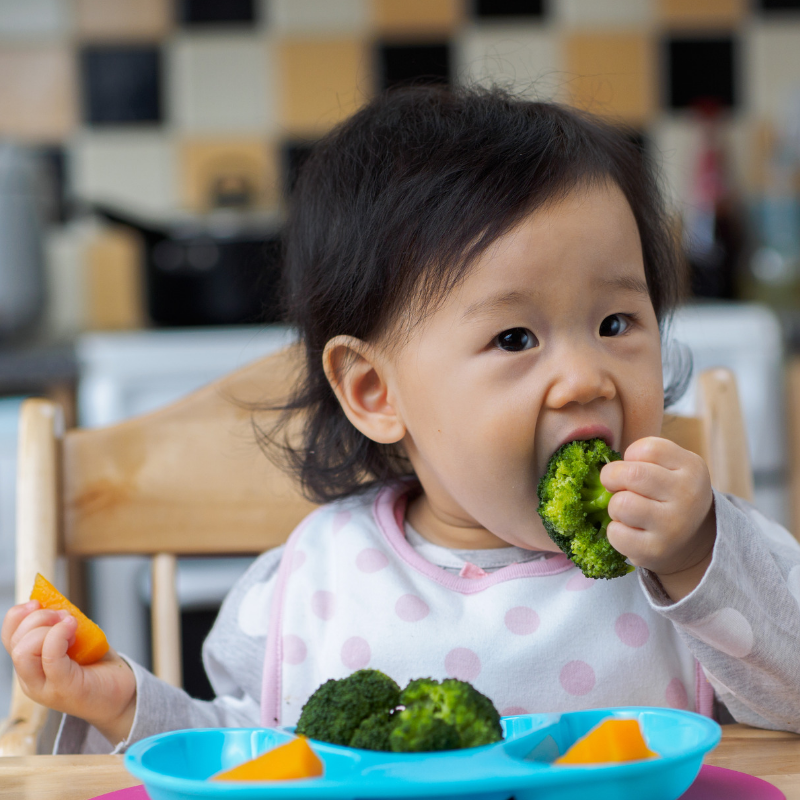
Wic baby food options
WIC-Authorized Baby Food | Gerber
Filter
Filter
Puree Type
Milestones
- Pregnancy
- Newborn
- Supported Sitter 28items
- Sitter 56items
- Crawler
- Toddler
- Preschooler
Ingredients
Needs
- Colic
- Crying
- Fussiness
- Gas
- Mild Spit-Up
- Uncomfortable Poops
- Teething
- Vitamin D
- On the Go
- Iron 7items
- Starting Solids 13items
- Expanding Textures 1item
- Probiotics
- DHA
- Prebiotics/2’-FL HMO
CLEAR ALL
Price - Low to High Price - High to Low Newest On Sale Top Sellers
Food Packages | Texas WIC
- Pregnant Women
Your WIC foods:
- Are low in fat and high in fiber.
- Provide nutritional variety.
- Help promote a healthy weight gain and a healthy baby.
Food Package
- Cereal: 36 ounces
- Whole grains: 1 pound
- Fruits and vegetables: $11.00
- Juice: 144 ounces (3 - 12 ounce frozen or 48 fluid ounces)
- Low-fat or fat-free milk: 4.5 gallons
- Yogurt or low-fat or fat-free milk: 1 quart
- Cheese: 1 pound
- Eggs: 1 dozen
- Beans and peanut butter: 1 pound dry or 4 cans and peanut butter 16 to 18 ounce jar
Before your baby is born, speak to a WIC counselor about choosing one of the three food packages for you and your baby.
- Are low in fat and high in fiber.
- Moms and Fully Breastfeeding Babies
This food package is the largest and does not contain any formula. Moms and babies can get this food package until baby’s first birthday.

Fully breastfeeding (feeding your baby only breastmilk) is the healthiest choice for you and your baby and this package gives you the most food. You will receive breastfeeding support throughout your baby’s first year. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends mothers exclusively breastfeed for the first six months.
Mom’s Food Package
- Cereal: 36 ounces
- Whole grains: 1 pound
- Fruits and vegetables: $11.00
- Juice: 144 ounces (3 - 12-ounce frozen or 48 fluid ounces)
- Low-fat or fat-free milk: 5 gallons
- Yogurt or low-fat or fat-free milk: 1 quart
- Cheese: 2 pounds
- Eggs: 2 dozen
- Beans and peanut butter: 1 pound dry or 4 cans and 16 to 18 ounce jar of peanut butter
- Canned tuna, salmon, sardines and mackerel: 30 ounces
Mothers who are fully breastfeeding multiples (twins, triplets, etc.) will receive additional amounts of foods.
Baby’s Food Package
When your baby is age 0-5 months:
- The best and only food source your baby needs during this time is your breastmilk.

When your baby is age 6-11 months:
- Infant cereal: 24 ounces (8 ounce or 16 ounce containers)
- Baby food fruits and vegetables: 64 containers, 4 ounces each
- Baby food meats: 31 containers, 2.5 ounces each
- Moms and Partially Breastfeeding Babies
This package contains less food than the fully breastfeeding food package but more than the formula feeding package, and it includes some formula. The amount of formula will vary depending on how much your baby needs and his or her age. Moms and babies can get this package until baby’s first birthday.
After the first month of your baby’s life, you can continue to provide only breastmilk or you can choose to combine breastfeeding with formula feeding. If you are using formula, WIC staff will help you figure out how much you need.
 Use only as much formula as you need, and only when you and your baby are not together or when you cannot provide your pumped milk. Every ounce of your breastmilk counts when it comes to your baby’s health and your health as well.
Use only as much formula as you need, and only when you and your baby are not together or when you cannot provide your pumped milk. Every ounce of your breastmilk counts when it comes to your baby’s health and your health as well.As a WIC mom, you will receive breastfeeding support.
Mom’s Food Package
- Cereal: 36 ounces
- Whole grains: 1 pound
- Fruits and vegetables: $11.00
- Juice: 144 ounces (3 - 12-ounce frozen or 48 fluid ounces)
- Low-fat or fat-free milk: 4.5 gallons
- Yogurt or low-fat or fat-free milk: 1 quart
- Cheese: 1 pound
- Eggs: 1 dozen
- Beans and peanut butter: 1 pound dry or 4 cans and 16 to 18 ounce jar of peanut butter
Baby’s Food Package
Breastfeed when you and your baby are together.
In your baby’s birth month
- Formula: You may be able to get 1 can of 12.4 ounce powder formula. Ask the staff at your local WIC office.
When your baby is age 1-3 months
- Formula: up to 4 cans of 12.
 4 ounce powder*
4 ounce powder*
When your baby is age 4-5 months
- Formula: up to 5 cans of 12.4 ounce powder*
When your baby is age 6-11 months
- Formula: up to 4 cans of 12.4 ounce powder*
- Infant cereal: 24 ounces (8 ounce or 16 ounce containers)
- Baby food fruits and vegetables: 32 containers - 4 ounces each
*All formula amounts are approximate
- Moms and Formula Feeding Babies (also includes some breastfeeding)
This is the smallest food package for moms and babies. This package includes more formula than the partially breastfeeding package, but not all the formula your baby may need. The amount of formula will vary depending on the age of your baby.
You can also choose to feed your baby only or mostly formula with some breastfeeding.
 The amount of formula provided by WIC may not be enough to meet the nutritional needs of your baby, so you should breastfeed any time you and your baby are together so you won’t have to buy more formula.
The amount of formula provided by WIC may not be enough to meet the nutritional needs of your baby, so you should breastfeed any time you and your baby are together so you won’t have to buy more formula.If you choose this package, your baby will receive the following foods throughout his or her first year. You will receive foods for yourself only during the first six months.
As a WIC mom, you will receive breastfeeding support.
Mom’s Food Package
- Cereal: 36 ounces
- Fruits and vegetables: $11.00
- Juice: 96 ounces (2 - 12-ounce frozen or 48 fluid ounces)
- Low-fat or fat-free milk: 3 gallons
- Yogurt or low-fat or fat-free milk: 1 quart
- Cheese: 1 pound
- Eggs: 1 dozen
- Beans or peanut butter: 1 pound dry or 4 cans or peanut butter 16 to 18 ounce jar
The Formula Feeding food package provides these foods for six months after your baby is born. Moms who choose the Fully or Partially Breastfeeding food packages will receive more food for one full year.

Baby’s Food Package
Breastfeed when you and your baby are together.
When your baby is age 0-3 months
- Formula: up to but no more than 9 cans of 12.4 ounce powder*
When your baby is age 4-5 months
- Formula: up to but no more than 10 cans of 12.4 ounce powder*
When your baby is age 6-11 months
- Formula: up to but no more than 7 cans - 12.4 ounce powder*
- Infant cereal: 24 ounces (8-ounce or 16-ounce containers)
- Baby food fruits and vegetables: 32 containers - 4 ounces each
*All formula amounts are approximate
- Children 1 to 2 Years
Your child’s WIC foods:
- Are low in fat and high in fiber.
- Provide nutritional variety.
- Help promote a healthy weight.
Food Package
- Cereal: 36 ounces
- Whole grains: 2 pounds
- Fruits and vegetables: $9.
 00
00 - Juice: 128 ounces (2 - 16 ounce frozen or 64 fluid ounces)
- Whole milk: 3 gallons
- Yogurt or whole milk: 1 quart
- Cheese: 1 pound
- Eggs: 1 dozen
- Beans or peanut butter: 1 pound dry or 4 cans or peanut butter 16 to 18 ounce jar
- Children 2 to 5 Years
How is this package different from the food package for children 1 to 2 years old?
- Whole milk is replaced with low-fat (1%) or fat-free milk.
- Peanut butter and canned beans are included as an alternative to dry beans.
Food Package
- Cereal: 36 ounces
- Whole grains: 2 pounds
- Fruits and vegetables: $9.00
- Juice: 128 ounces (2 - 16 ounce frozen or 64 fluid ounces)
- Low-fat or fat-free milk: 3 gallons
- Yogurt or low-fat or fat-free milk: 1 quart
- Cheese: 1 pound
- Eggs: 1 dozen
- Beans or peanut butter: 1 pound dry or 4 cans or peanut butter 16 to 18 ounce jar
Special baby food
Baby food special
Meals for children has its own characteristics and complexities.

When planning a child's diet, consider certain features of the child's body.
Child growth
The main difference between baby food is the growth of the child's body. That is, a baby needs more protein than an adult. Knowing about it many adults make the mistake of focusing on creating a high protein diet, although even ordinary protein foods consumed by adults contain
more protein than breast milk.
High mobility
Another feature of baby food is that children are very mobile in different from adults. Greater mobility of the child's body contributes to exchange normalization. If children are forcibly restricted in their movements, this provokes insufficient secretion of growth hormones, diseases, and as a result - developmental delay.
Consumption of sweets
Due to the high metabolic rate, children, unlike adults, are able to absorb significantly more sweets without much harm to themselves.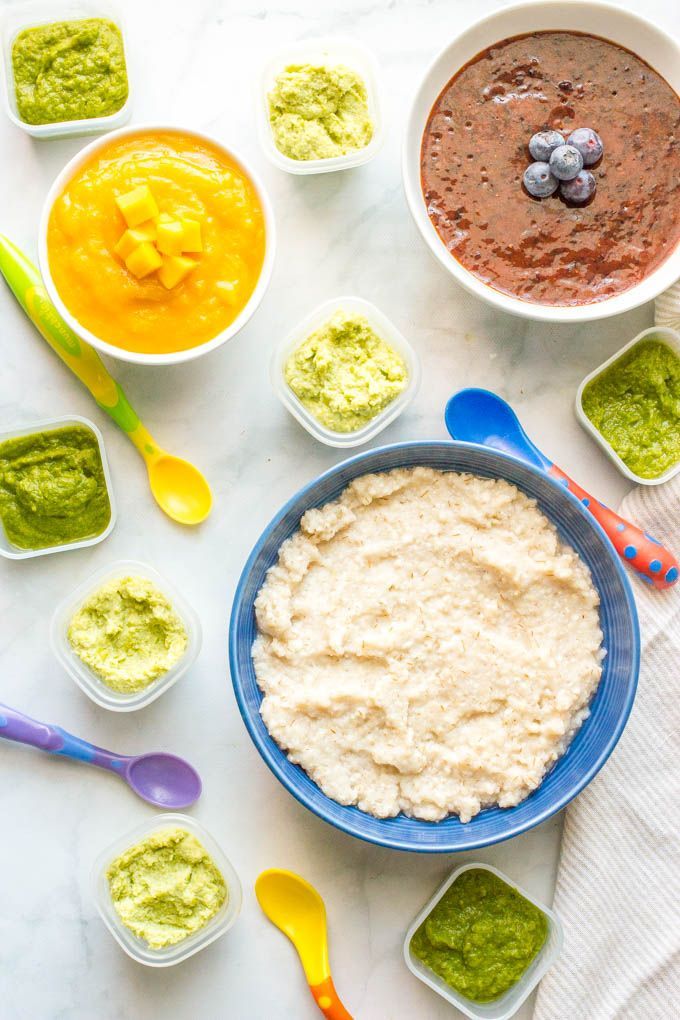 However, they should not be encouraged to do so. Although sweet foods are natural origin are very beneficial for the child.
However, they should not be encouraged to do so. Although sweet foods are natural origin are very beneficial for the child.
In addition, children are much more active than adults. use cholesterol. It is very important for health, is the main component of the membrane, which surrounds cells throughout the body. And the child grows, and he forms a lot new cells.
An important nuance is the fat cells that make up the "fat" according to most are formed during the first years of life. Subsequently they grow and grow in size. Therefore, what it looks like an adult is largely associated with nutrition in childhood.
Regulatory Excellence mechanisms
The most important feature of baby food . Regulatory mechanisms in the child's body controlling the inflow and outflow of energy, function perfectly. His The body knows exactly what food and in what quantities it needs. However, if there is an abundance of deliciously cooked (with spices, fried, fatty and etc.) and sweet dishes, the appetite will be coordinated by the tongue, and not by the physiological need.
However, if there is an abundance of deliciously cooked (with spices, fried, fatty and etc.) and sweet dishes, the appetite will be coordinated by the tongue, and not by the physiological need.
This level of regulation remains until the age of 14-17. Further it is preserved under the condition that a person leads a healthy lifestyle.
A number of general rules can be identified - recommendations to which it makes sense to listen in order to provide the child with the right diet.
1 baby food rule - diet
Proper nutrition of the child involves the absence of strict dietary compliance.
What kind of lunch if you need to launch a rocket or put a doll to bed sleep? Such matters are as important for a child as love is for an adult, interesting work, rest. Children are tiny but full-fledged people who are still in need of care.
Children are tiny but full-fledged people who are still in need of care.
In addition, when there is no feeling of hunger, then eat the body is not yet ready to eat, eat without pleasure, therefore food won't go well. When hungry, the baby will ask for it. And there is no problem in that the child ate instead of three, two or five times a day. If food normal and do not use violence against the child, then there will be neither malnutrition nor overeating.
2 baby food rule - non-violence In most cases, the child is persuaded to "eat for dad, grandfather, mother, etc.", or they simply order "until you finish eating, you won’t get up from the table." And if we imagine how we would feel in such a situation? The baby's body does not need food at the moment, so he does not want to, only Total. Appetite may arise after some time, and there is no point in being offended. However, the appetite should be for natural products - porridge, potatoes, apple, milk, not sweets and cookies.
 In some cases, however, there are whims and tricks.
In some cases, however, there are whims and tricks. 3 baby food rule - diseases
Separately, it is worth dwelling on proper nutrition children with diseases. very wide the practice of "feeding" sick children is practiced. There is an opinion that this gives the body extra energy to fight the disease.
Paradox - in following: the body really needs strength, it mobilizes all the resources to restore the shattered balance. And the patient has no appetite because all the energy is directed to the fight against the disease, and it simply does not remains on the process of digestion. Animal instinct is at work here. is aimed at survival, and no food simply "climbs". For example, patients animals do not touch food, even if it lies in front of their noses.
And force-feeding for medicinal purposes directly harm the child.
Preferably, offer him hot drink - tea with honey, warm fruit drink, etc.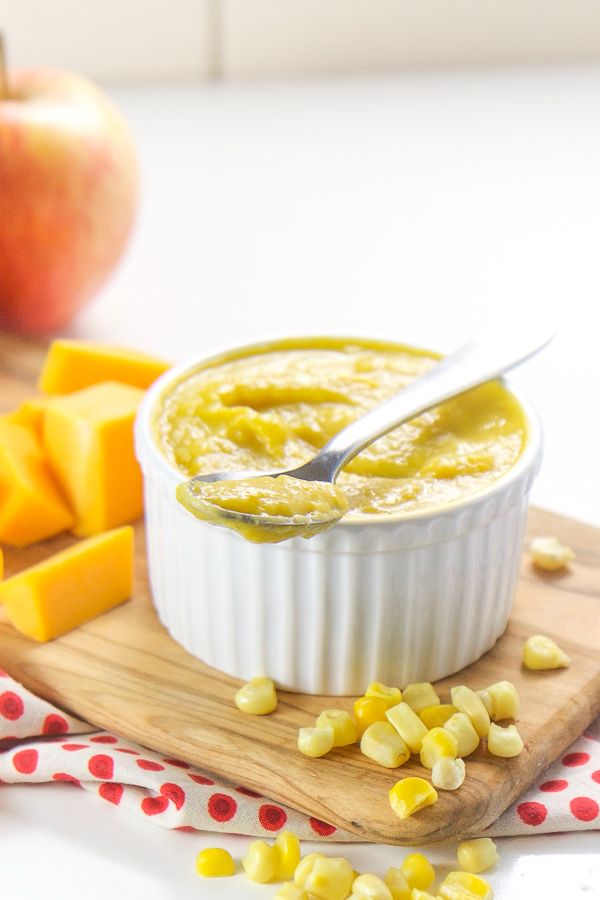
Rule 4 - freedom in everyday nutrition
In terms of everyday nutrition, it is better if children have choice of products. Thus, the problem itself is solved nutritionally balanced flax substances and dietary calories.
Based on long-term observations, it was found that with the presence of freedom of choice, children at the level of intuition or subconsciousness are able to create a menu that will be the best in every respect. adult function here - to orient the child in relation to the correct combination of products.
5 rule - fruit
Children can eat fruits without any restrictions, it is almost impossible to overeat them, and they are very useful. But if the child refuses, no need to force. With a lack of any mineral or vitamin, the child himself will ask he needs an apple or even greens.
It is only necessary to coordinate the combination of fruits with other products. These combination rules are objective for both children and adults. If the products are combined correctly, healthy children will lack gas emission, the stool will be odorless with a normal consistency, the tongue will be red and clean.
6 children's rule nutrition - protein food
Protein food should be given to the child 1-2 times a day for desire, but do not worry if he prefers rice or potatoes instead of cottage cheese or pea porridge. But an excess, like a lack of protein, can lead to unpleasant consequences.
You should not teach a child to sausage, because it unnatural food that deceives the taste organs. From natural products origin, the child should be able to choose from what they eat adults.
7 baby food rule - dairy products
Milk, curdled milk, kefir, yogurt represent makes great food for kids.
 However, they should not be combined with starches. A child at the age of one and a half should not be fed with cereals for milk. The best option is milk and dairy products (room temperature) give as a separate meal. good variation is a combination of cottage cheese with tomatoes (carrots) with kefir, yogurt or milk.
However, they should not be combined with starches. A child at the age of one and a half should not be fed with cereals for milk. The best option is milk and dairy products (room temperature) give as a separate meal. good variation is a combination of cottage cheese with tomatoes (carrots) with kefir, yogurt or milk. 8 baby food rule - sweets
If you feed your child with sweets, then definitely not after eating. Better just give half an hour - an hour before the main meal. As a rule, they always give after.
Sweet is really necessary for the children's body. Sweets natural origin - fruits, honey, dried fruits cover the needs child's body.
In case of painful conditions, reduced immunity, good options will offer him soaked dried fruits, fruits, melons, watermelons and hot drinks. And no more dishes and products. Several of these days month will replenish the resources of the child's body.
9 baby food rule - water
Water should be given as much as how much the child wants. The best is melt water. It is advisable to gradually teach the child to drink a quarter - half a glass of water. after waking up in the morning, 30 minutes before the main meal and before going to bed, in the evening.
10 baby food rule
Children should not be prohibited from playing, running, and especially not worth persuading them to lie down. Because children almost never they eat for the future, unlike adults, do not "jam" their sorrows, boredom and bad mood. And as a result, they don't overeat. Such mobility after eating is not will cause no harm to health.
Responsible under the SPR
E.S. Granchakova
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its administration is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc. ). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can we wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start introducing complementary foods to a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
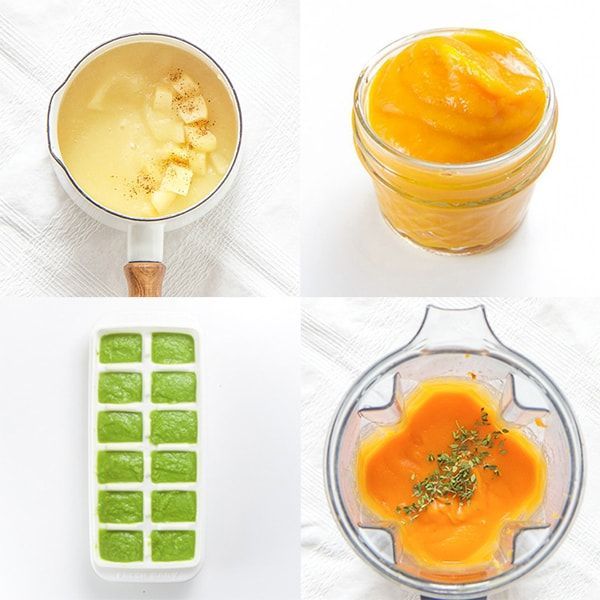
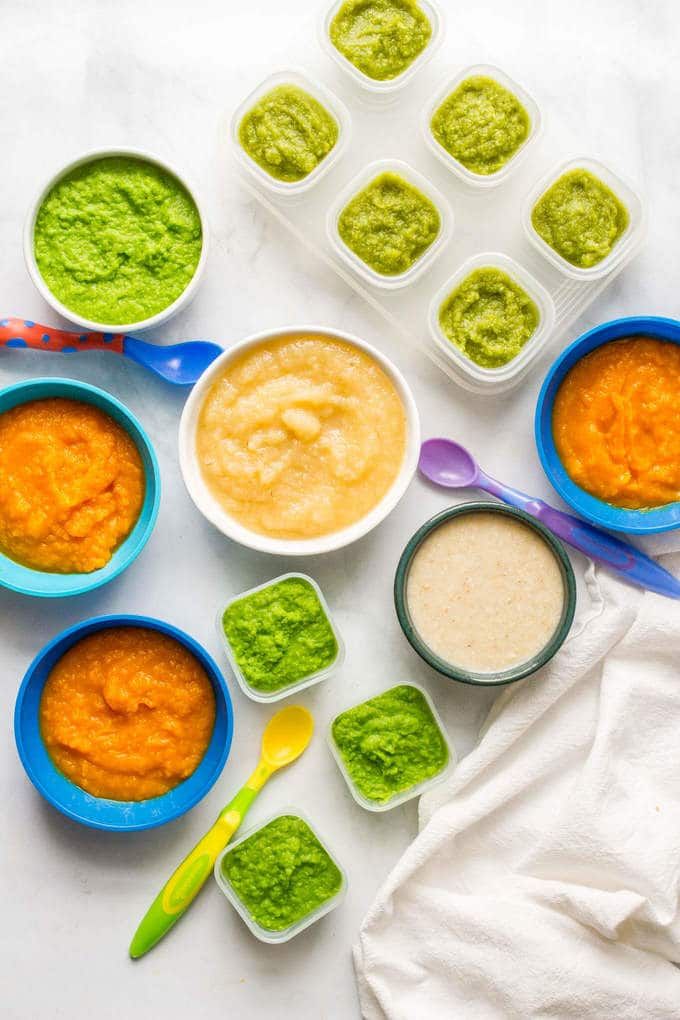
The first complementary foods can be vegetable puree or porridge, it is better to give fruit puree to the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to children's products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, and before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually "dilute" this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml | |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI 
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk 
Learn more











