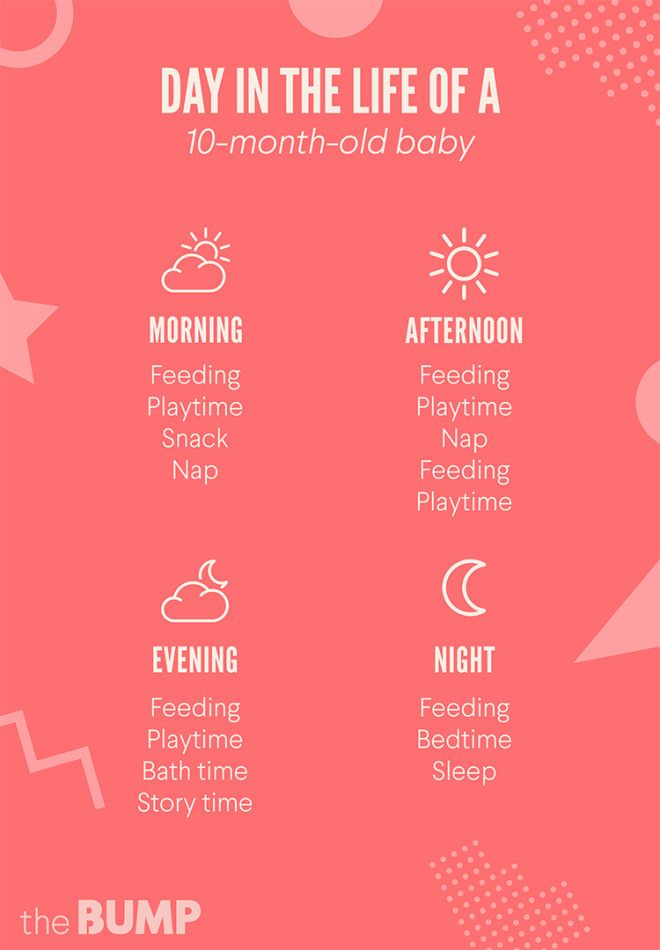
Which baby food first
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
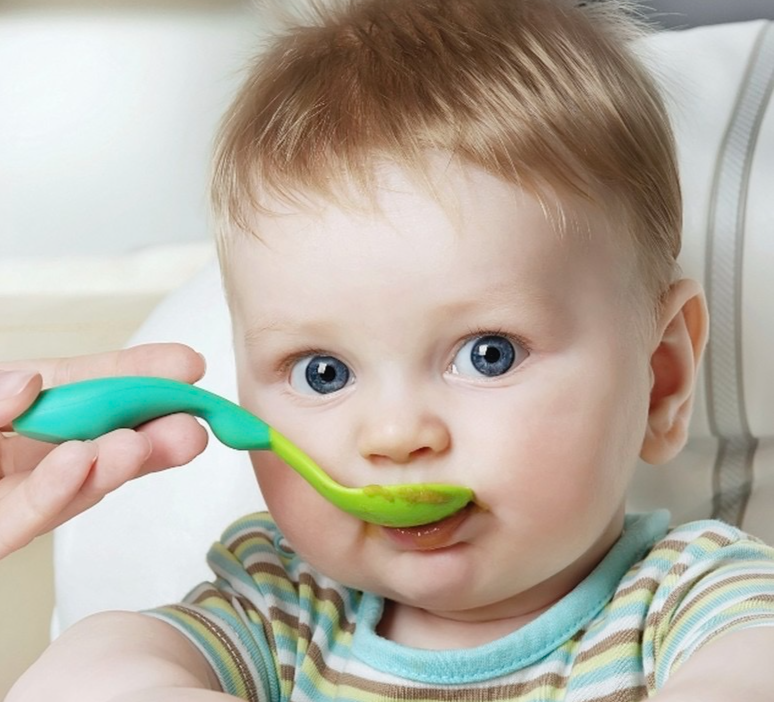
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday.
 It can cause botulism in babies.
It can cause botulism in babies. - unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
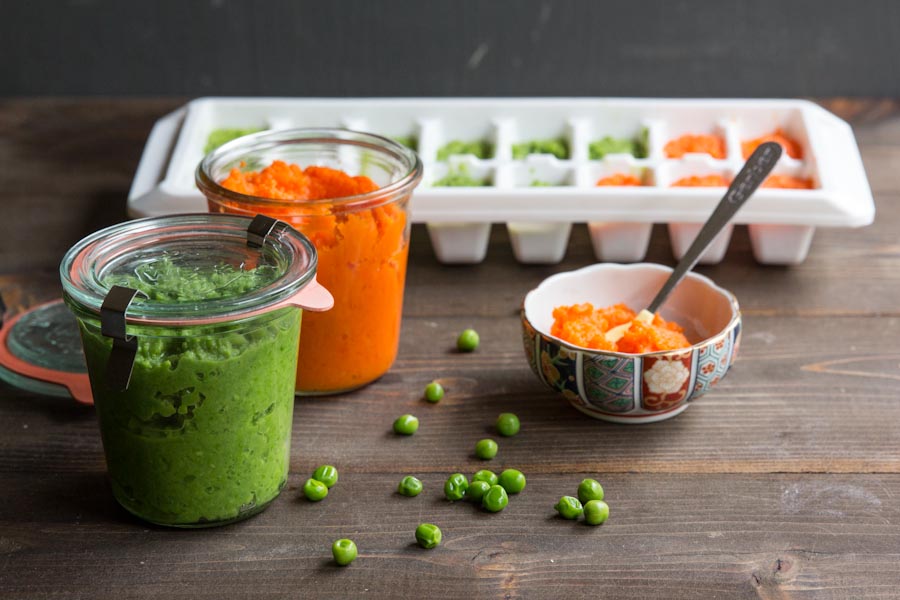
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.

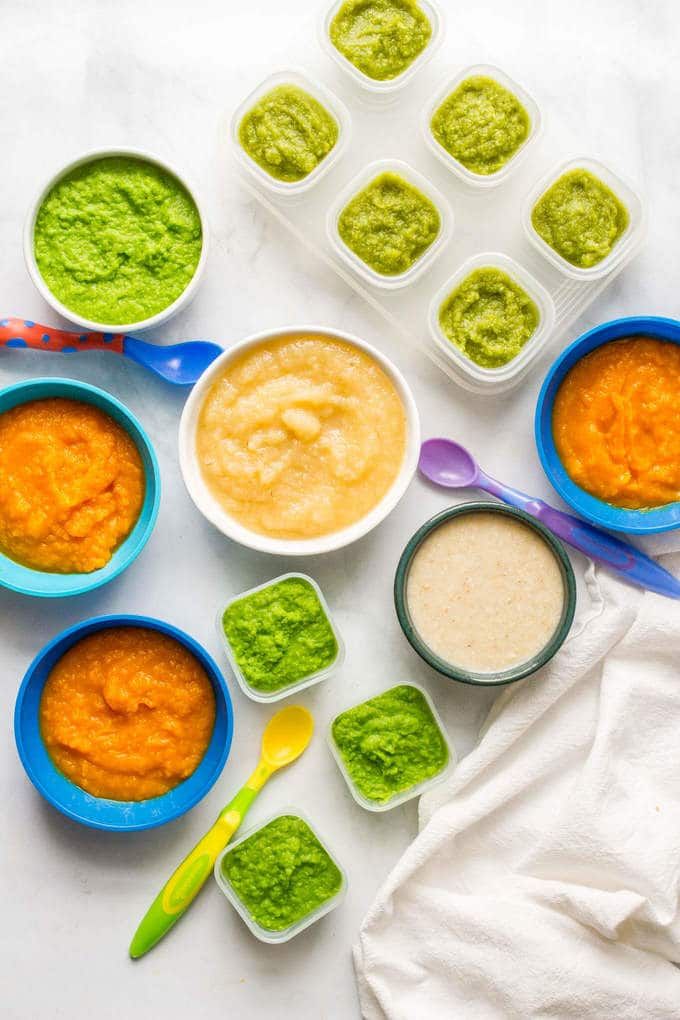
- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods. (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
- After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
When to Start Baby Food
Starting solids is an exciting and important milestone in baby’s development—one that not only opens them up to a brand-new world of flavors and textures, but also puts them on the right path to growing healthy and strong. Here’s what you need to know about how and when to start baby food for a smooth transition.
In this article:
When to start baby food
How to start baby on solids
Best first foods for baby
Introducing allergenic foods
When to Start Baby Food
Knowing when to start baby food is both crucial and tricky. Starting baby on solids too early means you might increase the risk of choking, obesity and bellyaches, but introducing solids too late means you might slow baby’s growth and encourage an aversion to solid foods, among other conditions. Fortunately, doctors have zeroed in on a sweet spot for starting baby food, which is sometime between 4 and 6 months of age—though, ideally, baby should be receiving their nutrition exclusively from breast milk until the six-month mark, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). How to tell if it’s time for starting solids for your little one? Baby will give you clues, including:
How to tell if it’s time for starting solids for your little one? Baby will give you clues, including:
• Baby can sit in a high chair comfortably on their own. This is a major sign in terms of when to start baby food, says Lauren Kupersmith, MD, a pediatrician at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital at NYU Langone in New York City. It means baby can hold their head up and doesn’t need to be propped up to stay in the upright position, which is important to avoid choking.
• Baby looks interested at mealtime. Babies likes to mimic what we do, so if your child likes to sit up like a big kid and watch you eat, then by all means let them try eating too.
• Baby can move food to the back of their throat to swallow. But if baby tends to push the food out of their mouth—not because they don’t like it, but because they can’t seem to get the food to where it needs to go—hold off on starting solids.
How to Start Baby on Solids
At 4 to 6 months, most of baby’s nutrition will still come from breast milk or formula, so don’t worry if baby doesn’t like eating food right away. Introducing solids is a gradual process, and every baby learns in their own time. Here are some general guidelines for how to start baby on solids:
Introducing solids is a gradual process, and every baby learns in their own time. Here are some general guidelines for how to start baby on solids:
• Feed baby with a spoon. Letting your child go at it with their hands may seem tempting (and super-cute), but it’s best that they learn the right way from the get-go. (And even then, be prepared to clean up more than a few messes!) Also, never put cereal (or any other food) in baby’s bottle—it’s a choking hazard.
• Start slowly. When introducing solids, a half spoonful will do at first—you may even want to talk baby through it (“Yummy!”). To make it easier for baby to get accustomed to the idea of swallowing solids, start mealtime with a little breast milk or formula, then offer some food (again, no more than a half teaspoon at a time) and finish off with more breast milk or formula. If baby cries or turns away when you present the spoon, try again some other time. Start off with introducing solids at one meal a day, then slowly work your way up. The morning is a good place to start, since baby is often hungriest at that time. When starting solids, baby typically won’t eat more than an ounce or two in one sitting.
The morning is a good place to start, since baby is often hungriest at that time. When starting solids, baby typically won’t eat more than an ounce or two in one sitting.
• Try new foods more than once. Since babies’ tastes will evolve, you may need to try a food 20 times before a baby actually likes it, says Kupersmith.
• Stick with the same food for three days before trying another one. This makes it easy to track whether baby is allergic to a particular food.
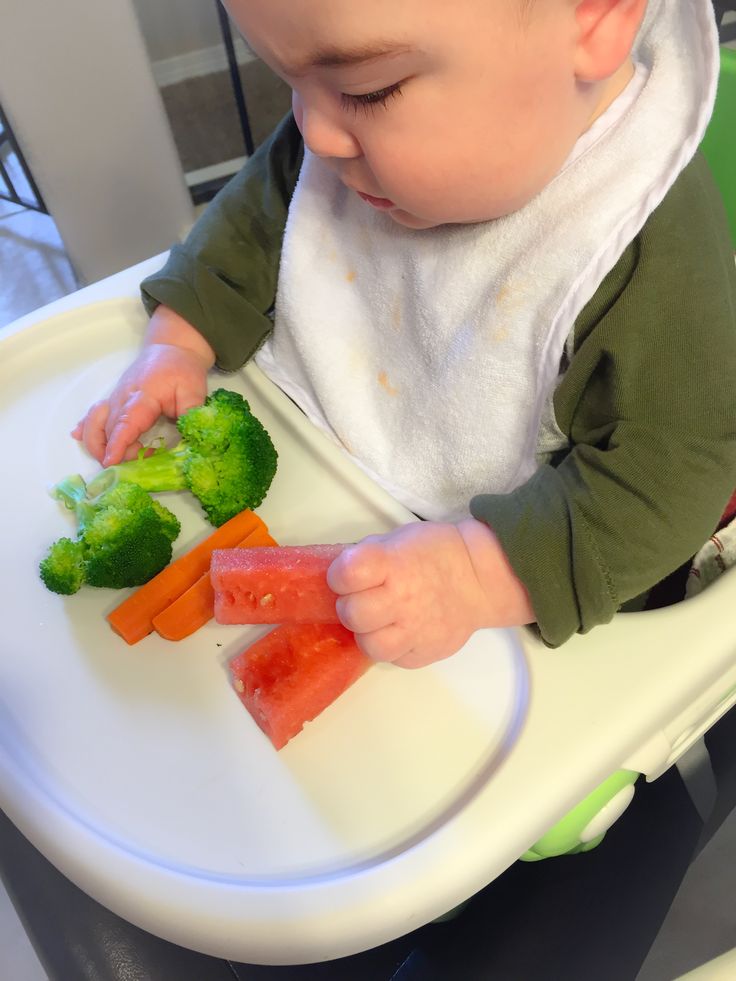
• Try foods in different forms. If baby doesn’t like pureed food, try it mashed. After all, baby is learning about new textures as well as new tastes. It may be a case of trial and error until you find a winner.
Best First Foods for Baby
Got baby safely strapped into the high chair and bib? You’re ready to finally start feeding baby solids! There aren’t any official food rules for babies starting solids, and there’s no scientific evidence suggesting you should introduce one type of food before another, assuming the foods aren’t choking hazards. Nevertheless, baby cereal (such as oatmeal, rice and barley) is an “easy training food,” says Kupersmith, which is why it’s often recommended as baby’s first food; you can always mix it with more milk to build up to a thicker consistency. Many doctors also recommend starting vegetables before fruits, but there’s no evidence that this would make babies like vegetables more when they grow up—babies innately love sweets, and the order of introducing solids to baby doesn’t change that.
Nevertheless, baby cereal (such as oatmeal, rice and barley) is an “easy training food,” says Kupersmith, which is why it’s often recommended as baby’s first food; you can always mix it with more milk to build up to a thicker consistency. Many doctors also recommend starting vegetables before fruits, but there’s no evidence that this would make babies like vegetables more when they grow up—babies innately love sweets, and the order of introducing solids to baby doesn’t change that.
So why not simply start introducing solids with something you think baby will like? Here are a few common first foods for baby that are healthy and easy to eat (and, in the case sweet potato and banana, also easy to digest). Whatever you decide to feed baby, mash it with a fork or puree before serving whenever introducing solids.
- Baby cereal, such as oatmeal, rice, barley
- Sweet potato
- Banana
- Avocado
- Apples
- Pears
- Green beans
- Butternut squash
If your child has been breastfeeding, check with your pediatrician about getting a jump on pureed chicken or beef when you’re starting solids. These foods contain easily absorbable forms of iron and zinc, which baby needs by 4 to 6 months, according to the AAP.
These foods contain easily absorbable forms of iron and zinc, which baby needs by 4 to 6 months, according to the AAP.
At around 9 months, baby should have already worked their way up to a variety of foods, including cereal, vegetables, fruits, meats, eggs and fish (see below regarding the last two). (Keep in mind, though, that baby will still get the majority of their nutrients from breast milk or formula until age one.) By now, baby will probably settle on three meals a day along with two snacks. Let them consume about 4 ounces of solids at each meal (equivalent to a small jar of strained baby food) and about half that amount for each snack.
Save honey and cow’s milk for after baby’s first birthday—there’s a risk for infant botulism with honey (a type of bacterial poisoning), and baby’s tummy isn’t prepared to digest large amounts of cow’s milk until they’re about one year old. Avoid adult processed foods and foods that are choking hazards (such as sticky foods, like large gobs of peanut butter; hard foods that are difficult to gum, like raw vegetables, nuts, seeds and popcorn; and round, slippery foods that haven’t been cut up, like grapes and cherry tomatoes). Instead, the first foods for baby, and those in the months that follow, should be soft and served mashed, pureed or (once baby seems ready to move up from the really mushy stuff) cut up into really little bits. “There’s pretty much free reign at that point,” Kupersmith says.
Instead, the first foods for baby, and those in the months that follow, should be soft and served mashed, pureed or (once baby seems ready to move up from the really mushy stuff) cut up into really little bits. “There’s pretty much free reign at that point,” Kupersmith says.
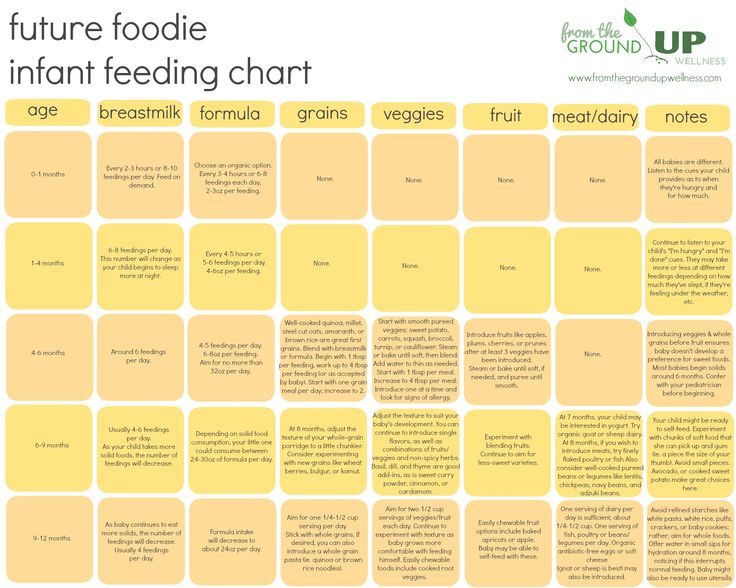
Introducing Solids Chart
Hesitant about improvising your first foods for baby? That’s okay too. If you prefer an “introducing solids chart” to help you plan out baby’s path, the guide below can come in handy.
Image: The Bump
Introducing Allergenic Foods
Much of the confusion around when to start baby food stems from questions concerning allergenic foods. These are foods that babies are most often allergic to. The major culprits include dairy, eggs, fish, peanuts and tree nuts. In the past, parents were advised to hold off on exposing baby to these foods, but now doctors recommend introducing them early, often and in age-appropriate format, which means starting off with purees and soft textures.
“Dairy is an easy starting point, given options such as yogurt and cheese,” says David Stukus, MD, director of the Food Allergy Treatment Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and a spokesperson for the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. You can also try scrambled eggs in small amounts, although baby may not be too pleased with the texture at first.
As far as peanut products go, the National Institutes of Health issued new guidelines in 2017 that encourage parents of children at high risk for peanut allergies to incorporate them into baby’s diet at 4 to 6 months of age. Giving these babies peanut products before the age of one actually decreases their risk of developing a peanut allergy before age 5 by 81 percent, compared to kids who are introduced to peanuts later in life. Parents of kids without the food allergy risk can start peanut products whenever they’d like, as long as the nuts are in an age-appropriate form: Peanut butter can be thinned out with water or mixed into a fruit or vegetable puree, and peanut powder can also be mixed into cereal and fruits. Don’t give whole peanuts or pieces of peanuts, since they’re a choking risk.
Don’t give whole peanuts or pieces of peanuts, since they’re a choking risk.
Allergic reactions to food are never just a fluke; they will happen with every exposure. Symptoms can range from mild (such as a rash or vomiting) to severe (such as trouble breathing). If baby has a food allergy, you’ll notice a reaction within minutes or up to two hours after eating the problematic food, Stukus says. If the symptoms are severe, call 911 right away. Otherwise, talk to your pediatrician; she can help confirm whether it’s an allergy or some other type of condition (such as a viral illness).
Expert bios:*
Lauren Kupersmith, MD, IBCLC, is a pediatrician and clinical instructor at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital at NYU Langone in New York City, as well as a certified lactation consultant. She earned her medical degree from New York Medical College in 2005.
David Stukus, MD, is the director of the Food Allergy Treatment Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, an associate professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology and a spokesperson for the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology.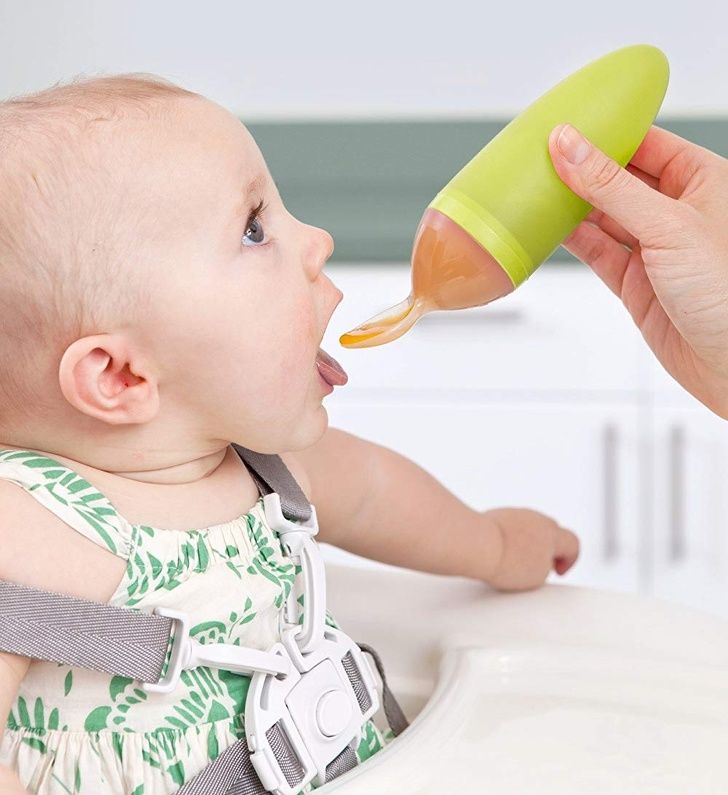 He earned his medical degree from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in 2002.
He earned his medical degree from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in 2002.
Updated January 2020
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
how to choose and what kind of baby food is better?
The ideal "baby food" for an infant is breast milk. However, not all mothers can breastfeed their baby, usually this is due to the health of the mother or child. It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk. Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
In this article, we will talk about what foods for babies are and how to choose the best baby food.
Legislation under "baby food" means food products that meet the physiological needs of the body of a child under 14 years of age. And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia created the National Program for feeding children in the first year of life and the National Program for optimizing the nutrition of children from one to three years old [2]. They describe recommendations regarding what formula to feed the baby from birth, how to introduce complementary foods and expand the baby's diet. These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages.
First you need to figure out what kind of baby food is [3]. Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Infant formula. There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3). The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
- In the initial mixtures, the amount of protein is reduced to 1.2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins.
- After six months, the baby's need for protein increases, mother's milk changes its composition. And babies on artificial feeding begin to be fed with a more nutritious mixture of formula 2. Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself.
 Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished.
Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished. - A child's diet changes after one year - he is already able to eat a variety of solid foods. However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.
Complementary foods As we have already noted, it is introduced when the baby is four to seven months old. This interval is called the "critical window" and is considered optimal for the initiation of complementary foods for several reasons:
- The baby needs a wider range of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients. In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula.

- At this age, the child develops an interest in food, and it is necessary to offer him the right foods to develop his taste.
- During this period, the risk of developing a food allergy to a new product is lower.
- Timely introduction of complementary foods prevents the risk of micronutrient deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia.
Usually the first food is vegetable puree or monocomponent gluten-free cereals, dairy or dairy-free. Over time, cereals containing gluten, supplements from fruits and berries, and also consisting of several cereals are added. A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
From the age of 12 months, complementary foods already make up the majority of your baby's diet. At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals.
Information
During the first feeding, the baby's eating habits are laid, and it depends on the parents how correct they will be. Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Domestic doctors are concerned about such irrational nutrition of young children - due to the wrong approach to nutrition, many babies experience a deficiency of vitamins and an excess of fast carbohydrates.
How to choose baby foods
Finding the right foods for your baby is not an easy task. Store shelves are bursting with boxes, jars and bottles, and manufacturers write on every second package that the baby will be healthy, strong and cheerful after feeding. Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
However, products for children differ in their properties. It is necessary to select food so that by the end of the first year of life the baby has actively developed chewing skills and an interest in independence, and the diet of complementary foods is reasonably varied.
For children from one to three years of age, the diet should be even more varied. It is important that the child receives daily something new from the main food groups: dairy, vegetables and fruits, meat and fish, cereals, butter and vegetable oil. Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health.
When organizing the nutrition of a child from the moment of introduction of complementary foods and up to three years, a mother needs not only to know what can be fed, but also to consider what foods should not be included in the diet. Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
- any mushrooms, vegetables and fruits in a marinade;
- pickles, preserves in tomato sauce;
- commercial juice concentrates, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea;
- various condiments - mustard, ketchup, hot sauces, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise;
- products containing flavors, industrial colors, including chewing gum;
- margarine and refractory fats - lamb, pork;
- chocolates, sweets and other sweets.
To choose the right baby food, you need to know exactly what you should pay attention to and what you don't need to worry about.
When choosing mixtures, it is important to check:
- Absence of palm oil. Formula manufacturers may use palm oil (more specifically palm extract) because, like breast milk, it is rich in palmitic acid. However, in human milk, palmitic acid is in the beta position, while in palm oil it is in the alpha position. Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5].
- Protein ratio. Breast milk protein is primarily whey proteins and casein. A child needs both types of protein, while proteins are easily digested, which cannot be said about casein.
 If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool.
If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool. - The presence of additional functional elements in the composition - lutein, nucleotides, pre- and probiotics. The task of lutein is to protect vision from ultraviolet rays. Nucleotides are low molecular weight compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in the intestines. And pre- and probiotics in the composition of infant formulas help to establish comfortable digestion.
When choosing complementary foods, pay attention to:
- Age appropriate. It is important that in the diet of a child under three years of age who receives complementary foods, special children's products predominate - in their composition the components are selected taking into account the age-related needs of the baby's body. It is impossible at an early age to transfer children to "adult" foods like pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and so on.

- Fortified products. It is important that the composition contains vitamins and minerals. The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies.
- For a varied diet. The menu for a baby up to six months is quite monotonous. But as they grow older, the baby needs more various nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- For the individual reaction of the baby. If the child is already receiving complementary foods, then it is worth introducing a new product only after the previous one has been fully introduced. If the baby is allergic to the product, then it should be administered carefully, carefully checking the reaction of the body.
Ingredient safety testing is optional. Of course, the content of any "chemistry" in the product for feeding a child, whether it be a mixture or complementary foods, is unacceptable. There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
Note
Baby food in jars (usually mashed potatoes) has a short shelf life after opening because it does not contain preservatives. However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food.
Features of the choice of dairy products
It is necessary to choose dairy products for babies, following the doctor's recommendations. The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the body. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
Goat milk baby food may be a suitable option for young children with a predisposition to allergies. Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed.
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, other dairy products will appear in the baby's diet. Unadapted fermented milk drinks, such as kefir, yogurt, biolact, can be introduced into the diet from eight months and in an amount not exceeding 200 ml. Also during this period, it is recommended to give cottage cheese - no more than 50 g per day, but according to indications, it can also be prescribed from the age of six months. Whole milk cannot be used as the main food, and it is advised to introduce it into the diet of babies no earlier than a year (in the amount of 100-150 ml per day) [8]. As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
To choose the best baby food, it is necessary to take into account the health of the baby, his tastes, as well as individual reactions of the body. Therefore, before going to the store, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will not only tell you which baby food to choose, but also give recommendations on how to make the child's diet balanced and healthy.
The history of baby food: how formula-feeding products came to be
29 Apr 6 9553
Vadim Erlikhman, archivist, historian: Today, the fast food market is the fastest growing in the food industry. It is hard to believe that even a century and a half ago the very idea of feeding babies with something other than mother's milk seemed wild.
It is worth recalling that, of course, there were no maternity leave in the old days. A week after giving birth, peasant women had to work in the field, maids - to scrub the floor, factory workers - to go to the machine. In addition, there was a belief that before the baptism of the child, the mother should not breastfeed him. At that time, the child remained in the care of relatives, who instead of milk gave him "zhevka" - a rag with chewed bread or porridge. Sometimes it was soaked in milk, vegetable oil or sugar water. The rich had their own problems: feeding spoiled the shape of the breast, especially for mothers with many children. If a wealthy lady decided to feed the child herself, it was considered - depending on the fashion - either a feat or a strange quirk. Usually, a nurse was hired for this purpose, since there were enough young healthy women with an excess of milk.
If a wealthy lady decided to feed the child herself, it was considered - depending on the fashion - either a feat or a strange quirk. Usually, a nurse was hired for this purpose, since there were enough young healthy women with an excess of milk.
The reason for this excess was not joyful: the huge infant mortality rate, which in the 18th century reached 40%. The main reason for this was the complete lack of hygiene: in Russian villages, in addition to a dirty rag, children were stuffed into their mouths with other rubbish, like a cut off cow's nipple. It was put on a horn, into which the same soaked bread or oatmeal was charged. Russian doctors wrote that in some provinces it was customary, along with the nipple, to give children wort, mash from the very first days. French peasant women, in order for their children to fall asleep better, gave them diluted wine to drink. Yes, and the nurses themselves drank wine and beer, it was believed that this adds milk. In one of Dickens' novels, a young mother drinks four glasses of port wine at dinner "under the pretext that she is breastfeeding. "
"
In most cultures, breastfeeding continued for up to 6 months, after which the child was switched to solid food. Sometimes this was celebrated with a solemn ritual like the Indian “annaprashana”, when the eldest member of the family blessed rice porridge with sugar, tasted it and gave it to the baby. In China, children were accustomed to normal food in stages: first, liquid rice porridge (sifan), then boiled vegetables, tofu, and fish. In Africa, the first solid food for babies was corn porridge. In ancient Greece, it was a liquid barley stew, to which bull's blood was added in Sparta so that the boy would grow up to be a real warrior.
When children teethed, they were fed the same as adults, only worse, because they were of no use. And this applied not only to poor peasants: Elizaveta Vodovozova recalls her childhood in a large landowner family in the middle of the 19th century: “Children were given everything that was worse and could not be used by adults .. . Every pot of spoiled jam or marinade was shown to mother by the nanny. Having tasted one or the other, mother sighed heavily and said something like this: “What a misfortune! Really, it's no good. Well, let's go to the children. ”And in order to prolong our pleasure, and not because we could get sick from spoiled food, she told us to give us a small saucer.”
. Every pot of spoiled jam or marinade was shown to mother by the nanny. Having tasted one or the other, mother sighed heavily and said something like this: “What a misfortune! Really, it's no good. Well, let's go to the children. ”And in order to prolong our pleasure, and not because we could get sick from spoiled food, she told us to give us a small saucer.”
Doctors learned to cope with indigestion in children, but the lack of mother's milk became an increasingly serious problem. In big cities, the intense rhythm of life, air pollution, constant stress led to the fact that 30% of women did not have enough milk to feed a child, especially if he was the first or, conversely, the fourth or fifth. In families that could not afford to hire a wet nurse, babies were fed cow's or goat's milk. However, in composition it was very different from breast milk, so it often caused indigestion. There was also the problem of hygiene, because of which the German doctor Biedert warned: “It is necessary to observe pedantic purity both in keeping cows and in milking and preserving milk . .. Since milk can acquire harmful properties from inappropriate food, cows should not be given even bards, no waste, because the toxic substances contained in them pass into milk and cannot be eliminated. ”There were also problems with the nurses, because they suffered from all kinds of diseases, up to syphilis, which were often transmitted to the child during feeding.
All this made scientists work hard to find a substitute for breast milk. Gradually, the necessary conditions for this arose: they learned how to preserve and disinfect products, and in 1855 the Englishman Grimweid began to make powdered milk. But if it were not for the son of the Frankfurt glazier Heinrich Nestle, who preferred to call himself Henri in French, all these discoveries might have existed on their own. The problem of baby food arose before Nestlé after the birth of his first child. A certified pharmacist who ran a pharmacy in the small Swiss town of Vevey, in 1867 made a mixture of powdered cow's milk, wheat flour and sugar, which he called "Henri Nestlé Milk Flour". Diluted with water, this mixture turned into the world's first artificial baby food.
Diluted with water, this mixture turned into the world's first artificial baby food.
According to legend, the first artificially fed baby was a premature baby of one of the local factory workers, who, of course, thanks to the Nestle formula, began to grow by leaps and bounds. The delighted pharmacist opened his own company, whose logo was a nest with chicks, because Nestle in German means "nest". Very soon, canned "milk flour" appeared in all European capitals. In 1872, it began to be sold in St. Petersburg, where a local merchant Alexander Wenzel became an agent of the Nestle company. He also sold other baby products, such as Maltos-Cannabis sugared hempseed extract, which was advertised as the best way to get a good night's sleep…
In Russia, baby food did not take root at that time, but in Europe its popularity grew rapidly. Feeding babies has become unprecedentedly simple - open a jar and dilute its contents in water. However, even then doctors warned about the dangers of this simplicity. The German physician Gottfried Kühner wrote: “As for mealy surrogates, such as Nestle, Gerbera, Kufeke, Hartenstein’s leguminous powder, rakout, arrowroot, avicen, maizena, avena, etc., the same thing must be said about all of them: they are in many cases are well tolerated by children, but only after the second or third month of life. Violation of this condition, as well as the rules of hygiene, led to the fact that in 189In Berlin, infants fed formula were 13 times more likely to die than breastfed infants in Berlin in 1999.
The German physician Gottfried Kühner wrote: “As for mealy surrogates, such as Nestle, Gerbera, Kufeke, Hartenstein’s leguminous powder, rakout, arrowroot, avicen, maizena, avena, etc., the same thing must be said about all of them: they are in many cases are well tolerated by children, but only after the second or third month of life. Violation of this condition, as well as the rules of hygiene, led to the fact that in 189In Berlin, infants fed formula were 13 times more likely to die than breastfed infants in Berlin in 1999.
The already mentioned Dr. Biedert noted: “The mass of artificial surrogates is not yet able to replace breast milk. Moreover, many of them, which came into use solely thanks to numerous and loud advertisements, should be recognized as directly harmful. At the same time, many considered the Nestle mixture to be the best: both milk and flour for it were made in the environmentally friendly conditions of the Swiss Alps. In the mid-1870s, the company launched another new product on the market - condensed milk. Although it was invented back in 1856 by American Gail Borden, it was Nestlé that made it a popular children's treat. True, the doctors were again unhappy: no one followed the recommendation to dilute condensed milk with water in a ratio of 1 to 10 and only then give it to children. Children fed with condensed milk became fat, anemic and sickly. Henri Nestlé sold the company in 1874. After 140 years, the profit of the largest food producer has reached almost 8 billion euros
Although it was invented back in 1856 by American Gail Borden, it was Nestlé that made it a popular children's treat. True, the doctors were again unhappy: no one followed the recommendation to dilute condensed milk with water in a ratio of 1 to 10 and only then give it to children. Children fed with condensed milk became fat, anemic and sickly. Henri Nestlé sold the company in 1874. After 140 years, the profit of the largest food producer has reached almost 8 billion euros
Competitors were stepping on the heels of Nestlé more and more actively. In 1896, the Dutchman Martinus van der Hagen invented his own way of drying milk in a bakery. With significantly less flour and sugar, his milk formula quickly gained popularity, laying the foundation for Nutricia's international prosperity. In the US, baby food was taken over by Clapp's Baby Food and Beech-Nut, and Pablum was the first to sell cereal for children. However, it was Daniel Gerber, a cannery manufacturer from Fremont, Michigan, who gave the real scope to the case. The reason for this was again personal: Sally. the sick daughter of Daniel and his wife, Dorothy, required special nutrition. Having learned how to make mashed vegetables, fruits and meat, Dorothy suggested that her husband start mass-producing it. The advice turned out to be successful, and at 1928 year baby food company "Gerber Products" went on sale.
The reason for this was again personal: Sally. the sick daughter of Daniel and his wife, Dorothy, required special nutrition. Having learned how to make mashed vegetables, fruits and meat, Dorothy suggested that her husband start mass-producing it. The advice turned out to be successful, and at 1928 year baby food company "Gerber Products" went on sale.
Its popularity was ensured not so much by new products - they were successfully fed to children before, but by a purely American advertising scale. Immediately after entering the market, the company announced a competition for the best advertising, which was won by the artist Dorothy Hope, who painted a portrait of her neighbors little daughter. This Gerber baby has been sold all over the country, appearing in magazines beloved by housewives and on billboards. The brainchild of the Gerber spouses flourished even during the years of the Great Depression - after all, then the children needed even more artificial feeding. The company is still one of the three largest baby food manufacturers in the world, along with Nestle and Heinz, also known for its ketchup. And in the US, where baby food is consumed the most, Gerber even occupies 70% of the market.
And in the US, where baby food is consumed the most, Gerber even occupies 70% of the market.
The Soviet Union lagged far behind in this area. Own baby food was not produced here for a long time. The elite could use the products of Nestlé and other Western companies, which were bought for foreign currency. For everyone else, there were dairy kitchens that had been open all over the country as far back as the 1920s. There, milk mixtures, fermented milk products, cottage cheese, juices, mashed fruits and vegetables were made from fresh products. Such kitchens were very useful: the children attached to them received good nutrition even during the years of famine and war. At 19In the 1950s, mass production of baby food began in the country: canned juices and purees, powdered milk mixtures, cereals and kissels. Twenty years later, in Istra, Voronezh, Novosibirsk, near Moscow, and then in other cities, factories were built that produce liquid mixtures for children, first in glass and then in cardboard containers.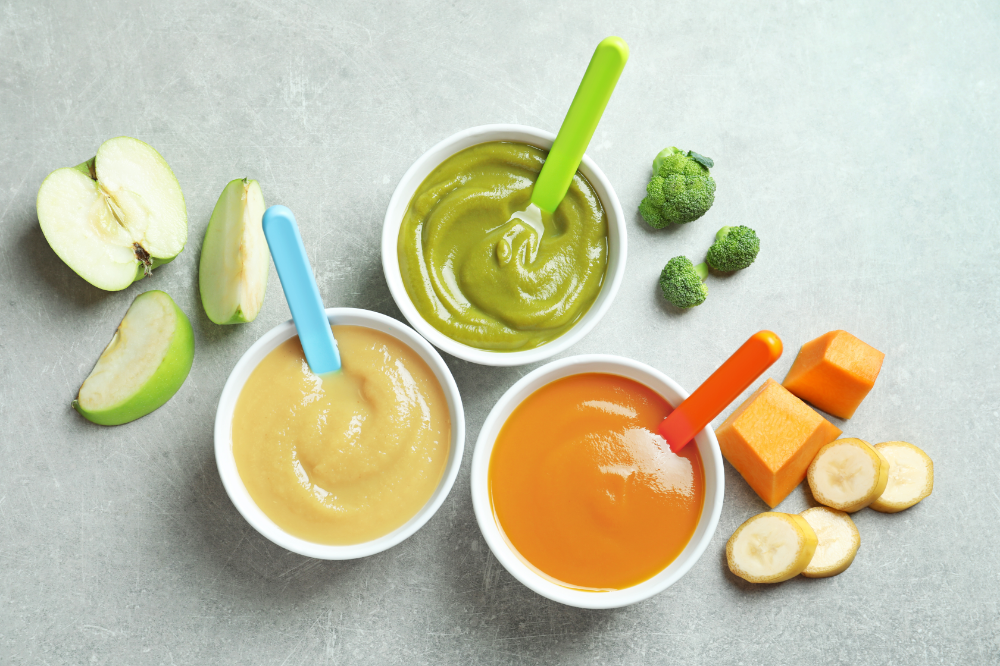 Now dairy kitchens did not prepare food, but gave out ready-made jars or bags.
Now dairy kitchens did not prepare food, but gave out ready-made jars or bags.
in the 1990s, our market was flooded with all the abundance of world baby products - milk formulas, kefir, yogurt, cereals. All this is sold in dry, liquid or frozen form and is certainly advertised as the most delicious and healthy food for children. In the competitive struggle, numerous companies adapt to different categories of consumers. For milk intolerant children, especially in East Asia, lactose-free formulas are made, where whey is replaced by no less nutritious soy protein. In New Zealand, Bibikol has developed infant formula from New Zealand goat milk, which they say differs in composition from goat milk common in Europe.
Whereas before, any microorganisms were tried to be expelled from products for children, today useful bifidobacteria are specially bred in them. Baby food has become so widespread that not only children use it. Hollywood stars go on a diet of puree and milk for other reasons: baby foods are so nutritious that even small portions of them allow you to fill up and not get fat. Products for astronauts were also created at one time on the basis of baby food. Some firms tried to reverse the operation, but when the “space” tubes fell into the hands of the kids, their contents were squeezed out anywhere but into the mouth.
Products for astronauts were also created at one time on the basis of baby food. Some firms tried to reverse the operation, but when the “space” tubes fell into the hands of the kids, their contents were squeezed out anywhere but into the mouth.
Children are special clients. To please them, the food must be not only healthy and tasty, but also bright, which is what producers use to make porridge or mashed potatoes red, orange or green. Sometimes this led to sad consequences. In the 1970s, a scandal erupted in the United States when a major company dyed a strawberry-flavoured children's breakfast cereal with an artificial dye that caused nausea. Thousands of parents called an ambulance - there was a complete impression that the children were vomiting blood. But the biggest scandal arose in the same 70s around the famous Nestle company - it was accused of killing many babies in "third world countries", in which, due to living conditions, mothers could not use the product correctly, they mixed food with dirty water or pour the mixture into unsterilized bottles. According to UNICEF, an unhygienic artificially fed infant is at least 6 times more likely to die from diarrhea alone than a breastfed infant.
According to UNICEF, an unhygienic artificially fed infant is at least 6 times more likely to die from diarrhea alone than a breastfed infant.
When a mother feeds her baby, she gives him not only nutrients, but also immunity to many diseases, and, no less important, strengthens the psychological bond with him. Speaking against artificial nutrition, activists from different countries created the World Alliance for Breastfeeding. Under his pressure, the World Health Organization in 1981 adopted the "Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes", adopted over time by all major manufacturers. It stated that companies should limit advertising and conduct sales of their products with the mandatory participation of medical professionals. True, this applies only to milk formulas, but other types of baby food are under close public scrutiny.
IN THE MIDDLE AGES, CHILDREN'S FEEDING BOTTLES were made of leather and wood. At the beginning of the 19th century, porcelain bottles began to be produced. They wore nipples made of leather or suede.
They wore nipples made of leather or suede.
The glass feeding bottle was patented in 1841 by Charles Windshiel of Massachusetts.
In 1981, the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes was created to control unacceptable marketing practices. The Code was developed by WHO/UNICEF. The official author of the code is IBFAN - International Active Baby Food Network. The code was approved by the World Health Assembly by a vote of 118 votes in favor, against 1 (the US refused to sign the code). A few years later, the rubber nipple was patented, and Windshield bottles were distributed worldwide. Mothers liked them very much. Such a bottle with an attached straw could be placed next to the child, and he could eat on his own. In the early 20th century, the Windshield bottle was banned. Rubber hoses clogged and became breeding grounds for bacteria.
International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes
The Code is addressed to governments and infant formula companies.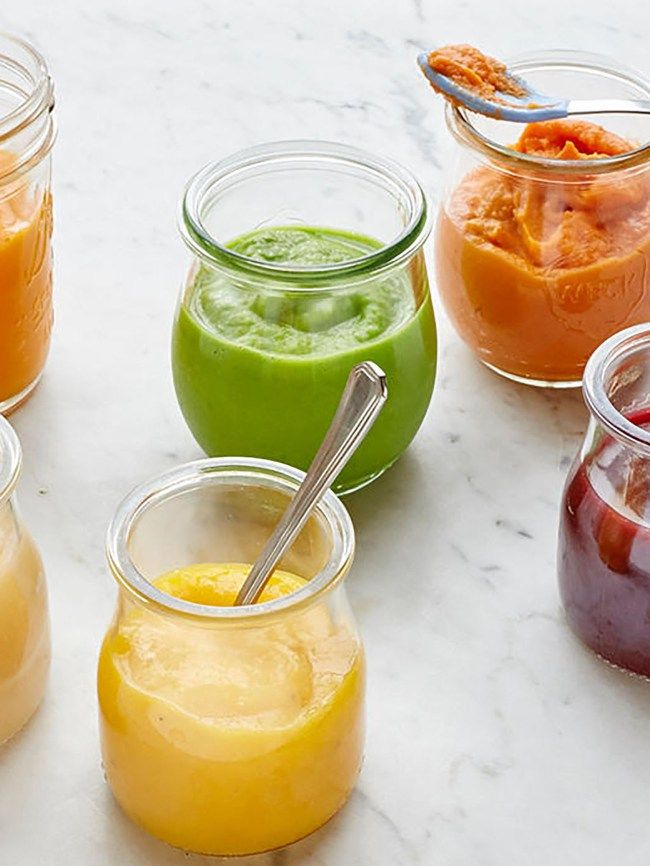 It is a concise guide to the marketing of breast milk substitutes. Its main task is to protect the lives of children by providing them with the best food - breast milk.
It is a concise guide to the marketing of breast milk substitutes. Its main task is to protect the lives of children by providing them with the best food - breast milk.
Products covered by the code include:
- artificial baby milk
- other artificial milks
- all types of baby food: juices, purees, soups, pates, etc.
- Feeding bottles and teats.
The Code contains the following guidelines:
- Information or educational materials, equipment or products may only be distributed free of charge with the written permission of the relevant authorities. (Company logo may appear but product brand may not)
- No company materials may be distributed to mothers.
- Health workers should support breastfeeding and encourage mothers to choose to breastfeed. They should help promote the principles of this code.
- Do not use the health system to market artificial breast milk.
- Health system display products such as posters, booklets, flyers, brochures, feeding bottles, labels, prescription forms, and other artificial nutrition promotional materials may not be used.

- Representatives of manufacturing companies should not work in the health care system, in the field of child care and should not be in contact with mothers.
- Demonstrations of artificial feeding techniques may only be conducted by health workers in families where there is an absolute medical indication for supplementary feeding. At the same time, information about the risk to the health of the child if the product is used incorrectly must be provided.
- Artificial milk may not be distributed free of charge or at reduced prices in the health care system. Donations in the form of artificial milk, feeding bottles and other products can only be given to orphanages and similar institutions, but not to hospitals and maternity hospitals.
- Hospitals and maternity hospitals should buy this formula just like everyone else.
- All information provided by health care professional firms must be limited to scientific facts and must not suggest that formula feeding is identical or superior to natural feeding.

- Promotion of products by healthcare workers, as well as their material and financial incentives, is not allowed.
- Health workers should not distribute artificial milk samples to pregnant women, mothers of infants and young children, or their family members.
Summary of the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes
- No advertising of these products to the public!
- No free samples for mothers
- No health promotion for this product, including free or cheap baby food.
- No company representatives to contact mothers.
- No gifts or samples for healthcare professionals. Health care workers should never give these products to mothers.
- No distribution of texts or graphic products idealizing formula feeding, including images of infants on labels.
- Information provided by healthcare professionals must be scientific and relevant.
- All information on bottle feeding should explain the benefits of breastfeeding and the costs and dangers associated with bottle feeding.