is necessary. Most likely, your little acrobat is simply expressing themselves with this natural and normal movement!
Other reasons include your little one having gas or reflux, or wanting to show off new back muscle skills.
This behavior isn’t typically something to worry about but be sure to contact your child’s healthcare provider with any questions or concerns. Together, you can explore why your baby arches their back and determine if any medical intervention or treatment is necessary. Most likely, your little acrobat is simply expressing themselves with this natural and normal movement!
why this happens and what needs to be done
When parents first encounter this phenomenon, they may be seriously alarmed. What is it - a symptom of a neurological disease or just whims? In most cases, when the baby arches, throwing his head back, there is nothing to worry about. But there are situations when the intervention of a specialist is necessary.
What you need to know if the baby throws his head back and arches
| The baby arches and throws his head back, but does not show discontent | Probably nothing to worry about. Perhaps he is trying to see something up or behind his back, or learning new skills. In some cases, this may be a manifestation of hypertonicity. In the first six months, this may be within the normal range, but if such phenomena are observed frequently or persist for a long time, you should see a doctor. Perhaps he is trying to see something up or behind his back, or learning new skills. In some cases, this may be a manifestation of hypertonicity. In the first six months, this may be within the normal range, but if such phenomena are observed frequently or persist for a long time, you should see a doctor. |
| The child shows anxiety | A lot here depends on the general condition of the baby. He may arch and whimper if his back is itchy or his nose is stuffy. More vivid signs of discontent will be if the child is tormented by colic, pain, or he is frightened. If you cannot find the cause and / or this condition recurs often, you need to see a doctor for a diagnosis. |
Variants of the physiological norm
In some cases, the child can pull the back of the head back for the simplest reasons: he is studying his body and the world around him. But there may be other reasons as well.
Below, we will consider in more detail all situations where “acrobatic stunts” are a physiological norm.
Hypertonicity in infants under 6 months
Physiological hypertonicity of the limb flexors in children under 6 months of age is considered normal. The fact is that at this age the maturation of the nervous system is still ongoing.
Mastering the skill
Baby mastering the skill of turning over on his stomach. In this case, the child lies on his side and throws his head back, trying to roll over from his back to his stomach. You can help the baby: throw one leg over the other crosswise in the direction where the child wants to roll over. After this, the baby must himself complete the coup with the upper body.
Hysteria
Often the baby, rolling in hysterics, arches, throws back his head, bursting into heart-rending crying. There is nothing wrong with this, take the baby in your arms and try to calm him down. You need to understand what alarmed him and eliminate the cause.
Affective-respiratory attacks
This is the name of the phenomenon when, for some reason, the child stops breathing for a short time. Often, such attacks are accompanied by tantrums, but they can also be provoked, for example, by fright or a sudden change in the environment (for example, when immersed in cold water). What it looks like: the child “rolls up” in a cry, his neck extensor muscles tighten, his torso arches, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, and at the height of the cry, the breath is suddenly held while inhaling, the skin turns blue (1). After a few seconds, the child comes to his senses, breathing becomes regular.
Often, such attacks are accompanied by tantrums, but they can also be provoked, for example, by fright or a sudden change in the environment (for example, when immersed in cold water). What it looks like: the child “rolls up” in a cry, his neck extensor muscles tighten, his torso arches, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, and at the height of the cry, the breath is suddenly held while inhaling, the skin turns blue (1). After a few seconds, the child comes to his senses, breathing becomes regular.
These seizures can occur in healthy children during the first year of life and are usually harmless. But if such situations are repeated often and, perhaps, for no apparent reason, you should consult a doctor to rule out various diseases.
Colic and bloating
A nightmare for parents of babies under the age of 3-4 months. Colic is also a variant of the norm, since intestinal motility in a child is not yet fully developed.
During colic, the baby screams heart-rendingly, arches and throws back his head, blushes strongly, clenching his fists and twisting his legs (2). The abdomen is hard and swollen, the child may refuse to eat. There are several ways to help a baby:
The abdomen is hard and swollen, the child may refuse to eat. There are several ways to help a baby:
- gently massage the tummy,
- put on a clean diaper, ironed with a hot iron,
- give medicine for colic (only after consulting a doctor!).
If the baby is breastfed, the mother should pay more attention to her diet and exclude foods that increase gas formation: cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks, chocolate. In the most extreme cases, the use of a gas outlet tube is acceptable.
Runny nose
It happens that with a runny nose, when it is difficult for an infant to breathe, he begins to arch and worry. Try to help the baby by raising his mattress by 30 degrees to improve the outflow of mucus, and also monitor the humidity and air temperature in the room where the child sleeps.
Trying to find a sleeping position
Sometimes babies arch their backs and tilt their heads back, trying to get comfortable before going to bed. The fact is that in the womb, children are often in unnatural positions, and in the first months of life they can unconsciously repeat them.
The fact is that in the womb, children are often in unnatural positions, and in the first months of life they can unconsciously repeat them.
Other reasons
If the child is arching but not complaining, he may be trying to look at toys hanging over him.
Try to hang the mobile and rattles so that the child does not have to dodge to look at them. Keep in mind that if the toys are hung too close to the baby's face, it may adversely affect his vision.
In addition, the child may arch for very banal reasons: perhaps his back or neck itches.
When the child should be seen by a pediatrician or neurologist
What to do if you are convinced that the baby does not suffer from colic, have tried all the ways, but the baby does not calm down and continues to cry and arch, throwing his head back? To relieve yourself of anxiety, seek the advice of a pediatrician or neurologist.
Let's consider situations when such behavior of the baby may indicate health problems.
Increased intracranial pressure
Sometimes, if the pregnancy was complicated, the child developed intrauterine hypoxia, or there was a difficult delivery, then in the first months the baby may have increased intracranial pressure, due to which he will arch, throw back his head and cry. If intracranial pressure is suspected, it is urgent to show the baby to the doctor to avoid complications.
CSF hypertension symptoms
Irritability, tearfulness, constant crying for no apparent reason, negative reaction to bright lights or loud sounds. Also, often increased intracranial pressure is accompanied by convulsions, profuse regurgitation after feeding. The baby sleeps little and constantly wakes up, when he screams, his lips and chin tremble violently, and the nasolabial triangle also turns blue. In severe cases, the baby's fontanel swells and protrudes, strabismus develops.
Raised intracranial pressure can sometimes be a symptom of a serious illness, such as meningitis, which develops atypically in young children.
Muscular hypertonicity
Arching of the back and tilting of the head may be a sign of muscular hypertonicity in a child. Often, hypertonicity is a consequence of oxygen starvation, fetal hypoxia during pregnancy or during prolonged labor. The most severe consequences can be encephalopathy and cerebral palsy.
Muscle tension can be all over the body or affect only one side of the baby's body. Parents should be alerted not only by the frequent arching of the child and throwing back the head, but also by the violation of the grasping function. Muscle hypertonicity is a reason to show the child to a doctor who, if necessary, will prescribe a course of treatment and massage.
Torticollis
Tilt-back of the child's head can also be caused by torticollis (a pathology of the musculoskeletal apparatus in the neck, due to which the child's head deviates to the side or can be turned to the side). Parents should be alerted if the child's head is always in the same position, and when you try to turn it in the other direction, the child worries and cries. Torticollis requires mandatory treatment, which includes wearing a special collar, massage courses and physiotherapy.
Parents should be alerted if the child's head is always in the same position, and when you try to turn it in the other direction, the child worries and cries. Torticollis requires mandatory treatment, which includes wearing a special collar, massage courses and physiotherapy.
Meningeal syndrome
A complication may occur as a result of otitis media if treatment is started late. This is due to the underdevelopment of the structures of the middle ear in young children.
In this case, the child throws back his head unconsciously, trying to alleviate his condition (3). The following symptoms may also be observed:
- convulsions,
- vomiting,
- confusion,
- decreased motor activity.
You must go to the hospital immediately.
Epilepsy
During an epileptic seizure, the child may arch, throwing back his head strongly, and freeze in this state for a while. After the attack passes, the child relaxes, begins to cry, urination or defecation occurs.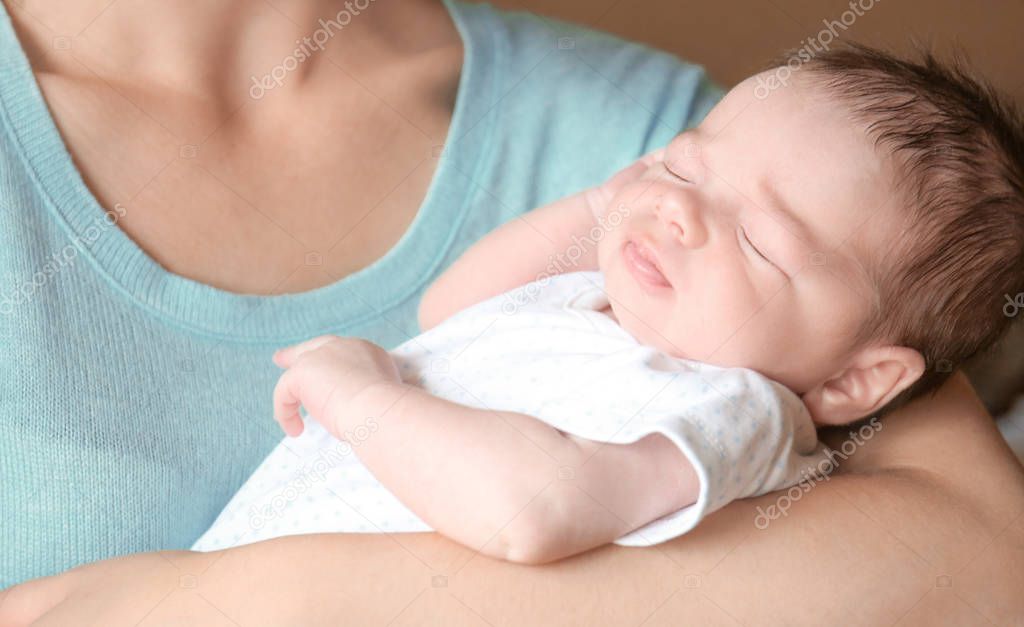 Treatment of epilepsy is prescribed only by a doctor and takes place under medical supervision.
Treatment of epilepsy is prescribed only by a doctor and takes place under medical supervision.
Cerebral palsy
If a child arches their back frequently for no apparent reason, this may be a sign of a pathology such as cerebral palsy (4). But other characteristic signs should also be observed:
- developmental delays (late crawling, sitting, walking, talking),
- low or increased muscle tone,
- problems with speech and swallowing, with only one hand, limps at an older age).
Some of these signs may also be observed in healthy children, but if something worries you, it is worth taking the child to specialists in order to rule out a problem or start treatment in time.
Diagnosis
Photo: Andrey Arkusha, globallookpress.com If you are worried that the baby often arches and throws his head back, it is better to seek advice from a doctor who will determine reliably whether this is a norm or a pathology. The doctor will listen to complaints, ask how the pregnancy, childbirth and the first days of the child's life proceeded, specify how often and under what circumstances the baby throws his head back, whether he cries or behaves calmly, whether the nasolabial triangle turns blue, whether the fontanel swells.
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe tests and examinations:
- general blood and urine tests,
- neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain through the fontanel),
- electroencephalography (to rule out epilepsy).
However, CT and MRI scans are extremely rare for young children, since these studies are performed under general anesthesia, so that the child is completely immobile.
Frequently asked questions and answers
Our expert answers readers' frequently asked questions, Veronika Oranskaya, neurologist, epileptologist, member of the League of Evidence-Based Medicine.
The baby throws back his head and arches after feeding - what can it be?
Sometimes tilting the head back after eating or only in a horizontal position during sleep can be a manifestation of the so-called Sandifer's syndrome, which occurs due to gastroesophageal reflux (reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus). Requires medical advice and treatment.
Requires medical advice and treatment.
Can tilting the head be a symptom of a child's vision problems?
If for some reason (myasthenia gravis, oculomotor neuropathy, congenital feature) the child cannot raise the upper eyelid, he will tilt his head back.
What other possible pathologies can the tilting of the head and arching of the child indicate?
Sudden paroxysmal tilting of the head may be epileptic seizures. A forced constant tilt of the head back may indicate a brain tumor. When combined with an increase in temperature, tilting the head back may indicate meningitis. But most often the reasons for head tilt are all benign: the child doesn't like something, he is learning to roll over, or he just wants to look at something that is behind his head. If in doubt, consult a doctor.
Sources
- Age-dependent manifestations of neuroses in children. M.Yu. Bobylova // Pediatric practice. 2007. URL: https://medi.ru/info/11859/
- Infantile intestinal colic.
 Modern data. N.I. Ursova // Questions of modern pediatrics. 2011. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mladencheskie-kishechnye-koliki-sovremennye-dannye/viewer
Modern data. N.I. Ursova // Questions of modern pediatrics. 2011. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mladencheskie-kishechnye-koliki-sovremennye-dannye/viewer - Features of the treatment of acute otitis media during the Covid-19 pandemic. S.V. Ryazantsev, I.V. Tkachuk, A.E. Golovanov, P.V. Kireev, K.A. Balatskaya, O.S. Don // Medical Council. 2022. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-lecheniya-ostrogo-srednego-otita-v-pandemiyu-covid-19/viewer
- What to Know About Back Arching in Babies. Dan Brennan // WebMD. URL: https://www.webmd.com/parenting/baby/what-to-know-about-back-arching-in-babies
10 Reasons Underlying Baby Arching and Head Throwing
and a thrown back head will cause gray hair in any young mother. This cryptic behavior of a toddler can disturb even the most experienced parents, causing them to quickly skim through hundreds of articles on the Internet and consult with many relatives and friends. Finally, in confusion and fear, she rushes to the doctor with her child.
When should you seek immediate medical attention? Also, in what cases would this situation become abnormal?
The situation when a small child throws back his head and arches his back
In fact, in 60-70% of cases, the tilt of the child's head is so normal that no medical intervention is required. But parents, of course, are worried about the cause of this symptom. This is especially worrisome if your baby starts crying or becomes restless around this time.
Does this also happen in healthy children?
Yes, and very often. However, while some mothers who are attentive to their children notice when their children make noise, others who are not very attentive do not. Why would a healthy child do this?
This symptom may be caused by:
- Increased normal flexor muscle tone in children under 6 months of age. This is the norm, since the myelination of fibers in the pyramidal region takes about a year.
- Attempt to master a new technique called "abdominal muscle drop".
 In this case, the baby sleeps on its side and throws its head back.
In this case, the baby sleeps on its side and throws its head back. - Babies with hysteresis may flex to get their mother's attention if their normal crying style doesn't get their attention.
- Flatulence, colic. This problem is often found in newborns up to 3-4 months due to the formation of microflora and peristalsis. In this case, the arching is accompanied by twisting, crying movements. To avoid such a situation, it is necessary to give simethicone during this period, which suppresses gas formation, with meals.
- Comfortable sleeping positions When they fall asleep in the womb in the unnatural position they are used to in the third trimester of pregnancy, they unconsciously imitate it.
- Desire to see toys above head or itching in occiput or neck.
If the colic is eliminated or the child has calmed down and continues to stand like a "bridge", this is a reason to seek medical help to exclude the neurological underlying reason for this condition.
Pathological mechanisms of behavior
The mechanisms of the position in which children tilt their heads are as follows.
- Generation of pathological impulses emanating from centers of damage to nerve cells. Develops with cerebral palsy, neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, etc.
- The action of overexcitation is generated in the epileptogenic area.
- Increased intracranial pressure or exposure to toxic substances irritate the meninges and stretch the nerve fibers (meningitis, hydrocephalus).
Increased intracranial internal pressure
Intracranial pressure may increase as a result of the pathological course of pregnancy and childbirth or as a result of diseases occurring in the first weeks of life. This condition is very serious and requires immediate medical attention as there is a risk of cerebral edema.
In addition to head tilt and arch, symptoms of cerebrospinal fluid hypertension include:
- anxiety, frustration
- He now responds to bright light and sound.

- Unreasonable monotonous crying voice
- He comes back many times after eating.
- Sleep interval short.
- Blue orbital triangle.
- Control your tongue and lips when you cry.
- Edema of the large pelvis and as it develops, divergence of the sutures is observed with a change in the shape of the skull.
- When compared to other indicators, the volume of the head overgrows.
- Eye exercise disorder in the form of Strabismus.
- Decreased appetite
Increased intracranial internal pressure is often a sign of a life-threatening condition such as meningitis, and 45% of children are not non-confidant.
Bridge baby with muscle hypertonicity
Muscular hemopic tension is often observed against the background of internal fetal hypoxia and long-term delivery. As a result, it becomes encephalopathy and cerebral. Excessive muscle tension can be affected not only on one side of the body, but on both sides. Six months can easily assess the extent of the disease, even for doctors.
Six months can easily assess the extent of the disease, even for doctors.
Parents usually pay attention not only to bending their back and bending their neck, but also to the fact that their limbs are always bent or one movement is slow. For example, children only use their right or left handles to catch toys.
Other conditions
Crooked is also different from other reasons to throw your head with a child. At the same time, the baby's upper body becomes stable in a certain direction, and if you try to change the situation that is lying, you will worry and cry. This state requires massage courses and medical intervention through physical therapy. In the case of severe illness, it is necessary to prescribe muscle relaxants, attach special colors, and sometimes do business.
In addition, bridging is often caused by epilepsy with integrated seizures. The baby hardens in a short time, is unresponsive, and has a bowel movement and urination after capture.
Which specialist will help you deal with the situation?
Parents who realize their bows are bent may not know what to do or which experts to contact. First, calm down and look at the child. Any doctor will start questioning for guidance, because it is difficult to show a clinical image enough without an answer.
First, calm down and look at the child. Any doctor will start questioning for guidance, because it is difficult to show a clinical image enough without an answer.
You must know clearly.
- At what point did your head come back, and how long will it last for one week or one month from the moment you were born?
- Did this event precede the infectious disease or fall?
- When the child turns: during sleep, awakening period or what accompanies: crying, orbital triangular Chiangose?
- Is the child currently responding to external stimuli?
After collecting and reviewing a detailed medical history, physicians can determine a minimum list of diagnostic tools.
If a newborn has a bridge symptom, you should first consult with a nearby pediatrician. He can doubt the pathology of the nervous system if his existence is instructed by a pediatric neurologist for further testing.
What diagnostic procedures are needed for a baby who arches his back and throws his head back?
To understand if the baby's neck is normal or painful, the doctor applies (represented from the parents), vital anesthesia (pregnancy, childbirth, newborn baby). Early progress), you need to collect the disease and conduct a detailed physical examination. If there are signs of damage to the nervous system, the following testing methods are usually recommended.
- Clinical test (clinical blood, urine).
- Neurosonography is a diagnostic procedure for children under 1 year of age who still have large fontanelles.
- EEG - to rule out epilepsy.
- Despite their high information content, CT and MRI are rarely used. These methods require the use of anesthesia to immobilize small patients.
In this case, the proposed diagnostic tools should not be abandoned, since serious diseases of the nervous system can be missed.
How can I help my baby?
If, according to the results of the examination, it turns out that the child is absolutely healthy, and the causes of ARC and disappearances are normal, parents should: reconsider the situation in which the baby is more attentive to him. development.
development.
Affects normal newborn massage such as stroking and gymnastics performed by mums and dads. Thickening of breadcrumbs and bath procedure Melissa baths or bathing with a special circle are also good.
Try to place the toys in such a way that your child does not tilt their head back into an uncomfortable position. Cribs should be equipped with special orthopedic pillows, and mobile phones should be hung in the center, not overhead.
Conclusion
Throwing the neck in infants is not always a pathology, and in many cases still remains a variant of the norm. But do not forget to undergo monthly examinations with a pediatrician so as not to miss a single neurological ailment. Also, when symptoms appear, worried parents should not delay seeking medical attention. Children under 1 year of age are more likely to recover without complications than they are detected earlier.
Parents cannot be silent when their child arches their back or tilts their head. This educational material will tell you what your child's behavior is telling you, if it's dangerous, and what you should do.
This educational material will tell you what your child's behavior is telling you, if it's dangerous, and what you should do.
Physiological causes
The cause of the odd posture, sometimes referred to in the medical world as the "acrobatic bridge", may be naturally harmless to children, but parents have nothing to worry about.
During pregnancy, babies were not able to rotate or extend their limbs in the womb under limited conditions, especially in later pregnancy. Children simply get used to the "compact" posture, and during the first few months of a non-industrial society, they adjust to a new environment that allows them to spread their legs and arms at will. Now it becomes clear why newborns in a dream take "dorsiflexion" and other strange postures.
It is also natural for babies to have increased muscle tone, so head tilt and back arching are normal during the first few months of life if nothing else causes them pain.
Children whose parents are in favor of tight swaddling often bend over.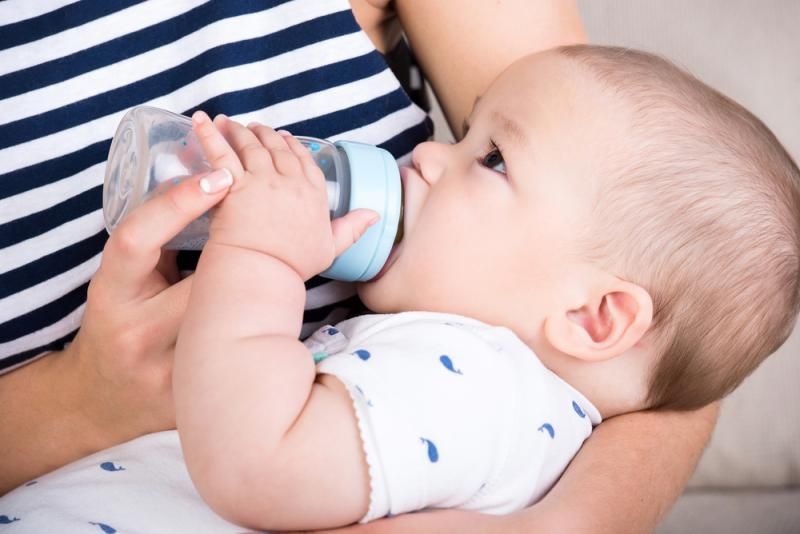 Usually, this position may indicate that the baby is uncomfortable in diapers, that his arms and legs are numb. Small children without diapers can bend over and stretch with pleasure.
Usually, this position may indicate that the baby is uncomfortable in diapers, that his arms and legs are numb. Small children without diapers can bend over and stretch with pleasure.
Another fairly common reason is the manifestation of emotions and feelings. His weapon, the child, does not have many tools for expressing his feelings and desires, such as screaming and posturing. If the parent's crying is not provoked, the child will inevitably lie on his back and tilt his head back to inform him of wet diapers and pain during crying.
By bending over, the baby can show that he is already ripe for his new position in space, that he is tired of sleeping on his back and that he is ready to roll over on his stomach. This normal flexion and stretching usually begins at 4-5 months of age, but if your baby has not yet begun to roll over by this time, you should not roll over.
If the toys on the crib are hung at the level of the child's face, and not at the level of the stomach, the deflection will become quite familiar, and the baby will visually follow the active game.
If your child is happy and active, eats well and sleeps well, you will not find diseases that you do not have. Episodes when the baby bends over or throws back his head in a dream on his back in a dream or during a massage should not cause panic.
However, in combination with massive and frequent regurgitation, loss of appetite, restlessness, muscle tension, incorrect position of the limbs even during sleep and difficult to raise to a normal position, flexion and straightening of the back of the parents should be warned and forced. should be examined regularly.
Pathological causes
Pathological causes of this phenomenon may be different. Without obtaining laboratory data, ultrasound data and other diagnostic methods, as well as without a preliminary examination of the child, no doctor can name the true cause. Let's look at the most common reasons why babies lie on their backs and throw their heads back.
intestinal colic
Infants from birth to 3-4 months are very common. This is associated with the establishment of bowel function and is characteristic of childhood flatulence and metabolism. Often occurs during breastfeeding and some time after breastfeeding. If the child is in the mother's arms, press the legs to the stomach and reflexively bend over (→ turn, → turn) and alternately cry.
This is associated with the establishment of bowel function and is characteristic of childhood flatulence and metabolism. Often occurs during breastfeeding and some time after breastfeeding. If the child is in the mother's arms, press the legs to the stomach and reflexively bend over (→ turn, → turn) and alternately cry.
The pain from the fermentation of intestinal gases is so severe that the child can tilt his head, lie on his back in the "bridge" position, throw his arms in different directions and cry at the same time. To understand the guilt of Gaza, it is enough to put a warm diaper on a pre-ironed stomach and give Simeton to an infant, or a preparation with its content, which minimizes the amount of gases in the intestines. Usually after 15-20 minutes the fever and such drugs will work and the baby will calm down. Upon awakening on an empty stomach, peanut body weight does not show conversion because preprandial colic does not occur.
rhinitis, colds, viral infections
Newborns have narrow nasal passages, so even mild rhinitis can interfere with breathing. Babies with a runny nose often throw their heads back, including during sleep. Concomitant symptoms should be noted, such as fever, snoring, coughing, and anorexia.
Babies with a runny nose often throw their heads back, including during sleep. Concomitant symptoms should be noted, such as fever, snoring, coughing, and anorexia.
The most noticeable is that the baby is not able to breathe freely through the nose, and the mouth is blocked by the breast or nipple, causing it to fly out or bend at the time of feeding.
hypertensive
Hypertension is not considered an independent problem and is typical both for relatively healthy children at the age of 6 months and for children with lesions of the central nervous system. It would be difficult to understand why. You need the help of a pediatric specialist, such as a pediatrician or a neurologist.
Increasing muscle tension is usually more stable and independent of factors such as food and sleep. In many cases, the harmonious development of the child and the normal care of the sick will be carried out over time. Parents can help their children relax, such as massage, bathing, walking and daily exercise.
In the case of the muscular skeletal system, spine, corset muscles and central nervous system, doctors prescribe appropriate treatment.
Increased intracranial internal pressure
Parents often hear similar results of the diagnosis. However, there is no tendency in modern pediatrics to treat it as a different disease. Various diseases, such as trauma during birth, nervous diseases, and hydrocephalus, can be accompanied by an increase in pressure in the skull.
Always loud, loud, falling asleep, bad meal, tearing violently. Show this to a neurologist.
Many of the instructions for depressurizing the skull are Strabismus, trembling limbs, pupils, convulsions, and bluish orbital triangles. These symptoms are quite different from the physiological malformations described above, and it is all too easy to confuse children with the curiosity of a baby's belly that wants to roll over but cannot strike.
Dr. Komarovsky's opinion
Well-known pediatrician Komarovsky, a well-known pediatrician, claims that he should not rush to a conclusion.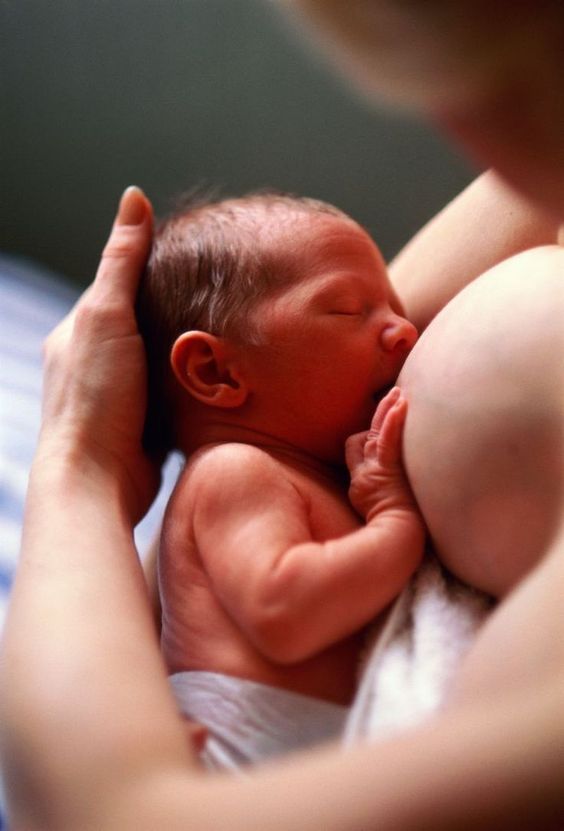 In most cases, a child who takes his hand to bend his back, or in some cases, bends over his back, is very healthy.
In most cases, a child who takes his hand to bend his back, or in some cases, bends over his back, is very healthy.
There are not many cases where the nervous system or the muscular skeletal system is affected. Rather, children often bend for no reason to give their parents a mental breakdown.
Doctors recommend that you calm down and observe. Record the frequency of bending and stretching, where it occurs (after eating, massage, gymnastics, bathing), etc. Will it disappear after the child's request is met, such as breastfeeding, changing clothes and treating pain.
Of course, if your child's muscles get too nervous during sleep and can't retract their limbs and heads normally, you need a doctor.
Children who sit up, lie down and bend their back and do this many times a day will need to see a neurologist.
What to do?
As Komarovsky says, it is important to first observe the children. If you don't have other painful symptoms, you don't need to do anything. Normal bathing, massage, gymnastics. If you have more problems, you should contact your doctor without extending the time.
Normal bathing, massage, gymnastics. If you have more problems, you should contact your doctor without extending the time.
At home, as you watch your parents' children, you can participate in the work of removing the external factors that make your child's situation strange.
- Check the position of the crib, toys, to the center of the baby bed to the center of the baby bed, screen, mobile phone, etc.
- Make sufficient attention to children (mosquito bite or freaky children often need to communicate with adults, not only succeed in eliminating diapers and hungry phlegm).
- Take care of bathing - you can teach any age from one month old. When you swim in a bath or in a pool, your muscle tissue will grow, develop and rapidly increase muscle tension.
- Don't panic e-calm mother can give her health and development much more hysterical.
And finally, the most important tips. When you go to the doctor, don't hit all the anxiety right away. In Russia, it is said that a healthy child is a "funny" mother, and it can be pathological, and overdiagnosis of overdiagnosis is to perform unnecessary treatment.
In Russia, it is said that a healthy child is a "funny" mother, and it can be pathological, and overdiagnosis of overdiagnosis is to perform unnecessary treatment.
Experienced doctors pay attention to whether children really have lesions in the nervous system or the muscular skeleton. In this case, he will always ask many questions, and the mother will be able to answer more.
Dr. Komarovsky talks about neural symptoms in children in the next video.
If the child turns his back, the parent reads it as a sign of discomfort and pain and due to external or internal causes. Most of your back arches when you cry, turn your head, or sleep. This may indicate either temporary fatigue or serious health problems.
What does Backback mean?
Children can bend their hips and float their arms in the air. Sometimes I drag my neck behind. If you are holding a child, it is dangerous because you can slip and get hurt.
If you are holding a child, it is dangerous because you can slip and get hurt.
Until the sixth month, the back cannot be bent. With this action, you will be able to express emotions such as discomfort and dissatisfaction through this action.
LOERS may be normal, but in some cases it may be symptoms such as some discomfort, indigestion, and mental and physical retardation.
Why is the baby around his back?
From simple fatigue to pain, a child's back deformity has many meanings.
The reason why the child bends his back.
1. 1.
Babies can't talk, but that doesn't mean they can't communicate. The back is one of the means to express dissatisfaction, anger, pain or similar emotions.
Like adults, babies can change their baby bottles, their diapers get wet, toys are boring, and they can get upset for a variety of reasons.
2. Fatigue
You may feel tired after breastfeeding or feel hungry after playing. The child may think of dorsiflexion, so it is convenient to communicate with parents.
If you want to avoid this situation, look for other non-aggressive signals and act accordingly.
A more serious reason for a child to bend back
This is a temporary anomaly that the back turns, but it may reflect more serious causes and health.
3. Breast after lactation-Gastral food reflux
If you bend your back while breastfeeding, there is a possibility of gastronomic reflux (acid reflux).
Acid reflux is a condition in which the contents of the stomach enter the esophagus due to a decrease in the muscles of the stomach.
The lower esophageal sphincter is a bundle of muscles at the border of the esophagus and stomach. It acts as a valve to prevent acid and food from refluxing from the stomach into the digestive tract. In infants, this valve is underdeveloped, allowing stomach contents to move up into the esophagus.
Gelb (gastrointestinal reflux) often occurs in infants when they drink milk. Children may arch their backs and complain. Reflux can also be accompanied by coughing, irritability while breastfeeding, and frequent spitting up.
Reflux can also be accompanied by coughing, irritability while breastfeeding, and frequent spitting up.
Flexion and stretching may also indicate silent regurgitation without tears, but with problems digesting food.
Another common cause of slouching back is colic. The second case is related to gas in the stomach, and the discomfort from the gas can cause the baby to cry. Flexion and stretching of the back reaches the stomach and relieves abdominal pain.
Colic begins at 4 weeks of age and subsides by 3 months of age.
how to cure reflux
- Maintain an upright posture after feeding. Gravity will naturally cause the food to fall down, making it less likely to rise back up.
- Feed frequently but for short periods of time. This will keep the belly from resting on the porch.
- Do not put the baby to bed immediately after breastfeeding. Instead, take your child out for a walk for a while.
- Do not force yourself to wear tight clothing as this may put pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter.

4. Crying and prostrations in case of jaundice (jaundice).
If the baby bends over and cries during jaundice or other liver problems, this may be a sign of kernicterus due to bilirubin encephalopathy.
Jaundice occurs due to an overproduction of bilirubin. In extreme cases, it can cross the blood-brain barrier and damage the brain, causing involuntary motor convulsions.
Kernicterus can cause brain damage, mental retardation and seizures. This condition should be reported to your doctor immediately.
5. The child sleeps with his head thrown back - obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
You can bend your back or rest on your back while you sleep. When changing position, the baby may return to a bent position or jump up and start crying. In such cases, you may have obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic upper airway blockage.
By tilting his head in an arc, he tries to relieve the pressure on his upper airways. This is done so that the air flows smoothly into the lungs, and babies subconsciously try to stay in this position during sleep.
Apnea occurs mainly during deep sleep, but can also occur when the child is drowsy and lying down. The disease is treated with medication or surgery.
6. Straighten your back - Neuralgia
If you were born prematurely or have postpartum neuropathy, you will bend over when you sit or are tired. The physical pressure during a difficult birth can damage the baby's nerves and lead to ERBA paralysis.
Backbends can be caused by hips, drooping shoulders and back pain.
As the teeth grow, irritation of the nerves originating in the gums can see the child bend back. In many cases, this pain spreads to other parts of the head and the child bends back.
Neurological causes and reasons why children bend their backs
Bending their backs with a child can be a symptom of a nerve problem.
If you bend your back in this state, your child will unconsciously bend over and be unable to control himself. If your child stretches too much or arches your back frequently, these are likely to be the initial symptoms of cerebral phalia.
Cerebral palsy is caused by brain damage, usually caused by the state of hypoxia during childbirth. As a result, physical exercise and mental development may be delayed or seizures may occur.
Cerebral palsy is one of a series of muscle disorders caused by damage to part of the motor function of the brain.
Be careful with bending and stretching on your back as you may have cerebral palsy.
- Severe labyrinth reflex: curves backwards and clumps during the first few months.
- Unplanned intense reflection. The child bends his back and shakes his neck. The legs are usually extended in the direction of rotation.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for brain polish, but various physical and mental treatment programs have been developed.
8. Autism
Autism is a genetic disorder that is delayed by nerve development. A specific physical gesture is one of the first signs of disability, such as rolling on your back while cuddling, sleeping, and falling head-first.
Autism is difficult to build healthy social relationships, so if this diagnosis is upset, even if you are a parent, you will be tough to avoid physical contact with people who keep themselves.
Asperger's syndrome is difficult to build social bonds, and are also equipped with non-calculative communication with eye contact and gestures. The prognosis is very similar to autism, but it gets milder as it progresses.
Asperger's is thought to be part of the autism spectrum, so back pain may be one of the symptoms.
10.
If there are no other autism spectrum symptoms, and you can see your body positioned or bent over in a seizure pattern, the child is likely to have a child. This is called trapping and is a type of neurological disorder in which a child unknowingly contracts muscles and arches their back and neck.
What to do when your baby flexes?
Whether you have a normal or serious condition, parents can help your child by looking at the following:
- Calm down baby.
 Take it to a quiet room with adequate lighting. It helps children on the autism spectrum.
Take it to a quiet room with adequate lighting. It helps children on the autism spectrum. - Hold the baby to your chest with a slight upright posture. A warm hug with a mother is peaceful for children.
- Baby Mind: This is an old way to soothe a baby and should be ideal for kids who are hunched over and stressed or frustrated.
- With light clothing. The baby may also bend due to tissue or tissue stimulation.
- Move: If your child only tends to bend over on a certain mattress or bed, change it to a more comfortable one.
Bending of the back is not a disease. This is usually a sign of irritability or discomfort in the child, but this behavior can also indicate an illness or disability.
the baby arches back
One of the reasons why babies arch their back and throw their head back is excessive tension in the superficial muscles of the neck and back. Test your child to determine this. Examinations are carried out from 3 months of age.
test 1
Lay the child on his back and see how he moves. If muscle tension is felt in the back, lay the child on his stomach, tilt his head back and tear his shoulders off the surface of the table without the help of hands. On the one hand, tension builds up, the body leans to that side, the head turns, and the child can naturally lie on his back. Active rollover from belly to back and self-holding of the head should be distinguished from random "turnover". The difference lies in the industrialization of exercise. It is commonly said that young children must learn to roll over from the supine position to the prone position. But still, in 5% of cases, the rear turn is first noticed. After removing excessive muscle tension, it is necessary to actively train the correct movement, appropriate for age.
test 2
Next, lying on your back, gently pull the child's arm. At the same time, children are not capable of collective action and throw their heads back. To get an idea of how tense the neck muscles are, place your hand under the child's neck. Slowly raise the back of your head above the surface of the water. When you try to bring the baby's chin closer to your chest, you will feel muscle resistance.
To get an idea of how tense the neck muscles are, place your hand under the child's neck. Slowly raise the back of your head above the surface of the water. When you try to bring the baby's chin closer to your chest, you will feel muscle resistance.
event information
In this case, some relaxation techniques and special exercises for the neck and back can help.
The first positive effect of your actions will be when your child stops holding his head and turns his back. In fact, it is reduced by excessive and unnecessary muscle tension, which interferes with the active movements of the child, for example, timely turns from the back to the stomach. After relaxing the muscles, you can proceed to strength and athletic exercises.
muscle tone correction
neck massage
If the child bends over, the stimulating massage is not performed. When the muscles of the back are constantly tense and the neck is extended, the chin cannot be brought closer to the chest even when lying on the back or lying down. In this case, the massage will be performed in a relaxed state, and its content will be as follows.
In this case, the massage will be performed in a relaxed state, and its content will be as follows.
During the massage, the baby should lie face down, arms bent at the elbows and brought under the chest. Start the massage with stroking. Run your palms along the back and sides of the neck, from the back of the head to the shoulders. Individually stroke the shoulder girdle from the neck to the shoulder joint. Repeat this slot 4-5 times.
types of muscle tension
Then move on to subtle stretching movements that work directly on these muscles.
Hold the back of the head with one hand and slowly pull the neck muscles from this part to the shoulder blade. It stops 2-3 seconds at the end of the operation. Repeat reception 3-5 times.
Finally, step forward and move on to the back massage.
Back Massage
Be sure to check the back muscles to determine why your child is distorting when choosing a massage method. If you have a lot of tension in these muscles, start with a relaxing massage. They require stroking and light stretching techniques. If you don't have that kind of tension and your neck isn't set yet, try massaging as a gripping motion. In this case, don't use the stretch method at all.
They require stroking and light stretching techniques. If you don't have that kind of tension and your neck isn't set yet, try massaging as a gripping motion. In this case, don't use the stretch method at all.
Rear Strawberry
First slot - move. Do this along the spine, raising and lowering your arms. Repeat reception 3-5 times.
Then, from the spine to the ribs, absorb it from the fingertips to the side. Repeat 2-3 times left and right.
Stretch Muscles
To release tension in the back muscles, he proceeds to a gentle stretching operation that works directly on the back muscles.
The back massage is completed by repeating the stroke.
This time train your neck muscles, tilt your head forward and add certain exercises to stretch your neck and back muscles.
Exercise 1
Lay the child on his back on his back and place a pillow for the child under his head and shoulder. Grab your child's shoulders with both hands from the back and float a little off the surface. Wait a few seconds until your child tries to put his head on his shoulders. Put the child on the bed and rest. Repeat this movement 5-7 times.
Wait a few seconds until your child tries to put his head on his shoulders. Put the child on the bed and rest. Repeat this movement 5-7 times.
Exercise 2
If you cannot raise your head on your own, put your hands behind the back of your head and help. Hold this pose for 3-5 seconds and gradually increase this time. Repeat this movement 5-7 times.
Exercise 3
While lying on your back, lift the top of your head to a 30 degree angle. To do this, place a pillow under your head and shoulder. The palm is applied to the back of the shoulder, neck and back of the head. Slowly slow your upper body on the surface of the water and hold for a few seconds. Repeat several times until you feel the muscle resistance disappear.
Exercise 4
EXERCISE 4: DANGEROUS TRAINING
By stimulating the active static head while lifting the torso, the previous operation is completed. To do this, the fingers are dropped from the back of the child for a few seconds in a high position.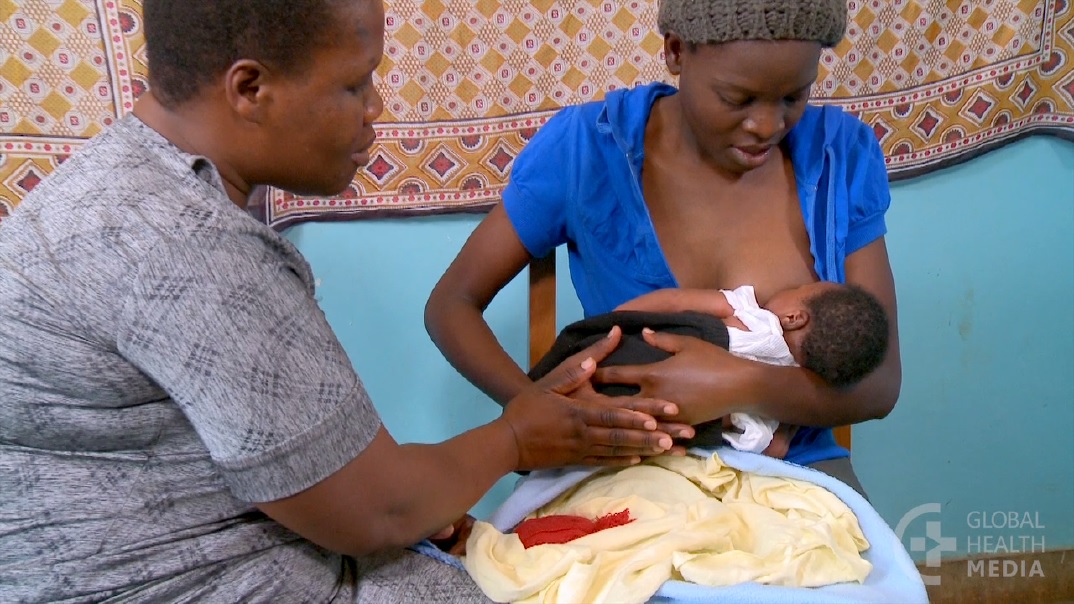 Once your child is holding your head, you can move on to the next step.
Once your child is holding your head, you can move on to the next step.
Exercise 5
Lift your torso off the pillow, but make sure your head is not supported. The child tries to separate the group so that, once he has succeeded a few times, remove the cushion so that he can lift from a horizontal surface.
Exercise 6
Exercise is positive. As the muscles on the back of the neck and trunk normalize and the flexible muscles of the neck increase, independent control of the baby's head can be started. As a result, exercises were developed using gymnastic balls. This is a form that rolls in all directions in all directions in a belly pose "flying" while rolling.
Recommended glasses for parents of manipulation teachers
Manipulation teacher's opinion, why is this a children's arch? In my clinic, I often encounter such violations. According to the observation, the causes of the arch may be the inappropriate position of the uterus of the fetus and the difficulty of childbirth.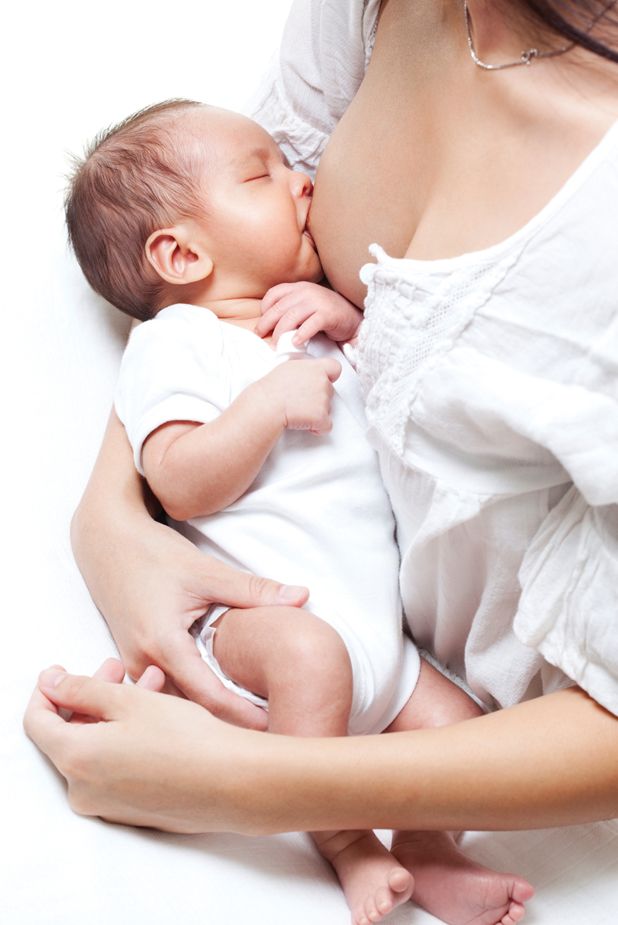 The suggestions I make fit well with osteopathic treatment. I diagnose the patient as an osteopath and correct the existing dysfunction. And, according to the advice, parents work with their children every day at home. On average, two weeks later, take the results and provide additional osteopathic therapy if necessary. This problem can be considered in most cases.
The suggestions I make fit well with osteopathic treatment. I diagnose the patient as an osteopath and correct the existing dysfunction. And, according to the advice, parents work with their children every day at home. On average, two weeks later, take the results and provide additional osteopathic therapy if necessary. This problem can be considered in most cases.
Cervical neck is caused by unsettled head and due to abnormal development of the busty muscle in piles. Symptoms such as facial asymmetry and neck rotation appear on one side of the head and the other side on the other side. In orthopedic surgery, this is a condition that occurs in 2% of newborns. Girls are bigger than boys, and the right defeat is dominant.
Article content
- Causes of pathology
- Cervix
- Infant symptoms
- Status diagnosis
- Treatment of convulsions in children
- Cervical prophylaxis
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Expert opinion
Causes of pathology
The cervix occurs in many children with the uterus behind. Bleeding occurs because the muscles have changed consciously and due to difficulties. As a result, there is a periodic change in the busty muscle in piles. The appearance of such a pathology is called congenital. Acquisition found in disease, trauma, nasopharyngeal process.
Bleeding occurs because the muscles have changed consciously and due to difficulties. As a result, there is a periodic change in the busty muscle in piles. The appearance of such a pathology is called congenital. Acquisition found in disease, trauma, nasopharyngeal process.
If your mother puts your child's head on one side, if your child's head is unsound, he is very often diagnosed with orthopedic surgery. If you have any questions, please contact our doctor. In a remote consultation, our doctors explain the possible causes of the pathological condition, answer all questions so that they can always contact them.
Cervix
There are the following types of diagonal neck.
- Mukimuki. This is due to the pathology of Master and Clabical Pectoralis. At the same time as the tilt of the neck, the face rotates.
- This is a bone. It also appears due to a violation of the formation of the skeleton
After an injury to the cervical spine, it appears as a result of neurological complications
This is the result of an inflammatory disease.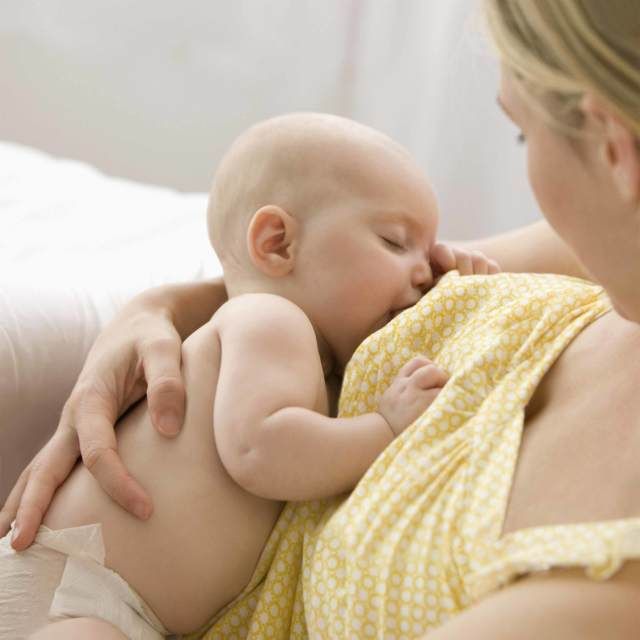 My head is tilted and due to hypercyne
My head is tilted and due to hypercyne
Very rare
- Neck changes
- Incinerated.
- Strabismus
- Severe direct spondylitis
Increased position without trying to turn the neck caused by neck pain
One-time muscle contraction and due to inflammation of the posterior orbital joint
It is characterized by local pain in the neck and forced head.
A mother who came to orthopedic surgery with a two month old baby. The child is forced to get to the left. This child has a history of Strabismus disease, which is a paralyzed muscle in the left eye. Introduced by an orthopedic surgeon, she was consulted by an orthopedic surgeon for suspected diagonal neck. The test did not reveal any x-any pathological. The unsubstantiated head is that the child tried to recover the binoculars. Recommended: massage, consultation with ophthalmologists and a positive attitude.
Infant symptoms
Cervical signs The neonatal cervix can be seen immediately in the first days. Late-type symptoms appear noticeable three weeks after birth.
Late-type symptoms appear noticeable three weeks after birth.
As a result of the consultation, the following symptoms of congenital cervical cervix are recognized.
- Always tilt your head over your shoulders and look away from you - correct torticollis.
- When the head is suddenly turned to the other side, the newborn cries out in pain.
- Marked facial asymmetry.
- Bilateral torticollis causes head tilt and back hunch.
- With osteogenic torticollis, the neck is shortened on one side, the head is low, and head mobility is limited.
- With neurogenic torticollis-hypertension, the hand on the side of the lesion is clenched into a fist, and the head continues to move.
At the age of 6, facial asymmetry with torticollis becomes noticeable. The affected side has flattened cheeks, low pulse and underdeveloped ears. With congenital torticollis, there is.
- hip dysplasia
- plagiocephaly
- hare lips?
- Malocclusion?
- skull with short tongue
Uncorrected torticollis causes secondary deformity of the skull. Children with this condition develop teeth slowly and may be slow to sit and crawl.
Children with this condition develop teeth slowly and may be slow to sit and crawl.
If your child has symptoms of torticollis, contact our doctor. During telemedicine, our doctors will explain the clinical symptoms of your condition, advise on how to treat your condition, advise which clinics to contact and a list of specialists to contact for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the condition
Diagnosis is based on physical examination and history. If necessary, the specialist may order the following examinations of the neck and entire spine:
To rule out other pathologies, the following appointments are possible:
Other conditions may be prescribed to rule out other conditions. In differential diagnosis, differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases.
Other diagnostic names: trauma, fracture, dislocation, hyperextension.
Inflammation: retropharyngeal abscess, cervical lymphadenitis, osteomyelitis
Neoplasms of the neck, posterior cranial fossa, soft tissues and bones
Acute calcification of the cervical intervertebral disc
First, doctors rule out neurogenic torticollis. Pay attention to neurological symptoms, the general condition of the baby.
Pay attention to neurological symptoms, the general condition of the baby.
Read also abdominal ultrasound.
Treatment of convulsions in children
If you notice that your baby turns his head to the side or throws it back, you should start treatment immediately. At home, you can move Alicia's face forward while changing the baby's position in the crib.
Conservative treatment includes the following:
- wearing colored shirts
- Using a neck brace.
- Torticollis in infants requires massage.
- physiotherapy exercises; physiotherapy exercises
- gymnastics, gymnastics
This therapy is effective for mild torticollis. In severe cases, treatment is long.
Surgical correction is indicated if conservative treatment fails to produce good kinetics. The operation is possible from 1 or 2 years. After the operation, you will be required to wear collars.
Medical therapy is the preferred treatment for neuropathic torticollis. This relieves muscle tension, excitability of the nervous system.
This relieves muscle tension, excitability of the nervous system.
Excellent The refractive and symptomatic forms are treated according to the condition causing the torticollis. Physiotherapy and corrective collars can be used.
Cervical prophylaxis
Any pathology is easier to prevent than to treat. Prevention methods include:
- swim.
- Strengthens your child's back, neck and back muscles.
- It is important to hold the baby correctly and toss and turn frequently during sleep so that the baby does not tip back and head back.
- The asymmetry of the skull caused problems with the eyes. And because of a bent neck, there can be spinal congestion, a developmental delay, and a psychological problem in older children.
This is the state in which the child throws his head in one direction and turns in the opposite direction. This gradually occurs from a few months after birth.
Frequently asked questions
Parents should be careful when the child tilts his head to the side and holds it in this position.



.jpg)







