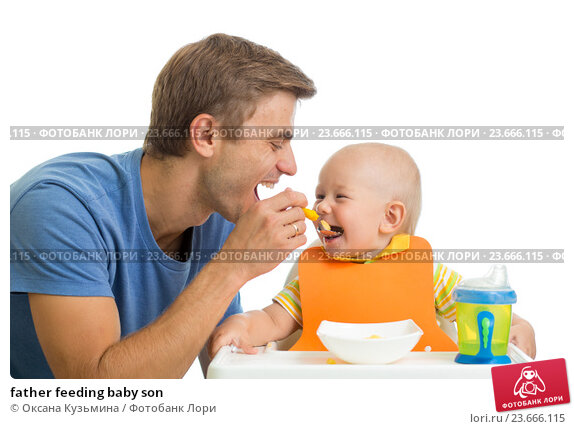
How often can i feed my baby rice cereal
When Can You Start Feeding Your Baby Rice Cereal
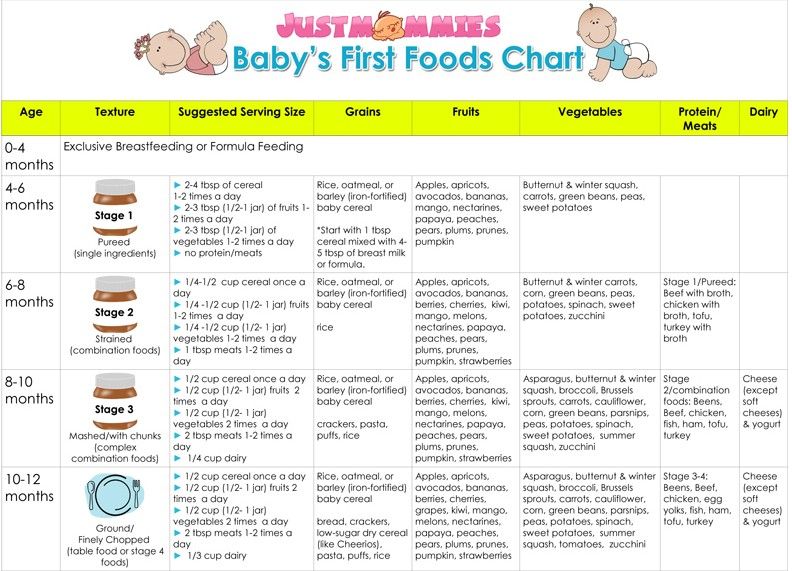
Adding solid foods to your baby’s diet is a big milestone, and you may be wondering when to begin the process and what foods to start with. In the past, single grain infant cereals have been the traditional first choice when transitioning to solid foods, with rice cereal being one of the more popular ones. These days, though it is still OK to start with cereal, experts say that there is no evidence that introducing foods in a certain order provides any advantage for your baby (though babies do tend to like cereal).
Keep in mind that experts highly recommend giving rice cereal as part of a mixed diet of single ingredient choices, rather than as an exclusive food.
Find out how to safely give rice cereal to your baby, and what other infant cereals you might want to give instead.
What Is Rice Cereal?
Rice cereal for babies has been a traditional first food for infants who are being introduced to eating solids. The most common type is a dry powdered cereal, to which liquid is added to form an oatmeal-like consistency, but it can also be purchased premixed. It's one of the single grain cereals that have been recommended for infants when they start on solid foods.
Is Rice Cereal Safe for Your Baby to Eat?
It’s OK to include rice cereal in your baby’s diet as long as you’re not exclusively feeding your baby rice cereal.
The reason experts recommend rice cereal be limited is because of the naturally occurring levels of inorganic arsenic in rice (in this case inorganic refers to the arsenic’s specific chemical compound bound with carbon).
As rice is grown, the plant absorbs more inorganic arsenic from its environment compared to other crops. Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that can enter the food supply through water, soil, or air.
When body weight is considered, a baby’s intake of inorganic arsenic through rice cereal could be three times more than an adult’s. Eating too much rice cereal as an infant can cause long-term health problems.
Eating too much rice cereal as an infant can cause long-term health problems.
What Infant Cereals Can You Give Your Baby Instead of Rice Cereal?
Instead of rice cereal, you can offer another single grain infant cereal such as oat or barley cereal. You can find many of these infant cereals in premixed or dry versions to which you would add breast milk, formula, or water to create a consistency that your baby will like.
Look for cereals that are specifically made for babies because they will be fortified with nutrients like iron and zinc that your baby needs.
Just remember that when introducing new foods — including different types of infant cereals — do so gradually, offering one new food at a time, and then waiting a couple of days before adding another food, to watch for any possible allergic reactions. Once your baby has become accustomed to eating solids, feel free to offer a variety of single ingredient, soft foods.
How Many Times a Day Should You Feed Your Baby Infant Cereal?
When your little one is just starting on solids, spoon-feed your baby a small amount of infant cereal once or twice a day, ideally just after he’s been bottle-fed or breastfed. Start with one or two teaspoons of cereal so that your baby can get accustomed to this new food.
Eventually you can introduce other foods one at a time—and you can even make your baby’s food at home.
Are Other Rice Products Safe to Give Your Baby?
Not necessarily. You can give rice to your older baby as part of a varied and balanced diet. However, it’s best to avoid certain rice-based products like rice syrup, often used as a sweetener in processed foods, as well as rice milk, which should not be used as a substitute for cow's milk.
If your child has turned 1 and is sensitive or allergic to cow’s milk, your healthcare provider will be able to recommend milk alternatives if needed, and can also weigh in on any rice products you’re considering giving.
At What Age Should You Start Feeding Your Baby Infant Cereals?
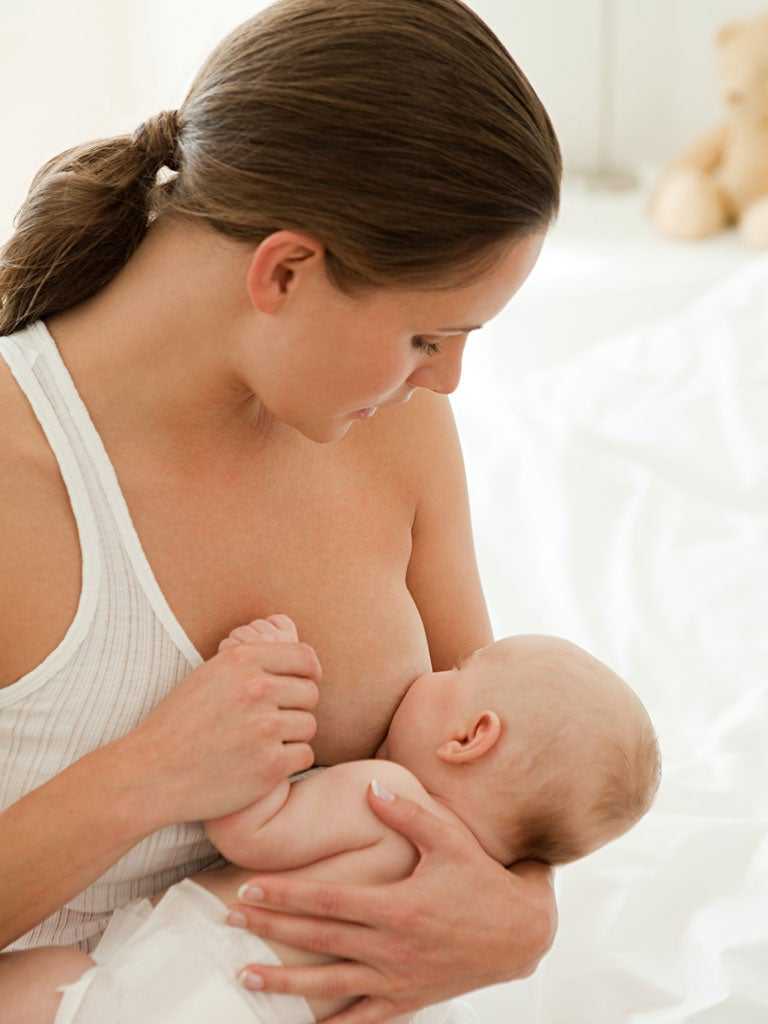
For most babies, 6 months is a good age to start to introduce solid foods, which can include infant cereals. Breast milk or formula will continue to provide most of your baby's nutrition for the first 12 months.
Waiting until this age is important because by this point your baby would have outgrown a natural reflex that all babies are born with that causes them to push their tongue against anything inserted into their mouths. Most babies grow out of this tongue thrust reflex between 4 and 5 months.
Can You Give a Baby Younger Than 6 Months Infant Cereals?
Most babies are not ready for solid foods, including infant cereals, until they are about 6 months old, though some babies could be ready a month or two earlier. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed or bottle-fed (with expressed breast milk or formula until 6 months of age.
How Do You Prepare Dry Infant Cereal for Your Baby?
If you’re using dry cereal, mix one tablespoon of dry cereal with four tablespoons of breast milk, formula, or water; or follow the recommended directions on the container.
Be sure not serve the cereal from a bottle for reasons we mention in the next section. Gradually, you can add less liquid to the dry cereal to find a thickness your baby likes.
Can You Feed Your Baby Cereal in a Bottle?
Although this might be a practice you’ve heard of, don't feed your baby cereal in a bottle unless your baby’s healthcare provider says otherwise. Feeding your baby through a bottle can lead to unnecessary calories—she may consume more food than she actually needs.
Although rice cereal may have been a popular choice, experts now say there are other infant cereals and first foods that may be safer for your baby. If you’re ever unsure about which infant cereal to give, or need advice about expanding your baby's menu, reach out to your baby’s healthcare provider for advice.
If you’re ever unsure about which infant cereal to give, or need advice about expanding your baby's menu, reach out to your baby’s healthcare provider for advice.
As your baby transitions to solid foods, you deserve lots of rewards for all those diaper changes. Download the Pampers Club app to get rewards for all your Pampers purchases.
How we wrote this article The information in this article is based on the expert advice found in trusted medical and government sources, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. You can find a full list of sources used for this article below. The content on this page should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult medical professionals for full diagnosis and treatment.
Baby Food for Thought: How Safe is Rice Cereal?
For generations, rice cereal has been a top choice for babies starting solid foods, but lately there’s growing concern about what’s in it besides the rice: arsenic. UR Medicine’s Dr. Ruth Lawrence, an internationally recognized expert on breastfeeding and infant nutritional needs, offers some information and advice for parents.
UR Medicine’s Dr. Ruth Lawrence, an internationally recognized expert on breastfeeding and infant nutritional needs, offers some information and advice for parents.
Arsenic occurs naturally in soil, air and water. Because rice is grown in water, any arsenic in the water supply binds to the rice as it grows. A known carcinogen, arsenic can influence risk of cardiovascular, immune and other diseases, and research has shown that even low levels can have a negative impact on babies’ neurodevelopment.
Both adults and infants are exposed to arsenic when eating rice, but it’s a bigger concern for babies. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says rice intake for infants, primarily through infant rice cereal, is about three times greater than for adults relative to body weight. In fact, people eat the most rice (relative to their weight) at approximately 8 months of age, a prime time for infant brain development.
The FDA recently proposed a limit of 100 parts per billion of inorganic arsenic in infant rice cereal. Their testing found that most infant rice cereals on the market either meet, or are close to, the proposed level. A JAMA Pediatrics study, published on the heels of the FDA’s recommendation, advises parents to keep an eye on the amount of cereal their babies eat. Researchers followed children for a number of years, noting the amount of rice products they ate and analyzing the arsenic levels in their urine. Babies who ate rice cereals had higher concentrations of arsenic than those who didn’t.
Their testing found that most infant rice cereals on the market either meet, or are close to, the proposed level. A JAMA Pediatrics study, published on the heels of the FDA’s recommendation, advises parents to keep an eye on the amount of cereal their babies eat. Researchers followed children for a number of years, noting the amount of rice products they ate and analyzing the arsenic levels in their urine. Babies who ate rice cereals had higher concentrations of arsenic than those who didn’t.
Here’s some advice for parents who are wondering if, why and when to consider feeding rice cereal to babies.
- Follow the “six-month” rule. Don’t feed your baby rice cereal—or any other solid food—prior to six months of age. Babies should be exclusively breastfed or given formula (or a combination of breast milk and formula) for the first six months of life. Breast milk, and even formula, is much more nutritious for babies at this age than solid-food alternatives.

- Note the benefits of rice cereal. There are reasons why rice cereal is so popular: it’s easy to digest, doesn’t trigger an allergic reaction as the gluten in wheat can, and is well tolerated by babies who are transitioning from breast milk or formula to solid food. In an appropriate quantity, it’s still a food you can include in your baby’s diet.
- Watch your baby’s intake. The greatest brain development occurs in the first year of life and a baby’s diet has an impact on that development. When you feed your baby rice cereal, follow the American Academy of Pediatrics’ advice: Don’t feed rice cereal every day and don’t make it the only food in the meal.
- Pick your brand of rice cereal wisely. Levels of inorganic arsenic can vary widely by brand in both baby foods and products for adults. (Check out Consumer Reports’ study of arsenic levels in a variety of products.)
- Expand your baby’s diet. Add other grain cereals to your baby’s diet, including barley, quinoa, and oats.
 Choose single-grain cereals, rather than multigrain so you can see how your baby reacts to various grains and avoid any that seem to cause a problem. When it’s time to add vegetables and fruits, follow the same principle and introduce one new food at a time.
Choose single-grain cereals, rather than multigrain so you can see how your baby reacts to various grains and avoid any that seem to cause a problem. When it’s time to add vegetables and fruits, follow the same principle and introduce one new food at a time. - Choose iron-fortified cereals. These help ensure your baby gets the nutrients it needs for optimum brain development.
- Don’t overlook other potential sources of arsenic. Arsenic can be found in other foods and other sources besides rice cereal—especially groundwater. If you have a well, be sure to have it checked periodically for arsenic as well as heavy metals such as lead, which also can be harmful to babies’ and adults’ health.
Ruth A. Lawrence, M.D., is a professor of Pediatrics and Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Rochester Medical Center, and medical director of the Ruth A. Lawrence Poison and Drug Information Center and of the Breastfeeding and Human Lactation Study Center. She is an internationally renowned expert in breastfeeding and author of Breastfeeding: A Guide for the Medical Profession, now in its eighth edition.
She is an internationally renowned expert in breastfeeding and author of Breastfeeding: A Guide for the Medical Profession, now in its eighth edition.
Rice porridge - Encyclopedia Baby food
Levchuk Victoria ©
Rice porridge is ideal for the first feeding, as it does not contain gluten.
Rice is different, so you can find on sale long-grained, medium-grained, round-grained, and rice also differs in color: white, brown, wild or black, yellowish. The most ideal option for usefulness for baby food is brown rice, which retains the shell of the cereal, which is the benefit. But you can use any kind of rice for baby food.
Brown rice and any other rice are unlikely to cause allergic reactions, the absence of gluten contributes to this. Nutritious and versatile, brown rice can be paired with any meal your child loves.
Brown rice is a minimally processed brown rice with a light nutty flavor.
Brown rice is more nutritious than white rice. This is because it is unrefined and the natural shell is preserved. Brown rice on the Russian market is a little more expensive than regular white rice, but it's worth it. Moreover, you can cook rice flour for baby porridge at home without industrial additives, which will reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Table of contents:
Rice in the form of porridge can be introduced into complementary foods for a child from 4 months of age. However, it is necessary to remember the WHO recommendation to introduce complementary foods at the age of 6 months.
The second step in starting complementary foods is to identify the first type of complementary food and the first product (see here). Usually mothers have a choice between cereals and vegetables, if there is a lack of weight, then, most likely, cereals are introduced into the baby's diet. But buckwheat and rice are considered the first complementary foods. Most often, buckwheat is chosen as the first porridge, since the child's stool most likely will not change. But rice porridge strengthens, it is ideal as a therapeutic diet for diarrhea.
Most often, buckwheat is chosen as the first porridge, since the child's stool most likely will not change. But rice porridge strengthens, it is ideal as a therapeutic diet for diarrhea.
But it should not be discarded and it can be introduced as the first complementary food, as it is easily digested, coats the stomach, helps to remove toxins from the body, and is often recommended for unstable stools and frequent spitting up. It is also necessary to note the nutritional value of rice, with its low calorie content, which is useful for overweight. Rice also helps the body meet the need for complex carbohydrates, which are then used to build muscle mass and feel full for a long time.
Rice is introduced into complementary foods like any new product, it is necessary to withstand the first 4-7 days to monitor the reaction of the child's body to a new product. Usually, butter is introduced along with porridge, so if a child is about 7 months old and porridge is introduced, then butter must also be introduced, also as a new product. With an undesirable reaction of the child's body in the form of worsening stools, rashes, etc. consult a doctor and stop giving rice.
With an undesirable reaction of the child's body in the form of worsening stools, rashes, etc. consult a doctor and stop giving rice.
How to select and store rice
It is best to choose local varieties of rice, as they travel less from seller to buyer. Our Krasnodar rice is ideal for baby food. Moreover, there is brown rice of Russian production, but you need to look for it. It will be difficult to choose rice, since there are more than 150 types, and it also differs in the way it is processed: polished, unpolished, steamed.
Therefore, mothers usually use rice, which the whole family eats for a long time. You can, of course, buy brown rice for your beloved baby, but this is decided individually with the pediatrician and at the family council.
When choosing rice, you should pay attention to the appearance of the cereal, which should be the same size throughout the package. If it is long-grain rice, then round-grain rice should not be found in the package. It is also worth checking for the presence of larvae, insects, checking the GOST sign and making sure that the rice does not smell of anything nasty.
It is also worth checking for the presence of larvae, insects, checking the GOST sign and making sure that the rice does not smell of anything nasty.
Whole grains can be stored for 12 to 18 months in a cool, dry, dark place. If the temperature becomes extremely warm in the house, you can store the grains in the refrigerator. However, do not forget to look at the expiration date on the package.
Cooked rice is stored for no more than three days, for a child it is worth preparing a new porridge every time.
Ground whole grains such as rice flour should be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator. Flour can be stored in a cool, dry place, but should be checked frequently.
When the grain is ground, the natural oils found in the rice can become rancid if left unrefrigerated. When buying any type of ground whole grain, it's best to buy a smaller amount to ensure it's used quickly and completely before it goes rancid.
By the way, brown rice should be stored in the refrigerator, and preferably in the freezer. If such rice is stored in the kitchen at above zero temperatures, then the oils begin to oxidize, which makes brown rice harmful.
If such rice is stored in the kitchen at above zero temperatures, then the oils begin to oxidize, which makes brown rice harmful.
Freezing rice or rice porridge
Freezing rice porridge does not behave very well, namely it becomes too soft and tasteless, therefore, it is best to freeze multi-ingredient dishes where there is very little rice porridge. Boiled rice is better than frozen rice porridge. Here's how food behaves after freezing.
Preparation of complementary foods: Rice
You can use a rice cooker, slow cooker, steamer and just a pot of water to cook rice porridge. Usually, rice in its pure form is not very suitable as the first complementary food, because after cooking it, whipping it into a homogeneous mass with a blender and other devices turns out badly, only a plastic grater will help, but it will take a lot of time. Therefore, rice must be prepared for the preparation of baby food. You need to pass it several times through a regular cereal mill, which is not difficult to buy in any store. Someday I will write a review of two mills that I have at home, one Soviet, the other modern. It turns out ordinary rice flour, from which it is easiest to cook children's rice porridge.
Someday I will write a review of two mills that I have at home, one Soviet, the other modern. It turns out ordinary rice flour, from which it is easiest to cook children's rice porridge.
Approximately ¼ cup of rice flour uses 1-2 cups of water, depending on the final consistency and the child's preferences. Next, rice flour is poured into boiled water, everything is whipped with a whisk to get rid of lumps. Then everything is cooked over low heat until cooked, see the recipe here.
I think everyone knows how to cook whole grain white rice, but remember, wash in several waters, you can soak for 1 hour, simmer for the first time, stirring until the rice is ready.
There is another original way to cook rice, but it is worth trying to understand whether it suits you or not.
Wash rice, boil water, add rice, cook at a boil for 1 minute, then turn off the heat, close the lid and leave to cool or reach for 5-10 minutes, until cooked. You will get fluffy rice.
Brown rice cooks a little differently because it is more firm. It is best to soak brown rice overnight in cold water, then wash it thoroughly in new water in the morning, pour new cold water over it. Boil for about 10 minutes, then rinse again with cold water, pour again and cook for 15 minutes. And then you need the rice to reach, so we remove it from the fire and wrap it in a blanket.
It is best to soak brown rice overnight in cold water, then wash it thoroughly in new water in the morning, pour new cold water over it. Boil for about 10 minutes, then rinse again with cold water, pour again and cook for 15 minutes. And then you need the rice to reach, so we remove it from the fire and wrap it in a blanket.
We would like to remind you that children should not be introduced to sugar and salt until they are one year old.
The difference between brown and white rice
The difference between brown and white rice is not only in color. A whole grain of rice has several layers. Only the topmost layer, the husk, is removed to make what we call brown rice. This process is the least damaging to the nutritional value of the rice and avoids the unnecessary loss of nutrients that occurs with further processing of the grain.
If brown rice is further milled to remove the bran and most of the germ layer, the result will be white rice, rice that has lost more nutrients.
However, the rice is still unpolished and is polished to make the white rice we are used to seeing. Polishing removes the aleurone layer of the grains, filled with essential fats. Because these fats are highly susceptible to oxidation when exposed to air, this layer is removed through a refining process to extend the shelf life of the product.
The resulting white rice is simply a refined starch that is largely stripped of its original nutrients.
How often should I give rice?
If the child is prone to constipation, a pediatrician should be consulted, as the product is too useful to be abandoned forever, it may be worth introducing it later into the child's diet or feeding rice porridge only 1 time per week.
If the child is healthy, then we still monitor the stool while rice porridge is introduced into the diet, then when other products are introduced, when the child’s menu expands significantly, rice porridge or rice should be given 2-3 times a week as part of various dishes, not only like porridge for breakfast.
Foods that go well with rice:
Fruits, vegetables, yogurt, meat, fish, poultry, seafood, seaweed, mushrooms, dried fruits are great foods to mix with boiled rice.
Herbs and spices, which perfectly complement the taste of rice:
- Cardamom
- Curcula
- GDs Lovely
- Chuskaya nut 0108
- rice porridge with apple and pumpkin
- cauliflower and rice puree
Don't be afraid and add me to VK and Odnoklassniki, Instagram!
Like this article? Subscribe to site updates
"Encyclopedia Baby Food"!
Don't forget to bookmark us! (CTRL+SHIFT+D) Subscribe to the site, comment, share in social networks.
On our site Encyclopedia Baby Food there is useful information on the nutrition of your children, which is useful for everyone, and we update the site "Encyclopedia Baby Food" constantly and try to search and write only excellent, verified and necessary information for you and your children.

Disclaimer No. 1: It must be understood that the author of the articles on the Baby Food Encyclopedia website is not a medical staff, “I am not a doctor.” The information I share is based on my own experience. My goal is not to teach you how to eat or feed your child, but to talk about how we did it, what new things I learned or read. This expands the picture of Baby Food knowledge, gives you a glimpse of the whole process so you can decide if you like it or not.
Disclaimer No. 2 : However, the above does not cancel visiting a pediatrician. Before you start complementary foods, you need to get his professional opinion on the best way to introduce new foods for your baby. I also draw your attention to the fact that you need to look at the original date of the published articles, because some of the "best practices" may have changed. Always check with your child's pediatrician about complementary foods and their health.
Disclaimer #3: Keep in mind that every family is unique, every situation is also completely unique. There are no universal solutions. Only you can find what works best for you. Certain goals require certain sacrifices and priorities - not everyone wants to make those choices, and that's GREAT! Just know what you want to achieve, and be ready to get to work, putting the best of your strength!
There are no universal solutions. Only you can find what works best for you. Certain goals require certain sacrifices and priorities - not everyone wants to make those choices, and that's GREAT! Just know what you want to achieve, and be ready to get to work, putting the best of your strength!
Disclaimer No. 4: On the Encyclopedia Baby Food website, photos from books on baby food with attribution are used to better understand the information (Article 1274, paragraph 1, part four of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Literature on baby food is found in the public domain on the Internet.
Apricot puree with chicken
Bannaya-glove puree
Banana puree
Borsch
Bousse Bullet with peas and rice
Botterbrod with kolrabi
Fast dessert
WIGHT FROM BACKS
Spring salad
Greek cereal 9020 Buckwheat porridge with apricots
Buckwheat porridge with banana
Buckwheat pilaf
Children's sausage
Children's milk porridge with banana
Children's vinaigrette
Children's ketchup
Children's cucumber salad
Children's salad Olivier
Children's porridge biscuits
Children's puree of strawberries, bananas, yellow cherries, yoghurt and biscuits with cereals
Children's puree with cottage cheese and fruit
Homemade yeast bread with flax flour
Homemade cheese
Homemade pizza
0 Breakfast outside Kohlrabi appetizer
Roasted cauliflower
Roasted carrots
Roasted carrots and cherries with millet
Winter salad with Jerusalem artichoke
Cabbage with white beans
Cabbage salad like in a canteen
Mashed potatoes
Quinoa and pumpkin porridge
Quinoa porridge
Breakfast cereals
Quinoa and apple
Strawberry puree
Strawberry puree with banana
Strawberry compote
Wild apple and raspberry compote
Thermo-steamed fruit compote for children 8 months
Corn porridge
Corn porridge with pear
Corn porridge with pumpkin
Corn porridge with pumpkin and carrots
Corn porridge with apple and carrots
Chicken liver in the oven
Chicken cutlets with carrots
Chicken with carrots, sweet peppers and potatoes
Navy pasta
Macaroni with orange sauce
Muffins with vegetables and egg
Baby potatoes in their skins
Vermicelli milk soup
Carrot and potato casserole 9020
Carrots with chicken
Fly agaric from eggs and tomatoes
Meat envelopes
Homemade Tarragon drink for children
Vegetable puree from cauliflower and carrots
Vegetable soup with maize semolina
Vegetable soup with cheese and corn semolina
Vegetable soup with spinach
Vegetable puree soup with bell pepper
Oatmeal porridge
Pollack fritters
Hot kefir fritters
Omelette in a bag
Omelet with broccoli and cauliflower cheese
Omelette pancake
Peach puree
Baked apples 7 months +
Zucchini and carrot pie
Zucchini pie
Rice and zucchini pie
Fish pie
Fish and potato pie
White cabbage pizza
Lavash pizza
Zucchini, tomato and sausage pizza
Tomato and olive pizza
Spinach pizza
Rabbit pilaf
Chicken pilaf with green peas and corn
Banana and cherry puree2 , cottage cheese and cereals 4 cereals
Broccoli (cauliflower) puree
Broccoli, courgette and cauliflower puree
Blueberry puree
Pear puree
Pear and banana puree
Pear and banana puree, baked
Pear and pumpkin puree 7 months +
Pear, pumpkin and peach puree
Pear, apple, plum and prune puree
Blackberry puree
Turkey puree
Zucchini puree
Zucchini and broccoli puree 902 carrot and potato puree
Quinoa and banana puree
Quinoa and carrot puree
Quinoa, banana and carrot puree
Quinoa, squash and carrot puree
Quinoa, peach and raspberry puree
Quinoa, cauliflower, apple, pea puree and mint
Quinoa, apple, pear and raisin puree
Quinoa, apple, carrot puree
Rabbit, broccoli and cauliflower puree
Chicken, carrot, potato, apple and pea puree
Raspberry, cherry and banana puree
carrots
Carrot and apple puree
Carrot, potato, broccoli puree with cheese
Carrot, potato, apple and quinoa puree
Carrot, pumpkin, apple and prunes puree
Carrot, apple and potato puree
Turnip and carrots
Plum puree
Cottage cheese, strawberry and banana puree
Pumpkin puree
Pumpkin and banana puree
Pumpkin and squash puree
Pumpkin and apple puree
Pumpkin, apple and banana puree
Cauliflower and broccoli puree
Cauliflower puree and potatoes
Cauliflower and rice puree
Cauliflower and apple puree
Cauliflower, green peas and courgette puree
Cauliflower, turkey and potato puree
Cauliflower, potato and courgette puree
Cauliflower, carrot and broccoli puree
Cauliflower, carrot, cheese and rice puree
Cauliflower, apple and courgette puree
Zucchini puree
Zucchini and potato puree
Zucchini, carrot and apple puree 902 cherries
Blueberry puree
Prune puree
Apple, pumpkin, carrot and some curry puree
Apple and pear puree
Apple and strawberry puree
Apple, strawberry and cherry puree
Apple, peach and banana puree
Carrot and pumpkin puree
Cottage cheese and banana puree
Turkey, potato and carrot stew
Zucchini, carrot and broccoli stew
Fish, potato, carrot and broccoli stew
Rice porridge
Whole grain rice porridge
carrot
Rice porridge with pumpkin
Rice porridge with apples
Rice porridge with apple and pear
Rice porridge with apple and pumpkin
Fish cakes with vegetables
Semi-cooked fish
Fish meatballs with ketchup
Baby Fish Soup
Salmon and Celery Fish Soup
Carrot and Kohlrabi Salad
Chickpea Salad
Chickpea and Cabbage Salad
The Laziest Soup
Creamy Kohlrabi Soup
Oatmeal Smoothie1 Pot Sauce
Cheesy Pizza
Pea and Bacon Soup
Baked Vegetable Soup
Kohlrabi Soup
Salmon Soup
Cauliflower Soup
Turnip Potato Soup
Meatball Soup for the Picky Eater
Green apple kohlrabi soup
Rabbit, pumpkin, potato, broccoli and cauliflower soup
Beetroot soup
Pumpkin mushroom soup
Broccoli and celery soup
Soup/stew Pork with Potatoes and Carrots
Cheese Pasties
Pumpkin Cheese Sauce (Annabelle Carmel Recipe)
Buzz Lightyear Sandwich
Pumpkin Apple Puree
Pumpkin Apple Juice
Pumpkin Cake
Pumpkin Soup9 Fruit Puree
Fruit Salad
201 Bread Lavash
Color Cabbage with cheese
Lipa tea and thyme
Experimental soup puree with vermichel and lentil
Apple puree
Apple juice
How to prepare rice for complementary foods
Content: Hide
7 Basic properties One of the first "adult" dishes on the baby's table is rice. This cereal has earned the trust of nutritionists, pediatricians and parents around the world. Rice is a gluten-free, low-allergenic cereal with a high content of "healthy" carbohydrates (up to 85%), which are perfectly digested in the baby's sensitive digestive tract. Rice is also traditionally used in the therapeutic diets of people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and intestinal infections.
This cereal has earned the trust of nutritionists, pediatricians and parents around the world. Rice is a gluten-free, low-allergenic cereal with a high content of "healthy" carbohydrates (up to 85%), which are perfectly digested in the baby's sensitive digestive tract. Rice is also traditionally used in the therapeutic diets of people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and intestinal infections.
Main useful properties
The main properties of rice porridge are its low calorie content (44 kcal per 100 g of product) and the optimal ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Rice has a low glycemic index, which contributes to a more efficient supply of glucose to the brain. Protein in rice contains a small amount, but due to its structure, it is perfectly absorbed by the human body (up to 98%). In the fat component of rice, 1/5 part (21%) belongs to fatty acids important for the child's body: oleic (37%), linoleic (41%) and linolenic. The low fat content in rice groats (0.7–1 g/100 g of groats), the optimal ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (7 g/1 g/74 g) create a long-lasting feeling of fullness when eating ready-made rice dishes. Since rice does not contain coarse dietary fiber, it can be used in the diet of people with diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by excessive motility and gas formation. The vitamin and mineral composition of rice cereal is not as rich as compared to buckwheat or oatmeal. However, rice grains contain a large amount of B vitamins, of which the most are pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and tocopherol (vitamin E).
The low fat content in rice groats (0.7–1 g/100 g of groats), the optimal ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (7 g/1 g/74 g) create a long-lasting feeling of fullness when eating ready-made rice dishes. Since rice does not contain coarse dietary fiber, it can be used in the diet of people with diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by excessive motility and gas formation. The vitamin and mineral composition of rice cereal is not as rich as compared to buckwheat or oatmeal. However, rice grains contain a large amount of B vitamins, of which the most are pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and tocopherol (vitamin E).
Rice dishes occupy one of the leading positions in the world gastronomic culture. About 5000 recipes based on this cereal are known. Therefore, in baby food, rice porridge does not lose its popularity.
For breakfast in Russia, porridge is traditionally prepared for children, because the first meal should be high-calorie, satisfying and tasty. The main components of a healthy breakfast should be complex carbohydrates, proteins and fats of animal origin, which take longer to be processed by digestive enzymes.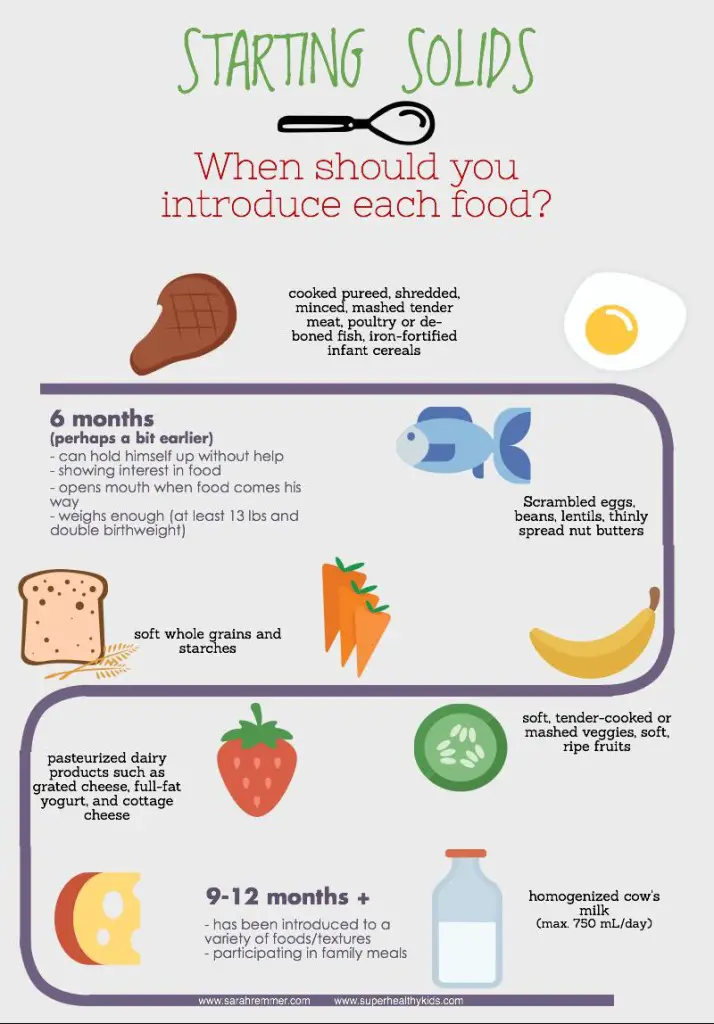 Therefore, the choice of parents in favor of porridge as the main dish in the morning is quite justified.
Therefore, the choice of parents in favor of porridge as the main dish in the morning is quite justified.
Rice porridge for children in the first year of life
Children's rice porridge is one of the most popular products in the Baby Premium line. Small gourmets can choose from dairy-free and milky rice porridges, with fruit additives. All cereals of the Baby Premium line have a high safety profile, are enriched with essential vitamins and minerals, which increases their nutritional value.
The use of fortified baby foods is an important part of nutrition in the first year of life. During the transition of a child from exclusive breastfeeding to the stage of introduction of complementary foods, short-term deficiency states for individual microelements may occur.
Lack of proper eating habits in the family, encouragement of the child's independent choice of foods, selectivity in nutrition, restrictive diets are factors that lead to a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the baby's diet.
In this regard, health professionals have developed a global strategy to reduce the risk of developing vitamin and mineral deficiencies - the mandatory fortification of daily food, especially regarding the children's menu.
Thus, it has been proven that no additional non-fortified food can provide the infant with an adequate level of zinc, the deficiency of which causes a decrease in growth rate, intestinal diseases and a decrease in immune tolerance. Accordingly, the child should receive additional zinc with enriched complementary foods.
The same risk factors include a high prevalence of iron deficiency in children of the 1st year of life due to poor control of maternal nutrition during pregnancy and lactation, obsession with diets, premature birth and the development of digestive disorders in the infant in the first months of life. Iron deficiency can cause delayed psychomotor development and other health problems in the baby. With the right balance of trace elements in the diet of both the mother and the baby, this condition can be avoided.
Baby Premium baby cereals contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals, but the content of such elements as iron, iodine, zinc, B, A, C vitamins is especially high, which cover up to 10% of the daily requirement for these substances.
The first complementary food with rice porridge for children
Every parent can offer children's rice porridge for breakfast. For healthy babies, complementary foods at 4-6 months can be started with safe, low-allergenic Baby Premium rice porridge and gradually move to milk-based rice porridge, which has a high nutritional value due to the ideal combination of animal proteins and cereals, as well as the additional introduction of vitamins and minerals . In terms of calories, milk porridges are comparable to breast milk (90 kcal and 70 kcal, respectively), in this regard, they perfectly maintain a long-term feeling of satiety and give a stable supply of energy to the little hero.
If it is necessary to make a more varied diet and introduce the child to new tastes in the Baby Premium line, you can choose milk rice porridge with fruits. Fruit additives in cereals are additional sources of dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and also develop the taste buds of a little gourmet.
Fruit additives in cereals are additional sources of dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and also develop the taste buds of a little gourmet.
If a child has health problems in the form of food allergies, malabsorption syndrome, celiac disease, then he can be recommended for a long time low-allergenic rice porridge, which is also a full-fledged dairy-free cereal dish. The ratio of the main nutrients, the content of vitamins and minerals in it correspond to all physiological norms of consumption in early childhood. Dairy-free rice porridge is enriched with prebiotics in the form of inulin, which will favorably affect the formation of a healthy microbiota in the intestines.
The use of Baby Premium cereals in the daily diet of young children allows parents to be confident in the high level of technological, microbiological and chemical safety of the product, its usefulness and ease of preparation in a variety of conditions.
Dietary Recommendations
1. Start introducing a new food into your diet with a tiny amount. For the first acquaintance with rice, a quarter of a teaspoon of porridge will be enough for a crumb. Every day, you can increase the serving, gradually trying to reach the amount of one serving recommended by the pediatrician.
Start introducing a new food into your diet with a tiny amount. For the first acquaintance with rice, a quarter of a teaspoon of porridge will be enough for a crumb. Every day, you can increase the serving, gradually trying to reach the amount of one serving recommended by the pediatrician.
2. It is best to offer this high-carbohydrate product to babies in the morning.
3. Postpone rice foods for a while if your baby has bloating, intestinal colic, or problems with bowel movements (constipation).
4. Having decided how to cook rice porridge for feeding, over time you can enrich the taste of the main dish by adding mashed apple, pear or squash puree to it.
5. In the Bebi Premium line, along with classic rice porridge, there are options with fruit, vegetable, and cream components. They will introduce the baby to new facets of the taste of a product already known to him a few months after the introduction of the first complementary foods.
6. Take the time to teach your child about food etiquette from an early age. Wash your hands before and after eating. If the baby is already more than 10 months old, let him try to feed himself. To do this, put a beautiful bowl in front of him and offer a spoon that will be comfortable for him to hold.
Wash your hands before and after eating. If the baby is already more than 10 months old, let him try to feed himself. To do this, put a beautiful bowl in front of him and offer a spoon that will be comfortable for him to hold.
How to cook rice porridge for babies
You can go in two ways - buy a package of regular rice or choose a special ready-made baby porridge from this cereal. Let's consider both options in more detail.
Rice groats
Several varieties of the product can be found on store shelves. These are parboiled, long-grain, round-grain and medium-grain rice. For the first feeding, the last option is best. Such a product absorbs a large amount of moisture during cooking and boils well. Before you cook rice porridge for the first feeding, you need to carefully prepare the grain.
- Sort by hand to remove possible pebbles and other debris.
- Rinse under water until liquid is clear.
- Soak rice in warm water, then rinse with cold.

It is important to consider the following information:
- it is not recommended to cook cereals for children under one year old with cow's milk;
- proportions: for 20 g of rice - 50 ml of water and 100 breast milk or formula;
- for babies, do not season porridge with salt, sugar.
Ready porridge
At the first feeding, the consistency of the food should be thin and as homogeneous as possible. The presence of even small lumps in the baby can provoke regurgitation and rejection of food. Therefore, for the smallest, it is permissible to begin acquaintance with rice in the form of ready-made powder for making porridge.
In this case, it is better to take the dairy-free version as the very first product. He leaves the mother the opportunity to prepare a dish with the addition of breast milk or a mixture - products with which the baby's body is already familiar. As a rule, a cooking recipe with exact proportions is indicated on the packaging of porridge.