Dha rich foods for babies
Why Toddlers Need DHA | Stonyfield
If you’re a card-carrying label reader–scouring the fine print on food packages and looking for basic, wholesome ingredients–you may have wondered why the ingredient list on your toddler’s yogurt includes…sardines?
DHA is an omega-3 fatty acid that may help your toddler’s growth and development.
Sardine and anchovy oil are natural sources of DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid that may help your toddler’s growth and development. DHA is found in abundance inside the brain. Synapses—the areas of the brain where messages are sent and received—are particularly rich in DHA. So it’s thought that DHA might be involved in communication between brain cells. That’s why dietitians like myself sometimes refer to DHA-rich fish as “brain food”.
First, a quick primer. There are three kinds of omega-3 fatty acids:
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) found in fish and their oils
- EPA (icosapentaenoic acid) found in fish and their oils, together with DHA
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) found in plant foods such as flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts, and canola and soybean oils.
Omega-3s can be trickier to get than other kinds of fats because the foods that are rich sources of omega-3s (like fish and nuts) aren’t mainstays of the average American diet. Yet these fatty acids have so many potential health benefits. Omega-3s are being studied for their possible link to improved heart health, memory, and mood. Some research has also found sharper vision in babies with higher blood levels of DHA—as well as higher IQs later in childhood among kids fed DHA-fortified formula compared to those given formula without it.
If you breastfed, your baby got DHA through breast milk. Infant formulas are now fortified with the fatty acid as well. But once your baby is exclusively eating table food, DHA can be harder to come by. According to government surveys, kids under the age of 6 are only getting a fraction of the DHA they need everyday.
Natural sources of DHA include fish such as salmon, herring, trout, sardines, and tuna (and their oils), shrimp, and much smaller amounts in chicken. Remember that most babies can start eating fish after six months. Though fish used to be discouraged in the first year of life because of potential allergic reaction, those recommendations have changed (if you or your baby have a history of food allergies, talk to your pediatrician about the best time to introduce fish). You can puree fish in the first months of starting solids and progress to soft pieces of poached or baked fish.
Remember that most babies can start eating fish after six months. Though fish used to be discouraged in the first year of life because of potential allergic reaction, those recommendations have changed (if you or your baby have a history of food allergies, talk to your pediatrician about the best time to introduce fish). You can puree fish in the first months of starting solids and progress to soft pieces of poached or baked fish.
You may have heard that you can get DHA from plant foods like walnuts and flaxseed. These foods are actually rich in ALA. Though it’s true that the body converts some of the ALA in these foods into DHA, the amount converted is quite small–less than one percent! So these foods just can’t be relied on as good sources of DHA.
Foods that are fortified with the fatty acid can help boost your child’s intake of DHA. YoToddler yogurt and YoTots pouches contain fish oil, naturally rich in DHA. Other fortified foods may be supplemented with algae, a vegetarian source of DHA (such as certain brands of eggs, which come from chickens fed a diet enriched with algal oil).
But however you choose to get it—through fish, fortified foods, or a combination of both—know that brain-building DHA will help your toddler get off to a great start.
DHA for Babies and Kids
DHA is an omega- 3 fatty acid. It is used to improve health in children. Found naturally in many sources, the expectant mother is the primary giver of this acid when she is pregnant. The prenatal period is a window when the baby’s brain develops with the help of the right nutrition supplied through the placenta. DHA influences the development of the brain, eyes and other primary neurological functions. It has a profound influence during the first two years of life and early stages of childhood. From birth until five years of age, the brain increases by 3.5 times its total mass and it is of critical importance that DHA is consumed in adequate amounts to support the rapid growth in the brain.
A healthy diet that provides about 600mg of DHA daily has a significant impact on the cognitive functions of the child and enhance the development of the brain and eyes. Organ meat and fatty fish are rich sources of naturally found DHA and unfortunately, these are not commonly consumed by children as they are picky eaters and prone to allergies at times. However, the growing awareness of its importance has led to its inclusion in milk, formula and other fortified foods making it easier for people of all age groups including children to obtain the benefits of this important nutrient.
Organ meat and fatty fish are rich sources of naturally found DHA and unfortunately, these are not commonly consumed by children as they are picky eaters and prone to allergies at times. However, the growing awareness of its importance has led to its inclusion in milk, formula and other fortified foods making it easier for people of all age groups including children to obtain the benefits of this important nutrient.
What is DHA?
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a part of the omega-3 fatty acid family is a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid often called “the healthy fats.” It has a large influence on our body as it keeps us healthy and is crucial for the optimal growth of the brain and eyes through our life. In fact, the nutrient takes centre stage when neural tissues, including vision, are being formed in the womb. DHA supports our cognitive, visual and mental faculties as we age.
What Are the Benefits of DHA for Babies and Kids?
DHA has undoubtedly gained a lot of attention and is appearing in all places from eggs, baby food to milk. Why should one care so much about this nutrient? Well, the answer is it is a beneficial fat. The role of DHA is accentuated during infancy and early years of childhood.
Why should one care so much about this nutrient? Well, the answer is it is a beneficial fat. The role of DHA is accentuated during infancy and early years of childhood.
For Babies
DHA plays a key role in the structural component in the brain, eyes and nervous system. Breastmilk is high in DHA content and breastfed babies have strong mental and visual acuity.
For Kids
During the early infant years until five years of age, the brain makes rapid development and increases to about 4 times its total mass. Adequate DHA intake during these crucial years in important for optimal development and enhancement of cognitive functions. It has been researched and proven that children who have a good intake of DHA until five years of age have better IQ scores, tremendous memory, good reading skills and strong vision.
DHA deficiency could be common in children suffering from Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD). In a nutshell, DHA is imperative for neurological and visual development.
While there are no guidelines for a daily DHA dosage for children, there are certain recommendations that exist for the intake of DHA plus eicosapentaenoic acid, or EPA.
For Babies
Babies who are breastfeeding will receive most of their DHA intake from the milk. Breastmilk is known to be high on DHA content. It is advisable for mother’s to increase their intake of DHA rich food while breastfeeding, A breastfeeding mother should aim at consuming at least 600-800 milligrams of DHA in a day via natural sources or supplements.
For Kids
From the age of 1.5 years to five years of age, the DHA requirement for children is recommended as 600 milligrams of combined DHA plus EPA per day for a child weighing 20 kilograms.
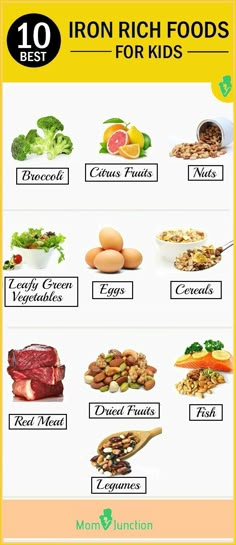
DHA Rich Food for Babies and Kids
There are certain foods that are rich in DHA that you can include in your child’s diet. Here are some DHA rich foods for children of different ages.
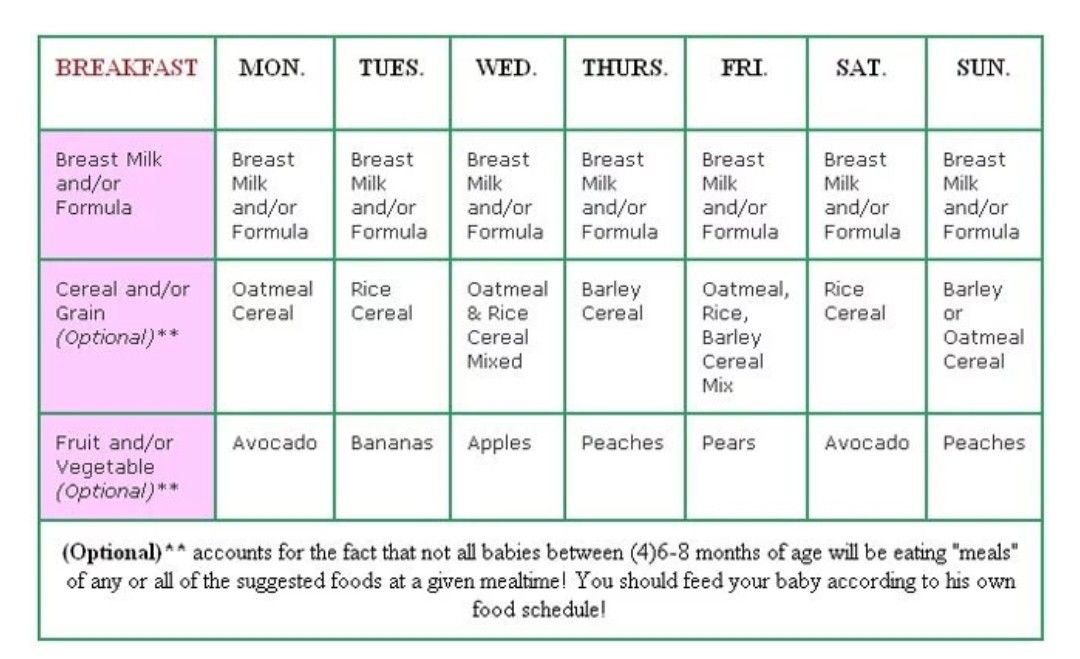
1. DHA for Breastfed Babies
The best source of DHA for breastfed babies is from breast milk. The amount of DHA varies according to the mother’s diet and the quantity of omega-3’s and DHA she is receiving. It is advisable for feeding mothers to include fish, eggs, yoghurts and dried nuts in their diet to help babies receive DHA for healthy development of the brain and retina of the eye. Formula-fed babies get their DHA intake only if the formula is fortified with it and so it is important to read the labels.
The amount of DHA varies according to the mother’s diet and the quantity of omega-3’s and DHA she is receiving. It is advisable for feeding mothers to include fish, eggs, yoghurts and dried nuts in their diet to help babies receive DHA for healthy development of the brain and retina of the eye. Formula-fed babies get their DHA intake only if the formula is fortified with it and so it is important to read the labels.
2. DHA Foods for Toddlers and Kids
There are a lot of natural varieties of DHA food for toddlers and kids. Some foods that could feature in your child’s regular diet are:
- Salmon contains the highest content of DHA among the fish varieties and offers a healthy proportion of good omega-3 fats
- Eggs contain small amounts of DHA naturally but you could also opt for DHA enriched eggs from chickens fed with a supplemented diet
- DHA enriched yoghurts are a staple on the supermarket shelves and you could offer it to kids as a breakfast or light snack
- Peanut butter could be substituted for the sugar-rich jam as a spread to morning toast for kids
- Serve a handful of walnuts to your toddler as a delicious or healthy snack.

- Formula milk now comes with fortified DHA as manufacturers have realised the importance of DHA. There are some products specially designed for children aged 1 year and above and you could buy them after checking the label thoroughly.
Are DHA Supplements for Infants and Children Safe?
Numerous studies have covered the effects of DHA supplements on childhood development. Some research has proven that supplements have an effect on the behaviour and cognitive abilities of a child. DHA supplements administered to children with learning disabilities helped them in developing their mental capabilities to a certain extent. However, due to lack of research, DHA supplements are not recommended as a treatment for any condition in children. It is possible to achieve the needed intake by eating fatty fish, nuts and eggs in your diet. Discuss with your paediatrician about giving your kids DHA supplements and take his advice about the best DHA supplement for toddlers.
Precautions to Take while giving DHA Supplements to your Child
Mercury levels prevalent in seafood, when consumed in excess, could have an adverse effect on the cognitive development of a child. It is then that parents resort to DHA omega 3 supplements for kids. Supplements containing fish oil are purified and devoid of contaminating metals or minerals. However, small amounts of toxins may still be present. For breastfeeding babies, parents can buy DHA drops for infants in India. But, an excess of fish oil could lead to bleeding in children. So, it is mandatory that you seek consultation from the paediatrician before giving DHA supplements to determine the safe and effective dosage.
DHA is an important nutrient that fuels your baby’s optimal development. A well-balanced level of DHA has been linked to good retinal health and cognitive ability. The best way to include DHA in your child’s diet is to make every bite count by avoiding empty calories and choosing super-foods that will give your baby the necessary nutrition.
Also Read:
Advantage of Protein for kids
Is Protein Powder Safe for Kids?
Necessary Vitamin for Babies
How to choose Omega 3 for children: how to take, EPA and DHA in
January 12 2021
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids that are essential for many aspects of health, including fetal development, brain function, heart health, and immunity (1). However, many parents are not sure if omega-3 supplements are necessary for children or even if they are safe for them?
There are three main types of omega-3s:
- alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
- eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
ALA is found in plant foods, including vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and some vegetables. However, this form is not active and requires conversion to active forms such as DHA and EPA. EPA and DHA are known to be found in sufficient amounts in fatty fish such as salmon, herring, tuna, etc. , and are also widely available in supplement form.
, and are also widely available in supplement form.
Important! There are many types of supplemental sources of omega-3s, the most common being fish oil, krill oil, and algae oil.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an important substrate for brain and CNS development during fetal development, and additional maternal sources of omega-3 fatty acids have been proposed as a means of optimizing fetal cognitive development (2).
Why does a child need omega-3 and fish oil?
Many studies show that supplemental omega-3s have a number of benefits for children:
- Improve brain function and mood in children, particularly learning, memory, and brain development (3). In addition, several studies show that omega-3 fats help prevent depression and mood disorders in children (4).
- Reduce the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, which comes with symptoms such as hyperactivity, impulsivity and difficulty focusing.
 A large review of 52 studies concluded that fish oil supplements were two of the most promising methods for reducing the symptoms of this condition in children (5).
A large review of 52 studies concluded that fish oil supplements were two of the most promising methods for reducing the symptoms of this condition in children (5). - Relieve the course of bronchial asthma. Some studies have shown that omega-3s help relieve these symptoms. For example, a study in children diagnosed with asthma found that taking 120 mg of combined DHA and EPA daily helped reduce asthma symptoms (6). A number of studies also point to a possible link between omega-3 fatty acids and a lower risk of developing asthma in children (7).
How to take Omega-3 for children?
All people, regardless of age or health condition, are advised to determine the level of omega-3 in the blood and consult a doctor who will give individual recommendations. You also need to pay attention to a number of conditions during the intake of fish oil by a child:
- If possible, eat fatty fish, at least twice a week.
- Reduce intake of omega-6 fats (usually found in vegetable oils, nuts).
 This is because omega-6 fats compete with omega-3s for enzymes, so excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids can replace omega-3s in cell membranes.
This is because omega-6 fats compete with omega-3s for enzymes, so excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids can replace omega-3s in cell membranes.
Omega-3s for newborns and infants
Expert organizations recommend that pregnant and lactating women get at least 1300 mg of ALA and 200 mg of DHA per day to ensure that the newborn receives the required amount of omega-3s through breast milk. Omega-3s are important for the continued development of the baby's brain and retina. If the child is bottle-fed, then be sure to purchase mixtures enriched with DHA and ALA. When the baby grows up and begins to eat solid foods, it is necessary to follow the recommendations for providing the child with omega-3 fats by introducing low-mercury seafood 50 grams 1-2 times a week.
Need to know! Remember that cow's milk does not contain omega-3s, unlike human milk or fortified formulas, so essential fatty acids must come from wholesome food sources. Omega-3 intake in the first few years of life is vital for continued cognitive and behavioral development.
Omega-3 intake in the first few years of life is vital for continued cognitive and behavioral development.
DHA accumulation in the retina is completed by birth, while accumulation in the brain continues during the first 2 years after birth. Therefore, omega-3 acids are very important for babies.
EPA and DHA in omega-3s
Omega-3 sources, including fish oils, contain the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which make up approximately 10% of total omega-3 fatty acid intake.
Check the supplement you buy for the type and amount of omega-3s. It should contain EPA and DHA in satisfactory amounts - and preferably an antioxidant to fight rancidity. For example, a product may contain 1,000 mg of fish oil, but the levels of these two substances may be much lower.
Omega 3 overdose and side effects
Usually the side effects of omega-3 supplements such as fish oil are usually very mild. The most common are:
- bad breath
- unpleasant aftertaste
- headache
- heartburn
- nausea
- diarrhea
Important! Make sure your child is on the recommended dosage to reduce the risk of side effects. You can start omega-3 supplementation at a lower dose and gradually increase it to the full dose to assess your tolerance.
You can start omega-3 supplementation at a lower dose and gradually increase it to the full dose to assess your tolerance.
Sometimes eating too much fish oil can have serious health effects and lead to side effects such as high blood sugar and an increased risk of bleeding. According to the European Food Safety Authority, omega-3 fatty acid supplements can be safely consumed at doses up to 5,000 mg per day. As a rule, if a person experiences any negative symptoms, it is enough to reduce the dose or stop taking it for a while.
Consult your physician and stick to the recommended dosage, and aim to get most of your omega-3 fatty acids from food sources to get the most nutritional value.
My child is allergic to fish oil, what should I do?
If a child has a tendency to develop allergic reactions, or there is a confirmed case of an allergy to fish or shellfish, then the possibility of developing a reaction to fish oil also occurs. In such cases, supplements based on fish oil and similar components such as cod liver oil and krill oil should be avoided.
Other omega-3 rich foods or supplements such as linseed or algae oil can be used instead. However, it should be remembered that the human body does not use omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in plant sources, as effectively as in seafood. Therefore, microalgae supplements such as spirulina are considered the most effective sources of DHA and EPA (8).
Be sure to check with your pediatrician or healthcare provider before making nutritional changes for you or your child.
WHO recommendations for daily omega-3 intake for children*
%E is the percentage of energy, for infants the recommended fat intake is expressed as % E.
*World Health Organization. (2008). Interim summary of conclusions and dietary recommendations on total fat & fatty acids. From the joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on fats and fatty acids in human nutrition, 10-14.
Drug Comparison Chart
About the Author
Maria Yavorovich
MD, pediatrician
Sources
- Swanson, D.
 , Block, R., & Mousa, S. A. (2012). Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: health benefits throughout life. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 3(1), 1–7.
, Block, R., & Mousa, S. A. (2012). Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: health benefits throughout life. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 3(1), 1–7. - Adams P, Lawson S, Sanigorski A, Sinclair A. Arachidonic acid to eicosapentaenoic acid ratio in blood correlates positively with clinical symptoms of depression. Lipids31,S157–S161 (1996)
- Stonehouse W. (2014). Does consumption of LC omega-3 PUFA enhance cognitive performance in healthy school-aged children and throughout adulthood? Evidence from clinical trials. Nutrients, 6(7), 2730–2758.
- Trebatická, J., Hradečná, Z., Böhmer, F., Vaváková, M., Waczulíková, I., Garaiova, I., Luha, J., Škodáček, I., Šuba, J., & Ďuračková, Z. (2017). Emulsified omega-3 fatty-acids modulate the symptoms of depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a pilot study. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 11, 30.
- Heilskov Rytter MJ, Andersen LB, Houmann T, Bilenberg N, Hvolby A, Mølgaard C, Michaelsen KF, Lauritzen L.
 Diet in the treatment of ADHD in children - a systematic review of the literature. Nord J Psychiatry. 2015 Jan;69(1):1-18
Diet in the treatment of ADHD in children - a systematic review of the literature. Nord J Psychiatry. 2015 Jan;69(1):1-18 - Nagakura T, Matsuda S, Shichijyo K, Sugimoto H, Hata K. Dietary supplementation with fish oil rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in children with bronchial asthma. Eur Respir J. 2000 Nov;16(5):861-5
- Li, J., Xun, P., Zamora, D., Sood, A., Liu, K., Daviglus, M., Iribarren, C., Jacobs, D., Jr, Shikany, J. M., & He , K. (2013). Intakes of long-chain omega-3 (n-3) PUFAs and fish in relation to incidence of asthma among American young adults: the CARDIA study. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 97(1), 173–178
- Peltomaa E, Johnson MD, Taipale SJ. Marine Cryptophytes Are Great Sources of EPA and DHA. MarDrugs. 2017;16(1).
Share
Share
Share
Share
New comment
Sign in with
Submit
What is DHA, how does it affect the development of the child?
12 December 2019
24 November 2022
3 minutes
22474
ProWellness
Contents
- Benefits of DHA for children
- DHA deficiency symptoms in children
- DHA intake for children
- DHA rich foods
Disclaimer
Please note that all information posted on the site Prowellness is provided for informational purposes only and is not a personal program, a direct recommendation for action, or medical advice. Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource.
Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource.
What is DHA and how does it affect a child's development?
DHA - docosahexaenoic acid, which is one of the most important omega-3 acids. The body produces a small amount of DHA, so it is recommended to take it in addition to food or in the form of special supplements. Fatty acids are essential for people of all ages, including children.
Benefits of DHA for children
The acid in question is of paramount importance in the formation of the hormonal, nervous, and immune systems. It has a positive effect on the functioning of the brain, affects the laying of molars.
During breastfeeding, the child receives almost all the necessary substances. A shortage occurs only if the mother herself is malnourished and therefore cannot provide a sufficient amount of the substances necessary for the baby.
Attention! Before the age of 14, children begin to develop their brains. During this period, the body needs at least 1 g of omega-3 acids per day.
DHA, in addition to the above qualities, has other useful properties:
- Fights inflammation in the body.
- Counteracts Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Numerous studies have shown that patients with this syndrome have low levels of dha in the blood.
- Helps develop normal vision. In order for the baby's eyes to function well, a woman should not only add DHA to the baby's diet, but also consume enough of it during pregnancy.
Also, the acid in question is responsible for the normal development of mental health.
Symptoms of DHA deficiency in children
If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should consult your doctor as your child may have a DHA deficiency:
- Appearance of diathesis and atopic dermatitis.
- Significant decline in cognitive abilities: memory, attention, school performance.
- Hyperactivity syndrome.
- Frequent allergic reactions.
- Reduced vision.
- Dry skin.
Attention! With a lack of DHA, it is recommended to enrich the diet with foods rich in this substance. And in case of acute deficiency - use pharmacy drops with docosahexaenoic acid.
Children's DHA
At the moment, the approximate dosage of DHA is known. It is 200-500 mg of acid per day. Upper limit - 3000 mg.
When prescribing the drug in capsules or drops, you should carefully read the instructions and adhere to the dosages indicated in it. You also need to consult with your doctor.
You also need to consult with your doctor.
DHA rich foods
In order to avoid a deficiency of docosahexaenoic acid, it is necessary to diversify the child's diet with the following products:
- lean meats;
- vegetable seafood;
- eggs;
- cheeses;
- yoghurts.
But the most common product is fish. The leaders in the content of DHA are trout, herring, carp, as well as fish oil.
Attention! Fish should be introduced into the child's diet carefully, as it can provoke an allergic reaction. In this case, it is better to switch to chicken meat and eggs. This food also contains the required amount of DHA.
Adults also benefit from enriching their diets with these important foods, as having enough DHA in the diet is the best prevention of Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis.
Disclaimer
Please note that all information posted on the site Prowellness is provided for informational purposes only and is not a personal program, a direct recommendation for action, or medical advice.