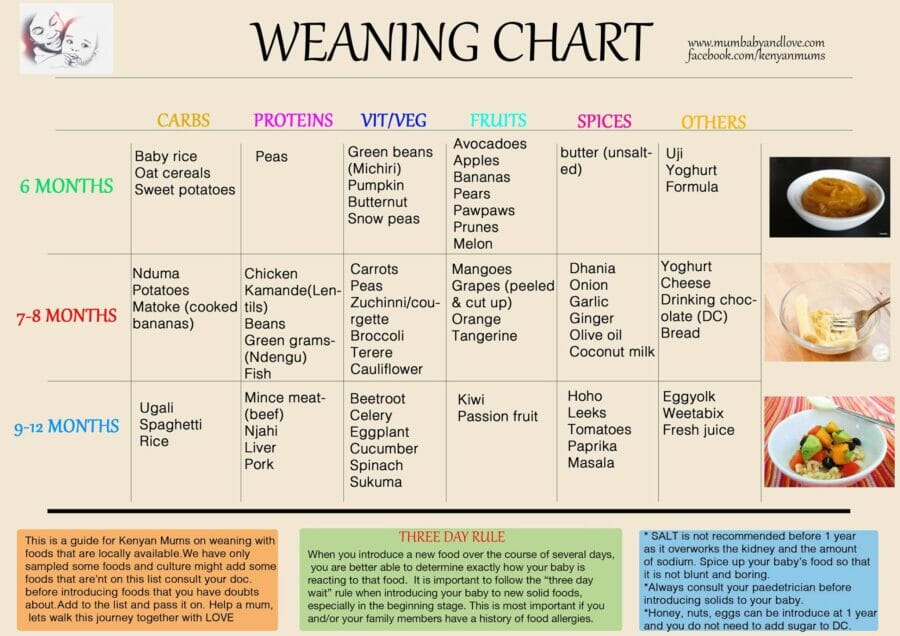
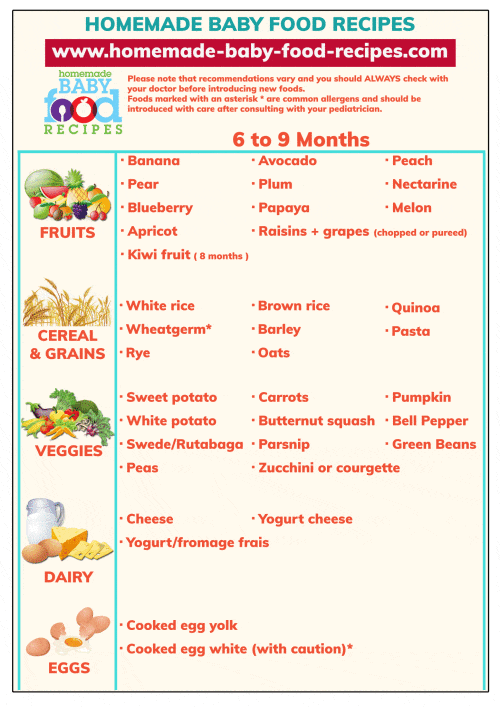
What age can you feed a baby
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods.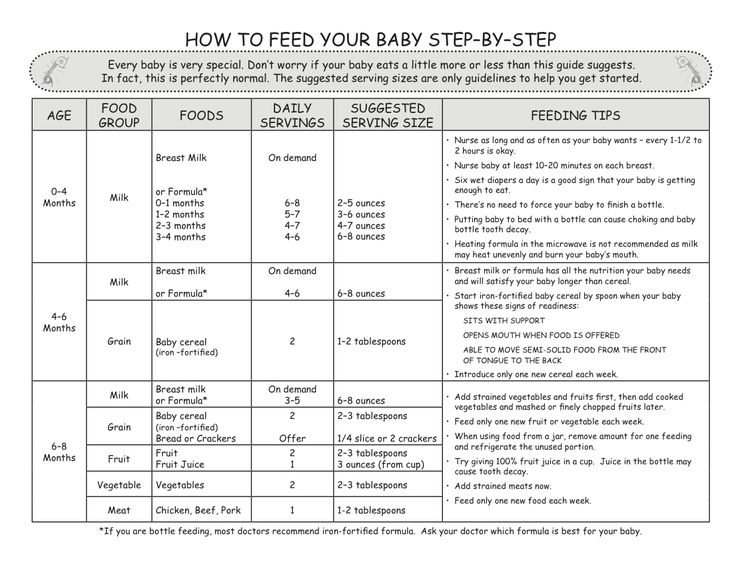 But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula.
 It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese. - foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.
- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods.
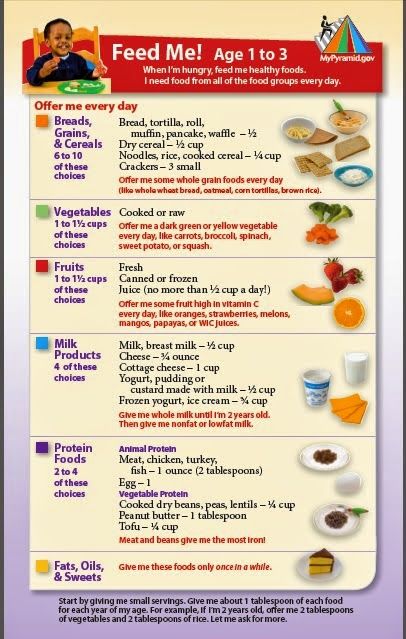 (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
(Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.) - After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods..jpg)
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to mixed or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc. ). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in an absolutely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in an absolutely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually “dilute” this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. The materials were prepared by the staff of the Healthy and Sick Child Nutrition Laboratory of the National Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of Russia and are based on the recommendations given in the National Program for Optimizing the Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation, approved at the XV Congress of Pediatricians of Russia (02.2009d.) Some new mothers try to do this as early as possible. Others continue to put the baby to the breast at 4 and 5 years. Play their role and "national" characteristics. For example, in the UK, only a third of babies in their six months still receive mother's milk, while the rest are transferred to formula. And in the UAE, the law prescribes to breastfeed children up to two years, otherwise you can get severe punishment. In fact, it is on the number “two years” that most doctors around the world agree. It is believed that after this age, mother's milk no longer brings additional health benefits. Is it so? we deal with experts. Tatyana Kuznetsova On the recommendation of the World Health Organization and the UN Children's Fund, it is desirable to maintain breastfeeding up to 2 years, longer - at the mutual desire of the mother and child. Domestic pediatricians, based on practical experience and scientific research, voice the figure up to 1.5 years. It is now not uncommon to see mothers who breastfeed their children after two years of age. Such prolonged breastfeeding is commonly referred to as long-term feeding. In any case, after 2.5 years, the child goes through the process of natural extinction of the sucking reflex, there is a gradual self-weaning and, thus, the smooth completion of breastfeeding. Regardless of the recommendations, the choice always remains with the mother. And the duration of breastfeeding will depend, first of all, on the readiness of both the mother and the child to stop this process. Breast milk substitutes do not contain anti-infectious factors, so an artificially fed baby is more likely to get intestinal infections and respiratory diseases. These include frequent acute respiratory viral infections, otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia, intestinal infections (usually of a viral nature) with prolonged diarrhea, fungal intestinal diseases, as well as a formidable life-threatening condition - necrotizing enterocolitis of newborns. Quite often in children on mixtures, intolerance to animal milk proteins (bovine, goat) develops with the development of allergic reactions, in particular, food allergies in the form of atopic dermatitis. Unfortunately, in the future such children are at risk for the development of allergic bronchitis, bronchial asthma. Artificial feeding increases the risk of developing diabetes mellitus, as well as obesity associated with excess formula intake that exceeds the needs of the child. Perhaps the development of seizures due to excess content in mixtures of sodium, calcium, phosphorus. Infants receiving artificial formula may have reduced intellectual development due to a lack of amino acids, omega fatty acids, which are necessary for the growing brain of a child. In addition, according to some studies, not breastfeeding increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Not only abroad, but also in Russia, there are many studies that have proven the benefits of mother's milk at any time of feeding. After a year, breast milk changes its composition, but not for the worse. The main reason for these changes is that milk is no longer the main food for the baby, and other functions come to the fore. The older the child becomes, the greater the concentration of immunoglobulins in milk increases, which protect the child from infectious diseases. Breast milk contains leukocytes and a number of anti-infectious factors, as well as antibodies against infectious agents previously transferred by the mother. Today it is becoming very fashionable to instill early independence in children, and premature weaning is seen by some parents as a means to make the child more independent. However, psychologists who are closely involved in the study of child development warn that premature weaning can, on the contrary, provoke a delay in emotional development and increase dependence on parents. Imposed independence turns into psychological isolation and abandonment. It is much better to give the child the opportunity to become independent when he is ready for it. This is well illustrated by the results of foreign studies: for example, one of them showed that the greatest achievements in school were in children who were fed longer. Yes, and Russian doctors, who undertook to study the effect of breastfeeding on the neuropsychic development of children, found that babies who ate their mother's milk for a long time show much better results both at two years, in tests of speech development, and at three years , in tests of the correct performance of skills. Many long-term mothers successfully combine feeding with work, and also take their children to kindergartens. Applications remain only at bedtime and at night. The rest of the time, the baby usually does not need to breastfeed. Ideally, the child should stop asking for breasts during the day, and then at bedtime and at night. As a rule, this happens about 2. But if the child continues to breastfeed after 3.5 years, this may indicate some psychological problems of the baby or mother, in this case it is advisable to contact a psychologist, but not an ordinary one, but a friendly one for long-term feeding. Sergey Butriy - One of the most "explosive" topics in the pediatrician's office after vaccinations is breastfeeding. Now it's fashionable to be for GW. Of course, formula is not quite the same as breast milk. There is only one "but". Mothers who fail to breastfeed for health reasons experience a tremendous sense of guilt. They are pressed by society, other mothers, breastfeeding consultants. Many become depressed because of this, trying to feed through physical pain. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VMS
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk
Pediatrician "SM-Doctor" about the age until which a child should be breastfed
TATYANA KUZNETSOVA
pediatrician, nephrologist, breastfeeding consultant at the SM-Doctor clinic.
What threatens the child's health with early weaning?
And what are the disadvantages of late weaning?
How does breastfeeding affect the child's psyche?
And in the course of another, they found that the longer a child breastfeeds, the better social adaptation goes later, at the age of six to eight. Both mothers and teachers acknowledged that babies who were breastfed for a long time were much less likely to develop problem behaviors.
5 - 3 years.
What if you can't breastfeed?
SERGEY BUTRIY
Pediatrician, author of books on child health
A well-known doctor spoke about this in a podcast for Cuprum.