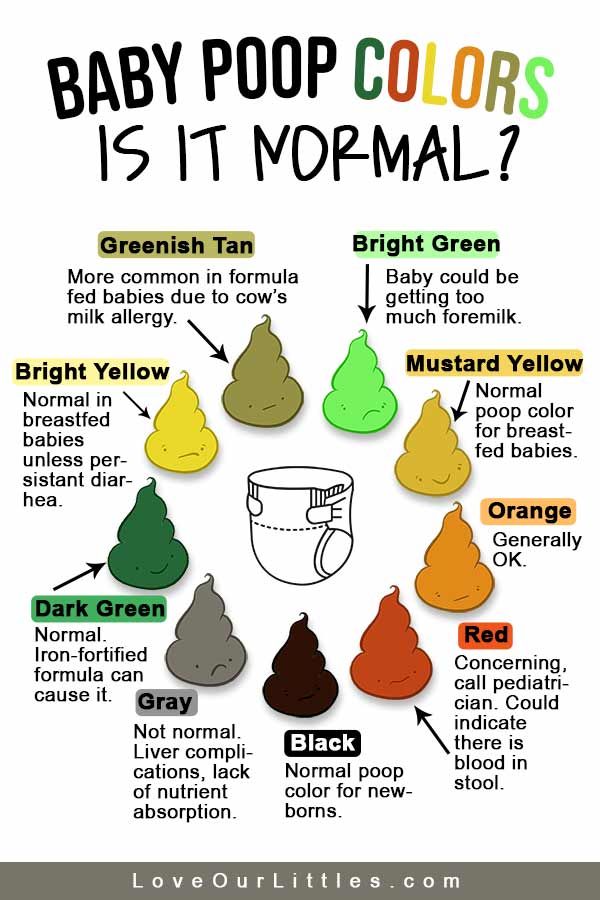
How often to feed formula fed baby
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development.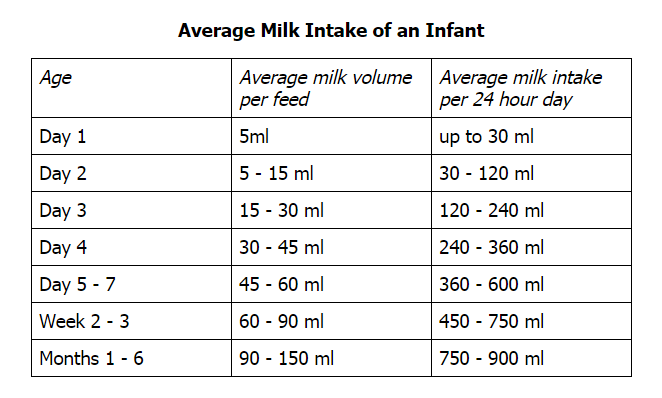 Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Feeding Your Newborn (for Parents)
How you feed your newborn is the first nutrition decision you make for your child. These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
Breast or Bottle?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for about the first 6 months. After they start on solid foods, babies should breastfeed through the first year of life and even beyond, if desired.
But breastfeeding isn't possible or preferable for all new moms. Deciding to breastfeed or bottle feed a baby is usually based on the mother's comfort level with breastfeeding and her lifestyle. In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
Remember, your baby's nutritional and emotional needs will be met whether you choose to breastfeed or formula feed.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding your newborn has many benefits. Perhaps most important, breast milk is the perfect food for a baby's digestive system. It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
Breast milk has
antibodiesthat help protect babies from many infections, including diarrhea and ear and lung infections. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop medical problems such as diabetes, high cholesterol, asthma, and allergies. Breastfeeding also might make a child less likely to become overweight.
Breastfeeding is great for moms too. It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Some moms find breastfeeding easier and quicker than formula feeding — it needs no preparation, and you don't run out of breast milk in the middle of the night. Also, breastfeeding costs little. Nursing mothers do need to eat more and may want to buy nursing bras and pads, a breast pump, or other equipment. But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
Breastfeeding meets a variety of emotional needs for both moms and babies. The skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection, and providing complete nourishment can help new moms feel confident in their ability to care for their newborn.
Limitations of Breastfeeding
With all the good things known about breastfeeding, why doesn't every mother choose to breastfeed?
Breastfeeding requires a big commitment from a mother. Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new mothers need to get back to work outside the home or separate from their babies from time to time for other reasons. Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Fathers and other family members may want to share in feeding the baby. When mom is breastfeeding, dad or siblings may want to stay close by. Helping mom get comfortable, or providing a burp cloth when needed, will let them be part of the experience.
When breastfeeding is going well, other family members can help by giving the baby pumped breast milk in a bottle when mom needs a break.
Some moms may feel embarrassed or worried about breastfeeding. These feelings usually end after a successful breastfeeding process is set. It can help to get advice from those who've gone through the experience. Most hospitals and birthing centers offer in-depth instruction on breastfeeding to new moms. Your pediatrician, nurse practitioner, or nurse can answer questions or put you in touch with a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.
In some cases, a mother's health may affect her ability to breastfeed. Moms getting chemotherapy for cancer and those who have HIV should not breastfeed, for example.
If you have a medical condition or take any medicines regularly, talk with your doctor about whether it's OK to breastfeed. If you have to stop nursing temporarily, continue to pump breast milk to maintain milk production.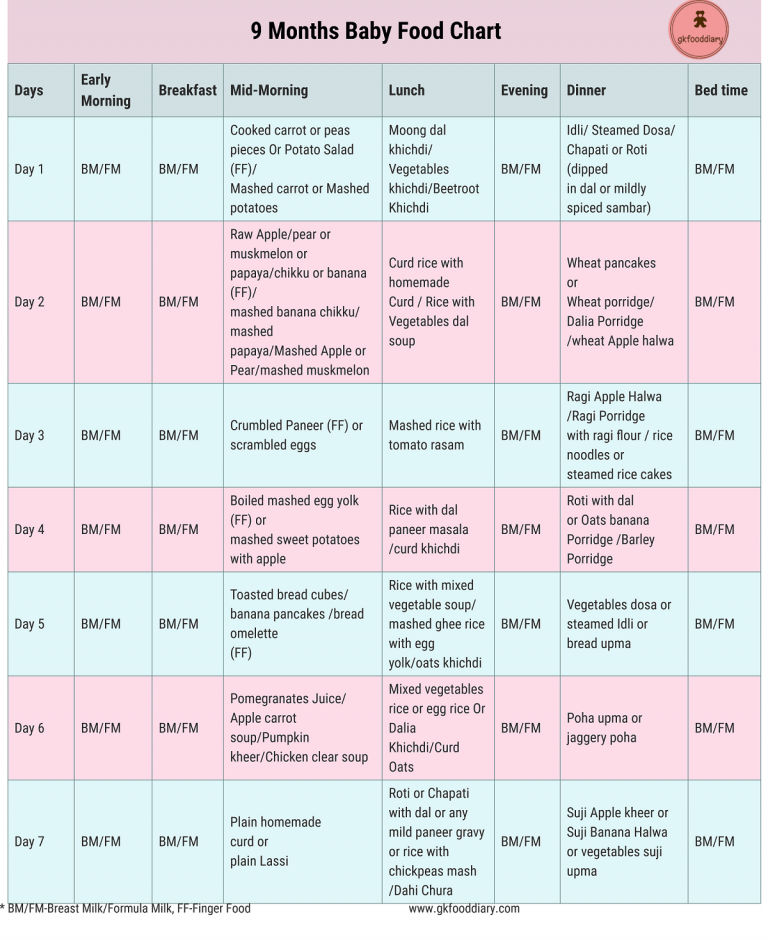 If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
In some situations, it may not possible to breastfeed, such as when a baby is very sick or born early. Mothers should talk with their baby's doctor about expressing and storing milk. Often, a baby who can't breastfeed can get breast milk through a feeding tube or bottle.
Some moms who have inverted nipples may have trouble breastfeeding, but a lactation consultant usually can help them overcome this. Likewise, women who have had plastic surgery on their breasts should be able to successfully breastfeed. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Hold off on pacifiers or bottles until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3–4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
Benefits of Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formula is a nutritious alternative to breast milk. Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Because babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, a baby who is getting formula may need fewer feedings than one who breastfeeds. Formula feeding also can make it easier to feed the baby in public, and lets the father and other family members help feed the baby, which can enhance bonding.
Limitations of Formula Feeding
Just as breastfeeding has its unique demands, so does bottle feeding. Bottle feeding takes organization and preparation, especially if you want to take your baby out. Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
It's important to make sure that you have enough formula on hand, and bottles that are clean and ready to be used.
Here are a few guidelines for formula feeding:
- Carefully follow directions on the label when preparing formula. Do not add more water than directed.
- Bottles left out of the refrigerator longer than 1 hour and any formula left in the bottle that a baby doesn't finish should be discarded.
- Prepared bottles of formula can be stored in the refrigerator up to 24 hours and carefully warmed just before feeding. You don't have to warm formula, but most babies prefer it.
- A bottle of formula can be warmed by holding it in running warm water or setting it in a pan of warm water. A bottle of formula (or breast milk) should never be warmed in a microwave. The bottle can heat unevenly and leave "hot spots" that can burn a baby's mouth.
How Often Do Newborns Eat?
Your newborn will nurse about 8 to 12 times per day during the first weeks of life. In the beginning, mothers may want to try nursing 10–15 minutes on each breast, then adjust the time as needed.
Breastfeeding should be on demand (when your baby is hungry), which is generally every 1–3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often and have longer stretches between feedings. Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling against their mothers' breasts
- crying
A feeding schedule is not necessary — you and your baby will get into a routine. Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. There may be other times when your infant seems hungrier than usual.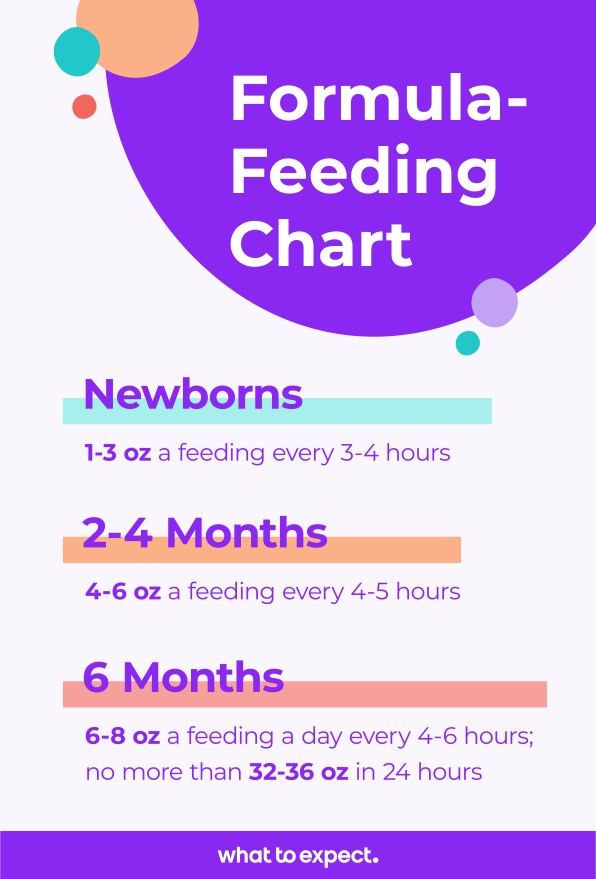 Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Is My Newborn Getting Enough to Eat?
New parents often worry about whether their babies are getting enough to eat.
Babies are getting enough to eat if they:
- seem satisfied
- have about 6–8 wet diapers a day
- have regular bowel movements (poops)
- sleep well
- are alert when awake
- are gaining weight
A baby who is fussing, crying, seems hungry, does not appear satisfied after feeding, and has fewer wet diapers may not be getting enough to eat. If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
Most infants "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, but a baby should not vomit after feeding. Vomiting after every feeding might be a sign of an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care.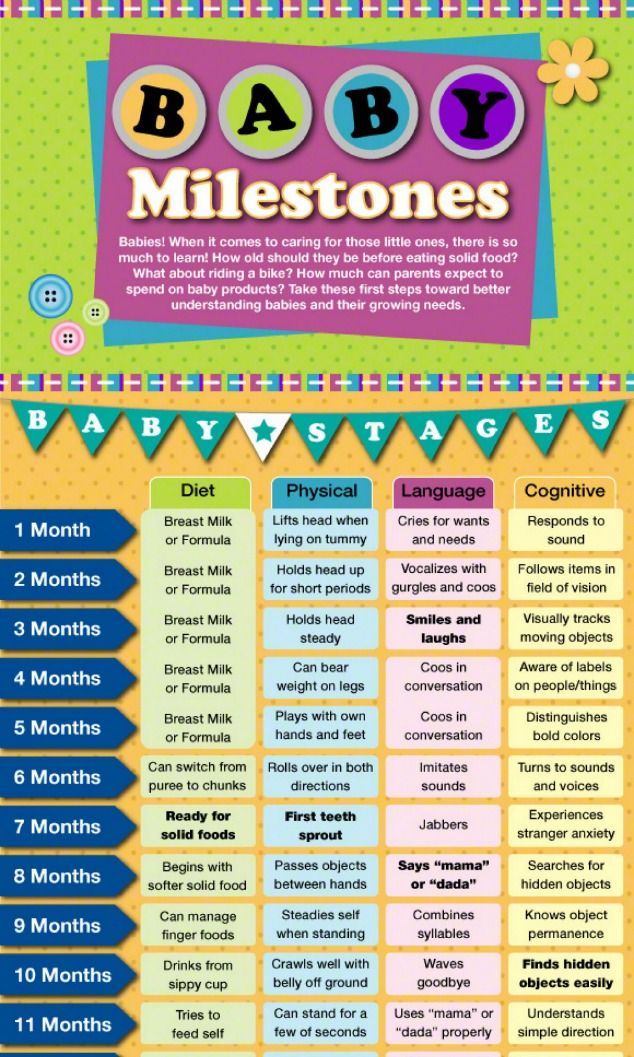 If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Should Newborns Get Nutritional Supplements?
Breast milk has the right combination of vitamins and easily absorbed iron for newborns. A healthy infant being nursed by a healthy mother doesn't need extra vitamins or nutritional supplements, with the exception of vitamin D. Breastfed babies should begin vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life, continuing until they get enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
Breastfeeding mothers who follow vegetarian diets that do not include animal products need vitamin B12 supplements.
Iron-fortified formula has the right blend of vitamins and minerals for a baby, so supplements usually aren't needed. Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Water, juice, and other foods usually aren't necessary during a baby's first 6 months. Breast milk and formula provide everything babies need nutritionally until they start eating solid foods.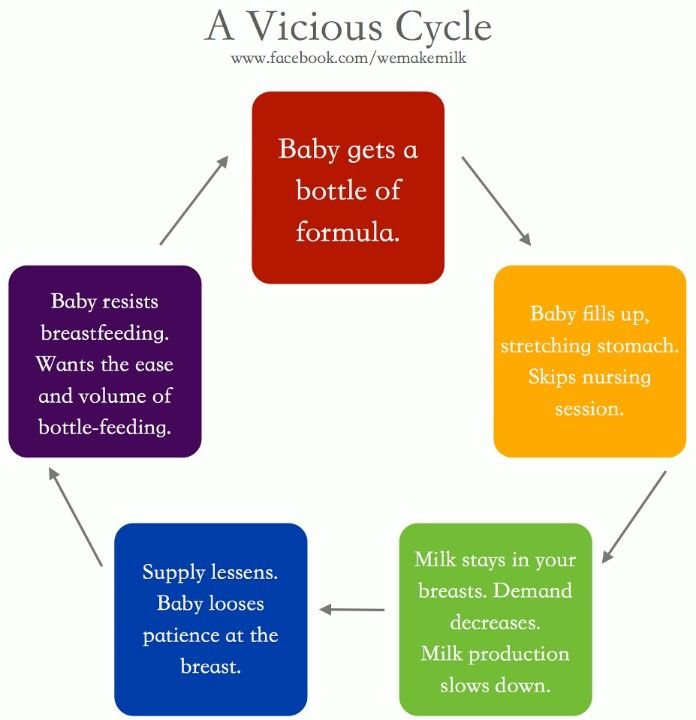 Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
Formula-fed regimen - Articles about baby food from pediatricians and experts MAMAKO
- Polina Alexandrovna, non-breastfeeding mothers are worried that formula will not provide their child with all the necessary nutrients so that he can fully grow and develop. How significant is the difference between breast milk and its substitute?
— Mom's milk is a living substance that, in addition to nutrients, microelements and other useful components, contains biologically active substances responsible for immunity and components that cannot be synthesized. An adapted milk formula is as close to the composition of human milk as possible, but it is not a 100% substitute. Therefore, breastfeeding is preferable. However, if it is not possible to breastfeed, this is not a disaster. The most valuable nutrients a child can get from infant formula. nine0005
nine0005
— What could be the reasons for transferring a child to artificial feeding?
— The most common reason why pediatricians recommend artificial feeding is because of the health of the child. In addition, artificial feeding can help a mother who is unable to feed her child on her own, for example, in cases where:
- lactation is difficult;
- there are contraindications for women's health;
- child and mother are not together; nine0016
- the nursing mother has obvious psychological discomfort.
— What products can be used for artificial feeding?
- Adapted infant formula or special therapeutic formulas, which may be dairy or, more rarely, dairy-free. You do not need to feed the baby with other products: whole cow's or whole goat's milk is not adapted for a small child. When the time comes for complementary foods, formula-fed babies, as well as breastfed babies, will gradually begin to try solid food in the same mode. nine0005
nine0005
— How common are colic, bloating, bottle-feeding disorders?
- When compared with breastfeeding, there is no particular prerequisite for colic, bloating or other disorders to occur more often from bottle feeding. In "artificial" stools become a little denser, which does not mean constipation. Changes in its consistency are caused by a certain composition of the milk substitute. This is completely normal. And colic, bloating and other problems may arise due to intolerance to some components of the mixture. A specialized therapeutic mixture will help to solve a specific problem and save the baby from these unpleasant sensations. nine0005
— Is it necessary to follow the feeding schedule for artificial feeding of the baby or is it better to feed the baby when he wants to?
- Formula-fed baby must be given a bottle on schedule, free feeding is not allowed. Surely many have heard that a newborn and a young child needs to be fed on demand, but on artificial feeding, the intervals between feedings should be at least 3 hours, even for a very small child.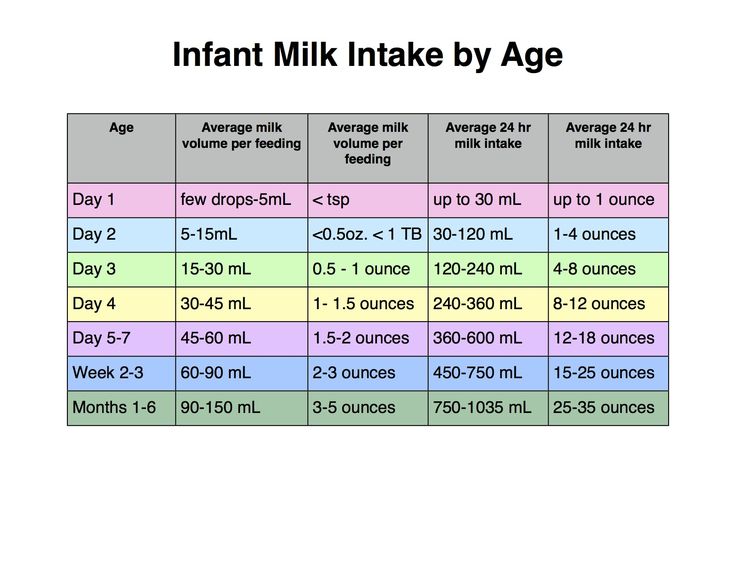 nine0005
nine0005
— Do I need to consult a specialist and take tests before formulating a formula diet?
- Before switching to an artificial formula, most often the mother consults with the pediatrician. The feeding mode (not the amount of food) is standard and does not depend on any features. Breaks equal to three hours should be stably maintained by the baby at one month and at six months. Skipping night feedings is possible, and breaks longer than three hours are acceptable, but still not less. nine0005
— What should be taken into account before drawing up a regimen?
— The most important thing is that the feeding regimen and the child's sleep and wakefulness regimens overlap with each other. When a mother builds a day regimen for artificial feeding, it is worth paying attention to what time she plans to put the baby to bed and wake her up so that feeding does not have to be in the middle of daytime sleep. Both mother and baby should be as comfortable as possible - so that they do not have to wake the baby for a meal or so that he does not wake up early from hunger. nine0005
nine0005
— What are the key and general rules for establishing a feeding schedule for a formula-fed baby?
- Feeding regimen with artificial feeding should overlap with the sleep regimen. It is important to separate the nutrition and sleep of the baby. With artificial nutrition, this is easier to do than with natural. However, formula-fed infants often form a negative association with sleep when a bottle of nutrition is needed to fall asleep or eat immediately after waking up. Therefore, between feeding and sleep should be a small period of time - 10-15 minutes before and after sleep. With a newborn, it is usually not possible to reach this gap, because the wakefulness of the child is too short and only accommodates feeding. This is normal, but you need to strive to ensure that breaks appear and increase. Then by the end of the first month, most likely, everything will work out. nine0005
— How to distribute meals throughout the day? Can parents calculate the number of feedings and portion sizes themselves?
— Composing the feeding regimen and calculating the amount of food, you need to focus on the age and weight of the child. Based on these indicators, the pediatrician determines the daily volume of the baby's food. Taking into account children's age, the daily amount of food is distributed over a certain number of feedings - the younger the baby, the more often he eats and the smaller his portion. nine0005
Based on these indicators, the pediatrician determines the daily volume of the baby's food. Taking into account children's age, the daily amount of food is distributed over a certain number of feedings - the younger the baby, the more often he eats and the smaller his portion. nine0005
Over time, the intervals between meals increase due to the skipping of night feedings. The portion that the child missed is distributed between daily feedings. Consequently, the portion increases, and the frequency of feeding decreases.
How often to give the baby a mixture per day, including how many times to feed the baby at night on the IV, is calculated by the doctor for each specific baby, taking into account his age and weight parameters. nine0005
Read also
- about what determines the amount of formula a baby eats and how to calculate how much formula a baby needs
— Polina Aleksandrovna, the schedule has been drawn up, but the child eats little or rarely — should I be worried?
- If the weight gain is within normal limits, then the baby is getting enough nutrition. It happens that children eat less than the norm, but at the same time they fulfill their needs, do not lag behind in physical and psycho-emotional development, which means that for these children the norm is less than average. nine0005
It happens that children eat less than the norm, but at the same time they fulfill their needs, do not lag behind in physical and psycho-emotional development, which means that for these children the norm is less than average. nine0005
The child eats little or rarely, the weight is added poorly - it must be shown to the doctor.
— Is it worth it to force a baby to live according to the regimen at night if he does not wake up and does not ask for food, but has not eaten the daily allowance?
- You need to watch how the child is gaining weight and growing, and monitor his condition, because situations are different.
- The baby eats normally, maintains the usual intervals and just starts to skip night feedings - it means that he has enough food during the day and it is not worth waking him up. nine0016
- The baby sleeps soundly until the morning, and during the day he gets off the routine and starts asking for food more often - therefore, he is malnourished, and you need to increase the size of the daily portion in order to maintain the daily norm, or wake the child up to feed at night.
 The first option is preferable, but, of course, within the age norm. It is most physiological when children eat less and less at night, and by one year they either sleep until morning or wake up once.
The first option is preferable, but, of course, within the age norm. It is most physiological when children eat less and less at night, and by one year they either sleep until morning or wake up once.
— Can children's health problems arise if the artificial feeding regimen has changed? nine0004
- You may run into problems if the diet has shifted very much. But you need to consider the reason for what is happening. When a sick child's appetite decreases, this is an adequate response to poor health, and it is not necessary to force-feed him. After recovery, he will try to compensate for the lack of food in the previous days and begin to eat more actively.
With the new regime, for example, due to the change in time zones, it may be difficult for the child to adapt, but this does not mean at all that he will be worried for a whole month. After one or two days, the regime returns to normal. And, of course, without the need to change the mode is impractical. nine0005
nine0005
— Polina Alexandrovna, tell us about the main advantages of MAMAKO ® baby food.
- The manufacturer has a fairly wide range of products. Parents can choose food according to the age and needs of their baby. With age-adapted milk formulas, it is easy to maintain an artificial feeding regimen from birth to three years. Porridges, mashed potatoes and cream soups are optimal for complementary foods. What is especially valuable, all these products are made on the basis of goat's milk, which children digest more easily and better than cow's milk and which is considered more suitable for children's nutrition. A child who initially tried the "goat" formula, and then switched to complementary foods with the addition of goat's milk, will have an easier time accepting them. nine0005
The composition of the milk formula is maximally adapted to children's needs, but still it is not saturated with absolutely all the components and biologically active substances that are found in women's breast milk. Technology does not yet allow this. Accordingly, breastfeeding is preferable for babies, but when it is not possible, ready-made products come to the rescue. When feeding with infant formula, it is recommended to adhere to a diet so that the baby does not overeat, easily digests and digests food comfortably. If the order of feeding has gone astray, try to return the usual diet for the child as soon as possible, and then everything will be fine. nine0005
Technology does not yet allow this. Accordingly, breastfeeding is preferable for babies, but when it is not possible, ready-made products come to the rescue. When feeding with infant formula, it is recommended to adhere to a diet so that the baby does not overeat, easily digests and digests food comfortably. If the order of feeding has gone astray, try to return the usual diet for the child as soon as possible, and then everything will be fine. nine0005
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
Feeding on demand or by the hour? What to do if the baby is bottle-fed
It would seem that strictly hourly feeding is a thing of the past, and we hear from everywhere that a newborn needs to be fed on demand.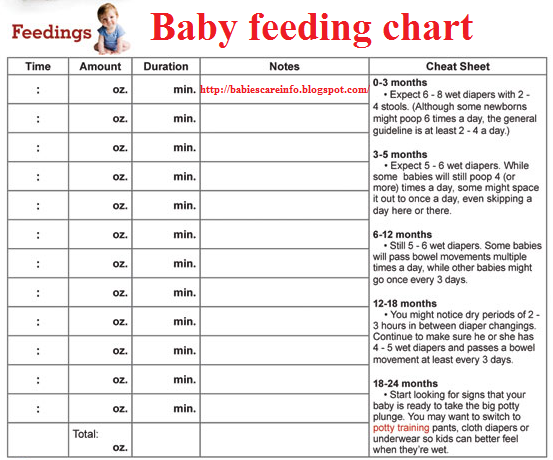 But this applies to breastfeeding, and in the case of artificial, everything is not so simple. How to feed an artificial baby and what is important to remember when choosing a mixture - in the material "Daily Baby".
But this applies to breastfeeding, and in the case of artificial, everything is not so simple. How to feed an artificial baby and what is important to remember when choosing a mixture - in the material "Daily Baby".
Feeding: on demand or by the hour? nine0125
In Soviet times, it was recommended to feed a newborn on any type of feeding strictly by the hour. There was no question of any wards of joint stay with the baby.
Times have changed, and today doctors are unanimous on this issue: it is more expedient to feed a baby "on the chest" on demand and apply it at his slightest request. But what are the norms for feeding an artificial child? Is it right to give the baby a mixture “on demand” or in this case, do you still need a diet? nine0005
Doctors recommend following a certain regimen when feeding a baby with artificial formula. Feeding a newborn "on demand" on an artificial form of feeding is almost impossible, because, firstly, it is not always convenient to quickly and at the first request of the child to prepare the mixture.
And secondly, when feeding on demand, it is difficult to track the amount of food received by the baby. And if it’s impossible to overfeed with a breast, then with a mixture it’s completely. Modern artificial mixtures, although they contain a lot of nutrients, but, whatever one may say, breast milk is easier and easier to digest. Therefore, when feeding with a mixture, the regimen is so important. Doctors insist: you need to feed the newborn with a mixture not at the request of the baby, but strictly on time. nine0005
Hourly formula feeding is also important because this type of feeding is an acute issue of hygiene. Bottles and nipples must be perfectly clean, and the mixture must be freshly prepared.
You also need to remember that the stool of a bottle-fed baby should be daily. Due to the fact that the formula is absorbed and digested longer, the frequency of meals should be lower than when breastfeeding. Otherwise, there is a risk of overfeeding the child, and there are not far from problems with the gastrointestinal tract and obesity. There is also the possibility of underfeeding, which is why nutritional order is so important. nine0005
Artificial feeding: how to properly feed
There is no single and clear schedule for feeding a newborn artificially. It is necessary to focus on a specific baby and adjust the nutrition plan for him. The optimal intervals between feedings and the volume of the mixture eaten must be selected individually. Parents should be patient and gradually accustom the child to the regime that suits him.
It is recommended to take notes while observing the behavior and well-being of the child. So you can adjust the daily routine, making it the most comfortable for the baby. At the same time, small deviations from the regime, in half an hour or an hour, are quite acceptable. nine0005
Artificial babies of the first month of life are fed about six to seven times a day, the interval between feedings is about three and a half hours. At night, it is desirable to withstand six hours without feeding. Haphazard or more frequent meals can cause indigestion, as well as the appearance of increased gas production in the baby, colic and frequent spitting up.
With age, the hours of feeding a newborn formula change: the intervals between meals increase. A six-month-old child is given a mixture about five times a day. From the age of 7 months, the baby is fed with a mixture approximately every 5 hours, taking into account the fact that at this age the baby is actively eating complementary foods. nine0005
“Children of the first year of life, especially the first half of the year, grow and develop very actively, and this requires a regular supply of nutrients. Formula-fed infants are usually fed once every 2-3 hours.
It is very important to calculate the child's daily energy requirement. For full-term healthy babies up to 6 months, this is 115 kcal per kilogram of weight. But children are also very large. There is an upper limit of the daily volume of the mixture: for three months it is 850 ml, for 5 months and above - no more than 1000 milliliters of the mixture per day. nine0005
nine0005
Unlike breastfeeding, the daily amount of formula must be controlled, because obesity and overfeeding during artificial feeding are more dangerous.
Children with a good appetite, who are already low on the maximum daily volume, after 4 months can be introduced complementary foods, but do not increase the mixture.
Bottle-fed water can be offered to children, but it is not necessary, at the request of the child. Again, the daily volume of water is important - no more than the volume of one feeding. nine0005
I would also add that formula-fed on-demand feeding is not recommended, since formulas, even the highest quality ones, do not have such good digestibility as human milk. And the risk of overfeeding is high,” says pediatrician Anna Ganina .
Pay attention to the stool of a bottle-fed newborn. The appearance of mucus in it, a strong liquefaction of the stool, or, conversely, constipation may warn that the mixture is not suitable for the baby.
However, it is important to remember that you should not change baby food too often and unreasonably. It is better if the child eats one, suitable for him, high-quality and healthy mixture.
If you follow all the rules of feeding, the growth and development of the baby on artificial feeding will proceed in accordance with the norms.
Kabrita Gentle Goat Milk Formula
Kabrita Goat Milk Based Infant Formula has an adapted protein composition. Goat's milk is closer in composition to breast than cow's, it is digested faster and easier than cow's milk, so feeding a newborn with goat's milk formula is preferable. Such food is faster digested, better absorbed and reduces discomfort when switching from breastfeeding to artificial or mixed. nine0005
Kabrita baby food is a state-of-the-art formula based on natural Dutch goat milk.
Kabrita formulas contain the unique Digest X fat complex that mimics the fat profile of breast milk.