What foods have dha for babies
Why Toddlers Need DHA | Stonyfield
If you’re a card-carrying label reader–scouring the fine print on food packages and looking for basic, wholesome ingredients–you may have wondered why the ingredient list on your toddler’s yogurt includes…sardines?
DHA is an omega-3 fatty acid that may help your toddler’s growth and development.
Sardine and anchovy oil are natural sources of DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid that may help your toddler’s growth and development. DHA is found in abundance inside the brain. Synapses—the areas of the brain where messages are sent and received—are particularly rich in DHA. So it’s thought that DHA might be involved in communication between brain cells. That’s why dietitians like myself sometimes refer to DHA-rich fish as “brain food”.
First, a quick primer. There are three kinds of omega-3 fatty acids:
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) found in fish and their oils
- EPA (icosapentaenoic acid) found in fish and their oils, together with DHA
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) found in plant foods such as flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts, and canola and soybean oils.
Omega-3s can be trickier to get than other kinds of fats because the foods that are rich sources of omega-3s (like fish and nuts) aren’t mainstays of the average American diet. Yet these fatty acids have so many potential health benefits. Omega-3s are being studied for their possible link to improved heart health, memory, and mood. Some research has also found sharper vision in babies with higher blood levels of DHA—as well as higher IQs later in childhood among kids fed DHA-fortified formula compared to those given formula without it.
If you breastfed, your baby got DHA through breast milk. Infant formulas are now fortified with the fatty acid as well. But once your baby is exclusively eating table food, DHA can be harder to come by. According to government surveys, kids under the age of 6 are only getting a fraction of the DHA they need everyday.
Natural sources of DHA include fish such as salmon, herring, trout, sardines, and tuna (and their oils), shrimp, and much smaller amounts in chicken. Remember that most babies can start eating fish after six months. Though fish used to be discouraged in the first year of life because of potential allergic reaction, those recommendations have changed (if you or your baby have a history of food allergies, talk to your pediatrician about the best time to introduce fish). You can puree fish in the first months of starting solids and progress to soft pieces of poached or baked fish.
Remember that most babies can start eating fish after six months. Though fish used to be discouraged in the first year of life because of potential allergic reaction, those recommendations have changed (if you or your baby have a history of food allergies, talk to your pediatrician about the best time to introduce fish). You can puree fish in the first months of starting solids and progress to soft pieces of poached or baked fish.
You may have heard that you can get DHA from plant foods like walnuts and flaxseed. These foods are actually rich in ALA. Though it’s true that the body converts some of the ALA in these foods into DHA, the amount converted is quite small–less than one percent! So these foods just can’t be relied on as good sources of DHA.
Foods that are fortified with the fatty acid can help boost your child’s intake of DHA. YoToddler yogurt and YoTots pouches contain fish oil, naturally rich in DHA. Other fortified foods may be supplemented with algae, a vegetarian source of DHA (such as certain brands of eggs, which come from chickens fed a diet enriched with algal oil).
But however you choose to get it—through fish, fortified foods, or a combination of both—know that brain-building DHA will help your toddler get off to a great start.
DHA for Babies and Kids
DHA is an omega- 3 fatty acid. It is used to improve health in children. Found naturally in many sources, the expectant mother is the primary giver of this acid when she is pregnant. The prenatal period is a window when the baby’s brain develops with the help of the right nutrition supplied through the placenta. DHA influences the development of the brain, eyes and other primary neurological functions. It has a profound influence during the first two years of life and early stages of childhood. From birth until five years of age, the brain increases by 3.5 times its total mass and it is of critical importance that DHA is consumed in adequate amounts to support the rapid growth in the brain.
A healthy diet that provides about 600mg of DHA daily has a significant impact on the cognitive functions of the child and enhance the development of the brain and eyes. Organ meat and fatty fish are rich sources of naturally found DHA and unfortunately, these are not commonly consumed by children as they are picky eaters and prone to allergies at times. However, the growing awareness of its importance has led to its inclusion in milk, formula and other fortified foods making it easier for people of all age groups including children to obtain the benefits of this important nutrient.
Organ meat and fatty fish are rich sources of naturally found DHA and unfortunately, these are not commonly consumed by children as they are picky eaters and prone to allergies at times. However, the growing awareness of its importance has led to its inclusion in milk, formula and other fortified foods making it easier for people of all age groups including children to obtain the benefits of this important nutrient.
What is DHA?
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a part of the omega-3 fatty acid family is a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid often called “the healthy fats.” It has a large influence on our body as it keeps us healthy and is crucial for the optimal growth of the brain and eyes through our life. In fact, the nutrient takes centre stage when neural tissues, including vision, are being formed in the womb. DHA supports our cognitive, visual and mental faculties as we age.
What Are the Benefits of DHA for Babies and Kids?
DHA has undoubtedly gained a lot of attention and is appearing in all places from eggs, baby food to milk. Why should one care so much about this nutrient? Well, the answer is it is a beneficial fat. The role of DHA is accentuated during infancy and early years of childhood.
Why should one care so much about this nutrient? Well, the answer is it is a beneficial fat. The role of DHA is accentuated during infancy and early years of childhood.
For Babies
DHA plays a key role in the structural component in the brain, eyes and nervous system. Breastmilk is high in DHA content and breastfed babies have strong mental and visual acuity.
For Kids
During the early infant years until five years of age, the brain makes rapid development and increases to about 4 times its total mass. Adequate DHA intake during these crucial years in important for optimal development and enhancement of cognitive functions. It has been researched and proven that children who have a good intake of DHA until five years of age have better IQ scores, tremendous memory, good reading skills and strong vision.
DHA deficiency could be common in children suffering from Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD). In a nutshell, DHA is imperative for neurological and visual development.
While there are no guidelines for a daily DHA dosage for children, there are certain recommendations that exist for the intake of DHA plus eicosapentaenoic acid, or EPA.
For Babies
Babies who are breastfeeding will receive most of their DHA intake from the milk. Breastmilk is known to be high on DHA content. It is advisable for mother’s to increase their intake of DHA rich food while breastfeeding, A breastfeeding mother should aim at consuming at least 600-800 milligrams of DHA in a day via natural sources or supplements.
For Kids
From the age of 1.5 years to five years of age, the DHA requirement for children is recommended as 600 milligrams of combined DHA plus EPA per day for a child weighing 20 kilograms.
DHA Rich Food for Babies and Kids
There are certain foods that are rich in DHA that you can include in your child’s diet. Here are some DHA rich foods for children of different ages.
1. DHA for Breastfed Babies
The best source of DHA for breastfed babies is from breast milk. The amount of DHA varies according to the mother’s diet and the quantity of omega-3’s and DHA she is receiving. It is advisable for feeding mothers to include fish, eggs, yoghurts and dried nuts in their diet to help babies receive DHA for healthy development of the brain and retina of the eye. Formula-fed babies get their DHA intake only if the formula is fortified with it and so it is important to read the labels.
The amount of DHA varies according to the mother’s diet and the quantity of omega-3’s and DHA she is receiving. It is advisable for feeding mothers to include fish, eggs, yoghurts and dried nuts in their diet to help babies receive DHA for healthy development of the brain and retina of the eye. Formula-fed babies get their DHA intake only if the formula is fortified with it and so it is important to read the labels.
2. DHA Foods for Toddlers and Kids
There are a lot of natural varieties of DHA food for toddlers and kids. Some foods that could feature in your child’s regular diet are:
- Salmon contains the highest content of DHA among the fish varieties and offers a healthy proportion of good omega-3 fats
- Eggs contain small amounts of DHA naturally but you could also opt for DHA enriched eggs from chickens fed with a supplemented diet
- DHA enriched yoghurts are a staple on the supermarket shelves and you could offer it to kids as a breakfast or light snack
- Peanut butter could be substituted for the sugar-rich jam as a spread to morning toast for kids
- Serve a handful of walnuts to your toddler as a delicious or healthy snack.

- Formula milk now comes with fortified DHA as manufacturers have realised the importance of DHA. There are some products specially designed for children aged 1 year and above and you could buy them after checking the label thoroughly.
Are DHA Supplements for Infants and Children Safe?
Numerous studies have covered the effects of DHA supplements on childhood development. Some research has proven that supplements have an effect on the behaviour and cognitive abilities of a child. DHA supplements administered to children with learning disabilities helped them in developing their mental capabilities to a certain extent. However, due to lack of research, DHA supplements are not recommended as a treatment for any condition in children. It is possible to achieve the needed intake by eating fatty fish, nuts and eggs in your diet. Discuss with your paediatrician about giving your kids DHA supplements and take his advice about the best DHA supplement for toddlers.
Precautions to Take while giving DHA Supplements to your Child
Mercury levels prevalent in seafood, when consumed in excess, could have an adverse effect on the cognitive development of a child. It is then that parents resort to DHA omega 3 supplements for kids. Supplements containing fish oil are purified and devoid of contaminating metals or minerals. However, small amounts of toxins may still be present. For breastfeeding babies, parents can buy DHA drops for infants in India. But, an excess of fish oil could lead to bleeding in children. So, it is mandatory that you seek consultation from the paediatrician before giving DHA supplements to determine the safe and effective dosage.
DHA is an important nutrient that fuels your baby’s optimal development. A well-balanced level of DHA has been linked to good retinal health and cognitive ability. The best way to include DHA in your child’s diet is to make every bite count by avoiding empty calories and choosing super-foods that will give your baby the necessary nutrition.
Also Read:
Advantage of Protein for kids
Is Protein Powder Safe for Kids?
Necessary Vitamin for Babies
Children's Omega 3 Benefits of DHA
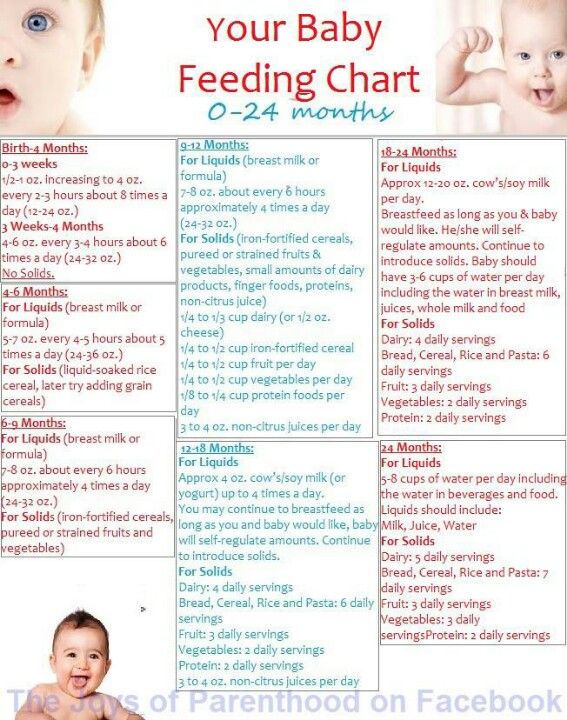
6-12 months
Article
0 reviews
It is important for every mother that her child is healthy, active, learns something new well and develops intellectually. Children are characterized by curiosity, a desire to explore the world, they quickly pick up the behavior and vocabulary of their parents.
3 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
But this is not always the case. In early school and adolescence, many children begin to have problems concentrating, and academic performance declines. The reason for this may be a banal lack of docosahexaenoic acid (Omega-3), which directly affects brain function.
What are the benefits of DHA for children and how to replenish the reserves of this acid in the child's body - further in the material.
What is DHA and EPA
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) are polyunsaturated fatty acids that act as a building material for our cells and are important for the normal functioning of the brain. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are very important during the growth and development of the child's body. Omega-3 and Omega-6 are simply necessary for the health of the organs of vision. Numerous scientific studies have established that DHA is a nutritional component for the retina. In addition, this acid is important for the functioning of neurons that are responsible for the learning ability and psychological health of children. nine0003
Read also: Does a child need cholesterol?
However, deficiency of polyunsaturated fatty acids in young children and adolescents is quite common. Our body is not able to produce these substances in the right amount, so the main source of unsaturated acids is the foods that we eat. If there are no difficulties with Omega-6 - they are in sufficient quantities in butter and vegetable oils, then with Omega-3 everything is somewhat more complicated. Docosahexaenoic acid is found in fatty fish and algae. But in order to provide the body with the right concentration of this substance, these foods must be eaten regularly. Every mother knows how difficult it is to make a child eat fish, and even more so seaweed. nine0003
Our body is not able to produce these substances in the right amount, so the main source of unsaturated acids is the foods that we eat. If there are no difficulties with Omega-6 - they are in sufficient quantities in butter and vegetable oils, then with Omega-3 everything is somewhat more complicated. Docosahexaenoic acid is found in fatty fish and algae. But in order to provide the body with the right concentration of this substance, these foods must be eaten regularly. Every mother knows how difficult it is to make a child eat fish, and even more so seaweed. nine0003
See also: Are seafood and baby compatible?
How to fill the deficiency of DHA
Regular fish oil can be an excellent alternative to fish, shellfish and algae unloved by children. Of course, we are not talking about its traditional format, which the older generation was fed in kindergartens from a spoon. Now there is a huge variety of concentrated fish oil in gelatin capsules without taste and smell. Adding drugs based on this component to the daily diet of a child is not difficult. nine0003
Adding drugs based on this component to the daily diet of a child is not difficult. nine0003
Healthy growth and immunity
NAN® 3 OPTIPRO® contains an optimized protein complex and probiotics that help normalize the intestinal microflora and increase the body's ability to fight infections.
To learn more
One capsule contains enough DHA to meet your daily requirement. It is worth noting that the course of the drug will help:
- Establish proper brain development
- Improve cognitive function
- Strengthen immunity
- Improve skin condition, which is especially important for children of transitional age
- Combat insomnia and restless sleep
- Calm the nervous system
In addition to the already mentioned fish and algae, Omega-3 polyunsaturated acids are also found in other foods. For example, they are found in meat, eggs and dairy products. It is also worth noting that not all varieties of fish contain these substances. Give preference to herring, mackerel, salmon, caviar and cod liver. nine0003
Give preference to herring, mackerel, salmon, caviar and cod liver. nine0003
DHA intake and side effects
The body's need for DHA increases before the age of 2 years, when the child's body is actively growing and developing. This element is extremely important for the formation of brain structures in the first days of life. DHA can be introduced into the infant's diet through breast milk. For children under two years of age, the daily intake is determined based on body weight. The optimal dose is considered to be 4.5-5.5 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. nine0003
Although omega-3s have many health benefits, they also have some serious side effects. So the consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids in excess of the norm can lead to problems with the blood. They are known to have the ability to thin the blood. And this in itself is dangerous, especially in childhood. The slightest scratches, abrasions or more serious wounds will be accompanied by profuse bleeding and bruising.
Omega-3 preparations are considered a dietary supplement and are sold without a prescription, but, like any drug, you should not prescribe it to a child on your own. This is just the case when excessive caution will not be superfluous. Talk to your doctor, do some simple medical tests, check your blood clotting rates, and if all is well, feel free to include DHA foods and supplements in your child's diet. nine0003
Latest reviews
Average customer rating
0 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 0
- 4 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- one 0
Recommended articles
6-12 months
Article nine0003
Antioxidants: what are the benefits and what foods contain
0 reviews
Antioxidants are very important substances for human health: they reduce the action of free radicals that can damage body cells, and thus reduce the risk of developing various diseases.
6-12 months
Article
Herbal teas in baby food nine0043
0 reviews
Herbal teas in baby food
6-12 months
Article
Chocolate for children: good or bad?
Chocolate in Latin means "food of the gods". It deserves such a name, because it has many useful properties. But can you give chocolate to children? And from what age?
nine0002 0-6 monthsArticle
Proper nutrition is the basis of future health
During the first 1000 days of a baby's life, optimal nutrition largely determines the growth and development of the child in the present and future. A balanced diet, which contains the most important macro and micronutrients, is an important investment in a child's future health.
6-12 months
Article nine0003
selenium for babies
0 reviews
Selenium is an essential element, i. vital. It plays a key role in the body's antioxidant defense system. This means that it protects the cells of our body from damage and death.
6-12 months
Article
Arachidonic acid (ARA): what are the benefits for children? nine0043
0 reviews
In the first years of life, the child's body actively grows and develops.
6-12 months
Article
Seafood and baby: compatible?
0 reviews
Seafood is the inhabitants of the sea, other than fish, i. e.: seaweed, shrimp, squid, lobster, spiny lobster, crabs, krill, scallops, oysters, etc.
e.: seaweed, shrimp, squid, lobster, spiny lobster, crabs, krill, scallops, oysters, etc.
6-12 months
Article
By-products are very important products
0 reviews
What are by-products? These include the heart, liver, kidneys, brains, tongue, lung. Let's say right away: young children are not given a lung, kidneys and brains. Therefore, we will talk about the rest of the by-products that are considered valuable for baby food.
nine0002 6-12 monthsArticle
Drink cow's milk for health?
0 reviews
Now there is a lot of talk about the dangers of cow's milk for babies, and it is on it that our grandmothers and mothers grew up. Is cow's milk really so harmful, and what exactly is its negative impact? When is it worth introducing cow's milk into a child's diet, and how to do it right? nine0003
Is cow's milk really so harmful, and what exactly is its negative impact? When is it worth introducing cow's milk into a child's diet, and how to do it right? nine0003
6-12 months
Article
The need for iron in children. Complex of vitamins and iron Iron +
0 reviews
Iron is one of the most important trace elements for the human body. It is part of a variety of tissue proteins, enzymes that provide metabolism in cells. The most important function of iron is participation (in the composition of hemoglobin) in the delivery of oxygen to all tissues of the body. nine0003
6-12 months
Article
Immunity Boosting Products
Oh, that mysterious capacious word "immunity"! Pediatricians attribute numerous catarrhal childhood diseases to his immaturity, saying that, they say, immunity will get stronger and the child will stop getting sick.
6-12 months
Article
Jelly and jelly in the diet of a child nine0043
0 reviews
Jelly is a gelatinous mass obtained from broths and sweet drinks by adding gelling agents, most often gelatin. Should I give my child jelly and jelly? There are different opinions on this matter.
6-12 months
Article
Eggs: how much, when, what?
After one year, we introduce egg white into the child's diet. Thus, the child can eat a whole egg in one of the meals. And here a lot of questions arise. Which eggs are preferable, chicken or quail; is it possible to eat eggs daily and in what quantity; and also in what form they should be served. Do we know? nine0003
6-12 months
Article
Products containing iron
0 reviews
A complete and balanced nutrition according to the main ingredients allows you to satisfy the physiological need of the child's body for trace elements. Let's look at the list of foods containing iron.
Let's look at the list of foods containing iron.
6-12 months
Article nine0003
nuts
What you need to know about nuts and when can you give them to your baby?
6-12 months
Article
At what age can a child be given kefir
0 reviews
It is allowed to give kefir to a child not earlier than from 8 months, and this age refers to kefir intended specifically for baby food
6-12 months
Article
Yogurt in the baby's diet
0 reviews
Children's yoghurts are a source of protein, calcium and other trace elements (iron, magnesium, zinc, iodine) and vitamins B, A, E and C, have a lower acidity compared to kefir. Thanks to lactic acid bacteria, yogurt is easily digested and absorbed. This product improves bowel function and strengthens the immune system. When to introduce yogurt into the baby's diet? Which yogurt do you prefer? nine0003
Thanks to lactic acid bacteria, yogurt is easily digested and absorbed. This product improves bowel function and strengthens the immune system. When to introduce yogurt into the baby's diet? Which yogurt do you prefer? nine0003
6-12 months
Article
Does a child need cholesterol?
0 reviews
Cholesterol plays an important role in a number of physiological processes in the body of children.
6-12 months
Article
Why is cow's milk not good for babies? nine0043
Cow's milk, which occupies a worthy place in the diet of adults and older children, is categorically not recommended for infants, even in the form of fermented milk products and diluted.
Join the Club
We know that being a mother is not only unlimited happiness, but also a great responsibility. We will help you!
We will help you!
Register
Still haven't found what you need? nine0003
Try our new search.
Search
How to choose Omega 3 for children: how to take, EPA and DHA in
January 12 2021
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids that are essential for many aspects of health, including fetal development, brain function, heart health, and immunity (1). However, many parents are not sure if omega-3 supplements are necessary for children or even if they are safe for them? nine0003
There are three main types of omega-3s:
- alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
- eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
ALA is found in plant foods, including vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and some vegetables. However, this form is not active and requires conversion to active forms such as DHA and EPA. EPA and DHA are known to be found in sufficient amounts in fatty fish such as salmon, herring, tuna, etc., and are also widely available in supplement form. nine0003
EPA and DHA are known to be found in sufficient amounts in fatty fish such as salmon, herring, tuna, etc., and are also widely available in supplement form. nine0003
Important! There are many types of supplemental sources of omega-3s, the most common being fish oil, krill oil, and algae oil.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an important substrate for brain and CNS development during fetal development, and additional maternal sources of omega-3 fatty acids have been proposed as a means of optimizing fetal cognitive development (2).
Why does a child need omega-3 and fish oil? nine0306
Many studies show that supplemental omega-3s have a number of benefits for children:
- Improve brain function and mood in children, particularly learning, memory and brain development (3). In addition, several studies show that omega-3 fats help prevent depression and mood disorders in children (4).
- Reduce the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, which comes with symptoms such as hyperactivity, impulsivity and difficulty focusing.
 A large review of 52 studies concluded that fish oil supplements were two of the most promising methods for reducing the symptoms of this condition in children (5). nine0052
A large review of 52 studies concluded that fish oil supplements were two of the most promising methods for reducing the symptoms of this condition in children (5). nine0052 - Relieve the course of bronchial asthma. Some studies have shown that omega-3s help relieve these symptoms. For example, a study in children diagnosed with asthma found that taking 120 mg of combined DHA and EPA daily helped reduce asthma symptoms (6). A number of studies also point to a possible link between omega-3 fatty acids and a lower risk of developing asthma in children (7).
How to take Omega-3 for children? nine0306
All people, regardless of age or health condition, are advised to determine the level of omega-3 in the blood and consult a doctor who will give individual recommendations. You also need to pay attention to a number of conditions during the intake of fish oil by a child:
- If possible, eat fatty fish, at least twice a week.
- Reduce intake of omega-6 fats (usually found in vegetable oils, nuts).
 This is because omega-6 fats compete with omega-3s for enzymes, so excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids can replace omega-3s in cell membranes. nine0052
This is because omega-6 fats compete with omega-3s for enzymes, so excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids can replace omega-3s in cell membranes. nine0052
Omega-3s for newborns and infants
Expert organizations recommend that pregnant and lactating women get at least 1300 mg of ALA and 200 mg of DHA per day to ensure that the newborn receives the required amount of omega-3s through breast milk. Omega-3s are important for the continued development of the baby's brain and retina. If the child is bottle-fed, then be sure to purchase mixtures enriched with DHA and ALA. When the baby grows up and begins to eat solid foods, it is necessary to follow the recommendations for providing the child with omega-3 fats by introducing low-mercury seafood 50 grams 1-2 times a week. nine0003
Need to know! Remember that cow's milk does not contain omega-3s, unlike human milk or fortified formulas, so essential fatty acids must come from wholesome food sources..jpg) Omega-3 intake in the first few years of life is vital for continued cognitive and behavioral development.
Omega-3 intake in the first few years of life is vital for continued cognitive and behavioral development.
DHA accumulation in the retina is completed by birth, while accumulation in the brain continues during the first 2 years after birth. Therefore, omega-3 acids are very important for babies. nine0003
EPA and DHA in omega-3s
Omega-3 sources, including fish oils, contain the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which make up approximately 10% of total omega-3 fatty acid intake.
Check the supplement you buy for the type and amount of omega-3s. It should contain EPA and DHA in satisfactory amounts - and preferably an antioxidant to fight rancidity. For example, a product may contain 1,000 mg of fish oil, but the levels of these two substances may be much lower. nine0003
Omega 3 overdose and side effects
Usually the side effects of omega-3 supplements such as fish oil are usually very mild. The most common are:
- bad breath
- unpleasant aftertaste
- headache
- heartburn
- nausea
- diarrhea
Important! Make sure your child is on the recommended dosage to reduce the risk of side effects. You can start omega-3 supplementation at a lower dose and gradually increase it to the full dose to assess your tolerance. nine0306
You can start omega-3 supplementation at a lower dose and gradually increase it to the full dose to assess your tolerance. nine0306
Sometimes eating too much fish oil can seriously affect your health and lead to side effects such as high blood sugar and an increased risk of bleeding. According to the European Food Safety Authority, omega-3 fatty acid supplements can be safely consumed at doses up to 5,000 mg per day. As a rule, if a person experiences any negative symptoms, it is enough to reduce the dose or stop taking it for a while. nine0003
Consult your physician and stick to the recommended dosage, and aim to get most of your omega-3 fatty acids from food sources to get the most nutritional value.
My child is allergic to fish oil, what should I do?
If a child has a tendency to develop allergic reactions or there is a confirmed case of an allergy to fish or shellfish, then the possibility of developing a reaction to fish oil also occurs. In such cases, supplements based on fish oil and similar components such as cod liver oil and krill oil should be avoided. nine0003
In such cases, supplements based on fish oil and similar components such as cod liver oil and krill oil should be avoided. nine0003
Other omega-3 rich foods or supplements such as linseed or algae oil can be used instead. However, it should be remembered that the human body does not use omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in plant sources, as effectively as in seafood. Therefore, microalgae supplements such as spirulina are considered the most effective sources of DHA and EPA (8).
Be sure to check with your pediatrician or healthcare provider before making nutritional changes for you or your child. nine0003
WHO recommendations for daily omega-3 intake for children*
%E is the percentage of energy, for infants the recommended fat intake is expressed as % E.
*World Health Organization. (2008). Interim summary of conclusions and dietary recommendations on total fat & fatty acids. From the joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on fats and fatty acids in human nutrition, 10-14.
Drug Comparison Chart
About the Author
Maria Yavorovich
MD, Pediatrician
References
- Swanson, D., Block, R., & Mousa, S. A. (2012). Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: health benefits throughout life. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 3(1), 1–7.
- Adams P, Lawson S, Sanigorski A, Sinclair A. Arachidonic acid to eicosapentaenoic acid ratio in blood correlates positively with clinical symptoms of depression. Lipids31,S157–S161 (1996)
- Stonehouse W. (2014). Does consumption of LC omega-3 PUFA enhance cognitive performance in healthy school-aged children and throughout adulthood? Evidence from clinical trials. Nutrients, 6(7), 2730–2758.
- Trebatická, J., Hradečná, Z., Böhmer, F., Vaváková, M., Waczulíková, I., Garaiova, I., Luha, J., Škodáček, I., Šuba, J., & Ďuračková, Z.
 (2017). Emulsified omega-3 fatty-acids modulate the symptoms of depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a pilot study. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 11, 30.
(2017). Emulsified omega-3 fatty-acids modulate the symptoms of depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a pilot study. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 11, 30. - Heilskov Rytter MJ, Andersen LB, Houmann T, Bilenberg N, Hvolby A, Mølgaard C, Michaelsen KF, Lauritzen L. Diet in the treatment of ADHD in children - a systematic review of the literature. Nord J Psychiatry. 2015 Jan;69(1):1-18
- Nagakura T, Matsuda S, Shichijyo K, Sugimoto H, Hata K. Dietary supplementation with fish oil rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in children with bronchial asthma. Eur Respir J. 2000 Nov;16(5):861-5
- Li, J., Xun, P., Zamora, D., Sood, A., Liu, K., Daviglus, M., Iribarren, C., Jacobs, D., Jr, Shikany, J. M., & He , K. (2013). Intakes of long-chain omega-3 (n-3) PUFAs and fish in relation to incidence of asthma among American young adults: the CARDIA study. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 97(1), 173–178
- Peltomaa E, Johnson MD, Taipale SJ.