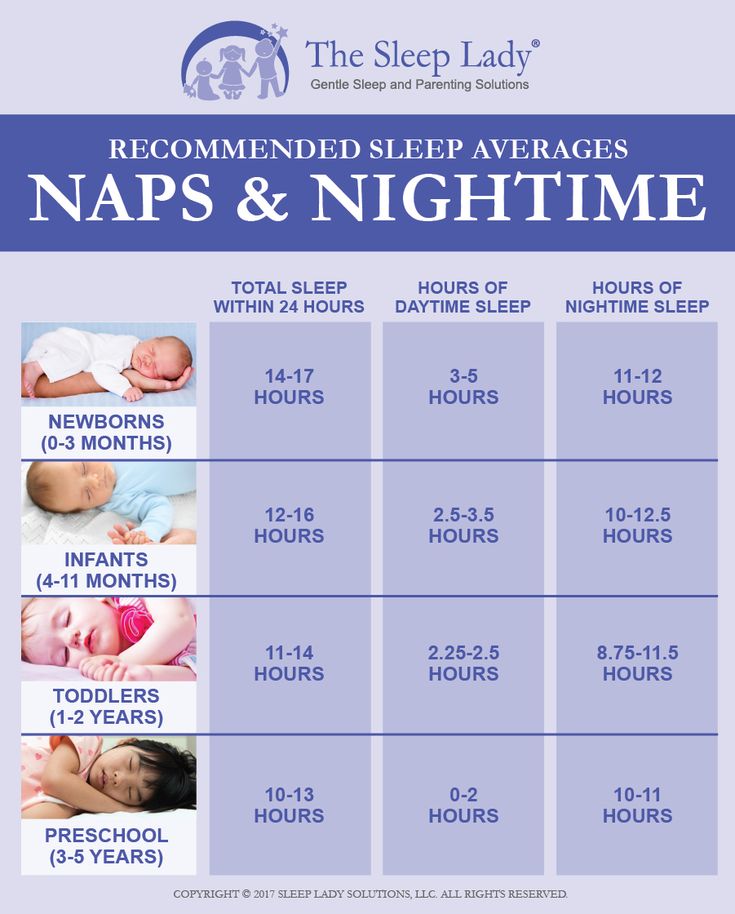
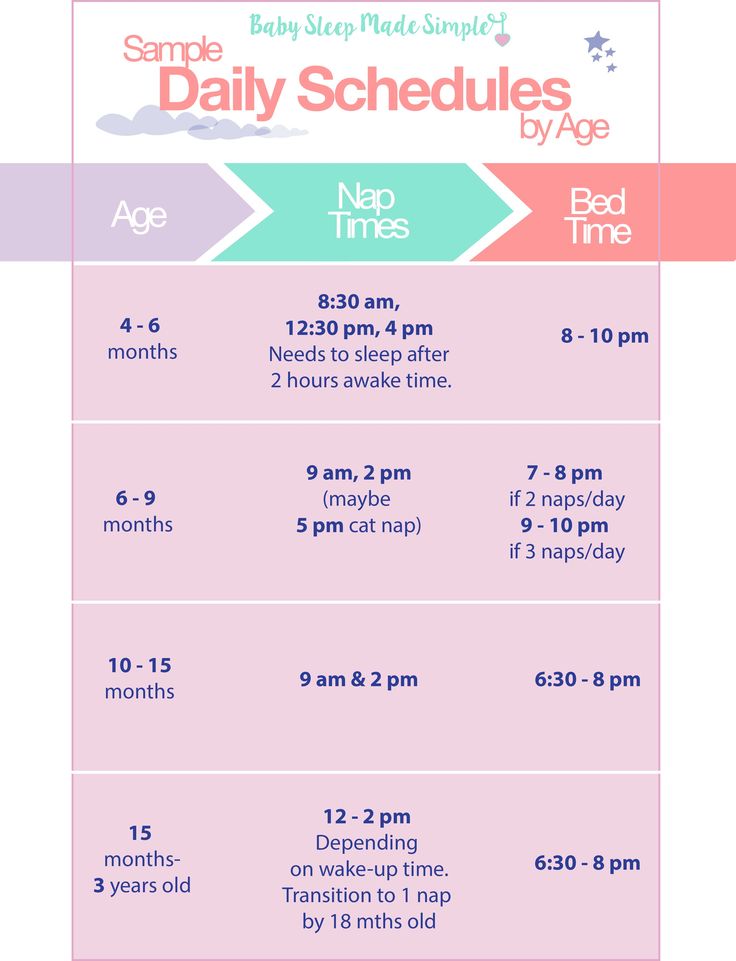
How often should i feed my 7 month old baby solids
7-Month-Old Feeding Schedule: Baby Menu
Breastfeeding helps reduce babies’ risk of being exposed to enteropathogens and decreases the risk of infection (pneumonia, meningitis, bacterial, urinary tract infections, and necrotizing enterocolitis), offers higher levels of immunologic factors, and lowers the risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Children who were breastfed are also less likely to be obese.
Breastfeeding can also benefit the mother’s health. It elevates maternal oxytocin levels, decreases postpartum bleeding, helps the uterus shrink faster, decreases menstrual blood loss, improves bone mineralization, decreases the risk of ovarian and breast cancer, increases mother-baby bonding, and saves on the costs of formula.
After six months, breastfed babies require more energy from iron-rich food sources, fluoride, and around 400 IU/day of vitamin D to continue to grow and develop. While some parents continue breastfeeding their child at seven months, it’s typically a good time to introduce complementary solid foods into a baby’s diet.
Before starting a solid food feeding schedule for a 7-month-old baby, it’s important to be sure they are physically able to eat solid foods. A baby is ready to eat solid foods if they can:
- Sit upright on their own
- Hold their head up unassisted
- Open their mouth when food is presented to them
- Swallow easily
Another good guideline for knowing if a baby is ready to eat solids is if they have doubled their birth weight. This generally indicates that their digestive system is sufficiently developed to process solid foods.
These are just guidelines, and it’s important to speak with the baby’s pediatrician to be sure that they are ready for solid food.
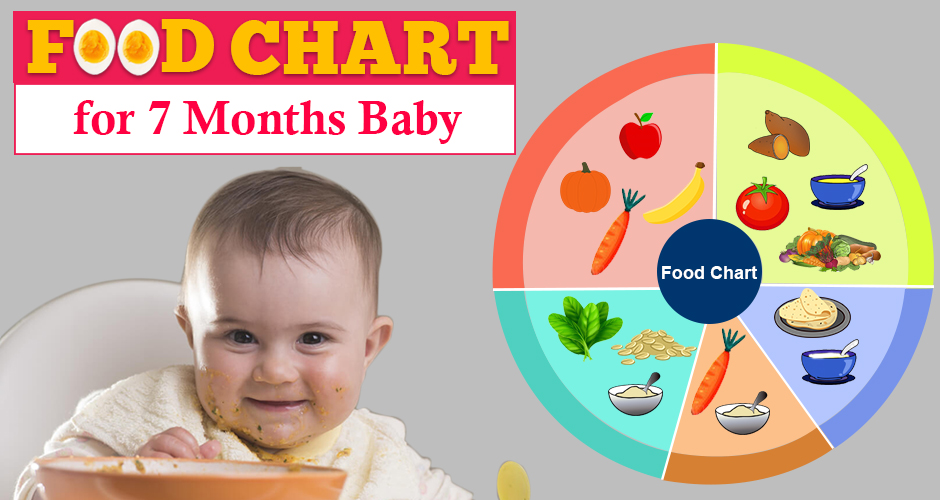
What kinds of solids are best for feeding a 7-month-old? The baby’s food should be as nutritious and unprocessed as possible — and easy to eat. The food should be soft enough for the baby to mash with their gums, as not all of their teeth will have come in by the seventh month. Often, they only have the lower central incisors at this age. At seven months old, boys need about 825 calories per day, and girls need about 765 calories per day.
Often, they only have the lower central incisors at this age. At seven months old, boys need about 825 calories per day, and girls need about 765 calories per day.
Here are some solid foods to try introducing:
- Pureed baby food from a jar or pouch, without added sugar or preservatives
- Cooked mashed foods like potatoes, squash, or carrots
- Whole grain, iron-fortified baby cereals
- Pureed fruits and vegetables (cooked)
- Soft or mashed legumes, such as split peas or lentils
A 7-month-old’s feeding plan should not include:
- Honey, which has been linked with infant botulism (a rare but potentially fatal disease)
- Cow’s milk, which can be difficult to digest and could trigger an allergic reaction
- Hard nuts, small fruits, grapes, gum, and candy, which can be choking hazards
- Processed foods and food with added sugars, as they are unhealthy and can cause indigestion and diarrhea
The baby’s health care provider can advise on what the baby can or can’t eat.
Once the baby begins eating solid foods, they can and should continue to breastfeed or bottle feed stored breast milk or formula. People who are taking certain medications can talk to a health care provider about whether or not it’s safe to breastfeed.
After learning what kinds of foods a baby can try, many parents ask: What is a good feeding schedule for a 7-month-old? We’ve prepared a sample feeding schedule for a 7-month-old baby.
A 7-month-old feeding schedule for a breastfed baby will look slightly different than one for a formula-fed one. Breastfed babies should continue to breastfeed every three to four hours and eat solid food three times per day, as follows:
- Early morning: Breastfeed when the baby first wakes up.
- Morning: Breastfeed the baby just before feeding them a small portion of solid foods (four to six ounces) for breakfast.
- Early afternoon: Breastfeed the baby after their morning nap and before feeding them a small portion of solid foods for lunch.

- Afternoon: Breastfeed the baby before and after their mid-day nap.
- Early evening: Breastfeed the baby before serving them a small portion of solid foods at dinner time.
- Evening: Breastfeed the baby before putting them down to bed.
A 7-month-old baby feeding schedule for formula-fed babies may look a little different. Formula-fed babies should be given 30–32 ounces of formula per day spread over three to five feedings, with solid food given three times per day.
Feeding a 7-month-old baby takes time, patience, and lots of trial and error. These tips can help gradually increase the amount of solid food in a baby’s diet:
- Start small, offering one tablespoon at a time and working up to 12 tablespoons of solid food with each meal, depending on how hungry the baby is.
- Limit finger foods that require more dexterity.
- Try to keep a consistent schedule. Solid foods should be served at the table and fed at regular meal times, like breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
- Introduce new foods individually and about a week apart in order to identify any allergies and intolerance the baby may have. It’s best to introduce foods from most bland to sweetest.
- Offer foods with different textures, like mashed, pureed, ground, and soft solids.
- Start with pureed foods, working up to mashed foods as the baby’s teeth grow and they become more comfortable with chewing.
- Avoid serving hard, round, or sticky foods that could pose a choking hazard. Cut solids into pieces smaller than ½ inch.
Many parents know how challenging it can be to keep to a rigid feeding schedule for a 7-month-old. Many parents find that their babies don’t stick to a typical schedule. Noticing if they lean into the spoon or reach for food on the plate can help determine if they are hungry. If they are, they’ll likely show it.
For more great tips on raising a baby, check out Flo.health.
7- and 8-month-old feeding schedules
How much does your baby need to eat and drink every day – and how can you make sure they're getting all the vitamins and nutrients they need? It can be tricky to find the balance, since 7- to 8-month-olds are eating more solid foods, but still need anywhere from 24 to 32 ounces of breast milk or formula each day. These feeding schedules for 7- and 8-month-olds will help you fit all the pieces of your baby's diet together.
These feeding schedules for 7- and 8-month-olds will help you fit all the pieces of your baby's diet together.
At 7 and 8 months old, your baby is focused on moving more, playing more, and learning more about the world around them. Also big on their to-do list is experiencing new solid foods. Now that they've got the basics of eating down, it's time to start expanding their palate and introducing them to new flavors and textures.
It can be a big help to see what other parents are doing. Below, you'll find several sample schedules modeled on those of real BabyCenter parents and reviewed by a pediatrician on our Medical Advisory Board.
As you're creating a schedule for your baby, here are some things to keep in mind:
- At 7 and 8 months old, babies need solid foods two to three times a day.
- They're still getting most of their nutrients from breast milk or formula, though. A formula-fed baby will drink about 24 to 32 ounces of breast milk or formula in a 24-hour period.
- At 7 months old, your formula-fed baby will most likely drink 6- to 8-ounce bottles three to five times a day. By the time they're 8 months old, they'll have three or four bottles per day. (Here's how to tell whether your baby is getting enough formula.)
- Breastfed babies also need about 24 to 32 ounces of breast milk daily, though it'll likely be on the lower end of that range. Your baby will most likely nurse three to five times a day at 7 and 8 months old. (Here's how to tell whether your baby is getting enough breast milk.)
Now's the time to start increasing the amount and variety of your baby's foods and to introduce finger foods and perhaps a sippy cup. If you're baby-led weaning, your baby is already familiar with finger foods but may be ready for you to expand their menu.
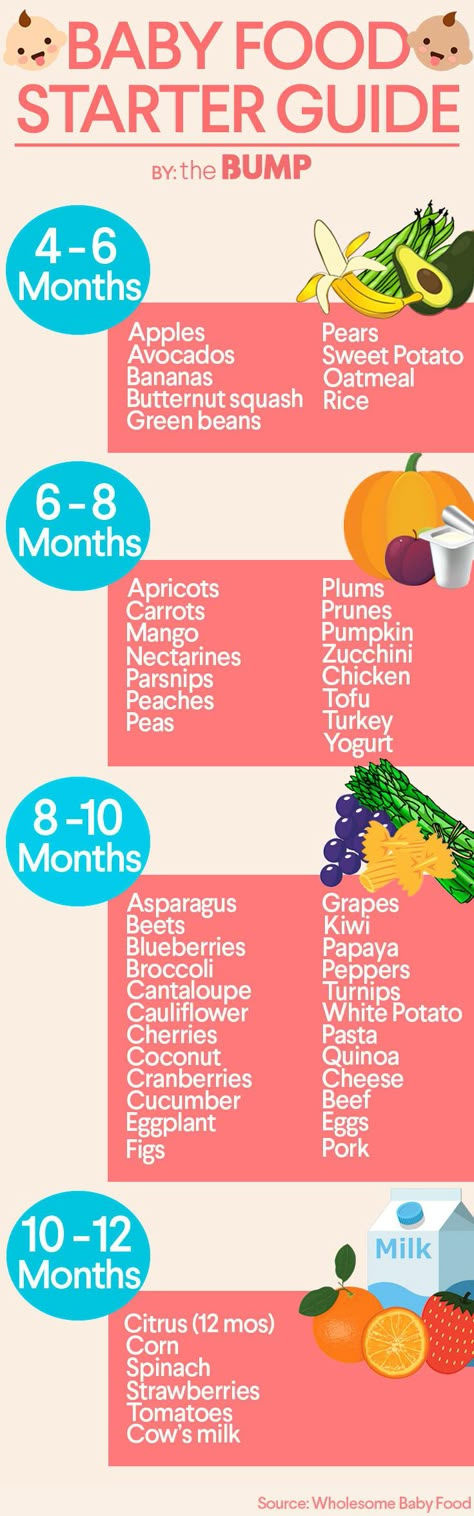
If you started with easy-to-eat foods like avocado, banana, and applesauce, you can start encouraging your baby to get a bit more adventurous. In fact, you can work on incorporating foods from the major food groups, offering bits of shredded chicken or fish, yogurt and pieces of cheese, soft fruits and veggies, and whole grains in the form of hot or cold cereal.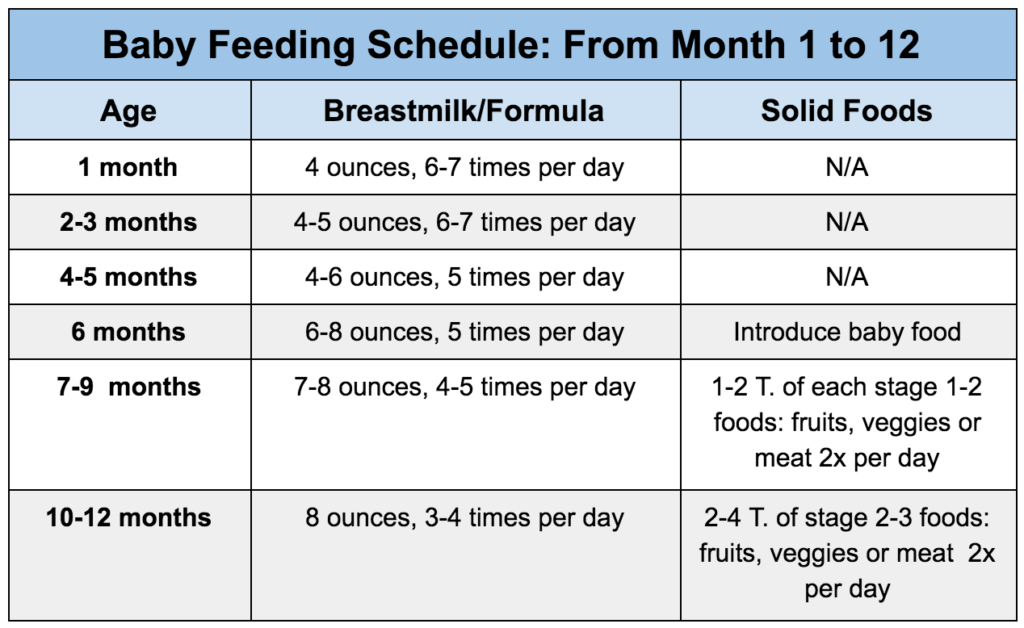
Also, talk to your pediatrician about the best way to introduce high-allergy foods such as peanuts, tree nuts, egg, wheat, soy, dairy, fish, shellfish, and sesame.
Keep in mind, though, that your baby's tummy is still on the small side, so they'll only eat a little bit of food at each meal. You can aim for 1 to 3 tablespoons of grains, fruits, veggies, and proteins per meal, and slowly increase that amount over the next few months.
Advertisement | page continues below
Sample 7-month-old feeding schedule
7 a.m.: Nurses.
8 a.m.: Breakfast – 3 tablespoons of baby cereal mixed with 2 ounces of breast milk, plus some pureed fruit.
8:45 a.m.: Playtime.
9:30 a.m.: Naptime.
11 a.m.: Nurses, then playtime.
11:45 a.m.: Naptime again.
12:30 p.m.: Lunch – 3 tablespoons of baby cereal mixed with 2 ounces of breast milk, some pureed fruit, and water in a sippy cup.
2 p.m.: Naptime.
3 p.m.: Nurses.
3:15 p.m.: Playtime.
5 p.m.: Dinner – 3 tablespoons of cereal mixed with 2 ounces of breast milk, some pureed veggies, and water in a sippy cup.
6:30 p.m.: Bath time.
7:15 p.m.: Nurses.
7:30 p.m.: Bedtime.
Sample 8-month-old feeding schedule
7 a.m.: 8-ounce bottle, then playtime.
8 a.m.: Breakfast – a pouch or jar of fruit.
9 a.m.: Playtime.
10 a.m.: 6-ounce bottle and nap time.
12:30 p.m.: Lunch – a pouch of meat and veggies.
1 p.m.: Playtime outside.
2 p.m.: 6-ounce bottle and naptime.
5 p.m.: 4-ounce bottle, then playtime.
6 p.m.: Dinner – half a jar of veggies and a half jar of fruit.
6:30 p.m.: Playtime.
7:15 p.m.: Bedtime routine, 8-ounce bottle, then bedtime.
Meal ideas for 7- and 8-month-olds
Not sure how to get started planning nutritious meals for your baby? You can follow the rule of four: give your baby one serving each of protein, carbohydrates, fruits, and veggies. If you're not sure how much to feed your baby, check out our visual guide.
Here are some simple things you can serve your 7- to 8-month-old.
Breakfast:
- Yogurt with pureed fruit
- Mashed sweet potatoes
- O-shaped cereal
- Baby oatmeal
- Cottage cheese with pureed fruit
- Scrambled eggs
Lunch:
- Mashed black beans
- Pureed chicken
- Ground beef and pureed veggies
- Lentils
- Turkey and zucchini puree
- Whole-grain crackers with a thin smear of peanut butter
- Mashed banana with Greek yogurt
Dinner:
- Pureed beef with steamed peas
- Small pieces of whole grain bread with mashed avocado
- Shredded turkey
- Whole-grain pasta with tomato sauce
Learn more:
- Your 7-month-old's growth and development
- Your 8-month-old's growth and development
- Recipes for babies 6 to 12 months old
- Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Baby menu at seven months
0-6 months
Article
5/5 1 reviews
What should be the menu of a child at 7 months? What foods and in what quantity can be introduced into the diet at this age? When and at what intervals to give the baby to eat? We will help develop an approximate menu for a 7-month-old baby and answer the most exciting questions regarding the nutrition of a baby up to a year old.
7 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
Contents
- Diet: when and how much should a child eat at 7 months
- Baby menu at 7 months: introducing new products
- Consistency of dishes
- Meal schedule and approximate daily menu
- Sample diet for a 7 month old baby allergic to cow's milk proteins: Table
- FAQ
- Breastfeed every 3-4 hours while breastfeeding.
- If you give your baby expressed breast milk, he needs approximately 710 grams per day. With 5-6 meals a day, this is about 120 to 200 grams of milk per meal.
- If the baby is formula-fed (FW), he needs 170 to 230 grams of formula up to 4 times a day, provided that 2 more feedings replace complementary foods. To find out how much mixture you need, be guided by the instructions on the package, the recommendations of the pediatrician.

- From the age of 6 months, only mother's milk or adapted infant formula is not enough for a baby - he needs a variety of complementary foods. Introduce no more than one new product per day into the child’s menu at 7 months and consult a pediatrician first. After getting acquainted with different foods, up to three complementary foods can be given daily: this can be one or two tablespoons or 115-170 grams (8-12 tablespoons), depending on the baby and the specific product.
Important
The calculation of portions and the number of feedings depends on the individual characteristics of the development and needs of the child. Therefore, first of all, be guided by the recommendations of your pediatrician and the needs of the baby.
Baby menu at 7 months: introducing new products
The basis of the diet is still breast milk or infant formula. To diversify the menu, children's adapted food will help: fruit and vegetable purees, milk and dairy-free cereals, juices, as well as some products from the "adult table".
Cereals
At 7 months, dairy-free and milk porridges, along with breast milk, are the basis of a child's nutrition. To start complementary foods, choose gluten-free liquid one-component cereals with a high iron content: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal. A little later - corn and semolina. Start complementary foods with half or a whole teaspoon, gradually increasing the serving to 150 grams.
Important
Dairy-free porridge is diluted with breast milk or milk formula, milk - with purified boiled water.
Find out more: Gerber® Baby Cereals: product range
Vegetable and fruit purees
Vegetable and fruit purees diversify the diet and introduce new tastes to the baby. According to WHO recommendations, the best product to start with is a one-component vegetable puree made from zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower or potatoes. These vegetables are less allergenic than other foods. If the child does not have allergies, pumpkin, carrot, pea and tomato puree can be given a little later.
Find out more: Gerber® Vegetable Purees
After introducing vegetable purees into your diet, it's time for your baby to get to know sweet and healthy fruit purees. Like vegetable, fruit complementary foods are also recommended to start with one-component low-allergenic foods. Apple, pear or banana puree is best for this. Start with half or a whole teaspoon and gradually increase the serving to 100-150 grams.
Find out more: Gerber® fruit purees
Meat
Meat is a developmentally necessary product, rich in iron and protein, which is well absorbed in the body. Start with homogenized options. The product must contain only one type of meat (diet turkey, rabbit, chicken, veal) and no additional components. If the crumbs have a tendency to food allergies, choose meat very carefully, it is better to consult a doctor in advance. Pay attention to the composition of baby food and its age-appropriate baby.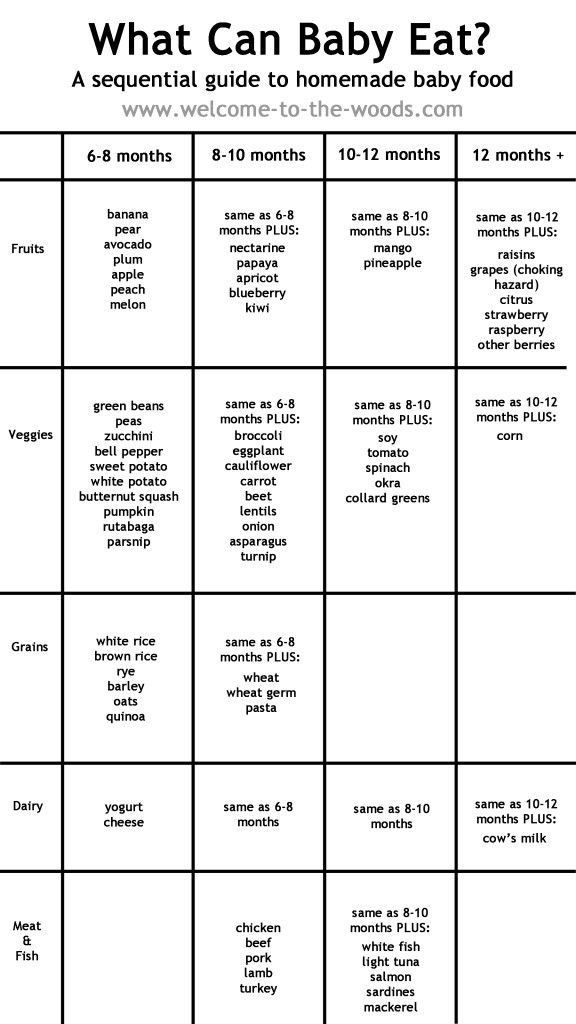 First, let the baby try half a teaspoon. If no adverse reactions occur, gradually increase the meat rate to 60 grams.
First, let the baby try half a teaspoon. If no adverse reactions occur, gradually increase the meat rate to 60 grams.
Find out more: Gerber® Meat Purees
Juices
Fruit juice is great for snacking and menu variety. Young children tolerate clarified apple and pear juice better, so they should be introduced first. Give the baby adapted baby juices: they do not contain sugar or other additives undesirable for the child. Ordinary store-bought juices can only be drunk by children over three years old.
See also: What kind of juice to start complementary foods for babies
Advice
Introduce your baby to juices after introducing cereals and vegetable purees. Often the child gets used to sweet juices and then does not eat foods with a less bright taste.
Egg yolk
In addition to cereals and mashed potatoes, boiled egg yolk is introduced at the age of 7 months, as it is an excellent source of omega-fats, selenium, phosphorus and vitamins.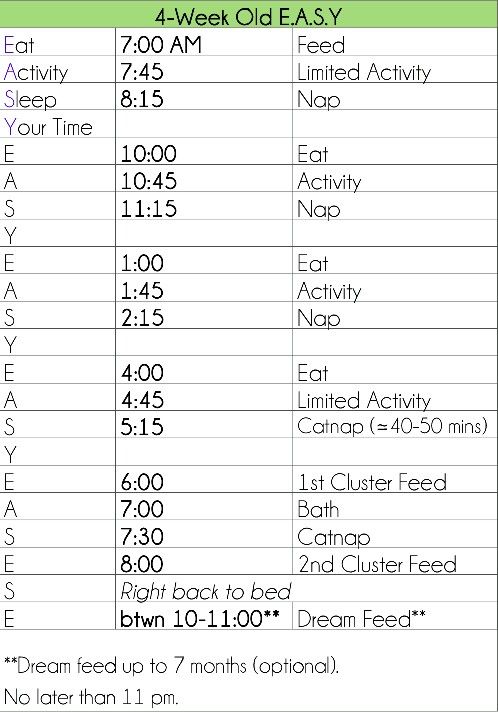 Please note that you need to give the egg not the whole, but only the yolk. But, like any other product that you give to try for the first time, it should be introduced carefully and little by little to make sure that the baby does not have an allergy. Do not combine with other food! Only when you "test" the yolk, it is allowed to add it to cereals and vegetable purees.
Please note that you need to give the egg not the whole, but only the yolk. But, like any other product that you give to try for the first time, it should be introduced carefully and little by little to make sure that the baby does not have an allergy. Do not combine with other food! Only when you "test" the yolk, it is allowed to add it to cereals and vegetable purees.
Important
It is believed that children with allergies can be fed quail eggs. But it is important to remember that quail eggs can also be allergic, as they also contain egg white - an allergen that is found in chicken eggs. Therefore, do not experiment, but seek the advice of a pediatrician.
See also: Introduction of complementary foods to children with food allergies
Baby biscuits and crackers
Some babies start teething at seven months. Therefore, you can add crackers and children's cookies to food.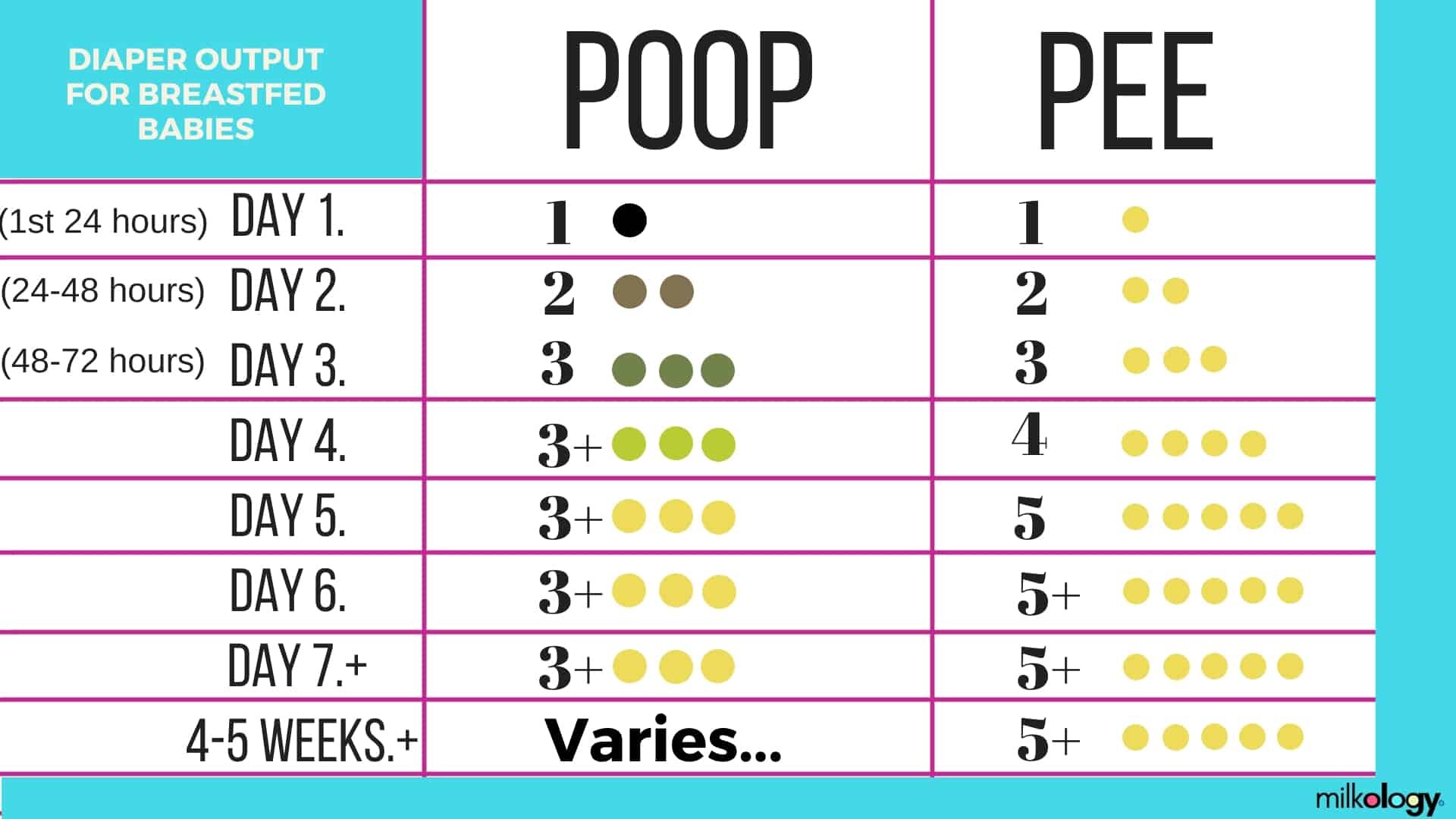 But do not forget that they should not be too hard so that the child does not get hurt and choke. It is also better to choose special products without added salt, sugar, synthetic leavening agents and preservatives.
But do not forget that they should not be too hard so that the child does not get hurt and choke. It is also better to choose special products without added salt, sugar, synthetic leavening agents and preservatives.
Important
The child should eat solid food in a sitting position and strictly under adult supervision.
Consistency of dishes
The main component of the diet remains liquid and homogeneous (without lumps) - breast milk or milk formula, milk and dairy-free cereals. As the baby grows, the baby's food should change from liquid and homogeneous to thicker and puree, mashed. When the body adapts and is able to digest solid food, they begin to carefully introduce small, medium and coarsely ground foods, give children's cookies and crackers. At 7 months, some babies already have teeth, but the child cannot yet chew thoroughly and safely swallow vegetables, fruits and meat. Therefore, solid food should be given only in a grated form. It is important that the puree is not too thick, otherwise the child may accidentally choke.
It is important that the puree is not too thick, otherwise the child may accidentally choke.
Advice
If you are making puree yourself, carefully remove everything that is not rubbed and can get into the crumbs' respiratory tract: bones, fat, veins, skin, films. To make the puree easier to swallow, add some boiled water, unsalted vegetable broth, vegetable puree already familiar to the baby, or breast milk (milk mixture).
By about 7 months of age, the baby has mastered the skill of "palm grip" and can independently hold solid food in the handle. From now on, you can give your child special baby cookies or snacks. At the same time, make sure that the baby eats slowly, in a sitting position and does not choke.
Important
Baby should be ready to eat more sticky or solid foods. Therefore, before changing the consistency of food for a child, consult a pediatrician.
What can be given to children at 7 months and at what time to feed? Parents can begin to form a classic division of food consumption per day.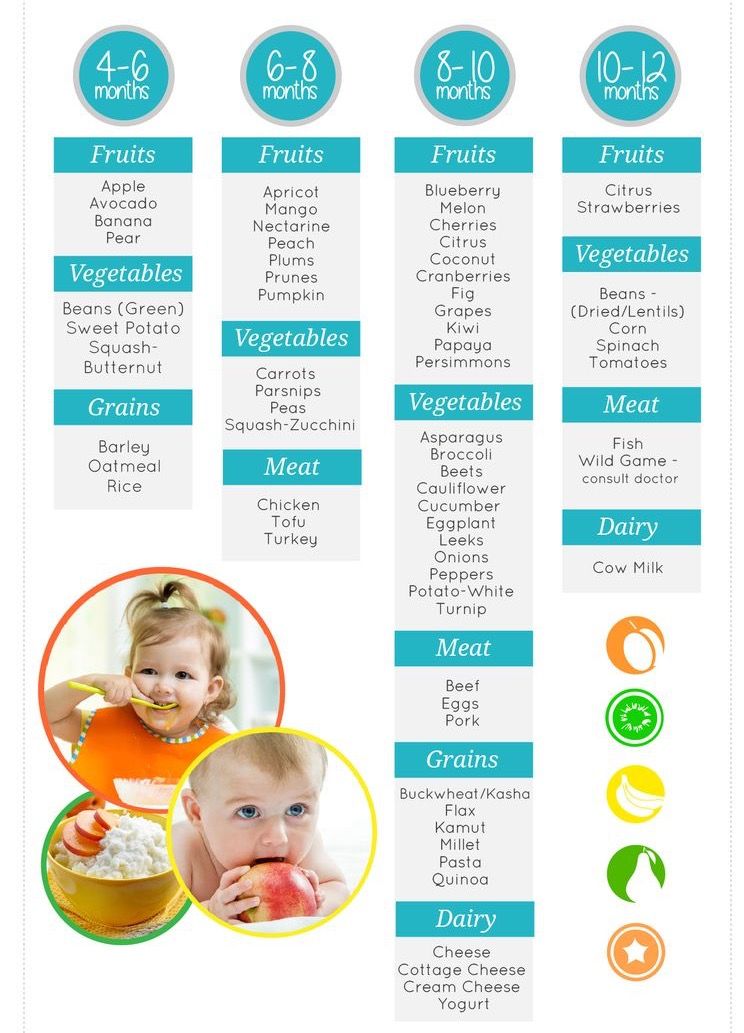 But at 7 months, the baby needs to be fed not three or four, but five times a day at intervals of four hours. The first and final feeding is mother's milk or formula. Complementary foods are not given at this time in order to prevent overeating.
But at 7 months, the baby needs to be fed not three or four, but five times a day at intervals of four hours. The first and final feeding is mother's milk or formula. Complementary foods are not given at this time in order to prevent overeating.
*Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or infant formula given to the baby. Milk porridge is diluted with water.
Tip
Do not salt or sweeten food. It is better to introduce the baby to sugar and salt after a year.
| Feeding time | Products | Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Nestle® Dairy-Free Rice Porridge* | 130 g |
| Vegetable oil (add to food) | about 1 tsp | |
| Gerber® Apple or Williams Pears Fruit Puree | 70 g | |
| III feeding 14 hours | Gerber® Vegetable Puree Broccoli, Cauliflower | 170 g |
| Vegetable oil (add to food) | about 1 tsp | |
| Gerber® Meat Puree Tender Vegetables with Rabbit | 30 g | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge** | 170 g |
| Vegetable oil (add to food) | about 1 tsp | |
| Gerber® Tender Turkey Meat Puree | 20 g | |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
*Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or formula for infants with intolerance to cow's milk proteins. **you can either alternate porridge or vegetables, or offer a mixed dish - porridge with vegetables.
**you can either alternate porridge or vegetables, or offer a mixed dish - porridge with vegetables.
Now you know what products and in what form can be introduced into the child's menu at 7 months. It is preferable if it is certified baby food that meets all age requirements and high safety standards.
See also: Do we cook ourselves or use baby food?
1. At what age should complementary foods start?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends introducing complementary foods to your baby's menu at 6 months of age.
2. Where to start complementary foods?
Experts advise starting complementary foods with one-component homogenized vegetable purees.
3. How much should a 7-month-old baby eat?
At 7 months, a baby needs a portion of food per day, which is equal to about ⅛ of body weight. This is 1000-1200 ml of food, excluding water, juices, children's tea. Divide this amount by 5 feedings and you will get an estimated amount of food per meal - 200-210 ml.
Divide this amount by 5 feedings and you will get an estimated amount of food per meal - 200-210 ml.
Articles on the topic:
Baby refuses new foods
Eating right and without mistakes
Introduction of complementary foods to an infant
Latest reviews
Average customer rating
1 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- 5 1
- 4 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- 1 0
Breastfeeding after 1 month: what to expect
Do you know when breast milk production stabilizes? And how does the frequency and duration of feedings change as the baby grows? You will find answers to these questions in our recommendations for breastfeeding after the first month.
Share this information
Congratulations: You made it through the first month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production is stabilizing, and there is little or no leakage from the breast. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production is stabilizing, and there is little or no leakage from the breast. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
When does breastfeeding decrease?
The "normal" feeding frequency for babies aged one to six months varies considerably, with some needing four times a day, others asking to be breastfed 13 times a day. 3
“From the age of one month, the amount of milk a baby consumes per feeding increases so that he can go without food for longer,” explains Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding, “A baby’s stomach grows, so he eat more at one time.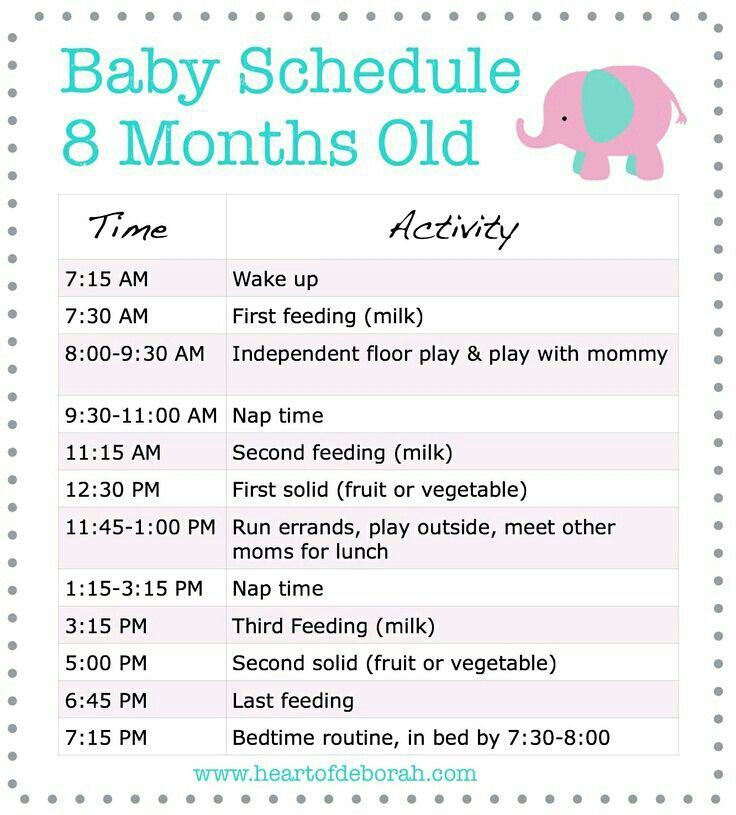 In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.”
In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.”
Feeding can last from 12 minutes to one hour -
the habits of babies vary so much! 3 But if the child is gaining weight and falls within this range, there is no cause for concern.
What is most surprising, no matter how often the baby eats, he consumes approximately the same amount of milk per day - both at one month and at six, when it is time to start complementary foods with solid food. 4
“However, sometimes the baby eats more and sometimes less, especially when he is unwell. It’s better to just listen to his needs,” Katie explains.
Is breast milk enough for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk contains everything a baby needs for the first 90,371 six months of life—exclusively breastfed babies don't even need to drink more water! 5 Until about six months of age, the child's digestive system is simply not adapted to the digestion of solid food, and he will be able to drink cow's milk only after a year.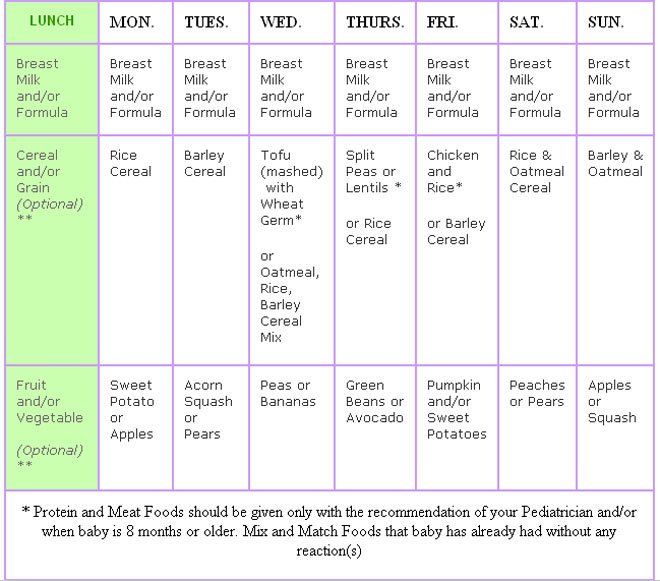
In addition, breastfeeding during this period prepares the child for further development. It strengthens the muscles of the mouth, develops the jaw and helps straighten the teeth 6.7 . All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
In addition, when your baby is sick, your body produces breast milk that is
rich in antibodies that help fight infection. 9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as he grows and becomes more active.
Breastfeeding is also very comfortable once you get used to it. Claudia, a mother of two from the UK, notes: “No need to sterilize a mountain of bottles, prepare formula, carry it all with you, warm it up - in general, breastfeeding turned out to be very convenient, especially when my babies grew up and we began to leave the house more often.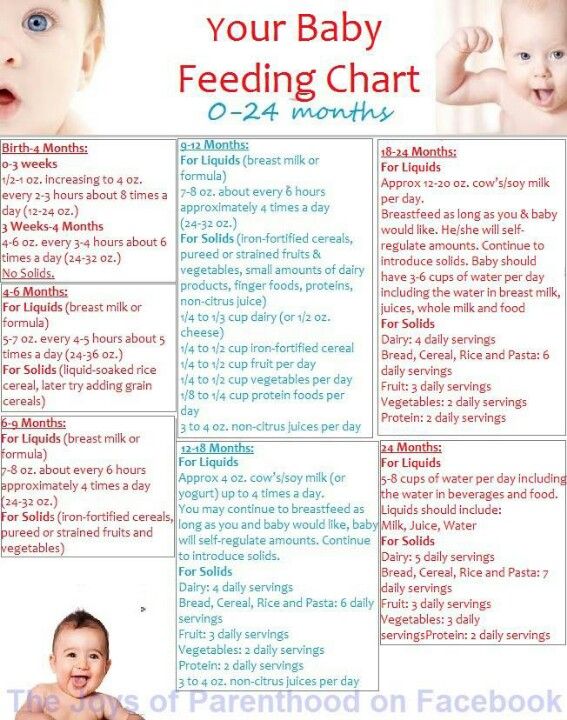 ".
".
At what age does a breastfed baby start sleeping through the night?
Waking up at night is normal for babies. Most babies between the ages of one and six months consume a fifth of their daily milk requirement at night, so nighttime feedings should not be neglected if you want your baby to get the required amount of calories. 3
“It really depends on what you mean by ‘sleep through the night,’” says Cathy. "And it's better than waking up every two hours anyway! I have met infants who, starting at six weeks old, fell asleep at 19:00 and woke up at 7:00, but most continue to wake up frequently at night after this age. All children are different."
In Wales, a study of more than 700 infants showed that almost 80% of children aged 6 to 12 months wake up at least once a night, and 25% of them wake up three times or more. And it did not depend on what type of feeding the child is on - breastfeeding or artificial. 10
And if nighttime awakenings are unavoidable anyway, breastfeeding is at least comfortable! Maina, a mother of two from Australia, agrees: “You can even take a nap while feeding in the middle of the night - both the body and the baby do their job on autopilot.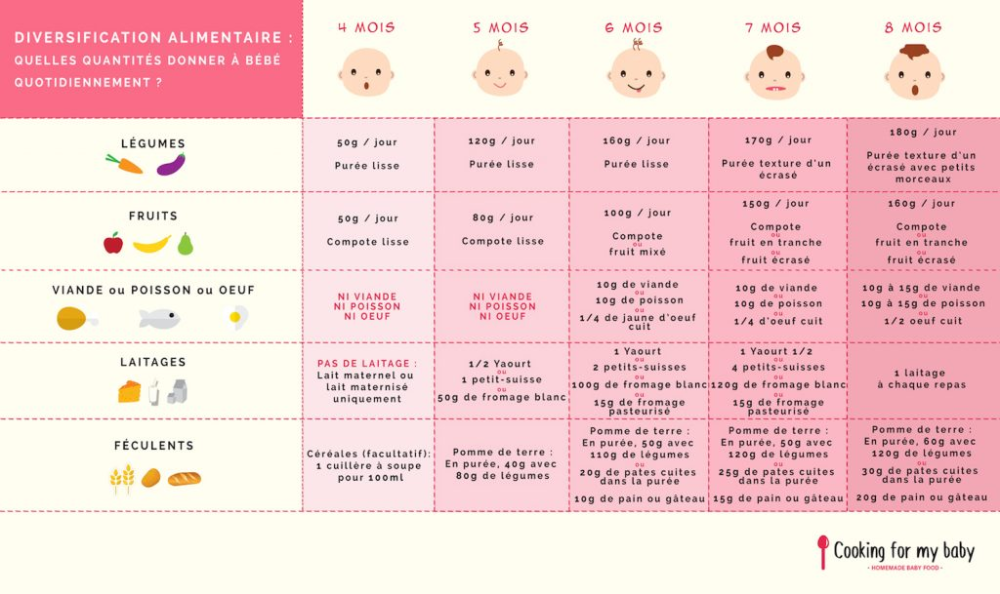 No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
My child wakes up more often. Perhaps he is hungry?
Around four months of age, a baby's sleep pattern changes as he, like an adult, develops deep and light sleep phases. Because of this, he may wake up more often at night. “At four months, sleep is more of a problem than feeding,” Cathy admits. “It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.”
Some people call this " a four-month sleep regression ", but "progress" is more appropriate here. From the outside it may look like a step back, but in fact the child is approaching an important stage of development. He learns quickly, begins to become aware of the world around him, his perception is sharpened and, perhaps, there is anxiety about being separated from his mother. Crying when waking up and being able to eat milk cuddled up to mommy’s chest is a way for a baby to calm down.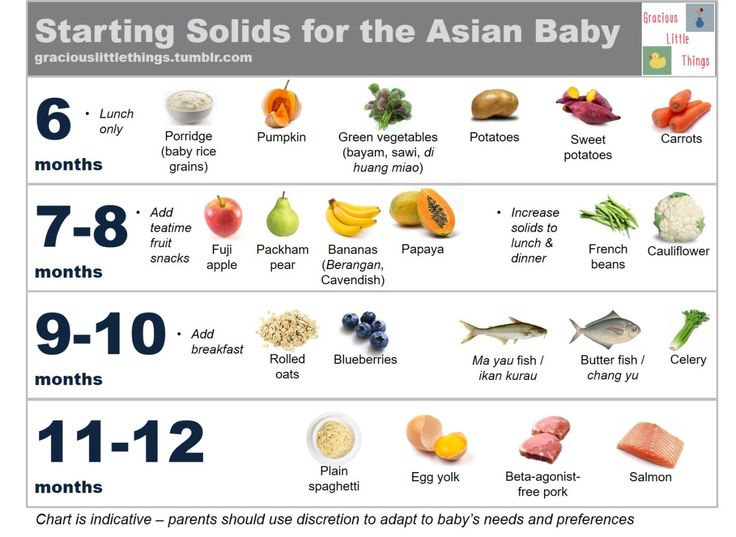 11–13
11–13
Resist the urge to “supplement” your baby with formula or start solid foods early
in an attempt to improve his sleep. Breast milk contains
hormones that make you sleepy and help you both relax
. Research shows that breastfeeding mothers actually sleep longer at night than mothers of formula-fed or mixed-fed babies
. 14
How does teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething usually begins around four months of age. When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
However, breastfeeding can be an excellent sedative.
Studies have shown that babies who are breastfed
during the vaccination period cry less and forget pain more quickly. 15 Breastfeeding while teething can have the same calming effect.
An unpleasant side effect may be the child's attempts to try out his new teeth on the mother's breast. “Sometimes children flirt and bite their mother’s nipples.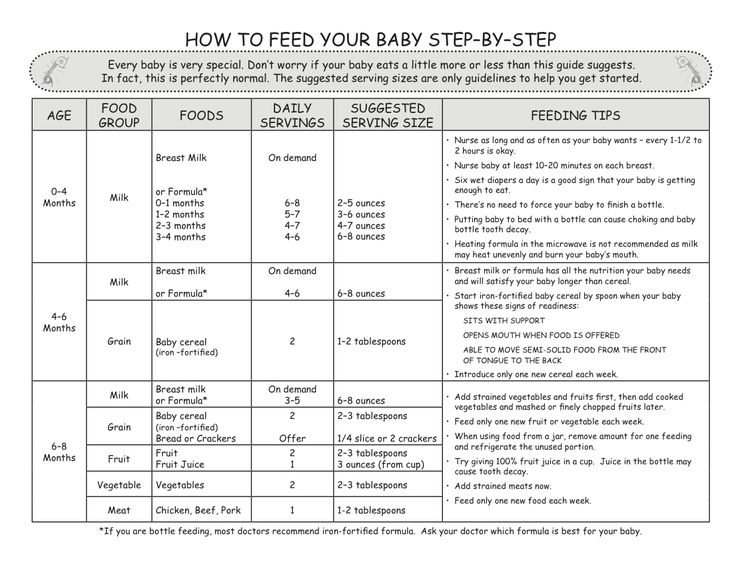 This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
How to continue feeding if you have to be separated from the baby?
It happens that during the first six months, when the baby is still fully breastfed, the mother needs to be away for several hours - or even longer if she has to go to work or go away on business for a couple of days.
But this does not mean that you should stop breastfeeding. You can still feed your baby healthy breast milk - just express it and have someone give it to your baby when you're away. Here's Katie's advice:
“Start expressing milk a couple of days in advance, in small batches, 40-60 ml at a time. So you will have the necessary supply for the time of your absence, but at the same time the amount of milk produced will remain the same.
If you have to return to work, check with your employer about your daily schedule. Many mothers breastfeed their babies in the morning, evening and night, and pump milk at lunchtime to relieve discomfort and create a reserve for the next day.
This usually turns out to be much easier than one might think, and today many companies are well placed to do this, notes Cathy. “Breast pumps make it easy to solve this problem.”
Natalie, mother from the USA, shares her experience: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes up, and sometimes again before leaving for work, in order to maintain milk production and not lose contact with the child. At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding."
Can breastfeeding continue after the introduction of solid foods?
When your baby begins to show interest in food and can sit up on his own - usually around six months of age - it's time to start solid foods. However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
Start complementary foods with solid foods, but remember that breast milk remains a more important source of calories and nutrients until the baby is eight to nine months old. By this time, he will be eating much more solid food, but he will still need to breastfeed four to five times a day. By 12 months, the frequency of feeding may be two to six times a day. All babies are different, and many of them at this age are still getting half their daily calorie intake from breast milk.”
Don't forget that breast milk can be added to solid foods, such as cereals and purees, so that the baby can taste the familiar taste. If possible, use milk expressed just before feeding (not thawed) and add just before serving to keep bacteria and nutrients alive. 16
You may be pressured by others to stop breastfeeding when your baby is six months old, but the longer you breastfeed or pump, the better for you and your baby.
How long can I continue breastfeeding?
“The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding along with solid foods until at least two years of age because it plays an important role in supporting immunity,” says Cathy. feels bad".
At eight months, the baby sometimes breastfeeds four times a day, but by one year old, the frequency of feedings can be reduced to two times a day. You yourself will understand which feeding regimen is more suitable for you and your baby. For example, Jane, a mother of two from the US, breastfed until the age of two: “I breastfed when I was at home - in the evenings and on weekends, when the children wanted to be close to me,” says Jane, “It helped a lot when they were sick . Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort."
“When my son got a little older and bolder, he still often asked me to breastfeed him - as if to calm down and gain strength,” recalls Amy, a mother of two children from Canada, “When he happened to hit or skin his knee , breastfeeding was a wonderful way to comfort him. ”
”
If your baby is over a year old and you are still breastfeeding, people around you will probably tell you that this way he will never wean. But if children are not pressured, they usually refuse to breastfeed themselves between the ages of two and four. 17
“I didn’t intend to breastfeed for so long, but as a result, I still breastfeed my four-year-old daughter and 22-month-old son,” says Suzanne, mother of two from the UK, “I breastfeed my youngest before and after work, and in I express milk on business trips. The eldest daughter likes to breastfeed a little before bed or when she is upset - this is a great way to make contact. When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.”
For more information on what to expect and lots of tips and tricks, see our guide Breastfeeding Problems After the First Month.
Literature
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-21. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol and Neonatal Nurse. 2012;41(1):114-121.
3 Kent JC Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
2006;117(3):e387-95.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans 9 Trop Med Hy1g 1990;84(4):602-604. - Elmroth S., Bidinger P.D., "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
6 Victora CG et al . Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104( S 467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition influences the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb] - All about baby sleep. [Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018].
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - The science of baby sleep. [Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay ; December 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - "The Myth of Baby Sleep Regression - What's Really Happening to Your Baby?" [Internet]. Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
14 Kendall - Tackett 0 al . The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression.