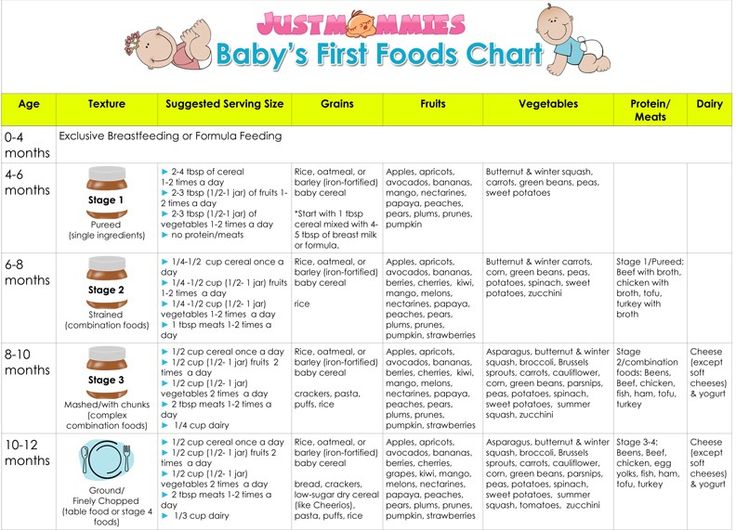
My baby vomits after every feed
Children and vomiting - Better Health Channel
Summary
Read the full fact sheet- Mild vomiting is normal in most babies and improves over time.
- Most babies need only simple treatment, or none at all.
- Changing feeding and sleeping positions may help.
- Medicine should not be given unless prescribed by your doctor.
- Give a child who is unsettled after vomiting a drink or a little food.
- If your child seems unwell or shows any worrying symptoms, see a doctor.
Vomiting can be part of many illnesses in children and babies. It is not usually a major concern as long as your child seems well in other ways.
Vomiting is common for babies and young children. Vomiting occurs when food is brought back up from the stomach. The amount of vomit can often seem larger than it actually is.
Types of vomiting
There are different types of vomiting, including:
- Possetting – this is when your baby vomits up small amounts after a feed.
- Reflux – this vomiting is common in babies. It is caused when the valve at the top of the stomach accidentally opens. The contents of the stomach come back up the food pipe (oesophagus) slowly. Reflux does not harm babies. They usually grow out of it by the time they are walking.
- Projectile vomiting – this is when your baby brings up the stomach contents in a forceful way. The amount of milk or food can seem large on the floor, but is usually only the amount of the last feed. Babies may projectile vomit occasionally, but if it happens after every feed, see your doctor right away as it may be due to a blockage caused by thickening of the muscle at the outlet of the stomach.
Causes of vomiting
Vomiting is usually caused by:
- minor infections like 'gastro' or the common cold
- gastro-oesophageal reflux
- motion sickness from travelling in a moving vehicle.
Sometimes, vomiting may be part of a more serious illness. Children may vomit if they have an infection, such as a urinary tract infection or meningitis, a bowel obstruction or appendicitis. If vomiting progresses to fever and diarrhoea, it will usually be caused by a virus infection. If this persists for 12 hours or more, dehydration is likely. so see your doctor or local hospital emergency department without delay.
Treatment for vomiting
Most babies and children vomit easily and recover quickly. After vomiting, your child may be hungry and thirsty. Give plenty to drink so your child does not become dehydrated. If your child keeps on vomiting and looks unwell, see your doctor. Do not use medication to try and stop the vomiting.
Reflux vomiting can be prevented or reduced
Different positions for feeding or in bed can help reduce your baby’s chance of vomiting. You can try to:
- Feed your baby in an upright position.
- Prop your baby up after feeds.
- Lay your baby on the left side.
- Avoid bouncing your baby after feeding.
To help with mild reflux, you can thicken your baby’s food with cornflour or infant food thickener. If your child is uncomfortable after vomiting or will not settle, try giving milk or water. This will wash any acid back into the stomach. Some babies get heartburn, which is a burning sensation in the chest. They may be unsettled after feeding or when lying flat. Your doctor can suggest an antacid to relieve heartburn.
When to see your doctor
Take your baby to the doctor if any of these symptoms occur:
- poor weight gain because of the loss of feeds in vomiting
- coughing or choking spells
- blood or yellow-green bile in the vomit
- heartburn
- vomiting increases or becomes forceful after every feed
- your baby seems unwell.
Where to get help
- Your doctor
- NURSE-ON-CALL Tel. 1300 60 60 24 – for expert health information and advice (24 hours, 7 days)
- Your local maternal and child health nurse
- The 24 hour Maternal and Child Health Telephone Service.
 Tel.13 22 29
Tel.13 22 29 - Your local hospital emergency or casualty department
Things to remember
- Mild vomiting is normal in most babies and improves over time.
- Most babies need only simple treatment, or none at all.
- Changing feeding and sleeping positions may help.
- Medicine should not be given unless prescribed by your doctor.
- Give a child who is unsettled after vomiting a drink or a little food.
- If your child seems unwell or shows any worrying symptoms, see a doctor.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
Infant Vomiting - HealthyChildren.org
My baby vomits a lot. Is this a sign of a problem?
Because many common childhood illnesses can cause vomiting, you should expect your child to have this problem several times during these early years. Usually it ends quickly without treatment, but this doesn’t make it any easier for you to watch. That feeling of helplessness combined with the fear that something serious might be wrong and the desire to do something to make it better may make you tense and anxious. To help put your mind at ease, learn as much as you can about the causes of vomiting and what you can do to treat your child when it occurs.
That feeling of helplessness combined with the fear that something serious might be wrong and the desire to do something to make it better may make you tense and anxious. To help put your mind at ease, learn as much as you can about the causes of vomiting and what you can do to treat your child when it occurs.
Vomiting vs Spitting Up
First of all, there’s a difference between real vomiting and just spitting up. Vomiting is the forceful throwing up of stomach contents through the mouth. Spitting up (most commonly seen in infants under one year of age) is the easy flow of stomach contents out of the mouth, frequently with a burp.
Vomiting occurs when the abdominal muscles and diaphragm contract vigorously while the stomach is relaxed. This reflex action is triggered by the “vomiting center” in the brain after it has been stimulated by:
Nerves from the stomach and intestine when the gastrointestinal tract is either irritated or swollen by an infection or blockage
Chemicals in the blood (e.
 g., drugs)
g., drugs)Psychological stimuli from disturbing sights or smells
Stimuli from the middle ear (as in vomiting caused by motion sickness)
Causes of Vomiting
The common causes of spitting up or vomiting vary according to age. During the first few months, for instance, most infants will spit up small amounts of formula or breastmilk, usually within the first hour after being fed. This “cheesing,” as it is often called, is simply the occasional movement of food from the stomach, through the tube (esophagus) leading to it, and out of the mouth. It will occur less often if a child is burped frequently and if active play is limited right after meals. This spitting up tends to decrease as the baby becomes older, but may persist in a mild form until ten to twelve months of age. Spitting up is not serious and doesn’t interfere with normal weight gain.
Occasional vomiting may occur during the first month. If it appears repeatedly or is unusually forceful, call your pediatrician. It may be just a mild feeding difficulty, but it also could be a sign of something more serious.
If it appears repeatedly or is unusually forceful, call your pediatrician. It may be just a mild feeding difficulty, but it also could be a sign of something more serious.
Persistent Vomiting
Between two weeks and four months of age, persistent forceful vomiting may be caused by a thickening of the muscle at the stomach exit. Known as hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, this thickening prevents food from passing into the intestines. It requires immediate medical attention. Surgery usually is required to open the narrowed area. The important sign of this condition is forceful vomiting occurring approximately fifteen to thirty minutes or less after every feeding. Anytime you notice this, call your pediatrician as soon as possible.
GERD
Occasionally the spitting up in the first few weeks to months of life gets worse instead of better—that is, even though it’s not forceful, it occurs all the time. This happens when the muscles at the lower end of the esophagus become overly relaxed and allow the stomach contents to back up. This condition is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. This condition usually can be controlled by doing the following:
This condition is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. This condition usually can be controlled by doing the following:
Thicken the milk with small amounts of baby cereal as directed by your pediatrician.
- Avoid overfeeding or give smaller feeds more frequently.
- Burp the baby frequently.
- Leave the infant in a safe, quiet, upright position for at least thirty minutes following feeding.
If these steps are not successful, your pediatrician may refer you to a gastrointestinal (GI) specialist.
Infection
After the first few months of life, the most common cause of vomiting is a stomach or intestinal infection. Viruses are by far the most frequent infecting agents, but occasionally bacteria and even parasites may be the cause. The infection also may produce fever, diarrhea, and sometimes nausea and abdominal pain. The infection is usually contagious; if your child has it, chances are good that some of her playmates also will be affected.
Rotaviruses are a leading cause of vomiting in infants and young children, with symptoms often progressing to diarrhea and fever. These viruses are very contagious, but are becoming less common than in the past, due to the availability of a vaccine that can prevent the disease. The rotavirus is one of the viral causes of gastroenteritis, but other types of viruses—such as noroviruses, enteroviruses, and adenoviruses—can cause it as well.
Occasionally infections outside the gastrointestinal tract will cause vomiting. These include infections of the respiratory system, infections of the urinary tract otitis media, meningitis , and appendicitis. Some of these conditions require immediate medical treatment, so be alert for the following trouble signs, whatever your child’s age, and call your pediatrician if they occur.
Blood or bile (a green-colored material) in the vomit
Severe abdominal pain
Strenuous, repeated vomiting
Swollen or enlarged abdomen
Lethargy or severe irritability
Convulsions
Signs or symptoms of dehydration, including dry mouth, absent tears, depression of the "soft spot", and decreased urination
Inability to drink adequate amounts of fluid
Vomiting continuing beyond twenty-four hours
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician.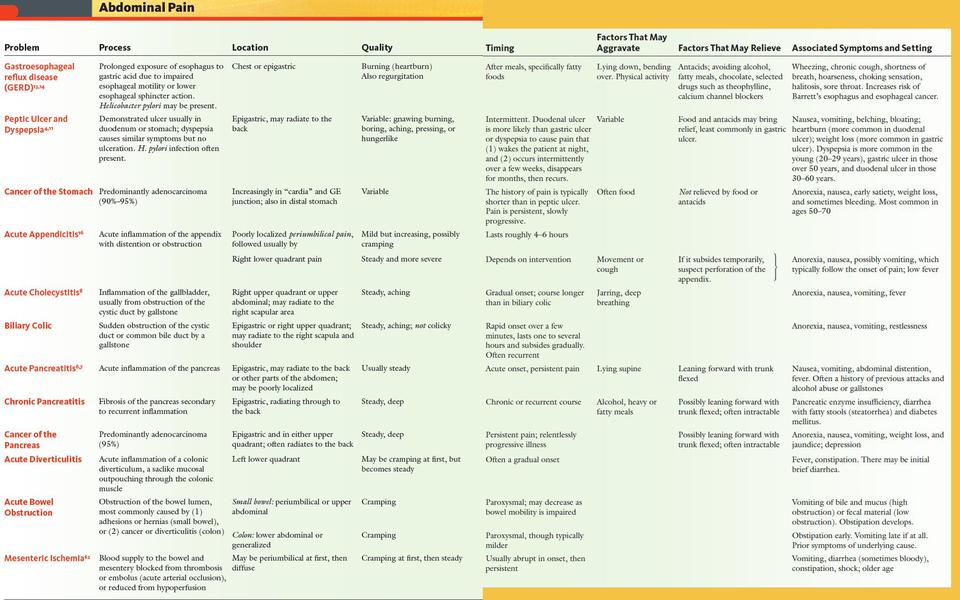 There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Article | Neurotic vomiting in children
Bobylova M.Yu. (neurologist)
Vomiting in children is not an independent disease, but a manifestation of various diseases. Vomiting can be caused by disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic diseases, tonsillitis, inflammation of the nasopharynx, pneumonia, influenza, SARS, acute appendicitis. Such vomiting is treated by a pediatrician. But there are also vomiting associated with dysfunction of the central nervous system. It develops in children of the first months of life who have undergone hypoxia during fetal development or childbirth. After 6 months, habitual vomiting is often associated with improper introduction of complementary foods if the child is force fed. Also, vomiting can be a sign of increased intracranial pressure. Vomiting attacks are characteristic of the childhood form of migraine.
Vomiting attacks are characteristic of the childhood form of migraine.
In infants , especially in the first 3 months of life, regurgitation of a small amount of food (15-30 ml) 2-3 times a day is a common phenomenon that disappears with the growth of the child. The horizontal position of the baby and the relatively large amount of food predispose to the occurrence of regurgitation in healthy infants. It is also characteristic of regurgitation when swallowing air during breastfeeding, when there is not enough breast milk in the mammary gland, or when the baby does not capture the areola. With artificial feeding - swallowing of air occurs when the nipple is not completely filled with milk, when there is a large hole in the nipple, when the position of the bottle during artificial feeding is horizontal.
Swallowing air is more common in infants who are hyperexcitable, greedily sucking, and also with general muscular hypotension.
Regurgitation, unlike vomiting, occurs suddenly, does not affect the behavior and general well-being of the child, while children do not lose weight gain.
Helping a child with spitting up: firstly, immediately after feeding and during sleep, you should hold the baby in an upright position. If regurgitation has occurred, it is necessary to turn the child's head to one side, toilet the child's nose and mouth (clean it from food debris). Wash and caress the baby.
Feeding rules must be observed: the baby should be fed in a semi-vertical position, which helps to expel swallowed air. These babies should sleep with their heads up.
If regurgitation is frequent and profuse, and the baby begins to lag behind in weight, then this may be a manifestation of a disease of the stomach or intestines (pylorospasm or pylostenosis). It is necessary to contact a pediatrician for timely examination, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of complications.
Neurological disorders as a cause of vomiting in a child
The vomiting center of a person is located in the brain, therefore, in case of any damage to the head (trauma, infection, vegetative-vascular dystonia, increased intracranial pressure), vomiting occurs not associated with food intake and fever .
Vomiting in children under 1 year of age is associated with hypoxia during fetal development and at birth.
Neurotic vomiting develops as a manifestation of neurotic reactions in response to nasty and undesirable actions: coercion, protest against punishment, feeding. Functional vomiting in such children is more often combined with refusal to eat, with selectivity in food, behavioral changes, and stubbornness. More common is functional vomiting in children who are emotional, easily excitable, vulnerable. There are no signs of intoxication of the body, pain in the stomach, diarrhea or temperature in the child. This behavior requires prompt treatment to a neurologist.
Vomiting in children, even if it is not accompanied by diarrhea and fever, requires the attention of parents. In no case should you self-medicate, since for each disease the methods of treatment are different.
Only a doctor can recognize the causes of the problem after a series of examinations. To clarify the cause of constant vomiting in a child, it is necessary to clarify when it began, what kind of character it is (periodic, after each feeding), whether it is somehow connected with food intake and with the time of day. Important information about possible diseases is also provided by the diagnosis of vomit. The masses are checked for the presence of mucus, bile, milk, blood, digested and undigested food debris. When making a diagnosis, the age of the child is taken into account. If in infants and young children, in most cases, vomiting is a symptom of CNS disorders due to asphyxia (intrauterine or postpartum), trauma, defects in the gastrointestinal tract, and intolerance to cow's milk, then in older children it is a sign of a possible migraine.
Diagnostic procedures in determining the cause include ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, blood, feces, examination by a neurologist, if necessary, tomography, EEG, neurosonography. In the complex treatment of vomiting, sessions with a psychologist are important.
Help with neurotic vomiting includes a wide range of preventive and therapeutic measures that require an integrated approach.
Required tasks:
1) elimination of emotional disorders (emotional lability, irritability, anxiety, etc.;
2) treatment of asthenic manifestations, overcoming physical and mental exhaustion;
3) regulation of autonomic disorders;
4) treatment of obsessions and fears, if any;
5) correction of personality traits;
6) elimination of negative factors;
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children, spitting up continues until the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of age, the stomach has a spherical shape. It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .
- Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract.
However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .
- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular apparatus of newborns is immature. It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors that contribute to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes post-feeding regurgitation and baby's predominantly horizontal position during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Regurgitation in many newborns can be triggered by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, strained cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems?
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children. Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up often, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after eating (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day. With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Neonatal regurgitation, which is considered normal and not of concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually lasts for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.

How to help a newborn who spit up often?
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 . The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach. To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to hold the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 . To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in a supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It turned out that it is associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 . If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc., it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy. 1 Zakharova I. Nagornaya 2906 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013. No. 5 (48). 3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67. 4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28. 5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition.
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air New Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve

References  N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.