Baby throws up milk after every feeding
Baby Vomiting After Feeding Formula: Causes and Treatment
Your little one is happily gulping their formula while cooing at you. They finish off the bottle in no time flat. But shortly after feeding, it seems to all come out as they vomit.
There are several reasons why your baby might be vomiting after a formula feeding, but it’s important to remember that it can be — and often is — very normal.
It’s common for babies to throw up sometimes after feeding on formula or breast milk. Their shiny new digestive systems are still learning what to do with all the yummy milk coming down into their tummy.
However, if your baby often has a hard time keeping their formula down on a regular and frequent basis, let your pediatrician know.
Having a baby around means getting used to soft mushy stuff coming out fairly often. This includes spit-up and vomit.
Spit-up and vomit might seem pretty much the same — and require similar amounts of cleaning to get them off of your sweater and the sofa — but they’re very different. Spitting up is an easy, gentle dribble of milk. Baby may even smile at you as the curd-like spit-up flows from their mouth.
Spit-up is normal in healthy babies, especially if they’re under the age of 1.
On the other hand, vomit takes more effort, as it comes from deeper in your little one’s stomach. It’s a sign that your baby’s stomach is saying nope, not now, please. You might see your baby strain and recoil just before they projectile vomit. This force happens because vomit is squeezed out by the stomach muscles.
Your baby might also look more uncomfortable during and after vomiting. And vomit looks and smells different. This is because it’s usually formula, breast milk, or food (if your baby is eating solids) mixed with stomach juices.
If you’re not sure whether your baby is vomiting or spitting up, look for other vomiting symptoms, like:
- crying
- gagging
- retching
- turning red
- arching their back
That said, there doesn’t seem to be agreed-upon definitions of these two terms among healthcare providers, caregivers, and others. Plus, their symptoms may overlap. For example, spitting up may sometimes be forceful, and vomiting may sometimes seem painless.
Plus, their symptoms may overlap. For example, spitting up may sometimes be forceful, and vomiting may sometimes seem painless.
Overfeeding
It’s easier for your baby to overfeed when they’re drinking from a bottle than when they’re breastfeeding. They can also gulp down milk faster from a bottle and rubber nipple. What’s more, because formula is always available, it’s easier for you to give them more milk than they need by accident.
Babies have tiny stomachs. A 4- to 5-week-old infant can only hold about 3 to 4 ounces in their tummy at a time. This is why they need lots of smaller feedings. Drinking too much formula (or breast milk) in one feeding can overfill your baby’s stomach, and it can only come out one way — vomit.
Not burping properly
Some babies need to be burped after every feeding because they swallow lots of air as they gulp down milk. Bottle feeding your baby breast milk or formula may lead to more air-swallowing, as they can gulp even faster.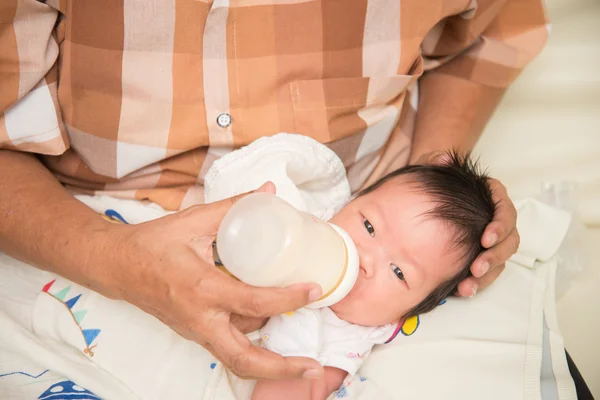
Too much air in the stomach can make your baby uncomfortable or bloated and trigger vomiting. Burping your baby right after feeding them formula may help prevent this.
To help prevent your baby from swallowing too much air and vomiting after formula feeding, check your baby’s bottle. Make sure you’re using a smaller bottle that’s just big enough to hold a few ounces of milk. Also, check to make sure the nipple hole is not too big, and don’t let your baby continue gulping when the bottle is empty.
Baby or infant reflux
Baby can have acid reflux, indigestion, or occasionally gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD just like grown-ups! This happens because their stomach and food tubes are still getting used to holding down milk.
Baby reflux happens when milk travels back up toward your baby’s throat and mouth. This usually just causes some painless spitting up, but it can irritate your baby’s throat and trigger gagging and vomiting.
Sometimes, smaller feedings can help prevent baby reflux. If not, don’t worry! Most little ones outgrow baby reflux by the time they’re 1 year old.
If not, don’t worry! Most little ones outgrow baby reflux by the time they’re 1 year old.
Constipation
While simple constipation would be an uncommon cause of vomiting in an otherwise healthy infant, sometimes baby vomiting happens because of what isn’t happening at the other end.
Most babies who are formula-fed need to poop at least once a day. Anything less than your baby’s typical pattern, though, might indicate they’re constipated.
If your baby is vomiting after a formula feeding, they might be constipated if they have other symptoms, including:
- gassiness
- not pooping for longer than 3–4 days
- a swollen or bloated stomach
- a firm or hard stomach
- crying bouts or irritableness
- straining very hard but not pooping or pooping only a little
- small, hard pellet-like poop
- dry, dark poop
Stomach bug
If your baby doesn’t usually vomit after having formula, they might have a stomach bug.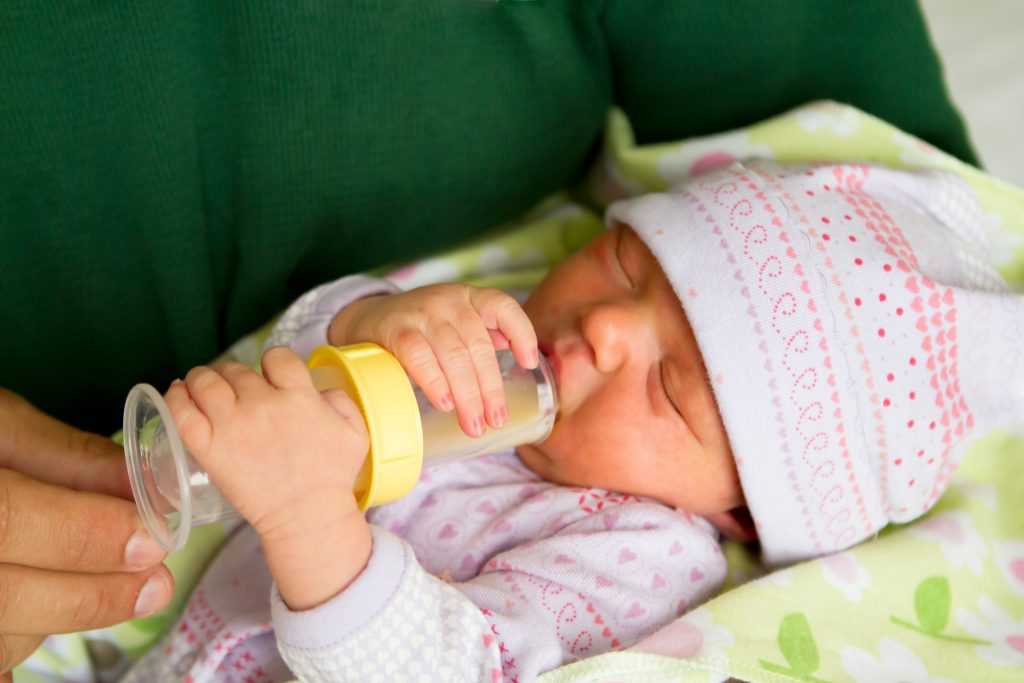 Also known as gastroenteritis or the “stomach flu,” a stomach bug is a very common cause of vomiting in babies. Your little one may vomit several times for up to 24 hours.
Also known as gastroenteritis or the “stomach flu,” a stomach bug is a very common cause of vomiting in babies. Your little one may vomit several times for up to 24 hours.
Other symptoms of a stomach bug include:
- crying
- stomach cramps
- stomach rumbling
- bloating
- diarrhea or watery poop
- mild fever (or none at all in babies)
Allergy
In rare cases, the cause of your baby’s vomiting might be in the formula. Although it’s uncommon for babies to be allergic to cow’s milk, it may happen to up to 7 percent of babies under the age of 1.
Most children outgrow a milk allergy by the time they’re 5 years old, but it can cause vomiting and other symptoms in babies. A cow’s milk allergy might cause vomiting right after your baby eats. It can also cause vomiting and other symptoms hours or rarely days later.
If your baby has an allergy to milk or something else, they might have other symptoms of an allergic reaction, like:
- skin rash (eczema)
- diarrhea
- cough
- hives
- difficulty breathing
- wheezing
Lactose intolerance
An allergy to milk is different than being lactose intolerant. Lactose intolerance usually causes digestive symptoms like diarrhea. It can also make your baby vomit after drinking formula containing cow’s milk.
Lactose intolerance usually causes digestive symptoms like diarrhea. It can also make your baby vomit after drinking formula containing cow’s milk.
Your baby might get temporary lactose intolerance after getting a tummy bug or gastroenteritis, although this is uncommon.
Other symptoms include:
- diarrhea or watery poops
- constipation
- bloating
- gassiness
- stomach pain
- stomach rumbling
Note that lactose intolerance is rare in babies under the age of 1.
Other causes
Some common health conditions can cause vomiting at any time, including after breastfeeding or formula feeding. Some rare genetic conditions can also cause vomiting in babies.
Other causes of vomiting in babies include:
- colds and the flu
- ear infections
- some medications
- overheating
- motion sickness
- galactosemia
- pyloric stenosis
- intussusception
In most cases, minor tweaks can help stop your baby’s vomiting. Remedies to stop your baby’s vomiting after formula depend on what’s causing it. Try some of these tried and tested methods to see what helps your baby:
Remedies to stop your baby’s vomiting after formula depend on what’s causing it. Try some of these tried and tested methods to see what helps your baby:
- feed your baby smaller amounts of formula more often
- feed your baby slowly
- burp your baby after the feeding
- hold your baby’s head and chest up while feeding
- hold your baby upright after a feeding
- make sure your baby doesn’t move around or play too much right after a feeding
- try a smaller bottle and smaller-hole nipple to feed
- check the ingredient list on your baby’s formula
- ask your baby’s doctor if you should try a different kind of formula
- talk to your baby’s doctor about a possible allergic reaction
- dress your baby in looser clothing
- make sure their diaper isn’t on too tightly
If your baby has the stomach flu, you’ll both usually just have to ride it out for a day or two. Most babies and children with a stomach bug don’t need treatment.
If your baby is vomiting, see your doctor or pediatrician right away if they:
- are vomiting often
- are vomiting forcefully
- aren’t gaining weight
- are losing weight
- have a skin rash
- are unusually sleepy or weak
- have blood in their vomit
- have green bile in their vomit
Also, see your doctor urgently if your baby has any sign of dehydration from all the vomiting:
- dry mouth
- crying without shedding tears
- a weak or quiet cry
- floppiness when picked up
- no wet diapers for 8 to 12 hours
It’s pretty common for babies to vomit, especially after feeding. This happens for many reasons, including that these little people are still just getting used to keeping down their milk.
Check with your doctor about what you can do. See your doctor urgently if your baby vomits often for any reason.
Baby Vomiting After Feeding Formula: Causes and Treatment
Your little one is happily gulping their formula while cooing at you. They finish off the bottle in no time flat. But shortly after feeding, it seems to all come out as they vomit.
They finish off the bottle in no time flat. But shortly after feeding, it seems to all come out as they vomit.
There are several reasons why your baby might be vomiting after a formula feeding, but it’s important to remember that it can be — and often is — very normal.
It’s common for babies to throw up sometimes after feeding on formula or breast milk. Their shiny new digestive systems are still learning what to do with all the yummy milk coming down into their tummy.
However, if your baby often has a hard time keeping their formula down on a regular and frequent basis, let your pediatrician know.
Having a baby around means getting used to soft mushy stuff coming out fairly often. This includes spit-up and vomit.
Spit-up and vomit might seem pretty much the same — and require similar amounts of cleaning to get them off of your sweater and the sofa — but they’re very different. Spitting up is an easy, gentle dribble of milk. Baby may even smile at you as the curd-like spit-up flows from their mouth.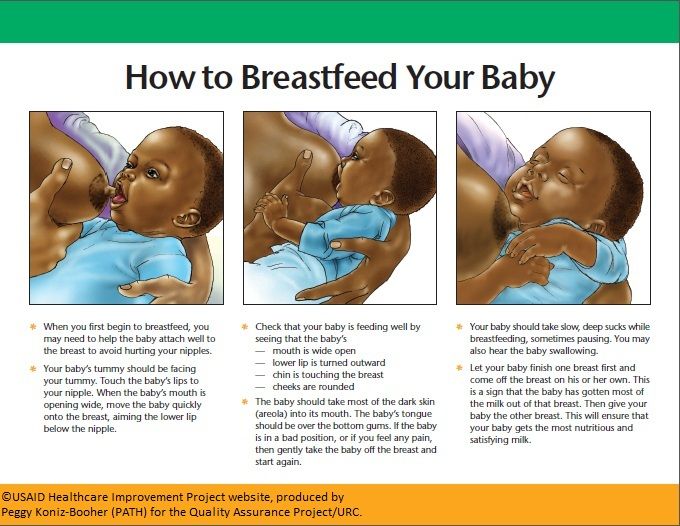
Spit-up is normal in healthy babies, especially if they’re under the age of 1.
On the other hand, vomit takes more effort, as it comes from deeper in your little one’s stomach. It’s a sign that your baby’s stomach is saying nope, not now, please. You might see your baby strain and recoil just before they projectile vomit. This force happens because vomit is squeezed out by the stomach muscles.
Your baby might also look more uncomfortable during and after vomiting. And vomit looks and smells different. This is because it’s usually formula, breast milk, or food (if your baby is eating solids) mixed with stomach juices.
If you’re not sure whether your baby is vomiting or spitting up, look for other vomiting symptoms, like:
- crying
- gagging
- retching
- turning red
- arching their back
That said, there doesn’t seem to be agreed-upon definitions of these two terms among healthcare providers, caregivers, and others. Plus, their symptoms may overlap. For example, spitting up may sometimes be forceful, and vomiting may sometimes seem painless.
Plus, their symptoms may overlap. For example, spitting up may sometimes be forceful, and vomiting may sometimes seem painless.
Overfeeding
It’s easier for your baby to overfeed when they’re drinking from a bottle than when they’re breastfeeding. They can also gulp down milk faster from a bottle and rubber nipple. What’s more, because formula is always available, it’s easier for you to give them more milk than they need by accident.
Babies have tiny stomachs. A 4- to 5-week-old infant can only hold about 3 to 4 ounces in their tummy at a time. This is why they need lots of smaller feedings. Drinking too much formula (or breast milk) in one feeding can overfill your baby’s stomach, and it can only come out one way — vomit.
Not burping properly
Some babies need to be burped after every feeding because they swallow lots of air as they gulp down milk. Bottle feeding your baby breast milk or formula may lead to more air-swallowing, as they can gulp even faster.
Too much air in the stomach can make your baby uncomfortable or bloated and trigger vomiting. Burping your baby right after feeding them formula may help prevent this.
To help prevent your baby from swallowing too much air and vomiting after formula feeding, check your baby’s bottle. Make sure you’re using a smaller bottle that’s just big enough to hold a few ounces of milk. Also, check to make sure the nipple hole is not too big, and don’t let your baby continue gulping when the bottle is empty.
Baby or infant reflux
Baby can have acid reflux, indigestion, or occasionally gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD just like grown-ups! This happens because their stomach and food tubes are still getting used to holding down milk.
Baby reflux happens when milk travels back up toward your baby’s throat and mouth. This usually just causes some painless spitting up, but it can irritate your baby’s throat and trigger gagging and vomiting.
Sometimes, smaller feedings can help prevent baby reflux. If not, don’t worry! Most little ones outgrow baby reflux by the time they’re 1 year old.
If not, don’t worry! Most little ones outgrow baby reflux by the time they’re 1 year old.
Constipation
While simple constipation would be an uncommon cause of vomiting in an otherwise healthy infant, sometimes baby vomiting happens because of what isn’t happening at the other end.
Most babies who are formula-fed need to poop at least once a day. Anything less than your baby’s typical pattern, though, might indicate they’re constipated.
If your baby is vomiting after a formula feeding, they might be constipated if they have other symptoms, including:
- gassiness
- not pooping for longer than 3–4 days
- a swollen or bloated stomach
- a firm or hard stomach
- crying bouts or irritableness
- straining very hard but not pooping or pooping only a little
- small, hard pellet-like poop
- dry, dark poop
Stomach bug
If your baby doesn’t usually vomit after having formula, they might have a stomach bug. Also known as gastroenteritis or the “stomach flu,” a stomach bug is a very common cause of vomiting in babies. Your little one may vomit several times for up to 24 hours.
Also known as gastroenteritis or the “stomach flu,” a stomach bug is a very common cause of vomiting in babies. Your little one may vomit several times for up to 24 hours.
Other symptoms of a stomach bug include:
- crying
- stomach cramps
- stomach rumbling
- bloating
- diarrhea or watery poop
- mild fever (or none at all in babies)
Allergy
In rare cases, the cause of your baby’s vomiting might be in the formula. Although it’s uncommon for babies to be allergic to cow’s milk, it may happen to up to 7 percent of babies under the age of 1.
Most children outgrow a milk allergy by the time they’re 5 years old, but it can cause vomiting and other symptoms in babies. A cow’s milk allergy might cause vomiting right after your baby eats. It can also cause vomiting and other symptoms hours or rarely days later.
If your baby has an allergy to milk or something else, they might have other symptoms of an allergic reaction, like:
- skin rash (eczema)
- diarrhea
- cough
- hives
- difficulty breathing
- wheezing
Lactose intolerance
An allergy to milk is different than being lactose intolerant. Lactose intolerance usually causes digestive symptoms like diarrhea. It can also make your baby vomit after drinking formula containing cow’s milk.
Lactose intolerance usually causes digestive symptoms like diarrhea. It can also make your baby vomit after drinking formula containing cow’s milk.
Your baby might get temporary lactose intolerance after getting a tummy bug or gastroenteritis, although this is uncommon.
Other symptoms include:
- diarrhea or watery poops
- constipation
- bloating
- gassiness
- stomach pain
- stomach rumbling
Note that lactose intolerance is rare in babies under the age of 1.
Other causes
Some common health conditions can cause vomiting at any time, including after breastfeeding or formula feeding. Some rare genetic conditions can also cause vomiting in babies.
Other causes of vomiting in babies include:
- colds and the flu
- ear infections
- some medications
- overheating
- motion sickness
- galactosemia
- pyloric stenosis
- intussusception
In most cases, minor tweaks can help stop your baby’s vomiting. Remedies to stop your baby’s vomiting after formula depend on what’s causing it. Try some of these tried and tested methods to see what helps your baby:
Remedies to stop your baby’s vomiting after formula depend on what’s causing it. Try some of these tried and tested methods to see what helps your baby:
- feed your baby smaller amounts of formula more often
- feed your baby slowly
- burp your baby after the feeding
- hold your baby’s head and chest up while feeding
- hold your baby upright after a feeding
- make sure your baby doesn’t move around or play too much right after a feeding
- try a smaller bottle and smaller-hole nipple to feed
- check the ingredient list on your baby’s formula
- ask your baby’s doctor if you should try a different kind of formula
- talk to your baby’s doctor about a possible allergic reaction
- dress your baby in looser clothing
- make sure their diaper isn’t on too tightly
If your baby has the stomach flu, you’ll both usually just have to ride it out for a day or two. Most babies and children with a stomach bug don’t need treatment.
If your baby is vomiting, see your doctor or pediatrician right away if they:
- are vomiting often
- are vomiting forcefully
- aren’t gaining weight
- are losing weight
- have a skin rash
- are unusually sleepy or weak
- have blood in their vomit
- have green bile in their vomit
Also, see your doctor urgently if your baby has any sign of dehydration from all the vomiting:
- dry mouth
- crying without shedding tears
- a weak or quiet cry
- floppiness when picked up
- no wet diapers for 8 to 12 hours
It’s pretty common for babies to vomit, especially after feeding. This happens for many reasons, including that these little people are still just getting used to keeping down their milk.
Check with your doctor about what you can do. See your doctor urgently if your baby vomits often for any reason.
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of life, the stomach has a spherical shape.
 It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .
It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 . - Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract. However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .
- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular system of newborns is immature. It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors contributing to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes regurgitation after feeding and a predominantly horizontal position of the baby during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Regurgitation in many newborns can be provoked by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, forced cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems?
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps you avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children. Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after meals (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day. With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Regurgitation in newborns, which is considered a normal variant and does not cause concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually continues for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.

How to help a newborn who spit up often?
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
- Frequent feeding of the baby
It is known that the baby is more prone to spit up if his stomach is full. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
- Correct feeding technique
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
- Choosing the right bottle and nipple
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air
The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air New Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve
The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach.
- Baby standing upright after eating
To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to keep the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 .
- Ensure the correct position of the baby during sleep
To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in the supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It was found to be associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 .
If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc.
 , it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
, it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
References1 Zakharova I. N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
Nagornaya 2900 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013. No. 5 (48).
3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67.
4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28.
5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition.
2009; 49(4): 498-547.
You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
I understand
Preventive measures against regurgitation in children
08.03.2017
Regurgitation is the spontaneous reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus and mouth. This condition is not uncommon in infants and is often a cause for concern for parents. The frequency of regurgitation syndrome in children of the first year of life is 18-50%: up to 4 months - 67%, up to 6 months 24%, up to 1 year 5%.
In most cases, regurgitation is "benign" and disappears on its own after 12-18 months. At the same time, “benign” or physiological regurgitation characterizes:
-
the age of the child is up to 12 months;
-
spitting up 2 or more times a day for 3 or more weeks;
-
sufficient weight gain;
The child has no signs of metabolic disorders, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or the central nervous system. The child does not experience difficulty in swallowing or feeding, there is no forced position of the body.
Do not confuse regurgitation with vomiting. When a child burps, the abdominal muscles do not tense up. With vomiting, on the contrary, muscle tension occurs and food is ejected by pressure not only through the mouth, but also through the nose. In some cases, there may be general anxiety, pallor, cold extremities. Often with vomiting, the temperature rises, loose stools appear, which is a sign of an infectious disease.
Vomit may contain unchanged milk, mucus, blood or bile.
What causes physiological regurgitation
What is the tendency of babies to spit up? This phenomenon is explained by the peculiarity of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract of young children. At the age of one year, the esophagus is shorter and wider, physiological narrowing is weakly expressed. The stomach is located horizontally, its capacity is small, and the muscles that close the entrance to the stomach and prevent the contents from being thrown back into the esophagus are poorly developed. As the child begins to walk, the axis of the stomach becomes more vertical. The capacity of the stomach increases by the year from 30-35 ml to 250-300 ml. The secretory apparatus matures, the work of the closing muscles (sphincters) improves, which leads to a gradual decrease in the frequency and disappearance of regurgitation. These features explain the predisposition of young children to regurgitation and even the inevitability of this condition.
However, there are measures to help reduce the frequency of regurgitation.
Factors contributing to physiological regurgitation include:
-
Overfeeding. As a rule, actively sucking babies begin to suffer from overfeeding, with abundant milk secretion, as well as when switching to artificial or mixed feeding with an incorrect calculation of the required amount of milk formula. Regurgitation appears immediately or some time after feeding in the amount of 5-10 ml. Milk can flow out unchanged or curdled.
-
Swallowing air during feeding (aerophagia). A similar situation arises if the child suckles greedily at the breast, and the mother's milk is not very plentiful; due to the retracted, flat nipple of the mother's breast, since the child fails to fully capture the nipple and areola; with artificial feeding, if the hole at the nipple of the bottle is large enough or the nipple is not completely filled with milk. Babies with aerophagia often experience anxiety after feeding, bulging of the abdominal wall (belly inflates).
After 10-15 minutes, the swallowed milk flows out unchanged, which is accompanied by a loud sound of air eructation.
-
Intestinal colic or constipation. These conditions lead to an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity and a violation of the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract, causing regurgitation.
Until the child is four months old, spitting up up to two teaspoons of milk after feeding, or one spitting up of more than three spoons during the day, is considered the norm. You can check the amount of spitting up in the following way: take a diaper, pour one teaspoon of water on its surface, and then compare this spot with the spot formed after the next spitting up.
Abnormal regurgitation may be due to:
-
surgical diseases and malformations of the digestive system;
-
diaphragmatic hernia;
-
pathology of the central nervous system, trauma of the cervical spine during childbirth;
-
food intolerance, lactase deficiency;
-
increased intracranial pressure.
Such regurgitation is characterized by intensity, systematicity, the child spits up a large amount of milk. At the same time, there is a violation of the general condition of the baby - the child is whiny, loses or does not gain weight, cannot eat the amount of food necessary for his age. In such a situation, a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, surgeon, allergist, neurologist should be examined. It also requires examination and exclusion of anomalies in the structure of the upper gastrointestinal tract, the preservation of regurgitation for more than 1 year.
Scale for assessing the intensity of regurgitation:
-
Less than 5 regurgitations per day with a volume of not more than 3 ml - 1 point.
-
More than 5 regurgitations per day with a volume of more than 3 ml - 2 points.
-
More than 5 regurgitations per day up to half the amount of formula or breast milk, not more often than in half of the feedings - 3 points.
-
Spitting up a small amount of milk for 30 minutes or more after each feeding - 4 points.
-
Regurgitation from half to full volume of formula or breast milk in at least half of the feedings - 5 points.
Regurgitation with an intensity of 3 or more points requires a visit to a doctor.
Preventive measures against regurgitation in children
If regurgitation is physiological in nature, then it is not worth treating or correcting in this case. It is necessary to deal with the elimination of the cause, if possible, and carry out prevention.
Prevention of regurgitation in children includes the following measures:
-
Postural therapy: when feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby at an angle of 45 °, make sure that he completely grasps the nipple with the areola; after feeding, hold the baby in an upright position ("column") for 20 minutes - to drain the swallowed air.
Due to this, the air that has entered the stomach will be able to go out. If nothing happened, then put the baby down and after a minute or two, lift him upright again.
-
Make sure that the opening in the bottle is not too large and that the nipple is filled with milk. Experiment with nipples - perhaps the other will be better. Milk should come out in drops, not a trickle.
-
Before you start feeding your baby, lay him belly down on a solid base.
-
After feeding, try to minimize the baby's physical activity, do not disturb him unnecessarily, and change clothes only if there is an emergency.
-
Avoid squeezing diapers or clothes on the abdomen of the child.
-
If the baby's appetite is good, then it is better to feed him often, but in small portions, otherwise, due to the large amount of food, the stomach may overflow, and this, as a result, leads to regurgitation of excess food.











