How often babies feed by age
Tips for the First Year
Eat, sleep, pee, poop, repeat. Those are the highlights in a day of the life of a brand new baby.
And if you’re a new parent, it’s the eating part that may be the source of many of your questions and worries. How many ounces should your baby take? Do you wake a sleeping baby to eat? Why do they seem hungry all the time? When can your child start solids?
Questions abound — and, despite Grandma’s insistence, the answers have changed since you were a tot. It’s now recommended that newborns, even formula-fed ones, eat on demand (consider it good preparation for the teenage years) and that babies wait to start solid foods until they’re 4 to 6 months old.
On day one of life, your baby’s stomach is the size of a marble and can only hold 1 to 1.4 teaspoons of liquid at a time. As your baby gets older, their stomach stretches and grows.
It’s hard (or impossible, really) to know how much milk your baby is taking in while breastfeeding. But if you’re bottle feeding due to any number of valid reasons, it’s a bit easier to measure.
Here, from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), a typical feeding schedule for bottle-fed babies.
| Age | Ounces per feeding | Solid foods |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 2 weeks of life | .5 oz. in the first days, then 1–3 oz. | No |
| 2 weeks to 2 months | 2–4 oz. | No |
| 2–4 months | 4-6 oz. | No |
| 4–6 months | 4–8 oz. | Possibly, if your baby can hold their head up and is at least 13 pounds. But you don’t need to introduce solid foods yet. |
| 6–12 months | 8 oz. | Yes. Start with soft foods, like one-grain cereals and pureed vegetables, meats, and fruits, progressing to mashed and well-chopped finger foods. Give your baby one new food at a time. Continue supplementing with breast or formula feedings.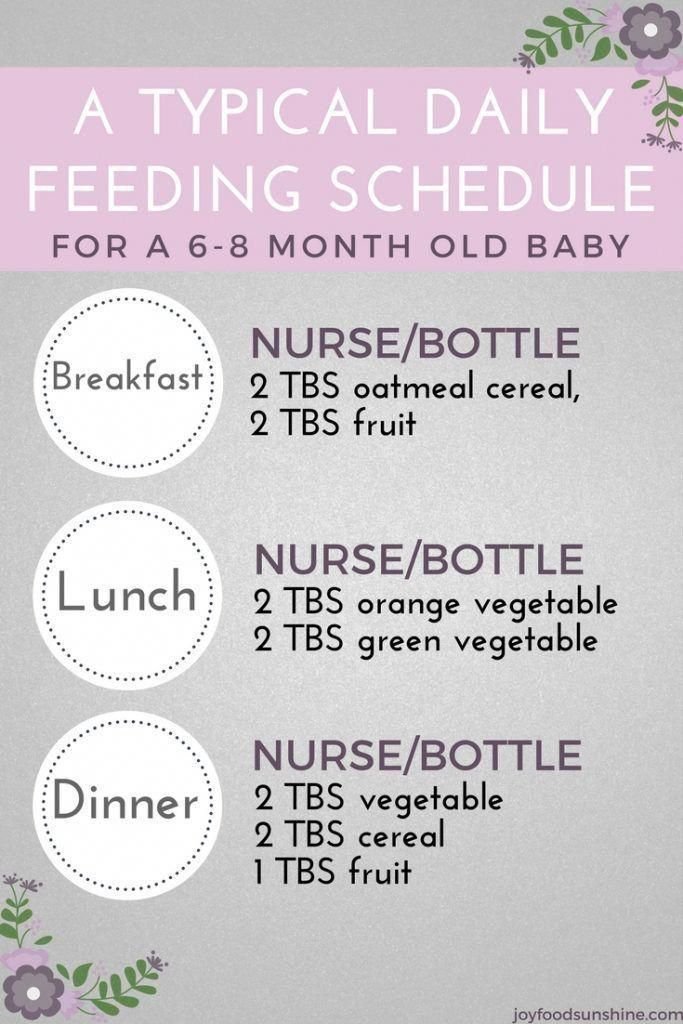 |
Every baby is unique — but one thing that’s pretty consistent is that breastfed babies eat more frequently than bottle-fed ones. That’s because breast milk is easily digested and empties from the stomach a lot quicker than formula.
Breastfed babies
There’s no rest for the weary. According to La Leche League International, you should begin nursing your baby within 1 hour of birth and provide about 8 to 12 feedings daily in the first few weeks of life (yeah, we’re exhausted for you).
At first, it’s important not to let your baby go more than 4 hours without feeding. You’ll likely need to wake them up if necessary, at least until breastfeeding is well established and they’re gaining weight appropriately.
As your baby grows and your milk supply amps up, your baby will be able to take in more milk in less time at one feeding. That’s when you might start to notice a more predictable pattern.
- 1 to 3 months: Your baby will feed 7 to 9 times per 24 hours.

- 3 months: Feedings take place 6 to 8 times in 24 hours.
- 6 months: Your baby will feed around 6 times a day.
- 12 months: Nursing may drop to about 4 times a day. The introduction of solids at about 6 months helps to fuel your baby’s additional nutritional needs.
Keep in mind that this pattern is just one example. Different babies have different paces and preferences, along with other factors that influence the frequency of feedings.
Bottle-fed babies
Like breastfed babies, bottle-fed newborns should eat on demand. On average, that’s about every 2 to 3 hours. A typical feeding schedule may look like this:
- Newborn: every 2 to 3 hours
- At 2 months: every 3 to 4 hours
- At 4 to 6 months: every 4 to 5 hours
- At 6+ months: every 4 to 5 hours
For both breastfed and bottle-fed babies
- Don’t give liquids other than formula or breast milk to babies under a year old. That includes juices and cow’s milk.
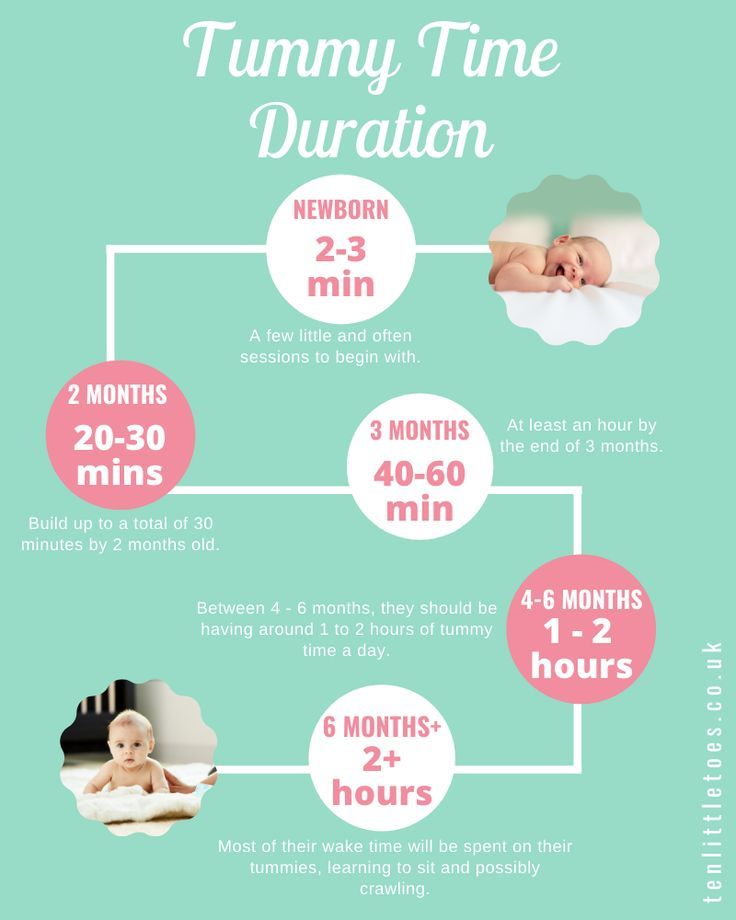 They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup.
They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup. - Don’t add baby cereal to a bottle.
- It can create a choking hazard.
- A baby’s digestive system isn’t mature enough to handle cereal until about 4 to 6 months of age.
- You could overfeed your baby.
- Don’t give your baby any form of honey until after their first birthday. Honey can be dangerous for a baby, occasionally causing what’s called infant botulism.
- Do adjust your expectations based on your baby and their unique needs. Premature babies are likely to follow feeding patterns according to their adjusted age. If your baby has challenges like reflux or failure to thrive, you may need to work with your doctor on the appropriate feeding schedule and amount they should be eating.
Schedules are the holy grail of every parent. Your child will naturally start to fall into a feeding pattern as their tummy grows and they can take in more breast milk or formula at one sitting. This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
For now, though, focus on learning your baby’s hunger cues, such as:
- rooting around your chest, looking for a nipple.
- putting their fist in their mouth
- smacking or licking their lips
- fussing that can escalate quickly (don’t wait until your baby’s hangry to feed them)
Once your baby is a few months old, you may be able to introduce a sleep/feed schedule that works for you.
Let’s say, for example, your 4-month-old wakes every 5 hours for a feeding. That means if you feed at 9 p.m., your baby wakes around 2 a.m. But if you wake and feed the baby at 11 p.m., just before you go to bed, they may not rouse until 4 a.m., giving you a decent chunk of nighttime winks.
In general, if your baby seems hungry, feed them. Your baby will naturally eat more frequently during growth spurts, which typically occur around 3 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Some babies will also “cluster feed,” meaning they’ll feed more frequently during certain periods and less at others. For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
Worried about overfeeding? While this isn’t really possible to do with an exclusively breastfed baby, you can overfeed a baby who’s taking a bottle — especially if they’re sucking on the bottle for comfort. Follow their hunger cues, but talk to your pediatrician if you’re worried your little one may be overeating.
Your baby is probably ready for solids if they’re 4 to 6 months old and:
- have good head control
- seem interested in what you’re eating
- reach for food
- weigh 13 or more pounds
Which food to start with? The AAP now says it doesn’t really matter much in what order you introduce foods. The only real rule: Stick with one food for 3 to 5 days before offering another. If there’s an allergic reaction (rash, diarrhea, vomiting are common first signs), you’ll know which food is causing it.
As your baby grows, move from pureed baby food to ones that have more texture (for example, mashed banana, scrambled egg, or well-cooked, chopped pasta). This generally happens around 8 to 10 months of age.
Your supermarket offers a variety of baby food products, but if you want to make your own, keep it sugar and salt free. Additionally, at this stage, don’t feed your baby anything that could be a choking hazard, including:
- hard foods, such as popcorn or nuts
- hard, fresh fruits, like apples; cook to soften or chop into very small pieces
- any meat that isn’t well cooked and very well chopped (this includes hot dogs)
- cheese cubes
- peanut butter (though talk to your pediatrician about this one — and the benefits of introducing diluted peanut butter before the age of 1)
As your baby nears their first birthday, they should be eating a variety of foods and taking in about 4 ounces of solids at each meal. Continue to offer breast milk or formula.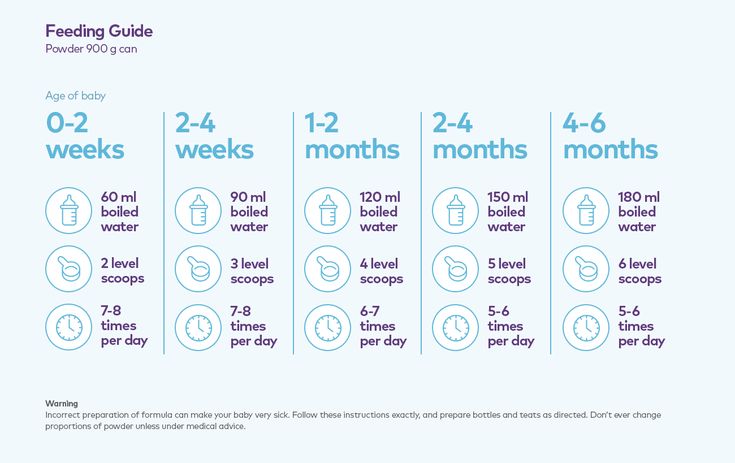 By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
Oh yeah, and buy some stock in a company that makes stain-fighting laundry detergent. It’ll pay for college.
Babies aren’t cookie cutter. Some will gain weight easily, while others will have problems. Things that can affect a baby’s weight gain include:
- having a birth defect like a cleft lip or palate, which creates problems feeding
- having a milk protein intolerance
- being premature
- being fed with a bottle versus the breast
A 2012 study of more than 1,800 babies found that the infants who were fed with a bottle — regardless of whether the bottle contained breast milk or formula — gained more weight in the first year than babies who nursed exclusively.
Your baby’s doctor is the best one to advise you on a healthy weight range for your baby.
How, when, and what to feed a baby are top worries of every parent — but there’s good news: Most babies are pretty good judges of when they’re hungry and when they’re full — and they’ll let you know it.
You just need to present them with the right choices at the right time and pay attention to their cues. If you have any questions or concerns, your pediatrician is there to help you along the way.
How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
By: Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP
One of the most common questions new parents have is how often their baby should eat. The best answer is surprisingly simple: in general, babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry.
How do I know when my baby is hungry?
For babies born
prematurely or with certain medical conditions, scheduled feedings advised by your pediatrician are best. But for most healthy, full-term infants, parents can look to their baby rather than the clock for hunger cues. This is called feeding on demand, or
responsive feeding.
Hunger cues
A hungry baby often will cry. But it's best to watch for hunger cues before the baby starts
crying, which is a late sign of hunger and can make it hard for them to settle down and eat.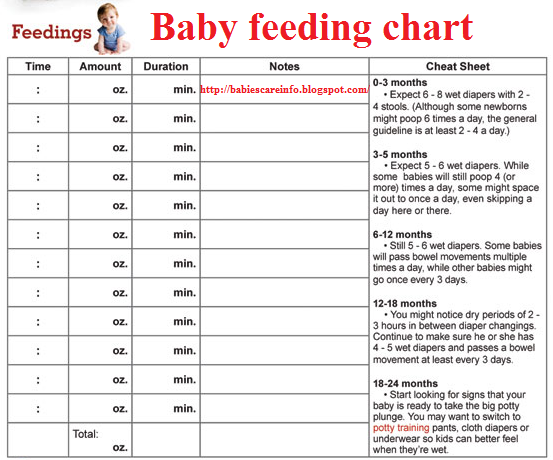
Some other typical hunger cues in babies:
Licking lips
Sticking tongue out
Rooting (moving jaw and mouth or head in search of breast)
Putting his/her hand to mouth repeatedly
Opening her mouth
Fussiness
Sucking on everything around
It is important to realize, however, that every time your baby cries or sucks it is not necessarily because he or she is hungry. Babies suck not only for hunger, but also for comfort; it can be hard at first for parents to tell the difference. Sometimes, your baby just needs to be cuddled or changed.
General guidelines for baby feeding
It is important to remember all babies are different―some like to snack more often, and others drink more at one time and go longer between feedings. However, most babies will drink more and go longer between feedings as they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk:
Most newborns eat every 2 to 3 hours, or 8 to 12 times every 24 hours.
 Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.
Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.At about 2 months of age, babies usually take 4 to 5 ounces per feeding every 3 to 4 hours.
At 4 months, babies usually take 4 to 6 ounces per feeding.
At 6 months, babies may be taking up to 8 ounces every 4 to 5 hours.
Most babies will increase the amount of formula they drink by an average of 1 ounce each month before leveling off at about 7 to 8 ounces per feeding. Solid foods should be started at about 6 months old.
Concerns about overfeeding or underfeeding your baby
Too full?
Babies are usually pretty good at eating the right amount, but they can sometimes take in more than they need. Infants who are
bottle feeding may be more likely to overfeed, because drinking from a bottle may take less effort than
breastfeeding.
Overfed babies can have stomach pains, gas, spit up or vomit and be at higher risk for obesity later in life. It's better to offer less, since you can always give more if your baby wants it. This also gives babies time to realize when they're full.
If you are concerned your baby wants to eat all the time―even when he or she is full―talk with your pediatrician. Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Trouble gaining weight?
Most babies will double their birth weight by 5 months of age and triple their birth weight by their first birthday. If your baby is having trouble gaining weight, don't wait too long between feeding―even if it means waking your baby. Be sure to talk with your pediatrician about how often and how much to feed your baby.
How do I know if my baby is getting enough to eat?
Daily diapers
A newborn's diaper is a good indicator of whether he or she is getting enough to eat. In the first few days after birth, a baby should have 2 to 3 wet diapers each day. After the first 4 to 5 days, a baby should have at least 5 to 6 wet diapers a day. Stool frequency is more variable and depends whether your baby is breastfed or formula fed.
Growth charts
During regular health check-ups, your pediatrician will check your baby's weight and plot it on a growth chart. Your baby's progress on the growth chart is one way to tell whether or not they are getting enough food. Babies who stay in healthy growth percentile ranges are probably getting a healthy amount of food during feedings.
Remember
Talk with your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby getting the right amount to eat.
More information:
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Amount and Schedule of Formula Feedings
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Ask the Pediatrician: With the baby formula shortage, what should I do if I can't find any?
- Ask the Pediatrician: How should we feed our baby if we're running low on money?
-
Airplane Choo Choo: A Feeding Guide for Children (National Dairy Council)
About Dr.
 Jain:
Jain:
Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP, is a Clinical Associate Professor of General Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. Within the American Academy of Pediatrics, he is a member of the Section on International Child Health and the Wisconsin State Chapter.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Union of Pediatricians of Russia
Nutrition for children from 1 to 3 years of age
The period from 1 to 3 years of life is a crucial stage in the transition to an adult type of nutrition, which has certain features. In order to ensure that all the necessary nutrients enter the child's body and at the same time prevent an excess of individual nutrients, nutrition should be balanced and varied.
The daily amount of food for children aged 1 to 1.5 years should be 1000-1200 g, from 1.5 to 3 years - 1200-1500 g, the amount of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml. The diet consists of three main meals per day and two snacks. It is considered optimal when breakfast is 25% of the total energy density of the diet, lunch is 30–35%, dinner is 20%, and additional meals are about 10%. In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family.
In the diet of a child of 1–3 years of age , must be present daily: meat of animals or poultry, dairy and sour-milk products, vegetables, fruits, bread, cereals, vegetable and butter; fish and eggs are included in the diet 2-3 times a week.
Cereal products: bread - 2-3 servings per day, cereals and side dishes - 1 time per day
Fruit and/or vegetables: at least 5 times a day
Dairy products: at least 3 servings per day (including those used to make cereals, yoghurts, fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese, infant formula or breast milk).
Domestic pediatricians recommend that when preparing a diet for children aged 1–3 years, preference should be given to specialized children's dairy products of industrial production that meet high quality requirements and safety indicators for this age. Most children's dairy products are additionally enriched with vitamins and/or minerals and other biologically active components, taking into account the physiological needs of children of this age. At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the brain and nervous system of the child.
Meat dishes: 2-3 times a day
Fish dishes: 2-3 servings per week
Eggs: 2-3 per week
Dietary fats: 3-4 teaspoons of butter and/or vegetable oils per day
When cooking, use the minimum amount of salt and sugar, and do not add them to industrial products.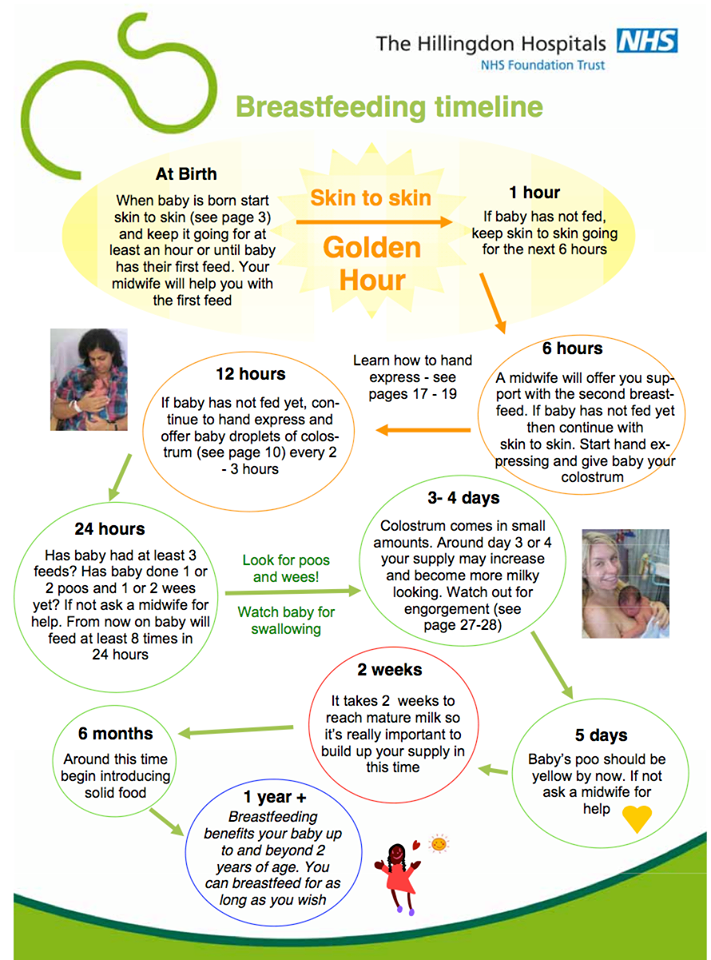
Offer your child a variety of foods and let them choose for themselves. Children love to eat on their own, so if possible, offer food that your child can eat with their hands.
It is important to remember that a baby can choke on pieces of food, so whatever you give your baby should be crushed or cut into small pieces that can be easily chewed.
Do not give to a small child: nuts, whole grapes, cherry tomatoes (unless quartered), whole carrots, seeds (such as pumpkin or sunflower seeds), round candies, legumes, raisins, because a child can eat them choke.
Also in the diet of children of the first 3 years of life should not be present:
Mushrooms; canned snacks, pickled vegetables and fruits
Home canned food
Dry concentrates for side dishes
Hot sauces, mustard, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise
Natural coffee
Juices and drinks in the form of dry concentrates; sweet carbonated drinks
Products containing food additives (flavorings, dyes of artificial origin, including chewing gum), popcorn
Combined fats; cakes and pastries
It is important to remember that children of this age should not be given too spicy and spicy foods.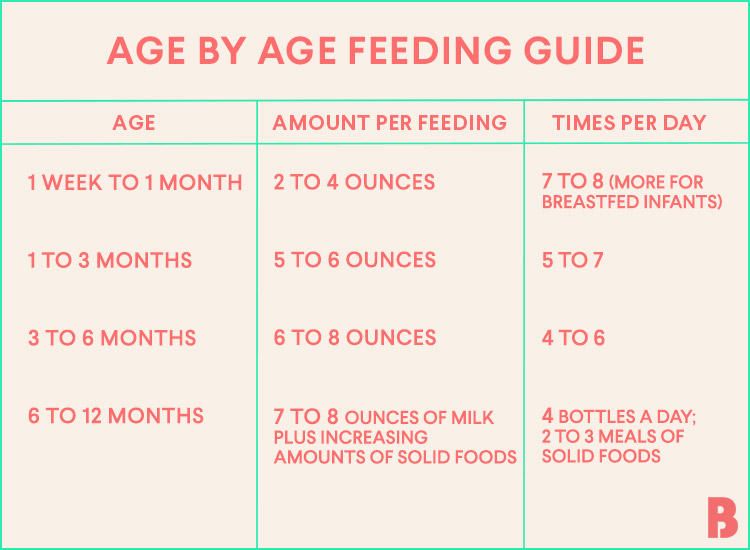
Diet for a 4 year old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.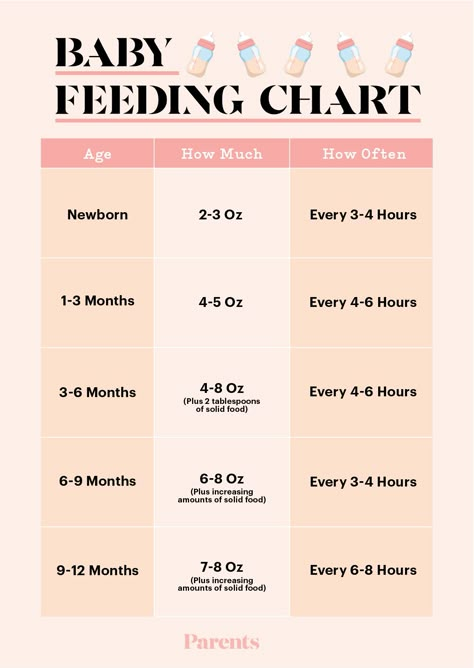 ). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
The optimal time to start introducing complementary foods to a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on the big
practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born at term, without malnutrition (because in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows and develops well.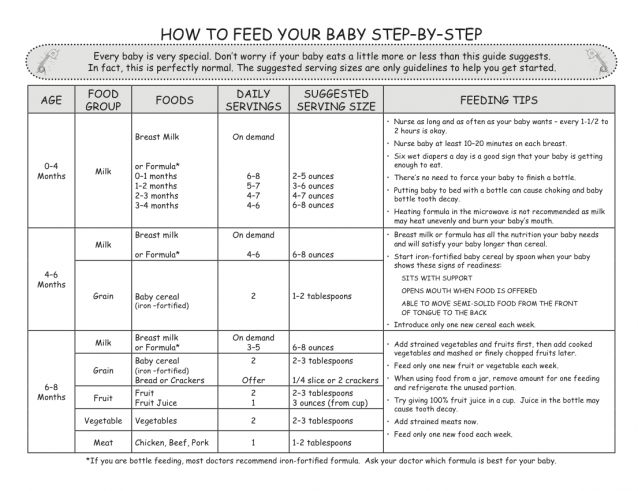 In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first food product can be vegetable puree or porridge, it is better to give fruit puree to the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.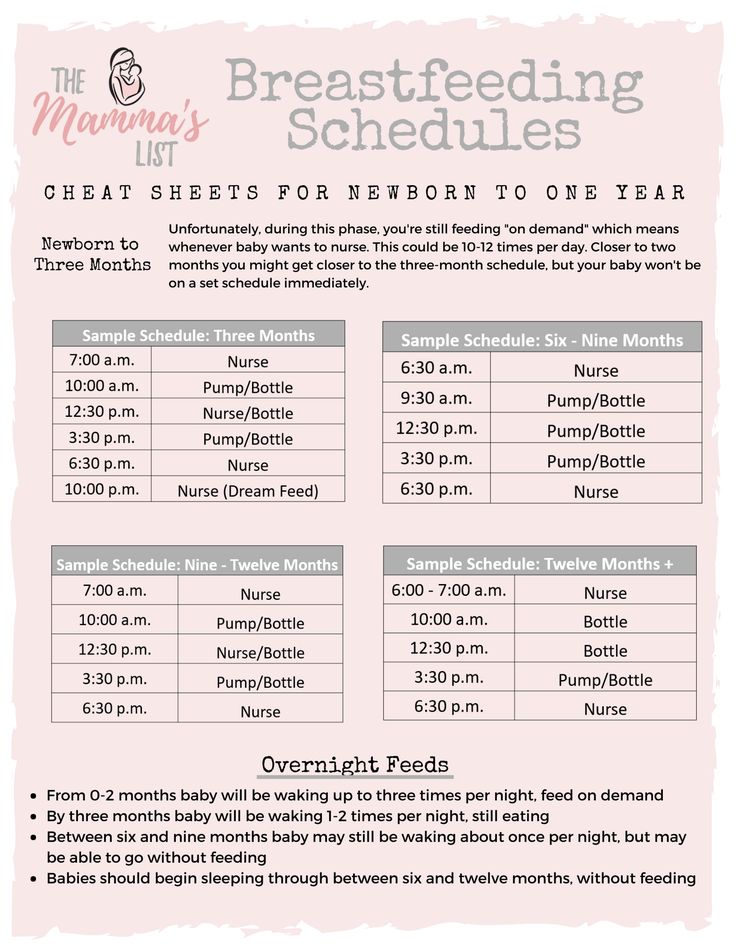
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to the 5-time feeding regimen.
Complementary feeding rules:
- Preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables) can be introduced faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, try one food first, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually "dilute" this product with a new one.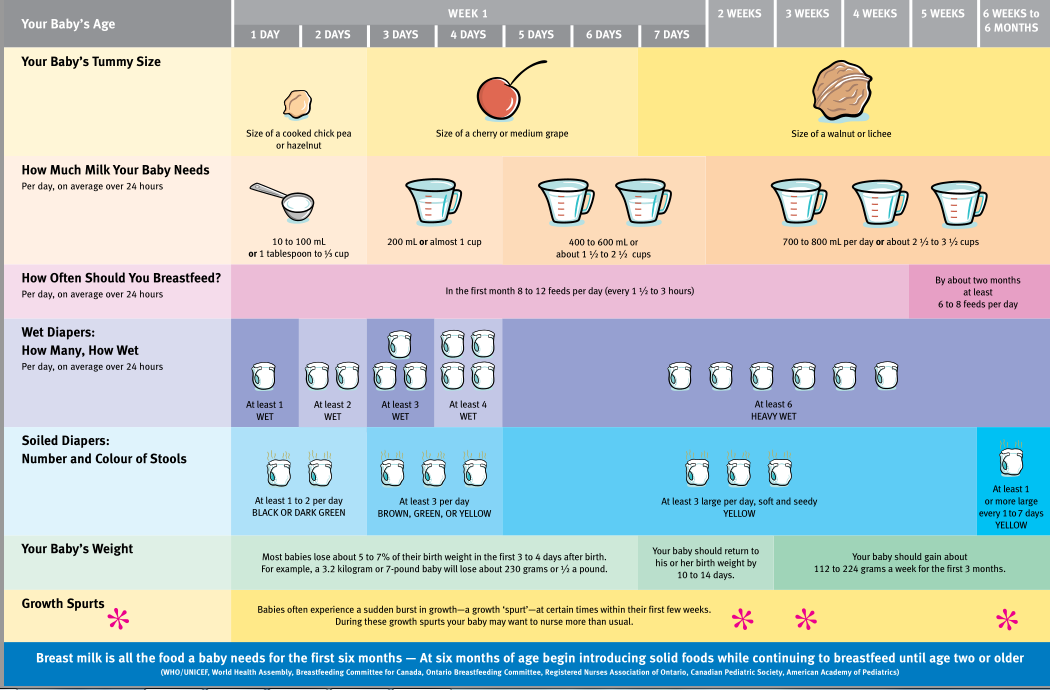 For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feed with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
explain how to make a diet, it is better on several examples that will help to navigate the menu for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
I feeding
6 hours
Breast milk or VHI*
200 ml
II feeding
10 hours
Dairy-free porridge**
Supplementation with breast milk or VHI*
150 g
50 ml
III feeding
14 hours
Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Supplementing with breast milk or VHI*
150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
30 ml
IV feeding
18 hours
Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI*
60 g
140 ml
V feeding
22 hours
Breast milk or VHI*
200 ml
* - Children's dairy mixture (VHI)
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.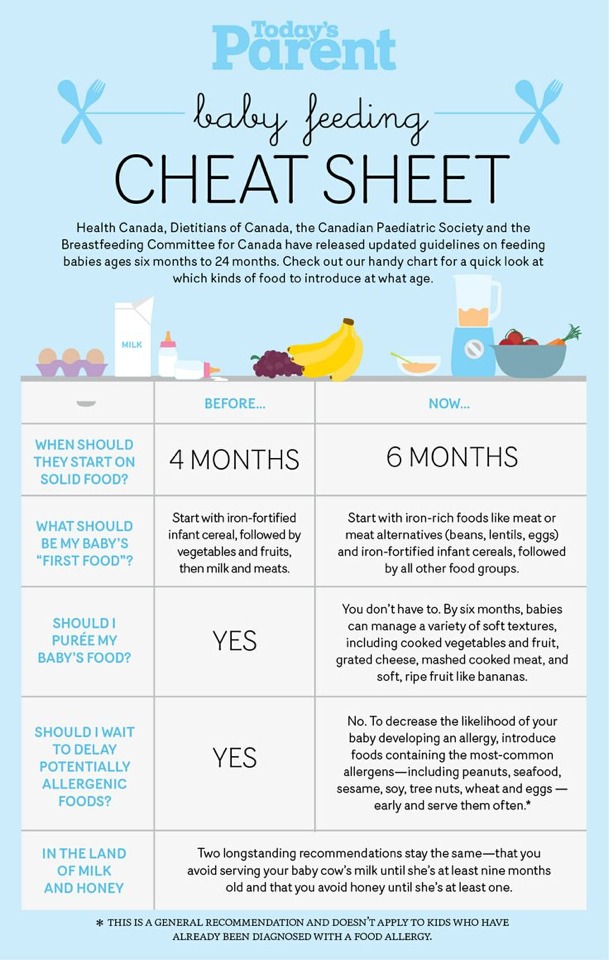
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000. baby 6 months, if complementary foods were introduced from 4 - 5 months:| I feeding | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding | Dairy-free porridge** | 150 g |
| III feeding | Vegetable puree | 150 g |
| IV feeding | Fruit puree | 40 g |
| V feeding | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - children's dairy mixture
** - diluted with breast milk or DMS
Option 3.
9000 9000 9000 9000 006
An approximate daily diet for a baby at 6.5 months on breast feeding, if complementary foods began to be administered from 6 months:
| I feeding | Breast milk | |
| II feeding | Dairy-free porridge** | 100 g |
| III feeding | Vegetable puree | 100 g |
| IV feeding | Breast milk |
|
| V feeding | Breast milk |
|
** - diluted with breast milk
Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree.











