Baby food portions 9 months
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor. It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here. Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done. Signs of being full include:
Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
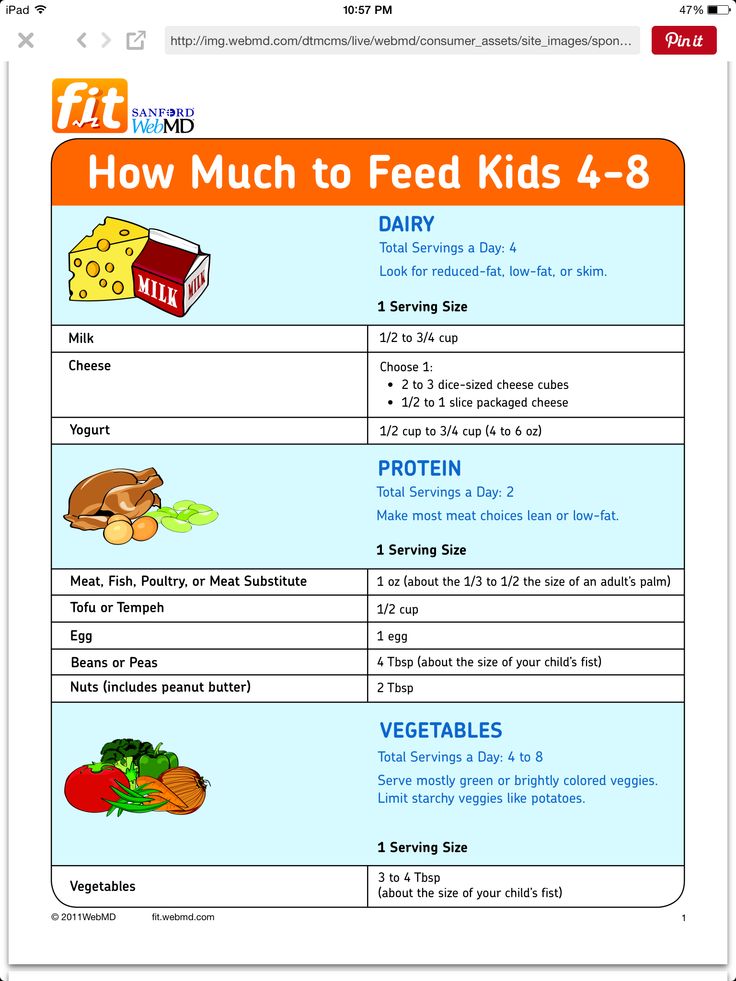
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods. The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal. The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
- Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.
Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars.
 "
" - Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.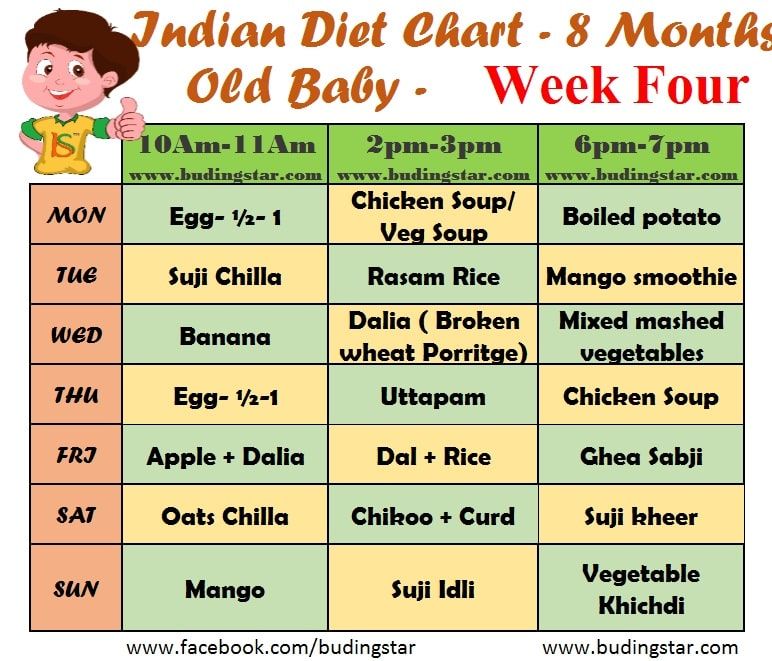
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.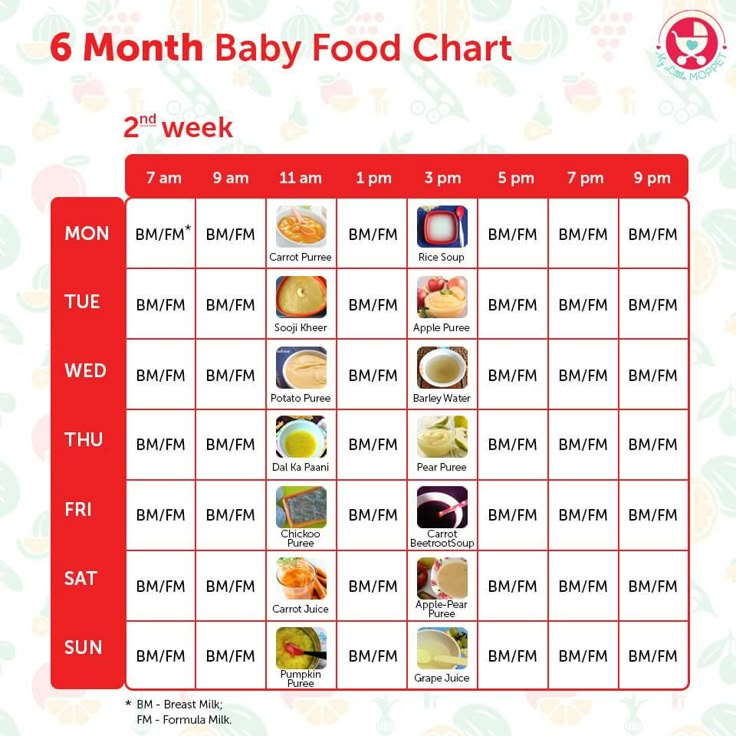
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
Advertisement | page continues below
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water. (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Baby menu at 9 months
6-12 months
Article
5/5 1 reviews
Although breast milk or formula remains the mainstay of infant nutrition at this age, a 9-month-old baby's menu becomes more varied with new complementary foods. The correct diet of the child is the basis of his harmonious development, good health and good mood. But how to organize a diet, what can be given at this age and how much should a child eat at one meal? nine0003
The correct diet of the child is the basis of his harmonious development, good health and good mood. But how to organize a diet, what can be given at this age and how much should a child eat at one meal? nine0003
8 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
The correct diet for a nine-month-old baby includes 5 meals: a day the baby receives liquid food twice and thick food three times. This is due to the fact that mashed potatoes and cereals take longer to digest than milk, so they give the baby a longer energy supply. Feeding is usually carried out at intervals of 4 hours. If the baby asks to eat 2-3 hours after liquid food, offer her a baby snack, fruit or vegetable (in small pieces or in the form of a puree). nine0003
A 9-month-old baby's daily diet includes many healthy foods and drinks that provide essential nutrients such as vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals. In addition to milk and infant formula, the following foods can be given to a child:
In addition to milk and infant formula, the following foods can be given to a child:
- Fruits and vegetables in the form of puree (apple, pear, cauliflower, etc.)
- Fruit juices and compotes without sugar.
- Meat in various forms.
- Fish. nine0017 Kashi from various cereals.
- Chicken or quail egg yolk.
- Children's fresh cottage cheese.
- Children's low-fat kefir.
- Children's cookies, croutons, bread.
Read also: The baby refuses new products
According to WHO recommendations, by the 9th month, all of the above products should already be on the menu. If something from the food is still unfamiliar to your child, it is recommended to gradually add it to the diet. nine0003
Start with smaller portions and see how your child reacts to the new food. If there is no allergic reaction to the product, you can increase the volume and add it to new dishes. New complementary foods are recommended to be introduced at intervals of 5-7 days. An indicative table for one day will help to create an optimal diet for health. It also shows how much formula or milk the baby should eat per day.
An indicative table for one day will help to create an optimal diet for health. It also shows how much formula or milk the baby should eat per day.
* infant formula.
**Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or infant formula given to the baby. Milk porridge is diluted with water. nine0003
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge* | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil < | about 1 tsp | |
| Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 70 g | |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree or pureed soup | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Meat puree (rabbit, turkey) | 50 g | |
| Fruit juice | 70 g | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree | 50 g |
| Vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge | 180 g | |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Meat puree | 50 g | |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
*dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or it is safe for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins.
** you can eat porridge or vegetables, so you can eat grass - porridge with vegetables. nine0003
1st day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Buckwheat porridge with pumpkin, juice |
| Lunch | Pumpkin steam cutlets, veal puree |
| Snack | Rusks or baby biscuits, yoghurt |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
2nd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal, berry juice |
| Lunch | Steamed fish, rice, fruit compote |
| Snack | Vegetable puree |
| Dinner | Vegetable puree |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
3rd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Semolina porridge, quail egg yolk |
| Lunch | Steamed zucchini, boiled veal, apple compote |
| Snack | Pumpkin and apple puree |
| Dinner | Curd casserole with carrots |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Fourth day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, fruit puree |
| Lunch | Mashed potatoes or turkey meatball soup |
| Snack | Carrot Apple Juice |
| Dinner | Kefir |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
5th day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula | nine0058
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal and apple puree |
| Lunch | Cream soup with chicken and vegetables |
| Snack | Carrot juice |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree, crackers or bread |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
6.
 Sixth day
Sixth day | First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, half yolk (chicken egg) |
| Lunch | Vegetable soup with chicken breast, juice |
| Snack | Baked apple |
| Dinner | Spinach mashed potatoes |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Seventh day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Millet porridge, croutons |
| Lunch | Steamed chicken cutlets, vegetable puree |
| Snack | Apple juice |
| Dinner | Curd with fruits | nine0058
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Parents need to gradually accustom the child to eating solid foods, because now he is moving to a new level of development: more teeth appear, so the baby can now chew food. If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
No need to grind fish and potatoes in a blender - just put the food on a plate and mash well with a fork. Meat can be offered in the form of meatballs to develop chewing skills. It can be turkey, rabbit, veal, beef, chicken. The norm of meat for one meal is 60-70 g.
It is quite normal if at first large pieces in a dish cause discontent in a child or even a gag reflex - he will soon get used to it. Sometimes it happens the other way around - the baby willingly tries the pieces, but refuses pureed food. Treat your baby with apple slices, bread, crackers or baby snacks. But the meat is still better to grind thoroughly. nine0003
At this age, consumption of mother's milk or adapted formula decreases. There are only two feedings per day - in the morning and in the evening. Everything else is "adult" food. Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Please note that uneaten food (already cooked) must not be stored and reheated. It is also not recommended to add sugar and salt to the dish. nine0003
If you give your child ready-made baby puree, we recommend that you do not feed him immediately from a jar, but pour the right amount onto a plate. In this case, the rest can be stored in the refrigerator for another 24 hours.
Find out more: Baby Portion
Pay attention to the quality of food you cook: appearance, smell and expiration date. It is better to use seasonal vegetables and fruits, and shop in trusted places.
Wash food thoroughly under running water before cooking. You can also use special children's products for washing fruits and vegetables. nine0003
nine0003
All products must be brought to full readiness, and then thoroughly crushed to the desired consistency, so that the baby can comfortably chew small pieces. After eating, wash the dishes with a special detergent.
How to properly feed a 9-month-old baby if he refuses food and does not eat the foods you suggest?
Poor appetite is one of the indicators of a baby's health. The problem may concern the digestive tract, glucose levels, central nervous system. The feeling of hunger appears when the level of sugar in the blood decreases. But for this you need to take breaks between meals. Also, the smell of food affects the appetite - it causes the release of gastric juice. nine0003
How to regain your appetite:
- observe the diet;
- develop a delicious menu for a baby at 9 months;
- Serve dishes beautifully and set the table;
- ventilate the room before eating;
- let your baby use cutlery.
See also: The baby does not eat well, how to feed?
In order for the baby to eat willingly, he must be in a good mood. Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere. nine0003
Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere. nine0003
If the baby refuses to eat or eats very slowly, do not rush or force him to eat. Also, do not force the little one to eat foods that he refuses. Otherwise, in the future, he will have a negative attitude towards the feeding process, refuse to eat any food at all. He can even feel sick and vomit only with one kind of food.
Important
Games and cartoons during meals do not really improve appetite. On the contrary, in this way you only teach the baby to eat without noticing the dishes. nine0512
With the help of our tips, you can create a menu for a child at 9 months for every day, which will meet the requirements of a healthy diet and preferences of the baby
1. What should not be given to a child at 9 months?
It is not recommended to give cow's milk until the age of one. It contains too much calcium, which overloads the kidneys, and protein, which is poorly digested.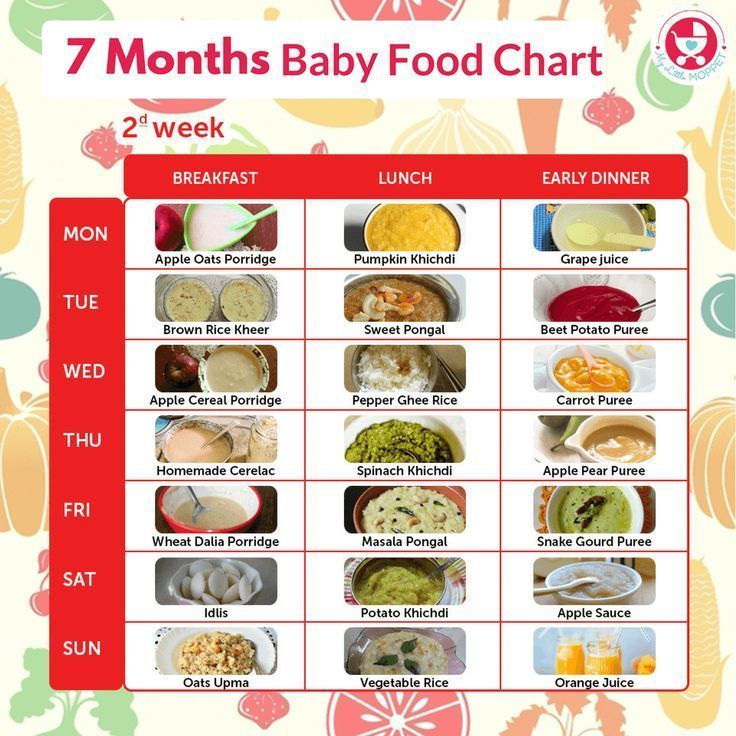 Also be careful with foods that can cause allergies or contain a lot of sugar
Also be careful with foods that can cause allergies or contain a lot of sugar
2. Should oil be included in a baby's diet?
A 9-month-old baby's menu should include animal and vegetable oil, as it contains many vitamins, proteins and fatty acids necessary for the proper development of the baby. Among the useful products of plant origin, it is worth noting olive, corn, sesame or linseed oil.
3. Can a 9-month-old baby be given fish?
Low-fat white fish can be a healthy addition to your baby's menu. It is recommended to give fish 1-2 times a week instead of a meat dinner - flounder, cod, hake or pike perch are suitable. If the baby responds well to the product, try making fish cakes or meatballs. nine0003
Related Articles:
Cooking or using baby food?
At what age can a child be given kefir
Last reviews
Average customer rating
1 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 1
- four 0
- 3 0
- 2 0 nine0017 1 0
menu for a week, diet for a 9 month old baby with artificial and breastfeeding
Published: 06/20/2020
Reading time: 5 min.
Number of reads: 227238
Author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Allergist-Immunologist
Your baby is 9 months old, and it's time to adjust his nutrition again. The activity of digestive enzymes is already high, teeth erupt in the crumbs, and the volume of the stomach becomes larger, which determines the possibility of increasing the amount of food per feeding and further expanding the diet. What can a child eat at 9months?" - this question very often worries the parents of a grown baby. By this age, the baby's nutrition already includes all the main food groups, and parents should try to diversify the child's menu, expanding the range of his taste sensations. In addition, a varied diet naturally provides a wide range of nutrients. Let's focus on the main food groups that should be on the menu of a 9-month-old baby.
Contents: 9-month-old baby is not enough, so mother's milk should now be no more than a third of the diet. It is best to leave breastfeeding (HF) before bed at night, as well as immediately after waking up in the morning. If the baby is formula-fed, an adapted formula for babies over 6 months of age can be offered at these meals.
It is best to leave breastfeeding (HF) before bed at night, as well as immediately after waking up in the morning. If the baby is formula-fed, an adapted formula for babies over 6 months of age can be offered at these meals.
See also: Complementary foods and dishesmonths in an amount of at least 200 grams per day. It is a source of minerals, vegetable fibers and organic acids. The assortment of vegetables is very wide, which allows them to be evenly distributed throughout the week. In addition to potatoes, zucchini, cabbage, carrots - traditional vegetable complementary foods for children in the second half of life, pumpkin, beets, spinach and tomatoes can be used in the nutrition of a 9-month-old baby. At this age, if the baby is not worried about excessive bloating, the diet can be diversified with legumes. Start with mashed green peas as a side dish with a meat dish or as an addition to a vegetable soup for dinner. nine0003
Fruit and berry complementary foods
Fruits and berries have low nutritional value, but, despite this, they are actively used in the daily diet of a 9-month-old child.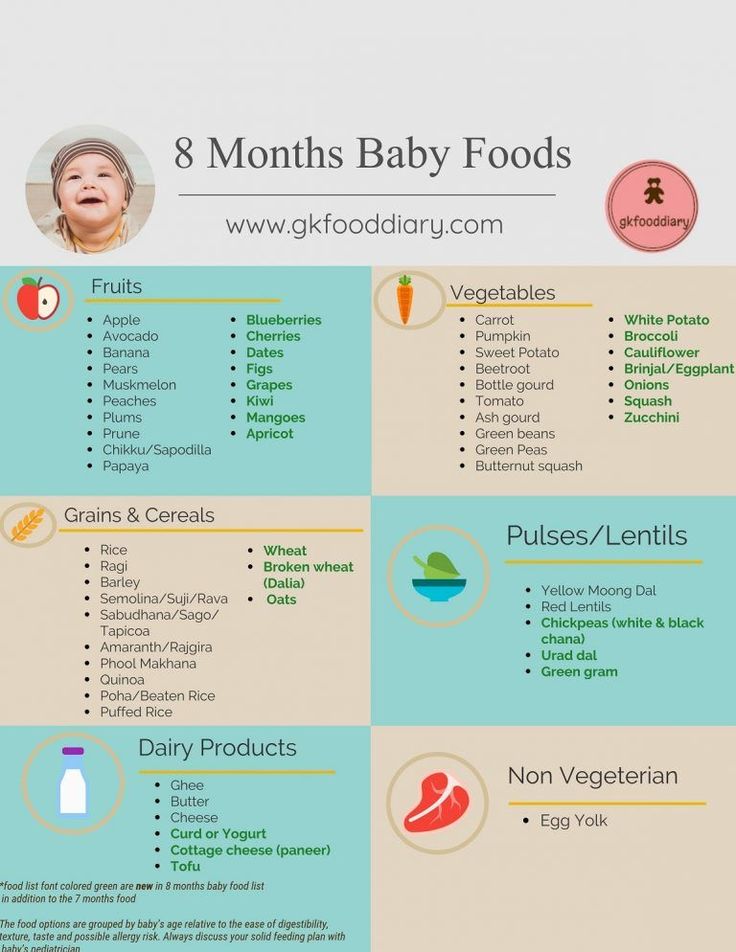 Fruits are rich in natural sugars and have an attractive aroma that enhances the palatability of many dishes and is liked by kids. In addition, such food is a source of valuable minerals, organic acids and fiber, which determines its biological significance. It is optimal to include a fruit and berry component 3-4 times a day, it can be a fruit dessert for an afternoon snack, an additional component in the composition of porridge or a curd dish. Every day, a baby can consume up to 90 grams of fruit. By 9 months, it is already permissible for a child to give garden and wild berries, bananas, plums and apricots. Expand the fruit menu consistently and take your time to introduce foods with high allergenic potential, such as citrus fruits, melons, strawberries and exotic fruits.
Fruits are rich in natural sugars and have an attractive aroma that enhances the palatability of many dishes and is liked by kids. In addition, such food is a source of valuable minerals, organic acids and fiber, which determines its biological significance. It is optimal to include a fruit and berry component 3-4 times a day, it can be a fruit dessert for an afternoon snack, an additional component in the composition of porridge or a curd dish. Every day, a baby can consume up to 90 grams of fruit. By 9 months, it is already permissible for a child to give garden and wild berries, bananas, plums and apricots. Expand the fruit menu consistently and take your time to introduce foods with high allergenic potential, such as citrus fruits, melons, strawberries and exotic fruits.
Grain-based complementary foods
Grain-based foods continue to be the most important source of nutrition and energy for a 9-month-old baby. By this age, the assortment of cereals is increasing, on the basis of which you can cook porridge for your baby. In addition to traditional buckwheat, rice, corn, oat and wheat groats, you can expand the diet with multi-cereal porridge, which may also include rye, barley and millet. When choosing a method for preparing porridge, preference should be given to industrial products. In addition to guaranteed environmental and microbiological safety, the enriched composition provides a daily supply of vitamins and minerals. AT 9months, the child can already eat bread and special baby biscuits without prior dissolution. It is preferable to use wheat bread, no more than 10 grams per day. It is better to dry it before use for easier digestion. Children's cookies are not only a delicacy and a source of energy for the baby, the multi-cereal composition and enrichment with a vitamin and mineral premix favorably distinguishes this healthy food product from traditional bakery products.
In addition to traditional buckwheat, rice, corn, oat and wheat groats, you can expand the diet with multi-cereal porridge, which may also include rye, barley and millet. When choosing a method for preparing porridge, preference should be given to industrial products. In addition to guaranteed environmental and microbiological safety, the enriched composition provides a daily supply of vitamins and minerals. AT 9months, the child can already eat bread and special baby biscuits without prior dissolution. It is preferable to use wheat bread, no more than 10 grams per day. It is better to dry it before use for easier digestion. Children's cookies are not only a delicacy and a source of energy for the baby, the multi-cereal composition and enrichment with a vitamin and mineral premix favorably distinguishes this healthy food product from traditional bakery products.
Meat food
By the age of 9 months, the baby is already well acquainted with meat foods, and he already has favorite combinations with vegetable and cereal products. What changes await him during this period? The development of the maxillofacial apparatus makes it possible to move from puree-like grinding of meat to various options for meatballs and steam cutlets. In the daily menu, meat complementary foods should be at least 60 grams. In addition to beef and veal, turkey, chicken and rabbit, the baby can be offered dishes based on pork, lamb and horse meat. Meat lure is a traditional lunchtime meal. This feeding accounts for up to 40% of the energy needs of the baby, which is satisfied by a rational combination of vegetables, meat and grains. nine0003
What changes await him during this period? The development of the maxillofacial apparatus makes it possible to move from puree-like grinding of meat to various options for meatballs and steam cutlets. In the daily menu, meat complementary foods should be at least 60 grams. In addition to beef and veal, turkey, chicken and rabbit, the baby can be offered dishes based on pork, lamb and horse meat. Meat lure is a traditional lunchtime meal. This feeding accounts for up to 40% of the energy needs of the baby, which is satisfied by a rational combination of vegetables, meat and grains. nine0003
Fish
At 9 months, a new food product appears in the baby's diet - fish. In addition to easily digestible protein, it is a valuable source of iodine, fluorine, phosphorus, iron, zinc and magnesium, as well as a number of vitamins. In the diet of young children, ocean fish is primarily used. This variety is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3, which are extremely important for the functional maturation of the central nervous system and the formation of the retina. However, fish protein is a powerful allergen, so this type of complementary food should be introduced with caution. Start with a teaspoon of fish puree at lunchtime and keep a close eye on changes in your baby's health. In the next two days, do not give the child any new foods so that there is no doubt about the tolerance of the product. Within a month, the amount of fish puree can be gradually increased to 30 grams, but introduced into the menu no more than 1-2 times a week. nine0003
However, fish protein is a powerful allergen, so this type of complementary food should be introduced with caution. Start with a teaspoon of fish puree at lunchtime and keep a close eye on changes in your baby's health. In the next two days, do not give the child any new foods so that there is no doubt about the tolerance of the product. Within a month, the amount of fish puree can be gradually increased to 30 grams, but introduced into the menu no more than 1-2 times a week. nine0003
Sour-milk products
Specialized unadapted sour-milk drinks (kefir, yogurt, biolact) can be used in a 9-month-old baby's diet. Unlike whole cow's milk, the protein and lactose in them are partially split, which determines their better digestibility, low allergenicity and a slight burden on the kidneys, provided that they consume no more than 200 ml per day. The most preferred choice among the products of this group are drinks based on probiotic cultures, which have a positive effect on their own intestinal microbiota. Cottage cheese is a valuable source of calcium and a complete protein in terms of amino acid composition. AT 9months, it is given to a child in an amount of not more than 50 grams per day in combination with a fruit, vegetable or cereal filler.
Cottage cheese is a valuable source of calcium and a complete protein in terms of amino acid composition. AT 9months, it is given to a child in an amount of not more than 50 grams per day in combination with a fruit, vegetable or cereal filler.
Fats
Butter is added to prepared meals in the amount of 5 grams per day, improving the taste of prepared complementary foods, as well as increasing their nutritional and energy value. Vegetable oils are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, so they should also be present in the baby's daily menu at 5 grams per day as an additive to meat, vegetable or fish dishes. nine0003
Drinks
Babies meet their physiological fluid needs through mother's milk or adapted formula. But at 9 months, the consumption of mother's milk is noticeably reduced, so it is necessary that the baby receive other drinks. If your child is thirsty, encourage him to drink baby water. The balanced mineral composition and the absence of sugars make it the best option for satisfying fluid needs.