When can i feed my infant baby food
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
When Can My Baby Start Eating Solid Foods? (for Parents)
A friend just started giving her 3-month-old applesauce and rice cereal. My son is just 2 weeks younger than hers, and I am wondering if I should be introducing solids soon too. When should I start?
My son is just 2 weeks younger than hers, and I am wondering if I should be introducing solids soon too. When should I start?
– Taylor
Doctors recommend waiting until a baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Starting before 4 months is not recommended.
At about 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — such as iron and zinc — that solid foods provide. It’s also the right time to introduce your infant to new tastes and textures.
Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but don't start until your baby is at least 4 months old.
How do you know it’s the right time to start solid foods? Here are some signs that babies are ready:
- They have good head and neck control and sit up in a high chair.
- They're interested in foods. For example, they may watch others eat, reach for food, and open their mouths when food approaches.
- They don’t push food out of their mouths, which is a natural tongue reflex that disappears when they’re between 4–6 months old.
- They weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it.
Talk to your doctor about the right time to start solid foods.
How Should I Start Solids?
When the time is right, you can start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal or other food to a baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain. Let your baby practice eating from a spoon and learn to stop when full.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce others, such as puréed meat, fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, or yogurt. Try one food at a time and wait a few days before trying something else new to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
When starting your baby on solids, avoid:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy drinks before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Also, do not give fruit juices to infants younger than 12 months old.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
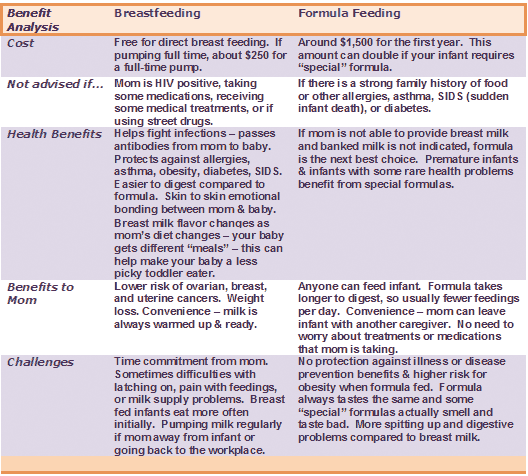
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding necessary for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. nine0004
nine0004
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way? nine0004
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1. 5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast? nine0004
5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast? nine0004
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast. nine0004
Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast. nine0004
This whole process is biologically justified. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs. nine0004
It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs. nine0004
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with breast in mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again. nine0004
The daytime naps of a one-month-old infant feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2. 5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself. nine0004
5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself. nine0004
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for suckling. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?” nine0004
A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?” nine0004
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person deliberately harming an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions. nine0004
For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions. nine0004
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
 nine0036
nine0036 - At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed noticeably less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen. And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
- At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening. nine0036
- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications.
 At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness. nine0036
At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness. nine0036 - At seven months, the frequency of application is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times.
 The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times. nine0035 In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times. nine0035 In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ... - Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons.
 The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours. nine0036
The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours. nine0036 - At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast. The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning. nine0036
- At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.
 e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down. nine0036
e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down. nine0036 - At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking. The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
 nine0036
nine0036
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to. nine0004
Moms who don't think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when breastfeeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is not true. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free. nine0004
In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free. nine0004
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking back at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long. nine0004
It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long. nine0004
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when I advise mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby. nine0004
Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby. nine0004
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples. nine0004
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists. These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
Breastfeeding is not only important for the baby, it is also important for the mother. During on-demand feeding, the woman's feelings change, a stronger attachment to the baby is formed, the woman becomes more sensitive to the needs of the baby. Deeper affection and understanding are not only preserved in infancy. They persist for life. For clarity, imagine what happens to a woman’s feelings if she tries to “withstand” a child, endures his crying, anxiety. What happens to a woman if she uses the recommendation from one very popular parenting book: "Go to the child if he cries for more than 15 minutes"? Speaking in abstract terms, humanity is interested in reviving the practice of breastfeeding. The revival of this practice is impossible without mothers realizing the true reasons for the child's need for attachment to the breast. nine0076
Lilia Kazakova, pediatrician,
Head of Breastfeeding and Child Care Counselors
Q&A - NCCH
Breastfeeding Essentials
1. Why is breastfeeding important?
Why is breastfeeding important?
Breast milk is a unique and irreproducible food product, which contains important components that reduce the risk of a child developing infectious pathologies, allergies, overweight, cardiovascular pathology, and diabetes mellitus. Only with breast milk can a child receive a unique complex of immunoglobulins, enzymes, growth factors, prebiotic fibers, which has not only an immediate, but also a long-term beneficial effect on the subsequent development of the child. During breastfeeding, a close psycho-emotional bond is formed between mother and child, laying the foundation for mental health for the rest of her life. nine0004
2. How to prepare the breast for feeding the baby? How to take care of the breasts?
Preparation of the breast for feeding includes the usual hygiene procedures (hygienic shower 2 times a day, washing hands with soap) and does not require any special treatment of the mammary glands. Underwear should not be too tight or, on the contrary, very loose.
3. What is the correct way to attach the baby to the breast?
To prevent painful sucking and nipple cracks, it is important that when sucking, the child must grasp not only the nipple, but also partially the areola, while the child's lower lip must be turned outward. nine0004
4. Is there a strict feeding schedule for an infant?
In the first 1-2 months. lactation - a period of adaptation - it is important to feed the child at his request, without missing night feedings. In the future, gradually the intervals between feeding will increase and a regimen that is convenient for mother and child will be formed.
5. Why might a baby be anxious while feeding?
The baby may be anxious during feeding for various reasons. It can be colic, abdominal pain, nasal congestion, as well as insufficient milk supply due to improper nipple grip or the presence of a lactation crisis. nine0004
6. What is a lactation crisis?
What is a lactation crisis?
Lactation crisis - a temporary decrease in milk production, which is of a functional nature, lasts no longer than 3-4 days, disappears on its own with frequent attachment of the child to the breast. During this period, supplementary feeding of the child with milk mixtures is not required.
7. How can a nursing mother eat so that her baby does not have allergies/colic?
If the child has allergies, the mother should analyze her diet and possible connection with the appearance of allergic reactions (skin or gastrointestinal), exclude foods with a high allergenic potential from the diet: whole cow or goat milk, seafood, honey, nuts, eggs , chocolate, peanuts, citrus fruits, mushrooms. nine0004
If the child has colic, whole cow's or goat's milk, fresh vegetables and fruits (which, however, can be taken in baked or boiled form), yeast-containing foods, spices, spicy and fried foods should be excluded.
8. Products that are recommended to be limited to a nursing mother.
Products that are recommended to be limited to a nursing mother.
The diet of a nursing mother should be varied, complete and balanced. You should not adhere to restrictive diets if the baby is well tolerated with breast milk. Only in the presence of manifestations of food allergies, with colic, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods with a high allergenic and gas-forming potential (beans, peas, white cabbage, fresh yeast pastries, carbonated drinks). nine0004
A breastfeeding mother should not eat fresh onions, garlic, other strong-smelling herbs and spices, pickled foods.
9. How much liquid should you drink per day?
It is advisable for a nursing mother to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
10. Should I express my milk?
It is not necessary to express milk after each feeding. However, pumping may be necessary if you need to stock your own milk (individual bank). In this case, you can express after each feeding of the baby and whenever you feel a “rush” of milk. nine0004
nine0004
11. What should I do if I have cracked nipples?
The resulting cracks must be treated with special healing creams that do not require rinsing before feeding the baby. In your underwear, you should put special absorbent pads to keep the nipple dry or special nipple shields that do not allow the nipple to come into contact with the linen. With deep cracks or severe soreness of the nipples, it is necessary to start feeding the baby through special silicone pads on the nipples. If sucking through the pads is impossible, then it is worth temporarily stopping feeding the child from the diseased breast until the cracks are completely healed. nine0004
12. If I have mastitis, can I continue breastfeeding? Is it dangerous for the baby?
In case of lactational mastitis, in case of taking antibiotics that are compatible with breastfeeding and the absence of pus with milk, you can continue feeding from the breast, including from the patient. This does not pose a danger to the baby, since breast milk contains a large number of antibacterial factors.
This does not pose a danger to the baby, since breast milk contains a large number of antibacterial factors.
13. What should I do if I am unable to establish lactation? nine0085
The vast majority of women can successfully breastfeed. Only in 2-3% of cases (primary hypogalactia) lactation is insufficient, in connection with which the child can be supplemented with milk mixtures with the continuation of measures to stimulate lactation.
14. Until what age should I breastfeed? How can I make it easier for both me and the baby to endure weaning?
It is considered permissible to breastfeed up to 2 years of age or more if the woman wishes. nine0004
However, after one year, the frequency of breastfeeding should be reduced to 1-2 times a day, and after 2 years, the advisability of breastfeeding is most likely questionable.
During the weaning period, a close friend or relative can help the mother. During this period, it is important to exclude the joint sleep of the mother with the child while providing him with increased attention during the daytime in the form of organizing joint games and developing activities.
15. Until what age should you feed at night? How to wean from night feedings? nine0085
Night feedings, if the mother wishes, can be kept up to 2 years of age, but not more than 1 time per night. The absence of night feedings contributes to a deeper sleep of the child, the proper functioning of his digestive organs and, as a result, the formation of a good appetite in the morning and afternoon.
Weaning from night feeds is best done with the help of a person close to the baby who is assigned night care for a few days.
16. Is it possible to partially replace breast milk with cow/goat milk? Which one is closer to my mother's? nine0085
If it is necessary to supplement with a lack of mother's milk, it is important to use only adapted infant formulas, which, unlike whole cow's or goat's milk, correspond to the physiological needs of the child.
17. How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
Often a lack of milk is suspected in case of restless behavior of the child during or after feeding, or judged by the amount of milk eaten per feeding or per day. However, both approaches cannot give a clear idea of sufficient lactation. A clearer indicator is the increase in the body weight of the child per day, which should be at least 20 g for a full-term child in the first months of life. In addition, it is important to assess the general condition of the child, tissue turgor, urination frequency, and the nature of the stool. nine0004
However, both approaches cannot give a clear idea of sufficient lactation. A clearer indicator is the increase in the body weight of the child per day, which should be at least 20 g for a full-term child in the first months of life. In addition, it is important to assess the general condition of the child, tissue turgor, urination frequency, and the nature of the stool. nine0004
18. When should I supplement my baby with formula?
Supplementation with formula milk should only be carried out after consultation with a pediatrician, after a thorough assessment of the child's nutrition, general condition and physical development.
19. How can I tell if formula is right for my baby?
If the mixture is well tolerated, the child does not experience discomfort while eating, does not vomit, has regular mushy stools without pathological impurities, clear skin, physiological weight gain. nine0004
20. How do I switch to another formula?
The transition to another mixture should be gradual - no faster than 3-5 days. On the first day of administration, the amount of the "new" mixture should be no more than 10-30 ml, which can be added to one bottle to the "old" mixture.
On the first day of administration, the amount of the "new" mixture should be no more than 10-30 ml, which can be added to one bottle to the "old" mixture.
In the future, the amount of the "new" mixture is increased daily by 30 ml. at every feeding.
21. Do I need to supplement my baby with water?
Breastfed babies do not need to drink water, except in special cases (high room temperature, dehydration of the baby in case of vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature). nine0004
A formula-fed baby may require additional water intake in the amount of one feeding - 150-200 ml/day. if desired by the child.
22. How do I hold my baby and bottle correctly if I'm formula feeding him?
It is important when bottle feeding your baby to hold him in your arms so that he lies as in a cradle. When holding the bottle, you must be careful to ensure that the mixture or milk completely fills the nipple. It is necessary to tilt the bottle so that the air bubble is above the level of the nipple and the baby cannot swallow air. nine0004
nine0004
Formula milk
23. What is formula and formula feeding?
Mixed feeding is the feeding of a child of the first year of life with breast milk in an amount of at least 1/5 of the daily amount of food (150-200 ml) in combination with infant milk formulas.
Artificial feeding is the feeding of a child only with infant formula or in combination with breast milk, the share of which is less than 1/5 of the daily amount of food. nine0004
24. Why should a baby not be allowed to fall asleep with a bottle?
Sucking on a bottle in bed while lying on your back can cause some milk to enter the Eustachian tube, which connects part of the larynx to the middle ear, which can cause inflammation of the middle ear. Also, when a child falls asleep, part of the milk mixture may remain in the oral cavity and promote the growth of bacteria that destroy tooth enamel. In addition, a child can get used to falling asleep only with a bottle and keep this habit for a long time.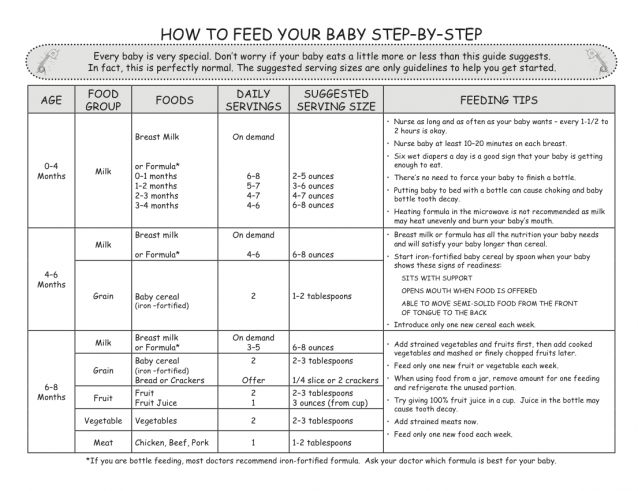 nine0004
nine0004
25. If we travel far from home, is it better to take ready-made formula with us or dilute it on the road?
It is recommended to use formula milk immediately after preparation. Therefore, it is better to take formula powder with you, a thermos with warm water to dilute it, and prepare the mixture just before feeding the baby.
The main thing about baby food
26. Why is nutrition so important in the first 2 years of life? nine0085
A child's nutrition in the first two years of his life has the greatest influence on the further development of the child's body. It is during this period that the foundations of proper metabolism are laid. A rationally organized diet at this time can reduce the risk of further development of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
27. Why is it said that "immunity is in the gut"?
The human gastrointestinal tract performs not only digestive, but also a pronounced immune function. Up to 80% of all immunocompetent cells of the human body are located in the intestinal mucosa, thanks to which protection against potentially dangerous microorganisms is carried out throughout a person's life. nine0004
Up to 80% of all immunocompetent cells of the human body are located in the intestinal mucosa, thanks to which protection against potentially dangerous microorganisms is carried out throughout a person's life. nine0004
28. Does the baby need additional vitamins in winter and spring?
If the child receives food that is not fortified with vitamins, then additional intake of vitamins in preventive doses should be carried out throughout the year, given the low level of vitamins in natural products.
29. How to choose food if you have been diagnosed with celiac disease?
With celiac disease, all products from wheat, rye, barley and oats are excluded from the child's diet: bread, pasta, confectionery, sausages, etc., including the flour of these cereals. nine0079 For celiac disease, products from rice, corn, buckwheat, millet (millet), sago are used.
30. Can adults eat mashed potatoes from a jar?
Baby food, including cans, is a product of high quality and guaranteed safety, therefore, if necessary, it can be used in the human diet at any age.
31. Will the child be able to get enough, will he have enough nutrients if I feed him only industrial food? nine0085
A diet made up of only industrial baby food products can fully satisfy a child's needs for essential nutrients and energy. However, for the formation of proper eating behavior and chewing skills from 8-10 months. it is desirable to gradually expand the child's diet by introducing some home-made products (meat soufflé, steam cutlets, finely chopped boiled vegetables, pasta), as well as bread and biscuits.
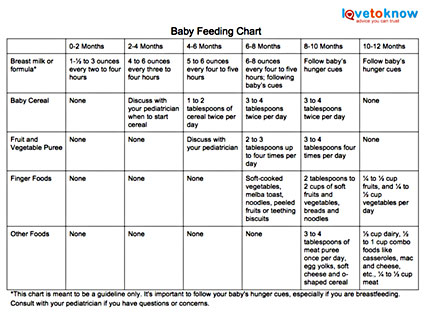
4 to 6 months - First food
The timing of the introduction of complementary foods is individual for each child and lies in the range of 4-6 months. The baby is ready to take the first solid food if he drinks well from a spoon and does not push it out with his tongue, if he remains unsatisfied after feeding with breast milk or formula, and if he actively shows interest in the parents' food and tries it. nine0004
nine0004
33. Where to start: with cereals, vegetables or fruits?
Complementary foods should be started either with vegetable puree or porridge. For children with reduced body weight and frequent loose stools, it is advisable to start with porridge, for children with overweight or with a tendency to constipation - with vegetable puree. After that, you can enter the fruit.
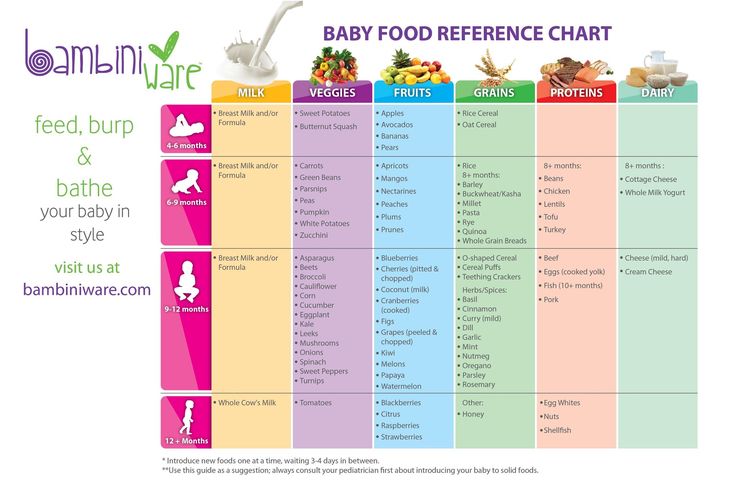
34. When, how and what to inject? (Complementary food table.) General recommendations.
| Name of products and dishes (g, ml) | Age (months) | |||
| 4 to 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 to 12 | |
| Vegetable puree | 10-150 | 170 | 180 | 200 |
| Milk porridge | 10-150 | 150 | 180 | 200 |
| Fruit puree | 5-60 | 70 | 80 | 90-100 |
| Fruit juice | 5-60 | 70 | 80 | 90-100 |
| Curd* | 10-40 | 40 | 40 | 50 |
Yolk, pcs.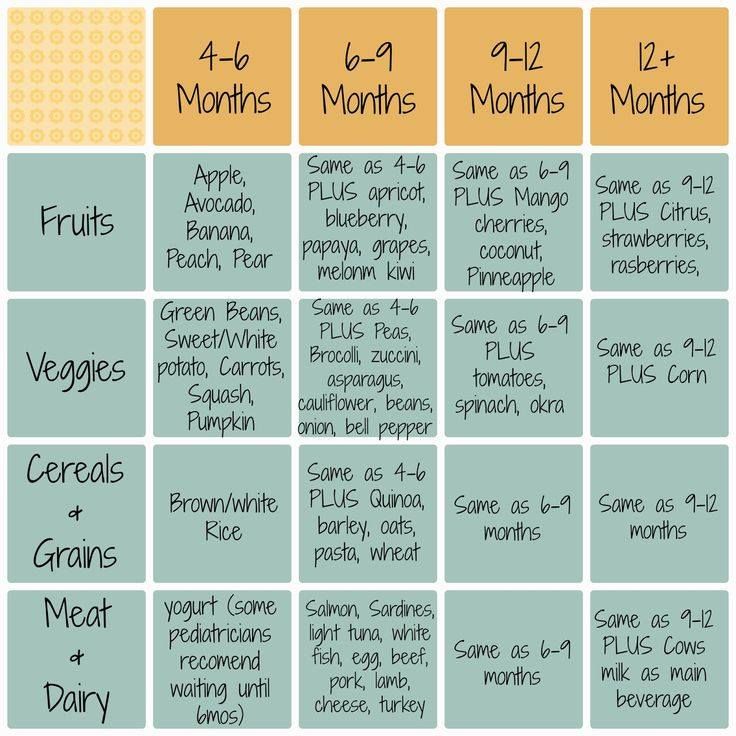 | - | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Meat puree* | 5-30 | 30 | 50 | 60-70 |
| Fish puree | - | - | 5-30 | 30-60 |
| Kefir and other fermented milk drinks | - | - | 200 | 200 |
| Rusks, biscuits | - | 3-5 | 5 | 10-15 |
| Wheat bread | - | - | 5 | 6 |
| Vegetable oil | nine0343 1-35 | 5 | 6 | |
| Butter | 1-4 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
* — not earlier than 6 months.
The sequence of introducing certain products and complementary foods depends on the nutritional status of the child and the functional state of his digestive system. So, for children with reduced body weight, frequent stools, it is advisable to prescribe cereals as the first complementary foods, with excess nutrition, constipation - vegetable puree. nine0004
So, for children with reduced body weight, frequent stools, it is advisable to prescribe cereals as the first complementary foods, with excess nutrition, constipation - vegetable puree. nine0004
New product to be given before breastfeeding/formula, starting at 1 tsp. with a gradual increase in volume to the age norm.
35. Why start with a one-component diet?
In order to identify a possible intolerance reaction to a particular food, it is important to start complementary foods with monocomponent meals.
36. Is it true that fruits contain acid that is harmful to teeth?
Fruits are rich in various organic acids that have a positive effect on digestion. However, excessive consumption of juices can adversely affect tooth enamel. Therefore, do not exceed the recommended age limits for fruit juices and purees. nine0004
37. Is it true that for a baby with a risk of developing allergies, it is better to start complementary foods as late as possible?
Numerous studies have shown that introducing complementary foods later (after 6 months) to children at risk of developing allergies does not reduce the likelihood of developing it, and in some cases even increases it.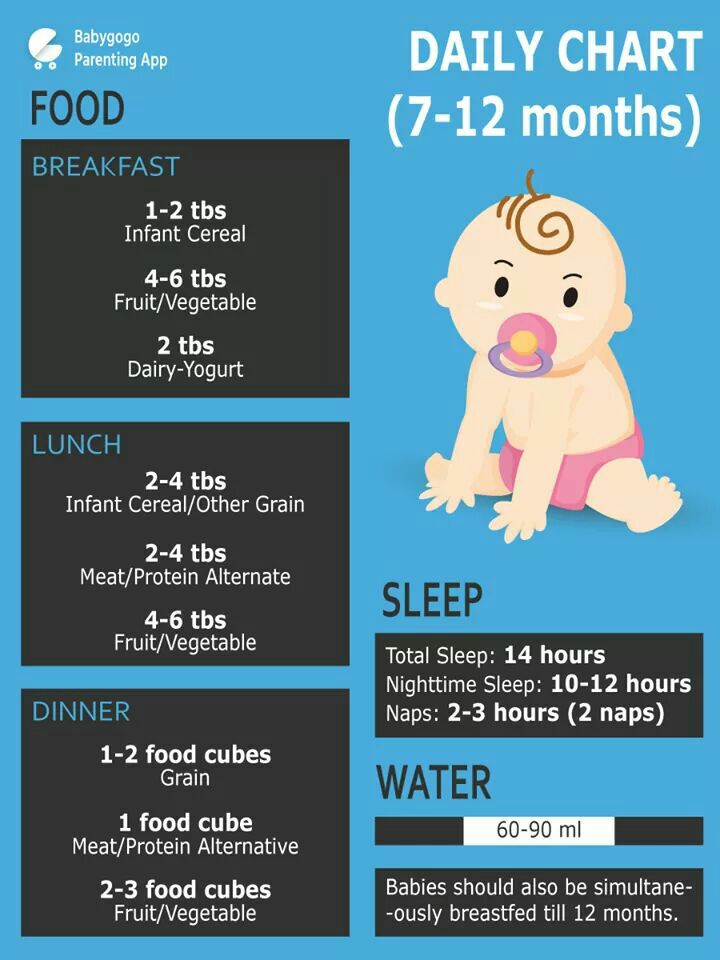
38. What measures to take to prevent allergies?
In order to prevent allergies, it is important to continue breastfeeding and start complementary foods with single-ingredient foods no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6 months. In this case, the first complementary foods should be dairy-free gluten-free cereals or vegetable purees from green-white vegetables. nine0004
39. How can a food allergy manifest itself?
Food allergies can manifest themselves in different ways. Skin manifestations of allergies can be in the form of dryness and redness of the skin, the appearance of single or multiple rashes on various parts of the body, itching. An allergic lesion of the gastrointestinal tract can be manifested by the presence of regurgitation, vomiting, refusal of the child to eat, abdominal pain, loose stools or constipation, mucus or blood in the stool. Less commonly, swelling of the eyes, nasal mucosa, and respiratory tract can develop. nine0004
nine0004
40. What should I do if I notice redness and rashes on my baby's skin after introducing a new product? When can I give the product that caused the allergy again? Or is this allergy for life?
If after the introduction of a new product, dry skin or rashes appear, then for some time the product should be excluded from the child's diet. This reaction to the product may be temporary, so its administration can be repeated after 1 month. after the complete disappearance of the pathological process on the skin. Most often, allergic reactions to food in early childhood do not persist for life. nine0004
41. What vegetables and fruits do not cause allergies?
Any product can cause an allergic reaction. However, it is possible to single out low-allergenic products to which allergic reactions develop the least. Among the vegetables are cauliflower, broccoli, zucchini, white cabbage, green beans, green peas, squash, potatoes. Among the fruits are green apples, pears, yellow plums.
From 6 to 9 months - diet expansion
42. What kinds of fish are recommended for a first acquaintance?
Fish is introduced into the diet of children from 8-9 months. age. It is better to start with low-fat or “lean” varieties of fish, which include: hake, haddock, pollock, pike perch, navaga.
43. When can I switch to multi-ingredient dishes?
Multi-ingredient meals are usually introduced to the child from 8 months. age.
44. What should be done to diversify the baby's diet? nine0085
Increasing the variety of the diet increases its nutritional value and "accustoms" the child to new tastes. In order to expand his child's diet, it is necessary to offer him not only new products, but also their various combinations, which is easiest to do with the help of industrial food products, a rich assortment of which at any time of the year will help form a varied and balanced diet for your baby.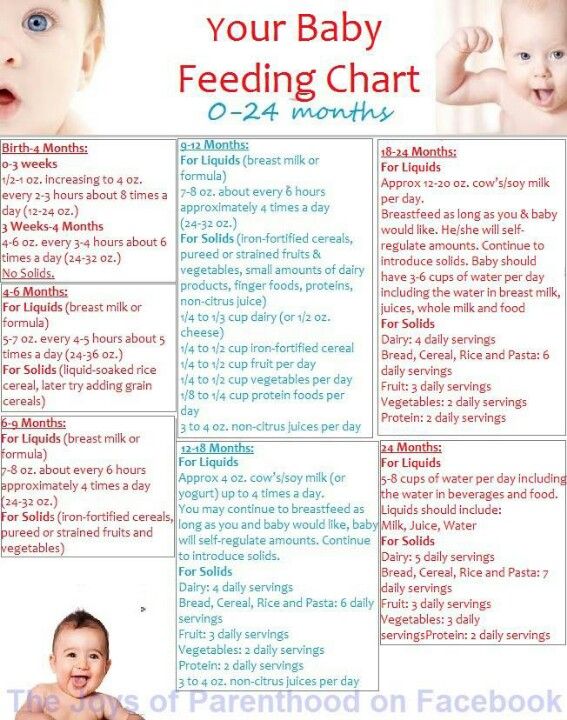
45. Should vegetable oil be added to vegetable puree? nine0085
Despite the fact that some vegetable purees of industrial production already contain vegetable oil, it is recommended to add it to vegetable puree or porridge, given the pronounced nutritional and energy value of this product.
46. Is it true that it is better to combine meat or fish with vegetables? What is a meat and vegetable and fish and vegetable dish?
The combination of meat or fish with vegetables promotes better absorption of animal proteins, iron, so this combination is considered optimal. nine0004
Meat-and-vegetable or fish-and-vegetable dishes are ready-made complementary foods, the content of meat or fish in them is 16-20%.
47. Why can't children under one year old drink cow's milk, but can you cook porridge based on it?
Whole cow's milk is not an adapted food product for a child of the first year of life, and therefore it is not recommended to use it as an independent food, but it can be used for cooking porridge in order to increase the nutritional value of the finished dish. nine0004
nine0004
From 9 to 12 months - adaptation to the adult table
After 1.5-2 years, the child's diet can be gradually expanded by introducing dishes from the "common" table, but on condition that a specialized product for children aged 1 to 3 years is preserved in 1 feeding (milk formulas, the so-called 3 or 4 formulas) and the presence of proper culinary processing of products. Boiling, baking, stewing, steaming is recommended. nine0004
49. How many fish per day can a child under one year old eat?
From 8 months age child 1-2 times a week instead of a meat dish, you can offer fish puree, in an amount of not more than 70 g per day.
50. What kind of food will help the baby to train chewing skills?
To develop the skills of chewing and swallowing hard food after 8 months. instead of pureed or mashed boiled vegetables, you can gradually begin to introduce finely chopped vegetables containing individual small pieces into the child’s diet; mashed and mashed boiled meat should be replaced with finely chopped meat, as well as meatballs, soufflé, steam cutlets. Cookies, bread, dryers, soft pieces of fruit, muesli also help to train the skills of chewing solid food. nine0004
Cookies, bread, dryers, soft pieces of fruit, muesli also help to train the skills of chewing solid food. nine0004
51. How much salt can a baby eat? What are the consequences of excess salt?
It is not recommended to add salt to a child's food until the age of one, taking into account the amount of natural mineral salts in food that is sufficient for this age. After a year, home-cooked food can begin to add a little salt. Additional salting of industrial products is prohibited. The rate of consumption of table salt is 3 g per day. (1/2 tsp). An excess of salt in a child's diet can lead to metabolic disorders and, as a result, to overweight, an increase in the load on the kidneys and heart, which can subsequently cause hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease. nine0004
52. Why is starch added to puree?
The addition of starch to some vegetable or fruit purees binds the excess water that is released during the puréeing of fruits and vegetables, resulting in a "steady" consistency of the finished product, which makes feeding the baby more convenient.
53. Why is vitamin C added to fruit purees?
During the preparation of fruit purees, the natural content of vitamin C in fruits decreases due to the heat treatment. To compensate for this loss, an additional amount of vitamin C is introduced into the puree, which is also a good natural preservative. nine0004
54. What does “no added (added) sugar” mean?
This means that no additional sugar (sucrose) has been added to this product, and the natural taste of the product, including its sweet taste, is due only to natural sugars that are part of the original fruits or vegetables.
55. Can cereals cause allergies?
Cereals, like any food, can cause food allergies, regardless of the type of cereal. nine0004
Myths about baby food
is an approved component and is included in most infant formulas and food products for both healthy and sick children.