How long to feed baby on each side
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts. Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
That's a personal choice. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, breastfeeding can continue until 12 months (and beyond) if it's working for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that breastfeeding can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
How Long Should I Breastfeed On Each Side? One Breast or Two
It’s important for mothers to know that there is no magic number when it comes to how long you should nurse on each breast. For many years, moms were instructed to nurse on each breast for a prescribed amount of time such as 15-20 minutes on each side. Now, mothers are being encouraged to follow their baby’s lead and let their baby tell them when they’re done! Allowing your baby to breastfeed on-demand and end the feeding when they’re ready ensures your baby takes a full feeding and let’s you RELAX and simply enjoy your baby.
How long your baby nurses can vary greatly from one session to the next and also throughout your breastfeeding journey. In the early weeks, breastfeeding sessions do tend to be longer and it’s not uncommon for your baby to want to nurse frequently – especially during the evening hours. Cluster feeding is your baby’s way of telling your body to continue to produce ample amounts of milk to support his or her growth throughout infant years. Your baby and your body work in perfect rhythm to match your milk supply with your baby’s needs.
Your baby and your body work in perfect rhythm to match your milk supply with your baby’s needs.
Sometimes, babies may simply want a small “snack” and other times they may be ready to enjoy a “four course meal,” both types of feedings can be normal. Just like how you and I might grab an orange and take a few sips of water at various points throughout the day or indulge in a succulent cheese burger with fries, a side salad, AND a milkshake at other points – your baby’s appetite varies, too!
Rather than scheduling feedings or watching the clock, focus on watching your baby and learning his or her hungry and full cues. As a general rule, you should:
-
-
-
- Alternate which breast you start with at each feeding – If you began nursing from your left breast at the previous feeding, consider beginning with the right breast for this feeding. If you cannot remember which breast you started with last, offer the fuller feeling breast first.
-
-
-
-
-
- Allow your baby to finish the first breast – Your baby may unlatch or begin to fall asleep as their hunger is satisfied.
 Your breasts should feel softer following the feeding.
Your breasts should feel softer following the feeding.
- Allow your baby to finish the first breast – Your baby may unlatch or begin to fall asleep as their hunger is satisfied.
-
-
-
-
-
- Offer your baby the other side – If she/he takes it, “great!,” if not, that’s OK, too; just be sure to let your baby decide if they are done. You may want to burp your baby or change their diaper before offering the other side.
-
-
As your baby matures, you may begin to notice a change in the duration of feedings (as well as the frequency). While newborns are still learning the “moves” to the dance we call ‘breastfeeding,’ older babies who have been nursing for several months may become extremely efficient nursers – taking in a full feeding in 10 minutes or less!
If you are worried about how long your baby nurses, the first thing to consider is how well they are gaining weight and the number of wet and dirty diapers they have each day (click here for more information on normal diaper output for breastfed newborns or click here for more information about normal diaper output for breastfed babies 6 weeks+). If your baby is gaining weight, following their growth chart, has adequate wet and dirty diapers per day, and is meeting milestones, continue nursing on-demand and take comfort in knowing that your baby is getting plenty of milk.
If your baby is gaining weight, following their growth chart, has adequate wet and dirty diapers per day, and is meeting milestones, continue nursing on-demand and take comfort in knowing that your baby is getting plenty of milk.
If you have concerns about your baby’s weight gain, diaper output or your milk supply, you should discuss your concerns with your pediatrician and schedule an appointment with a lactation consultant.
If your baby always nurses for extended periods or will not stay on the breast for more than a few minutes, call Lactation Consultants of Central FL’s breastfeeding warm line, email us at [email protected] or click here to schedule an in-home lactation visit.
Breastfeeding / Breastfeeding / Useful information / Children's polyclinic / Departments of the KDMC sometimes light as dew, sometimes enveloping like white clouds. How many times it healed me and I became strong again, or wrapped me in a sweet slumber when I was very tired.
 At your chest, I heard the singing of a lark high in the sky, and the whisper of leaves in a birch grove, and autumn rain outside the window, and the chime of waxwings on a winter day.
At your chest, I heard the singing of a lark high in the sky, and the whisper of leaves in a birch grove, and autumn rain outside the window, and the chime of waxwings on a winter day. Even after many years I will remember it, we will remember it...
E. Ibragimova
Published in the special issue of the magazine "Liza. My child" special issue 01/2016
Many mothers, expecting their first baby, seriously think about how childbirth will take place, and less often they think about how they will feed the baby. Meanwhile, childbirth is a very short period of time, and the rest of the time of life with the baby will be devoted to building relationships with him through breastfeeding.
Some mothers-to-be are hesitant to breastfeed at all.
Let's look at their assumptions first:
- Does breastfeeding ruin breast shape?
Breast shape changes during pregnancy. On the contrary, when feeding for more than a year and smooth weaning, the breast acquires an almost “pre-pregnant” shape. According to studies, smoking has a stronger effect on the shape of the breast than feeding.
According to studies, smoking has a stronger effect on the shape of the breast than feeding.
- Will it be impossible to leave the child?
The first 3 months are possible short (1-1.5 hours) separation from the child, from 3 months absence can be longer, after 9months, the mother can go to work full-time, leaving the baby with expressed milk.
- If the mother is nervous or very tired, does the milk “burn out” or become bad for the baby?
There are no conditions in the mammary gland for "burning out" of milk. When breastfeeding, endorphins are released into the blood of a woman, and HB helps her to endure stress more easily and is the best prevention of depression. Yes, and the child himself calms down at the breast, even if before that he sees the unusual behavior of his mother.
- Is formula practically the same as breast milk?
The manufacturers of infant formulas, who invest millions of dollars in advertising and bribes, have tried hard to make women have such doubts.
Let's look at a few differences between breastfeeding and formula feeding:
|
| GW | Blend |
| Economy | free | about 100 tr. in the first year of a child's life. If hypoallergenic mixtures are required, then about 240 tr. |
| Number of substances | over 700! | 30- 50 |
| Stem cells | yes | no |
| Antibodies against diseases | yes | no |
| Growth factors for maturation of the intestines | enough | little |
| Effect of | normal maturation of the gastrointestinal tract, normal development of the immune system | constipation, diarrhea, increased risk of many diseases: allergies, gastrointestinal problems, various infections, diabetes, etc. |
| Proteins | easily absorbed whey
| hard to digest casein clots
|
| Change in composition | adapts to the needs of the baby (varies depending on the season, time of day, age of the baby, etc.) | the composition is the same for all children |
| Vitamins and minerals | easily digestible | low absorption |
| Availability | no need to cook | it is necessary to go to shops, sterilize the bottle, dilute the mixture with water, etc. |
| Excess substances | no | cases of salmonella infection, radioactive particles, etc. |
| Emotional connection between mother and child | strong | weak |
And the list of differences goes on.
Can you imagine how a bottle of formula can replace the happy moments at the mother's breast?
With the right information and help, almost every woman can successfully and sustainably breastfeed. And you can!
What information can help you?
Firstly immediately after delivery (before measurements) skin-to-skin contact between the newborn and the dried, covered with a dry diaper, contact duration - at least 40 minutes, optimally 2 hours or more. (This right of mother and child is also enshrined in the Methodological Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2011 N 15-4 / 10 / 2-6796 "On the organization of the work of the obstetric service in the context of the introduction of modern perinatal technologies").
Why is this important:
a) At the same time, the baby's body is colonized by the same bacteria that live on the body of his mother. This, in combination with HB, is considered an important prevention of allergic diseases.
This, in combination with HB, is considered an important prevention of allergic diseases.
b) If a newborn is separated from his mother immediately after birth, he becomes vulnerable to aggressive hospital flora, the risk of nosocomial infections increases dramatically.
c) This calms the baby and mother, because they both experience severe stress in childbirth.
d) The baby is more likely to be able to latch on correctly (especially if the birth was completed without medication).
Second , breastfeed within the first hour after delivery. Don't panic if the baby doesn't take the breast right away. Children should eat when they show they are ready, and if the child is in close contact with the mother, she will notice this readiness. The recommended duration of application is at least 20 minutes from each breast.
The baby's first food should be colostrum. Colostrum is the secret of the mammary glands, which is produced during pregnancy and the first 3-5 days after childbirth (before milk arrives). It is a saturated thick liquid from light yellow to orange color. Do not be afraid that there is not enough colostrum. Colostrum is very concentrated, so the baby needs just drops.
It is a saturated thick liquid from light yellow to orange color. Do not be afraid that there is not enough colostrum. Colostrum is very concentrated, so the baby needs just drops.
Why is it important:
A) Colostrum contains several times more protein than mature milk, especially immunoglobulin A. Immunoglobulins are responsible for protecting the baby from infections and allergens, thanks to special mechanisms they are quickly absorbed in the baby's stomach and intestines.
B) Has laxative properties to help the baby quickly get rid of the original stool - meconium, and also reduces the risk of physiological jaundice in the baby.
C) The mother triggers the oxytocin reflex, which contributes to uterine contraction and faster recovery after childbirth.
Thirdly, the correct position of the baby at the breast and the correct attachment of to the breast. Let's dwell on the key points.
For example, you feed while seated. How to hold a baby:
How to hold a baby:
a) The child's body and head are on the same line.
b) The baby's belly should be turned towards the mother's belly and touch it.
c) The WHOLE body of the child must be supported.
The baby is brought to the breast with the NOSE to the nipple so that it is necessary to reach for the breast. When he opens his mouth wide, we press the baby to ourselves.
If it is not possible to attach the baby well, gently insert the little finger into the corner of the mouth and open the gums, remove the breast.
What does proper attachment look like? The baby's mouth is open wide; lips turned out; his chin touches his mother's breasts; areola capture radius is 2-3 cm from the base of the nipple; except for swallowing, sniffing and even breathing, no other sounds are heard (smacking, etc.); mom is not in pain.
There are many positions for feeding - sitting, lying down, close at hand, relaxed feeding, etc.
Nuance: good breast sucking is affected by the frenulum under the tongue of the baby, ask the pediatrician at the maternity hospital to check it.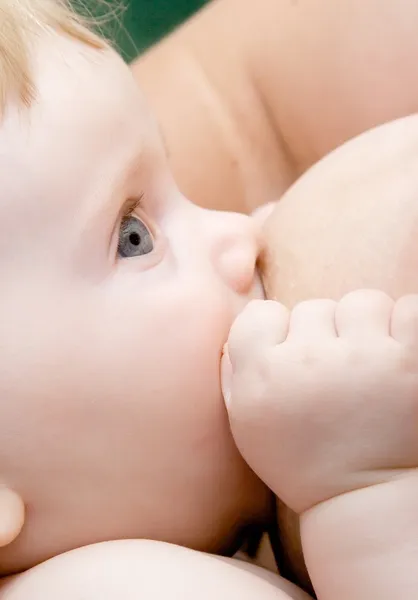 If it turns out to be short, it is better to cut it immediately.
If it turns out to be short, it is better to cut it immediately.
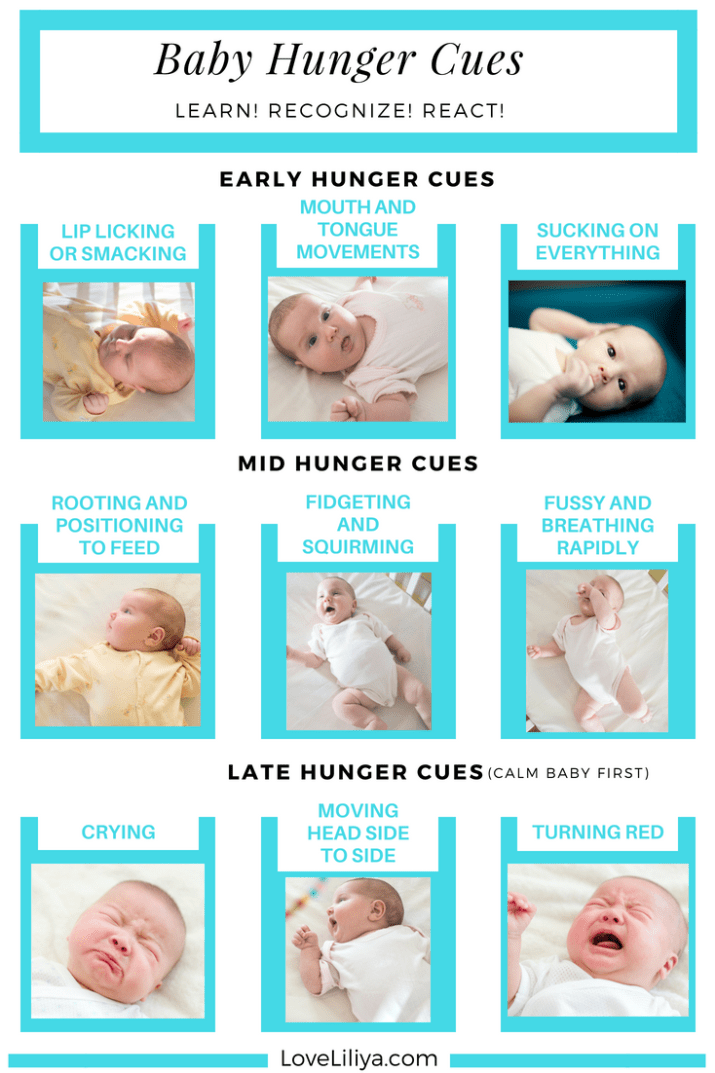
Fourth, frequent breastfeeding . The term “on demand” is commonly used, which confuses many moms. Many people think that a baby "demands" when it cries. At the same time, crying is the last thing a hungry child decides to do.
Signs of readiness to suckle in a newborn :
Muscles tense in the child, for example, he clenched his fists and flexed his arms at the elbows.
The child rolls, twists and arches his back.
The child makes different sounds.
The child draws his hands to his mouth (even if his eyes are closed, he can suck his own hand).
If the child's hand is close to the face, he turns towards the hand, pokes, opens his mouth.
A newborn in the first 3 months of life may want to kiss 15-25 times a day. After all, his stomach is very small (on the 1st day after birth - 5-7 ml, on the 3rd day - 22-27 ml, on the 7th day - 45-60 ml) and breast milk is quickly absorbed. In addition to receiving nourishment, the child also finds comfort in his mother's breast. Therefore, it is not recommended to feed the baby "according to the regime" - for example, once every 3 hours or to limit his time at the breast - for example, to feed no more than 15 minutes. Night feedings are crucial for successful lactation - thanks to them, the level of prolactin is maintained at the required level.
In addition to receiving nourishment, the child also finds comfort in his mother's breast. Therefore, it is not recommended to feed the baby "according to the regime" - for example, once every 3 hours or to limit his time at the breast - for example, to feed no more than 15 minutes. Night feedings are crucial for successful lactation - thanks to them, the level of prolactin is maintained at the required level.
Why frequent breastfeeding is important:
a) The number of prolactin receptors in the breast increases, which contributes to sufficient milk production in the future.
b) Promotes a more relaxed flow of milk, without pronounced symptoms of engorgement.
c) When feeding “according to the regimen”, there is a high risk that the child will be offended by the mother (after all, they do not immediately respond to his needs) and will behave restlessly at the breast.
Fifth, it is not recommended to give pacifiers to the child.
Why it's important:
a) Soothers artificially delay feeding time, resulting in poor weight gain and decreased milk production.
b) The child finds solace not at the mother's breast, but in a silicone object and may refuse the breast.
c) It spoils the grip of the breast, which leads to cracks, lactostasis.
Sixth, if you need to supplement with expressed milk and/or formula, then avoid the use of bottles.
Why is this important:
A) The baby gets used to a strong and constant flow of milk from the bottle and begins to behave restlessly at the breast, “lazy” to suck.
B) When sucking a bottle and a breast, different muscle groups are used, so the grip on the breast often deteriorates, the child sucks milk poorly, gains weight worse.
Seventh, the joint sleep of mother and child.
It is perfectly normal to sleep with your baby. A child should not be spoiled with attention or held too much in his arms. The more children are held in their arms, the more attention is paid to them, the better they grow. The presence of the mother, her smell, constantly encourages him to suckle the breast more often, which means sucking out more milk.
A child should not be spoiled with attention or held too much in his arms. The more children are held in their arms, the more attention is paid to them, the better they grow. The presence of the mother, her smell, constantly encourages him to suckle the breast more often, which means sucking out more milk.
Western parents are advised to leave their child to "shout out" before going to bed in order to raise an independent child who is used to loneliness and is able to calm himself down. However, modern research shows that in this case, the child's brain is irreparably damaged.
Safe sleep:
- The child should sleep on a clean and hard surface.
- Avoid sleeping with your baby if you are excessively tired.
- Do not leave your baby unattended in an adult bed.
- In cold weather, cover yourself with several layers of thin bed linen instead of one thick layer.
- Pets must not be in bed
- No one should smoke in the room where the baby sleeps.
Now consider some common cases:
- Mother's Rh negative or blood type incompatibility is not a contraindication to breastfeeding. Rh-conflict, blood type conflict or hemolytic disease of the newborn is not a contraindication. Rh antibodies are destroyed in the gastric juice of the newborn. Studies also show that in children with hemolytic disease, HB does not increase the breakdown of erythrocytes, red blood cells.
- The administration of anti-Rh immunoglobulin to prevent Rh conflicts in subsequent pregnancies in an Rh-negative mother is not a contraindication to breastfeeding. Anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin almost does not penetrate into breast milk. Most immunoglobulins are destroyed in the gastric juice of the newborn.
- Is it possible to breastfeed with jaundice?
Even with severe physiological jaundice in children in the first days of life, it is impossible to refuse breastfeeding. Early attachment of the baby to the breast and frequent feedings are an important factor in the prevention of jaundice, since colostrum, having a laxative effect, leads to a faster discharge of meconium (original feces).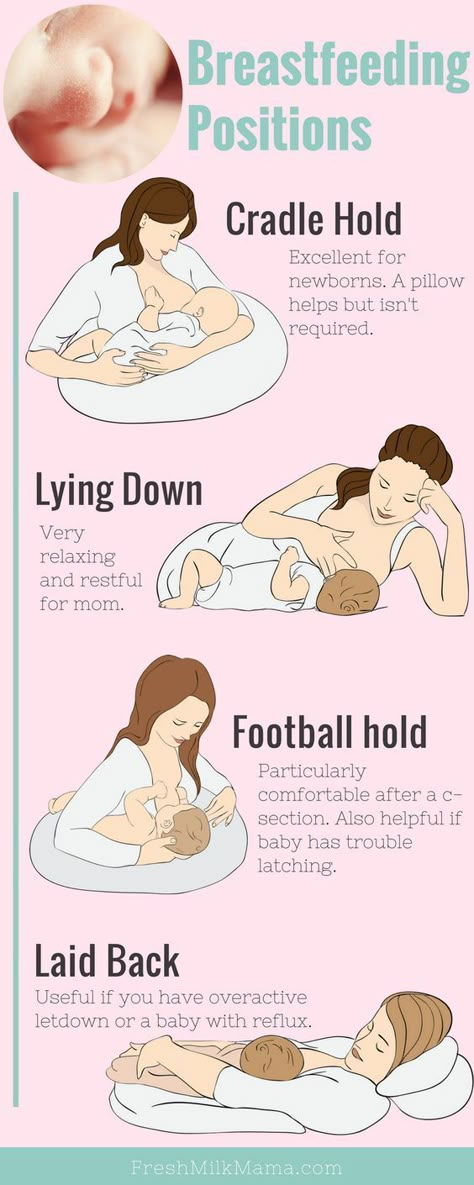 With insufficient nutrition of a newborn baby, jaundice may be more intense and prolonged due to the thickening of bile. (source - NATIONAL PROGRAM OF OPTIMIZATION OF FEEDING OF CHILDREN OF THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION, p.17).
With insufficient nutrition of a newborn baby, jaundice may be more intense and prolonged due to the thickening of bile. (source - NATIONAL PROGRAM OF OPTIMIZATION OF FEEDING OF CHILDREN OF THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION, p.17).
It is absolutely pointless to give the child water, glucose, activated charcoal, smectite, etc. in such a situation. - from this, the activity of liver enzymes, the function of which is reduced, will not increase. In some cases, it may be necessary to carry out phototherapy with special lamps, which can usually be rented from the hospital home.
- What to do if you are separated from your child?
It is recommended to express at least eight times a day. Whether you can pump something or not, breast stimulation is important to maintain and increase your milk supply.
If there is no joint stay in the maternity hospital, or if the baby was taken to the children's department for some medical reasons - do not hesitate to visit him and feed him there! If your and his condition allows, try to feed the baby only colostrum and then breast milk.
Try not to give supplements from a bottle, but from a spoon, pipette or syringe without a needle.
"Arrival" of milk.
Milk comes on 3-4 days after birth, less often - on 5-7. Your chest becomes hot, heavy, tight. If the mother rarely put the baby to the breast before, then engorgement may occur. At the same time, remember that you can do without pain and rough straining. Act according to the scheme: heat - light massage - removal of swelling from the areola - decant a little - attach the child - cold compress.
"Hard" straining, which is often used in the hospital, leads to severe swelling and worsening of the situation. Alcohol compresses, Vishnevsky ointment, etc. are not recommended.
How to remove swelling from the areola? Use the Pressure Softening technique introduced by international consultant Jean Kotterman.
It is necessary to evenly and gently press on the areola towards the chest and hold the pressure for at least a full minute (up to 2-3 minutes).
How to express properly? Fingers are placed on the border of the areola and white skin. First, the fingers are pressed in the direction of the chest: you seem to grab the milk-filled ducts that lie under the areola, and only then roll over them with your fingers. Important: the fingers do not fidget over the skin, they stand in one place on it.
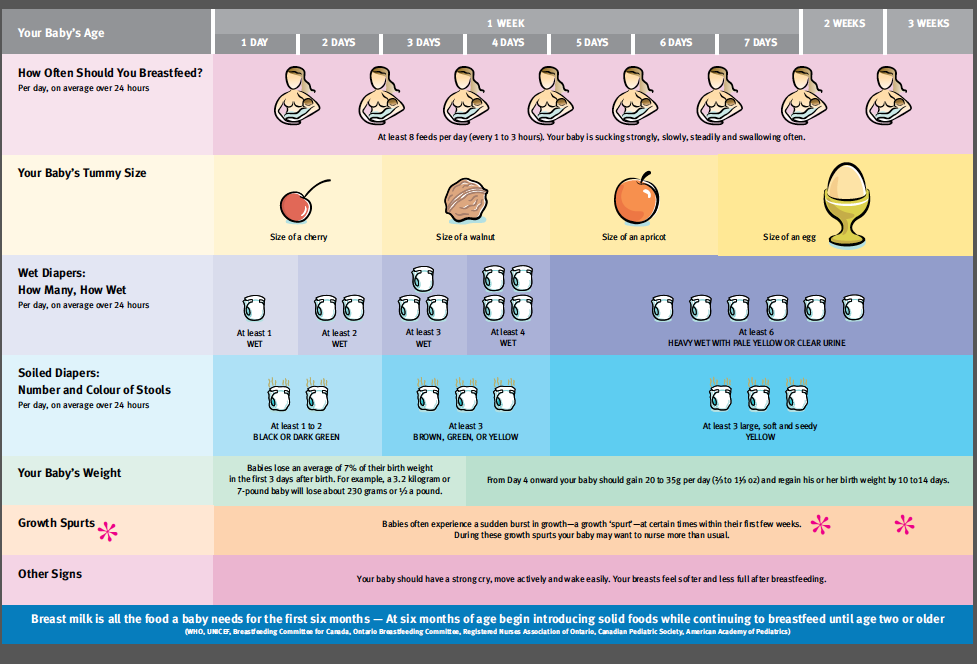
How do you know if your baby is getting enough milk?
Newborns lose up to 6-10% of their birth weight in the first two days of their lives. This is a physiological norm. Most children regain their weight or begin to put on weight by 5-7 days of life.
- "Wet diaper test" .
Urination rate (per day) for a child up to 10 days old = number of days + 1.
That is, for example, a 2-day-old baby who has enough milk pees 3 times a day.
Babies over 10 days of age should write 12 or more times a day.
These calculations are correct if there is no water addition and no drips.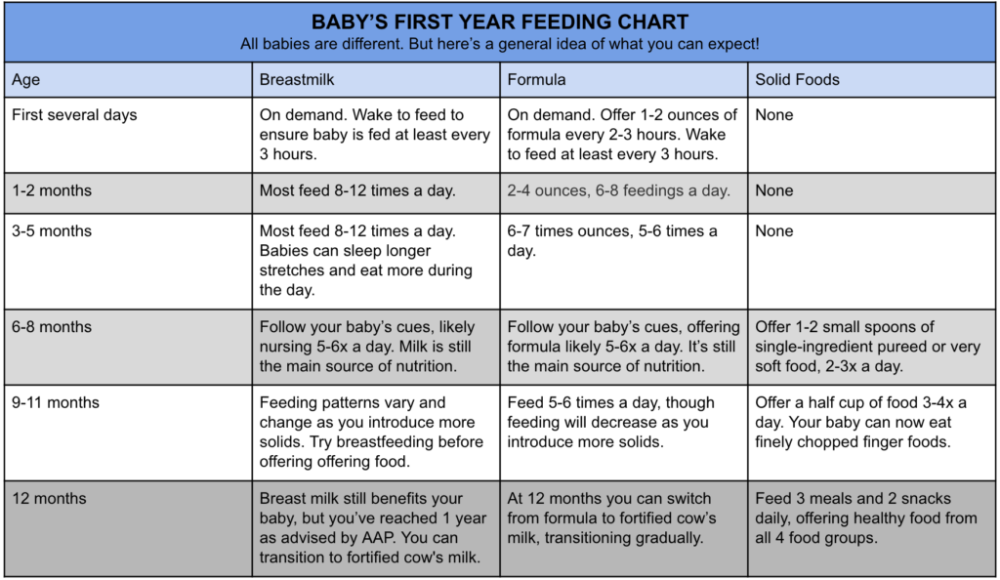
- Weight kit . The rate of weight gain for babies in the first 6 months of life is from 500 to 2000 g per month.
The set is not calculated from birth weight, but from the minimum (usually this is discharge weight). If the weight gain is less than 150g per week, we advise you to contact the AKEV specialists and the pediatrician.
- An infant should have at least 3-4 bowel movements per day (up to about 3-6 weeks). Then the chair is reduced - up to 1 time per day or less.
All other signs - crying of the baby, little pumping from the breast, no milk leakage, etc. - are not reliable signs of milk sufficiency / lack of milk .
Breastfeeding lifestyle:
- Care: it is recommended to wash the breasts 1-2 times a day while taking a shared shower (just with water, no soap).
- Diet: you should not sit on a "dry ration", the menu should be varied and healthy (without the use of chemical additives), eat according to your appetite.
 In large quantities, you should not consume whole milk, red vegetables and fruits, exotic fruits. Drink water and tea as needed.
In large quantities, you should not consume whole milk, red vegetables and fruits, exotic fruits. Drink water and tea as needed. - Sports: Moderate sports can be started as early as 6 weeks postpartum.
Don't worry if not everything was done at the maternity hospital. Feeding can still be improved. After discharge from the hospital, you can ask an experienced breastfeeding mother or breastfeeding specialists from large associations to help you.
Elvira Ibragimova, breastfeeding specialist in Naberezhnye Chelny, Association of Breastfeeding Consultants (AKEV), Republic of Tatarstan ), AKEV consultants: L. Kazakova, Y. Yakovlev, I. Ryukhova, E. Savosina, O. Gutyum, N. Zaslavskaya, M. Gudanova.
Breastfeeding rules
Breastfeeding rules and techniques.
Every woman can breastfeed her baby.
All troubles arise from ignorance of the rules and techniques of feeding.
The first rule is very important - early contact of the mother with the child in the maternity hospital, in the first minutes after birth.
Psychological benefits of breastfeeding.
Breast milk has a positive effect on the formation of the emotional and intellectual sphere, the development of creative abilities.
- emotional connection from both mother and child:
- close, loving relationship between mother and child;
- - emotional satisfaction of mother and child;
- - the child cries less, positive emotions are formed;
- - the mother becomes more affectionate, attachment to the child appears, self-confidence; : - less likely that the child will be abandoned or offended; breast milk also protects against the occurrence of neuroses.
- Development: the child shows the best results of intellectual development and creative abilities at an older age.
No less important is the correct laying of the baby to the breast, because this is a powerful stimulus to provide the right amount of milk - galactopoiesis.
- The position of the mother during feeding should be comfortable.
 It is better to feed the baby either from a lying or sitting position.
It is better to feed the baby either from a lying or sitting position. - Take the chest in the palm of your hand with 4 fingers from below and 1 from above.
- Touch the nipple to the baby's lips so that he opens his mouth.
- The baby should capture not only the nipple, but also the halo.
- If the mother felt pain in her chest while feeding the baby, this means that the baby did not take the breast correctly. In this case, it is necessary to carefully touch the child's lips with a finger so that he opens his mouth, and not pull it by force. Try to apply to the chest again.
- Feed the baby on demand. In the first days up to 10-14 times a day. After the formation of lactation (after approximately 2-3 weeks), the regimen is established independently and is 6-7 feedings per day.
7, It is not recommended to take night breaks in feeding.
- Frequent feeding, including night feeding, contributes to the development of the prolactin and oxytocin reflex.

Produced BEFORE and DURING breastfeeding causes milk to EXTRACT
Sensory suction impulses
- Promotes uterine contractions
- No additional food other than breast milk should be given to a child under 3-4 months of age.
- It must be remembered that during the day the baby sucks out different amounts of milk.
- Negative emotions block the oxytocin reflex, spasm occurs and milk is poorly excreted.
- What is important is the positive psychological attitude of the mother, the desire to breastfeed her child and the belief that breast milk is the best food for children.
- It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene (clean linen, hands, mother's chest).
- The duration of feeding is currently not limited.
Among the most important factors in the formation of full lactation in the early days are:
- Skin-to-skin contact;
- Early breastfeeding;
- Joint stay of mother and child in a maternity hospital;
- Feeding the baby "on demand";
- Application to both mammary glands;
- Exclusion of pre-lactation feeding and supplementation; • Exclusion of devices imitating mother's breasts (nipples, pacifiers).

There are certain rules to follow with an infant:
- There should not be co-sleeping with an infant!!!
- forbid yourself to take a baby to bed !!!!!!!
- the baby does not belong in a bed with other family members, also do not put him to sleep with each other, in order to avoid harm in a dream;
- do not overheat the baby, there is no need to wrap him in a large amount of clothes;
- no need to swaddle the baby tightly. He should be able to change the position of the head and body in case of lack of air;
- the surface of the bed should be pretty flat, without extra pillows, duvets, blankets. These items can accidentally cut off the oxygen supply to the baby. But even under the weight of your body, it should not fall through, otherwise there is a high probability that the child will get there on his face and strangulation may occur;
- there is no need to put the child to sleep between yourself and the back of the sofa, even if it is soft, so that he is not sandwiched between the fabric and the body of an adult;
- consider measures that will protect your baby from an unexpected fall from your bed.
Feeding technique Bottle feeding
Feeding technique Bottle feeding is not really difficult. However, there are a few feeding rules you should remember to avoid baby tears, food spills, and other problems.
The position taken by the feeder should resemble the natural position of the mother during breastfeeding:
- The child's head should rest on the left arm.
- The nipple that enters the baby's mouth must always be full of milk or formula - otherwise the baby will swallow air which can cause colic.
- The appearance of bubbles in the bottle means that the child is eating incorrectly and you need to help him, change the position, tilt the bottle in a different way.
- Do not leave a child alone with a bottle and do not let the baby sleep with a bottle in his mouth - in both cases, this can lead to choking.
- It is best to feed your baby when he is in your arms - babies feel most secure in their parents' arms.
- Remember that the baby's head should always be slightly higher than his torso.
- Make sure that the baby does not tilt the head too far back or forward - if the head is in the wrong position, it becomes more difficult for the baby to eat, the wrong position of the head can also cause food to enter the respiratory tract.
- When a baby eats from a bottle, he swallows air with nutrition, so he may feel full, despite the fact that he has eaten little.
- Take breaks every 5 minutes during feeding so that the baby has the opportunity to burp.
- After he has let out air and some food, he will feel hungry again.
- In order for the baby to burp, you need to change his position: put the baby's head on your shoulder and support his back with your hands.
- The child must be in an upright or semi-upright position. If the baby does not burp between feedings, the accumulated air will lead to the formation of painful gases.
- The sitting position is the most classic feeding position.