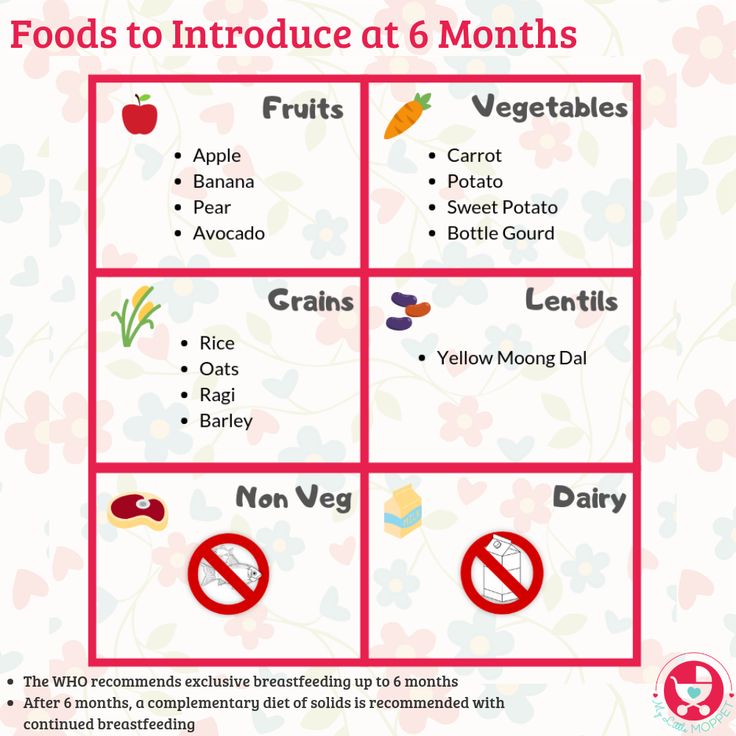
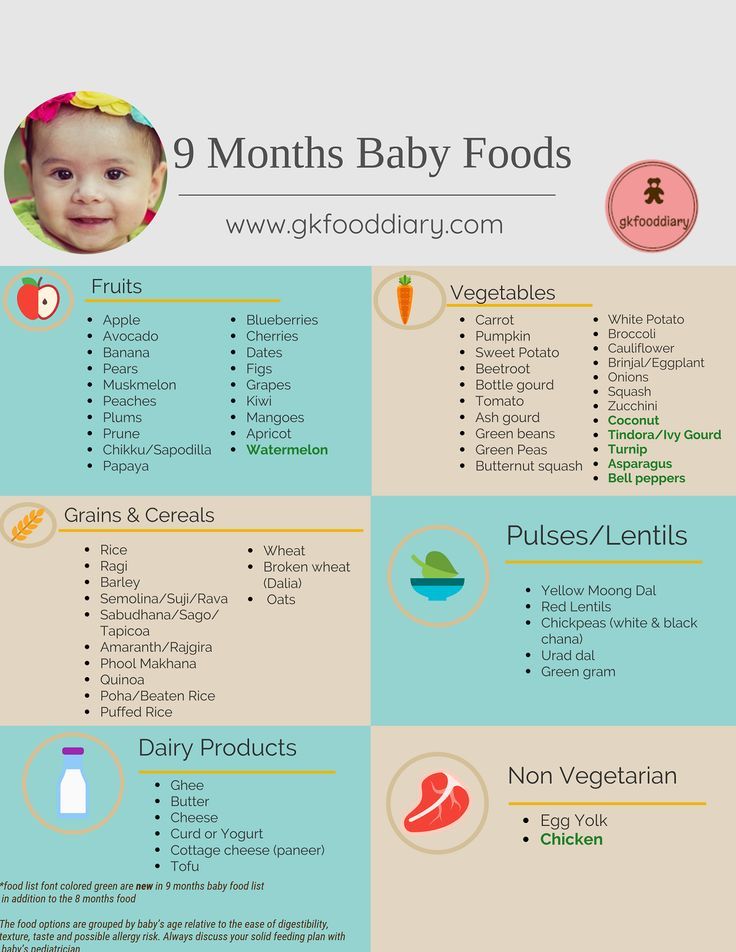
How to introduce baby foods
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Helpful Resources | Nutrition | CDC
If you would like more information on topics related to feeding your baby or toddler, here are some resources:
General
CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition microsite syndication
CDC offers a free Web Content Syndication service that gives public health partners the opportunity to syndicate CDC content directly to their sites without having to monitor or copy updates. To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
CDC’s Child and Teen Resources
This collection of resources provides parents and caregivers, health care providers, and partners with tools and information to help children and teens maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity.
CDC’s Child Development Positive Parenting Tips (Infants)
This CDC website provides information about infants’ development, as well as tips for positive parenting and promoting the safety and health of infants.
CDC’s Learn the Signs. Act Early.
This website includes tools to track children’s milestones and resources about children’s development.
CDC’s Parent Information
This CDC website provides resources and information on pregnancy, infants and toddlers, children, and teens. Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
CDC’s Division of Oral Health
Tooth decay (cavities) is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood in the United States. Untreated tooth decay can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing, and learning. CDC’s Division of Oral Health provides information on what parents and caregivers can do to ensure good oral health for your child.
Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025 pdf icon[PDF-30.6MB]external icon
These guidelines provide science-based advice for Americans on what to eat and drink to promote health, reduce chronic disease, and meet nutrient needs. The 2020–2025 edition provides recommendations for all life stages, including infants and toddlers.
Feeding Guidelines for Infants and Young Toddlers: A Responsive Parenting Approachexternal icon
This report presents recommendations for promoting healthy nutrition and feeding patterns for infants and toddlers from birth to 24 months, with an emphasis on dietary quality, portion sizes, and mealtime environment.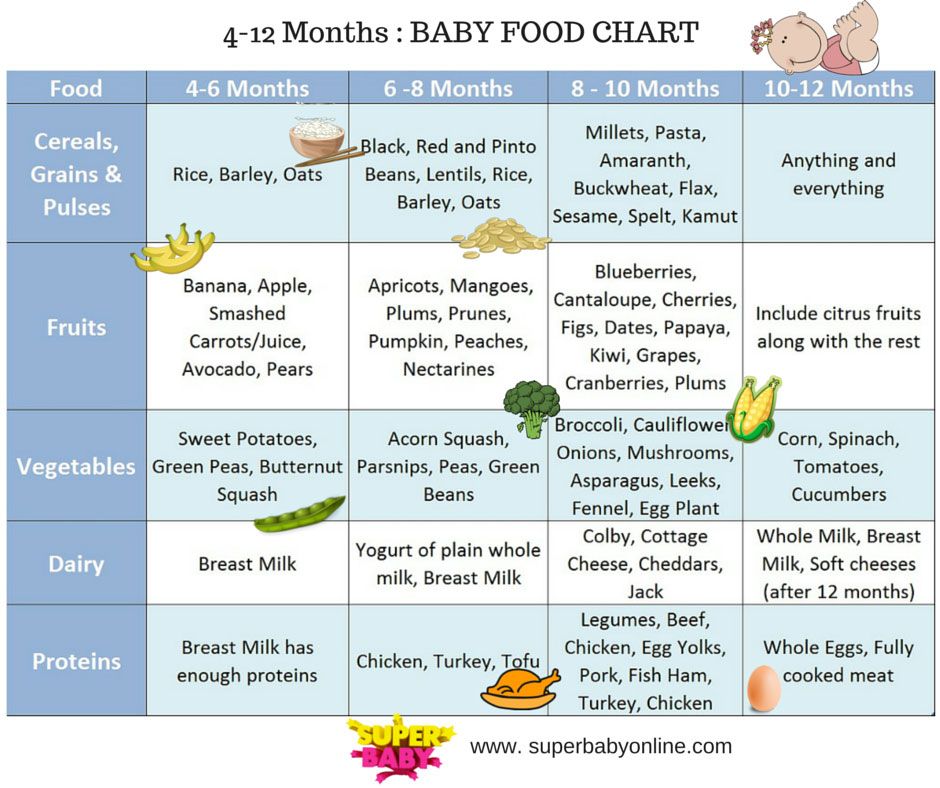
Healthy Childrenexternal icon
This website was developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics for parents. It features thousands of articles in English and Spanish on children’s health and safety, as well as interactive tools.
United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)external icon
The WIC Program provides support to low-income pregnant, postpartum, and breastfeeding women, babies, and children up to age 5. WIC provides nutritious foods, information on healthy eating, breastfeeding promotion and support, and referrals to health care.
United States Department of Agriculture Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)external icon
SNAP provides benefits to low-income individuals and families and provides economic benefits to communities.
Feeding and Beverage Recommendationsexternal icon
Healthy Eating Research, a national program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, offers science-based recommendations for parents and caregivers. Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Advice About Eating Fishexternal icon
The U.S. FDA and EPA provide advice regarding eating fish. This advice can help people make informed choices when it comes to the types of fish that are nutritious and safe to eat. It is especially important for those who might become pregnant, who are pregnant, or who are breastfeeding, as well as for parents and caregivers who are feeding children. This advice supports the recommendations of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Top of Page
Breastfeeding
CDC’s Breastfeeding Information
CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity (DNPAO) is committed to increasing breastfeeding rates throughout the United States. CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
International Lactation Consultant Association (ILCA)external icon
ILCA is the member association for professionals who care for breastfeeding families. ILCA’s “Find a Lactation Consultant Directory” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
United States Lactation Consultant Association (USLCA)external icon
USLCA is a professional association for International Board Certified Lactation Consultants (IBCLCs) and other health care professionals who care for breastfeeding families. USLCA’s “Find an IBCLC” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
WIC, the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children—Breastfeeding Support external icon
The United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) Breastfeeding Support website includes resources for expectant and current mothers about breastfeeding, overcoming common challenges, and thriving to make breastfeeding work for their families.
La Leche League USAexternal icon
La Leche League USA helps mothers to breastfeed through mother-to-mother support, encouragement, information, and education and promotes a better understanding of breastfeeding as an important element in the healthy development of the baby and mother.
Office on Women’s Healthexternal icon
The Office on Women’s Health’s vision is for all women and girls to achieve the best possible health outcomes. They provide information on breastfeeding to help women make infant feeding decisions and to guide mothers through the breastfeeding process.
Top of Page
Infant Formula
Questions & Answers for Consumers Concerning Infant Formulaexternal icon
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration regulates infant formula and has a list of questions and answers about infant formula.
Infant Formula Do’s and Don’tsexternal icon
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration provides information on infant formula preparation and storage, as well as other tips on how to keep infant formula safe.
Top of Page
Food Safety
Food Safety Concerns for Children Under Fiveexternal icon
Food safety is particularly important for young children. Foodsafety.gov provides information on safely preparing food for your child.
Top of Page
Meal Time
Fruits & Veggies—Have a Plant Movementexternal icon
A resource designed to help spread the word about the health benefits of adding more fruits and veggies to your diet.
USDA MyPlate Kitchenexternal icon
This online tool features a large collection of recipes and resources to support building healthy and budget-friendly meals. Site features include:
- Extensive search filters on cuisine, cooking equipment, nutrition content, and more.
- Detailed nutrition information.
- Cookbooks to browse and download or build your own.
- Recipe star ratings, review comments, and sharing on social networks.
Video Series on How to Introduce Solid Foods
1,000 Days has developed helpful videos about introducing solid foods to your baby. Topics include:
Topics include:
- Is your baby ready to start eating foods?
- What is a good first food for your baby?
- What to expect when introducing first foods
- How much should I feed my baby?
- How to win at mealtimeexternal icon
- What foods should my baby avoid?
- What should your baby eat in the first year?
Top of Page
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamin and Mineral Fact Sheetsexternal icon
The National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements has fact sheets for consumers and health professionals about vitamins, minerals, and dietary supplements.
Top of Page
Introduction of complementary foods to an infant
Breast milk contains enzymes, essential amino acids, antibodies, vitamins and other substances necessary for the growth and development of the baby. However, with age (between 6-24 months, according to WHO), the needs of the child change, and then it is necessary to introduce complementary foods.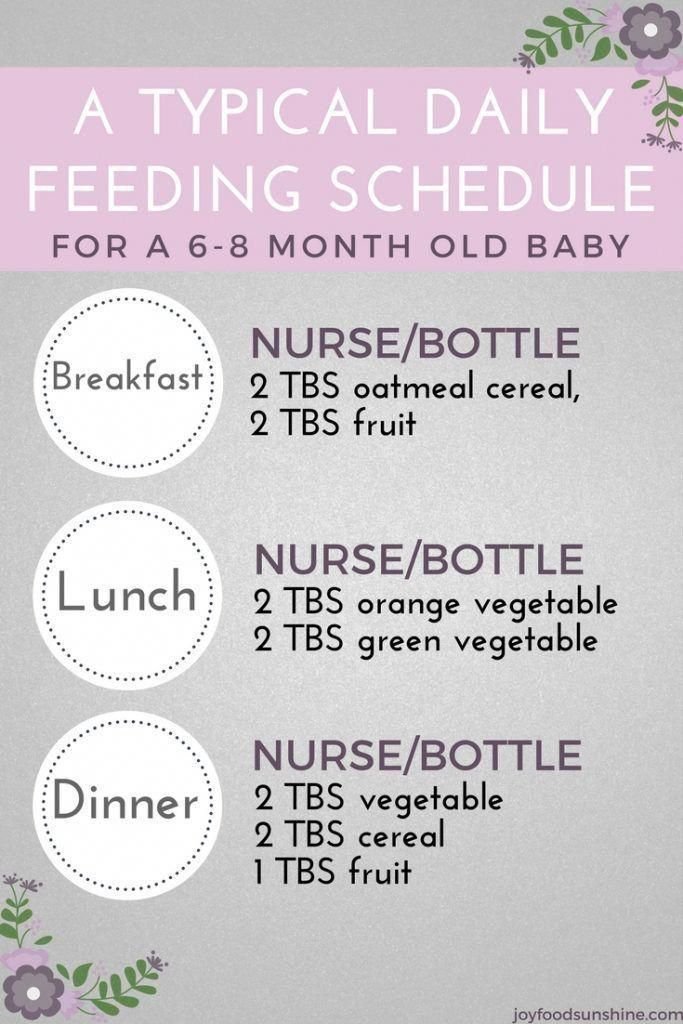 At the same time, it is not necessary to immediately turn off breastfeeding (WHO recommends breastfeeding until 2 years of age). Anna Aleksandrovna Tsaregorodtseva, a CTA pediatrician, spoke about how to competently introduce new foods into a child's diet.
At the same time, it is not necessary to immediately turn off breastfeeding (WHO recommends breastfeeding until 2 years of age). Anna Aleksandrovna Tsaregorodtseva, a CTA pediatrician, spoke about how to competently introduce new foods into a child's diet.
You can start feeding your baby if:
- He is 6 months old or older.
- He holds his head well.
- Can touch his mouth with his hand and actively "chews" various objects.
- If placed in a highchair or on an adult's lap, the child can sit up.
- He has a food interest: when adults eat, the baby watches, pulls his hands and wants to try.
Getting Started
The first foods should be puréed to make it easier for the baby to digest them!
As a rule, the child is first introduced to vegetables. If you want to introduce vegetables from jars, then it is better to buy mono-products - so that the puree contains only zucchini or only broccoli, etc. It is best to start with zucchini.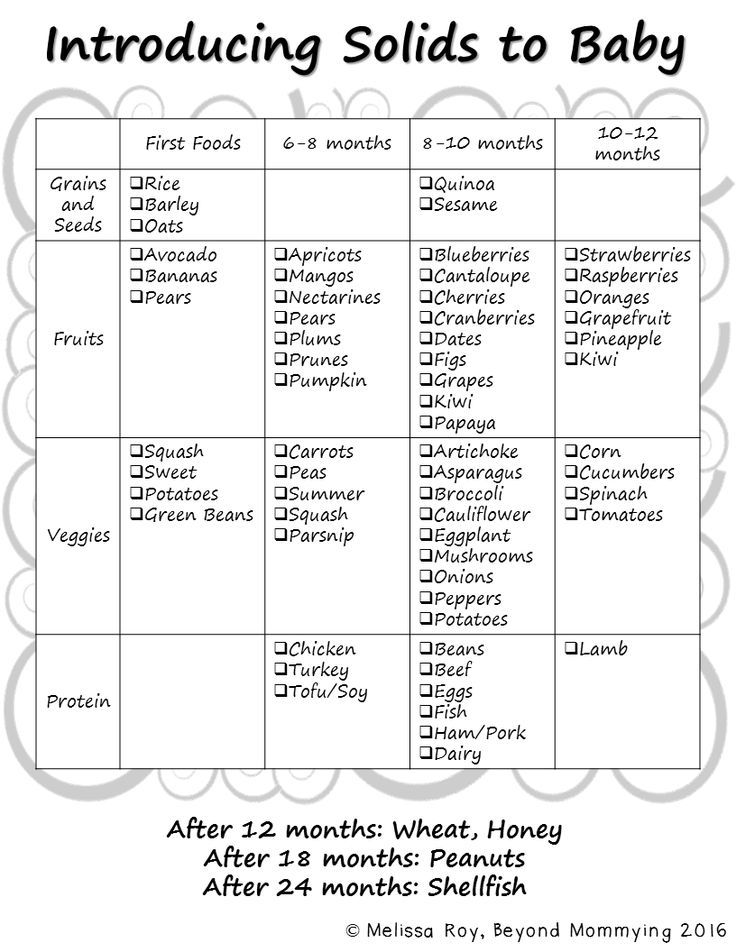 After that, you can enter cauliflower, then broccoli, then potatoes, pumpkin and carrots.
After that, you can enter cauliflower, then broccoli, then potatoes, pumpkin and carrots.
Enter at lunchtime (12-15 hours) and no more than one product at a time. Vegetable puree (like any other complementary foods) is given before breastfeeding or formula, 1 teaspoon. The next day, you need to observe the skin and stool of the child and do not give him complementary foods, but only breastfeed! If the body perceives the new product normally, in a day you can give 2 tsp already. zucchini. According to the same scheme - if everything is in order, you can increase the amount to 3 tsp. Gradually give more complementary foods (up to 5 spoons) and less and less often supplement the child with milk. When the volume of vegetables in the diet is approximately 150-200 g per day, you can stop breastfeeding your baby at this meal.
How to enter a new dish
The 2nd dish (cauliflower) must be added to the one already entered. That is, 5 tsp. zucchini and 1 tsp. cauliflower. On the "fasting day" you can give 5 tsp. zucchini, but discard the cabbage and watch. As a result, you will give the baby 5 tsp. zucchini and 5 tsp. cauliflower.
On the "fasting day" you can give 5 tsp. zucchini, but discard the cabbage and watch. As a result, you will give the baby 5 tsp. zucchini and 5 tsp. cauliflower.
Then you can enter the 3rd dish - broccoli - and then other vegetables. When the child is familiar with different vegetables, vegetable mixtures can be introduced.
If you want to feed your child with home-cooked vegetables, then note that it is best to boil vegetables in a double boiler. So it will be possible to save vitamins and minerals.
Fruits and berries
When the child digests vegetables well, fruits can be added to the diet. It is better to give them from jars. The time for the introduction of fruit is an afternoon snack (16-18 hours).
As the first fruit, it is better to take an apple, then a pear, then a prunes. The scheme is the same: 1 tsp. applesauce before breastfeeding. The next day, you do not give fruit and feed the child vegetables that he is already used to. A day later, the amount of applesauce increases to 2 tsp. and so on.
and so on.
Liquids
When complementary foods are introduced, the child should be offered bottled or boiled water. Pour water into a cup so that your baby does not get used to a bottle with a pacifier. Children drink well from a cup from birth!
Other products
You can also introduce ground cereals into the diet, gradually adding butter or vegetable oil to them. If this is baby porridge and needs to be diluted with liquid, then it is better to use mother's milk or a mixture, rather than cow's.
From 7-8 months, semi-solid food should be introduced so that the child develops chewing skills (and with them the correct work of the tongue and speech), fine motor skills, and eye work. Products can be kneaded, rubbed or ground. So it will be easier for the child to eat them.
From 8-9 months you can cut food (cooked vegetables and fruits) into small pieces and offer to your baby. He will take food with his hand, put it in his mouth and eat.
By the age of one, the child will be ready to eat solid food.
Page not found
How to buy a PlayStation Plus Essentials, Extra and Premium subscription in Russia
How a man came for a pension that he had not taken off for many years. But there was nothing to receive
The package was stuck at customs. What to do?
How to get compensation for the Soviet deposit
Everyone is interested
See all
Diaries of expenses
Investments for beginners
Financial pillow
benefits from the state
How to rent an apartment
How to repay a centor 9,0002
diaries of spending diarrhea.

Financial pillow
Benefits from the state
How to rent an apartment
How to pay off a loan
cm. All
Rules for entry into Turkey for Russians in 2023
Which countries accept tourists from Russia
9000
in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are in which countries are accept Russian UnionPay cards
Rules for entering Egypt for Russians in 2023
How much are the coins in your wallet
How the head of the department in the Moscow Region lives with a salary of 129 500 ₽
Rules for the entry into Georgia in 2023
In what countries can leave Russia
How to arrange a gift for a share of
How to retire earlier than
Best for six months
cm. All
partial mobilization in Russia: how it will be pass, who falls, who will not be called
0003
How to exchange rights
How to get a Green Card of the United States
Rules for the entry into Turkey for Russians in 2023
0057
How to calculate maternity payments
A new unified benefit for children from 2023: Basic conditions
How I ordered a car from Japan
which countries can leave Russia
as I was deceived by 15 000 ₽ ₽ with “Avito -delivery"
How to become an honorary donor of blood
Is it possible to leave Russia after the announcement of partial mobilization
How many coins are in your wallet
Courses will help
cm. All
green house
Win burnout
9032.07.21
Select the apartment
Improve life using Excel
Earn on shares
02.12.12.12.12.293
Understand charity
Travel safely
Earn on a credit card0371 14.08.20
Do not lose with a mortgage
Protect from scammers
Do not go bankrupt for health
0 9000
00 00 0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0 900 28.