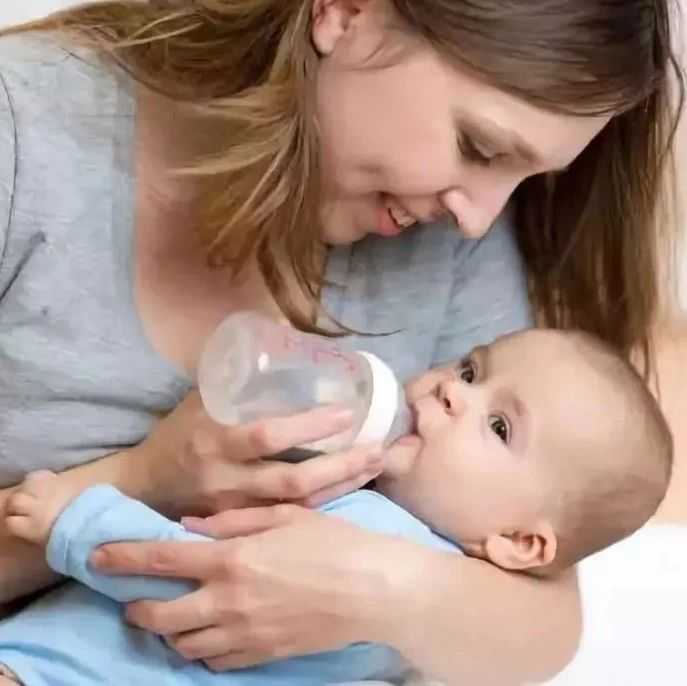
Can you feed your baby formula and breastmilk
How to combine breast and bottle feeding
It can take several weeks for you and your baby to feel happy and confident with breastfeeding.
Once you've both got the hang of it, it's usually possible to offer your baby bottles of expressed milk or formula alongside breastfeeding.
This is sometimes called mixed or combination feeding.
Why combine breast and bottle?
You may want to combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding if you:
- are breastfeeding and want to use a bottle to offer your baby some expressed breast milk
- want to breastfeed for some of your baby's feeds, but give bottles of formula for 1 or more feeds
- are bottle feeding your baby and want to start breastfeeding
- need to leave your baby and want to make sure they have some milk while you're away
Introducing formula feeds can affect the amount of breast milk you produce. There is also a small amount of evidence to show babies may not breastfeed as well because they learn to use a different kind of sucking action at the bottle than at the breast.
These things can make breastfeeding more difficult, especially in the first few weeks when you and your baby are still getting comfortable with breastfeeding.
Your breastmilk supply will usually not be affected if you start bottle feeding your baby when they are a bit older, you are both comfortable with breastbeeding, and you breastfeed every day.
Introducing formula feeds
If you're combining breastfeeding with formula feeds both you and your baby can carry on enjoying the benefits of breastfeeding.
If you choose to introduce infant formula:
- it's best to do it gradually to give your body time to reduce the amount of milk it makes – this helps lower your chance of getting uncomfortable, swollen breasts, or mastitis
- if you're going back to work, start a few weeks beforehand to give both of you time to readjust
- if your baby is 6 months old or more and can drink milk from a cup, you may not need to introduce a bottle at all
For more information, see drinks and cups for babies.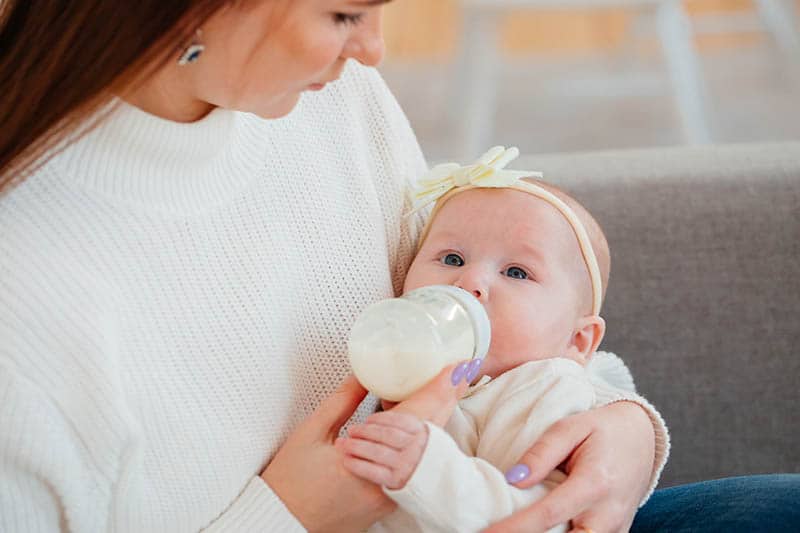
Giving your baby their first bottle
It may take a while for a breastfed baby to get the hang of bottle feeding, because they need to use a different sucking action.
- it usually helps to give the first few bottles when your baby is happy and relaxed – not when they're very hungry
- it may help if someone else gives the first bottle feeds, so that your baby is not near you and smelling your breast milk
- you might want to try using a different position for bottle and breastfeeding
See more advice on how to bottle feed.
Restarting breastfeeding
If you want to start breastfeeding more and give your baby fewer bottles, it's a good idea to ask your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter for support.
These tips may help too:
- Hold and cuddle your baby as much as possible, ideally skin to skin. This will encourage your body to make milk and your baby to feed.
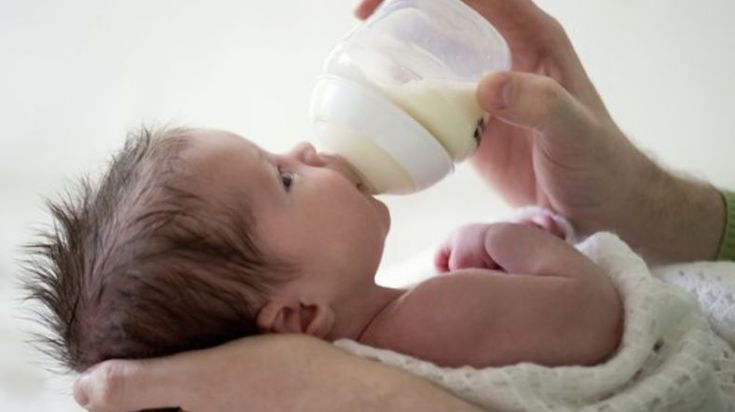

- Express your breast milk regularly. Expressing releases the hormone prolactin, which stimulates your breasts to make milk. About 8 times a day, including once at night is ideal. It may be easier to express by hand to begin with – your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can show you how.
- Try bottlefeeding while holding your baby skin to skin and close to your breasts.
- If your baby is latching on, feed little and often. Do not worry if your baby does not feed for long to begin with. See tips on how to get your baby properly positioned and attached.
- Choose times when your baby is relaxed, alert and not too hungry, and do not force your baby to stay at the breast.
- Decrease the number of bottles gradually, as your milk supply increases.
- Consider using a lactation aid (supplementer). A tiny tube is taped next to your nipple and passes into your baby's mouth so your baby can get milk via the tube as well as from your breast.
 This helps to support your baby as they get used to attaching to the breast. Your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can give you more information.
This helps to support your baby as they get used to attaching to the breast. Your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can give you more information.
See more tips on boosting your milk supply.
Help and support with mixed feeding
If you have any questions or concerns about combining breast and bottle feeding:
- talk to your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter
- call the National Breastfeeding Helpline on 0300 100 0212 (9.30am to 9.30pm, every day)
- find breastfeeding support near you
Video: why combine breast and bottle feeding?
In this video, 3 mothers discuss ways to combine breast and bottle feeding.
Media last reviewed: 22 March 2020
Media review due: 22 March 2023
Page last reviewed: 8 October 2019
Next review due: 8 October 2022
Formula Feeding and Breastfeeding: Can You Do Both?
Can you breastfeed and formula-feed a baby? The short answer is YES.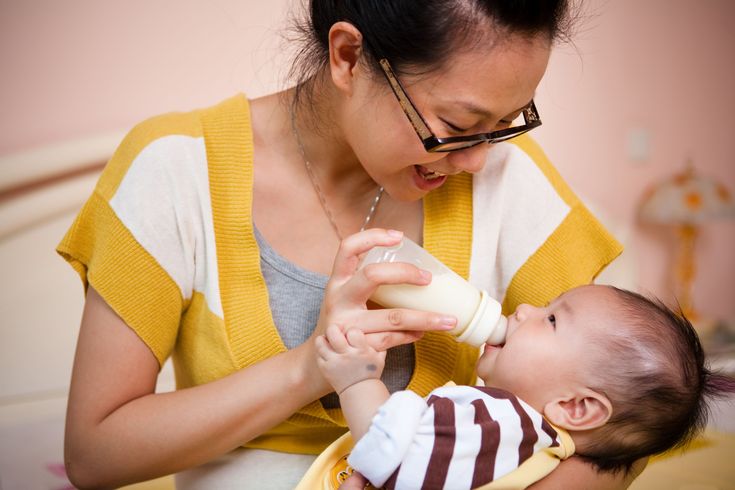 It’s called combination feeding, or more commonly, combo feeding. If you’re looking to supplement and extend your breastfeeding journey or if you want to make feedings possible by other parents or care-takers, combo feeding can be a great solution.
It’s called combination feeding, or more commonly, combo feeding. If you’re looking to supplement and extend your breastfeeding journey or if you want to make feedings possible by other parents or care-takers, combo feeding can be a great solution.
We sat down with Tiffani Ghere, a pediatric dietician, certified specialist in Pediatric Nutrition, and Bobbie medical advisor. It turns out that formula milk and breast milk aren’t black and white options. Here’s what we learned.
Table of Contents
- Is it ok to breastfeed and formula feed at the same time?
- 4 Tips to help ease your baby into combo feeding
- How does the transition from breast milk to baby formula affect mom?
- Benefits of breastfeeding for mom and baby
- Why parents choose formula feeding
- Doctors may recommend supplementation
- Our take on combo feeding
Is it ok to breastfeed and formula feed at the same time?
Often times, there’s a conversation about exclusively breastfeeding or exclusively formula feeding. It can make new parents feel that they have to make a choice. But did you know it’s actually quite easy to combo feed?
It can make new parents feel that they have to make a choice. But did you know it’s actually quite easy to combo feed?
We’ll give you a few pointers about what to consider if you decide to have both bottles of baby formula and bottles of breast milk on your little one’s menu.
A mother’s intuition helps decide the feeding choice
Following your intuition is always best! Trust what you think is right for your baby. You have the power to make great decisions for your baby, so don’t let anyone sway you otherwise.
Talk to your health care providers and your baby’s pediatrician to feel confident in the decision that works best for you and your family.
Is nipple confusion a concern?
When you mix formula feeding and breastfeeding in a baby’s diet, they likely won’t fuss about the real nipple or bottle nipple. They may not even know the difference most of the time, and nipple confusion isn’t as prominent as most expect.
Some doctors may recommend exclusive breastfeeding for the first few weeks until you introduce a bottle of formula to give them an easier introduction.
Breastfeeding poop can be different than formula poop
Since there’s a different type of milk entering your baby’s system, it makes sense that it may exit differently, too. Keep this in mind and watch to see if your baby’s stool looks different or irregular. Formula poop can be different than breast milk poop.
Make a note of how your baby is digesting their new diet, and seek the advice of your pediatrician if you have any concerns.
4 Tips to help ease your baby into combo feeding
If you’ve decided to start combo feeding, these helpful tips will make the transition easier for mom and baby alike.
1. Create similarities in the feedings
Give your baby as much of a similar experience as possible. This will give them a more familiar routine that they can look forward to, and it can help eliminate any nipple confusion they may experience.
Pro tip: When formula feeding, give your baby skin-to-skin contact and switch them from side to side to give the illusion of breastfeeding. This can help make the transition much easier for both you and your baby.
This can help make the transition much easier for both you and your baby.
2. Space out formula feedings
Since organic baby formula and breast milk are two separate mixtures, it’s best to introduce the formula slowly to better support your baby’s digestion. You can slide in a bottle of formula a couple of hours after the initial feeding session to get your infant used to the taste. This can make things much easier for you in the long run.
Our breast milk supply provides nutrients that can only be found wholly in our breast milk. But, thanks to modern science, there are similarly-composed baby formulas in the shopping aisle.
That being said, pay attention to which baby formulas have the quality ingredients and sourcing that you are looking for. If organic or non-gmo products are important to you, there are options. If you are looking for cow’s milk vs. a vegan formula, you can specifically look for that as well.
Talk to your pediatrician about vitamin D supplements—whether you’re breastfeeding or bottle-feeding—to ensure your baby is getting all of the nutrients they need.
Shop Bobbie Organic Infant Formula
Bobbie Organic Infant Formula is a USDA Organic, EU-style infant formula that meets all FDA requirements. It is a complete nutrition milk-based powder modeled after breast milk and is easy on tummies. It is non-GMO and doesn't have corn syrup, palm oil, or maltodextrin. Learn more about Bobbie.
Shop Bobbie
4. Look for the “Feeling Full” signal
Your baby will become well-versed in telling you when he’s no longer hungry. Trust and watch to make sure his weight-gain patterns are normal as he grows and develops, as this is an excellent sign of properly taking to a combination diet.
How does the transition from breast milk to baby formula affect mom?
The transition from breast milk can affect your body’s milk production in a few ways. Medical experts suggest making a clean switch if you feel comfortable doing so or doing so gradually if that works best for you.
To ensure a smooth transition, you can try these techniques to start:
A new feeding routine can disrupt your body’s milk production
Expert Tip: Try starting with one bottle of formula per day.
A new routine might throw your body off its game, and your body’s milk production system may not understand the transition right away. If you’re pumping multiple times per day and then instantly move to pump only once per day, your milk supply can drop pretty rapidly and may not be there if you really need it down the line.
Some parents like to start by replacing the night bottle with formula. This can help by allowing other people to participate in feeding as well, and it can become part of the regular nighttime feeding routine.
Your body may struggle to adjust to the new routine
Expert Tip: Build up the formula usage slowly, and don’t stop pumping right away.
Your body may not demonstrate that it can handle the new routine.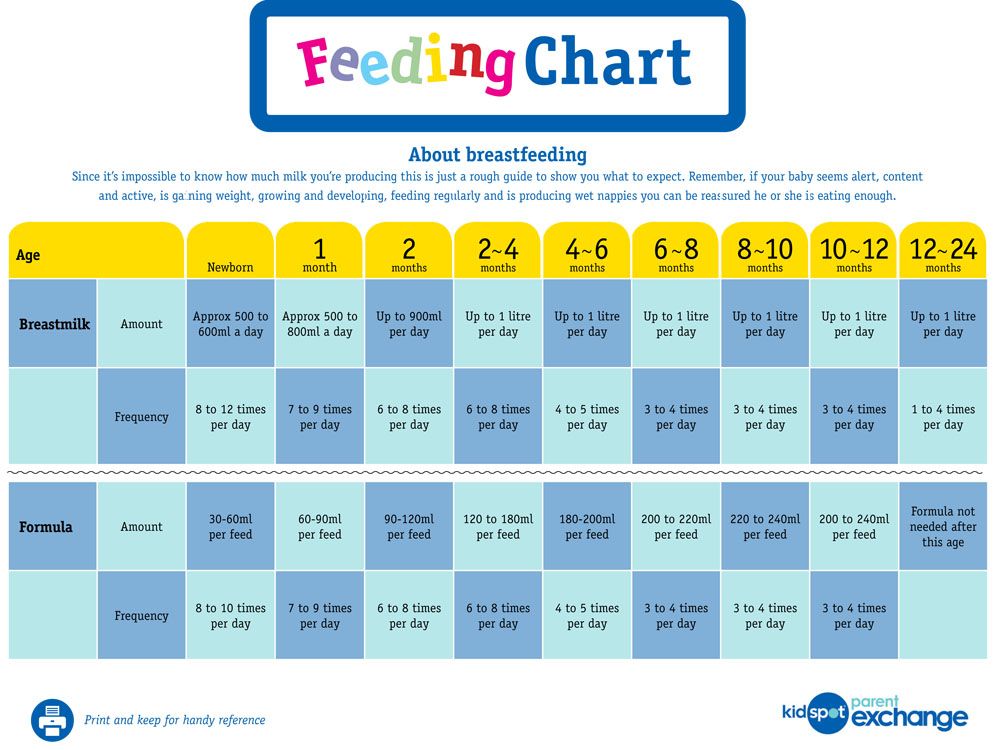 It may even cause breast engorgement or blocked milk ducts. If you’re struggling with the switch, you may need to build up the formula usage gradually.
It may even cause breast engorgement or blocked milk ducts. If you’re struggling with the switch, you may need to build up the formula usage gradually.
Additionally, it’s okay to pump even if the milk is not being used. It may even get rid of the heaviness you might feel if the breast milk isn’t released. You can store up the extra breast milk and extend the feeding journey using both breast milk and formula.
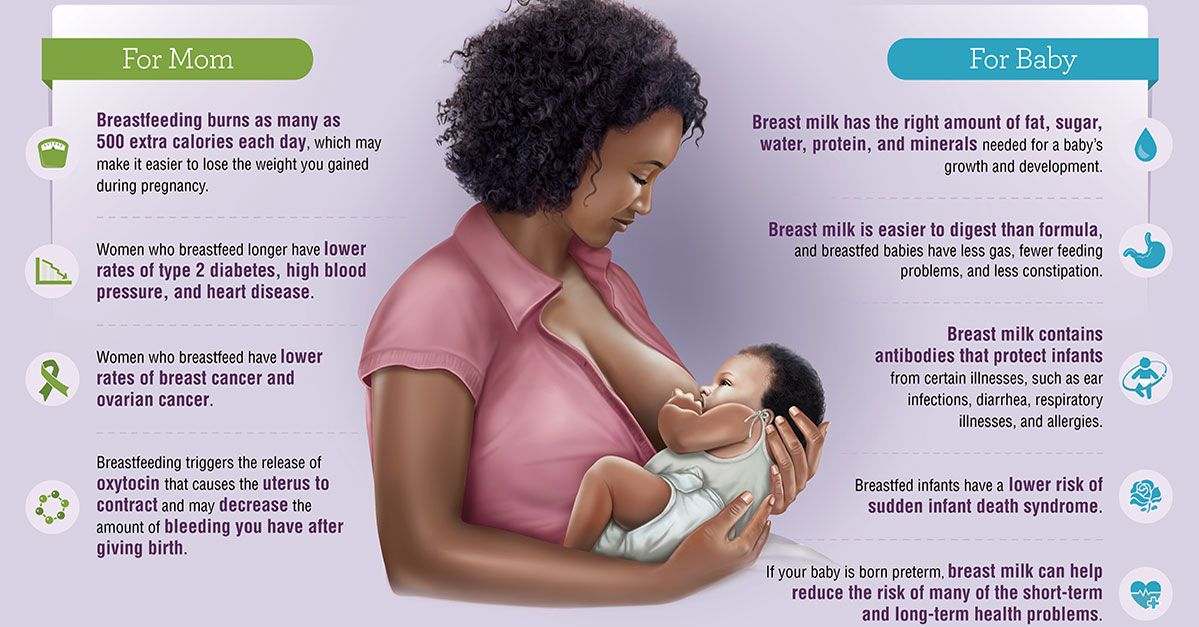
Benefits of breastfeeding for mom and baby
We don’t often talk about this, but breastfeeding delivers many benefits not only to your baby but also to you! The list of benefits to you and baby is long, here are a few key benefits worth mentioning:
- Babies may have a more well-supported immune system during childhood due to antibodies in breastmilk.
- Colostrum (found in breast milk) can support the baby’s digestive system to help with growth and proper functioning.
- Breast milk adapts as your baby grows.
- Even partial breastfeeding may promote quicker recovery after giving birth.

- Breastfeeding saves money.
- Breastfeeding may help lower the risk of certain diseases like ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and diabetes.
Why parents choose formula feeding
With all of life’s twists and turns, there are many reasons parents may formula feed from day one or choose to exclusively breastfeed before making the add or switch to baby formula. As with breastfeeding, there are amazing benefits for both you and your child when it comes to using baby formula:
- Formula feeding is very convenient; babies can be fed any time they express hunger cues.
- Availability of the exact amount of milk needed means pumping doesn’t need space on your personal schedule.
- Allows teamwork–your partner and other caretakers have the ability to help feed if needed.
- Allows you the ability to schedule feedings, especially with low milk supply not being a concern.
- Allows you to be less worried about your diet, including the revived ability to consume alcohol.
Sometimes, the choice to nurse versus formula feed is truly out of your control. If a baby isn’t reacting well to your breastmilk, there could be a deficiency or even an allergy that needs to be addressed. It could also be related to how the baby’s body reacts to different ingredients or products.
It’s important to remember that there’s no reason to feel pressure that your breastfeeding journey didn’t go as planned. Adding formula, otherwise known as supplementing, to your breastfeeding routine is very common.
A doctor may recommend formula supplementation if:
- A newborn loses a percentage of their body weight during the first few days of life.
- A newborn gains significant weight after the first few days of birth.
- A baby becomes dehydrated and demonstrates this through fewer wet diapers.
- A baby appears dissatisfied after feeding and, therefore may need more nutrition.
Ghere also shared that, “Supplementing may start as early as the first few days of life if the baby has lost too much weight and/or mom’s milk supply hasn’t been established.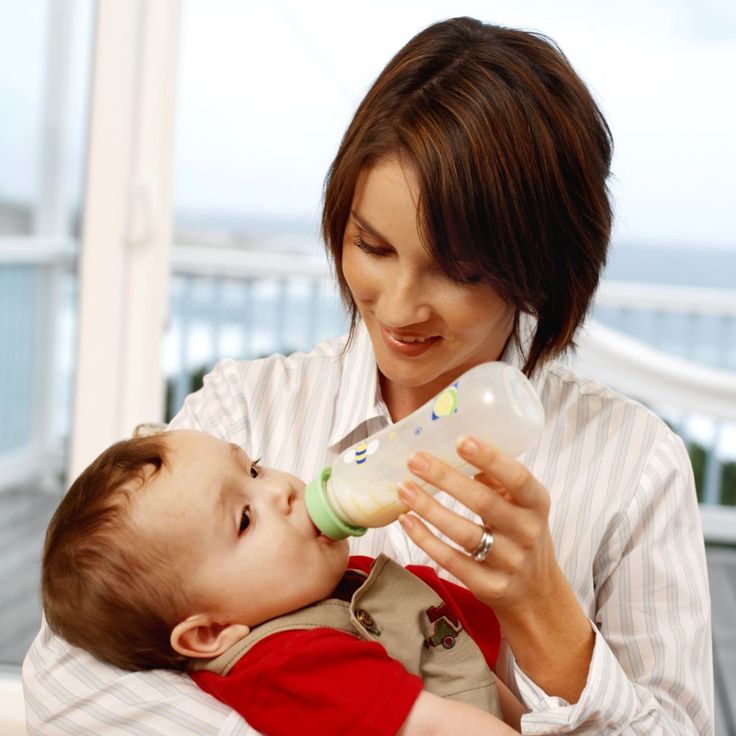 Other moms begin around 3-4 weeks to get the baby used to some bottle feeding, to allow others to feed the baby, or if mom has to return to work.”
Other moms begin around 3-4 weeks to get the baby used to some bottle feeding, to allow others to feed the baby, or if mom has to return to work.”
She even goes on to say that supplementation can support the mother’s health as well: “The truth is, supplementing happens whenever mom doesn’t have enough milk, the baby needs more than mom can supply, or someone other than mom is feeding the baby. It’s not an all-or-nothing choice. New parents need options and the flexibility to meet both the baby’s and mom’s needs.”
The decision or recommendation to supplement is always for the good of both parties, and no one would want it any other way!
Our take on combo feeding
So, is it ok to breast feed and formula feed a baby simultaneously?
After looking at both options and weighing the benefits of each, there really is no wrong decision when it comes to formula feeding versus breastfeeding. It is a personal choice, unique to each situation.
If you choose to breastfeed, formula feed, or both, this is perfectly fine unless otherwise directed by your pediatrician–we can’t stress enough that your pediatrician is the true expert to your specific journey with your little one! Remember, no two families’ journeys are the same!
Shop Bobbie Organic Infant Formula
Bobbie Organic Infant Formula is a USDA Organic, EU-style infant formula that meets all FDA requirements.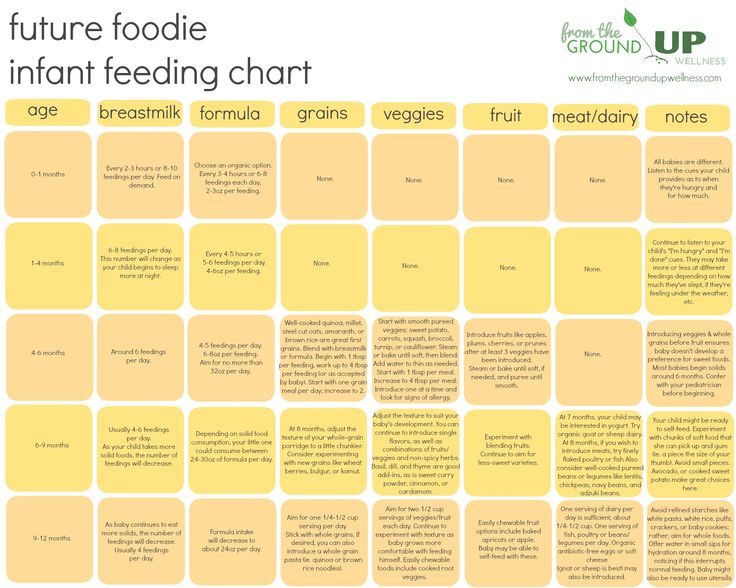 It is a complete nutrition milk-based powder modeled after breast milk and is easy on tummies. It is non-GMO and doesn't have corn syrup, palm oil, or maltodextrin. Learn more about Bobbie.
It is a complete nutrition milk-based powder modeled after breast milk and is easy on tummies. It is non-GMO and doesn't have corn syrup, palm oil, or maltodextrin. Learn more about Bobbie.
Shop Bobbie
Sources:
What Is Colostrum? Nutrition, Benefits, and Downsides | Healthline
Combining Breastfeeding and Formula Feeding | VeryWell Family
Supplementing With Formula: Combining Breastfeeding and Bottles | What to Expect
The content on this site is for informational purposes only and not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Discuss any health or feeding concerns with your infant's pediatrician. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay it based on the content on this page.
Mixed feeding of newborns: how to organize breastfeeding
No young mother is immune from the situation when a baby will need to be transferred from exclusive breastfeeding to a mixed one. When is it necessary and how to properly organize a new regime?
When is it necessary and how to properly organize a new regime?
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months Read more
Follow-up dry milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 2 NutriValio for feeding children from 6 to 12 months More
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
In our pediatric practice, the term "mixed feeding" refers to the combination of breast milk feeding (at least 250-200 ml) with its artificial substitutes (supplementary feeding, which is introduced if necessary up to 4 months).
First of all, it should be said that the decision to transfer the baby to mixed feeding (both breastfeeding and artificial mixture) must be made together with the pediatrician. If you decide to supplement the baby with a formula on your own, without good reason, you will only violate lactation.
If you decide to supplement the baby with a formula on your own, without good reason, you will only violate lactation.
As a rule, a woman is forced to introduce supplementary feeding with a mixture for one of two reasons - the baby does not have enough breast milk or the mother needs to go to work or study. And if everything is clear with the second situation without comment, then it is better to talk about the first in more detail.
Hypogalactia is a decrease in lactation. How to understand that the child does not have enough milk?
-
The infant rarely urinates (reduced daily urine volume is also called "dry diaper syndrome"). The liquid usually becomes concentrated, with a pungent odor.
-
Stool - rare or atypical (too liquid or thick, discolored).
-
The child is not gaining weight well. In the first 6 months, the baby should recover by 150-200 g per week, after six months - by 100-150 g.
Of course, these are average figures, but you can focus on them.
If you notice these symptoms, then you need to take action. First of all, a woman is recommended to try all the ways to improve lactation (no matter how wonderful the mixture is, breast milk for a child is the most valuable food). If milk is still not enough, you need to introduce artificial nutrition.
There are two types of mixed feeding:
Remember that milk should remain the main food for the baby - offer the baby the breast as often as possible (this is a necessary condition for lactation to increase, because mixed feeding is often a temporary measure, and under favorable conditions, the mother can return to natural feeding).
You can feed your baby with a mixture not only from a bottle (the fact is that it is easier for a child to suck from a nipple and often babies refuse to breastfeed, realizing this). You can feed the baby from a special silicone spoon - in this case, put the mixture on the cheek, and not on the tongue.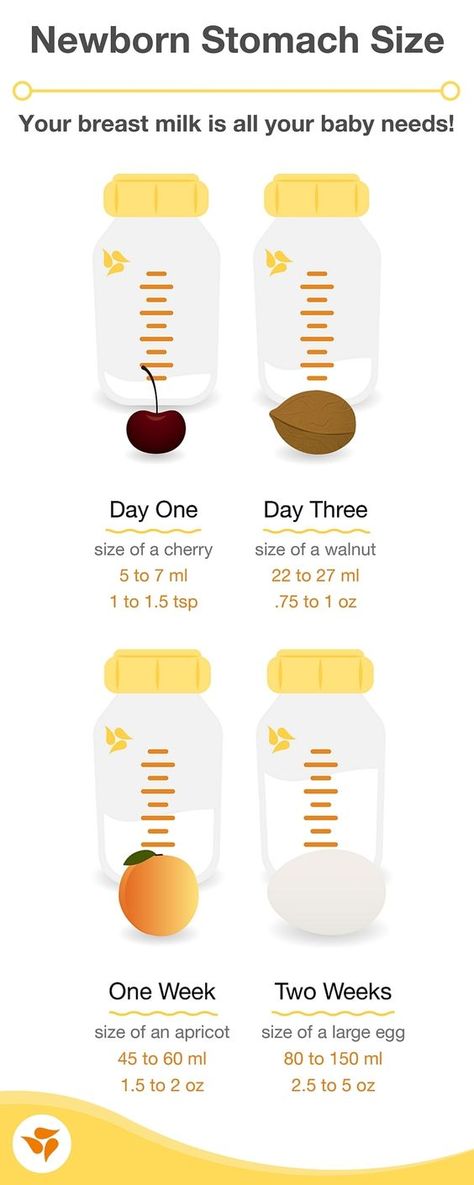 You can use a "syringe" (for example, a medicine dispenser) or a pipette. There are SNS systems - a bottle with a thin tube that is fixed on the mother's nipple. When a baby suckles, he receives both breast milk and formula. This is the ideal solution for hypogalactia as it helps to maintain close skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby, which has a beneficial effect on restoring lactation. If you are switching to mixed feeding because you need to leave home, it is better for your assistant to accustom the child to the bottle - so the child will not smell you and reach for the breast.
You can use a "syringe" (for example, a medicine dispenser) or a pipette. There are SNS systems - a bottle with a thin tube that is fixed on the mother's nipple. When a baby suckles, he receives both breast milk and formula. This is the ideal solution for hypogalactia as it helps to maintain close skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby, which has a beneficial effect on restoring lactation. If you are switching to mixed feeding because you need to leave home, it is better for your assistant to accustom the child to the bottle - so the child will not smell you and reach for the breast.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
For supplementary feeding, choose a high-quality, balanced mixture. Valio Baby baby food is made from the highest quality natural cow's milk and is as close as possible to the composition of breast milk. It will help the baby gain weight and strengthen the body.
3.04 24
FoodShare:
Oksana Ivargizova
Medical Institute. Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
Breast milk and formula: what do they have in common?
1 Cribb VL et al. Contribution of inappropriate complementary foods to the salt intake of 8-month-old infants. Eur J Clin Nutr . 2012;66(1):104. - Cribb V.L. et al., "Effects of inappropriate complementary foods on salt intake in 8-month-old infants". Yur J Klin Nutr. 2012;66(1):104.
Contribution of inappropriate complementary foods to the salt intake of 8-month-old infants. Eur J Clin Nutr . 2012;66(1):104. - Cribb V.L. et al., "Effects of inappropriate complementary foods on salt intake in 8-month-old infants". Yur J Klin Nutr. 2012;66(1):104.
2 Lönnerdal B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am 9 Clin Nutr . 2003;77(6):1537 S -1543 S - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
3 Savino F et al. Breast milk hormones and their protective effect on obesity. Int J Pediatric Endocrinol. 2009;2009:327505. - Savino F. et al., "What role do breast milk hormones play in protecting against obesity." Int J Pediatrician Endocrinol.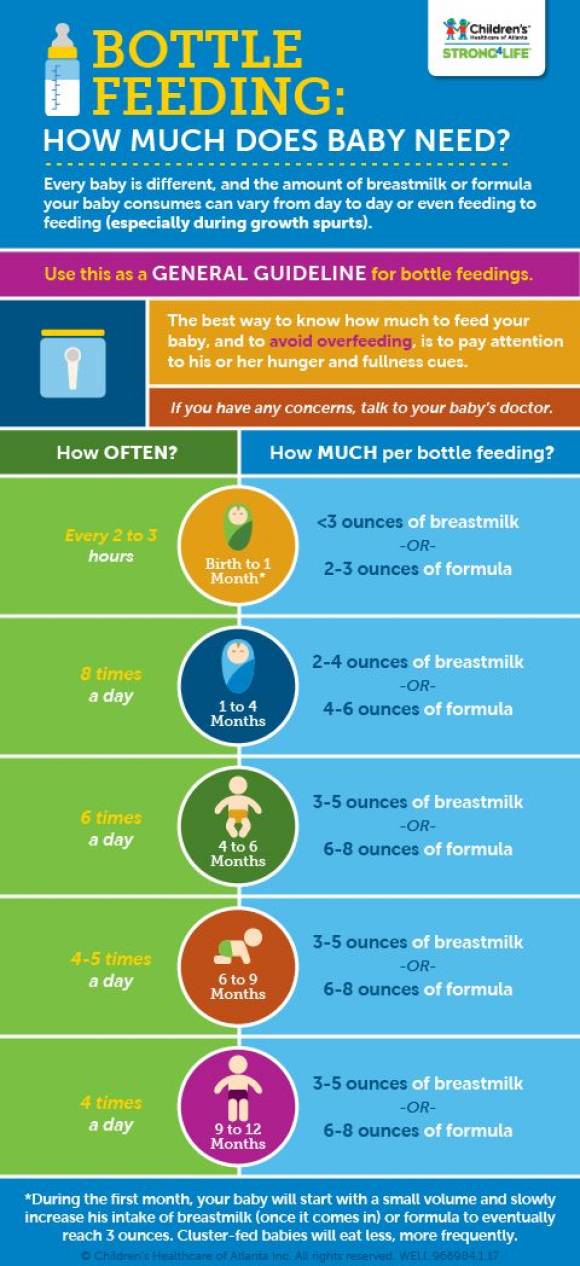 2009;2009:327505.
2009;2009:327505.
4 Hassiotou F, Hartmann PE. At the Dawn of a New Discovery: The Potential of Breast Milk Stem Cells. Adv Nutr . 2014;5(6):770-778. - Hassiot F, Hartmann PI, "On the threshold of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells." Adv. 2014;5(6):770-778.
5 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clinic Transl Immunology . - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
6 Pannaraj PS et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(7):647-654. - Pannaraj P.S. et al., "Bacterial communities in breast milk and their association with the emergence and development of the neonatal gut microbiome". JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
7 Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama.Glycobiology. 2012;22(9):1147-1162. - Bode L., "Oligosaccharides in breast milk: a sweet mother for every baby." Glycobiology (Glycobiology). 2012;22(9):1147-1162.
8 Deoni SC et al. Breastfeeding and early white matter development: A cross-sectional study. neuroimage. 2013;82:77-86. - Deoni S.S. et al., Breastfeeding and early white matter development: a cross-sectional study. Neuroimaging. 2013;82:77-86.
9 Birch E et al. Breast-feeding and optimal visual development. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993;30(1):33-38. - Birch, I. et al., "Breastfeeding and Optimum Vision Development." J Pediatrician Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993;30(1):33-38.
10 Sánchez CL et al. The possible role of human milk nucleotides as sleep inducers. Nutr Neurosci . 2009;12(1):2-8. - Sanchez S.L. et al., "Nucleotides in breast milk may help the baby fall asleep." Nutr Neurosai. 2009;12(1):2-8.
Nutr Neurosci . 2009;12(1):2-8. - Sanchez S.L. et al., "Nucleotides in breast milk may help the baby fall asleep." Nutr Neurosai. 2009;12(1):2-8.
11 Moukarzel S, Bode L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and the Preterm Infant: A Journey in Sickness and in Health. Clin Perinatol. 2017;44(1):193-207. - Mukarzel S., Bode L., "Breast milk oligosaccharides and the full-term baby: a path to illness and health." Klin Perinatol (Clinical perinatology). 2017;44(1):193-207.
12 Beck KL et al. Comparative Proteomics of Human and Macaque Milk Reveals Species-Specific Nutrition during Postnatal Development. J Proteome Res . 2015;14(5):2143-2157. - Beck K.L. et al., "Comparative proteomics of human and macaque milk demonstrates species-specific nutrition during postnatal development." G Proteom Res. 2015;14(5):2143-2157.
13 Michaelsen KF, Greer FR. Protein needs early in life and long-term health. Am J Clin Nutr . 2014;99(3):718 S -722 S . - Mikaelsen KF, Greer FR, Protein requirements early in life and long-term health. Am J Clean Nutr. 2014;99(3):718S-722S.
Protein needs early in life and long-term health. Am J Clin Nutr . 2014;99(3):718 S -722 S . - Mikaelsen KF, Greer FR, Protein requirements early in life and long-term health. Am J Clean Nutr. 2014;99(3):718S-722S.
14 Howie PW et al. Positive effect of breastfeeding against infection. BMJ .1990;300(6716):11-16. — Howie PW, "Breastfeeding as a defense against infectious diseases." BMJ. 1990;300(6716):11-16.
15 Duijts L et al. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in infancy. Pediatrics , 2010;126(1): e 18-25. - Duitz L. et al., "Prolonged exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in the first year of life." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2010;126(1):e18-25.
16 Ladomenou F et al. Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child . 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child.2010;95(12):1004-1008.
Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child . 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child.2010;95(12):1004-1008.
17 Vennemann MM et al. Does breastfeeding reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome?. Pediatrics . 2009;123(3): e 406- e 410. - Wennemann M.M. et al., "Does Breastfeeding Reduce the Risk of Sudden Infant Death?" Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2009;123(3):e406-e410.
18 Straub N et al. Economic impact of breast-feeding-associated improvements of childhood cognitive development, based on data from the ALSPAC. Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6. - Straub N. et al., "Economic Impact of Breastfeeding-Associated Child Cognitive Development (ALSPAC)". Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6.
et al., "Economic Impact of Breastfeeding-Associated Child Cognitive Development (ALSPAC)". Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6.
19 Heikkilä K et al. Breast feeding and child behavior in the Millennium Cohort Study. Arch Dis Child . 2011;96(7):635-642 - Heikkila K. et al., Breastfeeding and Child Behavior in a Millennial Cohort Study. Arch Dis Child. 2011;96(7):635-642.
20 Singhal A et al. Infant nutrition and stereoacuity at age 4–6 y. Am J Clin Nutr , 2007;85(1):152-159. - Singhal A. et al., Nutrition in infancy and stereoscopic visual acuity at 4-6 years of age. Am F Clean Nutr. 2007;85(1):152-159.
21 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
22 Horta B et al. Long - term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):30-37. - Horta B.L. et al., "Long-term effects of breastfeeding and their impact on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis." Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):30-37.
23 Lund-Blix NA. Infant feeding in relation to islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible children: the MIDIA Study. Diabetes Care . 2015;38(2):257-263.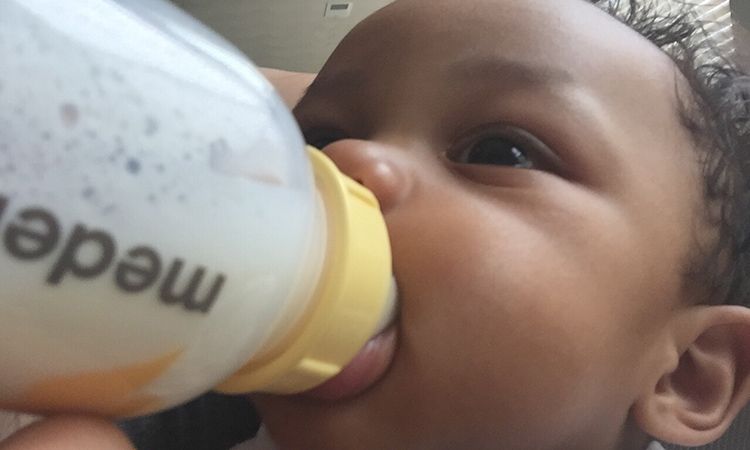 - Lund-Blix N.A. et al., "Breastfeeding in the context of isolated autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed children: a study MIDIA ". Diabitis Care. 2015;38(2):257-263.
- Lund-Blix N.A. et al., "Breastfeeding in the context of isolated autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed children: a study MIDIA ". Diabitis Care. 2015;38(2):257-263.
24 Amitay EL, Keinan-Boker L. Breastfeeding and Childhood Leukemia Incidence: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review0. JAMA Pediatr 2015;169(6): e 151025. - Amitai I.L., Keinan-Boker L., "Breastfeeding and incidence of childhood leukemia: a meta-analysis and systematic review." JAMA Pediatrics 2015;169(6):e151025.
25 Bener A et al. Does continued breastfeeding reduce the risk for childhood leukemia and lymphomas? Minerva Pediatr. 2008;60(2):155-161. - Bener A. et al., "Does long-term breastfeeding reduce the risk of leukemia and lymphoma in a child?". Minerva Pediatrician. 2008;60(2):155-161.
26 Dewey KG. Energy and protein requirements during lactation. Annu Rev Nutr . 1997;17:19-36. - Dewey K. J., "Energy and Protein Requirements During Lactation". Anna Rev Nutr. 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36.
Annu Rev Nutr . 1997;17:19-36. - Dewey K. J., "Energy and Protein Requirements During Lactation". Anna Rev Nutr. 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36.
27 Victoria CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
28 Jordan SJ et al. Breastfeeding and Endometrial Cancer Risk: An Analysis From the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium. Obstet Gynecol . 2017;129(6):1059-1067. — Jordan S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of endometrial cancer: an analysis of epidemiological data from the Endometrial Cancer Consortium". Obstet Ginekol (Obstetrics and Gynecology). 2017;129(6):1059-1067.
29 Li DP et al.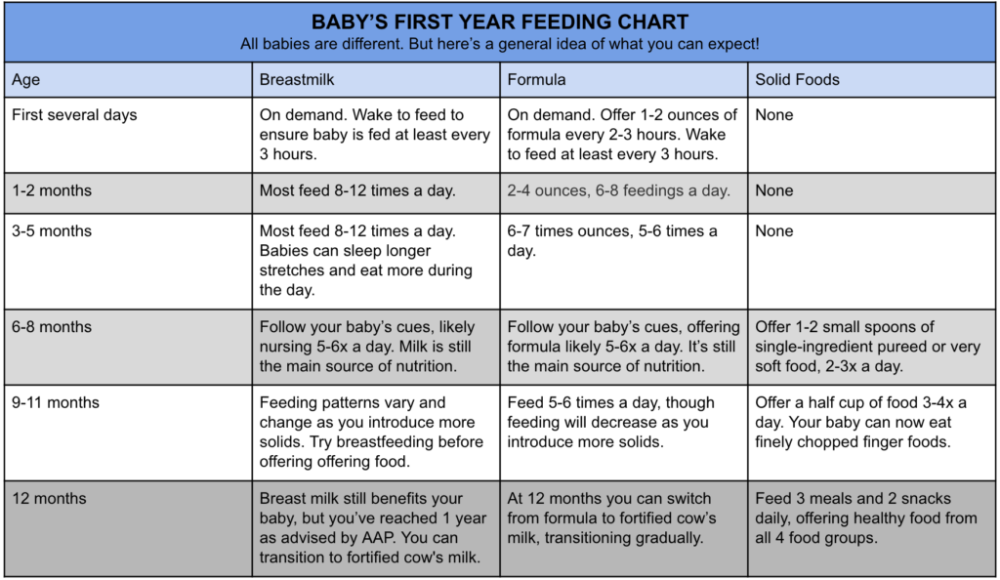 Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev . 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas W Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev . 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas W Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
30 Peters SAE et al. Breastfeeding and the Risk of Maternal Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women. J Am Heart Assoc . 2017;6(6). - Peters S.A. et al., "Breastfeeding and Maternal Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women". J Am Hart Assoc. 2017;6(6):e006081.
31 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet ; 2011 Jan 20 - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer, 20 January 2011 [cited 4 April 2018]
32 Doan T et al.











