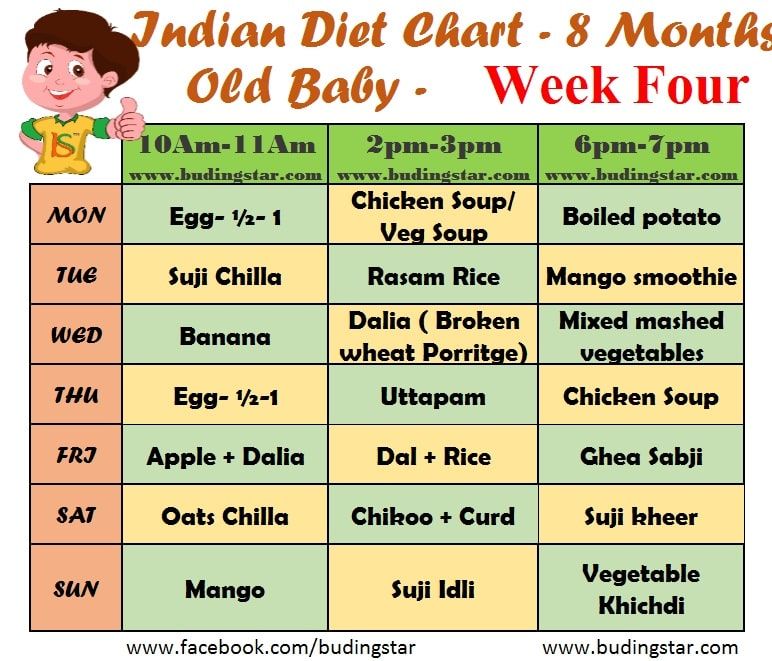
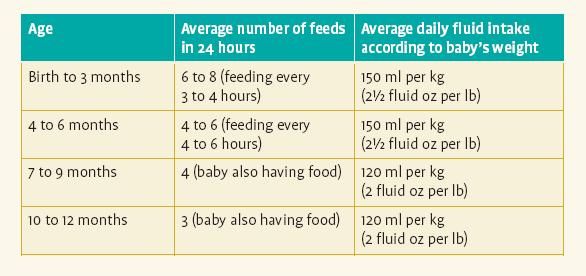
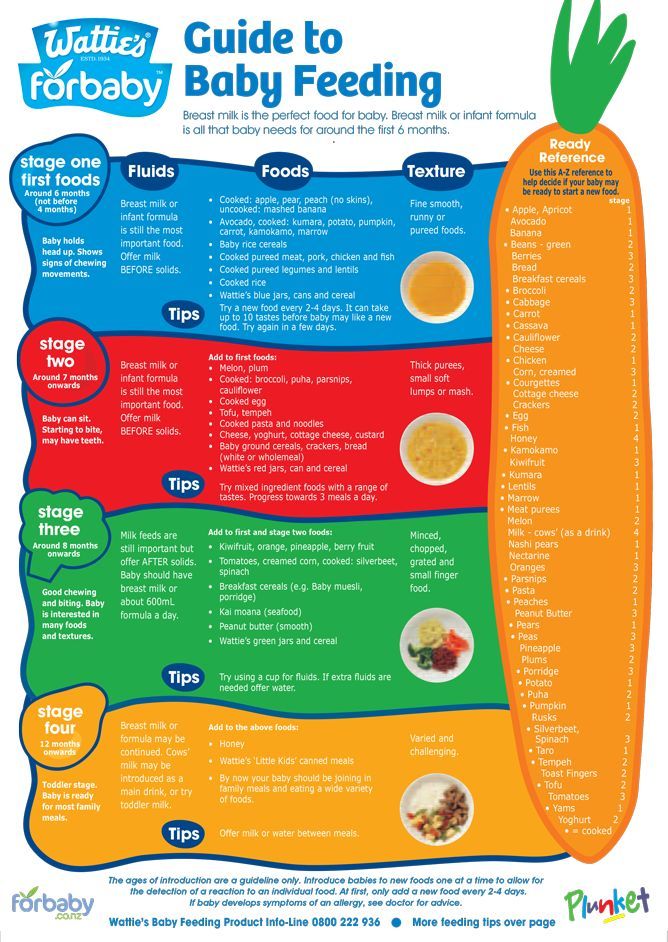
How to make baby gain weight food
15 Foods to Make Baby Gain Weight – Cafe Baby®
- by Jeannie Marrugo
- Mar 10, 2022
If you need to add foods to Baby’s diet to help them in gaining weight, be sure to add these to your grocery list or to your next Café Baby order. Sometimes every extra calorie counts in their tiny bellies.
If your child needs to be on high calorie fortified infant formula or breast milk, please talk to your pediatrician first. You need to know the right recipe to prevent an excess intake of nutrients to prevent constipation and dehydration.
1. Avocado
Avocados are a sugar-free healthy choice that contributes 2.5 grams of monounsaturated fat and 0.5 gram of polyunsaturated fat per 25-gram serving to Baby's diet.
2. Kidney Beans
Kidney beans are a plant-based protein, or non-heme iron source, rich in most B-vitamins, fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. They also contain two that are commonly deficient in babies: folate and iron.
3. Eggs
Not only are eggs a prime source of the best-quality proteins after breast milk, but one egg contains thirteen essential minerals like copper, zinc, selenium, calcium, iron, cholesterol, fat, fatty acids, and vitamins like vitamin D, B12, E, choline and folate.
4. Bananas
Bananas are loaded with nutrients like potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, folate, niacin, and vitamin B6 and can help babies gain weight by increasing calorie density.
5. Mango
Mangoes are rich in fibres and digestive enzymes, which means Baby won't have any trouble going number two. Mangoes are very low in fat but contain lots of good calories which can help Baby gain weight.
6. Lentils
Lentils are low in sodium and saturated fat, and high in potassium, fiber, folate, and plant chemicals called polyphenols that have antioxidant activity.
7. Ground Meat
Did you know it's important to add iron- and zinc-rich foods to Baby's diet? At about six months of age, Baby starts to run out of their natural iron stores that they were born with. Ground meats are an important source of heme iron, which is more easily absorbed into the body than non-heme iron (plant-based protein).
8. Whole Milk Yogurt
The best option is plain, unsweetened, pasteurized yogurt (regular or Greek) made from whole milk and containing "live cultures. " Yogurt made from whole milk is best for Baby because they need the calories and fat in full-fat dairy products.
" Yogurt made from whole milk is best for Baby because they need the calories and fat in full-fat dairy products.
9. Full-fat Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese has plenty of healthy fats and protein, plus some B vitamins, calcium, selenium, and zinc. To avoid loads of salt, look for options that are:
- Pasteurized
- Low in sodium (ideally less than 100mg sodium per serving)
- Made from whole milk
- Without added preservatives or sugars
10. Mashed Sweet Potato
Sweet potatoes provide nothing but good calories, making it a healthy food option for Baby. The high amount of calories in sweet potatoes help in weight gain and physical development in children.
11. Mashed Potatoes
Potatoes might be mostly white, but that doesn’t mean they don't contain nutrients. They are are a source of fiber-rich carbs, which are one of the best sources of fuel for Baby’s brain.
12. Mashed Butternut Squash
The Omega-3 fats that are found in butternut squash are present in the form of alpha-linolenic acid, and this is what helps to reduce inflammation.
13. Peanut or Almond Butters
Nut butters can be a source of fibre, protein and healthy fats, as well as minerals such as magnesium, calcium, iron and vitamin E. If you're worried about food allergies, check out our blog series about starting solids and allergies.
14. Fresh Goat Cheese
Fresh goat cheese has lots of protein and healthy fats, plus calcium, copper, iron, and vitamins A, B2, and B6—essential nutrients to power your baby’s growth. When selecting goat cheese for Baby, look for a cheese that is:
- Pasteurized
- Low sodium (less than 100mg per serving)
- Whole fat
15. Cooked Quinoa
Quinoa is a good source of calcium, iron, potassium and magnesium. It's also a great source of Omega 3, 6, 9 fatty acids, which are good for Baby's brain and eye development.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Cafe Baby® Fresh Baby Food (@cafebabytogo)
Sources:
https://patient. uwhealth.org/healthfacts/343
uwhealth.org/healthfacts/343
https://solidstarts.com/foods/kidney-beans/
https://parenting.firstcry.com/articles/banana-for-babies-when-to-introduce-health-benefits-and-more/#How_Much_Banana_Can_a_Baby_Eat_in_a_Day
https://parenting.firstcry.com/articles/mango-for-babies-health-benefits-and-recipes/#Nutrition_Facts_of_Mango
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/food-features/lentils/
https://newwaysnutrition.com/babies/meat-baby/
https://solidstarts.com/foods/cottage-cheese/
https://parenting.firstcry.com/articles/sweet-potato-for-baby-benefits-and-recipes/#Nutritional_Value_of_Sweet_Potato
https://parenting.firstcry.com/articles/butternut-squash-for-babies-health-benefits-and-recipes/#Nutritional_Value_of_Butternut_Squash
https://www.whattoexpect.com/first-year/baby-feeding/when-can-babies-eat-potatoes#benefits
https://www.srnutrition.co.uk/2021/04/peanut-butter-for-babies-when-to-introduce-it-and-which-type/
https://solidstarts. com/foods/goat-cheese/
com/foods/goat-cheese/
https://www.momjunction.com/articles/is-quinoa-safe-for-babies_00120055/
The Best Foods for Your Baby to Gain Weight
It’s hard to imagine that your little one could be any cuter — but you might be wondering whether they’re growing as fast as they should.
If you’re worried that your baby might weigh too little, bear in mind that newborns normally lose 3–7% (and up to 10%) of their birth weight in their first few days of life, which they regain by about the end of their second week (1, 2, 3).
Until they reach the 6-month mark, infants should gain about 1 pound (0.45 kg) or more each month. They should weigh about triple their birth weight around the end of their first year (1, 2, 3).
Keep in mind that these numbers are averages, and a healthy baby may have different weight gain numbers depending on their birth weight, rate of linear growth, and other factors.
You can ask your baby’s pediatrician about weight gain at any time, such as at their well-baby exam.
If you and your healthcare practitioner have ruled out medical reasons for your baby’s slow weight gain, such as heart or digestive issues, consider feeding them calorie-dense whole foods. These may encourage healthy weight gain (4).
Here are the 7 of the best foods to help your baby gain weight. We’ve grouped them below by age group.
A baby under 6 months that’s putting on less weight than average can be troubling. Since all or most of their calories at this point come from breastmilk, formula, or both, what you can control right now is how often they feed and whether they’re getting enough (4).
1. Breastmilk or infant formula — often and enough
Breastfed newborns will feed every 2–3 hours, so account for 8–12 or more feedings per day for the first 4 months.
Be sure to let your infant fully empty your breast. One reason this is recommended is because hindmilk, which comes out last during a feeding, may be richer than foremilk, which comes out first.
Let your baby feed fully, until your breast feels very soft. This will ensure they’re getting all the milk available, and it sends your body a message to make more.
You can try consuming foods that are thought to increase breastmilk production. These include lactation teas or bars with fenugreek, blessed thistle, or fennel. Oatmeal and dark beer may also help. Still, more research on these solutions is needed (5).
Additionally, avoid wearing tight-fitting bras or tops.
Until your baby begins solid foods, they will not need to drink water. Offer them breastmilk or formula instead to maximize the number of calories you’re getting into their tiny tummies.
Your doctor may also ask about any latching issues and investigate any underlying medical issues that may affect your baby’s nutrient absorption or metabolism at this age.
Speak with a pediatrician for guidance if you’re considering whether to supplement breastfeeding with formula or wondering which formula to choose.
These choices are complicated and depend on many personal factors, and a doctor can help you make informed decisions. You may also consider talking with a lactation consultant.
Most babies will start to show readiness to eat solid foods around the 6-month mark.
Speak with your healthcare professional about when to start your baby on complementary solid foods.
2. Avocado
Whether you’re taking a baby-led weaning approach, a more traditional puréed foods style, or a combination of the two — avocado is a great transitional food for babies starting on solids.
What’s more, avocado’s healthy fats and relatively mild taste make this a great food for when you’re trying to get your baby to gain weight (6, 7).
Mash it up or serve it in thick spears. You can also add it to other foods, such as rice cereal or another fruit.
It’s a good idea to introduce new foods one at a time. This way, if your child has any sort of allergic reaction, you have a better sense of what might have caused it.
3. Oatmeal
Oatmeal cereal is another wonderfully rich food that’s easy to add to your baby’s diet.
To make it, blend plain oats cooked in water, adding water as needed to achieve a soupy texture. To make it heartier, cook and thin out the oatmeal with formula or breastmilk instead. Gradually thicken it as your baby gets more comfortable.
Oatmeal packs lots of fiber, including beta glucan, which is one form of soluble dietary fiber. It promotes the growth of your baby’s beneficial gut bacteria and may encourage bacterial diversity in the gut (8).
What’s more, oatmeal is fairly neutral in taste, which makes it easy to combine with other hearty, healthy foods. For instance, you can spoon in puréed fruit and cinnamon for more flavor.
Avoid honey
Be sure to never feed a baby under 1-year-old honey, as doing so can put them at risk of botulism and pose a choking hazard (9).
4. Peanut butter
Peanut butter packs protein and fats — both of which can encourage weight gain in your baby.
Keep in mind that peanuts are one of the 8 allergens that can cause the most serious allergic reactions in the United States (10).
The latest evidence supports feeding infants as young as 6 months foods that commonly cause allergies. This includes peanuts. Research suggests this approach may actually help prevent allergies from developing (11, 12).
You’ll want to introduce allergenic foods methodically, always one at a time and introducing new, higher-risk foods at least a week apart.
It’s important to feed these to your baby on a regular basis — always watching for signs of allergies, including hives, redness around the mouth, or wheezing. If this occurs, seek medical help immediately (11, 12).
Never feed your baby peanut butter straight from the jar, as doing so may pose a choking hazard.
The best way to feed them natural peanut butter, or any other type of nut butter, is to blend them with either warm water, applesauce, breast milk or formula, or — if you’ve already introduced dairy — yogurt.
You can add it to oatmeal for added richness.
If your child is at a higher risk of allergies or has had eczema, speak with a healthcare professional before feeding them any nut butters or higher-risk foods.
They may advise waiting until they’re older and then want to supervise this in their office or suggest an allergy test first (13).
8 most common food allergies
- cow’s milk
- eggs
- fish
- crustacean shellfish, like shrimp
- wheat
- soy
- peanuts
- tree nuts
Learn more about food allergies here.
5. Eggs
Eggs are another powerhouse food that’s great for infants and adults alike. They provide a filling combination of fats and protein. They’re often gentle on the stomach, versatile, and easy to prepare (14,15).
Be mindful because this is another common allergenic food that you’ll want to introduce slowly and methodically. Keep an eye open for an allergic reaction. Seek immediate emergency care if your baby is wheezing or having trouble breathing (11, 12).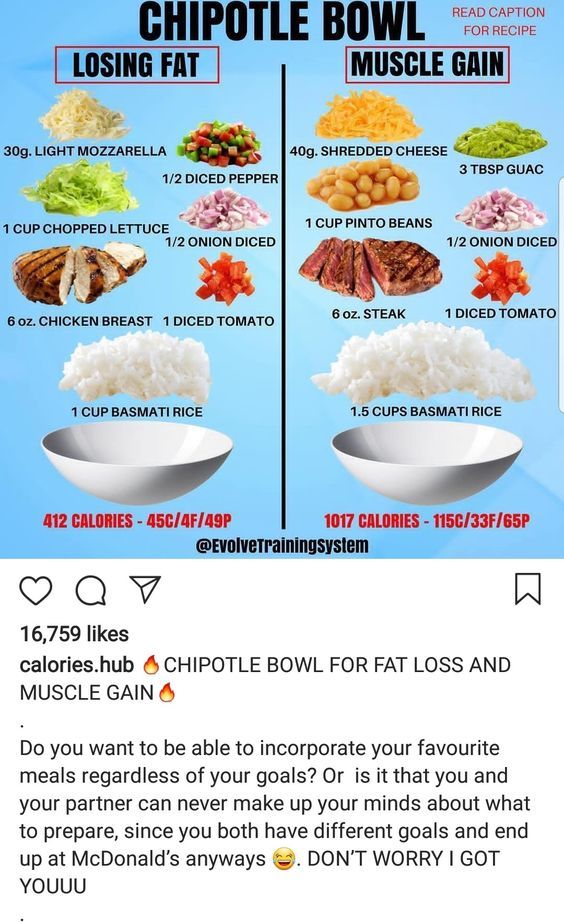
Once eggs are a mainstay in your baby’s diet, you could try scrambling them and sprinkling in some cheese and veggies for added nutrients.
You can also use eggs in other dishes. For example, try adding them to rice with cheese and veggies for some quick rice patties, then cut these into strips to serve.
You certainly don’t have to hold off until the 9-month mark to introduce fish, but it might be easier for babies to handle the texture at this age than earlier in life.
6. Fish
Fish delivers protein and healthy fats that are vital to your little one’s growth. Do be mindful to seek out low mercury fish, like salmon, herring, and trout (16).
Furthermore, these and other fish contain brain-nourishing docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid that’s essential for proper brain development in early childhood (17).
Pair fish with a rich lemon full fat yogurt dip or marinara sauce for added nutrients.
It seems counterintuitive, but when babies hit their 12-month milestone, you may find they’re eating less.
This is because their growth rate slows. In fact, most toddlers will only put on about 5 pounds between their first and second birthday (18).
Of course, they’re still growing and needing lots of nourishment — they are simply not growing quite as rapidly as they were in those first 12 months of life.
So, don’t be worried if your champion eater suddenly slows down or plateaus at this phase. If they still have the energy to play and seem alert, they’re probably doing just fine.
7. Olive or avocado oils
Your toddler should get a fair amount of healthy fats. In fact, 30–40% of your toddler’s calories should come from fats (19).
They need roughly 1,000-1400 calories each day at this age, so that translates to about 30–50 grams of fat per day (19).
If your toddler needs a bit more support, consider adding a splash of olive oil or avocado oil to their food, about 1/4–1/2 tablespoon (4–7 mL) to start. You can add it into a bowl of soup or hummus or sop some whole grain bread into it.
Take care not to feed your baby too much oil, as doing so could cause gastric upset or diarrhea.
If your baby has energy to play and is tracking along with developmental milestones, they’re probably growing just fine.
Unless a healthcare professional has identified an issue with your baby’s weight, you probably don’t need to worry.
Keep in mind that babies born prematurely and those with special health needs may not track along with general growth charts.
That said, parental instinct is real. Always voice any concerns with your child’s healthcare professional. Take note of what exactly you observe that troubles you, in as much detail as possible.
For example, you could record the times, dates, and amounts and types of food your child has eaten.
If your baby seems lethargic, is refusing to feed, or isn’t meeting developmental milestones, you should make an appointment to speak with a healthcare professional, such as a pediatrician.
In addition to a medical evaluation, they may refer you to another specialist, lactation consultant, occupational therapist, or dietitian.
Your little one’s early nutrition can have lifelong impacts. Making sure they’re getting enough to eat — and growing enough — is a concern for many parents.
If your child is not tracking along or suddenly not feeding as well as they used to, speak with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying causes. Do keep in mind that babies’ food intake normally slows at around the 12-month mark.
There are many wonderful, nourishing foods to help support your baby’s growth — including eggs, avocados, and peanut butter.
If they’re younger, or under 6 months, try to provide enough opportunities for them to breastfeed or drink enough formula according to their hunger cues.
All that said, if your little one seems alert, is meeting the developmental milestones for their age, and has enough energy to play, they’re probably getting enough to eat.
Just one thing
Try this today: The article 21 Homemade Baby Food Recipes is a great resource with tips on how to make a variety of tasty, nutritious meals for your baby once they start eating solid foods.
The birth of a small child is not uncommon today. Often, such babies are born on time or a little earlier, but due to a lack of weight, they can significantly lag behind their peers in development. Pediatricians and neuropathologists closely monitor the child's condition, because a child's body weight deficiency is a risk factor for changes in the neurological status, functional disorders of the cardiovascular and autonomic nervous systems. But because of their weakness, underweight children do not eat well, and the rate of weight gain in children born with low body weight determines their further physical and psychomotor development and the formation of the immune system.
How much should a newborn gain in weight?
To assess the development of your child and the compliance with the norm of the main indicators (height, weight), you can contact a pediatrician or independently - according to existing tables. In the first months, the child is actively growing, adding up to 25-60 grams per day. Small children with adequate nutrition can increase body weight more intensively than their peers. For the first month of life, children should gain up to 1.3-1.7 kg. After 5-6 months of life, the intensity of weight gain decreases somewhat - in 30 days, the increase can be only 400-700 grams.
Small children with adequate nutrition can increase body weight more intensively than their peers. For the first month of life, children should gain up to 1.3-1.7 kg. After 5-6 months of life, the intensity of weight gain decreases somewhat - in 30 days, the increase can be only 400-700 grams.
The length of the child's body during the first month increases by 4-7 cm, and after 5-6 months of life, growth is added less intensively - by 2-3 cm. But parents should understand that these figures are approximate. Each child is individual. Its weight and height depend on many factors: heredity, the quality of the mother's nutrition, the state of health of the newborn, the severity of childbirth.
Why is the child not gaining weight well?
The main cause of underweight in the neonatal period is the baby's refusal to breastfeed. Small children have poor appetite and spend most of the day sleeping. Often, parents have to wake up the child for a long time, and after a few minutes of sucking on the breast or a bottle of formula, the newborn falls asleep again. Children are especially sleepy, in whom pronounced physiological jaundice was observed in the first days of life.
Children are especially sleepy, in whom pronounced physiological jaundice was observed in the first days of life.
As a result, after the next weighing, the doctor can tell the mother that the newborn has not gained weight at all or the increase is insignificant. If the situation does not improve for several months, the mother and baby may be hospitalized for a comprehensive examination and tube feeding in a hospital setting.
Sometimes the cause of low weight gain lies in non-compliance with breastfeeding tactics. Pediatricians recommend applying the baby to only one breast during feeding so that it sucks out the "hind" milk, which is of particular energy value and rich in nutrients. Due to their inexperience, mothers offer both breasts to newborns. In this case, the child sucks the upper milk without making any effort and quickly falls asleep, slightly satisfying his hunger.
If the baby has had an infectious disease, has been ill for a long time, suffered from a high temperature or an intestinal disorder, then the monthly weight gain may be significantly less than usual. In this case, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is also shifted, and during the period of illness, in general, many children practically refuse to eat, which is reflected in their weight. Parents should actively communicate with the pediatrician, if necessary, ask him questions of interest and adhere to all recommendations.
In this case, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is also shifted, and during the period of illness, in general, many children practically refuse to eat, which is reflected in their weight. Parents should actively communicate with the pediatrician, if necessary, ask him questions of interest and adhere to all recommendations.
How to help a child gain weight and catch up with his peers in his development?
If you are breastfeeding, pay special attention to your diet. Drink as much liquid as possible: low-fat milk, compotes, hypoallergenic juices. Your diet must include boiled or baked meat. Take extra vitamins (as advised by the doctor). Breastfeed your baby immediately after waking up, when he is active, in a good mood and does not want to sleep.
But sometimes women's milk is produced in insufficient quantities or the baby does not have enough strength to suck it out. In this case, it is necessary to start supplementing with special infant formula as soon as possible. For children prone to allergic reactions, special hypoallergenic products are intended, which can be bought at a pharmacy, having previously discussed the mixture option with a pediatric nutritionist or pediatrician. Small babies are not adapted to intensive sucking, so the nipple on the bottle must be soft and pliable so that the child can fill up without problems.
For children prone to allergic reactions, special hypoallergenic products are intended, which can be bought at a pharmacy, having previously discussed the mixture option with a pediatric nutritionist or pediatrician. Small babies are not adapted to intensive sucking, so the nipple on the bottle must be soft and pliable so that the child can fill up without problems.
In addition, in order to increase the rate of weight gain and, accordingly, for the proper growth and development of the child, it is recommended to give courses of preparations containing L-carnitine (levorcarnitine), an essential vitamin-like substance that has anabolic properties and has proven itself to normalize body weight in case of its deficiency. In addition, by increasing the secretory and enzymatic activity of gastric and intestinal juices, appetite and digestion improve. One of these drugs is Elkar, containing an aqueous solution of L-carnitine. Elkar is included in the "National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life" as a means of correcting malnutrition of the II degree.
In children, in contrast to the adult body, where levocarnitine is among the substances produced, the synthesis of this compound covers only 1% of the required amount. Of course, the required amount of L-carnitine is found in breast milk, but if natural feeding is impaired or impossible, the drug must be added to the diet.
In underweight children, psychomotor development is often retarded, which can subsequently manifest itself in the form of speech defects, instability of the nervous system. Elcar improves the energy supply of brain activity, which will help to avoid or reduce the degree of development of functional failure in various areas of the child's neuropsychic response (motor, emotional-motivational, vegetative, cognitive spheres).
Another very important point: levocarnitine improves immunity, which is vital for small children, since almost all of them are predisposed to the development of infectious diseases.
The rate of weight gain is influenced by many external and internal factors.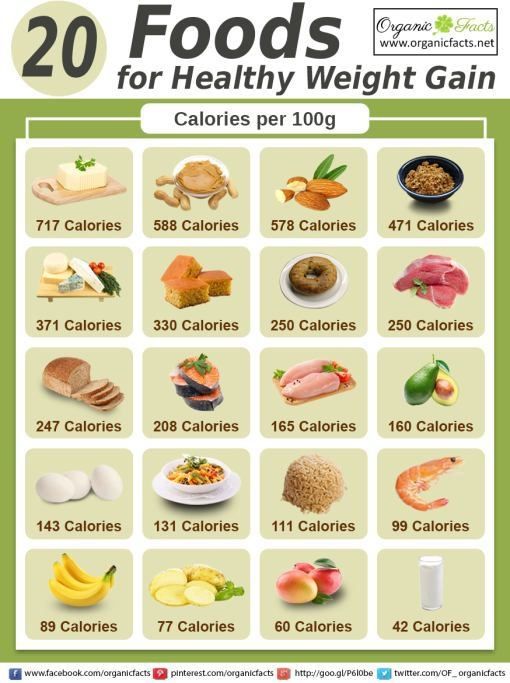 The task of parents is to help the crumbs get stronger as soon as possible. Walk more with your child in the fresh air so that his body receives the necessary amount of oxygen. And don't forget to visit your pediatrician. Small children need professional medical supervision and the attention of loved ones.
The task of parents is to help the crumbs get stronger as soon as possible. Walk more with your child in the fresh air so that his body receives the necessary amount of oxygen. And don't forget to visit your pediatrician. Small children need professional medical supervision and the attention of loved ones.
Underweight infant | Bibikol
When a child is born, his parameters immediately begin to be compared with various norms established for all children: height, weight, Apgar scores are given, and so all his life they will compare his development with some kind of developed and established framework, but we are all unique and are individual. We are influenced by genetics, living conditions and ecology - everything that surrounds us, one way or another, affects us and our children, so minor deviations from the norms are not considered critical.
In this article, we want to talk to you about the weight of an infant - when poor weight gain indicates serious problems, and when you should not panic, but just regularly monitor changes in baby's weight.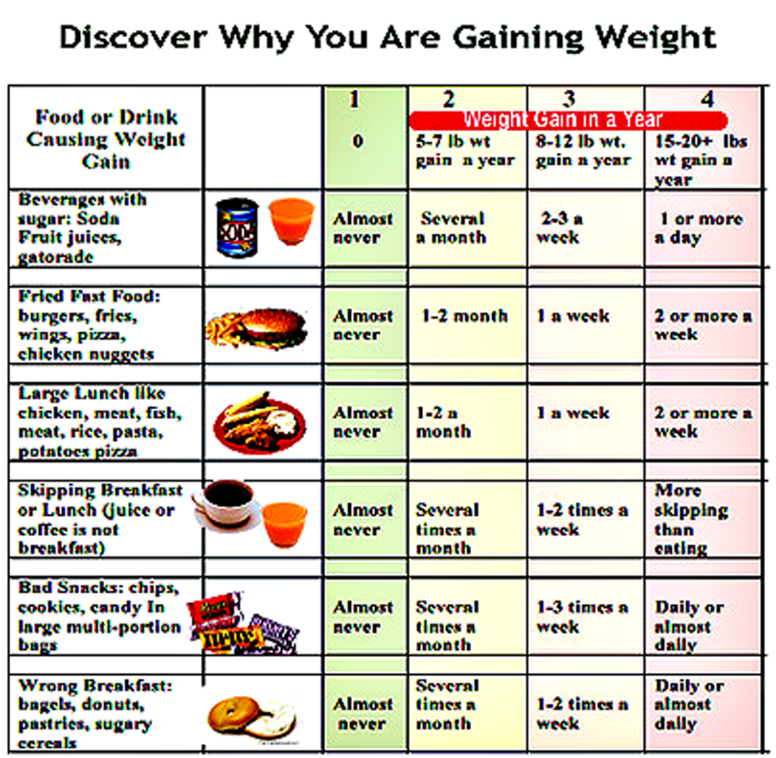
It is generally accepted that a newly born baby should add an average of 200 grams every week, and for a month in the region from 600 to 800 grams, and such an active increase goes up to six months. Then the baby continues to grow and gain weight, but not at such a pace - after six months, about 400-500 grams per month can be considered the norm. And this is only an average indicator, which in no way says that every month there should be, for example, +600 grams on the scales, no, in one month a child can gain all 800 grams, in the next 500 grams, but in in total, he will have +1300 grams in two months, which means 650 grams per month and this will be considered the norm!
Yes, it would be ideal to gain 800 grams every month, but again, everyone's bodies are different and if your baby fits into the average norms, then you should not sound the alarm. After all, you have a pediatrician who is obliged to help if any health problems arise. As a result, when the child reaches 12 months, his weight should be at least 10 kg. There is one more “but”, the height and weight of a healthy child are always interconnected and an increase in one indicator entails an increase in another, but if they increase out of proportion, then special attention must be paid to the health of the baby.
There is one more “but”, the height and weight of a healthy child are always interconnected and an increase in one indicator entails an increase in another, but if they increase out of proportion, then special attention must be paid to the health of the baby.
In each individual case, weight gain is considered individually, since the type of feeding plays a role here - breast milk or adapted milk formula, the constitutional characteristics of the child and other factors. For example, sometimes common colds can affect weight gain, but this is acceptable during the period of illness, and if a child loses weight for several months in a row, then it is worth considering and looking for other reasons. Usually, at the time of discharge from the hospital, the weight of the child is slightly lower than that with which he was born, but this is a common situation that you should not focus on. In the future, if the child is not gaining weight well, then it is necessary to exclude serious diseases and find out the cause of underweight.
Lack of body weight is called malnutrition and has three degrees, the first of which is insignificant, the reason for this may simply be a lack of mother's milk. In this case, it is worth increasing the number of feedings, especially if it is less than or equal to 5 times a day, slow sucking and falling asleep during feeding - here you should wake up the baby and offer to eat more, on average, the child should eat from 15 to 30 minutes. Too warm clothes can also interfere with the baby in the process of feeding and cause malnutrition. An insufficient amount of mother's milk is also the cause of underweight in the baby, here you should try to increase lactation or switch to mixed feeding, that is, breastfeed the baby first, and then supplement it with an adapted milk formula.
Too early or, conversely, late introduction of complementary foods can also affect the baby's weight - remember that a child who is bottle-fed should begin to get acquainted with other products from 4 months, and a baby who eats breast milk from 5 or even 6 months.
Another reason for underweight can be an incorrectly selected mixture. This usually happens when the mother makes her own decision, choosing an unbalanced diet for her crumbs. For example, feeding children with therapeutic mixtures must be approved by a doctor and have really serious indications for this, and in other cases, either changing the mixture or using other methods of treatment can be dispensed with without compromising the child in good nutrition. For example, the use of Nanny formula for feeding a baby has a beneficial effect on weight gain, and on the growth and development of a child, and is also great for children prone to allergies.
There is also such a problem as poor digestion of food. It would seem that the child eats well and in normal quantities, and gains weight poorly, then we can assume lactase deficiency, dysbacteriosis or fermentopathy. If the problem really exists in the gastrointestinal tract, then problems with the stool are not excluded - pay special attention to this and consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion.