What foods to feed baby at 8 months
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
Listen
Español
Text Size
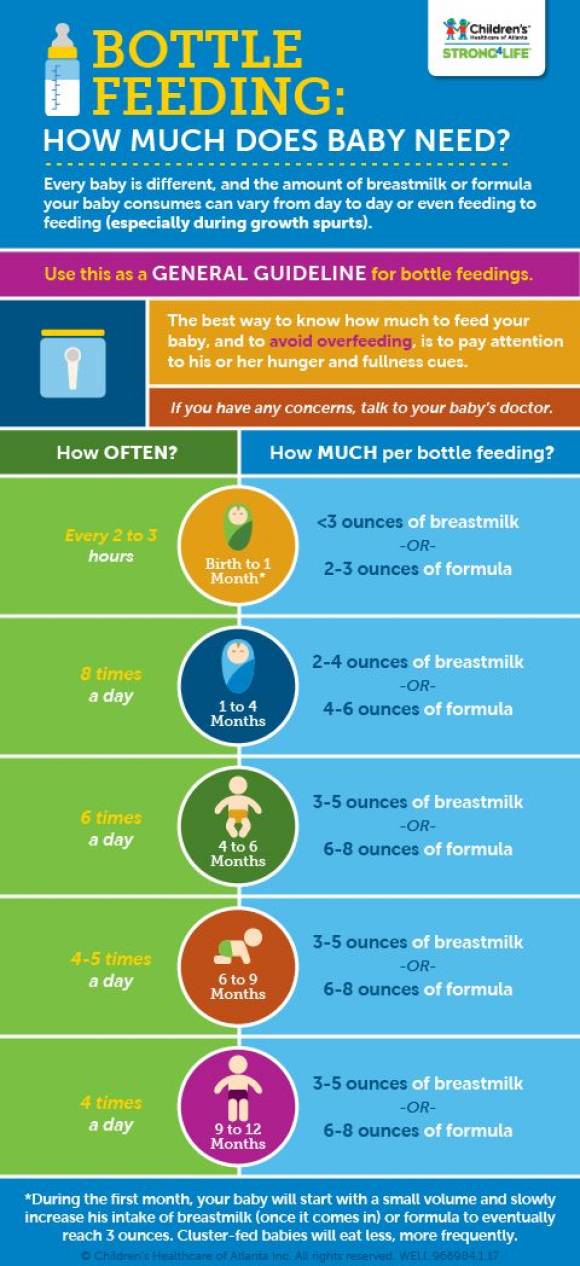
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water. (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Foods to avoid feeding your baby
Foods to avoid giving your baby include honey, cow's milk, soy milk, fruit juice, sugar-sweetened beverages, unpasteurized foods, and foods with added sugars or too much sodium. Choking hazards are a serious concern, so don't offer large chunks, raw vegetables, nuts and seeds, hard or crunchy foods, sticky foods, or dollops of nut butters. If allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema, check with the doctor about introducing allergenic foods such as egfgs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, and shellfish.
Choking hazards are a serious concern, so don't offer large chunks, raw vegetables, nuts and seeds, hard or crunchy foods, sticky foods, or dollops of nut butters. If allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema, check with the doctor about introducing allergenic foods such as egfgs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, and shellfish.
As your baby grows, they'll be eager to sample food from your plate – and you'll be eager to introduce some variety. But not all foods are safe for your child.
Foods to avoid: Birth to 6 months
All food and beverages except breast milk or formula: The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends feeding your baby only breast milk or formula for about the first 6 months.
Foods to avoid: 6 to 12 months
Honey: Honey can harbor spores of Clostridium botulinum, which causes botulism. An adult's intestinal tract can prevent the growth of these spores, but in a baby the spores can grow and produce life-threatening toxins.
Cow's milk and soy milk: Stick with breast milk or formula until your child's first birthday. Why? Your baby can't digest the proteins in cow's milk and soy milk during the first year, and these beverages contain minerals in amounts that can damage your baby's kidneys.
Fruit juice and sugar-sweetened beverages: Juice (even 100 percent fruit juice) and sugar-sweetened beverages such as soda and sports drinks aren't recommended for children under 12 months. When babies fill up on these drinks, they miss out on getting the nutrients they need. And though fruit juice seems healthy, it has far more calories and sugar than fresh fruit and can contribute to weight gain and tooth decay. The AAP recommends no fruit juice for babies, and just 4 ounces per day maximum for toddlers ages 1 to 3.
Unpasteurized foods: Don't give babies and children unpasteurized juice or cider or unpasteurized (raw) dairy products. These may contain harmful bacteria and parasites that can lead to serious illness or death.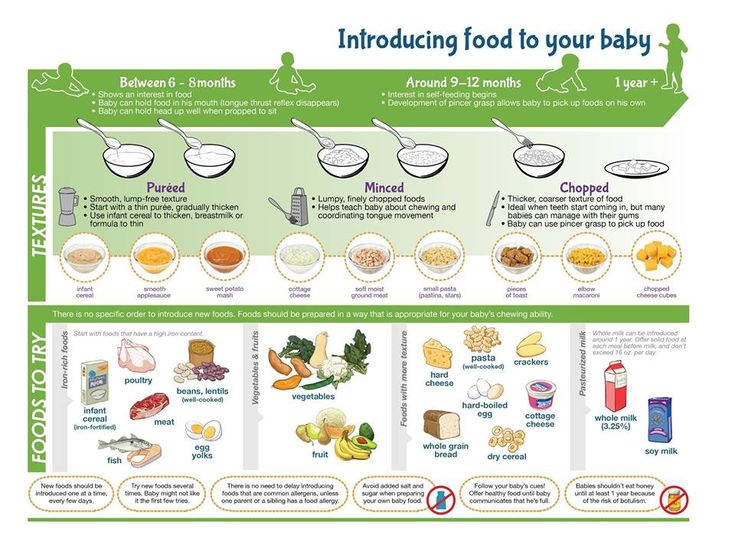
Added sugars: Avoid added sugar in the diets of children under age 2, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services advise. These are sugars and syrups that are added to foods or beverages when they are processed or prepared. This doesn't include sugars found in milk and fruits. Too much added sugar in children's diets has been linked to obesity and increased risk for future health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and avoid those that list 1 g or more of "Added Sugars."
Too much sodium: Sodium is an essential nutrient primarily consumed as salt. However, too much can be harmful. Children this age don't need more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day, according to the USDA and DHHS. Check the Nutrition Facts label when buying canned, frozen, and packaged foods.
Large chunks: A chunk of food can get stuck in your baby's throat. The AAP recommends that you cut food into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch. For example, cut up fruits such as grapes, cherry tomatoes, and strawberries, and shred or finely chop meats, vegetables, and cheeses.
The AAP recommends that you cut food into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch. For example, cut up fruits such as grapes, cherry tomatoes, and strawberries, and shred or finely chop meats, vegetables, and cheeses.
Raw vegetables: Soft-cook vegetables such as carrots, celery, and broccoli, and dice, shred, or cut them into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch before serving.
Nuts and seeds: Remove seeds and pits from fresh fruit such as watermelon, peaches, plums, and cherries before serving. And don't feed your baby nuts or seeds, such as sunflower or pumpkin seeds. Seeds may be too small to choke on but can get stuck in a child's airway and cause an infection.
Hard or crunchy foods: Nuts, popcorn, and pretzels are all choking hazards, as are all hard candies and cough drops.
Sticky foods: Chewing gum and sticky foods – such as jelly or gummy candies, dried fruit, and marshmallows – can get lodged in your baby's throat. Stringy, melted cheese can also be a choking hazard.
Stringy, melted cheese can also be a choking hazard.
Nut butter: The sticky consistency of peanut butter and other nut butters can make it hard for your baby to swallow it. Spread nut butter thinly on bread or crackers. Or thin it with water or applesauce.
Learn more about preventing choking in young children.
Find out about choosing safe finger foods and which foods can be unsafe for toddlers and children up to age 5.
The latest on children and food allergies
Doctors used to recommend waiting until age 1 or even later to introduce solid foods that are common allergens, especially with children at risk for allergies. But the AAP has changed its tune, because studies show that these delays don't help prevent allergies and may even increase the risk of them.
You may be told to introduce foods one at a time, waiting three to five days after each new food to watch for any allergic reaction. Or your doctor may say it's fine to start multiple new foods at once. If you believe your baby is likely to have food allergies – for example, if allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema – check with their doctor to determine the best strategy for introducing allergenic foods, which include eggs, milk, peanuts, wheat, soy, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
If you believe your baby is likely to have food allergies – for example, if allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema – check with their doctor to determine the best strategy for introducing allergenic foods, which include eggs, milk, peanuts, wheat, soy, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
Read more about food allergies in children.
Diet for an 8-month-old baby
In the ninth month, fish can be introduced into the diet of children. Along with animal meat, fish is a source of complete protein with a well-balanced composition of amino acids, fat, vitamins B2, B12 and minerals. Compared to meat, fish contains 5 times less connective tissue, due to which it is quickly boiled soft, has a delicate texture after heat treatment and is easier to digest. Fish oil is characterized by a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the ω-3 class. These substances are necessary for the child to mature the brain, retina, strengthen the cardiovascular and immune systems.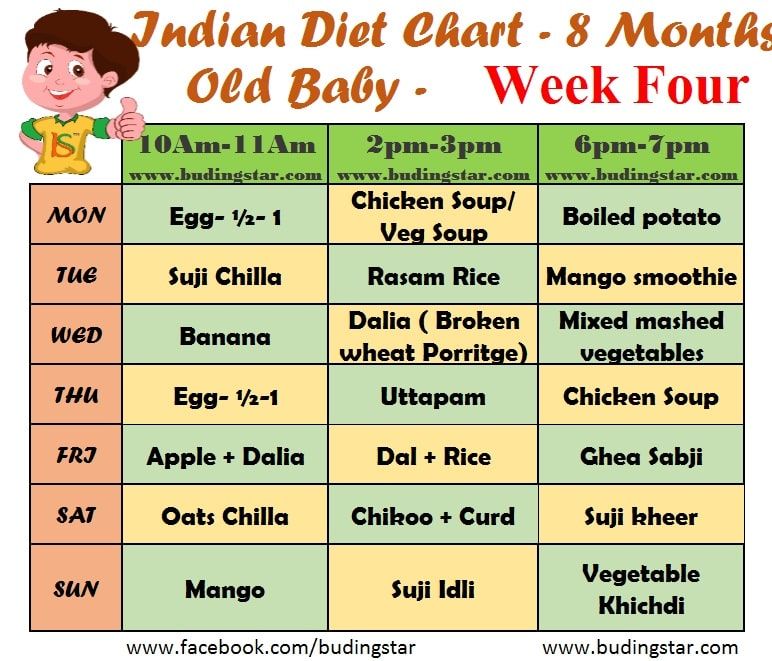 Sea fish contains such important trace elements for the child's body as iodine and fluorine. The child should be given 1-2 times a week instead of meat, be sure to monitor how the child tolerates fish in general and its individual varieties. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock), red salmon can be recommended, river pike perch, carp.
Sea fish contains such important trace elements for the child's body as iodine and fluorine. The child should be given 1-2 times a week instead of meat, be sure to monitor how the child tolerates fish in general and its individual varieties. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock), red salmon can be recommended, river pike perch, carp.
Self-cooked fish is given to a child with boiled and mashed vegetables. You can also offer your baby fish and vegetable canned food, but they contain only 10 - 20% of fish.
At this age, when all the main food groups have already been introduced, special attention should be paid to the diversity of the composition of dishes. New, possibly combined products are introduced, for example, not only purees from various fruits and berries, but also their combinations with cottage cheese, cream, cereals, etc.
From the age of 8 months, the child's diet can be expanded to include fermented milk products (baby kefir, biokefir, bifidokefir, yogurt, bioyogurt, biolact). Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Fermented milk products improve the composition of the intestinal microflora of the child, are rich in B vitamins and calcium. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, stimulates appetite, and increases the absorption of micronutrients. Children's dairy products are introduced into the baby's diet gradually, starting with 1 tsp. and with good tolerance increase their volume to 150-200 ml per day.
Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Fermented milk products improve the composition of the intestinal microflora of the child, are rich in B vitamins and calcium. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, stimulates appetite, and increases the absorption of micronutrients. Children's dairy products are introduced into the baby's diet gradually, starting with 1 tsp. and with good tolerance increase their volume to 150-200 ml per day.
Sample menu for a healthy baby 8 months
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free* or milk porridge Butter Boiled egg yolk Fruit puree Fruit juice | 180 g |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Vegetable oil Meat puree Fruit juice | 170 g 1/2 tsp 50 g 50 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Cottage cheese Baby biscuits Fruit puree Supplementation with breast milk or baby kefir/yogurt | 40 g |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
* - diluted with breast milk, infant formula or water
Approximate daily ration for an 8 month old baby allergic to cow's milk proteins
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for children allergic to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 o'clock | Dairy-free* porridge Vegetable oil Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 120 g 1 tsp 80 g |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Vegetable oil Meat puree | 170 g 1 tsp 40 g |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Vegetable puree or porridge Vegetable oil Meat puree | 170 g 1 tsp 30 g |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for children allergic to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
* - diluted with breast milk or therapeutic formula for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins
Baby's menu at 8 months: what you can, diet
PreviousNext
- What does a child eat at 8–9 months and what new foods should be introduced?
- What to give a baby at 8 months - what consistency should his food be?
- What diet should an eight-month-old baby have?
- What should you refrain from in feeding a child?
- Approximate menu for feeding a baby at 8 months
Contents:
The older the child gets, the more questions young parents have about feeding. The introduction of products has already begun, but what's next? What does an 8 month old baby eat? What is impossible? What to feed the baby? What is the feeding schedule? How much does an 8 month old baby eat? And if he is breastfed or artificial?
The introduction of products has already begun, but what's next? What does an 8 month old baby eat? What is impossible? What to feed the baby? What is the feeding schedule? How much does an 8 month old baby eat? And if he is breastfed or artificial?
By this age, the baby should be receiving adequate complementary foods, but breast milk and its substitutes are still the mainstay of an eight-month-old baby's diet (World Health Organization, American Academy of Pediatrics). Recall that the purpose of the introduction of complementary foods is to introduce the child to foods and new textures, teach him to chew, replenish the supply of nutrients that is missing for a growing body and prepare for the transition to a common (parental) table. By the way, do you know what a baby should be able to do at 8 months? Look in this article.
Did you know that...
Baby's skin is several times thinner and more delicate than that of adults, so the diaper should be as soft as a cloud.
And we took care of it! 4 in 1: soft, absorbent, breathable, hypoallergenic! All these are new smart diapers Huggies Elite Soft
At 8–9 months, in addition to nutrients from breastmilk or its equivalent, a baby needs approximately 400 kcal, 6 grams of protein, 200 mg of calcium, 3.5 mg of iron, as well as fats, carbohydrates, and a range of vitamins and minerals daily, which should be supplied with complementary foods.
What does a baby eat at 8–9 months and what new foods should be introduced?
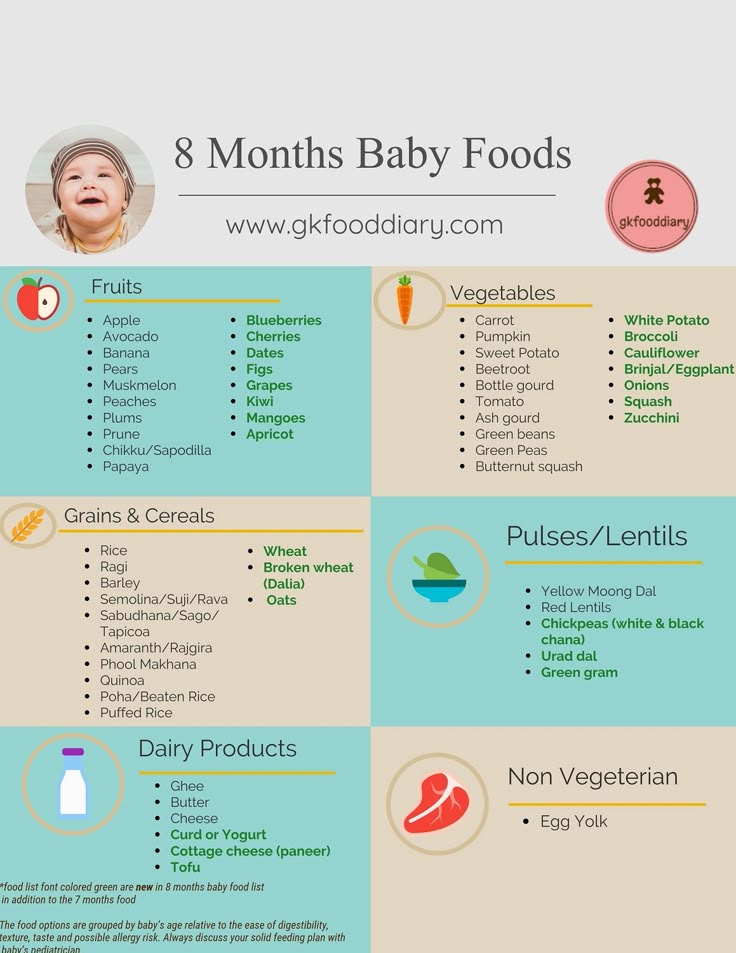
By the age of eight months, the baby already has a sufficient set of complementary foods: various vegetables (zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, potatoes, pumpkin, carrots, sweet potatoes), fruits (apple, pear, banana, peach, apricot), cereals (buckwheat, rice, corn), meat (turkey, rabbit, beef, chicken), butter and vegetable oils.
Experts in the field of baby food recommend that at this age fish should be introduced into complementary foods as a source of Omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, minerals and trace elements. You should start with white fish (hake, cod, perch, pollock). Serving size should not exceed 30-50 grams per serving, 1-2 times a week instead of meat dishes. Fish can be combined with vegetables or cereals.
8 months is the time to start introducing fermented milk products (kefir, unsweetened biolact or yogurt up to 150 ml per day), cottage cheese (no more than 50 grams per day) and cheese into the diet. An additional source of calcium is extremely important for a fast-growing organism. In addition, lactic acid bacteria help the baby's digestion.
Parents often have a question: is it possible to give milk to a child of 8 months? No, WHO does not recommend doing this before 12 months due to the high risk of developing an allergic reaction.
As an additional source of fat, it is recommended to add 1 tsp. butter in cereals and 1 tsp. vegetable oil in vegetable dishes.
butter in cereals and 1 tsp. vegetable oil in vegetable dishes.
What to give a baby at 8 months - what consistency should his food be?
The consistency of food for an eight-month-old baby should be soft, but not homogenized - mashed potatoes, minced meat, ground on a grater. From 8 months, it is recommended to introduce pieces into complementary foods: you should start with small ones, no more than 0.5 × 0.5 cm of soft consistency (for example, boiled zucchini, banana, ripe pear, etc.).
In addition to the food that the baby receives from a spoon, it is important to offer him the so-called finger food - food that the child will independently hold in his hand and eat. For example, fresh fruits cut into large pieces (banana, peach, melon) or cooked vegetables (potatoes, carrots, bell peppers). Eating on your own while holding the product in your hand is an important skill that a child must acquire at the stage of acquaintance with food. So the child will learn to bite off small pieces, chew and swallow them. In addition, it is great for training coordination and fine motor skills, and learning the texture of the product is an important part of development.
In addition, it is great for training coordination and fine motor skills, and learning the texture of the product is an important part of development.
What diet should an eight-month-old baby have?
At 8 months, the baby should have approximately 2-3 full meals and 2-3 snacks, while breastfeeding may still be on demand.
And there are no fundamental differences between cooked food at home and in industrial conditions. Use the one that is comfortable for you.
Regarding how much a baby eats at 8 months, there are disagreements in the opinion of experts. Experts from WHO and the Union of Pediatricians of Russia recommend increasing the volume of complementary foods to 180-200 ml per feeding. However, if parents plan to continue breastfeeding, such large serving sizes may crowd out feedings, so the volume of a single serving should not exceed 120 ml.
We figured out the feeding regimen. What about your baby's sleep schedule? Are there problems? Find out how to solve them with our guide, which contains the most important tips for parents from a pediatrician and a baby sleep consultant.
What should one refrain from in feeding a child?
For a long time, fruit juice was used as the first complementary food. However, now pediatricians around the world recommend including these drinks in the baby’s diet no earlier than a year. A large amount of sugars (even natural ones) has a negative effect on the immature gastrointestinal tract of the baby, and especially on the liver and pancreas. Therefore, it is worth waiting 12 months.
Also, currently fashionable cow's milk substitutes - oatmeal, coconut, almond, buckwheat and others are of no use. Such products have a low energy value, and they only take up additional volume in the stomach.
Tea, even for children, even herbal, should also not be introduced into complementary foods at 8 months. WHO experts recommend introducing your baby to this wonderful drink no earlier than 5 (!) years.
And, of course, in recipes for an 8-month-old baby, you should refrain from refined sugar (including baby biscuits), honey (risk of botulism infection), mushrooms, fatty fish and meat, sausages and sausages.