What do you feed a baby canadian goose
Brooding and Rearing Ducklings and Goslings, G8920
Glenn Geiger and Harold Biellier
Department of Animal Sciences
Brooding requirements
Natural brooding
Goslings and ducklings can be successfully brooded by broody chicken hens and most breeds of ducks and geese. If the young birds were not hatched by the broody female, place them under her at night. Be certain broody birds are free of lice and mites. Provide the hen and her brood with a dry comfortable shelter.
The hen will need grain and plenty of fresh, clean water supplied in a container that will not allow the young to get wet.
Artificial brooding
Today, hatcheries produce day-old ducklings and goslings in large numbers. Commercial growers brood and rear them in about the same way they would baby chicks.
Ducks and geese are hardy and are not susceptible to many of the common poultry diseases. This makes them easy to raise. Brooding requirements are simple and special housing or equipment is not necessary. Because of their rapid growth and early feathering, they do not require as long a brooding period as do baby chicks.
Types of brooders
The infrared heat lamp type of electric brooder is recommended for brooding small groups of birds. Many commercial raisers use gas brooders, but any type of good baby chick brooder may be used successfully. When using infrared brooders, allow one 250-watt lamp per 25 goslings or 30 ducklings. With other types, you can determine the number of birds per hover by cutting the brooder's rated chick capacity by half for ducklings and by one-third for goslings. Because ducklings and goslings are larger, it usually is necessary to raise the hover 3 to 4 inches higher than for chicks.
Brooding temperatures
The behavior of the young birds is a better guide than a thermometer. When brooder temperature is too hot, the birds will crowd away from the heat. High temperatures may result in a slower rate of feathering and growth.
When the temperature is uncomfortably cold, goslings tend to huddle together under the brooder or crowd in corners. Keeping a light on the birds at night will discourage such crowding. An infrared brooder provides enough light for this purpose.
Keeping a light on the birds at night will discourage such crowding. An infrared brooder provides enough light for this purpose.
When the brooding temperature is right, the goslings will be well distributed over the floor. At night, the birds should form a circle around the hover.
A starting temperature near 90 degrees at the edge of the hover is about right. This temperature should be reduced about 5 to 10 degrees per week until 70 degrees is reached. When using infrared brooders, air temperature is not so important. Heat usually is not required after the fifth or sixth week, and in good weather, the young birds can be taken out to pasture.
The brooder house
A special building is not required. It simply must provide protection from the weather and be reasonably well lit and ventilated. For brooding small numbers, a colony brooder house or any small building may be used. For brooding larger numbers, a barn, large poultry house or regular broiler house is recommended.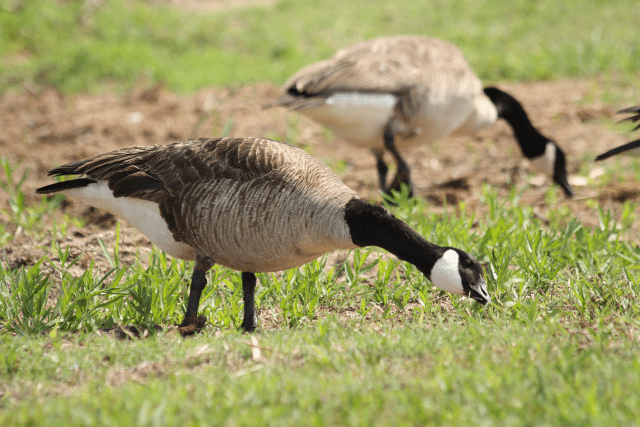
A wood, concrete, or dirt floor is satisfactory. Allow about 1-1/2 square feet of floor space per bird and cover the floor with about four inches of absorbent litter. Sawdust, shavings, ground corn cobs, cottonseed hulls, peanut hulls or peat moss are all good. Dampness is apt to be more of a problem with ducklings and goslings than it typically is in brooding baby chicks. Removal of wet spots and frequent additions of clean, dry litter are recommended.
Feeding
Goslings and ducklings are ready for feed and water when they arrive. Use crumbilized chick or poult starter for the first week to 10 days. A pelleted grower ration plus cracked corn, wheat, milo, oats or other grain can be fed after this time. Keep feed before the birds at all times. Also, provide insoluble grit. Place feed on rough paper or cup flats for the first few days. Do not use chick box tops or other smooth-surfaced lids or paper as feeders. When such slick-surfaced materials are used, leg damage results.
Be certain the feed you are using contains only those additives approved for ducks and geese. Certain types of drugs that are sometimes included in chick starting and growing mashes for coccidiosis control are harmful to goslings. They may cause lameness or even death. Coccidiosis has not been a problem in waterfowl production in this area.
Commercially grown ducklings generally are ready for market in seven to eight weeks. Goslings usually are marketed in the fall months at 24 to 30 weeks of age. Finishing rations should contain some protein similar to turkey finishing rations.
Water
Plenty of drinking water should be available at all times. Goslings and ducklings consume enormous quantities due to rapid growth. Use waterers that the birds cannot get into and splash. This is important in the brooder house. Water for swimming is not necessary; however, ponds provide an easy way to water goslings on pasture. Hog waterers make good range waterers for waterfowl.
Pasture for goslings
Make arrangements to provide pasture or lawn clippings starting as early as the first week. When the weather is mild, goslings can be let out and allowed to graze when only a few days old.
When the weather is mild, goslings can be let out and allowed to graze when only a few days old.
Grass is the natural food of goslings. Great savings in feed can be made by providing good pasture throughout the growing period. At five or six weeks of age they can subsist entirely on good pasture, although some supplemental feeding is recommended until the birds are completely feathered.
Experience has shown that ladino clover makes fine pasture for goslings. Other types of white clovers also are very good, as are most varieties of grasses. In Missouri, bluegrass, orchardgrass, timothy and bromegrass have been used. Small grains such as barley, wheat and rye make excellent early or fall pasture. Goslings or geese will scarcely touch sweet clover, lespedeza or alfalfa.
Allow about one acre of pasture for each 20 to 40 birds. The amount required depends on the size of the goslings and quality of pasture. When the pasture is poor, supplemental grain feeding is necessary.
A pasture rotation system is recommended. Protect goslings from rain or wet grass for the first few weeks, especially when the weather is cool. Shade must be provided in hot weather.
Protect goslings from rain or wet grass for the first few weeks, especially when the weather is cool. Shade must be provided in hot weather.
Because ducks do not forage as well as geese, it is recommended that commercial growers rear ducks without access to pasture. Ducks will, however, use some green feed and eat insects. The small grower probably will not want to confine his flock.
Be certain that pasture and green feeds you use do not have any chemical treatment that would be harmful to the flock.
Fencing
It usually is necessary to fence the pastures or fields. Most woven wire field fencing is of small enough mesh to confine birds 4 to 6 weeks or older. Two-inch mesh poultry netting is commonly used for younger birds. The fence does not need to be higher than ordinary heights since the birds seldom fly. Eighteen inches to two feet is an adequate height. Several farmers have reported good success using electric fencing.
References
- Brooding Chicks With Infra-red Lamps, U.
 S.D.A. Leaflet number 397.
S.D.A. Leaflet number 397. - Raising Ducks, U.S.D.A. Farmer's Bulletin number 2215.
- Standard of Perfection for Domesticated Land Fowl and Water Fowl, American Poultry Association, Inc., Crete, Nebraska 68333.
- Duck and Goose Raising, Bulletin number 532, Ontario Department of Agriculture, Parliament Building, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
- Raising Geese, Fact Sheet, Poultry number 44, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota 55101.
- Raising Geese, U.S.D.A. Farmer's Bulletin number 2251.
The authors are grateful to Fred Cervinka, Heart of Missouri Poultry Farm and Hatchery, Columbia, Missouri, for information, assistance and advice in the preparation of this guide.
Skip to main content
Skip to main content
What Do Canadian Geese Eat? 20+ Foods They Prefer
More Great Content:
Canadian geese, also called the Canada goose, are large waterfowl that live in North America and migrate to many far-flung places in the world during winter. Since they live in so many diverse places throughout the year, it’s only fair to ask, what do Canadian geese eat? Although they’re waterfowl that are frequently seen chomping on vegetation, the answer to that question is not cut and dry.
Since they live in so many diverse places throughout the year, it’s only fair to ask, what do Canadian geese eat? Although they’re waterfowl that are frequently seen chomping on vegetation, the answer to that question is not cut and dry.
We’ll explore the various foods that Canadian geese consume throughout their lifespans while also considering how they fare in less-plentiful situations.
What Foods Do Canadian Geese Eat?
Canadian geese eat grass, aquatic plants, and insects.Roxana Bashyrova/Shutterstock.com
Canadian geese eat grass, aquatic vegetation, algae, and insects. They are herbivorous most of the time, but they also integrate other foods into their feeding habits as necessary. For example, these birds will often consume more insects when they’re young and more roots as adults during winter when their preferred foods are not as widely available.
Consider the various foods that Canadian geese survive on throughout the year:
- Kentucky Bluegrass
- Cattails
- Grasshoppers
- Eelgrass
- Grains
- Earthworms
- Corn
- Root bulbs
- Sedge
- Duckweed
- Freshwater snails
- Tadpoles
- Shrimp
- Alfalfa
- Tall fescue
- Bermudagrass
- Bentgrass
- Mice
The favorite food of most Canadian geese is grass. It’s plentiful, easy to come across, and available just about everywhere they live or migrate to throughout the year. Of course, Canadian geese eat different foods depending on whether they are spending time on the water or land.
It’s plentiful, easy to come across, and available just about everywhere they live or migrate to throughout the year. Of course, Canadian geese eat different foods depending on whether they are spending time on the water or land.
Much of the time, geese do not directly search for mollusks and crustaceans to eat. They just happen to be near the different vegetation that the geese are eating, and they get are an added morsel.
Sometimes, Canadian geese will start to look for insects, mollusks, and other creatures when they have a nutritional deficiency. Like other waterfowl, most people refer to these creatures as herbivorous even though they’re not strictly plant-eaters. They’re certainly omnivorous.
How Do Canadian Geese Find Food?
Canadian geese find food by upending in water or grazing.Millie Bond – Copyright A-Z Animals
Canadian geese do not have extraordinary senses with which to find food. They have a decent sense of smell and a good sense of sight that provides them with the opportunity to find and distinguish between different foods.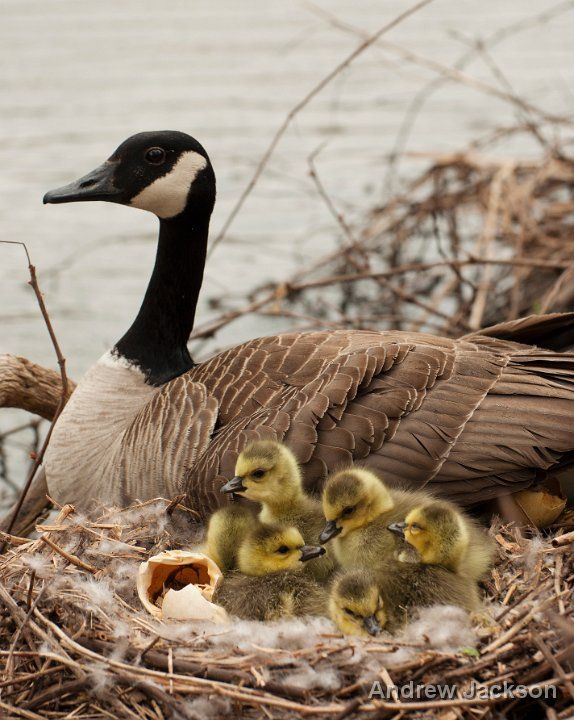
The primary way that Canadian geese find food is by grazing through the vegetation on land. They will bite the grass or plants and then tear away from it to break it since they lack teeth. They do possess tomia like some other waterfowl, rudimentary teeth-like protrusions on their bills, and tongues that help them tear through vegetation quickly.
Canadian geese often look for and consume foods while they are on the water too. Like other waterfowl, they will spot something they want to eat while paddling on the surface, and then dive to get it. This behavior is called upending as they tip their bodies into the water to feed, leaving just their tails above the water. The geese grab and tear water vegetation much as they do on land.
When it comes to eating insects, mollusks, or other invertebrates, the geese do not necessarily hunt. They opportunistically snatch up these creatures when they are near, especially when they lack access to their other preferred foods.
What Do Baby Canadian Geese Eat?
Goslings start eating grass and other vegetation as soon as they’re born.
Leena Robinson/Shutterstock.com
Baby Canadian geese are called goslings, and they can find their own food from the time they hatch. Like adults, they will prefer to feed on grass because it is plentiful and easy to consume. Sometimes, they will consume clover as well as dandelions that are mixed in their natural grazing areas.
Goslings will also eat small insects that they find, like mosquitoes and worms. These insects are filled with protein that will help the goslings get the nutrition they need.
Although they mostly stick to dry land when looking for food for the first few weeks of life, the goslings soon follow their mother into the water. Once there, they will include aquatic vegetation in their diet and assume fully adult eating habits.
What Do Canadian Geese Eat During Winter?
These geese migrate to warmer lands and eat grains, roots, and grass in the winter.iStock.com/Wayne Marinovich
The wintertime is a period of change for geese as many of them migrate south in search of warmer climates and food. In North America, Canadian geese can migrate all the way from Alaska to the southern portions of the United States and into Mexico.
In North America, Canadian geese can migrate all the way from Alaska to the southern portions of the United States and into Mexico.
Living in areas with less access to their favorite foods means geese have to diversify their diet to stay healthy. Among the foods that geese add to their diet are:
- Roots
- Berries
- Grains
- Sorghum
- Cracked corn
- Herbs
- Barley
- Berries
These birds will try to supplement their diet to include more carbohydrates to give them the energy they need to continue their migration and make it through the less-plentiful times of winter.
Canadian Geese often stop in fields that were just harvested for vegetables and will gladly stop at homes that put out fresh vegetables, especially leafy greens, for them to eat.
What Predators Eat Canadian Geese?
Coyotes can make a quick meal of Canadian geese.iStock.com/GatorDawg
Like other waterfowl, they have a reputation for being aggressive creatures, especially when it comes to defending their young. They are not all bluster, either. These geese will provide a warning with a threat display including spread wings and loud screeches. They will attack if the threat doesn’t scare off the encroacher.
They are not all bluster, either. These geese will provide a warning with a threat display including spread wings and loud screeches. They will attack if the threat doesn’t scare off the encroacher.
Although their threat display is enough to scare off some of their predators, it is not enough to protect them all the time.
The common predators of Canadian geese include:
- Coyotes
- Raccoons
- Eagles
- Bobcats
- Crows
- Ravens
- Foxes
- Bears
- Skunks
- Snakes
- Snapping turtles
- Humans
Goslings face the greatest threat of predation, especially from snakes, eagles, and snapping turtles. They have no defenses against these creatures, and their parents can only protect them to a certain extent.
Adult Canadian geese are viewed as pests by humans, but they are also protected from outright slaughter by laws. Sometimes, the geese are culled in local areas, but these birds do not have a struggling population by any means.
Canadian geese are migratory herbivores that do eat some insects, invertebrates, and mollusks from time to time. They are a common sight throughout North America, where they have become known for their threat displays and unique coloring that includes a black head and white cheeks.
Although they may be noisy creatures, they’re not a threat to people that leave them be and keep their distance, just like most other wild animals.
How to feed geese at home: recommendations for feeding, diet
Proper and balanced nutrition of geese brings a good income to the breeder. Birds give a lot of eggs, meat, soft fluff. They get sick less often, the survival rate of chicks increases. Feed costs are repaid by increasing the productivity of geese and reducing the cost of veterinarians. Many breeders are interested in how to ensure proper nutrition for free-range and caged birds, in winter and summer, which foods are better to add and which ones to limit or eliminate from the diet.
Content:
- Features of the diet of geese
- Composition of feed mixtures for geese and diet
- Specifics of feeding geese by seasons
- Prohibited products
- Farmers advice on feeding geese
Features of the diet of geese
Compound feed and greens form the basis of the nutrition of agricultural birds. The diet of geese should also include fresh vegetables: potatoes, beets, pumpkin, cabbage, silage and tops. In addition to herbal ingredients, whey, skim milk, fishmeal, yeast and salt are added to goose feed. It is not necessary to give all foods daily, but each of them must be regularly present in the diet.
Since it is difficult for geese to digest whole grains, dry crumbly compound feed is not recommended for them. Small particles can be inhaled. Birds begin to choke and choke. It is better to give them granulated feed. Geese with appetite eat oilseeds and legumes meal and cake, and prefer clover from meadow grasses.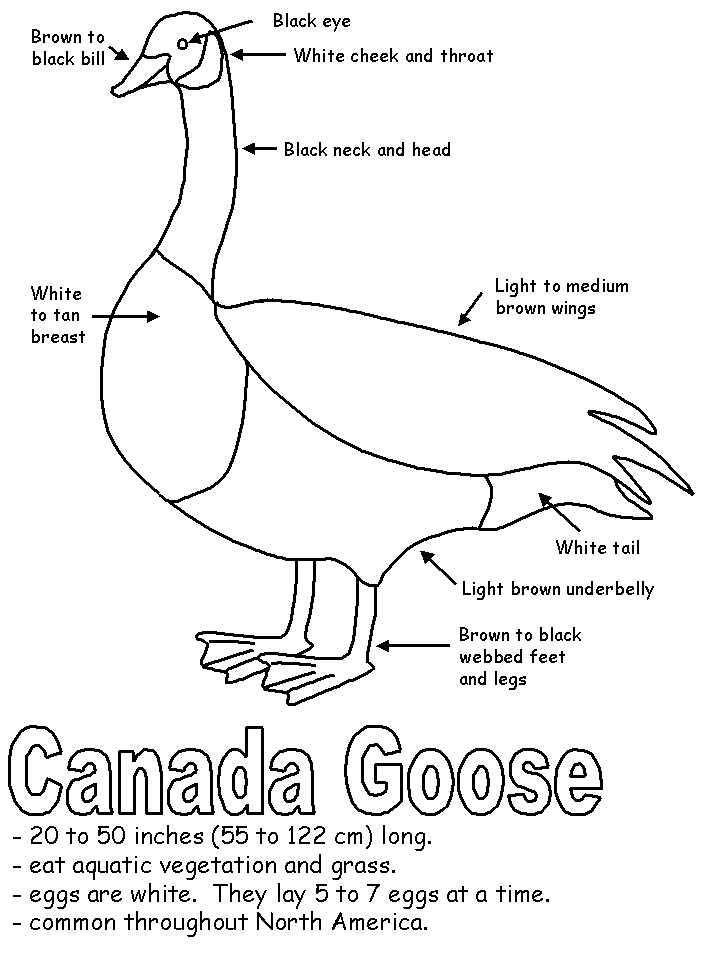
In order to prevent the predominance of fat mass over muscle, geese are fed only greens once a week. They tolerate the absence of grain without damage to health and growth, but they cannot do without grass or hay.
Composition of feed mixtures for geese and diet
The diet of birds is made taking into account the conditions of their keeping. There are 3 modes of feeding geese: dry, wet and combined. Regardless of the type, each of them provides for the use of:
- compound feed,
- greenery,
- roughage,
- vegetable crops.
Dry feeding, as less labor intensive, is more often used in large poultry farms. For small and medium-sized farms, wet or combined is preferable.
Dry mixes are the most economical and easy to use option. They are undemanding to storage conditions. They include wheat, millet, barley, corn, rye products. All components are carefully crushed and mixed in equal amounts, so it is enough to pour them into bird feeders. However, geese gain weight more slowly on dry food, so such mixtures are usually given during the non-productive period. Also, they can't be used all the time. With the constant use of only dry food, the risk of intestinal blockage is high.
However, geese gain weight more slowly on dry food, so such mixtures are usually given during the non-productive period. Also, they can't be used all the time. With the constant use of only dry food, the risk of intestinal blockage is high.
Wet mashes are given to birds three times a day. Such feed cannot be stored for a long time, so they are prepared directly on the day of consumption. Stale mixtures can cause indigestion. To prepare feed, crushed grain components are poured into wooden containers and poured with water at a ratio of 1.5 liters per 1 kg, and then yeast is added. The stirrer is infused for 6 hours. After that, chopped vegetables (beets, carrots, potatoes, cabbage) and fresh chopped greens are added to the feed. The preparation of such mixtures is a rather laborious process, therefore its organization at a medium and large poultry farm is not always advisable.
Ready mixed food combines the advantages of dry and wet food. It is easy to prepare and provides a high average daily weight gain. Roughage in combination with moist foods is much better digested, and the birds get more nutrients. A mixture of grains and vegetables is served along with a small amount of table salt.
Roughage in combination with moist foods is much better digested, and the birds get more nutrients. A mixture of grains and vegetables is served along with a small amount of table salt.
In all feeding regimes, birds must be provided with clean drinking water. In addition, geese require mixtures of sand, gravel and small shells to cleanse their stomachs.
Feed for farm birds must fully meet their need for vitamins and minerals. There may be an insufficient amount of biologically active substances (BAS) in grain fodder and vegetables, especially in winter or early spring. In this case, premixes rich in vitamins A, D, E, B2, as well as pantothenic and nicotinic acids, which are necessary for the normal growth of birds, are introduced into goose feed. Due to the high concentration of biologically active substances, premixes should not be given as the main product. They are added to the feed mixture in the amount of 1-5%. An excess of vitamins and minerals is no less harmful than their lack.
It is recommended to adhere to the following feeding schedule for geese:
- 7:00 - dry mixes containing germinated grains;
- 15:00 - vegetable crops with the addition of vitamin-mineral complexes and hay dust;
- 20:00 - a mixture of flour and grains.
Geese need special fattening before laying for at least 30 days. Their diet must include wheat and oats, legumes, vegetables, meal and oilseed cake, as well as bone or fish meal. Geese are fed 4 times a day, giving them dry and wet mixtures alternately. 1 week before laying eggs, vitamin complexes are added to the diet.
Feeding specifics of geese by seasons
In summer, the main part of the bird's diet is a variety of greens. Geese grazing on the range feed on:
- fresh nettles,
- dandelions,
- cereals,
- sorrel,
- legumes,
- plantain,
- yarrow,
- clover,
- alfalfa.

Swimming in reservoirs, they catch duckweed, cattail, reeds, chastukha. Grazing provides significant savings in feed, but they cannot be completely excluded, since greenery alone is not enough for birds to gain weight. Normally, geese eat about 2 kg of fresh grass per day, and they get the rest of the calories from grain fodder, vegetables, roughage (hay and branches).
For accelerated weight gain, it is preferable to give them a mixture of high grains twice a day: oats, barley, wheat, rye, corn. On average, in addition to greens, geese daily need:
- 700 g of cereals and legumes;
- 500 g potatoes;
- 250 g carrots and beets;
- 300 g hay dust or flour;
- 100 g silage;
- 25 g minerals (salt, shell).
In addition, it is useful for geese to give cottage cheese, eggs, chalk (10 g per bird). Solid legumes are introduced only in boiled form, so that they cannot be choked on. Cereals can be partially replaced with dried bread in an amount of up to 60 g, coniferous hay flour (up to 20 g).
Geese who are constantly in the house must be fed three times a day. In winter, the diet is based on cereals:
- barley,
- oats,
- ground corn,
- wheat bran,
- millet.
The lack of fresh herbs is compensated by silage, dried tops, hay dust and premixes. In a warm climate, short-term grazing on water bodies is possible, during which geese feed on the remains of duckweed and other algae. A significant place in their diet in the autumn-winter period is occupied by silage, which in its composition is closest to green fodder. It is also useful to add needles of pine or spruce. It compensates for the lack of vitamin C, stimulates the appetite and immunity of geese, helps to increase the number and improve the nutritional quality of eggs. It is important to consider that needles require preliminary preparation. It is first dried and then carefully ground. It is more profitable for owners of medium and large poultry farms to order ready-made vitamin complexes with a similar composition.
Sunflower meal and cake are often added to hay dust and flour. Geese eat oilseed products well and put on weight quickly. Dried gray bread is introduced as a delicacy to stimulate appetite, but it is not recommended to give it in large quantities.
Prohibited foods
Not all herbs are good for geese. The use of some of them can provoke indigestion, decrease in productivity, and in some cases lead to death in the poultry house. Especially dangerous herbs are:
- sedge,
- cuff,
- goose foot.
Geese usually avoid them. However, with insufficient nutrition and the absence of other vegetation on the pasture, they can begin to eat harmful grasses. Breeders need to check grazing areas and make sure the geese are getting enough calories while feeding in the poultry house. This question is especially relevant in early spring. On the first outings on the water, geese that did not receive fresh greens can eat harmful algae, silt, small fish and become infected with intestinal infections. To avoid this, birds are fed and released at first for no more than 3-5 hours before walking.
To avoid this, birds are fed and released at first for no more than 3-5 hours before walking.
In addition to wild grasses, outbreaks can be caused by freshly harvested rye, cereals contaminated with mycotoxins, or sprouted potatoes with green areas containing solanine. All ingredients must be carefully checked before use. Rye should rest for at least 3 months, cereals damaged by mold and green potatoes are thrown away.
Farmer's recommendations for feeding geese
- The type of diet depends on the direction of the birds. To obtain meat, it is important to provide geese with high-calorie nutrition. If you plan to breed chicks, it is important to reconsider the feeding regimen for geese. Overweight females are less healthy and less likely to lay eggs. On the other hand, just before laying, geese require a hearty diet high in vitamins and minerals. To meet the needs of birds in calories and prevent obesity, their diet is enriched with fresh fish, skim milk and whey.

- The immune system of chicks begins to form already at an early age, but their stomachs are not yet able to digest all the components of the feed. Therefore, in the first 3-4 days they are given a yolk pre-cooked and mixed with boiled water, gradually adding chopped onion feathers to it.
- Starting from the 6-7th day, the ration of goslings is replenished with fresh alfalfa and nettle. From a week old, wheat or corn porridge and boiled potatoes are added to the feed. However, the number of new products should not exceed 15%. By 12 days, goslings are able to absorb well-chopped raw vegetables.
- Chicks at the age of 17-28 days are independent enough to pluck greens on the run. They are released to pasture along with adult birds, but in the morning and evening they are fed separately with crushed and steamed grain with the addition of fresh vegetables. The content of cereals in the diet during this period should not exceed 20%. It is useful for goslings to give carrots, beets, pumpkins, boiled potatoes so that they receive enough vitamins of groups A and B.
- After 4 weeks the chicks switch to an adult diet and start fattening them for meat. In order for geese to gain weight better, from this age they are given high-calorie compound feed with a high grain content. In the finished product, all the necessary components are balanced for rapid weight gain, strengthening of the skeleton and normal digestion.
- Approximately 30 months before slaughter, geese are transferred to enhanced fattening. The daily portion of cereals alone reaches 400 g. Birds must always have food and enough water. If you leave the feeders lit, the geese will eat even at night. During this time, they gain about 1.5 kg.
- With the intensive rearing method, the total fattening period is on average 2.5 months. Geese are not released to pasture to limit their movement. Birds are kept in special boxes with a hole for the head, and feeders are placed in front of them. To accelerate weight gain and increase slaughter weight, force-feeding is used.

Compiling a balanced diet for geese of different ages is a difficult task. Buying ready-made feed and premixes greatly simplifies it. In our company, you can order safe, high-quality mixtures for meat and egg-laying poultry.
Amazing Goose Facts for Kids
Interesting Geese Facts
What kind of animal is a goose?
Canada goose is a bird belonging to the biological family Anatidae, scientifically referred to as Branta canadensis. The Canadian goose is considered the largest in the goose family worldwide. Not only can these Canada geese fly long distances during migratory periods, but these large waterfowl can also swim thanks to their evolutionary adaptations and are quite adept at foraging for food in the water.
Which animal class does the goose belong to?
Canada goose belongs to the class Aves; these are organisms that are recognized by the presence of feathers and the transformation of the forelimbs into wings.
How many geese are there in the world?
In the early to mid-20th century, Canada Goose were critically endangered in their native North American lands, spreading as far as Canada. However, today's numbers tell poultry farmers and conservationists a very different story regarding the conservation status of Canada geese. The decline in their global population in the 20th century was largely due to human hunting for food. Today, however, the world population of Canada geese is estimated to be around 7 million, according to reports from the Canadian Wildlife Service. These numbers continue to grow thanks to their adaptive abilities.
Where does the goose live?
The Canada Goose is commonly found near secluded forest areas that are slightly higher in elevation than the surrounding areas and are located close to a body of water, such as a pond or lake. These birds are primarily found in regions of North America extending as far as Canada and sometimes around Mexico and the southernmost parts of the United States of America.
What is the habitat of the goose?
Canada geese usually make their lives in places that are at a higher altitude than their surroundings and very close to a body of water, such as a pond or lake. Canada geese's habitat is usually close to areas of tall grass, as geese tend to eat grass as part of their diet. Proximity to the grass allows them to feed their children. As a result of rapid urbanization, Canada Geese are quite common in parks as they are flat land, allowing them to be aware of any predators.
Who do the geese live with?
Canada geese are usually birds that congregate. Therefore, most often Canadian geese are combined into a large group called a flock of geese. Along with regular daily activities, the pack will also flock together when it is time for them to move to other areas. Geese are the most faithful birds to their comrades. They only try to find another helper if their original helper dies.
How long does a goose live?
The typical lifespan of Canada Goose in their natural wild habitat can be between ten and 25 years. Some exceptions can live up to 35 years. However, in captivity, these birds can live up to 40 years.
Some exceptions can live up to 35 years. However, in captivity, these birds can live up to 40 years.
How do they reproduce?
After about three years of age, Canada geese start looking for a mate. Having found a partner, a man and a woman make a couple for life. Canada geese always nest and mate in their native areas. Males are selected based on the similarity of their size and the female's belief in protecting the male. Between February and April, female geese and geese lay an average of five to ten eggs per year. Canada goose eggs are slightly larger than chicken eggs.
What is their conservation status?
Because Canada geese are a growing species, their conservation status is of least concern. Canada goose are found in sufficient numbers throughout the region that no major conservation effort is required.
Interesting facts about geese
What do geese look like?
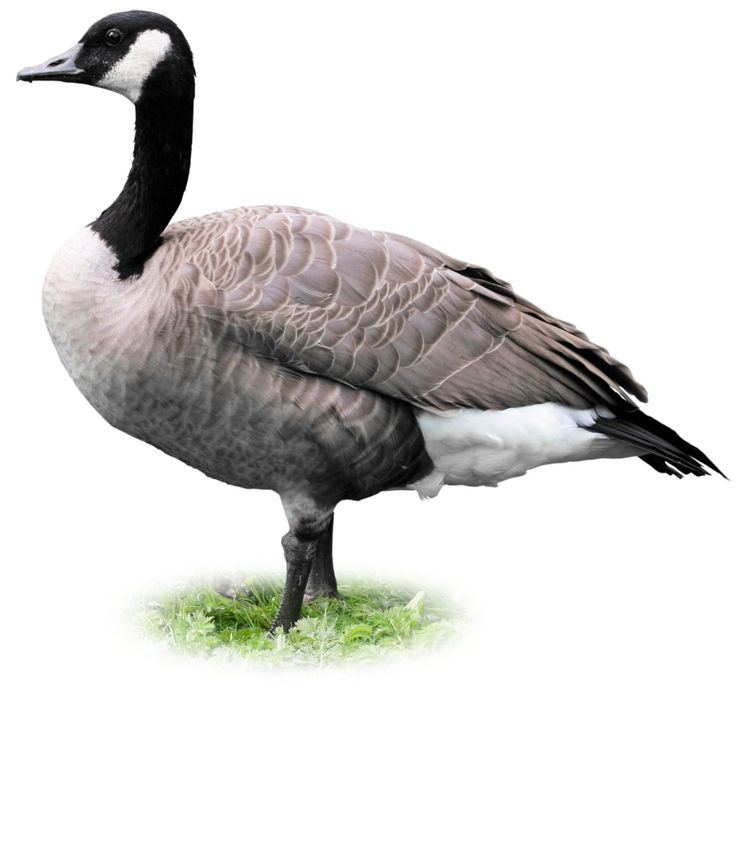
The Canada Goose differs in appearance from the common geese, but is primarily distinguished by its massive size, which makes it the largest type of geese in the world.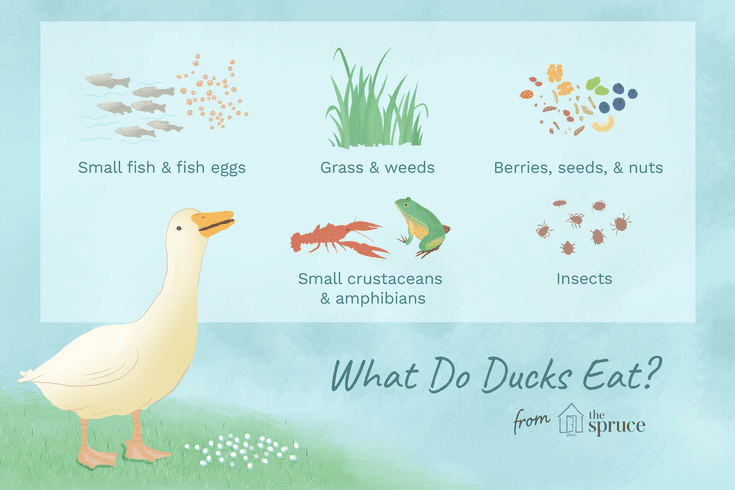 The Canada Goose also has contrasting colors scattered throughout the body, usually with a black head and neck. This contrasts strongly with the white colored chinstrap. The Canada Goose's chest is usually light in color and the back is a contrasting brown. Like all geese, even Canada geese have long necks. To be capable swimmers, they have webbed feet that connect their toes. Although there are no goose teeth in the goose mouth, you will still find a tomia. Tomiya is cartilage with sharp edges that look like tiny teeth but are not.
The Canada Goose also has contrasting colors scattered throughout the body, usually with a black head and neck. This contrasts strongly with the white colored chinstrap. The Canada Goose's chest is usually light in color and the back is a contrasting brown. Like all geese, even Canada geese have long necks. To be capable swimmers, they have webbed feet that connect their toes. Although there are no goose teeth in the goose mouth, you will still find a tomia. Tomiya is cartilage with sharp edges that look like tiny teeth but are not.
How cute are they?
Canada geese are not cute birds due to their large size and generally aggressive nature. They can be called beautiful or bright. However, the Canadian goose will only receive two points on the attractiveness scale, with an upper limit of five.
How do they communicate?
Canada geese are known for being noisy and social. These birds are actually quite loud creatures and have about 13 observable communication cues. Their calls are commonly referred to as beeps and one can observe calls for different situations and emotions such as warning beeps, happy beeps, welcome beeps, satisfied beeps, mourning beeps, beeps demanding a group meeting, and soon. In general, the Canada goose is a noisy bird that can often cause problems in urban environments for the people who live there.
Their calls are commonly referred to as beeps and one can observe calls for different situations and emotions such as warning beeps, happy beeps, welcome beeps, satisfied beeps, mourning beeps, beeps demanding a group meeting, and soon. In general, the Canada goose is a noisy bird that can often cause problems in urban environments for the people who live there.
How big is Goose ?
The Canada Goose is about 30-42 inches (72-106 cm) long and has a huge wingspan of about 52-68 inches (132-172 cm) in length. In addition to this, Canada goose can weigh between 5.3 and 14 pounds (2.4-6.3 kg). Compared to the common crow, the Canadian goose would be about twice as large.
How fast can a goose fly?
Although mostly aquatic birds, Canada Geese are very fast when it comes to their flying abilities. Not only can they fly at speeds in excess of 35 miles per hour (56 km per hour), but they can also travel serious distances while doing so. Canada geese can fly between 1,200 and 1,500 miles a day during their migratory season, depending on the weather.
Canada geese can fly between 1,200 and 1,500 miles a day during their migratory season, depending on the weather.
How much does a goose weigh?
Adult Canada Geese weigh between 5.3 and 14 pounds (2.4-6.3 kg), and the goose is usually smaller than the gander.
What are the male and female names of the species?
Males are called goose and females are called goose.
What would you call a little goose?
Baby geese are called goslings. Chicks can often be seen in flocks following their mother.
What do they eat?
Goose diet consists of grass, plants and cereals, but sometimes they prefer to eat fish from lakes and ponds, and sometimes insects.
Are they dangerous?
Although not considered dangerous, Canada Geese are easily spooked and intimidated, and when threatened become aggressive and may slap or beat their wings.
Will they make a good pet?
Because Canada Geese are notoriously loud birds, they will not be an ideal pet for most people living in urban and suburban environments. However, on the farm, they could lead a comfortable life without causing inconvenience to people.
Did you know...
The oldest Canadian goose to survive in the wild was 33 years old before being shot. Canada geese are widely known as the largest member of the waterfowl family, including swans.
During their migration, these birds follow the same path every year, known as flyways. Some of the common flyways used by Canada Goose are the Atlantic Flyway, the Mississippi Flyway, the Central Flyway, and the Pacific Flyway.
Canada geese observe mourning behavior when they lose their eggs or mating partner.
Is a duck a goose?
No, a duck is not a goose. The first difference between the two birds is that the goose is usually much larger than the duck. In addition, geese have longer necks, beaks, and legs compared to ducks. While ducks prefer to be in the water, geese do not have such compulsions and are comfortable in the water, on land and in the air.
In addition, geese have longer necks, beaks, and legs compared to ducks. While ducks prefer to be in the water, geese do not have such compulsions and are comfortable in the water, on land and in the air.
Eating goose and other derived products
The most popular way to cook and eat goose meat is to roast it. However, it is a little tricky to cook, as even the slightest overcooking can make it tangy and unappetizing. When it comes to eating Canada geese, you must remember that game meat cannot be sold. If you either hunt it during the appropriate hunting season or buy it from a legitimate meat seller, you can eat it legally.
In fact, goose is a fairly nutritious meat with high reserves of protein and other micronutrients such as iron, potassium, vitamins B1 and B2 and magnesium. When cooked properly, goose can be a delicious dish. In fact, if you prefer juicy meat, the higher the fat content, the better it will taste. In general, Canadian goose must be cooked correctly, otherwise it will not be a pleasure to eat it.