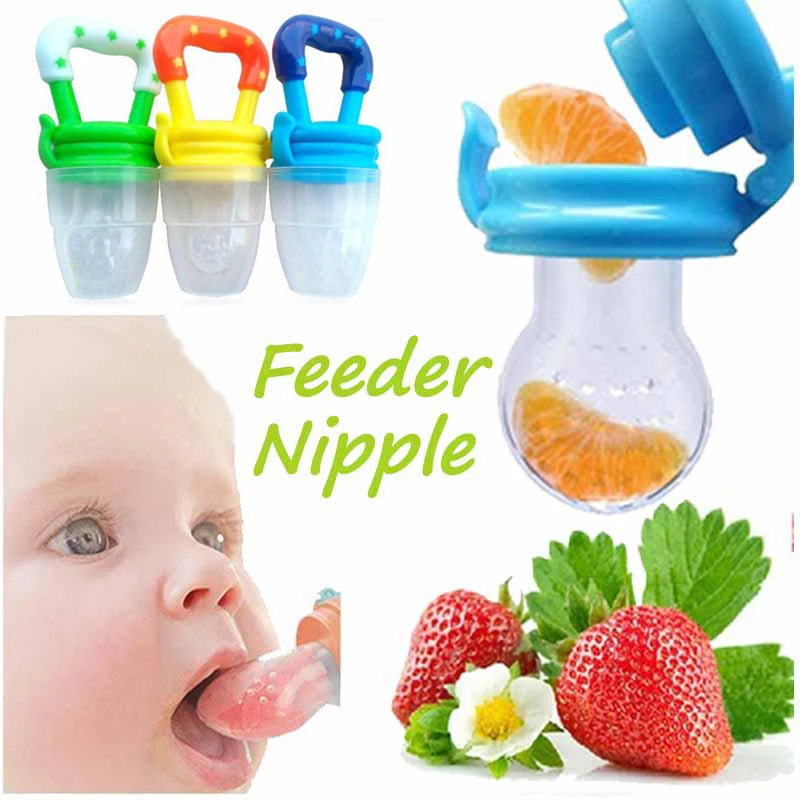
When to start table food baby
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
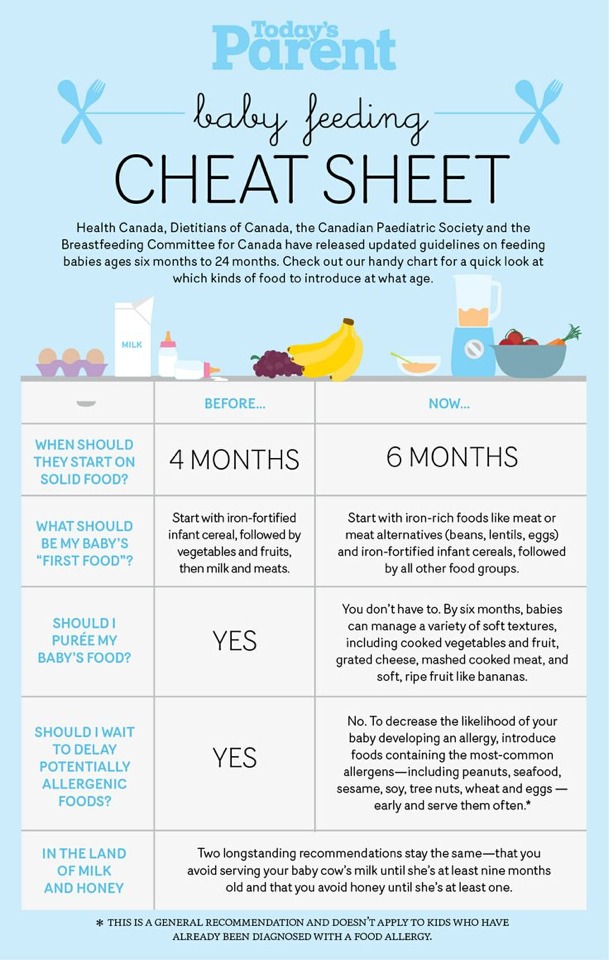
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
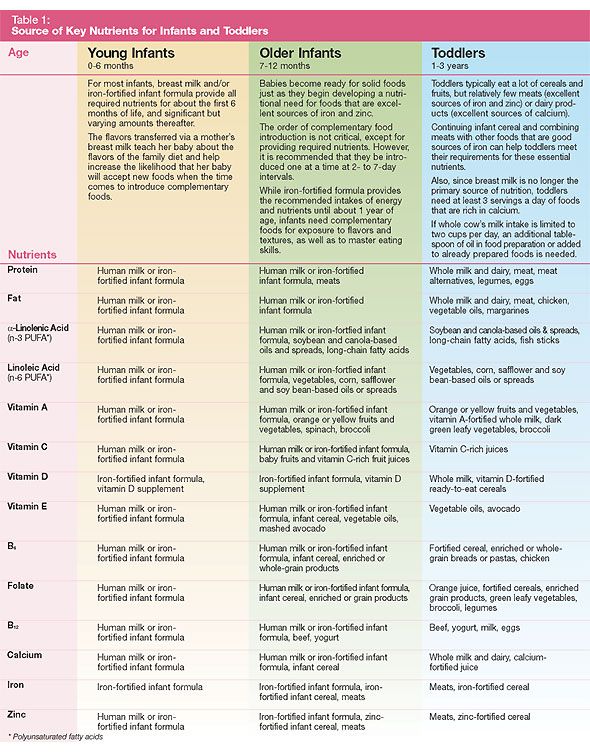
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
How to Transition Your Baby to Table Foods Easily and Safely
Learn when babies start eating table foods and how to transition them to eating table and finger foods. With this plan from an occupational therapist, you’ll feel confident you’re doing it safely!
With this plan from an occupational therapist, you’ll feel confident you’re doing it safely!
As an occupational therapist that specializes in feeding, I often get asked how to transition a baby or toddler onto table foods. These questions usually come from parents that are struggling through the process with a baby (under 12 months old) or from parents that now have toddlers and are still stuck on pureed baby foods.
This post will help you no matter which situation you find yourself in!
Keep in mind that for babies and toddlers that won’t eat finger or table foods, the approach may need to be tweaked and adjusted specifically for your child based on the underlying cause. Difficulty with transitioning to table foods is *sometimes* a red flag for sensory sensitivity, oral motor delays, or some underlying medical diagnosis like reflux.
You can read more about those causes, and what to do about them in Why Kids Don’t Eat.
Because I want to give you a complete step by step plan, this post is part 1 of 2, in it you’ll learn when and how to start introducing table foods to your baby.
In part 2 of transitioning babies to table foods, you’ll learn how to fully get your baby eating table foods without needing baby food any longer. As well as some helpful examples of a baby and toddler’s feeding schedule once they’re eating table foods. Lastly, you’ll find out what to do if your baby won’t eat table or finger foods.
You Need Patience for Transitioning from Baby Food to Table Food
As a mom, each time I had to transition my boys onto table foods, I was frustrated and overwhelmed even though I’m a feeding therapist that had helped many families through it before. It’s different when you’re the mom living it day in and day out.
Experiencing that as a mom showed me how challenging it can be. The little baby food routine you had starts to shift, as they are also beginning to wean from breast or bottle and learn to drink from some type of cup (ideally a straw cup).
As parents, we worry, “Are they eating enough?”
With jarred food, you can know exactly how much they’ve eaten, but it gets a little blurry when half of the diced up food you give them is on the floor. It’s tempting to stop serving table foods and to focus baby food because you know how much they’re eating – but there’s a problem with that as you’ll learn shortly.
This process does require some patience because your baby is learning a new skill, something I had to remind myself of quite often.
My best advice as a mom and OT is to take heart and know it’s all part of the process. Remember that until 1 year of age, their milk source (breast milk or formula) is their main source of nutrition.
This is why people say, “food before one is just for fun.”
We want to teach our babies how to eat table and finger foods so they have the skill, but not get stuck on how much they are actually eating. This is an exciting time, and it’s absolutely adorable when your chubby little baby is gnawing on a bread stick or getting puffs stuck on their face!
Now that you’re in the right frame of mind, let’s dive into the details of when and how to introduce table foods to your baby!
When Do Babies Start Eating Table Food?
Generally speaking, a good time to start introducing table foods for most babies is around 8-9 months. However, it may be later for your child, especially if they were a preemie. You will know they aren’t quite ready if they refuse, gag, or cough a lot when you try. That’s okay, don’t be discouraged, this just means you will need to take it slower and consistently offer safe foods they won’t choke on.
However, it may be later for your child, especially if they were a preemie. You will know they aren’t quite ready if they refuse, gag, or cough a lot when you try. That’s okay, don’t be discouraged, this just means you will need to take it slower and consistently offer safe foods they won’t choke on.
If you’re nervous about how to handle gagging or your baby is gagging a lot on foods, head to Everything You Need to Know About Baby Gagging.
For other babies, they may start eating table foods even earlier, sometimes at 7 months. As a feeding therapist, I can’t recommend starting too much earlier, but of course, it is your choice if you feel they are ready. It is likely that they will be mostly swallowing (not chewing) most of the food though.
If you’re thinking about baby led weaning, check out my pros and cons of BLW.
One critical word of caution is to NOT wait too long to start transitioning to table foods. Babies will instinctively chew from 7-8 months to around 11 months old, which means the transition will come easier. Check out this Weekly Meal Plan of Table Foods For Your Baby or Toddler to help give you ideas.
Check out this Weekly Meal Plan of Table Foods For Your Baby or Toddler to help give you ideas.
Waiting past 10 months, unless your child has developmental delays, a diagnosis, swallowing difficulties, or was born prematurely, can make transitioning to table foods even harder when they’re a toddler. See this chart as a quick reference:
Affiliate links used below. See our full disclaimer
Step #1: Transitioning to Table foods
Some signs your baby is ready for this transition are:
- Looking at or grabbing your food
- Making a chewing motion with their mouth when they watch you eat
- Picking up small objects
- Are 8-9 months old. See 9 Month Old Baby Food + Table Food Ideas.
Remember, you want to start this by 10 months even if you aren’t seeing some of these signs, as long as they don’t have any of the reasons listed in the previous section to delay the start of table foods.
A week or two before you begin to introduce solids, start to thicken their baby food. Thicker foods require more movement of the tongue and muscles in the mouth, which helps lay a good foundation for moving a solid piece of food around in their mouth.
Thicker foods require more movement of the tongue and muscles in the mouth, which helps lay a good foundation for moving a solid piece of food around in their mouth.
If you’re making your own baby food (get the DIY here), then add less water or liquid when pureeing. Use stage 2 baby food if you’re buying premade baby food.
Beware that some stage 3 type foods are great because they are thicker, but many of the jarred varieties have whole pieces of food mixed in with the puree, don’t go there – yet. That is putting the cart before the horse. For now, it’s crucial to stick with smooth purees, gradually increasing their thickness, as your baby tolerates it. NO CHUNKS.
The mixed in chunks can cause gagging and a negative experience. It’s actually harder for babies to eat than table foods. Babies that eat chunks in their baby food well are just swallowing it all without chewing.
I’d also recommend increasing the thickness of store bought baby food by adding cereal (this is one of my favorites) or freshly pureed foods into jarred baby foods.
Step #2: Eating Table Foods to Teach Your Baby
Once you start thickening their baby food, it would also be great to start eating at the same time you feed your baby, if you aren’t already. Your baby will watch what you do and learn a lot from it.
When you see that you have their attention, begin to dramatically chew for them, even with your mouth open. Show them how you put a small piece of food into your mouth using your hand. It may take finding the right moment to get their attention, but this will help pique their interest in table foods, as well as teach them what they should do when you hold that piece of food up to them for the first time.
The Best First Table Food for Babies
Before we move on, you need to know what table food to offer your baby. A great place to start, and the best choice for a lot of babies first table food is a meltable puff. I’ve used Gerber puffs many times, but there are so many brands, just test whatever type of puff you buy by letting it sit in your mouth and seeing how quickly it dissolves.
The dissolving factor is important because if your baby doesn’t chew the puff, it will dissolve in their saliva.
Puffs are perfect because they are hard and crunchy initially, which helps babies realize there is something in their mouth. That crunchy texture also helps them find it and maneuver it around in their mouth.
It may seem to make sense to start with a soft table food like eggs or banana. Not bad logic, but because those foods are so soft, babies have a hard time feeling exactly where it is in their mouth. For some babies, this means they will refuse table foods and for others, it means they aren’t chewing and just swallowing.
The wonderful thing about puffs is that they dissolve in saliva in just a few seconds. So, if your baby doesn’t chew while they are learning to eat and they swallow, they aren’t going to choke on it. That is peace of mind.
Puffs are also great because they can be broken into really small pieces for those first attempts, if needed. And, babies can pick them up easily! Read more in when can babies eat cheerios and puffs? (Cheerios are much later, they don’t dissolve)
And, babies can pick them up easily! Read more in when can babies eat cheerios and puffs? (Cheerios are much later, they don’t dissolve)
Step #3: Introducing Table Foods to Your Baby
The very first time you give your baby an actual table food, you’ll want to try and pick a time with little distractions and that you can give them your full attention.
Make sure they are seated in their high chair because this keeps them in a safe position and will help prevent choking. Read about how to make sure your baby is seated safely for eating.
Place the table food on their tray and allow them to touch and explore it for a few minutes. Some babies will pick it up and put it right into their mouth, depending on their age. While that is certainly ideal, your baby may may need some more help.
If they aren’t putting the table food into their mouth, demonstrate picking it up and putting it into your mouth. Then, pick up a piece and put it into their mouth, right where their molars will be. Or, if they’re holding the food, gently guide their hand towards their mouth for them as you smile reassuringly.
Or, if they’re holding the food, gently guide their hand towards their mouth for them as you smile reassuringly.
If they munch up and down and swallow, you can offer more bites.
However, on the first attempt, some babies cough or gag. Other babies will spit it out. Be encouraging, peaceful (they will sense your stress, fake it if you have to), and know when to call it quits. Often, it may take a few meals over a few days before babies get the hang of it.
If your baby turns their head or pushes your arm away when you try to put the food in their mouth, then respect that and don’t force it. They may need some more exploration with the food first.
Step #4: Transitioning Baby to Table Foods
Continue to offer puffs for a few days to a week at every meal alongside their pureed food, until you can see them munching up and down with their jaw most of the time.
Ideally, they should be feeding themselves the puffs, too, but don’t let that be a deal breaker on moving forward. You can help them put the puffs in their mouth as long as they’re willingly opening their mouth. Find baby feeding schedules for 8, 9, and 10 month olds here and 11-14 months here.
You can help them put the puffs in their mouth as long as they’re willingly opening their mouth. Find baby feeding schedules for 8, 9, and 10 month olds here and 11-14 months here.
Once your baby is enjoying puffs, you’ll want to try small pieces of other foods that dissolve really quickly. Some examples are: Town House Crackers (not Ritz, this texture actually requires more chewing), Graham Crackers, Teething Wafers, Baby Cheese Puffs, rice husks, and other stage 1 table foods you find in the baby aisle at the grocery store.
If you aren’t sure if a finger food is safe, do a taste test yourself. How quickly does it dissolve compared to a puff? How much do you need to chew it?
Step #5: Transitioning from Baby Food to Table Food
As your child eats a variety of crunchy but melt-able foods well, then you can start with soft foods like bananas, noodles, cheese, breads, and overly cooked veggies in a cube shape.
You can also try these cubed “jellies” or little frittatas, that are perfect for this stage too. It may take a few days or weeks before you’re ready to move onto these soft foods.
It may take a few days or weeks before you’re ready to move onto these soft foods.
When your baby is eating several cracker like foods and several soft foods, you can pull back from giving as much baby food and perhaps skip the baby food at some meals. As they eat more and more of the table foods, you’ll serve less and less baby food, skipping it more and more until you no longer need it.
To learn more about helping your baby or toddler transition to table foods completely, while avoiding some common pitfalls, grab a free seat in my online workshop (I’ll email you the link of where to watch) by click below:
Click here to get a free seat in my 5 Big Feeding Mistakes that are Stopping Your Child from Learning to Eat Table Foods
Important Tips for Transitioning Baby to Table Foods Easily
- Once you begin introducing table foods, offer one table food at each meal. Then, slowly increase the variety of foods they are eating as they are managing more foods.

- Continue to steadily increase the thickness of baby foods as you progress with table foods. If you aren’t making your own baby foods, try pureeing what you are eating for dinner or mix this into the jarred baby food. This will help get your child used to more textures and tastes. I love using a magic bullet for this!
- Carefully monitor all new foods. Some coughing and an occasional gag is normal. If you are seeing this frequently, the texture you are giving them may be too difficult for them. Wait a week or so before introducing it again and then proceed slowly. Discuss persistent gagging and choking with your doctor.
Keep reading about transitioning your baby or toddler to table foods in Part 2 of this series.
If you need more inspiration for table foods, check out my Mega List of Table Food Ideas and Pinterest for more ideas.
Free Printable: Learn How to Eat Table Foods Cheat Sheet!!
Want to have all these steps in your hands so you can reference them in a heartbeat? We’ve got you covered you’ll find all the steps for transitioning your baby or toddler to table foods in this handy free printable:
Click here to get the free Learn How to Eat Table Foods Cheat Sheet
More on Transitioning Baby to Table Foods from Your Kid’s Table
The Ultimate List of Baby/Toddler Meal Ideas
The Best High Calorie Foods for Babies
Getting Picky Eaters to Eat New Foods
A Weekly Meal Plan of Table Foods For Your Baby or Toddler: So You Can Save Your Sanity
Alisha Grogan is a licensed occupational therapist and founder of Your Kid’s Table. She has over 18 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
She has over 18 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
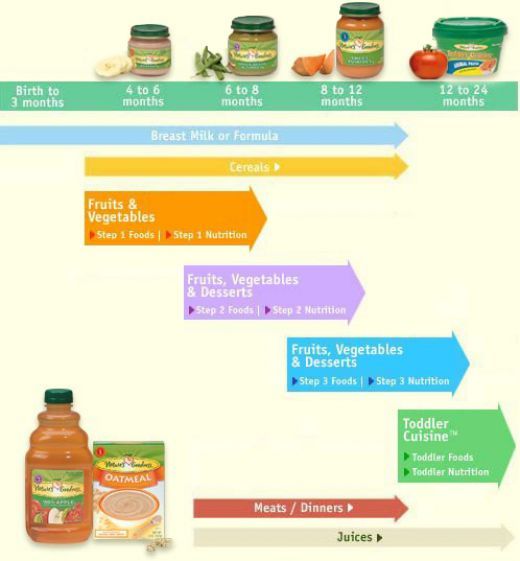
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to mixed or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.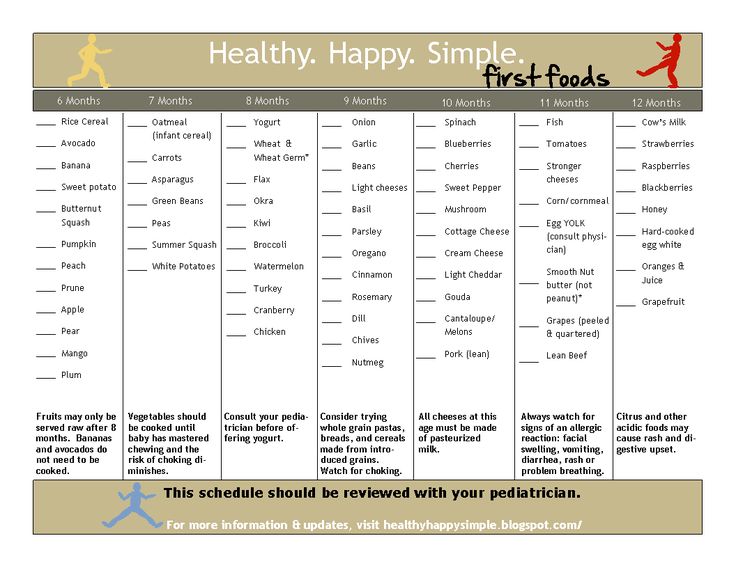
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary food is introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually “dilute” this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. The materials were prepared by the staff of the Healthy and Sick Child Nutrition Laboratory of the National Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of Russia and are based on the recommendations given in the National Program for Optimizing the Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation, approved at the XV Congress of Pediatricians of Russia (02.2009d.) Breast milk is the best food for your baby. It is recommended to start introducing complementary foods into the baby's diet no earlier than 4 months, but no later than 6 months*. At this age, the baby is in the active phase of development and reacts with curiosity to everything new! Some babies at 4 to 5 months of age can no longer satisfy their appetite with breast milk alone and need complementary foods for healthy growth. If your baby spits out the first spoonfuls of puree, be patient. After all, he must first learn to swallow it. Start with a few scoops and give your child time to get used to the new form of feeding. *Recommendation of the Nutrition Committee of the European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) After 4-6 months of life, mother's milk or milk formula alone is not enough to supply the child's body with all the nutrients and necessary energy. Gradually replace one breastfeed with complementary foods. First for lunch, then for dinner and finally for lunch. The mouse eats breakfast with the usual dairy food. Starting complementary foods with HiPP products is easy. The first spoons will be vegetable or fruit purees HiPP: We recommend that you start complementary foods at lunchtime with HiPP vegetable puree (for example, "Zucchini. My first puree", "Cauliflower. My first puree" or "Broccoli .My first puree"). Then, for satiety, feed your baby as always: breast or bottle. The amount of vegetable puree can be increased daily by 1 spoon. Be patient if your baby does not immediately love vegetables. If your baby tolerates vegetables well, in the third week you can introduce grain porridge into the diet, and as a dessert, offer a few spoons of fruit puree enriched with vitamin C. Vitamin C helps to better absorb iron in the body. Once your baby starts eating a whole serving of mashed potatoes for lunch, you can eliminate breast milk or formula during that meal. Tip: Reheat as much puree as needed for feeding. Store leftover puree in a sealed jar in the refrigerator. Use the contents of the opened jar within a day. Important! If you are using a microwave, please remove the lid before heating the puree. Stir after heating. To prevent damage to the jar, please use only a plastic spoon. Always check food temperature before feeding. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VMS 
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk 
4 to 6 months
It is very important that the baby consumes breast milk for as long as possible. The right age to start complementary foods
 Other children have enough breast milk, and they are ready for the introduction of complementary foods only after 6 months. The decision to start complementary foods should always be made according to your baby's development. Do you feel like your baby is not getting enough breast milk? Does your baby hold his head on his own, show interest in new foods or a spoon? Then it's time to start feeding. If in doubt, consult your pediatrician.
Other children have enough breast milk, and they are ready for the introduction of complementary foods only after 6 months. The decision to start complementary foods should always be made according to your baby's development. Do you feel like your baby is not getting enough breast milk? Does your baby hold his head on his own, show interest in new foods or a spoon? Then it's time to start feeding. If in doubt, consult your pediatrician. Why is complementary foods important for the baby?
 In addition, the transition to solid food trains the muscles of the mouth. And finally, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child will get acquainted with the variety of taste directions, which is also important for his development.
In addition, the transition to solid food trains the muscles of the mouth. And finally, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child will get acquainted with the variety of taste directions, which is also important for his development. When to start complementary foods?
First step: lunch
 Try repeating the vegetable puree in the following days. Next week, you can expand your diet with other varieties of HiPP vegetables (for example, "Carrots. My first puree" or "Potatoes. My first puree").
Try repeating the vegetable puree in the following days. Next week, you can expand your diet with other varieties of HiPP vegetables (for example, "Carrots. My first puree" or "Potatoes. My first puree").