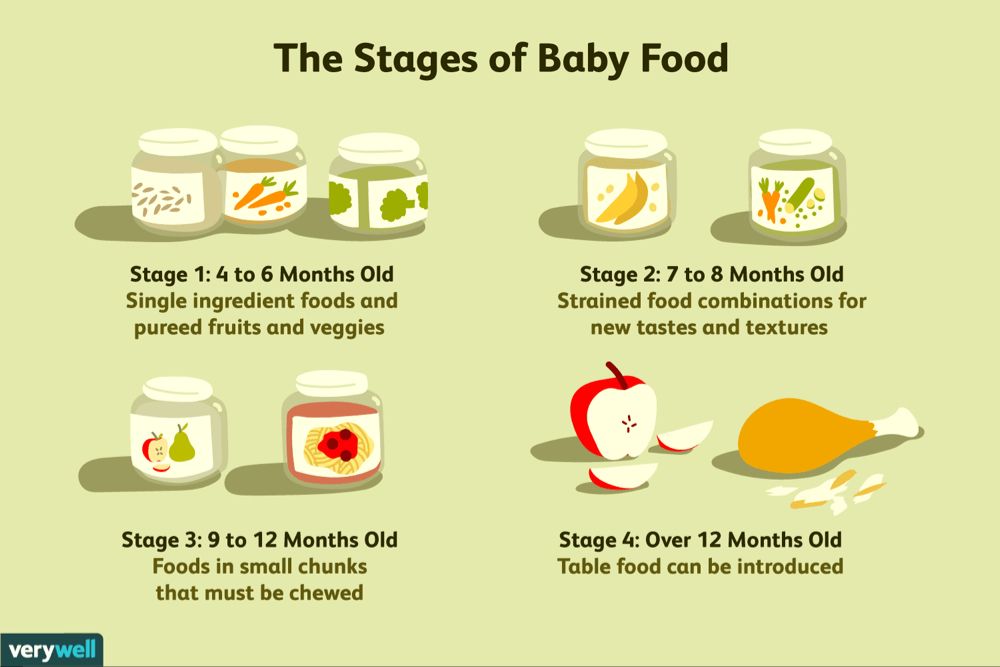
When can i feed my baby fruit
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.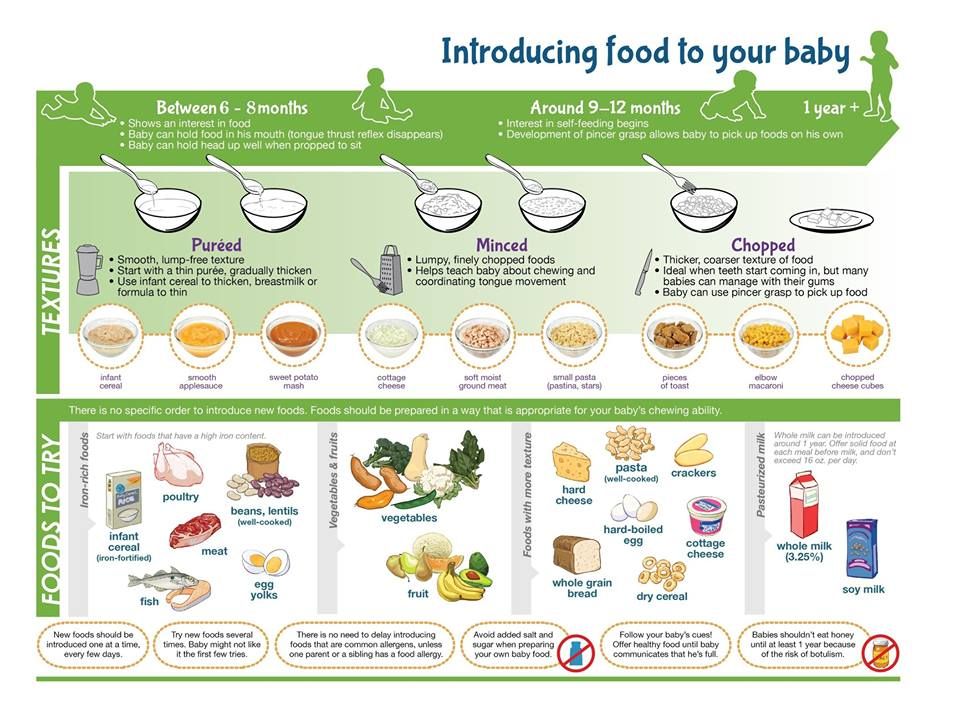
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor. It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here.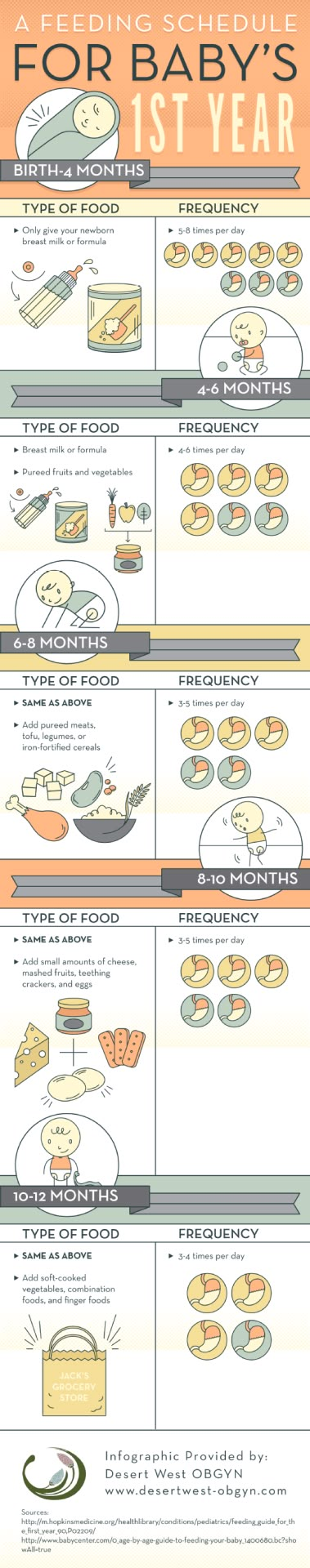 Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done. Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods. The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal.
 The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods. - Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.
Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
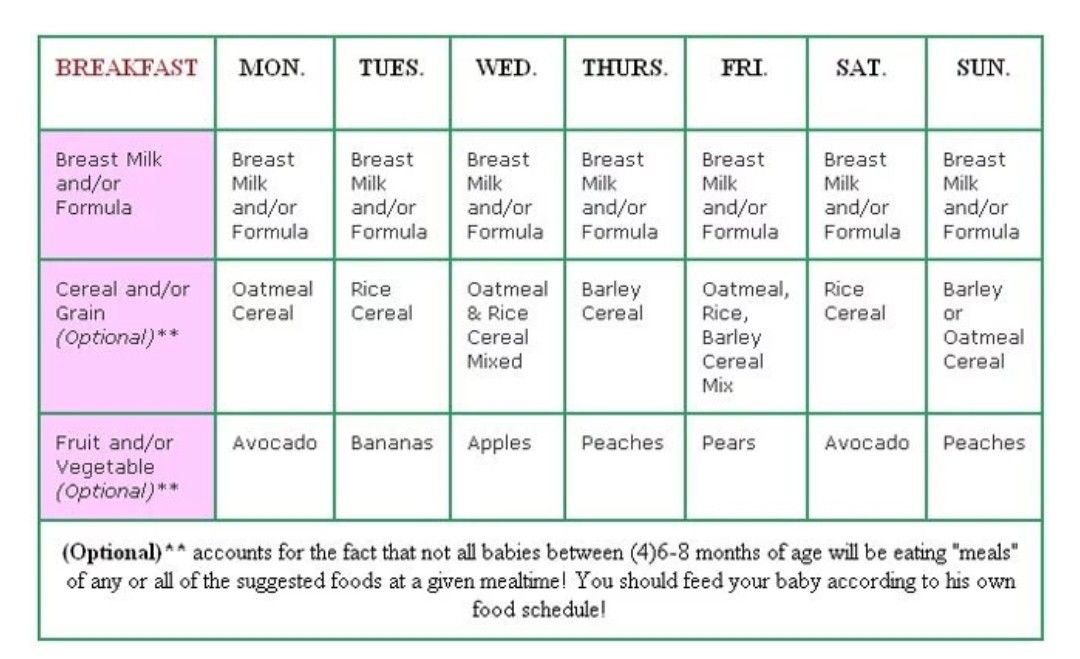
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
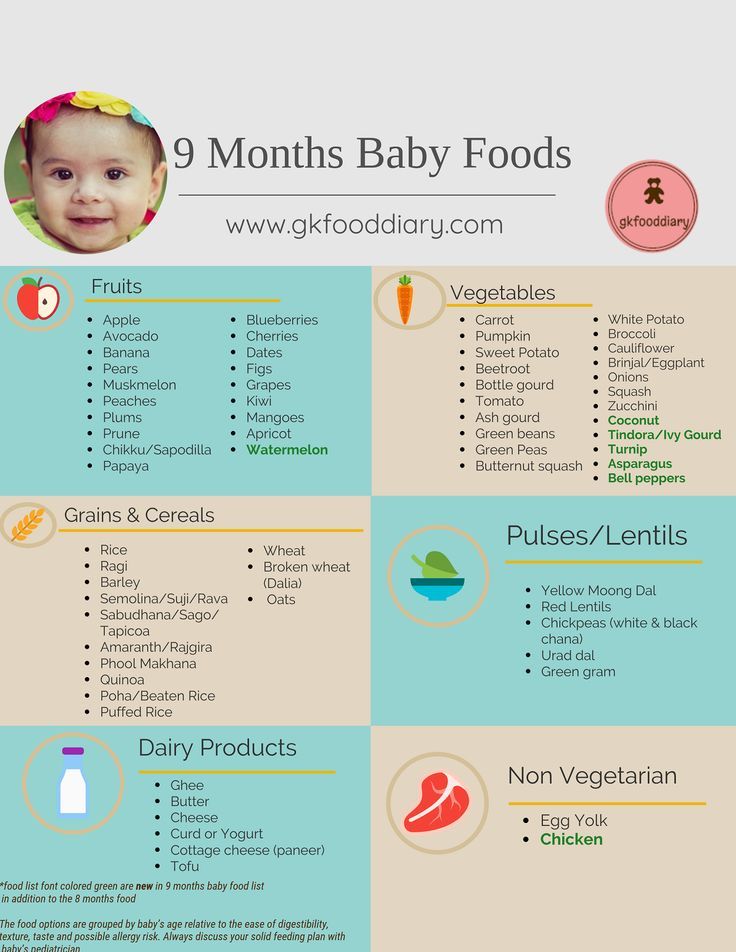
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.
 ) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
Advertisement | page continues below
Complementary foods for a child - the introduction of fruit puree, fruits and juices into the diet of infants
Historically, fruit juice was recommended by pediatricians as a source of vitamin C, calcium, and other vitamins. The juice is delicious, sweet, children drink it with pleasure, and suddenly it turned out that there are potential risks: the high sugar content in the juice increases calorie intake, overweight and the risk of caries. More recently, about twenty years ago, doctors recommended the introduction of complementary foods, starting with juices and fruits. But now the situation has changed. Children's nutritionists believe that the optimal time for the introduction of juices is 1 year after the child gets used to the main complementary foods: vegetables, cereals, meat, fish, fruits. At the same time, you can find recommendations to give juices from 6 months or after 3 years. Carbohydrates, which are abundant in juice, change the child's appetite, but to get the required amount of vitamins, you need to drink a lot of it, about 1 liter! In addition, they do not give a feeling of satiety and the child may be prone to overeating.
More recently, about twenty years ago, doctors recommended the introduction of complementary foods, starting with juices and fruits. But now the situation has changed. Children's nutritionists believe that the optimal time for the introduction of juices is 1 year after the child gets used to the main complementary foods: vegetables, cereals, meat, fish, fruits. At the same time, you can find recommendations to give juices from 6 months or after 3 years. Carbohydrates, which are abundant in juice, change the child's appetite, but to get the required amount of vitamins, you need to drink a lot of it, about 1 liter! In addition, they do not give a feeling of satiety and the child may be prone to overeating.
Introduction of fruit juice American Academy of Pediatrics recommendations: download
- Optimal to completely avoid the use of juice in infants until 1 year of age;
- AAP and the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry guidelines state that juice should be offered to babies in a cup, not a bottle, and that babies should not go to bed with a bottle in their mouth.
- They concluded that long-term exposure to the sugar contained in the juice on the teeth is the main factor influencing dental caries.
- After 1 year, fruit juice can be used as part of a meal or snack. It should not be drunk like water during the day or used as a means to calm an upset child.
- Do not give juices if the child has diarrhea, oral rehydration solutions only.
- The development of perioral rash in some children after feeding freshly squeezed citrus juice is most likely due to the chemical irritant effect of the acid.
- Diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms that some children experience are most commonly associated with carbohydrate malabsorption.
- Although fruit allergy can develop at an early age, this is rare.
Baby food - fresh juices
It is not recommended to introduce freshly squeezed juices to children under one year old. But there is no strict ban.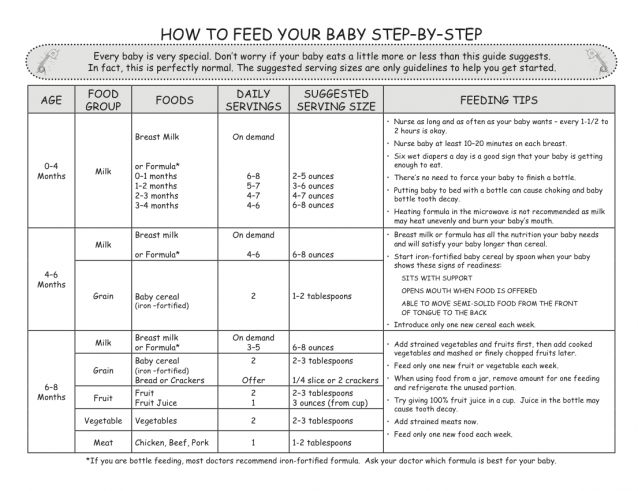 Juice up to a year is not useful, unlike children older than one year . It contains a lot of fruit acid, which can lead to increased peristalsis and intestinal walls, pain, and digestive disorders. Dilute with water in a ratio of 1:1. And remember, fresh retains its maximum amount of vitamins in the first half hour, so do not store juice for later. With a later introduction of juice, their better tolerance is noted. This is due to the maturation of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract and its readiness for the absorption of juice. But even with this, the child may experience pain and bloating, regurgitation, and stool disorders. This is due to the presence of organic acids in juices, which have an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Juice up to a year is not useful, unlike children older than one year . It contains a lot of fruit acid, which can lead to increased peristalsis and intestinal walls, pain, and digestive disorders. Dilute with water in a ratio of 1:1. And remember, fresh retains its maximum amount of vitamins in the first half hour, so do not store juice for later. With a later introduction of juice, their better tolerance is noted. This is due to the maturation of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract and its readiness for the absorption of juice. But even with this, the child may experience pain and bloating, regurgitation, and stool disorders. This is due to the presence of organic acids in juices, which have an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
How do I start adding juice to my baby?
First, a teaspoonful (about 5 ml) between feedings, observing the baby's reaction. For children under 3 years old, juices are recommended to be diluted with boiled or baby water in a ratio of 1:2. Freshly squeezed juices - up to 7-8 years. The amount of juice: from 1 year to 1.5 years - up to 100 ml, should not be exceeded. At 2 years - 200 ml.
For children under 3 years old, juices are recommended to be diluted with boiled or baby water in a ratio of 1:2. Freshly squeezed juices - up to 7-8 years. The amount of juice: from 1 year to 1.5 years - up to 100 ml, should not be exceeded. At 2 years - 200 ml.
It is best to give green apple or pear juice first. Juice from plums, apricots, peaches - it is better to give at an older age, they have a slight laxative effect.
Then you can give a mixture of juices from 2 or 3 fruits. You can give a mixture of cherry, cherry, currant, raspberry juice, orange juice, pineapple, mango, grapefruit and mixtures thereof. It is better to give grape juice from 5-6 years old, there are a lot of carbohydrates.
It must be remembered that:
- Apple, carrot and pear juice - strengthen
- Plum, pumpkin, apricot, peach - weakening
This can be used if there are digestive problems.
If we choose industrial juices - carefully read what is written on the label, there should be no artificial additives, dyes and preservatives. Do not use opened packages. Should I give industrial juices for baby food? Why not? They are made from high quality, proven, specially selected raw materials, production is strictly controlled, they have balanced compositions and optimal taste. Until the age of 3, buy juices for your child only marked “baby food” on the package.
Introduction of fruit and fruit puree - European recommendations
If your young child has already tasted vegetables and accepted them, it's time for fruit. The season is always for them, but the best is in autumn, when the most delicious apples, pears and plums appear. Fresh fruits from all over the world are available in stores all year round, but it's worth starting with seasonal, locally grown ones. And these are: apricots, raspberries, apples, pears, plums.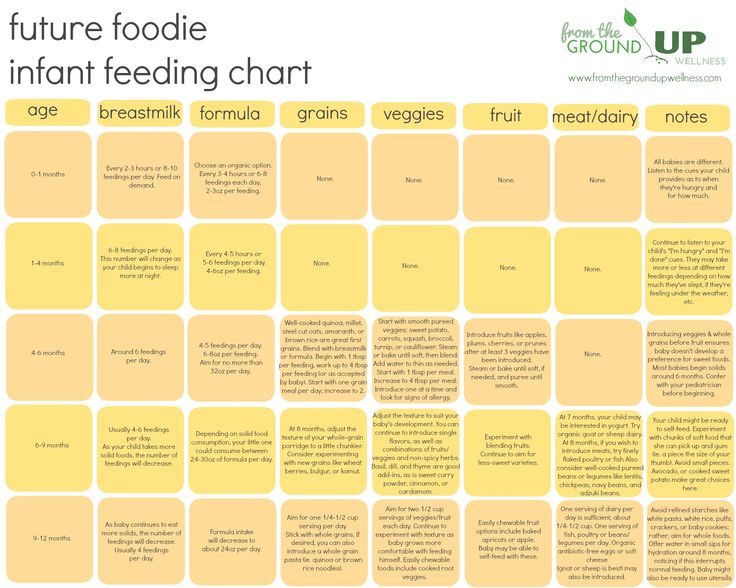 They contain not only vitamins, dietary fiber, but also minerals, including valuable microelements, which should be present in the child during the expansion of the diet.
They contain not only vitamins, dietary fiber, but also minerals, including valuable microelements, which should be present in the child during the expansion of the diet.
Fruit is usually recommended from 6-7 months of age. Complementary foods often begin with fruit or vegetable purees. But it is better to start with vegetables. Fruit puree tastes better, is sweeter, and the child may then eat vegetables worse. But vegetable puree will not affect the baby's desire to eat fruit dishes. Therefore, more often pediatricians are advised to give fruit dishes after the introduction of vegetables and cereals. Start complementary foods with fruits in the form of mashed apples or bananas or pears. Then you can add fruits that grow in your area of \u200b\u200bresidence. Then you can include fruit and fruit and vegetable mixtures.
Fashionable but exotic fruits or with strong flavors - strawberries, mangoes, kiwis, currants - are best introduced later. But there is no strict ban.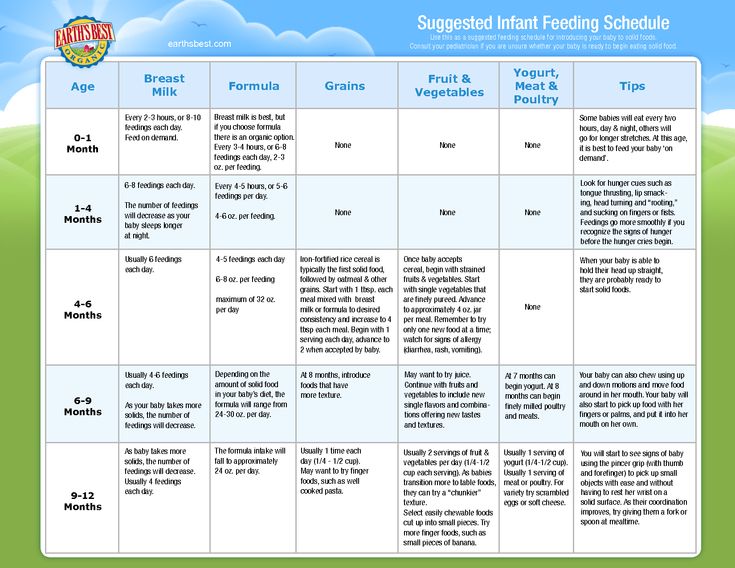
Fruit puree should be started with 1 teaspoon in the morning, increasing to 100 g over 2 weeks.
Homemade or factory made? As you wish, subject to the basic hygiene rules of cooking. If you have time, make your own fruit puree. Plums, apricots, banana can be mashed in a mortar or blender. Grate apples and pears on a fine plastic grater. For the first time, the apple can be boiled, then it will be soft. Pour the prunes with boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. Do not add sugar!
Homemade fruit puree - don't forget about hygiene
Pour boiling water over a grater, preferably a plastic one or a blender, wash and peel the fruit.
Gradually make the fruit puree coarser.
Start with liquid puree, at 8 months - finely ground puree, at 10 months of age. - puree from larger particles.
When the child has 6-8 teeth, you can give pieces of fruit and he will eat them on his own.
Properties of various fruit purees
- Banana puree is a good source of trace elements: magnesium and potassium, calcium, iron and phosphorus.
 Bananas rarely cause allergic reactions
Bananas rarely cause allergic reactions - Prune puree can act as a mild laxative that increases intestinal motility. Contains potassium, vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin).
- Blueberry puree contains tannin - tannin, contains pectin, which has a disinfectant and anti-inflammatory effect, contains a large amount of provitamin A - beta-carotene, which is good for vision, manganese. In addition, blueberries are low allergenic. Apricots are an excellent source of potassium, carotene, vitamin C and pectin.
Tips from the Nyankovskih Healthy Child University
- Fruits are sweet and can be used instead of sweets.
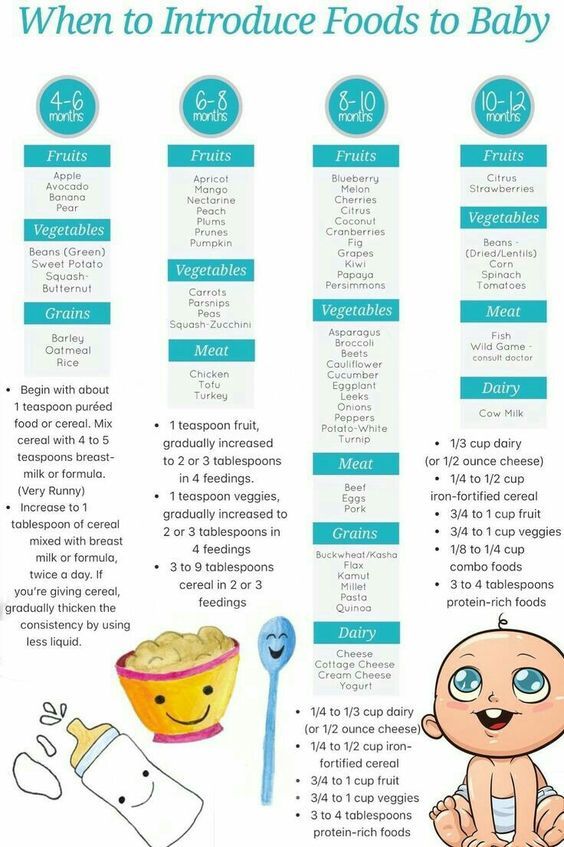
- Fruits should be included in the child's diet as the second food group after vegetables. They can be given quite early, when the baby is four months old (between 17 and 26 weeks of age).
- Initially it can be a mousse (or puree from a jar) and then an apple scraper with a spoon.
- In a few days the child can try other fruits, berries, currants, raspberries. You can serve them on their own or add them to cereals, desserts. When a child is 10-11 months old and knows how to eat fruit purees and mousses, he should start learning to eat fruits in the form of soft particles, as well as himself, with a pen. Offer him peeled peaches, apricots, plums, grapes (no seeds!).
- The new rules for baby food are a real revolution. Parents no longer have to stick to rigid patterns. The parents decide what the child eats and the child decides how much he eats.
Video: child feeding - introduction of fruits, fruit puree, juices, feeding in gdudnoy and artificial feeding
9000 Let your children be healthy!
Other news in category
Newborn - online course "Mom's Way: Newborn" from Professor Nyankovsky on caring for a baby in the first months of life
Baby's first litter. Porridge or vegetable puree?
Porridge or vegetable puree?
Consumption norms for fruits and berries
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
40474 views
September 15, 2021
Login or register to save articles and products as favorites
Fruits are an essential part of a child's diet. They enrich the baby's diet with minerals and vitamins, fiber and fruit sugars. Moreover, each fruit and each berry has its own, only their inherent properties.
Useful substances in berries and fruits
Thus, the champions in the content of vitamin C are black currants, rose hips. Apricots are the richest in beta-carotene. Plums are known for their high content of pectins, which are good for digestion.
Apricots are the richest in beta-carotene. Plums are known for their high content of pectins, which are good for digestion.
Baby's introduction to fruits
For infants, fruits are introduced in the form of puree according to all the rules for the introduction of complementary foods. The first acquaintance of the baby occurs no earlier than 4 months with a monocomponent hypoallergenic fruit puree. Usually it is apple or pear puree. Then you can enter the puree of their plums, apricots.
New flavors, as well as multi-component purees, are introduced later - from 5 months. From this age, a wider range of fruits is allowed, as well as some berries - peach, raspberry, blackcurrant, blueberry, cherry, rosehip. The rule for the introduction of multicomponent purees is that the baby should already try all the fruits and berries that are part of it, or only one fruit or berry can be new. This is necessary in order to track the possible intolerance of one or another component of the puree.
Puree from citrus fruits, bananas, mangoes can be given to a baby from 6 months, and puree from such exotic fruits as papaya, kiwi, passion fruit - not earlier than 8 months.
As for how much fruit puree can be given to a baby, then up to a year the daily volume is calculated simply - the age in months is multiplied by 10, but up to a year the volume should not exceed 100 g. at 5 months, the baby should eat 50 g of fruit puree, at 6 months - 60 g, per year - 100 g.
Fresh berries and fruits
A baby up to a year old, while he has not yet learned to chew, and his gastrointestinal tract is not yet ready to eat food without cooking, fresh fruits and berries can be given only for informational purposes. In addition, pieces of fruit or berries should be given to the baby very carefully so that he does not choke, and only if you are completely confident in the quality of the product and the pediatrician gave the go-ahead.
It should be noted that, in accordance with the recommendations given in the National Program for Feeding Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation, food and dishes of industrial production should be used in the child's diet.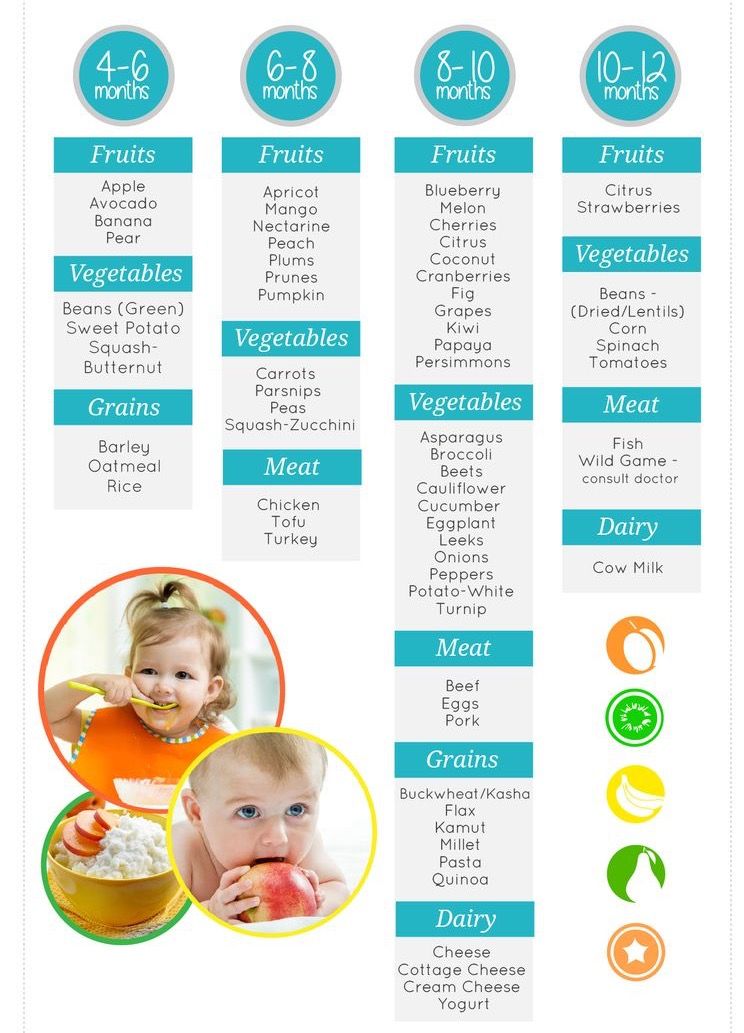
After a year, when the baby's first teeth erupted, he learned, at the very least, to swallow, gnaw and eat food not only in a puree form, fruits and berries can already be offered to him in the form of a fruit salad. You can give him a bite of apple slices.
From one to two years old, the baby is supposed to have about 100-150 g of fruit per day per day, and berries can make up a third of this volume. At this age, the baby can be offered strawberries, but very carefully, as this is a highly allergenic berry.
A preschooler can eat fruits completely fresh - up to 200 g (a third of this volume can be berries), and a schoolboy - 300 g.
Fruits and berries must be present in the baby's daily diet.
In the daily diet of children of the first year of life, familiar with complementary foods, not only fruit purees in residual quantities, but also children's fruit juices and nectars must be present without fail. Juice with pulp is especially useful, as it contains fiber.