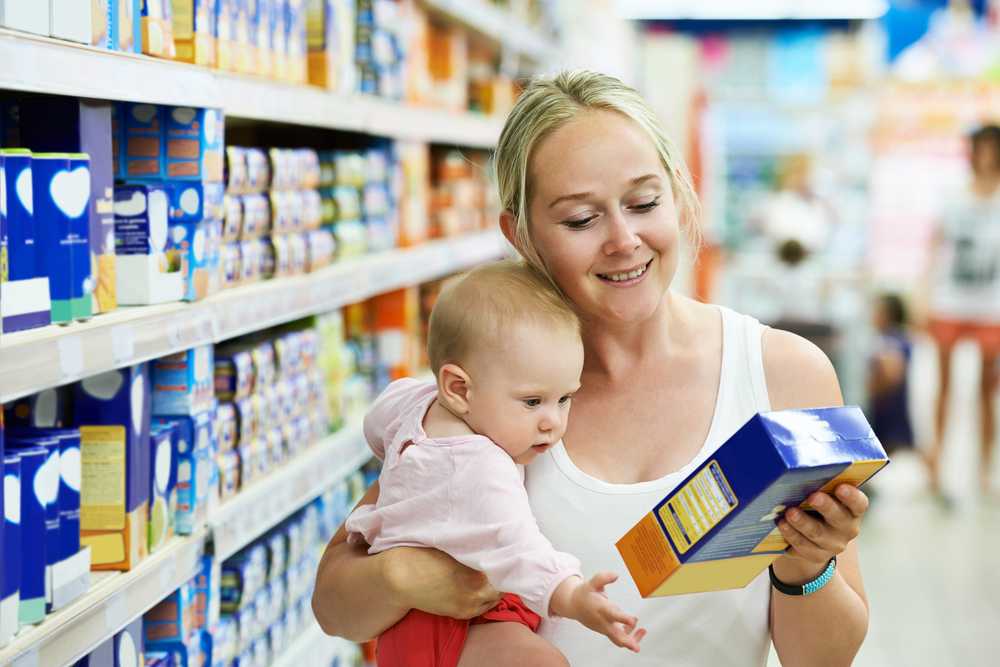
How many times a day should i feed my baby cereal
Balancing introducing solids with milk feeds
At around 6 months of age babies need to start having solid foods as well as breastmilk or formula. Find out how to get started with solid foods and what are the best foods to start with.
When to introduce solids?
At 6 months, your baby will still be getting most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula.
As you introduce solid foods, continue feeding with breastmilk or formula until at least 12 months of age.
Start to introduce solid foods at around 6 months of age when:
- your baby can sit up with support and has good head control
- your baby starts to show interest in food such as watching and reaching out when they see food
Even though some babies show these signs from an earlier age, continue to offer your baby breastmilk or formula if they appear hungry. This is usually all they need until around 6 months. It’s recommended that you don’t introduce solids before 4 months.
How to introduce solid foods into your baby’s diet
Start feeding your baby solids once a day. Your baby will take only small amounts of solid foods at first. Try one teaspoon at first of pureed vegetable, fruit, or rice cereal in between milk feeds.
From 6 to 9 months continue to give your baby breastmilk or formula first, then try solids after the milk.
From 9 months you can try to give solids first, then breastmilk or formula. This allows for your baby to naturally transition to solids by around 12 months.
At around 8 to 9 months try giving your baby solids as part of breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
Continue breastmilk or formula through the first year of life while foods are being introduced. From around 6 months you can try small amounts of cooled boiled water out of a sippy cup.
Which foods first?
From 6 months of age baby’s first foods should contain iron. Foods that have iron, include:
- iron-fortified baby cereals
- meat
- poultry
- fish
- legumes - lentils, beans, or chickpeas
Guidelines recommend that you can introduce foods in any order and at a pace that suits your baby, family, and cultural backgrounds, as long as some foods servings contain iron.
Your baby’s first foods can be smooth, mashed or have soft lumps.
Choose from the 5 food groups.
Vegetables and legumes
Give your baby cooked and pureed:
- pumpkin
- sweet potato
- carrots
- potato
- peas
- broccoli
- cauliflower
- zucchini
Over time puree them less so the texture gets lumpier.
Then introduce vegetables that are cooked but not pureed.
Fruit
Give your baby stewed and pureed:
- apples
- pears
- peaches
- apricots
- berries
Your baby might also like to try mashed ripe banana.
Gradually introduce pieces of cooked fruit, banana, peach and grated raw apple.
Avoid larger pieces of raw apple; babies can choke on them.
Grains and cereals
Give your baby fortified infant cereals (e.g. rice cereal) to start.
Move to cooked rolled oats, wholegrain breakfast biscuits (Weetbix, Vita Brits) or thick infant cereals.
Don’t add sugar or honey or offer cereals with chocolate or added sugar.
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, legumes, tofu
Meat, fish, poultry eggs, legumes, tofu should always be pureed when you start introducing solids.
When your baby accepts this, offer them bite size pieces of:
- chicken
- minced meat
- flaked fresh or canned fish (in spring water)
- mashed tofu
- mashed legumes
- scrambled or mashed boiled eggs
Don’t add salt. Also avoid processed meats as they have a lot of salt.
Milk, cheese, yoghurt
Formula should be used only until your baby is 12 months old. Then small amounts of milk can be added to foods like porridge. Breast feeding is recommended to continue until the age of 2 or longer.
Grated cheese is good in mashed vegetables.
Choose yoghurt without added sugar. Add fruit for extra flavour
What drinks should I be giving my baby?
After 12 months of age breastmilk, water (clean tap water or bottled water) and full fat cow’s milk should be the main drinks you offer your baby.
Keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
Switch from formula to full fat ordinary cow’s milk after 12 months. Your child doesn’t need toddler milk products. Offer your baby a cup to drink from rather than a bottle. Your one-year-old should be exclusively drinking from a toddler cup.
From about 12 months, you can try rice milk and oat milk (fortified with at least 100mg calcium/100mL) if you want. But these drinks don’t have enough protein and vitamin B12. Your baby will need to have plenty of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, yoghurt, or cheese to make up for what they’re not getting from cow’s milk.
How much should I feed my baby?
Your baby will grow at different rates at different times. Their appetite can vary, even from day to day.
Babies don’t know what to eat but they know how much. Provide wholesome, healthy unprocessed food choices. Take your cue from your baby. Babies tend to turn away or lose interest when they’ve had enough to eat.
Finger foods and self-feeding
By 9 to 12 months, most babies like finger foods. Finger foods are foods they can hold themselves.
Some also like to hold their own spoon at that age. It will be messy! But learning to feed themselves is important.
By 12 months, your baby can eat the same healthy food you serve your family.
Foods to limit or avoid when introducing solids
There are some foods and drinks you should limit or avoid:
- coffee and tea, herbal drinks are not recommended
- fruit juice
- honey until 12 months (to prevent botulism)
- processed foods
- raw or runny eggs (bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies)
- sugar sweetened drinks
- unpasteurised milks
Low-fat milks are not recommended in the first 2 years of life. Goat’s milk, sheep’s milk, soy milk, coconut milk and almond milk should also be avoided before the age of 2 unless your doctor recommends them.
Avoid small hard foods such as whole nuts and uncooked vegetables until 3 years. These can be choking hazards.
If your family doesn’t use animal products, your baby may need a vitamin B12 supplement. Discuss this with your doctor.
Seek help from your health care professional if you are worried about your baby’s eating or development.
Fruit — give your baby stewed and pureed apples, pears, peaches, apricots and berries, or mashed ripe banana. Gradually introduce pieces of cooked fruit, banana, peach and grated raw apple. Avoid larger pieces of raw apple; babies can choke on them.
Grains and cereals — give your baby fortified infant cereals (e.g. rice cereal) to start. Move to cooked rolled oats, wholegrain breakfast biscuits (Weetbix, Vita Brits) or thick infant cereals. Don’t add sugar or honey and don’t use cereals with chocolate or added sugar.
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, legumes, tofu — make them pureed at the start. When your baby accepts this, offer them pieces of chicken, minced meat, flaked fresh or canned fish (in spring water), mashed tofu, mashed legumes, scrambled or mashed boiled eggs. Don’t add salt and avoid processed meats as they also have a lot of salts.
When your baby accepts this, offer them pieces of chicken, minced meat, flaked fresh or canned fish (in spring water), mashed tofu, mashed legumes, scrambled or mashed boiled eggs. Don’t add salt and avoid processed meats as they also have a lot of salts.
Milk, cheese, yoghurt — breast milk or formula should be used for up to 12 months, then small amounts of milk can be added to foods like porridge. Grated cheese is good in mashed vegetables. Choose yoghurt without added sugar. Add fruit for extra flavour.
How much?
Babies grow at different rates at different times. Their appetite can vary even from day to day.
Babies don’t know what to eat but they know how much. Take your cue from your baby. Healthy babies turn away or lose interest when they’ve had enough.
Finger foods and self-feeding
By 9 to 12 months, most babies like finger foods.
Some also like their own spoon at that age. It will be messy, but learning to feed themselves is important.
By 12 months, serve the same healthy food you serve your family, but without hot spices.
Encourage infants to feed themselves.
If you have stopped breastfeeding, switch to ordinary cow’s milk after 12 months. Use a cup rather than a bottle. Limit the amount of cow’s milk to around 500ml per day. Under health professional supervision, you can use full fat rice milk or oat milk with at least 100mg calcium per 100mL if you want, as long as other sources of protein are included (meat, chicken, fish, eggs, legumes or nut butters).
Your child doesn’t need toddler milk products.
If your family doesn’t use animal products, your baby may need a vitamin B12 supplement. Discuss this with your doctor.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
When Can You Start Feeding Your Baby Rice Cereal
Adding solid foods to your baby’s diet is a big milestone, and you may be wondering when to begin the process and what foods to start with. In the past, single grain infant cereals have been the traditional first choice when transitioning to solid foods, with rice cereal being one of the more popular ones. These days, though it is still OK to start with cereal, experts say that there is no evidence that introducing foods in a certain order provides any advantage for your baby (though babies do tend to like cereal).
In the past, single grain infant cereals have been the traditional first choice when transitioning to solid foods, with rice cereal being one of the more popular ones. These days, though it is still OK to start with cereal, experts say that there is no evidence that introducing foods in a certain order provides any advantage for your baby (though babies do tend to like cereal).
Keep in mind that experts highly recommend giving rice cereal as part of a mixed diet of single ingredient choices, rather than as an exclusive food.
Find out how to safely give rice cereal to your baby, and what other infant cereals you might want to give instead.
What Is Rice Cereal?
Rice cereal for babies has been a traditional first food for infants who are being introduced to eating solids. The most common type is a dry powdered cereal, to which liquid is added to form an oatmeal-like consistency, but it can also be purchased premixed. It's one of the single grain cereals that have been recommended for infants when they start on solid foods.
It's one of the single grain cereals that have been recommended for infants when they start on solid foods.
Is Rice Cereal Safe for Your Baby to Eat?
It’s OK to include rice cereal in your baby’s diet as long as you’re not exclusively feeding your baby rice cereal.
The reason experts recommend rice cereal be limited is because of the naturally occurring levels of inorganic arsenic in rice (in this case inorganic refers to the arsenic’s specific chemical compound bound with carbon).
As rice is grown, the plant absorbs more inorganic arsenic from its environment compared to other crops. Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that can enter the food supply through water, soil, or air.
When body weight is considered, a baby’s intake of inorganic arsenic through rice cereal could be three times more than an adult’s. Eating too much rice cereal as an infant can cause long-term health problems.
What Infant Cereals Can You Give Your Baby Instead of Rice Cereal?
Instead of rice cereal, you can offer another single grain infant cereal such as oat or barley cereal. You can find many of these infant cereals in premixed or dry versions to which you would add breast milk, formula, or water to create a consistency that your baby will like.
Look for cereals that are specifically made for babies because they will be fortified with nutrients like iron and zinc that your baby needs.
Just remember that when introducing new foods — including different types of infant cereals — do so gradually, offering one new food at a time, and then waiting a couple of days before adding another food, to watch for any possible allergic reactions. Once your baby has become accustomed to eating solids, feel free to offer a variety of single ingredient, soft foods.
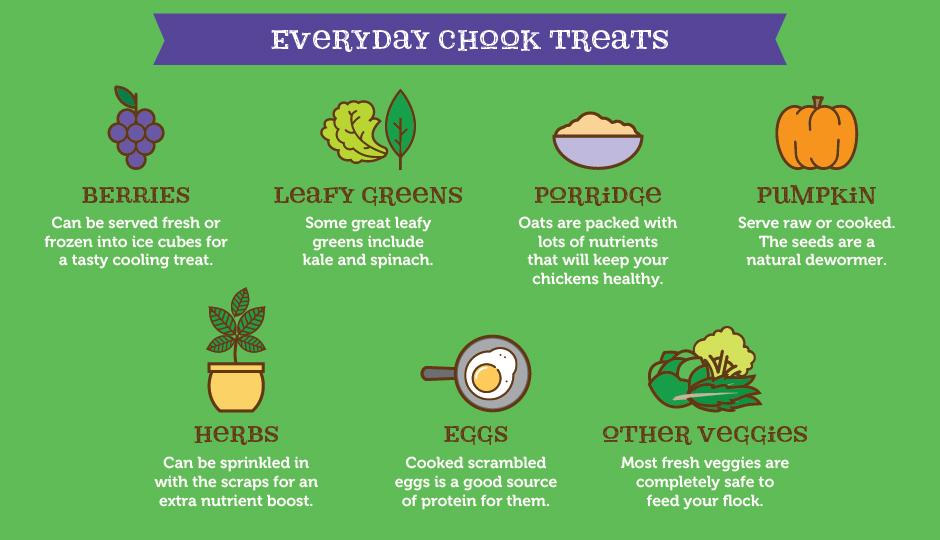
How Many Times a Day Should You Feed Your Baby Infant Cereal?
When your little one is just starting on solids, spoon-feed your baby a small amount of infant cereal once or twice a day, ideally just after he’s been bottle-fed or breastfed. Start with one or two teaspoons of cereal so that your baby can get accustomed to this new food.
Start with one or two teaspoons of cereal so that your baby can get accustomed to this new food.
Eventually you can introduce other foods one at a time—and you can even make your baby’s food at home.
Are Other Rice Products Safe to Give Your Baby?
Not necessarily. You can give rice to your older baby as part of a varied and balanced diet. However, it’s best to avoid certain rice-based products like rice syrup, often used as a sweetener in processed foods, as well as rice milk, which should not be used as a substitute for cow's milk.
If your child has turned 1 and is sensitive or allergic to cow’s milk, your healthcare provider will be able to recommend milk alternatives if needed, and can also weigh in on any rice products you’re considering giving.
At What Age Should You Start Feeding Your Baby Infant Cereals?
For most babies, 6 months is a good age to start to introduce solid foods, which can include infant cereals. Breast milk or formula will continue to provide most of your baby's nutrition for the first 12 months.
Breast milk or formula will continue to provide most of your baby's nutrition for the first 12 months.
Waiting until this age is important because by this point your baby would have outgrown a natural reflex that all babies are born with that causes them to push their tongue against anything inserted into their mouths. Most babies grow out of this tongue thrust reflex between 4 and 5 months.
Can You Give a Baby Younger Than 6 Months Infant Cereals?
Most babies are not ready for solid foods, including infant cereals, until they are about 6 months old, though some babies could be ready a month or two earlier. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed or bottle-fed (with expressed breast milk or formula until 6 months of age.
How Do You Prepare Dry Infant Cereal for Your Baby?
If you’re using dry cereal, mix one tablespoon of dry cereal with four tablespoons of breast milk, formula, or water; or follow the recommended directions on the container.
Be sure not serve the cereal from a bottle for reasons we mention in the next section. Gradually, you can add less liquid to the dry cereal to find a thickness your baby likes.
Can You Feed Your Baby Cereal in a Bottle?
Although this might be a practice you’ve heard of, don't feed your baby cereal in a bottle unless your baby’s healthcare provider says otherwise. Feeding your baby through a bottle can lead to unnecessary calories—she may consume more food than she actually needs.
Although rice cereal may have been a popular choice, experts now say there are other infant cereals and first foods that may be safer for your baby. If you’re ever unsure about which infant cereal to give, or need advice about expanding your baby's menu, reach out to your baby’s healthcare provider for advice.
As your baby transitions to solid foods, you deserve lots of rewards for all those diaper changes. Download the Pampers Club app to get rewards for all your Pampers purchases.
Download the Pampers Club app to get rewards for all your Pampers purchases.
How we wrote this article The information in this article is based on the expert advice found in trusted medical and government sources, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. You can find a full list of sources used for this article below. The content on this page should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult medical professionals for full diagnosis and treatment.
How Much Should a Newborn Baby Eat
Search Support IconSearch Keywords
Home ›› How Much Milk Should a Newborn Baby Drink?
Home ›› How much milk should a newborn baby drink?
↑ Top
Like every new mom, you're probably wondering, "How often should a newborn eat?" and “How many milliliters does a newborn baby drink at a time?”. A mother's body is designed to provide her baby with all the nutrients she needs, but every mom needs practical advice and confidence when it comes to how much milk a newborn should drink.
Whether you are breastfeeding, bottle feeding or a combination, here you will find all the information you need to know about how much food your baby needs to grow and develop properly.
Signs indicating that the child is hungry
Every mother has a wonderful maternal instinct, but we cannot guess the child's desires from the first time. Over time, you will learn your child's unique gestures and body movements, as well as signs that he is hungry. In the meantime, here are some of the most common signs that a child is hungry:
- turns head towards your breast or bottle;
- clenches;
- puts pens in mouth;
- pouts, smacks or licks lips.
If your child is showing any of these signs, they are probably trying to tell you it's time to eat. Ideally, your baby should be fed on demand when he is hungry. If you're breastfeeding, on-demand feeding is a good way to keep your milk supply going as your body will naturally respond to your baby's needs and continue to produce the required amount of milk. Bottle-feeding on demand can also be beneficial for your baby, as it allows him to self-regulate his feeding needs.
Bottle-feeding on demand can also be beneficial for your baby, as it allows him to self-regulate his feeding needs.
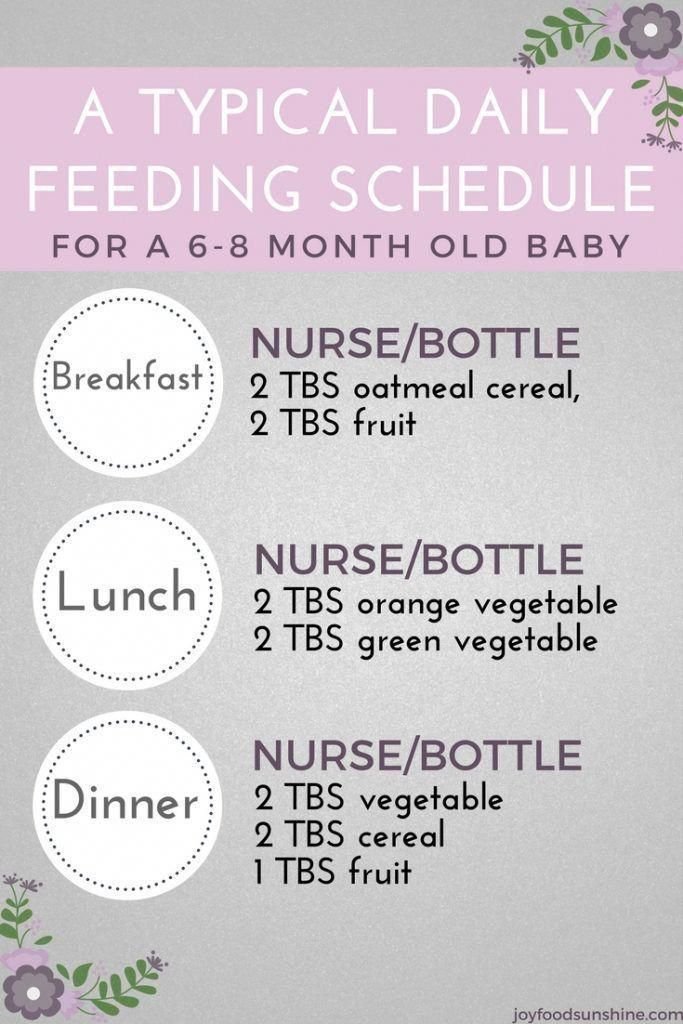
How much breast milk should a newborn drink?
So, how much should a newborn baby eat? A remarkable feature of each child is its uniqueness, so it would be wrong to feed the baby strictly according to the instructions. Don't panic if the recommendations below don't fit your own feeding schedule, but please contact your healthcare provider or pediatrician if you have any questions.
Although every baby is different, newborns typically eat every two to three hours, for a total of 8 to 12 meals a day.
How many milliliters does a newborn baby drink? At the very beginning, your body will only produce a small amount of yellowish and thick breast milk called colostrum. This milk is an ideal source of nutrients that your newborn needs, in addition, it has many immunological components. 1
How much milk does a newborn baby drink? Infants drink 30-60 ml per feeding, while this volume increases to 60-90 ml by two weeks of age.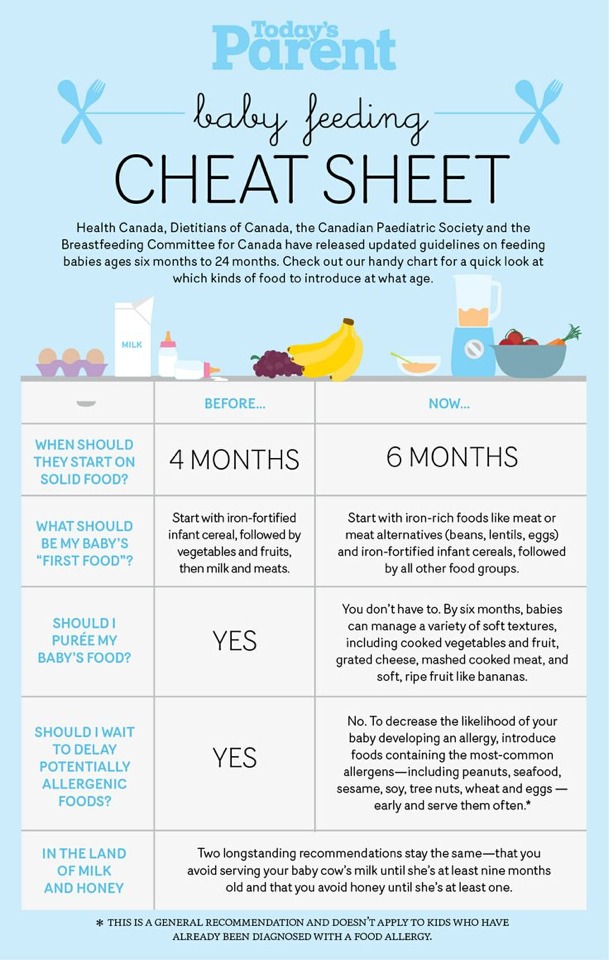 So don't worry if you don't feel like your body is producing much milk in those first few days after your baby is born! Feeding times will also vary, ranging from 10 to 30 minutes at the very beginning and then gradually increasing as your baby grows.
So don't worry if you don't feel like your body is producing much milk in those first few days after your baby is born! Feeding times will also vary, ranging from 10 to 30 minutes at the very beginning and then gradually increasing as your baby grows.
How much breastmilk the baby takes if bottle feeding
If you choose to bottle feed your baby from time to time, do so at the same intervals and for the same period of time as if you were breastfeeding. Pumping is a great option for breastfeeding your baby. It will allow you to separate from the baby if necessary and at the same time retain all the benefits of breastfeeding.
It's also important to get a bottle that helps make bottle feeding more natural for both you and your baby. For example, take a look at this Philips Natural bottle. Its wide, physiologically shaped nipple promotes a natural latch that is identical to that of a mother's breast, making it easier to alternate between bottle and breastfeeding.
Philips Avent
Natural Baby Bottle
SCF033/27General assessment /5
- Reviews reviews reviews
-{Discount -Value}
the child is full
How to understand that the child is already full? When breastfeeding or bottle feeding, look out for the following signs that may indicate that your newborn baby is full:
- baby closes his mouth;
- turns head away from bottle or breast;
- handles are not clenched and relaxed;
- falls asleep quickly.
If the baby shows signs of fullness, stop breastfeeding or bottle feeding, even if the bottle is not yet empty. 2
2
The right choice for you and your baby
Remember that every child is different and no one is as close to you as you are. Choose the feeding option that works best for you and your newborn, whether breastfeeding, bottle feeding, or a combination.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
I understand
Child nutrition in the 2nd year of life: routine, diet, menu, necessary products | Mamovediya
The child in this period of life grows intensively and therefore must receive nutrition that quantitatively and qualitatively satisfies the needs of his body.
Nutrition should be rational: balanced and consistent with the daily routine. Balance - the inclusion of all the necessary nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, trace elements) in the appropriate proportions that the child's body can absorb.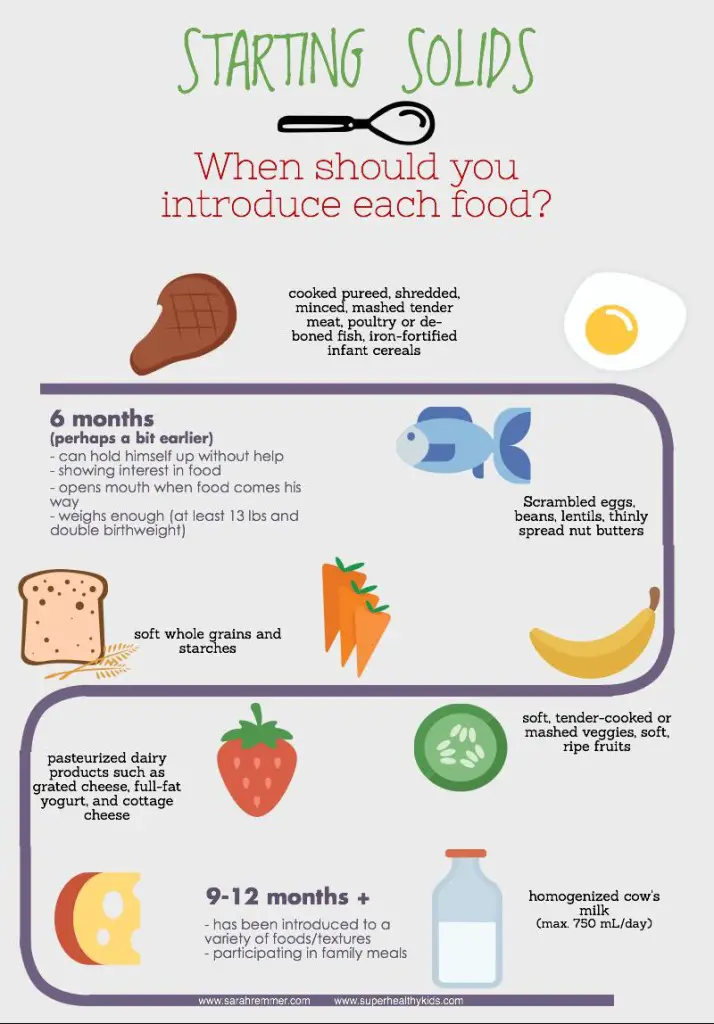
Nutrition is considered rational if it meets the age needs of the child and is carried out according to the daily routine.
In addition, the so-called rational nutrition includes the culinary processing of food used for a given age, and the correct methodological methods of parents in the process of feeding a child.
The environment surrounding the baby during meals, the appearance of the dishes served should excite the child's appetite.
Child's appetite is a state of organic need for food, expressed in the child's desire to eat. At the same time, an adequate positive attitude of the child to food is noted.
A good appetite, as a rule, depends not only on how well the menu is compiled, but also on the correct organization of the feeding process. To form and maintain a good appetite, parents must clearly know: what, when and how to feed the child.
How nice it is to feed a child who has a good appetite.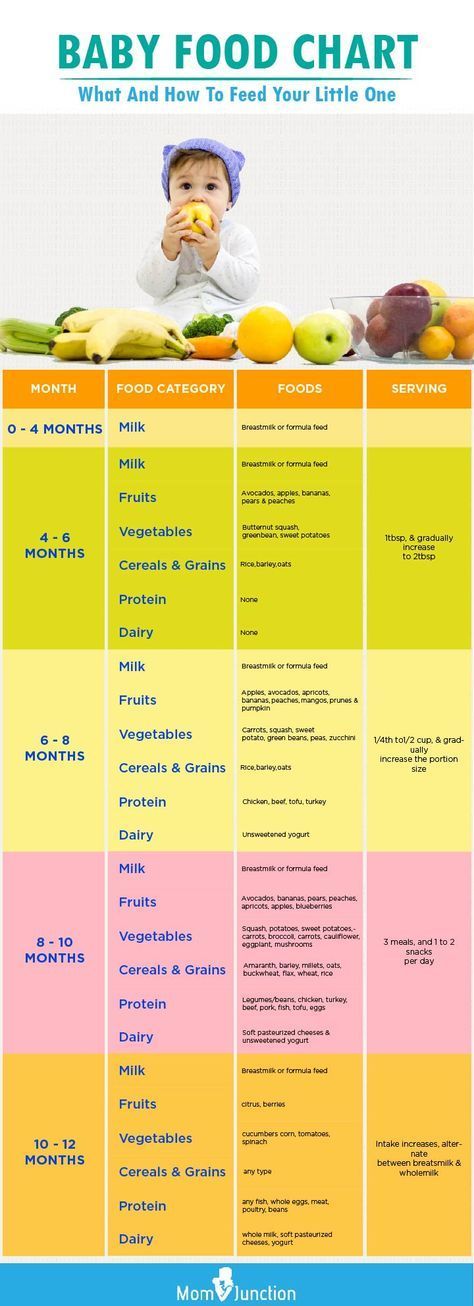 It brings pleasure to adults and great benefits for the baby. However, very often it is necessary to observe cases of violation of normal appetite from small deviations (decrease in appetite, refusal of certain dishes) up to its complete absence (anorexia - as it is called in medical practice).
It brings pleasure to adults and great benefits for the baby. However, very often it is necessary to observe cases of violation of normal appetite from small deviations (decrease in appetite, refusal of certain dishes) up to its complete absence (anorexia - as it is called in medical practice).
A child with a decrease or lack of appetite at the mere sight of writing or a reminder of food expresses protest, turns away, defends himself, tightly closes his lips and teeth. It looks like an unnatural negative reaction of the baby to food. Why does a child lose his appetite? Who is to blame for this? The reasons often lie in the wrong method of feeding (strong pressure on the child's tongue with a spoon, the child's lack of interest in food), in the negative sensations associated with eating (too hot food, poor taste), improper organization of the situation during feeding (distraction with a book, toy, punishment), etc.
Many parents, seeing a decrease in appetite, try to force-feed their child, but this further reinforces the child's negative attitude towards food and everything connected with it. This is strictly prohibited.
This is strictly prohibited.
If a child suddenly lost his appetite, first of all think about whether you could have made mistakes in the process of upbringing and feeding, in especially persistent cases, you should consult a pediatrician.
During feeding, do not forget to introduce the child to the names of dishes (soup, cutlet, compote, etc.) and the properties of objects (food is tasty, sweet, sour, salty, hot, cold, a large spoon, a small one, etc.) .). In this way, the child will form the first ideas, concepts.
Eating processes should be organized in such a way that the child has a desire to eat. Before eating, you should arrange a calm pause after a long walk or noisy and active games.
You should not give your child new interesting toys shortly before feeding, and quickly take them away before eating. By doing this, you will cause a strong emotional reaction that will slow down food arousal and reduce appetite.
While eating with a child, one should only talk about what is connected with this process, concentrating his attention on food, developing the child's active participation in eating.
A child's appetite is increased not only by deliciously cooked food, but also by its beautiful design, attractive dishes specially painted for children. Children should only be seated at the table when food has already been served. You should not put all the dishes on the table at once, the child is distracted from the first dish, reaches for the third or second, as a result, the sequence of eating is disturbed. Remember that many violations in the health of the baby are associated with errors in his diet.
By the age of 1 year 3 months, the baby can already eat solid food with a spoon, and at 1 year 6 months he can eat any food - thick and liquid. Try to develop these independent skills and abilities, which are very important for later life, in your son or daughter. How joyful it is to look at a baby who skillfully takes food from a plate with a spoon, without mistake brings it to his mouth and actively removes it with his lips. Something, of course, still pours from the spoon past and remains on the lips or chin of the child, but these errors in eating will soon pass, and the baby will learn to carefully eat the entire portion. Remember that a large amount of food contributes to a decrease in appetite, and an insufficient one does not cause a feeling of satiety.
How joyful it is to look at a baby who skillfully takes food from a plate with a spoon, without mistake brings it to his mouth and actively removes it with his lips. Something, of course, still pours from the spoon past and remains on the lips or chin of the child, but these errors in eating will soon pass, and the baby will learn to carefully eat the entire portion. Remember that a large amount of food contributes to a decrease in appetite, and an insufficient one does not cause a feeling of satiety.
A child of this age should be able to chew food. Make sure that he does not keep the pieces in his mouth for a long time, but swallows them in time.
A child of the 2nd year of life is fed 4 times a day with an interval of 3.5-4.5 hours. However, in the first half of the year, the baby can receive another fifth feeding - kefir or milk at 23-24 hours if he wakes up at night or at 6 o'clock in the morning.
Establishing rational nutrition is painstaking and very responsible work, but if you do it systematically, without giving "indulgence" to yourself and your child, then your reward will be good health and good physical development of the baby.
When compiling the menu, it is necessary to correctly distribute how much and what kind of food the child will receive during the day. Feed your baby 4-5 times a day. In the morning it is better to cook dairy dishes, lunch should always consist of soup, meat in the form of mashed potatoes or meatballs with a vegetable side dish, compote or jelly, fruits, kefir are given in the afternoon, a vegetable dish is prepared for dinner.
The one-time amount of food consumed in children of the 2nd year of life is different - up to 1.5 years, somewhat less than in the second half of the year.
Under no circumstances should children of this age be given food from the common table. This is very harmful. Malnutrition of a child older than a year will undoubtedly affect his health in the future. Injury by coarse food to the still unprotected mucous membrane of the child's stomach, the stressed state of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the formation of early gastritis, enteritis, cholecystitis and other diseases.
The menu can be diversified by replacing meat with cottage cheese, fish, eggs, introducing a variety of vegetable or cereal dishes, changing the culinary processing of food (mashed potatoes, cutlets, jelly, compote, etc.), improving its taste, adding greens (dill, parsley, celery, etc.).
If a dairy dish is served for breakfast, then in the afternoon you should feed the baby with vegetables and vice versa; if vegetable soup is prepared for lunch, then the second dish should be cereal, etc. To maintain appetite, make sure that meals are not repeated during the day.
This set of products does not have to be used every day, and it is practically difficult, for example, to measure 3 g of cheese for a child. It is important that during the week the proposed list of products be used in baby food. Therefore, cheese can be used once a week and immediately in the amount of 20 g (3 x 7, say, give the baby vermicelli with grated cheese for breakfast.
A few words about food products intended for baby food, or rather, their brief description.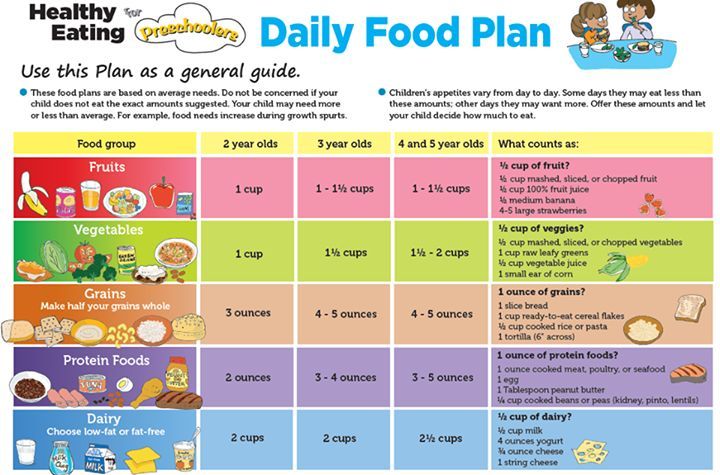
Milk and dairy products. Natural milk can be given to a child only after boiling. One-day kefir and cottage cheese are very useful. Milk should be boiled in a heavy-bottomed saucepan with the lid closed. When preparing dishes from milk (porridge, mashed potatoes), raw milk is added and allowed to boil once with ready-made cereals or vegetables. Milk must not be boiled twice. It should be remembered that excessive milk reduces the child's appetite, so milk should not be given to quench thirst instead of water.
Oils. In the diet of children of the 2nd year of life, both butter and vegetable oil can be used, and the amount of vegetable oil should not exceed 10-15% of the total amount of oil consumed per day (i.e., not more than 2 g per day) . Vegetable oil should be stored in a sealed container, protected from light and air. It cannot be boiled, so it is better to lay it in the finished dish. In the diet of children, it is not recommended to use refractory fats - beef, pork, cooking oil, and margarine.
Meat and meat products. Lean beef, rabbit meat, chickens are useful for children You can use offal - liver, tongue, heart, brains, chicken giblets. Meat should not be soaked in water, as this transfers some of the nutrients into the water. The liver should be fried under the lid and given to the child in a puréed semi-liquid form. For children under 1.5 years old, meat, like other food, should be cooked pureed. This is due to the absence of chewing teeth in a child at this age, the underdevelopment of chewing muscles and the insufficient activity of digestive juices.
Fish and fish products. Children can only be given low-fat varieties of fish - hake, cod, sea bass, pike perch. Fish is equivalent to meat in its nutritional properties, but, in addition, it contains trace elements important for the growth and development of the child (iodine, phosphorus, copper, etc.). Keto or sturgeon caviar should be treated with caution, as it can cause unwanted allergic reactions in children.
Eggs. It is recommended to give children only chicken eggs and be sure to boil them. Raw eggs should not be served, as they can be contaminated with pathogens due to the porosity of the shell, and raw protein is poorly digested in the stomach, and raw yolk can cause allergies. Duck, goose, and eggs of other birds are prohibited from being included in the children's menu.
Bread and bakery products. It is useful for children to give both rye and wheat bread. You can give bagels, bagels, crackers, by the way, children love them very much.
Cereals and pasta. The most valuable in terms of mineral composition are bean, buckwheat, oat and millet groats. But you can use their other types - semolina, peas, as well as pasta. The groats are boiled in water (oatmeal and buckwheat - for l '/g h, millet - 1 hour, semolina - 20 minutes), then unboiled milk is added, and after removing the porridge from the heat - butter and sugar to taste.
Sugar and confectionery . In children's food - in tea, milk, cereals, compotes, kissels - you can add sugar, but in moderation. Remember that excess sugar is harmful to a child, as it can contribute to obesity or diabetes. Other sweets are recommended marmalade, jams, marshmallows, marshmallows, cookies, especially oatmeal, waffles. Do not give children cakes with rich creams, chocolates and chocolates, as well as lozenges, especially rounded ones.
Vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs. All these products are very useful for young children, because, in addition to vitamins, they contain fiber, organic acids, pectin, tannins and volatile substances, as well as minerals and trace elements. Raw vegetables can also be used in children's nutrition. At the same time, they must be thoroughly washed, poured over with boiling water, and then grated on a fine grater. Fruits and berries are best given fresh to a child, and raw juice should be added to a boiled fruit and berry dish. In the nutrition of children, you can use canned vegetables and fruits specially prepared for baby food, as well as compotes, juices, freshly frozen and dried vegetables and fruits. Boil vegetables and fruits in a saucepan with a lid to preserve as many vitamins as possible.
In the nutrition of children, you can use canned vegetables and fruits specially prepared for baby food, as well as compotes, juices, freshly frozen and dried vegetables and fruits. Boil vegetables and fruits in a saucepan with a lid to preserve as many vitamins as possible.
From 1 year to 1 year 3 months
You can be told about the methods of preparing various children's meals by a district nurse or a nurse in a healthy child's office in a children's polyclinic.
The menu for a baby at this age can be compiled as follows:
Breakfast
- Porridge (vegetable puree) -150.0
- Tea with milk (milk) -100.0
- Bread with butter 9003 9003 9003 2 Lunch
- Soup (vegetable, meat) -100.0
- Puree meat (cutlet) - 40.0
- Garnish (vegetable puree, vermichel) - 50.0
- compote (fruit juice) —100.0
POLY 9000 9000
- - 30.0
- kefir (milk) with a bun of –150.
 0
0 - Fruits - 50.0
Dinner
- Vegetable puree (porridge) –150.0
- tea with milk -150.0
- Kefir (milk) -150.0
Recall that the second dinner is provided for those children who wake up at 23-24 hours.
From 1 year 3 months to 1 year 6 months vegetable oil. This is a very healthy dish, because, in addition to the vitamins it contains, it makes the baby chew food thoroughly, which means it stimulates the development of the child's chewing apparatus.
The following foods can be included in a sample menu:
breakfast
Porridge (vegetable puree) –150.0
Tea with milk (milk) –150.0
Bread with oil
- vegetable salad - 10.0
- Soup —150.0
- Cutlet (meat, fish, liver) — 50.0
- Garnish (cereal, vegetable) — 80.
 0
0 - Compote —100.0
- Snack
- Cottage cheese — 50032
- Fruit -100.0
- Tea with biscuits -150.0
Dinner
- Vegetable puree (porridge) -150.0
- Kefir (milk) -150.0
From 1 year 6 months to 1 year 9 months
Are children considered to taste? Children very early begin to distinguish tasty food from tasteless, they have favorite and unloved dishes. Try not to include foods that are vital for the development of the child's body.
Sample menu for a child at this age.
breakfast
- Ground carrots - 30.0
- Dairy porridge --150.0
- tea with milk –150.0
- Bread with oil
9000
- Kefir with a bun -200.0
- Fruit -100.
 0
0
Dinner
- vegetable- (porridge) –200.0
- milk (kefir) –150.0
from 1 year 9 months to two years
Children's food in this age period in this age period it can be liquid, semi-liquid, steamed, and also in the form of pieces (for the development of the child's chewing apparatus). The kid should equally willingly eat any food, no matter in which of the listed types it is served. We recommend the following menu:
Breakfast
- Milk porridge (noodles, vermichel)
- coffee with milk (tea)
- roll with butter (jam, cheese)
- vegetable salad (fresh)
- soup
- cutlets (meat, fish)
- Garnish
- compote
SUPPORT
- Kefir with fruits
9000 9000 9000
032